Punjab State Board PSEB 7th Class Science Book Solutions Chapter 6 Physical and Chemical Changes Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 6 Physical and Chemical Changes
Science Guide for Class 7 PSEB Physical and Chemical Changes Intext Questions and Answers
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 59)
Question 1.
Mention whether the cutting of paper is a reversible or irreversible change.
Answer:
Cutting a paper is not a reversible change because the pieces cannot be reconnected to form the original piece. So this is an irreversible change
Question 2.
Is the cutting of paper a physical or a chemical change?
Answer:
Cutting of paper into pieces changes its shape, but no new material is formed. Therefore, it is a physical change.

Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 59)
Question 1.
Can you recover chalk from dust?
Answer:
Yes we can get chalk from chalk powder by making a paste of chalk powder. Then giving it a shape of chalk and allowing it to become dry.
Question 2.
Does chalk powder dissolve in water?
Answer:
No, chalk powder is insoluble in water.
Question 3.
What is the nature of above change. Is it physical or chemical?
Answer:
Chalk powder can be made into chalk, meaning you can get the basic substance (chalk powder) from it which has same properties as before but has changed in shape and size. It can be beaten to make chalk powder again. So this is a physical change only.
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 60)
Question 1.
Ice melts into water with ……………….. in temperature.
Answer:
Ice melts into water with increase in temperature.
Question 2.
Water changes to ice with …………………. in temperature.
Answer:
Water changes to ice with decrease in temperature.
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 61)
Question 1.
What is Evaporation ?
Answer:
Evaporation. This is the process by which a liquid is heated to a certain temperature and get converted into its gaseous form.
Question 2.
Define Condensation.
Answer:
Condensation. This is the process by which the vapours are cooled and converted into a liquid. This process is the opposite of evaporation process.
In the same way if the water vapours are cooled, then they are converted into water (liquid form).

Question 3.
Water changes into gaseous form with ………………… in temperature.
Answer:
Water changes into gaseous form with increase in temperature.
Question 4.
Water changes from gaseous state to liquid state with ………………. of temperature.
Answer:
Water changes from gaseous state to liquid state with decrease of temperature.
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 61)
Question 1.
Which colour do you notice on heating the free end of hacksaw blade ?
Answer:
When heated, the free of the blade becomes red and when it is removed from the fire it is cooled and returns to its original colour.
Question 2.
Is the physical change reversible or irreversible ?
Answer:
Physical change is a reversible change because no new substances having new properties are seen to be formed in the process and on reversing the circumstances it returns to its original state.
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 62)
Question 1.
Define a physical change.
Answer:
Physical change. It is a temporary change in which the physical properties of an object change such as change in colour, size, length, etc.
Question 2.
Is a new substance formed during a physical change ?
Answer:
During physical change no new substance with new properties is formed.
Question 3.
Explain any two examples of physical change from your surroundings.
Answer:
Examples of physical change:
- Melting of wax,
- Melting of ice,
- Freezing of water into ice,
- Dissolving sugar in water.
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 64)
Question 1.
What type of metal oxide is formed on burning of magnesium ribbon ?
Answer:
Magnesium combines with oxygen of the air to form Magnesium ribbons. Magnesium oxide is a basic oxide.

Question 2.
What is the colour of magnesium oxide formed on heating magnesium ?
Answer:
Magnesium ribbon during combustion form white coulred powder of magnesium oxide.
Question 3.
Which paper do you use to check acidic or basic nature of any solution ?
Answer:
To test the nature of magnesium oxide, red litmus paper is used, which turns blue because the solution is basic (alkaline) in nature.
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 65)
Question 1.
What is the common name of copper sulphate ?
Answer:
The common name for Copper sulphate is Blue vitriol.
Question 2.
Write the colour and chemical formula of ferrous sulphate.
Answer:
The chemical formula of Iron sulphate is FeSO4 and colour of iron sulphate is green.
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 66)
Question 1.
What is the formula of lime water ?
Answer:
Chemical formula of lime water is Ca(OH)2.
Question 2.
How the presence of CO2 gas can be detected ?
Answer:
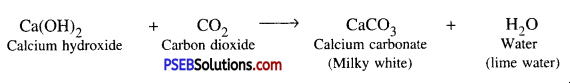
When Carbon dioxide gas is passed through freshly prepared lime water, then lime water turns milky due to the formation of calcium carbonate.

Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 67)
Question 1.
What is a chemical change ?
Answer:
Chemical change. A change in which one or more new substances are formed which differ in structure and properties from the original reacting substances, is called chemical change.

Question 2.
Write two observations to see chemical change.
Answer:
- Formation of a substance having new properties.
- Change in chemical composition.
Question 3.
What is lime water ?
Answer:
Lime water a solution of Calcium hydroxide.
Question 4.
What happens when carbon dioxide is passed through lime water ?
Answer:
When carbon dioxide passes through lime water, calcium carbonate is formed due to which its colour becomes milky.
Question 5.
Name the gas evolved when acetic acid (vinegar) reacts with baking soda.
Answer:
When vinegar (Acetic acid) reacts with baking soda, it produces carbon dioxide gas.

Question 6.
What is the colour and formula of copper sulphate ?
Answer:
Colour of Copper sulphate. Blue Chemical formula of Copper sulphate. CuSO4
Question 7.
Name some compounds formed as a result of chemical reactions.
Answer:
Names of some compounds formed as a result of chemical reactions-
- Calcium carbonate,
- Sodium chloride,
- Sodium nitrate,
- Copper Sulphate,
- Water,
- Carbon dioxide,
- Magnesium oxide.
Question 8.
In Chapter 5, you neutralised an acid with a base. Is neutralisation a chemical change ?
Answer:
Neutralisation is a chemical change because acids and alkalis combine to form salt and water as products. The composition and properties of salts are different from acid nor alkali, i.e. a new substance with new properties is formed. From this it is clear that neutralisation is a chemical change.

Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 69)
Question 1.
What is end product in the process of crystallisation ?
Answer:
In the process of crystallization only clear crystals are formed. No new substance having new composition and new properties is formed. So this is a physical change.
Question 2.
When will you stop dissolving copper sulphate powder to hot water ?
Answer:
Continue to dissolve the Copper Sulphate powder in hot water till it is not possible to dissolve more of Copper sulphate. This state is called the saturation state. When more copper sulphate cannot be dissolved, then leave the solution to cool.
PSEB 7th Class Science Guide Physical and Chemical Changes Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Fill in the Blanks:
(i) A changes in which only physical properties of a substance are changed, is a ……………….
change.
Answer:
Physical
(ii) Changes that lead to formation of new substance are called ………………. changes.
Answer:
Chemical Change
(iii) Fossil fuels produce …………………. gas on burning.
Answer:
Carbon dioxide
(iv) When carbon dioxide is passed through lime water, it turns ……………… .
Answer:
Milky White
(v) ……………….. is the method for the prevention of rusting of iron objects.
Answer:
Coating
2. Match the Column ‘A’ with Column ‘B’:
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (i) Physical change |
(a) Galvanization |
| (ii) Chemical change |
(b) Formation of a new substance |
| (iii) Prevention from rusting |
(c) Mixing of vinegar and Baking Soda |
| (iv) Evolution of carbon dioxide |
(d) Reversible change |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (i) Physical change |
(d) Reversible change |
| (ii) Chemical change |
(b) Formation of a new substance |
| (iii) Prevention from rusting |
(a) Galvanization |
| (iv) Evolution of carbon dioxide |
(c) Mixing of vinegar and Baking Soda |

