Punjab State Board PSEB 10th Class Social Science Book Solutions Geography Source Based Questions and Answers.
PSEB 10th Class Social Science Solutions Geography Source Based Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Read the below questions carefully and answer the given questions.
Due to this vastness, India is called an Indian sub-continent. The sub-continent is a large and independent region. The boundaries of whose terrain are drawn by various natural features which distinguish it from the surrounding areas. India also crosses the Agil, Muzigh, Kunlun, and Karakoram, Hindukush and Jaskar mountain range from Tibet across the Himalayas in the north, from Pak, Jal Damru in the south and Gulf of Mannar from Sri Lanka, east. In the direction, Arakan separates Yoma from Myanmar (Burma) and in the western direction from the vast Dhar desert, Pakistan. Due to such a vast area of India many cultural, economic, and social variations are found. But despite this unity is found in climate, culture, etc. in the country.
(a) Why is India called the sub-continent?
Answer:
India is given the status of sub-continent due to its expansion and position. The sub-continent is a vast and independent landmass whose boundaries are formed by different topography. These topographies separate it from its surrounding areas. Agile across the Himalayas in the north of India. The mountain ranges of Mugtgh, Kunlun, Karakoram, Hindukush, etc. distinguish it from the north-western parts of Asia. In the South, the Pak strait of central and the gulf of Mannar separate it from Sri Lanka. Formerly Arakan Yoma separates it form Myanmar. The Thar Desert separates it from a very large part of Pakistan. Despite this, we cannot call present day India a sub¬continent. The Indian sub-continent is formed by the combination of undivided India, Nepal, Bhutan and Bangladesh.
(b) Which elements contribute to maintaining unity in the diversity of the country?
Answer:
India is a country of diversity. Yet a distinct unity appears in our society. The main elements that provide unity to Indian society are the following:
1. Monsoon Season. The monsoon winds make most of the rainfall in summer. This affects the agriculture of the country as well as other business. Monsoon winds make the power supply reliable by raining the mountainous regions. Infact, monsoon rainfall is the basis of the entire country’s economy.
2. Religious Culture. There are two things in favor of religious culture. One is that religious places have united the people of the country in one sutra. Secondly, religious saints have instilled a sense of brotherhood through their teachings. People from all parts of the country come and worship at Tirupati, Jagannathpuri, Amamath, Ajmer, Harimandir Sahib, Patna, Hemkunt Sahib and other pilgrimage places. The saints have also tried to create religious harmony.
3. Language and Art. Almost all the northern India. Vedas were propogated in Sanskrit language. Urdu was born in the middle age of this language. English is the contact language and Hindi is the national language. Together, these have provided an opportunity to understand each other closely. Siinlarly, folk songs and folk arts have also created an opportunity for people to express similar feelings.
4. Traffic and means of communication. Railways and roads have played an important role in bringing people of different areas closer. The means of communication like Doordarshan and newspapers have also connected the national stream by giving the national thinking of the people.
5. Migration. Many people from villages have started coming to the cities. Despite their racial differences, they have come to understand each other and thus they have come closer to each other. The truth is that many natural and cultural elements have given unity to our country.
![]()
Question 2.
The vast northern plains along the Himalayas provide habitat and livelihood to 40% of the country’s population. Their fortile soil, suitable climate, flat surface have contributed significantly in the spread and development of rivers, canals, roads, railways and cities and in the development of agriculture. Therefore, this plain region has the distinction of being the granary of the country. These plains have built a special kind of civilization and society since the Aryans. People from all over the country consider Ganga to be a holy river and the Rishikesh, Haridwar, Mathura, Prayag, Ayodhya, Kanshi etc. places in its valley have been the center of attraction for sufi saints and religious people living in different parts of the country. Later in these plains, great men like Sikh Guru, Mahatma Buddha, Mahavir Jain were born and different religious were established. Its deep impact can be seen in the Himalayan mountains and also in South India.
