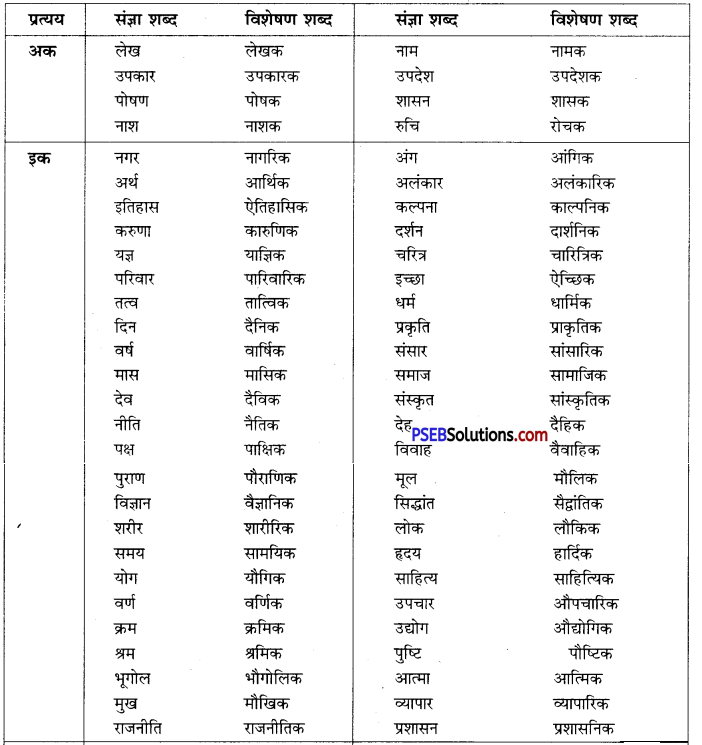
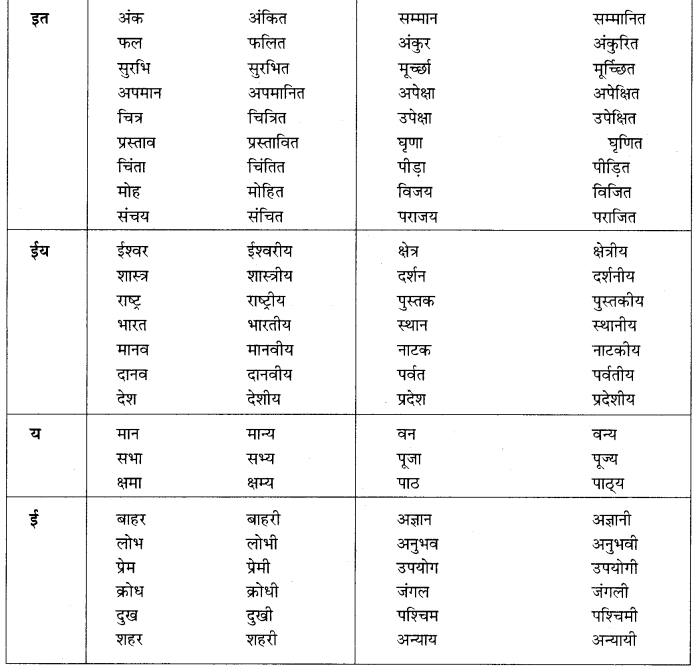
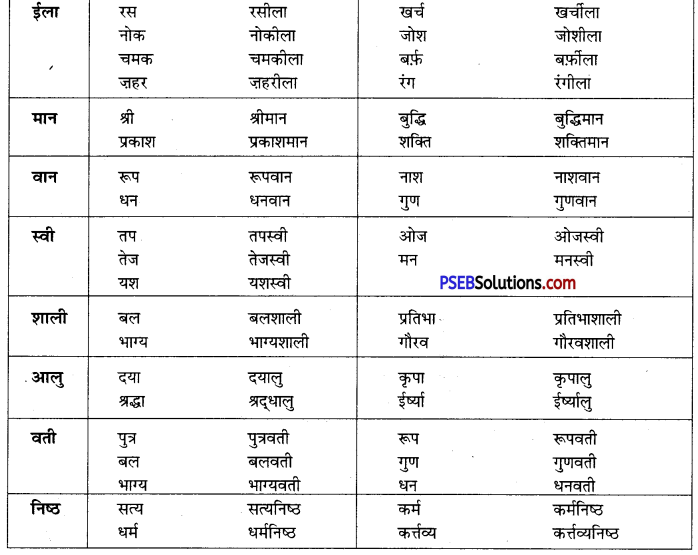
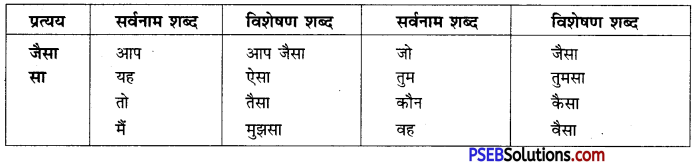
Punjab State Board PSEB 10th Class English Book Solutions English Grammar Punctuation Exercise Questions and Answers, Notes.