3. Choose the Correct Answer:
Question (i)
The example of chemical change is:
(a) erruption of volcano
(b) burning of candle
(c) cooking of food
(d All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above.
Question (ii)
When acetic acid is mixed with baking soda, the gas evolved is:
(a) hydrogen
(b) oxygen
(c) carbon dioxide
(d) carbon monoxide
Answer:
(c) carbon dioxide.
Question (iii)
For rusting of iron objects, the essential requirement is:
(a) air (oxygen)
(b) moisture (water)
(c) open surface of object
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above.
Question (iv)
For prevention of rust, we use:
(a) a coat of oil and grease
(b) a coat of paint
(b) galvanization
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above.
Question (v)
The chemical formula of Rust is:
(a) Fe2O3
(b) FeCO3
(c) Fe2O3xH2O)
(d) FeCO3.xH2O
Answer:
(c) Fe2O3xH2O).
4. State True or False:
(i) Cutting a log of wood into pieces is a chemical change.
Answer:
True
(ii) Formation of manure from leaves is a physical change.
Answer:
False
(iii) Iron pipes coated with zinc do not get rusted easily.
Answer:
True

(iv) Iron and rust are the same substances.
Answer:
False
(v) Condensation of steam is not a chemical change.
Answer:
True
5. Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Question (i)
What is Rust ? Write its chemical formula.
Answer:
Rust.
When iron and items made of iron are exposed to the environment then the objects are attacked both by oxygen (air) and moisture present in the atmosphere. The surface of iron and iron items get covered by a layer of red, brown or orange color substance. This layer is called rust and this process is called corrosion of iron (Rusting of iron).
Chemical formula of rust: Fe2O3xH2O)
Question (ii)
Write the conditions necessary for rusting of iron.
Answer:
Conditions for rusting are:
- The open surface of an object made of iron.
- Presence of air (oxygen).
- Presence of moisture (water).
Question (iii)
Why are iron objects painted frequently ?
Answer:
Iron objects are painted so that the surface is not exposed to air (oxygen) and water in order to prevent the surface of iron from rusting.
Question (iv)
What is galvanization ?
Answer:
Galvanization. The process of depositing a layer of inert metal such as aluminium or zinc on the surface of iron objects, is called Galvanization.
Question (v)
Name two metals which are deposited on the surface of iron objects during the process of galvanization.
Answer:
Metals that are deposited on Iron are:
- Chromium and
- Nickel.

Question (vi)
Burning of candle is an example of which type of change-physical or chemical change ? Give reasons.
Answer:
Burning of candle is a chemical change because the wich of candle is made up of carbon and hydrogen. Candle flame burns to produce carbon dioxide and water which enters the atmosphere. On the other hand candle wax melts as a result of which its length decreases. Which is a physical change. Therefore it is an example of both physical and a chemical change.
Question (vii)
Why burning of fireworks is harmful ?
Answer:
The explosion of fireworks is a chemical change. Such explosions produce heat, light, noise and toxic gases, which pollute the atmosphere. So the pleasure of exploding fireworks is harmful exercise. The process of obtaining you are, therefore, advised not to use firecrackers.
Question (viii)
What is crystallisation ?
Answer:
Crystallisation.
Pure and large-sized geometrical shape of a substance from saturated solution of a substance is called crystallisation.
6. Short Answer Type Questions:
Question (i)
Mixing of baking soda and vinegar is a chemical change or a physical change. Discuss.
Answer:
When Vinegar (acetic acid) is mixed with baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) carbon dioxide, sodium acetate and water are formed. The composition and properties of these products are .very different from the reactants vinegar and baking soda, i.e. new substances with new properties are formed. So this reaction is a chemical change.
Question (ii)
Explain how cutting and burning wood are different type of change ?
Answer:
Cutting a piece of wood is a physical change because there is no formation of new substance having new properties.
Burning of wood on the other hand is a chemical change because after burning wood new substances carbondioxide water and ash are formed. We cannot reverse the process to get original substance (wood).
Question (iii)
What will happen when carbon dioxide is passed through lime water ?
Answer:
When carbon dioxide is passed through lime water, lime water becomes milky as it becomes Calcium carbonate.
Question (iv)
Why does the colour of copper sulphate (CuSO4) solution change, when an iron nail is dipped into it ? Write chemical equation also.
Answer:
Iron nail dipped here iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution in Copper sulphate solution changes the colour of Copper sulphate solution from blue to green due to the
formation of Iron sulphate.
Chemical Equation:


