Punjab State Board PSEB 10th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions Ex 5.3 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions Ex 5.3
Question 1.
Find the sum of the following APs:
(i) 2, 7, 12, … to 10 terms.
(ii) – 37, – 33, – 29, ………….. to 12 terms.
(iii) 0.6, 1.7, 2.8, … to 100 terms.
(iv) \(\frac{1}{5}\), \(\frac{1}{12}\), \(\frac{1}{10}\), ………… to 11 terms.
Solution:
(i) Given AP. is 2, 7, 12, …
Here a = 2, d = 7 – 2 = 5 and n = 10
Sn = \(\frac{n}{2}\) [2a + (n – 1) d]
∴ S10 = \(\frac{10}{2}\) [2 × 2 + (10 – 1)5]
= 5 [4 + 45] = 245.
(ii) Given A.P. is – 37, – 33, – 29…
Here a = -37, d = – 33 + 37 = 4 and n = 12
Sn = \(\frac{n}{2}\) [2a + (n – 1) d]
∴ S12 = [2(-37) + (12 – 1)4]
= 6 [- 74 + 44] = – 180.
![]()
(iii) Given A.P. is 0.6, 1.7. 2.8.
Here a = 0.6, d = 1.7 – 0.6 = 1.1 and n = 100
Sn = \(\frac{n}{2}\) [2a+(n – 1) d]
∴ S100 = \(\frac{100}{2}\) [2(0.6) + (100 – 1) 1.1]
= 50 [1.2 + 108.9] = 5505.
(iv) Given AP. is \(\frac{1}{5}\), \(\frac{1}{12}\), \(\frac{1}{10}\), ………… to 11 terms.
Here a = \(\frac{1}{5}\), d = \(\frac{1}{5}\) and n = 11
Sn = \(\frac{n}{2}\) [2a +(n – 1)d]
∴ S11 = \(\frac{11}{2}\left[2\left(\frac{1}{15}\right)+(11-1) \frac{1}{60}\right]\)
= \(\frac{11}{2}\left[\frac{2}{15}+\frac{10}{60}\right]=\frac{11}{2}\left[\frac{2}{15}+\frac{1}{6}\right]\)
= \(\frac{11}{2}\left[\frac{4+5}{30}=\frac{9}{30}\right]=\frac{33}{20}\).
![]()
Question 2.
Find the sums given below:
(i) 7+ 10\(\frac{1}{2}\) + 14 + …………… + 84
(ii) 34 + 32 + 30 + ………. + 10
(iii) – 5 + (- 8) + (- 11) +………+ (- 230)
Solution:
(i) Given A.P. is
7 + 10\(\frac{1}{2}\) + 14 + ………….. + 84
Here a = 7, d = 10\(\frac{1}{2}\) – 7 = \(\frac{21}{2}\) – 7
= \(\frac{21-14}{2}=\frac{7}{2}\)
and l = Tn = 84
or a + (n – 1) d = 84
or 7 + (n – 1) \(\frac{7}{2}\) = 84
or (n – 1) \(\frac{7}{2}\) = 84 – 7 = 77
or n – 1 = 77 × \(\frac{2}{7}\) =22
n = 22 + 1 = 23
∵ Sn = \(\frac{n}{2}\) [a + l]
Now, S23 = \(\frac{23}{2}\) [7 + 84]
= \(\frac{23}{2}\) × 91 = \(\frac{2093}{2}\).
(ii) Given A.P. is 34 + 32 + 30 + …………… + 10
Here a = 34, d = 32 – 34 = -2
l = Tn = 10
a + (n – 1) d = 10
or 34 + (n – 1) (- 2) = 10
or – 2(n – 1) = 10 – 34 = -24
or n – 1 = 12
n = 12 + 1 = 13
[∵ Sn = \(\frac{n}{2}\) [a + l]]
Now, S13 = \(\frac{13}{2}\) [34 + 10]
= \(\frac{23}{2}\) × 44
= 13 × 22 = 286.