PSEB 10th Class English Grammar Punctuation
Note : A complete Answer Key has been given at the end of the exercises. Punctuate the following :
I.
1. my sister is an m a bed
2. ramesh the director of the company has gone to delhi
3. the rich and the poor the high and the low the weak and the strong visit this temple
4. he asked me why i was crying
5. the sun having risen we started our journey
6. god save me from such friends
7. tibet the roof of the world is an old land
8. she is no doubt the happiest girl under the sun
9. we bought apples oranges peaches and bananas
10. unless you work hard you cant stand first
Answer:
1. My sister is an M.A., B.Ed.
2. Ramesh, the director of the company, has gone to Delhi.
3. The rich and the poor, the high and the low. the weak and the strong, visit this temple.
4. He asked me why I was crying.
5. The sun having risen, we started our journey.
6. God. save me from such friends
7. Tibet, the roof of the world, is an old land.
8. She is, no doubt, the happiest girl under the sun.
9. We bought apples, oranges, peaches and bananas.
10. Unless you work hard, you can’t stand first.
II.
1. kashmir the Switzerland of india is very beautiful
2. may i come in sir
3. well well meet at the station tomorrow
4. money is after all not the most important thing
5. she is an american she a dutch
6. mohan in his heart of hearts felt sad
7. harpreet was elected an mla
8. balwinder to tell you the truth is a crook
9. there are five m a beds in our school
10. sita is a dancer gita a singer an
Answer:
1. Kashmir, the Switzerland of India, is very beautiful.
2. May I come in, sir ?
3. Well, we’ll meet at the station tomorrow.
4. Money is, after all, not the most important thing.
5. She is an American; she, a Dutch.
6. Mohan, in his heart of hearts, felt sad.
7. Harpreet was elected an M.L.A.
8. Balwinder to tell you the truth is a crook.
9. There are five M.A., B.Eds in our school.
10. Sita is a dancer; Gita, a singer.

III.
1. ram singh the captain of the team is from makhan majra
2. he passed the ba exam last year
3. balinder came first he was therefore given a prize
4. bill clinton the president of the usa was a very active politician
5. the ramayana is a sacred book of the hindus
6. Harpreet is a student of khalsa college amritsar
7. she is a phd student
8. do as I tell you said the magician
9. gitanjali was composed by tagore
10. the teacher said students don’t make a noise
11. I like the poems of Amrita pritam
12. he lost money reputation and friends
Answer:
1. Ram Singh, the captain of the team, is from Makhan Majra.
2. He passed the B.A. exam last year.
3. Balinder came first. He was, therefore, given a prize.
4. Bill Clinton, the-President of the U.S.A., was a very active politician.
5. The Ramayana is a sacred book of the Hindus.
6. Harpreet is a student of Khalsa College, Amritsar.
7. She is a Ph.D. student.
8. “Do as I tell you,” said the magician.
9. ‘Gitanjalf was composed by Tagore.
10. The teacher said, “Students, don’t make a noise.”
11. I like the poems of Amrita Pritam.
12. He money, reputation and friends.
IV.
1. portia is the heroine of Shakespeare’s merchant of Venice
2. I would rather die she said than beg
3. the brave and the coward the intelligent and the dull the weak and the strong came to ashok for guidance
4. his story was in several ways improbable
5. mahatma gandhi was killed on 30th january 1948 and was cremated at raj ghat delhi
6. example as the proverb says is the best precept
7. friends romans countrymen lend me your ears
8. we want help not sympathy
9. being dissatisfied he resigned his post
10. john smith lived soberly honestly and prudently
Answer:
1. Portia is the heroine of Shakespeare’s ‘Merchant of Venice’.
2. “I would I rather die,” she said, “than beg.”
3. The brave and the coward, the intelligent I and the dull, the weak and the strong, came to Ashok for guidance.
4. His story was in several ways improbable.
5. Mahatma Gandhi was killed on 30th January, 1948, and was cremated at Raj Ghat, Delhi.
6. Example, as the ! proverb says, is the best precept.
7. “Friends, Romans, countrymen, lend me your ears.”