(a) Name the major landforms created by the rivers in the vast plains of the north.
Answer:
The landforms formed by the rivers in the northern plains are alluvial fins, alluvial cones, sepentine turns, hilly staircases, natural dams and floodplains.
(b) Describe the huge northern plains contribute to the development of the country.
Answer:
The Himalayan regions have the following contribution to the development of the country.
- Rain. The monsoon winds from the Indian Ocean hit the Himalayan mountains and rain heavily. Thus, it donates rain to the northern plain. There is enough rainfall in this ground.
- Useful Rivers. All the major rivers flowing in northern India originate from the Himalayan mountains like Ganga, Yamuna, Sutlej, Brahmaputra, etc. These rivers flow throughout the year. In the dry season, Himalayan ice burns these rivers.
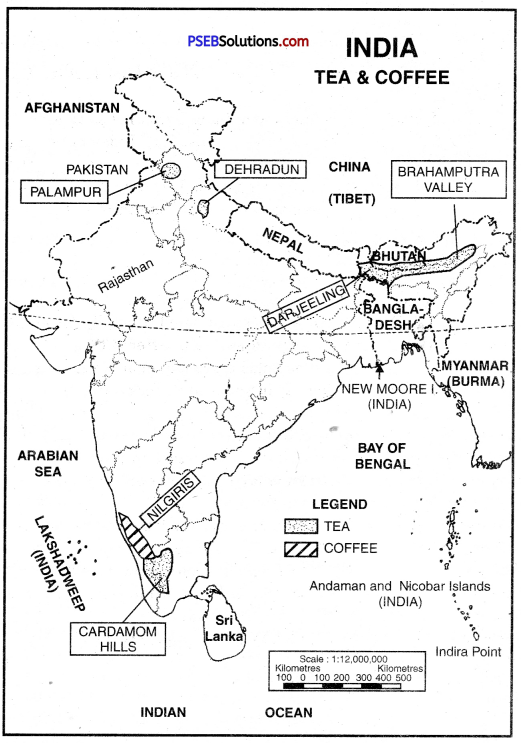
- Fruit and Tea. The slopes of the Himalayas are very useful for tea cultivation. Apart from these, fruits are also grown on the mountain slopes.
- Useful Wood. Dense forests are found on the Himalayan Mountains. These forests are our wealth. Many industries in India depend on the wood derived from them. This wood is also used in building works.
- Good Pastures. Beautiful and green pastures are found on the Himalayas. Animals are fed in them.
- Mineral Substances. Many types of mineral substances are found in these mountains.
![]()
Question 3.
The word ‘climate’ or ‘wind water’ refers to the long-term seasonal conditions in a place, in which the temperature of that place is the amount of water in the air flowing from there. These conditions are mainly determined by important elements such as surface variation of the place, distance from the coastline and distance from the equator. It has a profound effect on human and human activities. India is a vast country. Its vast sin-face units, the peninsular position and the tropic of cancer passing through it have a profound effect on its climate. Due to the largest surface variations of temperature, rainfall, winds and clouds etc.
(a) Describe the (two) elements affecting the climate of India.
Answer:
The main elements influencing the climate of India are :
- Distance from the equator.
- Surface Pattern.
- Air pressure system
- Seasonal winds and
- Proximity to Indian Ocean.
(b) What are the regional variations of Indian climate?
Answer:
The regional variations of Indian climate are as follows:
1. In winter the temperature reaches – 45°C in the Kargil regions of the Himalayan mountain but at the same time it is more than 20°C in Chennai (Madras) metropolis in Tamil Nadu. Similarly in summer the western direction of the Aravali mountains is crossed 50° centigrade, while the Srinagar is less than 20° centigrade. There is a temperature of 204 centimeters in Srinagar.
2. The annual rainfall is located in the mountain range of Mawsymaram, 1141 cm. Annual rainfall in Jaisalmer is less than 10 cm. in the year.