![]()
(iii) Give A.P. is – 5 + (- 8) + (- 11) + ……………. + (- 230)
Here a = – 5, d = – 8 + 5 = – 3
and l = Tn = – 230
a + (n – 1) d = – 230
or – 5 + (n – 1) (- 3) = – 230
or – 3(n – 1) = – 230 + 5 = – 225
or n – 1 = \(\frac{225}{3}\) = 75
or n = 75 + 1 = 76
Now, S76 = \(\frac{76}{2}\) [- 5 + (- 23o)]
= 38 (- 235) = – 8930.
Question 3.
In an AP:
(i) given a = 5, d = 3, an = 50 find n and Sn.
(ii) given a = 7. a13 = 35, find d and S13.
(iii) given a12 = 37, d = 3. find a and S12.
(iv) given a3 = 15, S10 = 125, find d and a10.
(y) given d = 5, S9 = 75, find a and a9.
(vi) given a = 2, d = 8, Sn = 90, find n and an.
(vii) given a = 8, an = 62, Sn = 210, find n and d.
(viii)given an = 4, d = 2, Sn = -14, find n and a.
(ix) given a = 3, n = 8, S = 192, find d.
(x) given l = 28, S = 144, and there are total 9 terms. Find a.
Solution:
(i) Given a = 5, d = 3, an = 50
an = 50
a + (n – 1) d = 50
or 5 + (n – 1) 3 = 50
or 3 (n – 1) = 50 – 5 = 45
or n – 1 = \(\frac{45}{3}\) = 15
or n = 15 + 1 = 16
Now, Sn = latex]\frac{n}{2}[/latex] [a + l]
= latex]\frac{16}{2}[/latex] [5 + 50] = 8 × 55 = 440.
![]()
(ii) Given a = 7, a13 = 35
a13 = 35
a + (n – 1) d = 35
or 7 + (13 – 1) d = 35
or 12 d = 35 – 7 = 28
or d = \(\frac{7}{3}\).
∵ [Sn = latex]\frac{n}{2}[/latex] [a + l]
Now, S13 = \(\frac{13}{2}\) [7 + 35]
= \(\frac{13}{2}\) × 42 = 273
(iii) Given a12 = 37, d = 3
∵ a12 = 37
a + (n – 1) d = 37
or a + (12 – 1) 3 = 37
a + 33 = 37
a = 37 – 33 = 4
∵ [Sn = latex]\frac{n}{2}[/latex] [a + l]
Now, S12 = \(\frac{13}{2}\) [4 + 37]
= 6 × 41 = 246.
![]()
(iv)Given a3 = 15, S10 = 125
∵ a3 = 15
a + (n – 1) d = 15
a + (3 – 1) d = 15
or a + 2d = 15 …………….(1)
∵ S10 = 125
∵ [Sn = latex]\frac{n}{2}[/latex] [2a + (n – 1)d]
\(\frac{10}{2}\) [2a + (10 – 1) d] = 125
or 5[2a + 9d] = 125
Note this
or 2a + 9d = \(\frac{125}{5}\) = 25
or 2a + 9d = 25 …………(2)
From (1), a = 15 – 24 …………..(3)
Substitute this value of (a) in (2i, we c1
2(15 – 2d) + 9d = 25
or 30 – 4d + 9d = 25
5d = 25 – 30
or d = \(\frac{-5}{5}\) = -1
Substitute this value of d in (3), we get
a = 15 – 2(- 1)
a = 15 + 2 = 17
Now, a10 = 17 + (10 – 1)(- 1)
∵ Tn = a + (n – 1) d = 17 – 9 = 8.
