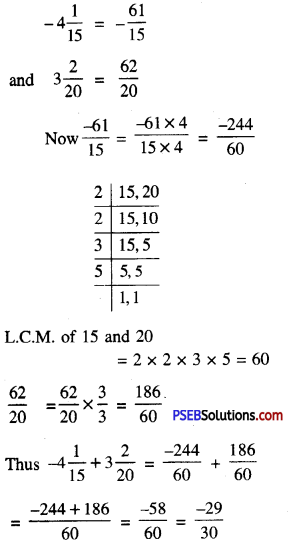
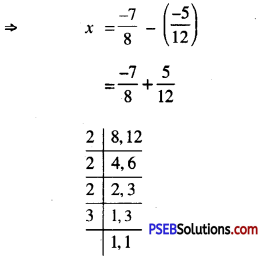
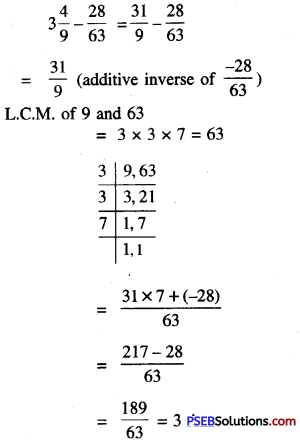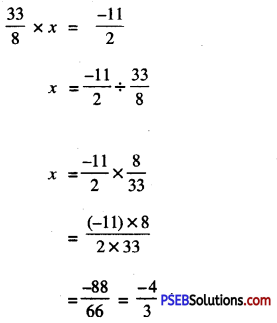Punjab State Board PSEB 10th Class Hindi Book Solutions Hindi Grammar prapatra poorti प्रपत्र पूर्ति Exercise Questions and Answers, Notes.
PSEB 10th Class Hindi Grammar प्रपत्र पूर्ति
प्रपत्र पाठ्यक्रम-बैंक, डाकघर तथा रेलवे से संबंधित प्रपत्र पूर्ति
‘प्रपत्र’ अंग्रेज़ी शब्द फार्म का अनुवाद है। आम बोलचाल की भाषा में प्रपत्र को फार्म भी कहते हैं। प्रपत्र शब्द पत्र के आगे ‘प्र’ उपसर्ग लगाने से बना है। बालक के जन्म से लेकर मृत्यु तक के प्रपत्र भरकर बालक का जन्म प्रमाण-पत्र तथा मृतक का मृत्यु प्रमाण-पत्र प्राप्त करना होता है। इसके अतिरिक्त स्कूल, कॉलेज में प्रवेश के लिए, परीक्षा देने के लिए, नौकरी के लिए, प्रतियोगी परीक्षाओं के लिए, राशन कार्ड, आधार कार्ड, बिजली-पानीटेलीफोन-मोबाइल, गैस कनेक्शन लेने के लिए, पासपोर्ट बनवाने, बैंक/डाकखाने में पैसे जमा कराने या निकालने के लिए, रेल-हवाई यात्रा के समय आरक्षण कराने के लिए, विवाह के पंजीकरण, वाहन पंजीकरण, व्यवसाय पंजीकरण आदि अनेक कार्यों के लिए भी प्रपत्र भरने होते हैं। कोई भी प्रपत्र भरते समय निम्नलिखित तथ्यों का ध्यान रखना चाहिए-
(क) प्रपत्र के साथ दिए गए निर्देशों को अच्छी प्रकार से पढ़ कर ही प्रपत्र भरना चाहिए।
(ख) प्रपत्र में दिए गए निर्देश के अनुसार ही प्रपत्र को पैन/बॉलपैन/पेंसिल से भरना चाहिए।
(ग) प्रपत्र में जिन स्तंभों (कॉलमों) को अंग्रेज़ी के बड़े (कैपिटल) अक्षरों में भरना हो, उन्हें बड़े अक्षरों में भरना चाहिए।
(घ) प्रपत्र पर अपना छायाचित्र (फोटो) उचित स्थान पर चिपकाएं या पिन से नत्थी कीजिए। यदि फ़ोटो को सत्यापित (अटैस्ट) कराना है अथवा अपने हस्ताक्षर करने हैं, तो वह भी कीजिए।
(ङ) प्रपत्र के साथ निर्देशानुसार स्वहस्ताक्षरित अथवा राजपत्रित अधिकारी द्वारा सत्यापित (अटैस्टिड) दस्तावेज़ लगाएँ।
(च) प्रपत्र का कोई भी स्तम्भ (कॉलम) रिक्त न छोड़ें। यदि वह स्तम्भ आप पर लागू नहीं होता तो वहां लागू नहीं लिख दीजिए।
(छ) प्रपत्र में दिए गए स्थान पर अपने हस्ताक्षर कीजिए तथा स्थान और दिनांक लिखिए।
(ज) प्रपत्र साफ़, स्पष्ट, सुंदर तथा पढ़ा जा सके-ऐसे अक्षरों में भरा जाना चाहिए।
(झ) प्रपत्र भरकर व्यक्तिगत रूप से जमा कराते समय उसकी जमा करने वाले कार्यालय से रसीद ले लें। डाक से रजिस्ट्री अथवा स्पीड-पोस्ट से प्रपत्र भरकर भेज सकते हैं। यहाँ कुछ प्रपत्रों को भरने के उदाहरण दिए जा रहे हैं।

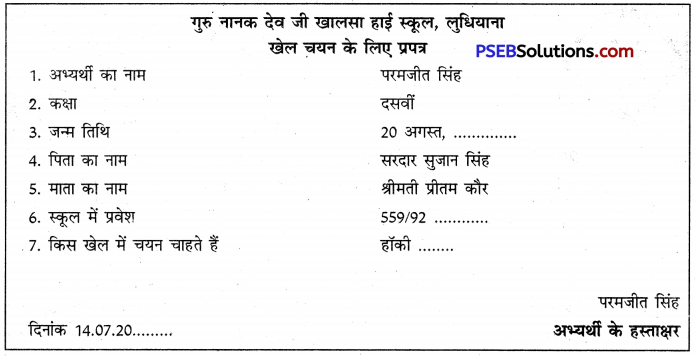
1. उदाहरण-किसी खेल में चयन के लिए दिए गए प्रपत्र को भरना-
2. उदाहरण-नौकरी के लिए दिए गए प्रपत्र को भरना
(क) व्यक्तिगत तथा पारिवारिक विवरण
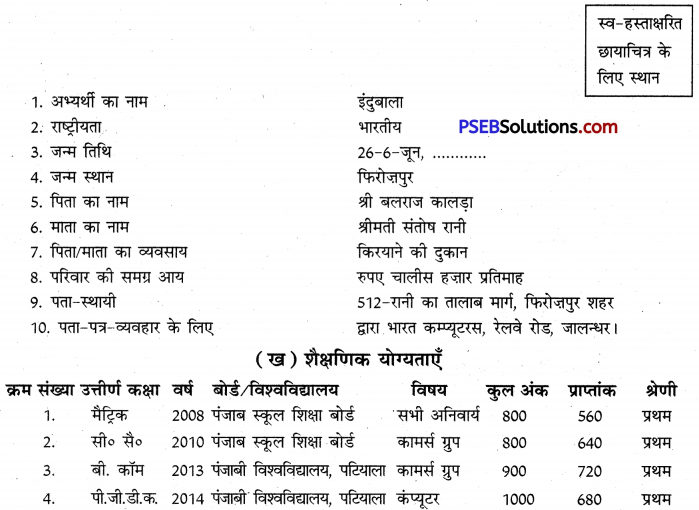
(ग) व्यावसायिक अनुभव (यदि कोई हो)

