Punjab State Board PSEB 10th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Ex 7.3 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Ex 7.3
Question 1.
Find the area of the triangle whose vertices are:
(i) (2, 3); (- 1, 0); (2, – 4)
(ii) (- 5, – 1); (3, – 5); (5, 2)
Solution:
(i) Let vertices of the ∆ABC are A (2, 3); B(- 1, 0) and C (2, – 4)
Here x1 = 2, x2 = – 1 x3 = 2
y1 = 3, y2 = 0, y3 = – 4 .
∴ Area of ∆ABC = \(\frac{1}{2}\) [x1 (y2 – y3) + x2 (y3 – y1) + x3 (y1 – y2)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) [2 × (0 + 4) – 1 × (- 4 – 3) + 2 × (3 – 0)]
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) [8 + 7 + 6] = \(\frac{21}{2}\)
= 10.5 sq units.
(ii) Let vertices of the ∆ABC are A (- 5, – 1); B (3, – 5) and C (5, 2)
Here x1 = – 5, x2 = 3, x3 = 5
y1 = – 1, y2 = – 5, y3 = 2
∴ Area of ∆ABC = \(\frac{1}{2}\) [x1 (y2 – y3) + x2 (y3 – y1) + x3 (y1 – y2)]
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) [- 5 (- 5 – 2) + 3 (2 + 1) + 5 (- 1 + 5)]
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) [35 + 9 + 20]
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 64 = 32 sq units.
![]()
Question 2.
In each of the following find the value of ‘k’ for which the points are coimear.
(i) (7, – 2); (5, 1); (3, k)
(ii) (8, 1); (k, – 4); (2, – 5)
Solution:
(i) Let given points be A (7, – 2); B (5, 1) and C (5, k)
Here x1 = 7, x2 = 5, x3 = 3
y1 = – 2, y2 = 1 y3 = k
Three points are collinear iff
\(\frac{1}{2}\) [x1 (y2 – y3) + x2 (y3 – y1) + x3 (y1 – y2)] = 0
or \(\frac{1}{2}\) [7 (1 – k) + 5(k + 2) + 3(- 2 – 1)] = 0
or 7 – 7k + 5k +10 – 9 = 0
or – 2k + 8 = 0
or – 2k = – 8
or – k = \(\frac{-8}{-2}\) = 4 .
Hence k = 4.
(ii) Let given points be A (8, 1); B (k, – 4) and C(2, – 5)
Here x1 = 8 x2 = k, x3 = 2
y1 = 1, y = – 4, y = – 5
Three points are collinear iff
\(\frac{1}{2}\) [x1 (y2 – y3) + x2 (y3 – y1) + x3 (y1 – y2)] = 0
or \(\frac{1}{2}\) [8 (- 4 + 5) + k (- 5 – 1) + 2 (1 + 4) = 0]
or 8 – 6k + 10 = 0
or – 6k = – 18 .
or k = \(\frac{-18}{-6}\) = 3.
Hence k = 3.
![]()
Question 3.
Find the area of the triangle formed by joining the mid-points of the sides of the triangle whose vertices are (0, – 1), (2, 1) and (0, 3). FInd the ratio of the area of the triangle formed to the area of the given triangle.
Solution:
Let vertices of given triangle ABC are A(0, – 1); B (2, 1) and C (0, 3).
Also, D, E, F be the mid points of AB, BC, CA respectively.
Using mid point formula,
Coordinates of D = \(\left(\frac{0+2}{2}, \frac{-1+1}{2}\right)\) = (1, 0)
Coordinates of E = \(\left(\frac{2+0}{2}, \frac{1+3}{2}\right)\) = (1, 2)
Coordinates of F = \(\left(\frac{0+0}{2}, \frac{3-1}{2}\right)\) = (0, 1)
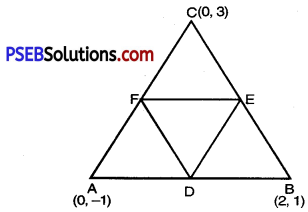
∴ Co-ordinates of the vertices of DEF are D (1, 0); E (1, 2); F (0,1).
Here x1 = 1, x2 = 1, x3 = 0
y1 = 0, y2 = 2, y3 = 1.
Area of ∆DEF = \(\frac{1}{2}\) [x1 (y2 – y3) + x2 (y3 – y1) + x3 (y1 – y2)]
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) [1 (2 – 1) + 1 (1 – 0) + 0 (0 – 2)]
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) [1 + 1 + 0] = \(\frac{2}{2}\) = 1.