(v) Given d = 5, S9 = 75
∵ S9 = 75
∵ [Sn = \(\frac{n}{2}\) [2a + (n – 1)d]
\(\frac{9}{2}\) [2a + 40] = 75
or [2a + 40] = \(\frac{50}{3}\)
or 2a = \(\frac{50}{3}\) – 40
or a = \(-\frac{70}{3} \times \frac{1}{2}\)
or a = – \(\frac{35}{3}\)
Now, a9 = a + (n – 1) d
= – \(\frac{35}{3}\) + (9 – 1)0 × 5
= – \(\frac{35}{3}\) + 4o = \(\frac{-35+120}{3}\)
a9 = \(\frac{85}{3}\).
![]()
(vi) Given a = 2, d = 8, Sn = 90
∵ Sn = 90
\(\frac{n}{2}\) [2a + (n – 1)d] = 9o
or \(\frac{n}{2}\) [2 × 2 + (n – 1) 8] = 90
or n [2 + 4n – 4] = 90
or n (4n – 2) = 90
or 4n2 – 2n – 90 = 0
or 2n2 – 10n + 9n – 45 = 0
S = – 2
P = – 45 × 2 = – 90
or 2n [n – 5] + 9(n – 5) = 0
or (2n + 9) (n – 5) = 0
Either 2n + 9 = 0 or n – 5 = 0
Either n = – \(\frac{9}{2}\) or n = 5
∵ n cannot be negative so reject n = – \(\frac{9}{2}\)
∴ n = 5
Now, an = a5 = a + (n – 1) d
= 2 + (5 – 1) 8 = 2 + 32 = 34.
(vii) Given a = 8, an = 62, Sn = 210
∵ Sn = 210
\(\frac{n}{2}\) [a + an] = 210
or \(\frac{n}{2}\) [8 + 62] = 210
or \(\frac{n}{2}\) × 70 = 210
or n = \(\frac{210}{35}\) = 6
Now, an = 62
[∵ Tn = a + (n – 1) d]
or 5d = 62 – 8 = 54
or d = \(\frac{54}{5}\).
![]()
(viii) Given an = 4, d = 2, Sn = – 14
∵ an = 4
a + (n – 1) d = 4
or a + (n – 1)2 = 4
or a + 2n – 2 = 4
or a = 6 – 2n ……………(1)
and Sn = – 14
\(\frac{n}{2}\) [a + an] = – 14
or \(\frac{n}{2}\) [6 – 2n +4] = – 14 (Using (1))
or \(\frac{n}{2}\) [10 – 2n] = – 14
or 5n – n2 + 14 = 0
or n2 – 5n – 14 = 0
S = – 5
P = 1 × – 14 = – 14
or n2 – 7n + 2n – 14 = 0
or n(n – 7) + 2 (n – 7) = 0
or (n – 7) (n + 2) = 0
either n – 7 = 0
or n + 2 = 0
n = 7 or n = -2
∵ n cannot be negative so reject n = – 2
∴ n = 7
Substitute this value of n in (1), we get
a = 6 – 2 × 7
a = 6 – 14 = – 8.
(ix) Given a = 3, n = 8, S = 192
∵ S = 192
S8 = 192 [∵ n = 8]
∵ Sn = \(\frac{n}{2}\) [2a + (n – 1)d]
or \(\frac{8}{2}\) [2 × 3 + (8 – 1) d] = 192
or 4 [6 + 7d] = 192
6 + 7d = \(\frac{192}{4}\) = 48
or 7d = 48 – 6 = 42
or d = \(\frac{42}{6}\) = 6.
![]()
(x) Given l = 28, S = 144 and there are total 9 terms
∴ n = 9; l = a9 = 28; S9 = 144
∵ a9 = 28
or a + (9 – 1) d = 28
∵ [an = Tn = a + (n – 1) d ]
or a + 8d = 28 …………….(1)
and S9 = 144
∵ [Sn = \(\frac{n}{2}\) [a + an]]
\(\frac{9}{2}\) [a + 28] = 144
or a + 28 = \(\frac{144 \times 2}{9}\) = 32
a = 32 – 28 = 4.
Question 4.
How many terms of the A.P : 9, 17, 5… must be taken to give a sum of 636?