दसवीं के पाठ्यक्रम में बैंक, डाकघर तथा रेलवे से संबंधित प्रपत्रों की पूर्ति निर्धारित है। इसलिए यहाँ इन्हीं तीनों विभागों से संबंधित प्रपत्रों पर विस्तार से चर्चा की जा रही है-
(क) बैंक से संबंधित प्रपत्र
आधुनिक युग में बैंकों का हमारे दैनिक जीवन में बहुत महत्त्व है। इससे हमारे लेन-देन तथा व्यवसाय में बहुत सहायता मिलती है। बैंक में खाता खुलवाने के लिए कुछ प्रमाण-पत्रों की आवश्यकता होती है, जो निम्नलिखित हैं-
- आवासीय पते का प्रमाण-पत्र; जैसे-राशन कार्ड, आधार कार्ड, ड्राइविंग लाइसेंस, पासपोर्ट, वरिष्ठ नागरिक प्रमाण-पत्र आदि।
- जिस बैंक में खाता खुलवाना हो वहाँ के किसी खाताधारी से गवाही।
- फ़ोटो।
- पैनकार्ड की प्रतिलिपि।
- जन-धन योजना में शून्य राशि से खाता खुल सकता है।
- विद्यार्थियों को अपने विद्यालय के पहचान-पत्र तथा प्राचार्य के हस्ताक्षरित खाता खोलने के फार्म के आधार पर बैंक में शून्य राशि से खाता खोलने की सुविधा है।
- बैंक में खाता खोलने वाले को बैंक में अपने नमूने के हस्ताक्षर भी देने पड़ते हैं, जिससे कोई अन्य व्यक्ति उसके खाते से रुपए नहीं निकाल सके।
- बैंक में खाता खोलने के बाद मिलने वाले ए०टी०एम० कार्ड से खाता धारक किसी भी ए०टी०एम० बूथ से कभी भी पैसे निकलवा सकता है तथा खरीददारी भी कर सकता है।
बैंक में खातों के प्रकार-बैंक में खातों के अनेक प्रकार होते हैं; जैसे-बचत खाता, चालू खाता, आवर्ती खाता, सावधि जमा खाता आदि। विद्यार्थियों को बचत खाता खुलवाना चाहिए, जिसमें उनकी छात्रवृत्ति, अपनी बचत आदि जमा हो सकती है। बचत खाता, आवर्ती खाता तथा सावधि खाता पर बैंक जमा राशि पर नियमानुसार ब्याज भी देते हैं, जो खाताधारक के खाते में जमा होता रहता है। बैंक के लेन-देन में मुख्य रूप से निम्नलिखित प्रपत्र प्रयोग में आते हैं-
- बैंक में खाता खोलने का प्रपत्र
- रुपए नकद जमा करने का प्रपत्र
- राशि चैक द्वारा जमा करने का प्रपत्र
- रुपए निकलवाने का प्रपत्र/चैक
- ड्राफ्ट बनवाने का प्रपत्र।
यहां प्रमुख प्रपत्रों की रूपरेखा तथा उनके भरने के उदाहरण दिए जा रहे हैं-
1. बैंक में खाता खोलने का प्रपत्र
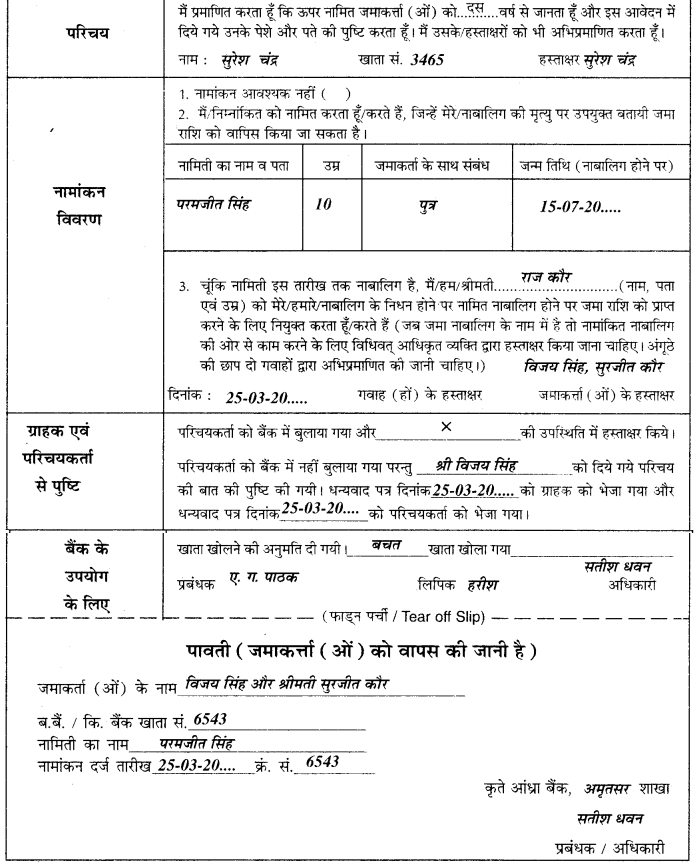
बैंक में खाता खोलने के प्रपत्र के प्रत्येक कॉलम को ध्यान से पढ़कर साफ़-साफ़ शब्दों में भरिए। खाता एक व्यक्ति अकेले या दो-तीन व्यक्ति मिलकर भी खोल सकते हैं तथा इस संबंध में परिचालन का विकल्प चुन सकते हैं। किसी खाता धारक से परिचय भी दिया जाता है तथा नामांकन का पूरा विवरण भी भरिए। नामिती नाबालिग हो तो उसके संरक्षक का नाम भी लिखना होता है। खाता खोलने हेतु आवेदन फार्म का एक उदाहरण यहां दिया जा रहा है-
1. खाता खोलने का प्रपत्र
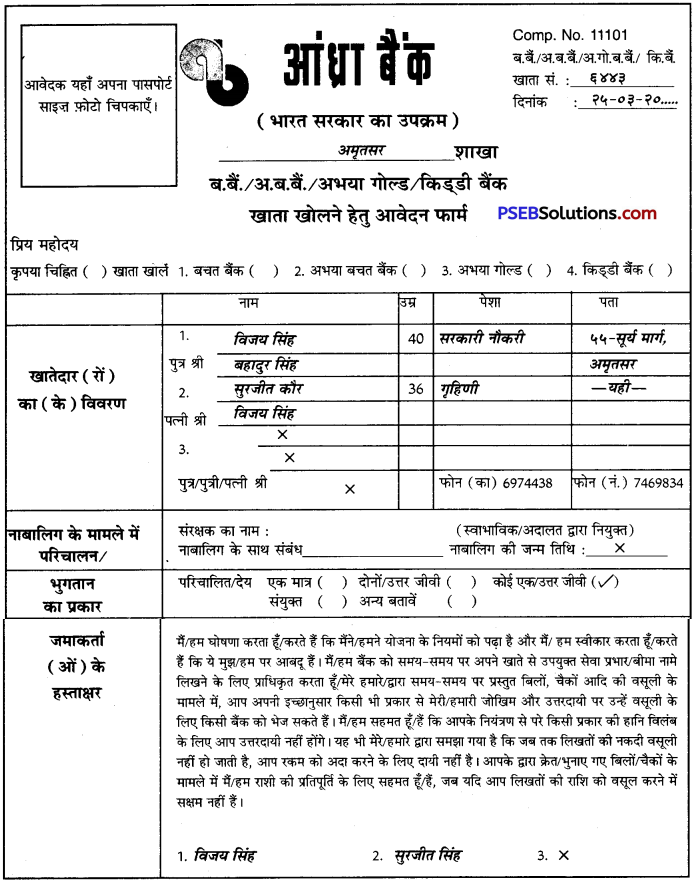
प्रश्न 1.
विद्यार्थियों को बैंक में खाता खुलवाने के लिए किन-किन दस्तावेज़ों की आवश्यकता होती है?
उत्तर:
आधुनिक युग में बैंकों का हमारे दैनिक जीवन में बहुत महत्त्व है। इससे हमारे लेन-देन तथा व्यवसाय में बहुत सहायता मिलती है। बैंक में खाता खुलवाने के लिए कुछ प्रमाण-पत्रों की आवश्यकता होती है, जो अग्रलिखित हैं-
- आवासीय पते का प्रमाण-पत्र ; जैसे-राशन कार्ड, आधार कार्ड, ड्राइविंग लाइसेंस, पासपोर्ट वरिष्ठ नागरिक प्रमाण-पत्र आदि।
- जिस बैंक में खाता खुलवाना हो वहाँ के किसी खाताधारी से गवाही।
- फ़ोटो।
- पैनकार्ड की प्रतिलिपि।
- जन-धन योजना में शून्यराशि से खाता खुल सकता है।
- विद्यार्थियों को अपने विद्यालय के पहचान-पत्र तथा प्राचार्य के हस्ताक्षरित खाता खोलने के फार्म के आधार पर बैंक में शून्य राशि से खाता खोलने की सुविधा है।
- बैंक में खाता खोलने वाले को बैंक में अपने नमूने के हस्ताक्षर भी देने पड़ते हैं, जिससे कोई अन्य व्यक्ति उसके ख़ाते से रुपए नहीं निकाल सके।