3. In Barner and Jaisalmer are carved clouds, but the whole year is the same as the same year throughout the year.
4. Due to the effect of the sea in Mumbai and other coastal cities, the temperature ramains almost same of the year. In contrast, the National area is found to be huge difference in the cold and hot temperature in the area and surrounding areas.
![]()
Question 4.
The economy, the relief and social development is deeply influenced the economic progress. In the social development, the area can be applied to the development of economic progress there. Indian agriculture, almost completely dependent on. agriculture (aggregated). In which development of the monsoon has given significant contributions to providing a major and strong basis. Monsoon is called a pivotal point of the country. Apart from agriculture, the entire production is dependent oh agricultural production, If monsoon rainfall is in appropirate amount, the agricultural production increases. But because of the failure of monsoon, the crops dried. The country goes dry and the grains are reduced in the stores.
(a) Discuss the important features of the monsoon.
Answer:
In India rainfall is mainly in July to September. This is the period of southwest monsoons blowing from sea to land. There are three important features of the monsoon rainfall.
- Erratic. Rainfall is not reliable in India. It is not necessary that rain continues to be same. Due to this erratic situation of rain, the situation of starvation and famine is arranged. This erratic situation of rainfall is more in the inner parts of the country and in Rajasthan.
- Uneven Distribution. There is uneven distribution of rainfall in India. Western slopes of western ghats and Meghalaya or in the hills of Assam. There is more than 250 cm. rainfall. In contrast Rajasthan, West Gujarat, North Kashmir etc., the rainfall is less than 25 cm.
- Uncertainty. The amount of rainfall in India is not certain. Sometimes monsoon winds reached before time, It rains a lot. But sometimes the rainfall is low or sometimes ends up before a time. As a result the situation of drying is generated in the country.
(b) Why the Indian Economy (budget) is called gambling of monsoon winds?
Answer:
Indian monsoon is a gambling of monsoon winds. This sentence reveals that the advancement of India’s economy depends on that how much appropriate time of any year, distribution and quantity.
If the rain comes on time and its quantity is also suitable, a good crop of agriculture can be expected.
For example-crops are good due to good monsoon, so three things happen.
- Fair raw materials available for factories. The industry-related factors of cotton, jute, oil seeds etc. are flourishing.
- When the agriculture and industires are strengthened from good monsoon, the
productivity increases. On one hand, the export is promoted. On the other hand international trade is flourishing. Wealth grows in the country and people’s standard of living improves. - Due to good monsoon, there is an increase in water in the rivers, the water level of the dams rises high. Where this water helps in the production of hydropower, the irrigation system improves. This creates a stir in economic activities in the country. There is no doubt that today due to the advancement of science, we can grow a good crop even in the absence of monsoon, but we have to think about whether all farmers can benefit from lack of rainfall or unequal distribution of rainfall. A good monsoon affects every section and every region of the country. If the monsoon is suitable, the country’s economic development is assured. Therefore, it is fair to call the Indian economy a gamble of monsoon winds.
![]()
Question 5.
Agriculture has an important role in the Indian economy. The agricultural sector employs about two-thirds of the country’s workforce. The region derives 29.0 percent of the total national income and agricultural products a1 so have an important place in foreign exports. Many products of agriculture are used as raw materials in our factories. Due to the progress in the field of agriculture, the achievement of food grains per person, which was 395 grams in the 1950’s has increased to 510 grams per person per day in 1991.
India also ranks fourth in the world in the use of chemical fertilizers. The area under pulses in our country is the highest in the world. In the field of cotton products, India is the first country in the world, where the first efforts were made to produce improved varieties of cotton. The country has made significant achievements in the preparation of prawn fish and pest culture technological development.
(a) What percentage of land is cultivable in India?
Answer:
51% of the land in India is cultivable.
(b) Why is agriculture called the mainstay of the Indian economy?