Solution:
Given A.P. is 9, 17, 25, …………
Here a = 9, d = 17 – 9 = 8
But Sn = 636
\(\frac{n}{2}\) [2a + (n – 1) d] = 636
or \(\frac{n}{2}\) [2(9) + (n – 1) 8] = 636
or \(\frac{n}{2}\) [18 + 8n – 8] = 636
or n [4n + 5] = 636
or 4n2 + 5n – 636 = 0
a = 4, b = 5, c = – 636
D = (5) – 4 × 4 × (- 636)
= 25 + 10176 = 10201
∴ n = \(\frac{-b \pm \sqrt{\mathrm{D}}}{2 a}\)
= \(\frac{-5 \pm \sqrt{10201}}{2 \times 4}=\frac{-5 \pm 101}{8}\)
= \(\frac{-106}{8} \text { or } \frac{96}{8}\)
= \(-\frac{53}{4}\) or 12
∴ n cannot be negative so reject n = \(-\frac{53}{4}\)
∴ n = 12
Hence, sum of 12 terms of given A.P. has sum 636.
![]()
Question 5.
The first term ofan AP is 5, the last term is 45 and the sum Is 400. Find the number of terms and the common difference.
Solution:
Given that a = T1 = 5; l = an = 45
and Sn = 400
∴ Tn = 45
a + (n – 1) d = 45
or 5 + (n – 1) d = 45
or (n – 1) d = 45 – 5 = 40
or (n – 1) d = 40 ……………….(1)
and Sn = 400
\(\frac{n}{2}\) [a + an] = 400
or \(\frac{n}{2}\) [5 + 45] = 400
or 25 n = 400
or n = \(\frac{400}{25}\) = 16
Substitute this value of n in (1), we get
(16 – 1) d = 40
or 15d = 40
d = \(\frac{40}{15}\) = \(\frac{8}{3}\)
Hence, n = 16 and d = \(\frac{8}{3}\)
Question 6.
The first and last terms of an AP are 17 and 350 respectively. 1f the common difference is 9, how many terms are there
and what is their sum?
Solution:
Given that a = T1 = 17;
l = an = 350 and d = 9
∵ l = an = 350
a + (n – 1) d = 350
17 + (n – 1) 9 = 350
or 9 (n – 1) = 350 – 17 = 333
or n – 1 = \(\frac{333}{9}\) = 37
n = 37 + 1 = 38
Now, S38 = \(\frac{n}{2}\) [a + l]
= \(\frac{38}{2}\) (17 + 350]
= 19 × 367 = 6973.
Hence, sum of 38 terms of given A.P. arc 6973.
![]()
Question 7.
Find the sum of first 22 terms of an AP. in which d = 7 and 22nd term is 149.
Solution:
Given that d = 7; T22 = 149 and n = 22
∵ T22 = 149
a + (n – 1) d = 149
or a + (22 – 1) 7 = 149
or a + 147 = 149
or a = 149 – 147 = 2
Now, S22 = [a + T22]
= \(\frac{22}{2}\) [2+ 149] = 11 × 151 = 1661
Hence, sum of first 22 temis of given A.P. is 1661.
Question 8.
Find the sum of first 51 terms of an AP whose second and third terms are 14 and 18 respectively.
Solution:
Let ‘a’ and ‘d’ be fïrst term and common difference
Given that T2 = 14; T3 = 18 and n = 51
∵ T2 = 14
a + (n – 1) d = 14
a + (2 – 1)d = 14
or a + d = 14
a = 14 – d …………….(1)
and T3 = 18 (Given)
a + (n – 1) d = 18
a + (3 – 1) d = 18
or a + 2d = 18
or 14 – d + 2d = 18
or d = 18 – 14 = 4
or d = 4
Substitute this value of d in (1), we get
a = 14 – 4 = 10
Now, S51 = \(\frac{n}{2}\) [2a + (n – 1) d]
= \(\frac{51}{2}\) [2 × 10 + (51 – 1) 4]
= \(\frac{51}{2}\) [2o + 2oo]
= \(\frac{51}{2}\) × 220 = 51 × 110 = 5610
Hence, sum of first 51 terms of given A.P. is 5610.