2. बैंक में पैसे जमा कराने का प्रपत्र
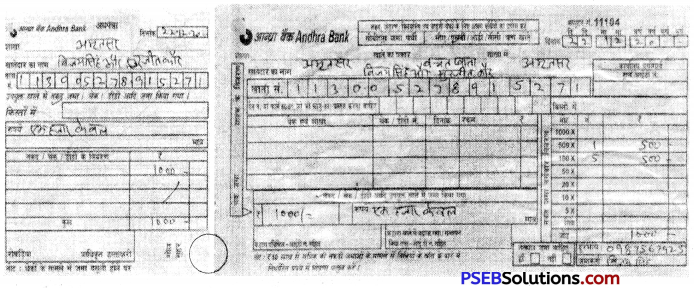
बैंक में नकद राशि जमा करने के लिए जो प्रपत्र भरना होता है, उसके दो हिस्से होते हैं। एक बैंक की प्रति तथा दूसरी ग्राहक की प्रति होती है। इन दोनों हिस्सों को भरना होता है, जिसमें दिनांक, खाता संख्या, खाताधारी का नाम, जमा राशि तथा जमा राशि का विवरण कि किस-किस राशि के कितने नोट हैं लिखना होता है। दिए गए स्थान पर मोबाइल नंबर लिखकर जमाकर्ता के हस्ताक्षर होते हैं। यहाँ एक उदाहरण दिया जा रहा है जिसमें विजय सिंह और सुरजीत कौर के खाते में एक हज़ार रुपए नकद जमा करने के लिए प्रपत्र भरा गया है-
3. बैंक में चैक द्वारा राशि जमा कराने का प्रपत्र बैंक में चैक जमा कराने का प्रपत्र भी दो भागों में होता है। एक प्रति बैंक की तथा दूसरी ग्राहक की होती है। इसमें दिनांक, खाते का प्रकार तथा संख्या, खातेदार का नाम, चैक संख्या, चैक जारी करने वाले बैंक तथा शाखा का नाम, दिनांक तथा राशि भरनी होती है। यहाँ एक उदाहरण दिया जा रहा है जिसमें मनमोहन सिंह अपने खाते में दस हज़ार रुपए का चैक जमा कर रहे हैं-
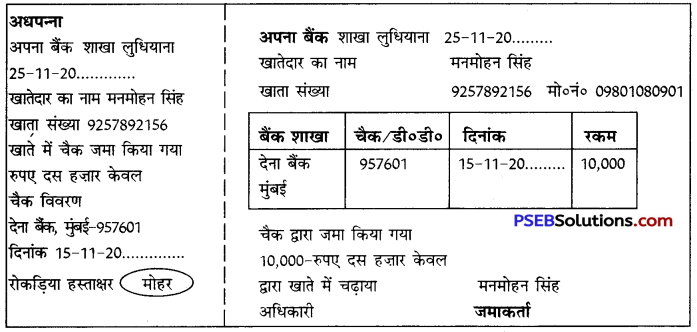
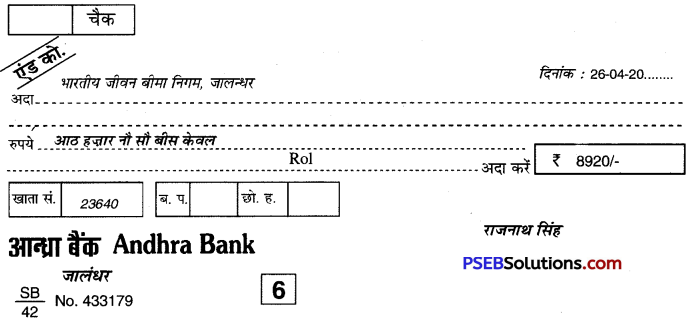
4. बैंक से रुपए निकलवाने का प्रपत्र/चैक बैंक से रुपए निकलवाने के लिए बैंक के भगतान प्रपत्र तथा बैंक द्वारा दिए गए चैक का प्रयोग किया जाता है। चैक द्वारा किसी संस्था अथवा व्यक्ति को भी भुगतान कर सकते हैं। बैंक से भुगतान प्रपत्र पर रुपए निकलवाने के लिए पासबुक साथ लगानी पड़ती है। इसमें खातेदार अपने खाते की संख्या, निकाले जाने वाली राशि, दिनांक तथा अपने हस्ताक्षर कर के राशि निकलवा सकता है। प्रीतम कौर अपने खाते से दस हज़ार रुपए भुगतान प्रपत्र पर निकाल रही है। इसका उदाहरण यहाँ दिया जा रहा है-