In ∆ABC,
x1 = 0, x2 = 2, x3 = 0
y1 = – 1, y2 = 1, y3 = 3.
Area of ∆ABC = \(\frac{1}{2}\) [x1 (y2 – y3) + x2 (y3 – y1) + x3 (y1 – y2)]
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) [0 (1 – 3) + 2 (3 + 1) + 0 (- 1 – 1)]
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) [0 + 8 + 0] = \(\frac{8}{2}\) = 4
Required ratio = \(\frac{\text { Area of } \triangle \mathrm{DEF}}{\text { Area of } \triangle \mathrm{ABC}}\)
= \(\frac{1}{4}\)
![]()
Question 4.
Find the area of the quadrilateral whose vertices taken in order, are (- 4, – 2); (- 3, – 5); (3, – 2); (2, 3).
Solution:
Let co-ordinates of the given quadrilateral ABCD are A(- 4, – 2); B(-3, – 5); C(3, – 2) and D (2, 3).
Join AC then Quad. ABCD divides in two triangles
i.e. ∆ABC and ∆CDA
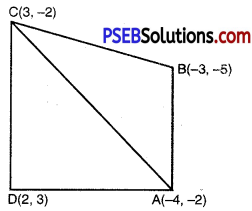
In ∆ABC
Here x1 = – 4, x2 = – 3, x3 = 3
y1 = – 2, y2 = – 5, y3 = – 2
Area of ∆ABC = \(\frac{1}{2}\) [x1 (y2 – y3) + x2 (y3 – y1) + x3 (y1 – y2)]
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) [- 4 (5 + 2) + (- 3) (- 2 + 2) + 3 (- 2 + 5)]
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) [12 + 0 + 9] = \(\frac{21}{2}\) sq. units.
In ∆CDA
x1 = 3, x2 = 2, x3 = – 4
y1 = – 2, y2 = 3, y3= – 2
Area of ∆CDA = \(\frac{1}{2}\) [x1 (y2 – y3) + x2 (y3 – y1) + x3 (y1 – y2)]
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) [3 (3 + 2) + 2 (- 2 + 2) + (-4) (- 2 – 3)]
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) [20 + 15 + 0] = \(\frac{35}{2}\) sq. units.
Now, Area of quadritateral ABCD = (Area of ∆ABC) + (Area of ∆ACD)
= \(\frac{21}{2}+\frac{35}{2}=\frac{21+35}{2}\)
= \(\frac{56}{2}\) = 28 sq. units.
![]()
Question 5.
You have studied in Class IX, (Chapter 9, Q. 3) that a median of a triangle divides it into two triangles of equal areas. Verify this result for ∆ABC whose vertices are A(4, – 6), B(3, – 2) and C(5, 2).
Solution:
Given that coordinates of the vertices of ∆ABC are A(4, – 6); B (3, – 2) and C (5, 2)
Let CD is the median i.e. D is the mid point of AB which divides AABC into two pails i.e.
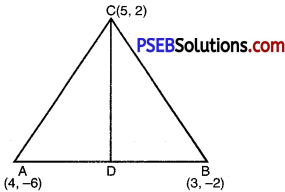
∆ADC and ∆CDB
Coordinates of D = \(\left(\frac{4+3}{2}, \frac{-6-3}{2}\right)\)
= \(\left(\frac{7}{2}, \frac{-8}{2}\right)\) = (3.5,- 4).
In ∆ADC
x1 = 4, x2 = 3.5, x3 = 5
y1 = – 6, y2 = -4, y3 = 2
Area of ∆ADC = \(\frac{1}{2}\) [x1 (y2 – y3) + x2 (y3 – y1) + x3 (y1 – y2)]
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) [4(—4—2)+3.5(2+6)÷5(—6+4)]
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) [- 24 + 28 – 101]
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × -6
= 3 sq. units (∵ area cannot be negative).
In ∆CDB
x = 5, x = 35, x = 3
y = 2, y = – 4, y = – 2
Area of ∆CDB = \(\frac{1}{2}\) [x1 (y2 – y3) + x2 (y3 – y1) + x3 (y1 – y2)]
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) [5 (- 4 + 2) + 3.5 (- 2 – 2) + 3 (2 + 4)]
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) [- 10 – 14 + 18]
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × – 6 = – 3
= 3 sq. units(∵ area cannot be negalive)
From above discussion it is clear that area of ∆ADC = area of ∆CDB = 3 sq. units
Hence, a median of a triangle divides it into two triangles of equal areas.