![]()
Question 9.
If the sum of first 7 terms of an AP is 49 and that of 17 terms is 289, find the sum of first n terms.
Solution:
Let ‘a’ and ‘d’ be the first term and common difference of given A.P.
According to 1st condition
S7 = 49
\(\frac{n}{2}\) [2a + (n – 1) d] = 49
or \(\frac{7}{2}\) [2a + (7 – 1) d] = 49
or \(\frac{7}{2}\) [2a + 6d] = 49
or a + 3d = 7
or a = 7 – 3d
According to 2nd condition
S17 = 289
\(\frac{n}{2}\) [2a+(n – 1)d]=289
\(\frac{17}{2}\) [2a + (17 – 1) d] = 289
a + 8d = \(\frac{289}{17}\) = 17
Substitute the value of a from (1), we get
7 – 3d + 8d = 17
5d = 17 – 7 = 10
d = \(\frac{10}{5}\) = 2
Substitute this value of d in (1), we get
a = 7 – 3 × 2
a = 7 – 6 = 1
Now, Sn = \(\frac{n}{2}\) [2a + (n – 1) d]
= \(\frac{n}{2}\) [2 × 1 + (n – 1) × 2] = n [I + n – 1] = n × n = n2
Hence, sum of first n terms of given A.P. is n2.
Question 10.
Show that a1, a2, ……., an, … form an AP where is defined as below.
(i) an = 3 + 4n
(ii) an = 9 – 5n
Also find the sum of the first 15 terms In each case.
Solution:
(i) Given that an = 3 + 4n ………..( 1)
Putting the different values of n in(1), we get
a1 = 3 + 4(1) = 7;
a2 = 3 + 4 (2) = 11
a3 = 3 + 4 (3) = 15, …………
Now, a2 – a1 = 11 – 7
and a3 – a2 = 15 – 11 = 4
a2 – a1 = 11 – 7 = 4
and a3 – a2 = 4 = d(say)
∵ given sequence form an A.P.
Here a = 7, d = 4 and n = 15
∴ S15 = \(\frac{n}{2}\) [2a + (n – 1)d]
= \(\frac{15}{2}\) [2(7) + (15 – 1) 4]
= \(\frac{15}{2}\) [14 + 56] = \(\frac{15}{2}\) × 70
= 15 × 35 = 525.
![]()
(ii) Given that an = 9 – 5n ……………….(1)
Putting the different values of n is (1), we get
a1 = 9 – 5(1) = 4;
a2 = 9 – 5(2) = -1;
a3 = 9 – 5(3) = -6.
Now, a2 – a1 = – 1 – 4 = – 5
and a3 – a2 = – 6 + 1 = – 5
∵ a – a1 = a3 – a2 = – 5 = d (say)
∴ given sequence form an A.P.
Here a = 4, d = – 5 and n = 15
∴ S15 = \(\frac{n}{2}\) [2a + (n – 1) d]
= \(\frac{15}{2}\) [2(4) + (15 – 1) (-5)]
= \(\frac{15}{2}\) [8 – 70]
= \(\frac{15}{2}\) (-62) = – 465
Question 11.
If the sum of the first n terms of an AP is 4n – n2, what is the first term (that is S1) ? What is the sum of two terms? What is the second term ? Similarly, find the 3rd, the 10th and the nth terms.