चैक द्वारा किसी को भुगतान करने अथवा स्वयं रुपए निकालने के लिए चैक में दिनांक, खाता संख्या, किसे भुगतान करना है, राशि तथा खाताधारी के हस्ताक्षर करना आवश्यक होता है। यहाँ एक चैक राजनाथ सिंह द्वारा भारतीय जीवन बीमा निगम को आठ हजार नौ सौ बीस रुपए का जारी किया गया है उसका प्रारूप यहाँ दिया जा रहा है। चैक को रेखांकित कर देना चाहिए इस चैक को कोई अन्य नहीं भुना सकता।
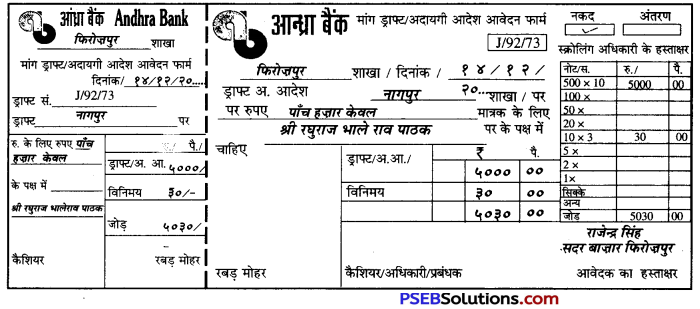
5. बैंक ड्राफ्ट बनवाने का प्रपत्र
बैंक ड्राफ्ट एक मांग-प्रपत्र होता है, जिसे कोई भी व्यक्ति बैंक को निर्धारित शुल्क देकर बनवा सकता है। यह बैंक की एक शाखा द्वारा अपनी उस शाखा के नाम जारी किया जाता है जहाँ ग्राहक ने अपनी राशि भेजनी है। बैंक ड्राफ्ट पाने वाला व्यक्ति उस शाखा से ड्राफ्ट की राशि नकद अथवा अपने बैंक खाते में जमा करवा कर प्राप्त कर सकता है। बैंक ड्राफ्ट के प्रपत्र में दिनांक, आवेदन का नाम पता, किसके पक्ष में, कहाँ भेजना है, ड्राफ्ट की राशि, शुल्क आवेदक के हस्ताक्षर, मोबाइल नंबर भरने होते हैं। यहाँ राजेन्द्र सिंह द्वारा श्री रघुराज भालेराव पाठक को नागपुर पाँच हज़ार रुपए का ड्राफ्ट बनवाने का प्रपत्र उदाहरण के रूप में भरकर दिया जा रहा है। ड्राफ्ट के लिए राजेन्द्र सिंह ने दिए पाँच हजार तीस रुपए हैं परन्तु उसे ड्राफ्ट पांच हज़ार रुपए का ही मिलेगा। तीस रुपए ड्राफ्ट बनवाने का शुल्क है। इसके भी दो भाग होते हैं। एक ग्राहक के लिए तथा दूसरा बैंक के लिए-
बोर्ड परीक्षाओं में पूछे गए प्रपत्र-पूर्ति सम्बन्धी प्रश्नोत्तर
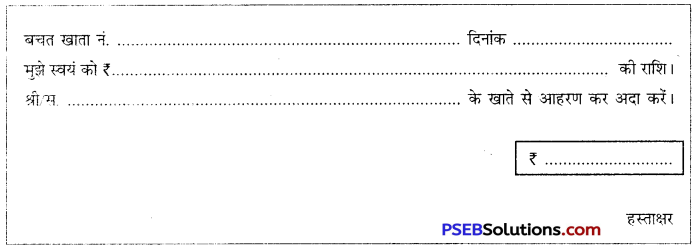
प्रश्न 1.
मान लो आपका नाम निर्मला देवी है। आपको सेविंग्स बैंक खाता नं0 79684 में से दस हज़ार रुपये निकलवाने हैं। अत: आप नीचे दिए गए प्रपत्र की रूपरेखा को अपनी उत्तर-पुस्तिका पर उतार कर भरें-
उत्तर:

प्रश्न 2.
मान लो आपका नाम तमन्ना है। आपका मुख्य डाकघर, अमृतसर में बचत खाता नं0 764329 है। आपके इस खाते में ₹4,500/- हैं। आपको इस खाते में ₹ 1,500/- जमा करवाने हैं। इसलिए नीचे दिए गए प्रपत्र के प्रारुप को अपनी उत्तर-पुस्तिका पर उतार कर भरें-
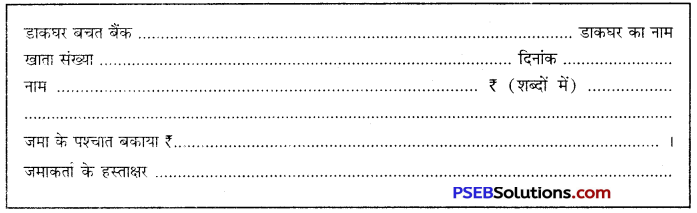
उत्तर:
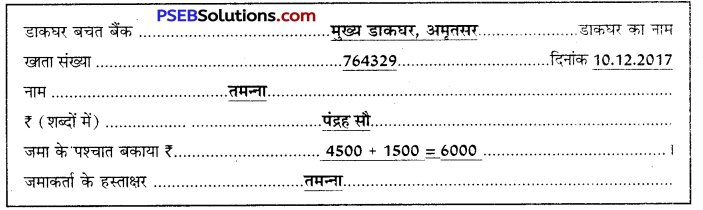

प्रश्न 3.
मान लीजिए आपका नाम विनोद कुमार है। आप पटियाला में रहते हैं। आपको अपने बचत खाता नं० 17321986 में र दो हज़ार जमा करवाने हैं। अत: आप नीचे दिए गए प्रपत्र की रूपरेखा को अपनी उत्तरपुस्तिका पर उतार कर भरें-

उत्तर:
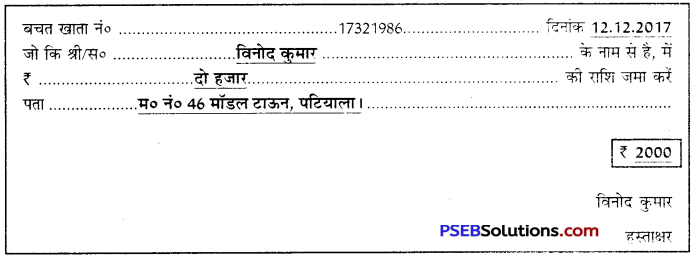
(ख) डाकघर से संबंधित प्रपत्र
डाकघर में भी बैंक की तरह अनेक प्रकार से लेन-देन होता है तथा यहाँ भी रुपए जमा करने, निकालने, मनीआर्डर से रुपए भेजने आदि से संबंधित अनेक कार्य होते हैं, जिनके लिए अनेक प्रपत्रों का प्रयोग करना पड़ता है। डाकखाने में प्रयोग में आने वाले मुख्य प्रपत्र अग्रलिखित हैं-
- खाता खोलने का प्रपत्र
- रुपए जमा कराने का प्रपत्र
- रुपए निकलवाने का प्रपत्र
- मनीआर्डर से रुपए भेजने का प्रपत्र
1. डाकघर में खाता खोलने का प्रपत्र
डाकघर में खाता खोलने के लिए दिए गए प्रपत्र को ध्यानपूर्वक पढ़कर सभी कॉलम साफ़-साफ़ शब्दों में भरने चाहिए। खाता एक व्यक्ति अथवा संयुक्त रूप से दो-तीन व्यक्ति भी खोल सकते हैं। परिचायक का नाम, पता तथा खातेदारों के हस्ताक्षर करने होते हैं। खाते में नामांकन भी किया जा सकता है। उदाहरण के लिए एक भरा हुआ प्रपंत्र यहाँ दिया जा रहा है-
डाकघर बचत-बैंक
खाता खोलने के लिए आवेदन पत्र
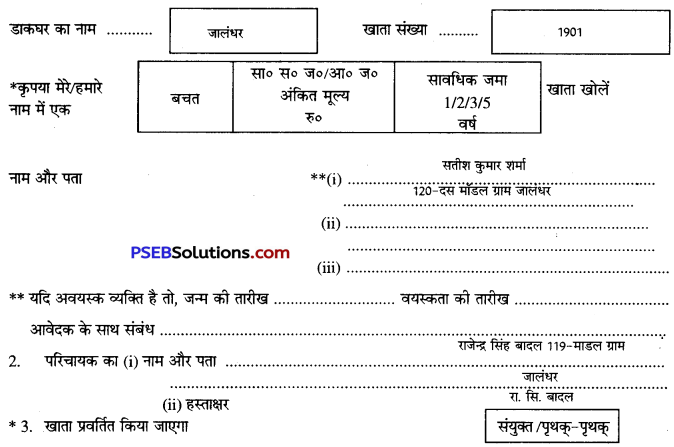
4. मैंहम किसी भी समय सुसंगत नियम में विनिर्दिष्ट सीमा के भीतर अपने सभी एकल या संयुक्त बचत बैंक/सा० स० ज० खातों में अतिशेष बनाए रखने का और डाकघर बचत बैंक से मांग किए जाने पर ऐसे सभी खातों की विशिष्टियां भी देने का वचन देता हूँ/देते हैं।
5. मैं/हम केंद्रीय सरकार द्वारा बनाए गए ऐसे नियमों का पालन करने के लिए सहमत हूँ/हैं जो समय-समय पर खाते को लागू हों।
6. मैं हम सरकारी बचत बैंक अधिनियम, 1873 (1873 का 5) की धारा 4 के अधीन नीचे व्यक्ति (व्यक्तियों) को अपनी मृत्यु हो जाने की दशा में खाते में जमा रकम के लिए एकमात्र प्राप्तकर्ता (प्राप्तकर्ताओं) के रूप में नाम निर्दिष्ट करता हूँ करते हैं।