Answer:
Agriculture is the mainstay of the Indian economy. Even though agriculture now contributes only 33.7% of the total national production, its importance is no less.
- Agriculture sustains 2/3 of our population.
- The agriculture sector provides employment to about two-thirds of the country’s workers.
- Most of the industries get raw materials from agriculture. The truth is that the place of industries is being built on the foundation of agriculture.
![]()
Question 6.
A decline in per capita achievement of pulses in Punjab and other parts of the country is a matter of concern. It seems that the wave of ‘Green Revolution’, which has revolutionized the production of wheat and rice in the country has not made any special contribution in increasing the production of pulses. Actually, if it is said that there is harm then there will be no wrong. Because in the years following the Green Revolution, the area of pulses has been diverted to a large number of high yielding crops like wheat and rice. This has happened especially on a large scale in commercially agricultural states like Punjab.
(a) In Punjab, what kind of changes has occurred in the pulses production area after Green revolution.
Answer:
After the green revolution, the area of pulses production decreased from 9.3 lakh hectares to 9.5 thousand hectare.
(b) What are the main reasons for the decline in the production of pulses?
Answer:
The production of pulses has decreased in the last decades. The main reasons for this are as follows :
- The area with pulses has been subjected to crops like wheat and rice, which produce more after the Green Revolution.
- Some areas have been subjected to canals, roads, and other development projects due to development work.
- The growing area of pulses has also declined due to increasing land demand for
housing of the growing population.
![]()
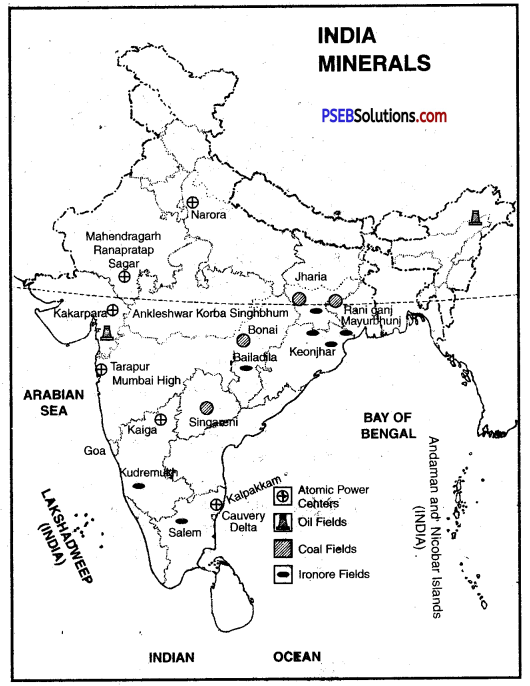
Question 7.
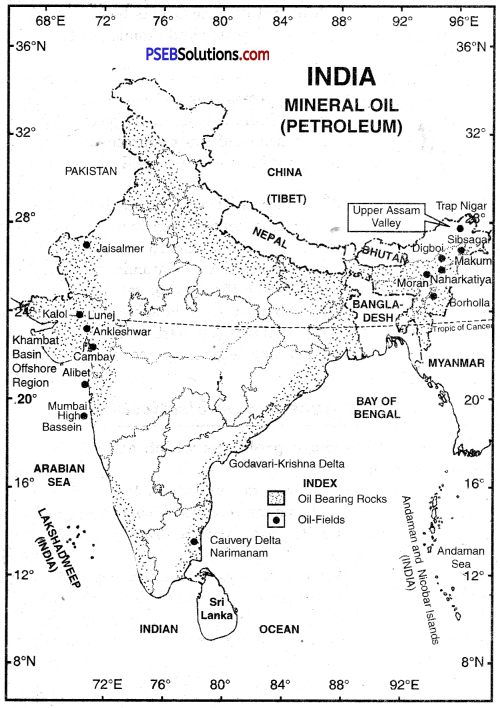
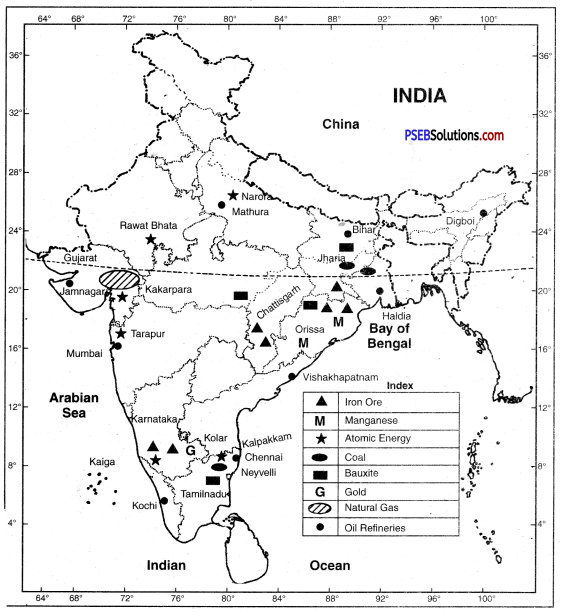
Our country is also considered very rich in terms of mineral wealth. It is estimated that the country accounts for one fourth of the total iron ore reserves in the world. There are also huge deposits of manganese, a major mineral used in the iron and steel industry. There are also abundant reserves of coal, limestone, bauxite and mica in the country. But non-ferrous minerals such as zinc, lead, copper and gold are in very limited quantities. The sulfur reserves in the country are almost nil, while sulfur is the mainstay of modern chemical industry. We also have plenty of water power resources and nuclear minerals. Their use as a power tool is increasing rapidly due to their power efficiency and very little tampering with the environment. For this reason, solar energy is also being used as a power tool. Solar energy is the priceless power store of God. Its use will increase rapidly as a source of power in the future.