Solution:
Given that, sum of n terms of an A.P. are
Sn = 4n – n2
Putting n = 1 in (1), we get
S1 = 4(1) – (1)2 = 4 – 1
S1 = 3
∴ a = T1 = S1 = 3
Putting n = 2, in (1), we get
S2 = 4(2) – (2)2 = 8 – 4
S2 = 4
or T1 + T2 = 4
or 3 + T2 = 4
or T2 = 4 – 3 = 1
Putting n = 3 in (1), we get
S3 =4(3) – (3)2 = 12 – 9
S3 = 3
or S2 + T3 = 3
or 4+ T3 = 3
or T3 = 3 – 4 = – 1
Now, d = T2 – T1
d = 1 – 3 = -2
∴ T10 = a + (n – 1) d
= 3 + (10 – 1) (- 2)
T10 = 3 – 18 = – 15
and Tn = a + (n – 1) d
= 3 + (n – 1) (- 2)
= 3 – 2n + 2
Tn = 5 – 2n.
![]()
Question 12.
Find the sum of the first 40 positive integers divisible by 6.
Solution:
Positive integers divisible by 6 are 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36 42, …
Here a = T1 = 6, T2 = 12, T3 = 18, T4 = 24
T2 – T1 = 12 – 6 = 6
T3 – T2 = 18 – 12 = 6
T4 – T3 = 24 – 18 = 6
∵ T2 – T1 = T3 – T2 = T4 – T3 = 6 = d (say)
Using formula, Sn = \(\frac{n}{2}\) [2a + (n – 1) d]
S40 = \(\frac{40}{2}\) [2(6) + (40 – 1)6].
= 20 [12 + 234]
= 20 (246) = 4920
Hence, sum of first 40 positive integers divisible by 6 is 4920.
Question 13.
Find the sum of first 15 multiples of 8.
Solution:
Multiples of 8 are 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, …………..
Here a = T1 = 8; T2 = 16; T3 = 24 ; T4 = 32
T2 – T1 = 16 – 8= 8
T3 – T2 = 24 – 16=8
T2 – T1 = T3 – T2 = 8 = d(say)
Ùsing formula. Sn = [2a + (n – 1) d}
S15 = \(\frac{15}{2}\) [2(8) + (15 – 1) 8]
= \(\frac{15}{2}\) [16 + 112]
= \(\frac{15}{2}\) × 128 = 960
Hence, sum of first 15 multiples of 8 is 960.
![]()
Question 14.
Find the sum of the odd numbers between 0 and 50.
Solution:
Odd numbers between 0 and 50 are 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, …………, 49
Here a = T1 = 1; T2 = 3; T3 = 5 ; T4 = 7
and l = Tn = 49
T2 – T1 = 3 – 1 = 2
T3 – T2 = 5 – 3 = 2
∵ T2 – T1 = T3 – T2 = 2 = d (say)
Also, l = Tn = 49
a + (n – 1) d = 49
1 + (n – 1) 2 = 49
or 2 (n – 1) = 49 – 1 = 48
n – 1 = \(\frac{48}{2}\) = 24
n = 24 + 1 = 25.
Using formula, Sn = \(\frac{n}{2}\) [2a + (n – 1) d]
S25 = \(\frac{25}{2}\) [2(1) + (25 – 1)2]
= \(\frac{25}{2}\) [2 + 48]
= \(\frac{25}{2}\) × 50 = 625
Hence, sum of the odd numbers between 0 and 50 are 625.
Question 15.
A contract on construction job specifies a penalty for delay of completion beyond a certain date as follows: ₹ 200 for
the first day, ₹ 250 for the second day, ₹ 300 for the third day, etc., the penalty for each succeeding day being ₹ 50 more than for the preceding day, How much money the contractor has to pay as penalty, if he hasdelayed the work by 30 days?
Solution:
Penalty (cost) for delay of one, two, third day are ₹ 200, ₹ 250, ₹ 300
Now, penalty increase with next day with a difference of ₹ 50.
∴ Required A.P. are ₹ 200, ₹ 250, ₹ 300, ₹ 350, …
Here a = T1 = 200; d = ₹ 50 and n = 30
Amount of penalty gives after 30 days
= S30
= \(\frac{n}{2}\) [2a + (n – 1) d]
= \(\frac{30}{2}\) [2(2oo) + (30 – 1) 50)
= 15 [400 + 1450]
= 15 (1850) = 27750
Hence, ₹ 27350 pay as penalty by the contractor if he has delayed the work 30 days.