2. डाकघर में पैसे जमा कराने का प्रपत्र
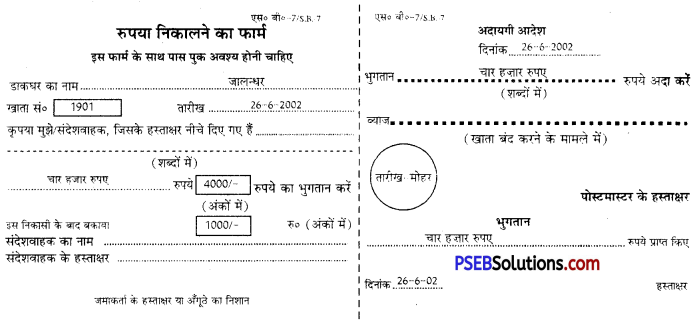
डाकघर में धनराशि जमा करवाने के प्रपत्र में खाताधारी को डाकघर का पता, दिनांक, खातेधारी का नाम, खाता संख्या, जमा कराने की राशि शब्दों और अंकों में, जमा के बाद कुल राशि लिख कर अपने हस्ताक्षर करने होते हैं। इसके साथ डाकघर बचत बैंक की पास बुक भी लगानी होती है, जिसमें बचत बैंक सहायक जमा की गई राशि लिखकर, डाकघर की मोहर लगाकर तथा अपने हस्ताक्षर कर जमाकर्ता को वापिस कर देता है। यहां जालंधर के डाकघर में सतीश कुमार शर्मा के खाता संख्या 1901 में एक हज़ार रुपए जमा करने के प्रपत्र को भरकर उदाहरण के रूप में दिया जा रहा है।

3. डाकघर बचत बैंक से पैसे निकलवाने का प्रपत्र
डाकघर बचत बैंक से पैसे निकलवाने के लिए प्रपत्र में जमाकर्ता को डाकघर का नाम, दिनांक, खाता संख्या, निकाली गई राशि, शेष राशि, यदि आवश्यकता हो तो संदेशवाहक का नाम, हस्ताक्षर देने होते हैं। अदायगी आदेश में राशि मिलने के हस्ताक्षर खातेदार अथवा संदेशवाहक द्वारा किए जाते हैं। यहां एक उदाहरण के रूप में भरा हुआ प्रपत्र दिया जा रहा है-

प्रश्न 3.
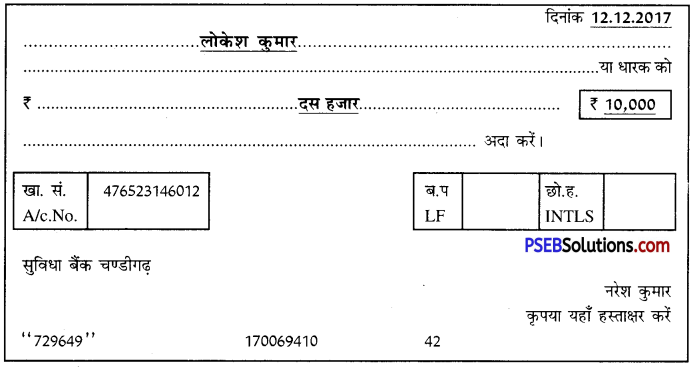
मान लीजिए आपका नाम नरेश कुमार है। आपको लोकेश कुमार को दिनांक 10.04.2016 को ₹10,000/- का स्वहस्ताक्षरित रेखांकित किया हुआ चेक लिखकर देना है। इस अनुसार निम्नलिखित चेक के प्रपत्र को भरें-
उत्तर:
4. मनीऑर्डर से रुपये भेजने का प्रपत्र
मनीऑर्डर से रुपए भेजने का काम डाकघर में वर्षों से हो रहा है। डाकघर से मनीऑर्डर प्रपत्र लेकर भरना होता है। इसके 6 भाग होते हैं। पहला भाग जिसे रुपये भेजने हैं रुपयों की संख्या शब्दों और अंकों में प्राप्तकर्ता का नाम, पता, पिनकोड, दिनांक लिखकर भेजने वाला अपने हस्ताक्षरकर्ता है। चौथा भाग में भेजने वाले का नाम पता तथा पिन कोड लिखना होता है। छठे भाग में भेजने वाला संदेश लिख सकता है। दूसरा, तीसरा और पांचवां भाग डाक विभाग ने भरना होता है। डाविभाग भेजने वाली राशि पर निर्धारित शुल्क भी लेता है। यहाँ मनीऑर्डर प्रपत्र को भर कर प्रस्तुत किया जा रहा है-

(संदेश के लिए स्थान)
जालन्धर शहर प्रिय, सुजान
02-12-2000 तुम्हारे पत्र के अनुसार 800 सौ रुपए भेज रहे हैं । मिलने पर सूचना देना और रुपयों की ज़रूरत हो तो लिखना। सब को सत श्री अकाल कहना।
तुम्हारा मित्र,
सुखदेव सिंह
5. इलेक्ट्रानिक मनीआर्डर (ई०एम०ओ०) आधुनिक युग में इंटरनेट की प्रगति के साथ-साथ अपनी धनराशि किसी दूसरे को भेजने का इलेक्ट्रानिक मनीऑर्डर जल्दी से जल्दी और सरलता से भेजने का डाक विभाग द्वारा चलाया गया मनीऑर्डर का नया रूप है। इससे आम मनीआर्डर भेजने की अपेक्षा कम समय लगता है। जिस दिन ई०एम०ओ० किया जाता है, वह उसी दिन प्राप्तकर्ता को मिल जाता है। इस पर भी डाक विभाग निर्धारित शुल्क लेता है। इसके प्रपत्र की रूपरेखा यहाँ प्रस्तुत की जा रही है-