(a) What is the contribution of minerals to the national economy?
Answer:
Minerals have great importance in the national economy. The following facts will make it clear.
- The industrial development of the country depends mainly on minerals. Iron and coal are the basis of the machine age. We have one-fourth of the world’s iron ore deposits. There are also huge reserves of coal in India.
- State governments get income from mining operations and provide employment to millions of people.
- Coal, petroleum, natural gas etc. are important sources of mineral energy.
- Equipment made from minerals helps in the growth of agriculture.
(b) Why is solar energy called the source of future energy?
Answer:
Coal and mineral oil are exhaustive resources. There will come a day when the people of the world will not get enough energy from them. Their stores must have been exhausted. Unlike then, sun energy is a never-ending means. This gives a tremendous amount of energy. When the reserves of coal and mineral oil are exhausted, then power will be obtained and we will be able to do it easily with our domestic work and plants.
Question 8.
All the trees, thorn bushes, plants and grasses etc. are included in the natural vegetation which grow without human intervention. Before starting its study, it is necessary to know the related words like Flora, Vegetation and Forests. Different species of plants that grow in a certain time and in a certain area are included in the flora, shrubs, plants, grass etc. that grow at a place in a certain environment are called vegetation. Whereas a large area surrounded by dense and adjacent trees, plants, thorn bushes etc. is called forest. The term jungle is mostly used by environmental scientists and forest guards and geographers. Each type of developed vegetation has to go through a long life cycle by creating a delicate balance with its environment, which depends on the quality of its mutual cohesion and ability to adapt. The entire flora found in our country is not local, but 4Q% of it belongs to foreign castes which are called Boreal and Paleo-Tropical species.
(a) Name the foreign castes and quantities in the country.
Answer:
- The foreign vegetation species present in the country are called as Boreal and Paleo-Tropical.
- The amount of foreign vegetation in India is 40%.
(b) Write briefly on the autumn or monsoon vegetables.
Answer:
The vegetation that leaves its leaves before the start of summer to prevent further evaporation is called the autumn or monsoon vegetation. This vegetation can be divided into two sub-parts which are and wet based on rainfall.