![]()
Question 16.
A sum of ₹ 700 is to be used to give seven cash prizes to students of a school for their overall academic performance. If
each prize is ₹ 20 less than its preceding prize, find the value of each of the prizes.
Solution:
Let amount of prize given to 1st student = ₹ x
Amount of prize given to 2nd student = ₹ (x – 20)
Amount of prize given to 3rd student = ₹ [x – 20 – 20] = ₹ (x – 40)
and so on.
∴ Required sequence are ₹ x, ₹ (x – 20), ₹ (x – 40), … which form on A.P. with
a = ₹ x, d = – 20 and n = 7
Using formula, Sn = \(\frac{n}{2}\) [2a + (n – 1) d]
S7 = \(\frac{7}{2}\) [2(x) + (7 – 1) (- 20)]
S7 = \(\frac{7}{2}\) [2x – 120] = 7 (x – 60)
According to question,
7 (x – 60) = 700
x – 60 = 7 = 100
x – 60 = 7 = 100
x = 100 + 60
x = 160
Hence, 7 prizes are ₹ 160, ₹ 140, ₹ 120, ₹ 100, ₹ 80, ₹ 60, ₹ 40.
Question 17.
In a school, student thought of planting trees in and around the school to reduce air pollution. It was decided that
number of trees, that each section of each class will plant, will be the same as the class, in which they are studying, e.g. – a section of Class I will plant 1 tree, a section of Class II will plant 2 trees and so on till Class XII. There are three sections of each class. How many trees will be planted by the students?
Solution:
Number of trees planted by three sections of class I = 3 × 1 = 3
Number of trees planted by three sections of class II = 3 × 2 = 6
Number of trees planted by three sections of class III = 3 × 3 = 9
…………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………..
……………………………………………………………………
Number of trees planted by three sections of class XII = 3 × 12 = 36
:. Required A.P. are 3, 6, 9, …………., 36
Here a = T1 = 3; T2 = 6; T3 = 9
and l = Tn = 36; n = 12
d = T2 – T1 = 6 – 3 = 3
Total number of trees planted by students
= S12
= \(\frac{n}{2}\) [a + l]
= \(\frac{12}{2}\) [3+ 36]
= 6 × 39 = 234
Hence, 234 trees will be planted by students to reduce air pollution.
![]()
Question 18.
A spiral is made up of successive semicircics, with centres alternately at A and B, starting with centre at A, of radii 0.5 cm, 1.0 cm, 1.5 cm, 2.0 cm, …. as shown in Fig. What is the total length of such a spiral made up of thirteen consecutive semicircies? (Take π = \(\frac{22}{7}\))
[Hint: Length of successive semicircies is ‘l1’ ‘l2’ ‘l3‘ ‘l4‘ … wIth centres at A, B, A, B, …, respectively.]
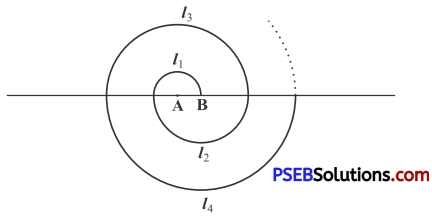
Solution:
Let l1 = length of first semi circle = πr1 = π(0.5) = \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)
l2 = length of second semi circlem = πr2= π(1) = π
l3 = length of third semi circle = πr3 = π(1.5) = \(\frac{3 \pi}{2}\)
and l4 = length of fourth senil circle = πr4 = π(2) = 2π and so on
∵ length of each successive semicircle form an A.P.
Here
a = T1 = \(\frac{\pi}{2}\); T2 = π;
T3 = \(\frac{3 \pi}{2}\); T4 = 2π……… and n = 13
d = T2 – T1 = π – \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)
= \(\frac{2 \pi-\pi}{2}=\frac{\pi}{2}\)
Length of whole spiral = S13
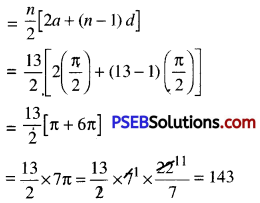
Hence, total length of a spiral made up of thirteen consecutive semi circies is 143 cm
Question 19.