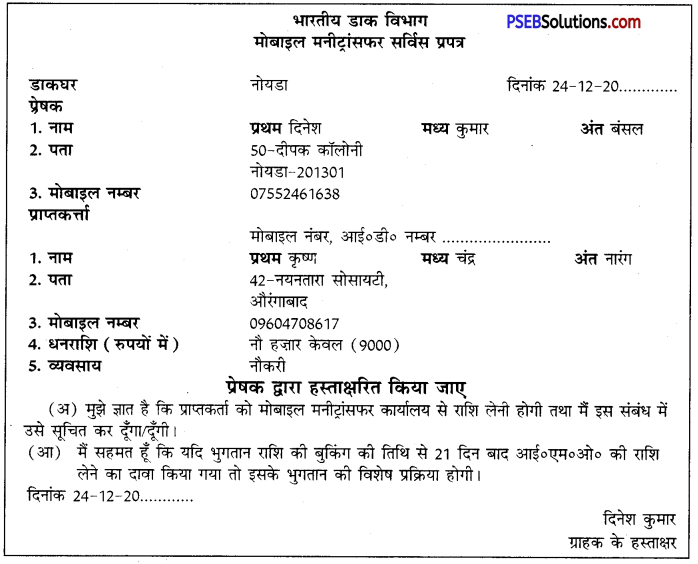
6. मोबाइल मनीट्रांसफर सर्विस (इंसटेंट मनीऑर्डर) मोबाइल मनीट्रांसफर सर्विस धन भेजने का सबसे तेज़, सुविधाजनक, विश्वसनीय और सरल माध्यम है। इसे इंसटेट मनीऑर्डर अथवा तत्काल मनीआर्डर भी कहते हैं। इस माध्यम से कुछ ही मिनटों में धनराशि प्राप्तकर्ता को मिल जाती है। डाकघर से प्राप्त प्रपत्र को भर कर अधिकारी को देने पर प्रेषक को कम्प्यूटर द्वारा सोलह अंकों का सीलबंद गुप्त नम्बर दिया जाता है, जिसे प्रेषक प्राप्तकर्ता को फोन, एस०एम०एस० अथवा ई-मेल द्वारा बता देता है, जो इंसटेंट मनीऑर्डर के अपने नगर के केंद्र पर जाकर वहाँ के अधिकारी को बताता है तथा अपनी पहचान का फोटो पहचानपत्र दिखाकर प्रेषक द्वारा उसे भेजी गई राशि प्राप्त कर सकता है। इस सेवा में उन्नीस हज़ार रुपए तक की राशि नकद प्राप्त की जा सकती है जबकि बीस हज़ार रुपए अथवा उससे अधिक राशि का भुगतान चैक द्वारा किया जाता है। इस सेवा को प्राप्त करने का प्रपत्र अग्रलिखित है-

प्रश्न 1.
इन्सटेंट मनीऑडर्र (आई०एम०ओ) किसे कहते हैं?
उत्तर:
मोबाइल मनीट्रांसफर सर्विस धन भेजने का सबसे तेज़, सुविधाजनक, विश्वसनीय और सरल माध्यम है। इसे इंसटेट मनीऑर्डर अथवा तत्काल मनीआर्डर भी कहते हैं। इस माध्यम से कुछ ही मिनटों में धनराशि प्राप्तकर्ता को मिल जाती है। डाकघर से प्राप्त प्रपत्र को भरकर अधिकारी को देने पर प्रेषक को कम्प्यूटर द्वारा सोलह अंकों का सीलबंद गुप्त नम्बर दिया जाता है, जिसे प्रेषक प्राप्तकर्ता को फोन, एस०एम०एस० अथवा ई०-मेल द्वारा बता देता है, जो इंसटेंट मनीऑर्डर के अपने नगर के केंद्र पर जाकर वहाँ के अधिकारी को बताता है तथा अपनी पहचान का फोटो पहचानपत्र दिखाकर प्रेषक द्वारा उसे भेजी गई राशि प्राप्त कर सकता है। इस सेवा में उन्नीस हजार रुपए तक की राशि नकद प्राप्त की जा सकती है जबकि बीस हज़ार रुपए अथवा उससे अधिक राशि का भुगतान चैक द्वारा किया जाता है।
7. अंतर्राष्ट्रीय धन अंतरण
डाकघर में विदेशों से धन मंगवाने अथवा भेजने के लिए मनीऑर्डर सेवाओं के अन्तर्गत अंतर्राष्ट्रीय धन अंतरण सेवा, मनीग्राम, इलेक्ट्रानिक क्लियरेंस सेवाएं (ई०सी०एस०) आदि भी समुचित मूल्य पर उपलब्ध हैं।
8. इंडियन पोस्टल ऑर्डर
इंडियन पोस्टल ऑर्डर डाकघर से निश्चित राशि के प्राप्त किये जा सकते हैं। इनके द्वारा एक व्यक्ति किसी दूसरे व्यक्ति अथवा संस्था को धनराशि भेज सकता है। ये भारत के सभी डाकघरों से प्राप्त किए जा सकते हैं। विभिन्न प्रतियोगी परीक्षाओं, नौकरियों के आवेदन-पत्रों आदि का शुल्क इंडियन पोस्टल ऑर्डर द्वारा मांगा जाता है। इन्हें रेखांकित भी कर सकते हैं। इसकी खरीद तिथि से वैधता दो वर्षों की होती है। इसे प्रयोग नहीं करने पर निश्चित अवधि में वापस करने पर खरीदी हुई राशि वापस भी ली जा सकती है।
इसके दो भाग फॉइल और काउंटर फॉइल होते हैं जिसके नाम इंडियन पोस्टल ऑर्डर भेजा जाता है उसे फॉइल कहते हैं और जो हिस्सा भेजने वाले के पास रहता है उसे काउंटर फॉइल कहते हैं। पोस्टल आर्डर में राशि प्राप्तकर्ता का नाम, पता, शहर, प्रेषक का नाम पता, दिनांक तथा जिस डाकघर से प्राप्तकर्ता को धनराशि प्राप्त करनी है उसका नाम लिखा जाता है। यदि इसे रेखाकिंत करना है तो वह भी किया जाता है। यहाँ इंडियन पोस्टल ऑर्डर का एक उदाहरण दिया जा रहा है, जिसमें गुरनाम सिंह, फिरोजपुर, पंजाब लोक सेवा आयोग, लुधियाना को एक रुपए का पोस्टल ऑर्डर भेज रहा है-

9. रजिस्ट्री-पत्र की पावती
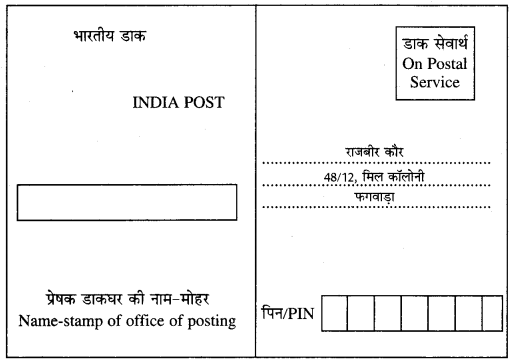
डाकघर से किसी को रजिस्ट्री-पत्र भेजते समय उसके साथ रजिस्ट्री-पत्र की पावती भी लगानी होती है। यह पावती रजिस्ट्री-पत्र प्राप्तकर्ता हस्ताक्षर कर प्रेषक के पास भेज देता है। इसमें भेजने वाले को अपना तथा प्राप्तकर्ता का पूरा पता लिखना होता है। इसके आगे-पीछे दो भाग होते हैं। इसका प्रारूप निम्नलिखित है-
रजिस्ट्री-पावती प्रपत्र