Question (v)
Magnesium ribbon is burnt and the ash formed is mixed with water. Now answer the following:
(a) Write equation for the burning of magnesium.
(b) What will happen when the mixture of ash and water is added to (a) blue litmus solution and (b) red litmus solution.
(c) Name the substances formed by mixing ash and water. Is acidic or basic ?
Answer:
(a) 2Mg + O2 > 2MgO (Magnesium oxide)
(b) When blue litmus is added to a solution of magnesium ash and water it does not change in colour. But on adding red litmus, the colour of litmus turns blue. This is because the solution of magnesium oxide is alkaline therefore, turns red litmus to blue.
(c) When Magnesium oxide ash is mixed with water it forms Mg (OH)2 which is alkaline.
7. Long Answer Type Questions:
Question (i)
What are physical and chemical changes ? Write differences between physical and chemical changes.
Answer:
Physical change.
It is a temporary change in which only the physical properties of a substance change i.e. change in colour, size, length, etc. This is therefore, a physical change. Physical change can be reversed by reversing the conditions. No new substance is formed in such a change.
Examples : Melting of wax, freezing of water into ice, magnetization of iron etc.
Chemical change.
A change in which new substances with one or more new properties are formed is called chemical change.
Examples : Burning of coal or wood, making of yogurt from milk, burning of magnesium ribbon, food spoilage, etc.
Differences between Physical and Chemical changes:
| Physical change |
Chemical change |
| (i) This is a temporary change. |
(i) This is a permanent change. |
| (ii) No new substance is formed in it. |
(ii) New substances with new properties are formed in it. |
| (iii) Products can be returned by simple methods. |
(iii) Products cannot be reversed by ordinary
means. |
| (iv) No difference in the composition of the substance. |
(iv) Great difference in the composition of
material. |
| (v) There is no energy change. |
(v) There is energy change. |
Question (ii)
What do you understand by rusting of iron ? Write the necessary conditions required for rusting of iron objects. How rusting of iron and iron objects can be prevented ?
Answer:
Iron rust.
This is a change in which iron and iron products are attacked when they come in contact with atmospheric air (oxygen) and moisture (water). As a result of this a reddish layer is formed on the surface of iron. This process weakens the strength of iron. This process and is called corrosion. This red dish brown layer formed on iron surface is called rust.
Conditions required for rusting :
(1) The open surface of an iron object.
(2) Presence of air (oxygen)
(3) Presence of moisture (water).
Measures to prevent iron from rusting : By preventing iron objects from coming into contact with oxygen (air) and water, we can prevent or reduce the process of rusting iron.
Iron can be prevented from rusting in the following ways :
(1) Applying a grease or oil coating. Applying a thin layer of grease / oil on the surface of iron products can prevent rusting.
(2) Paint. Corrosion can be prevented by applying a uniform and continuous layer of paint on the surface.
(3) Galvanisation. By depositing a layer of inert metal on the iron surface, the iron surface can be prevented from coming in contact with air and water. This process is called Galvanisation. Metals such as chromium and nickel are commonly used for iron coating.
Question (iii)
Give detail of process of crystallisation of copper sulphate (CuSO4).
Answer:
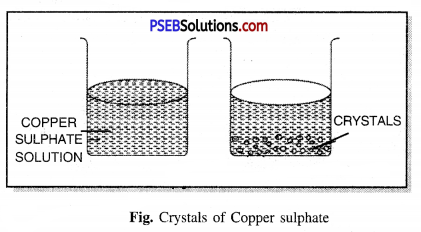
Method of making crystals of Copper Sulphate. Fill a beaker with water add a few drops of sulphuric acid. Heat it on a spirit lamp. When water starts boiling, add Copper sulphate powder slowly in it and keep stirring the solution. When the copper sulphate dissolves, add more copper sulphate powder until it does not dissolve any more powder. It is a saturated solution of Copper sulphate. Now leave this solution to cool. After a while you will see crystals of Copper sulphate formed. Filter it and keep the crystals to dry.
PSEB Solutions for Class 7 Science Physical and Chemical Changes Important Questions and Answers
1. Fill in the blanks:
(i) When carbondioxide is passed through lime water, it turns milky due to formation of ……………… .
Answer:
Calcium carbonate
(ii) The chemical name of baking soda is …………………
Answer:
Sodium bi-carbonate
(iii) Two methods by which rusting of iron can be prevented are ………………. and …………..
Answer:
Painting, galvanization
(iv) Changes in which only …………………. properties of a substance change are called physical
changes.
Answer:
physical