200 logs are stacked in the following manner : 20 logs in the bottom row, 19 in the next row, 18 in the row next to it and so on (see Fig). In how many rows are the 200 logs placed and how many logs are in the top row?
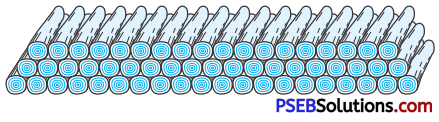
Solution:
Number of logs in the bottom (1st row) = 20
Number of logs in the 2nd row = 19
Number of log in the 3rd row = 18 and so on.
∴ Number of logs in the each steps form an
Here a = T1 = 20; T2 = 19; T3 = 18…
d = T2 – T1 = 19 – 20 = – 1
Let S, denotes the number logs.
Using formula, Sn = \(\frac{n}{2}\) [2a + (n – 1) d]
= \(\frac{n}{2}\) [2 (20) + (n – 1) (-1)]
∴ Sn = \(\frac{n}{2}\) [40 – n + 1]
= \(\frac{n}{2}\) [41 – n]
According to question,
\(\frac{n}{2}\) [41 – n] = 200
or 41 – n2 = 400
or – n2 + 41n – 400 = 0
or n2 – 41n + 400 = 0
S = – 41, P = 400
or n2 – 16n – 25n + 400 = 0
or n (n – 16) – 25 (n – 16)=0
or (n – 16) (n – 25) = 0
Either n – 16 = 0 or n – 25 = 0
Either n = 16 or n = 25
∴ n = 16, 25.
Case I:
When n = 25
T25 = a + (n – 1) d
= 20 + (25 – 1)(- 1)
= 20 – 24 = – 4;
which is impossible
∴ n = 25 rejected.
Case II. When n = 16
T16 = a + (n – 1) d
= 20 + (16 – 1)(- 1)
= 20 – 15 = 5
Hence, there are 16 row and 5 logs are in the top row.
![]()
Question 20.
In a potato race a bucket ¡s placed at the starting point which Ls 5 m from the first potato, and the other potatoes are placed 3 m apart in a straight line. There are ten potatoes in the line (see Fig.)
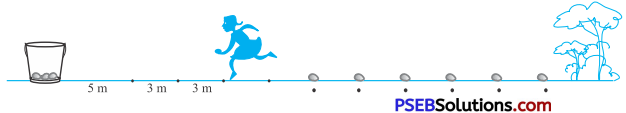
Each competitor starts from the bucket, picks up the nearest potato, runs back with It, drops It in the bucket, runs back to pick up the next potato, runs to the bucket to drop it In, and the continues in the same way until all the potatoes are in the bucket. What is the total distance the competitor has to run?
(Hint : To pick up the first potato and second potato, the distance run is [2 × 5 + 2 × (5 + 3)] m)
Solution:
Distance covered to pick up the Ist potato = 2(5) m = 10 m
Distance between successive potato = 3 m
distance covered to pick up the 2nd potato = 2(5 + 3) m = 16 m
Distance covered to pick up the 3rd potato = 2 (5 + 3 + 3) m = 22 m
and this process go on. h is clear that this situation becomes an A.P. as 10 m, 16 m, 22 m, 28 m, …
Here a = T1 = 10; T2 = 16; T3 = 22, …
d = T2 – T1 = 16 – 10 = 6 and n = 10
∴ Total distance the competitor has to run = S10
= \(\frac{n}{2}\) [2a + (n – 1) d]
= \(\frac{10}{2}\) [2(10) + (10 – 1) 6]
= 5 [20 + 54]
= 5 × 74 = 370
Hence, 370 m is the total distance run by a competitor.