- Autumn Forest. This type of vegetation is found in four big areas, where the annual rainfall varies from 100 to 200 cm. Trees are less dense in these areas but their height reaches 30 metres. Sal, Sheesham, Teak, Chandan, Jamun, Amltas, Haldu, Ebony, Mulberry are the major trees of these forests.
- Dry Deciduous Vegetation. This type of vegetation is found in areas with rainfall less than 50 to 100 cm. Its long strip starts from Punjab and extends to the adjoining areas of the southern plateau. Kelkar, Babool, Banyan, Haldu are the main trees here.
![]()
Question 9.
In our country, along with the diversity of vegetation, there is a large variety of fauna. In fact there is a deep interconnection between the two. About 76 thousand species of fauna are found in the country. 2500 species of fish are found in the fresh and salt water of the country. Similarly, there are 2000 species of birds. 400 species of snakes are found in India. Apart from this, amphibians, reptiles, mammals and small insects and worms are also found. Mammals have majestic elephants with majestic chicks. It is an organism of equatorial tropical forests. In our country, it is found in the forests of Assam, Kerala and Karnataka. It rains heavily and the forests are also very dense. In contrast camels and wild asses are found in very hot and dry deserts. Camel Thar is the common animal of the desert, while wild plants are found only in the Rann of Kuchh. They have a horned rhinoceros in the opposite direction. They live in marshy areas in northern parts of Assam and West Bengal. Among Indian animals, the Indian bison, the Indian buffalo are particularly notable.
(a) Name the animals found in the Himalayas.
Answer:
In the Himalayas, wild sheep, mountain goat, a long horned wild goat and tapir etc, are found, while pandas and Himatendua animals are found in high mountain
(b) What are the works being done to look after the animals in the country?
Answer:
Indian Wildlife Protection Act was enacted in 1972. Under this, 1,50,000 square kilometers of area (2.7% of the country and 12 percent of the total forest area) in various parts of the country were declared as national parks and wildlife sancturies.
Near Extinction Special attention has been paid to wildlife.
The work of counting animals and birds has been started at the National level. At present there are 16 tiger reserves in different parts of the country.
A special scheme for rhinoceros conservation is being carried out in Assam. The truth is that till now 18 Biosphere Reserves have been established in the country.
Under the scheme, the first life reservation area was created in Nilgiri. Protection of every animal is mandatory under this scheme. This natural heritage is for future generations.
Question 10.
A combined mixture of light, loose and unstructured rocky shreds and fine-grained bacteria found on the earth’s surface is called soil which has the power to give rise to plants. Deposition of this mixture is found in deep layers ranging from 15-30 cm to several metres. But the soil scientist is divided into three layers called A, B and C respectively, depending on the depth and quantity of soil colour, texture, size of particles etc. Due to the high quantity of humus in ‘A’ Horizon soils, they begin to turn black. But due to being situated in the zone of leaching on this layer, the minerals dissolve and go down and the colour starts to turn dark black. The colour of sub-layer with ‘B’ Horizon under this layer is brown due to the mineral matter leaking from the top layer. But the aihount of humus in it decreases. Below this layer, a layer of ‘C’ Horizon soil is found in which the substances separated from the above rocks do not have any special change and later go to the main base rock. The colour of this sub-rocky surface is grey or light brown,
(a) Describe the definition of soil.
Answer:
The combined mixture of light, loose and unstructured rock crust (shell powder) and fine granules found on the earth’s surface is called soil.
(b) What is the contribution of primary rocks in the birth of soil?
Answer:
The primary rocks in the country consist of lofty rocks of the northern plains or lava-formed rocks of the plateau. They contain various types of minerals. Therefore, they make good soil. The colour, formation, texture, etc. of the soil formed by the primary rocks depends on how long the rocks are being affected and by what kind of climate. In a state like West Bengal, the spil is highly developed due to the effects of chemical reactions in the climate and humus. But in dry area like Rajasthan, due to lack of vegetation, soil fertility decreases. Likewise, soil erosion is more in areas with high rainfall and high winds. Fertility decreases as a result.