(v) Changes in which new substances are formed are called ………………… changes.
Answer:
chemical
2. Match the Column I with Column II:
| Column I |
Column II |
| (i) Carbon dioxide |
(a) Temporary change |
| (ii) Chemical changes |
(b) Turns lime water milky |
| (iii) Burning of magnesium wire in air |
(c) Evaporation |
| (iv) Physical change |
(d) Chemical change |
| (v) Conversion of water to vapours. |
(e) Formation of new products |
Answer:
| Column I |
Column II |
| (i) Carbon dioxide |
(b) Turns lime water milky |
| (ii) Chemical changes |
(e) Formation of new products |
| (iii) Burning of magnesium wire in air |
(d) Chemical change |
| (iv) Physical change |
(a) Temporary change |
| (v) Conversion of water to vapours. |
(c) Evaporation |
3. Choose the Correct Answer:
Question (i)
Rust is:
(a) Carbon dioxide
(b) Oxygen
(c) Iron
(d) Iron oxide
Answer:
(d) Iron oxide.
Question (ii)
Which of the following is not a physical transformation?
(a) Rusting of iron
(b) Melting of ice
(c) Dissolving sugar in water
(d) Freezing of water
Answer:
(a) Rusting of iron
Question (iii)
…………………. is a physical change.
(a) Rusting of iron
(b) Burning of magnesium ribbon
(c) Switching on light bulb
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Switching on light bulb.
Question (iv)
Whose crystals cannot be obtained?
(a) Sodium Chloride
(b) Copper Sulphate
(c) Carbon
(d) Iron sulphate
Answer:
(c) Carbon.
Question (v)
…………….. is the reaction of acid and alkali.
(a) Mixing
(b) Neutralisation
(c) Galvanization
(d) None
Answer:
(b) Neutralisation.

Question (vi)
The method of zinc coating on iron object is:
(a) Making alloys
(b) Neutralisation
(c) Galvanization
(d) Crystallization
Answer:
(c) Galvanization.
State True or False:
(i) Cutting a log of wood into pieces is a chemical change.
Answer:
False
(ii) Formation of manure from leaves is a physical change.
Answer:
False
(iii) Iron pieces coated with zinc do not get rusted easily.
Answer:
True
(iv) Iron and rust are the same substances.
Answer:
False
(v) Condensation of steam is not a chemical change.
Answer:
True
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Which type of change occurs when a rubber band is stretched ?
Answer:
Physical change.
Question 2.
Give an example of physical change caused due to air.
Answer:
Blowing a balloon.

Question 3.
What happens when a chemical change takes place ?
Answer:
New substance having new properties is formed.
Question 4.
What is rust ?
Answer:
Rust. It is a film of brownish iron oxide formed on iron articles due to moist air of the atmosphere.
Question 5.
What are two conditions necessary for rusting ?
Answer:
Presence of (i) air and (ii) water.
Question 6.
What happens when ash obtained from burning magnesium ribbon is dissolved in water ?
Answer:
Magnesium hydroxide is formed.
Question 7.
What is the nature of magnesium hydroxide ?
Answer:
It is basic in nature.
Question 8.
What is colour of copper sulphate solution ?
Answer:
Blue.