(ग) रेलवे आरक्षण प्रपत्र
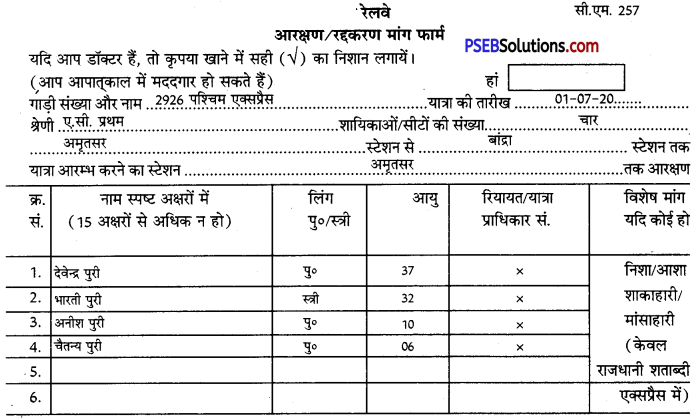
रेलवे में आरक्षण करवाने अथवा आरक्षण रद्द करवाने के लिए प्रपत्र भरना होता है। दोनों ही स्थितियों में एक प्रकार का ही प्रपत्र प्रयोग में आता है। भरने से पहले उस पर लिखना होता है कि आरक्षण लेने के लिए प्रपत्र भर रहे हैं । अथवा आरक्षण रद्द करवाने के लिए। इस प्रपत्र में तीन भाग होते हैं । प्रथम भाग में आरक्षण लेने अथवा रद्द की जाने वाली रेलगाड़ी का नाम, क्रमांक, यात्रा करने की तिथि, श्रेणी, कहां से कहाँ तक, यात्रियों के नाम, आयु, लिंग, आवेदक का नाम, पता, मोबाइल नम्बर तथा हस्ताक्षर होते हैं। दूसरा भाग में वापसी यात्रा का विवरण तथा तीसरा भाग रेलवे के कर्मचारी भरते हैं। इसका एक उदाहरण यहाँ दिया जा रहा है-
रेलवे आरक्षण कराने के लिए प्रपत्र का नमूना
उत्तर:
आगे की यात्रा/वापसी यात्रा का विवरण

टिप्पणी : 1. अधिकतम अनुपेय यात्रियों की संख्या प्रति मांग पत्र 6 व्यक्ति।
2. एक बार एक व्यक्ति से केवल एक ही मांग पत्र स्वीकार किया जाएगा।
3. कृपया खिड़की छोड़ने से पहले अपने टिकट और शेष राशि की जांच कर लें।
4. ठीक ढंग से न भरे हुए तथा अपठनीय फार्म स्वीकार नहीं किए जाएंगे।
5. विशेष मांग पर उपलब्धता के आधार पर विचार किया जाएगा।
अब रेलवे आरक्षण/आरक्षण रद्द करने की सुविधा इंटरनेट/मोबाइल फोन द्वारा भी उपलब्ध है, जिसकी पूरी जानकारी आई०आर०सी०टी०सी० की बेबसाइट पर उपलब्ध है।
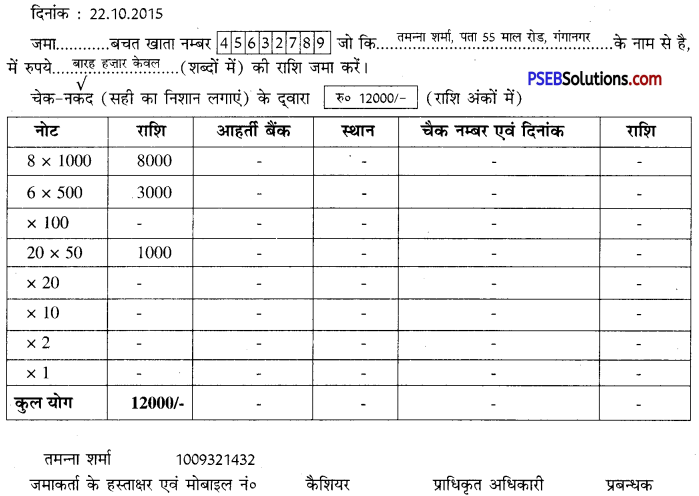
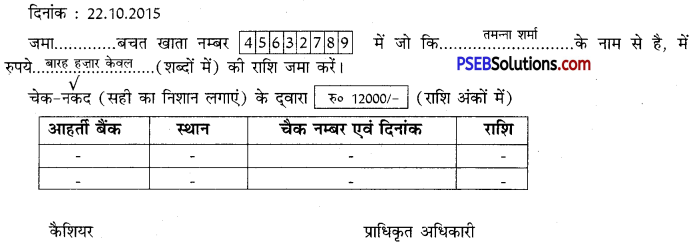
1. मान लीजिए आपका नाम तमन्ना शर्मा है।आपका गुड बैंक, शाखा गंगानगर में एक बचत खाता है। आपका खाता नम्बर-45632789 है। आपका मोबाइल नं0 1009321432 है। आपको दिनांक 22.10.2015 को अपने इस खाते में 12,000 रुपये नकद जमा करवाने हैं। आपके पास जमा करवाने के लिए एक हज़ार के 8 नोट, पांच सौ के नोट तथा पचास के 20 नोट हैं। इस अनुसार निम्नलिखित प्रपत्र भरें:
उत्तर:
गुड बैंक, गंगानगर
बैंक में रुपये जमा करवाने के लिए प्रपत्र ( बैंक प्रति)
गुड बैंक, गंगानगर
बैंक में रुपये जमा करवाने के लिए प्रपत्र (ग्राहक प्रति)

2. मान लीजिए आपका नाम रत्नलीन कौर है। आपका मोबाइल नम्बर 1890876535 है। आपका हिमालय बैंक, शाखा सोलन में एक बचत खाता नम्बर 96237180 है। आपको दिनांक 11.08.2015 को अपने इस खाते में से 7,000 रुपये निकालवाने हैं। इस अनुसार निम्नलिखित प्रपत्र भरें
उत्तर:

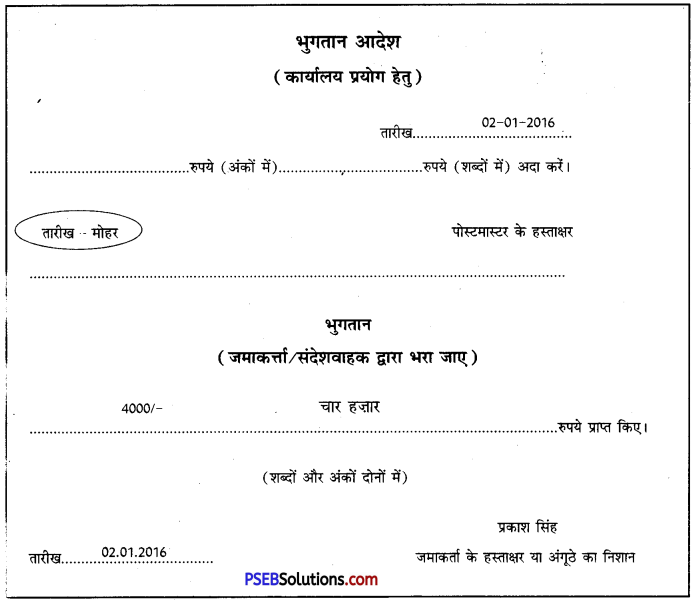
3. मान लीजिए आपका नाम प्रकाश सिंह है। आपका भारतीय डाक के सेक्टर 15 चंडीगढ़ में 344565 नम्बर एक बचत खाता है। आपके इस खाते में अब तक 45,000 रुपये जमा हैं। आपको दिनांक 02.01.2016 को अपने इस खाते में से 4,000 रुपये निकलवाने हैं। इस अनुसार निम्नलिखित प्रपत्र भरें:
उत्तर:

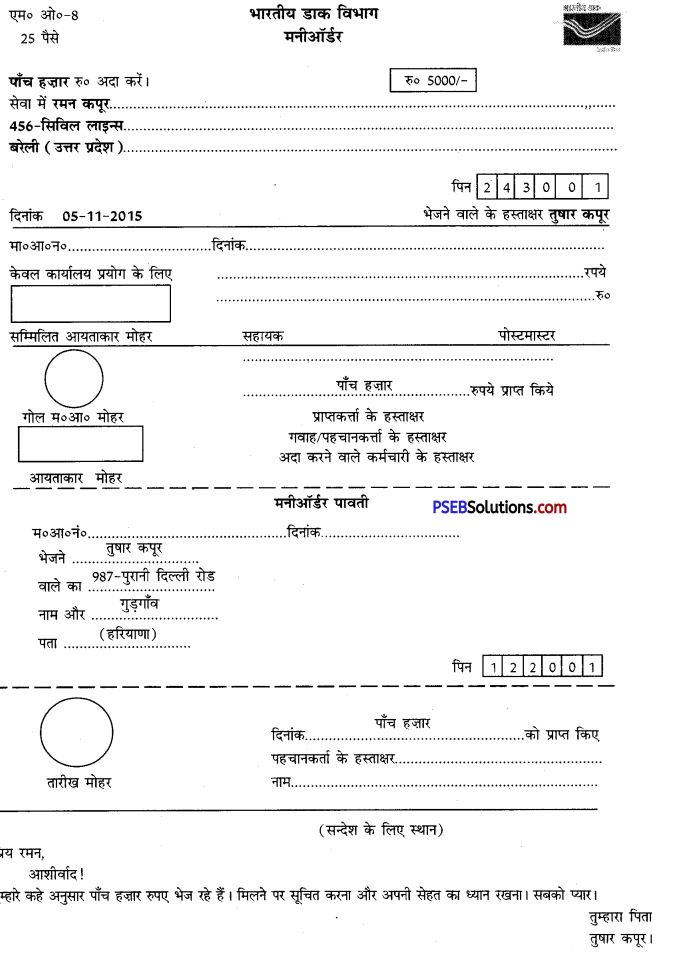
4. मान लीजिए आपका नाम तुषार कपूर है। आप मकान नं० 987, पुरानी दिल्ली रोड, गुड़गाँव (हरियाणा)-122001 में रहते हैं। आपका बेटा मकान नं० 456 सिविल लाइन्स बरेली (उत्तर प्रदेश) 243001 में रहता है। आप अपने बेटे को भारतीय डाक के माध्यम से दिनांक 05.11.2015 को मनीआर्डर के द्वारा 5,000/- रुपये भेजना चाहते हैं। इस प्रपत्र में उसे संदेश भी लिखें ‘अपनी सेहत का ध्यान रखना’। इस अनुसार निम्नलिखित प्रपत्र भरें।
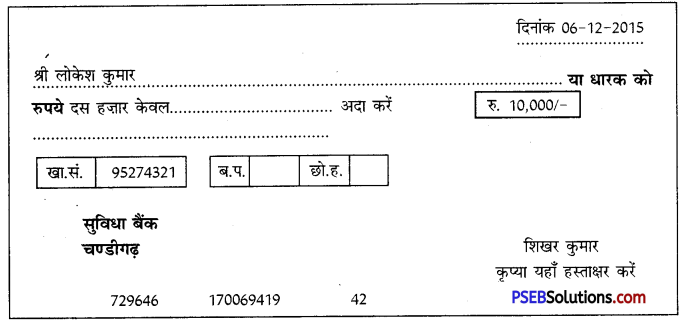
5. मान लीजिए आपका नाम शिखर कुमार है। आपको लोकेश कुमार को दिनांक 6.12.15 को 10,000/- रु० का स्वहस्ताक्षरित रेखांकित किया हुआ चेक लिखकर देना है। इस अनुसार निम्नलिखित चैक के प्रपत्र को भरें:
बोर्ड परीक्षा में पूछे गए प्रश्न
निम्नलिखित में से किसी एक प्रपत्र को अपनी उत्तर-पुस्तिका पर उतारकर भरें
1. (क) मान लीजिए आपका नाम सुलोचना कुमारी है। आपका हिमालय बैंक, शाखा-शिमला में एक बचत खाता है, जिसका नम्बर, 18954326781 है। आपको अपने इस खाते में से 2500 रुपये निकलवाने हैं। इस अनुसार निम्नलिखित प्रपत्र भरें-

उत्तर:

(ख) मान लीजिए आपका नाम रूप सिंह है। आपका भारतीय डाक के सेक्टर 15, करनाल में एक बचत खाता है, जिसका नम्बर 128947654431 है। आपको अपने इस खाते में से 4000/- रुपये निकलवाने हैं। इस अनुसार निम्नलिखित प्रपत्र भरें:

उत्तर:


2. (क) मान लीजिए आपका नाम पीयूष सिन्हा है। आपका कल्याण बैंक, शाखा-भुवनेश्वर में एक बचत खाता है, जिसका नम्बर 1150000234567 है। आपको अपने इस खाते में 18000/- रुपये जमा करवाने हैं। इस अनुसार निम्नलिखित प्रपत्र भरें:

उत्तर:

(ख) मान लीजिए आपका नाम दीदार सिंह है। आपका भारतीय डाक के सेक्टर-25, देहरादून में एक बचत खाता है, जिसका नम्बर 18634956744 है। आपको अपने इस खाते में से 10000/- रुपये निकलवाने हैं। इस अनुसार निम्नलिखित प्रपत्र भरें:

उत्तर:

3. (क) मान लीजिए आपका नाम निर्मला कौर है। आपका भारतीय डाक के सेक्टर-42, जम्मू में एक बचत खाता है, जिसका नम्बर 62745367823 है। आपको अपने इस खाते से 8200/- रुपये निकलवाने हैं। इस अनुसार निम्नलिखित प्रपत्र भरें-

उत्तर:

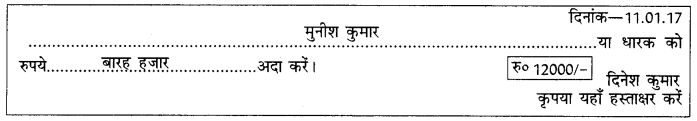
(ख) मान लीजिए आपका नाम दिनेश कुमार है। आपको मुनीश कुमार को 12000/- रु० का स्वहस्ताक्षरित चेक लिखकर देना है। इस अनुसार निम्नलिखित चेक के प्रपत्र को भरें:

उत्तर:
4. (क) निम्नलिखित में से किसी एक प्रपत्र को अपनी उत्तर-पुस्तिका पर उतारकर भरें-
(i) मान लीजिए आपका नाम पूनम कुमारी है। आपका भविष्य बैंक, शाखा-शिमला में एक बचत खाता है, जिसका नम्बर 373748488 है। आपको अपने इस खाते में से ₹ 5500/- निकलवाने हैं। इस अनुसार
निम्नलिखित प्रपत्र की रूपरेखा अपनी उत्तर पुस्तिका पर उतार कर भरें-

उत्तर:


(ख) मान लीजिए आपका नाम सुप्रिया देवी है। आपका भारतीय डाक के सेक्टर-15 नोएडा में एक बचत खाता है, जिसका नम्बर 834747993 है। आपको अपने इस खाते में से दिनांक 23.05.2018 को ₹4500/- निकलवाने हैं। इस अनुसार अग्रलिखित प्रपत्र की रूपरेखा अपनी उत्तर-पुस्तिका पर उतार कर भरें:

उत्तर:

![]()
![]()
![]()