![]()
Question 11.
In today’s knowledge and information-based world, the important contribution of human resources is being realized in national construction and development much better than before. Today all the countries of the world, especially the developing countries, are paying more attention to the development of human resources than before. Children can you think why is this ? In the countries of South Korea, Taiwan, Hong Kong, Singapore, Malaysia etc., known as ‘Asian Tigers’, the rapid development of economic development is being attributed to the huge investment made in the development of human resources in the last few decades. In human resource development, not only the parameters like education, technical skills, health and nutrition but also human-ethics-ideas, civilization- culture, species and nation-pride should be included. Only then will human resource development becQme a complete ideology.
(a) What is the most valuable resource of a country?
Answer:
Intellectually and physically healthy citizens.
(b) Why is it important to study the population structure of the country?
Answer:
There are many reasons why it is necessary to know the population structure of a country.
- Various characteristics of the population of any country for social and economic planning such as the age structure of the population, gender structure, business structure etc. data is required.
- Different components of the population structure are closely related to the economic development of the country. While the population structure components are affected by economic development from another, they are also unable to remain untouched by the impact of progress and level of economic development. For example, if the percentage of children and old people in the age structure of a country’s population is very high, then the country will have to spend more and more financial resources on basic facilities like education and health. On the other hand, the rate of economic development of the country is accelerated due to the higher proportion of working-age groups in the age structure.
Question 12.
The study of the regional pattern of population distribution provides the basis for understanding all demographic components of the population. For this reason, it is very important to understand the regional pattern of distribution of population. Here first we must also clarify the difference between population distribution and population density. Population distribution is related to place and density is related to ratio. Population distribution implies that what is the regional pattern of population in any part of the country, that is, the population pattern is nucleated or agglomerated in one place. On the other hand in density, which is related to population size and area, attention is given to the ratio of man and area. The history of human settlements in India is very old. That is why the population resides in every part of the country which is the sum of human. habitation. Yet the distribution of population is greatly affected by the fertility* of the land. As India is an agricultural country, the pattern of population distribution depends on agricultural productivity. For this reason, in states where the productivity of agriculture is high, the concentration of population is equally high. Apart from agricultural productivity, the variation of physical factors, industrial development and cultural elements also contribute significantly in influencing the population distribution pattern of India.
(a) Name the largest and least populous states of the country.
Answer:
The most populous state in the country is Uttar Pradesh and the least state is Sikkim.
(b) Describe the format giving the salient features of the regional pattern of population distribution in the country?
Answer:
The regional pattern of population distribution in India and its important features are as follows:
1. The distribution of population in India is very uneven. Population is very dense in river valleys and seaside plains, but the population is very sparse in the mountainous desert and scarcity areas. Only 3% of the population lives on 16 percent of the country’s land in the hilly regions of the north, while 40 percent of the population lives on 18 percent of the country’s land in the northern plains. In Rajasthan, 6 percent of the population lives on only 6 percent of the country’s land.
2. Majority of the population is settled in rural areas. About 71% of the total population of the country resides in rural areas, about 29% in cities. Large cities have a large population of urban population. Two thirds of the total urban population lives in first-tier cities with population of one lakh or more.
3. The concentration of minority communities in thei country is in the most sensitive and important outer border areas. For example, the Sikhs in Punjab and the Muslims in Jammu and Kashmir are in abundance near the Indo-Pak border in north western India. Similarly there is a gathering of people of Christianity along the borders of China and Burma (Myanmar) in the northeast. Many social, economic and political difficulties arise from such distribution.
4. On the one hand, the population is dense in the coastal plains and valleys of the rivers. On the other hand, the population in the mountainous, plateau and desert parts is sparse. -This distribution resembles a demographic divide.