Question 9.
What happens when a nail is dipped in copper sulphate solution ?
Answer:
Blue colour of copper sulphate solution changes to green colour.
Question 10.
Which gas is formed when vinegar is mixed with baking soda ?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide gas.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Classify the following as physical or chemical changes:
(i) Melting of glass.
(ii) Burning of agarbatti.
(iii) Tearing of cloth.
(iv) Formation of seed from flower.
(v) Cooking of food.
(vi) Formation of cloud.
Answer:
Physical changes. Melting of glass, Tearing of cloth, Formation of cloud.
Chemical changes. Burning of agarbatti, Formation of seed from flower, Cooking of food.
Question 2.
Write characteristics of a physical change.
Answer:
Characteristics of a physical change:
- The final products are similar to the original substances.
- No new substances are formed.
- This change is easily reversible.
- It is a temporary change.
- The energy evolved during this change is very low.
- The total mass of reactants as well as products remains same.
Question 3.
Give characteristics of chemical change.
Answer:
Characteristics of chemical change:
- One or more new substances are formed.
- It is a permanent change and cannot be reversed easily.
- Energy change during chemical change is usually large.
- Total mass of reactants and products remains constant during the change.
Question 4.
Why is burning magnesium ribbon a chemical change ?
Answer:
Burning of Magnesium ribbon. When magnesium ribbon is burned in air, it gives out white bright light and changes into white ash. Since ash (magnesium oxide) is a new substance having different properties. So, burning of magnesium ribbon is a chemical change.

Question 5.
Why dissolving sugar in water is a physical change ?
Answer:
Dissolution of sugar in water. When sugar crystals are stirred in water, a clear solution is obtained. It is a physical change on the following basis:
- No new substance is formed.
- Sugar can be recovered by the process of crystallization.
- The change is not accompained by heat.
- Mass of sugar solution is equal to mass of water and sugar crystals.
Question 6.
When baking soda is mixed with lemon juice, bubbles are formed with the evolution of gas. What type of a change is it ? Explain.
Answer:
When baking soda is mixed with lemon juice (a weak acid) then carbondioxide is evolved in the form of bubbles.
This change is an example of a chemical change.
Question 7.
Explain why burning of wood and cutting it into small pieces are considered as two different types of changes.
Answer:
Burning of wood is a chemical change as wood on burning produces gases and ash.
Cutting of wood into its pieces have same physical properties. It is therefore, a physical change.
Question 8.
Explain how painting of an iron gate prevents it from rusting.
Answer:
Prevention of iron gate from rusting by painting. Rusting occurs in the presence of both water and air. If a coat of paint is applied to iron gate, its contact with air is broken and rusting is prevented.
Question 9.
Explain why rusting of iron objects is faster in coastal areas than in deserts.
Answer:
Faster rusting in coastal areas. The presence of humid air in coastal areas increases the rate of rusting. But on the other hand in deserts, air is dry, which inhibits the rate of rusting of iron.
Long Answer Type Question
Question 1.
What is crystallization? How will you prepare crystals of alum?
Answer:
Crystallization. It is the process of separating a pure substance in the form of crystals having well defined, geometrical shape from its hot saturated solution by cooling. This process is very commonly used to purify solid substances.
To prepare crystals of alum
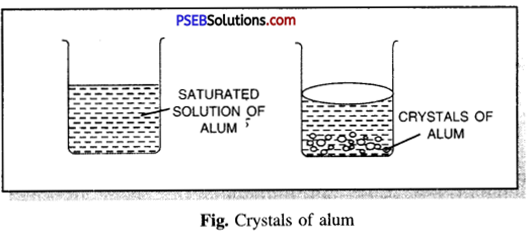
Take some distilled water in a beaker. Go on adding alum powder in installments slowly simultaneously with continuous stirring of the solution with a glass rod. Heat the beaker gently and try to dissolve more alum powder till it stops dissolving more alum powder. Filter the hot saturated solution in a glass beaker and allow it to cool. Observe the solution. Well-defined crystals of alum will be obtained after some time.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()