8. We want help, not sympathy.
9. Being dissatisfied, he resigned I his post.
10. John Smith lived soberly, honestly and prudently.

V.
1. i have opted for punjabi, english, economics and philosophy
2. some men are born great some achieve greatness and some have greatness thrust upon them
3. william the conqueror is remembered for his courage and fortitude
4. anand and not you is to blame
5. have you read shakespeares as you like it
6. long live the president
7. the headmaster said to the student yes come in
8. Ashoka the great declared buddhism as the state religion
9. the examination being over we decided to have a holiday
10. the room was spacious but dark and suffocating
Answer:
1 have opted for Punjabi, English, Economics and Philosophy.
2. Some men are born great; some achieve greatness; some have greatness thrust upon them.
3. William, the conqueror, is remembered for his courage and fortitude.
4. Anand and not you is to blame.
5. Have you read Shakespeare’s ‘As You Like It’
6. Long live the President!
7. The Headmaster said to the student,”Yes. come in.”
8. Ashoka, the great, declared Buddhism as the State Religion.
9. The examination being over, we decided to have a holiday.
10. The room was spacious; but. dark and suffocating.
VI
1. if you go to agra do visit the taj mahal
2. welcome he said have a seat what can i do for you
3. on tuesday the prime minister of afghanistan reaches india
4. sir said the lamb you surely see that the water flows from you to me how can i then make the water muddy
5. he said asha looks terrible is she ill
6. reading makethat full man speaking a ready man writing an exact man
7. men may come and men may go but I go oh for ever
8. i tell you sir i have read king lear
9. my uncle DRC i sharma lives in shimla
10. how stupid I have been said vandana
Answer:
1. If you go to Agra, do visit the Taj Mahal.
2. “Welcome,” he said. “Have a seat. What can I do for you ?”
3. On Tuesday, the Prime Minister of Afghanistan I reaches India.
4. “Sir !’’ said the lamb. “You surely see that the water flows ! from you to me.
How can I then make the water muddy ?”
5. He said, “Asha ! looks terrible. Is she ill ?”
6. Reading maketh a full man; speaking a ready man; writing an exact man.
7. Men may come and men may go; but I go on for ever.
8. I tell you, sir. I have read ‘King Lear’.
9. My uncle, Dr. C.L. Sharma, lives in Shimla.
10. “How stupid I have been !” said Vandana.

VII.
1. i now fully understand who he was why he came to kolkata and where he went away
2. once during a break in the rains there was a cool soft breeze blowing a bird was singing a sweet song among the green trees
3. he studies in hindu college
4. O death where is thy sting
5. i left this place on Sunday the 9th of October and returned on Thursday the 15th of November
6. your son is certainly a boy of ability said the headmaster but all depends upon you whether he is to do well at school what an extraordinary statement said the father how can his progress possibly depend upon me you can see replied the headmaster that he does his homework carefully oh yes said the father i can do at least that much
7. one day walking together up a hill i said to Hemant do you not wish yourself in your own country again yes he said what would you do there said i would you turn wild and eat mens flesh again he looked full of concern and shaking his head said no no
8. a gentleman thinking he was charged too much by a porter for the delivery of a parcel asked him what his name was my name replied the man is the same as my fathers
9. no smoking in this compartment said the ticket inspector to the traveller i am not smoking was the travellers reply but you have got your pipe in your mouth answered the inspector yes was the sharp reply i have got my feet in my boots but i am not walking
10. you coward he said gently as if to himself then with neither hurry nor any particular violence he struck the man in the mouth the man sprang to his feet and cried a blow I would not take a blow from god almighty.
11. a blind man carrying a lantern in his hand and a pitcher on; his shoulder was walking along one night alone when he met a thoughtless young fellow who asked him to explain the use of a lantern to a blind man
12. I wish i had lots of money said the wife if one could get what one wished for i think i should wish for common sense not for money said the husband naturally everybody wishes for what he has not got said the wife
13. who is the man you speak of asked rama leaving his seat buttoning up his coat and moving towards the door
14. the hare said to the tortoise you bulky fellow how slowly you crawl i could run a mile while you ran a dozen yards the tortoise replied o boaster do you really think so let us have a race and we shall see who is faster
15. a few years ago a man named smith was tried on a charge of entering a house and committing theft there he had made an opening into which he had thrust the upper part of his body and he had removed the articles he could lay his hands on his pleader said my lord my client did not enter the house only his upper half went in
Answer:
1. I now fully understand who he was. why he came to Kolkata, and where he went away.
2. Once, during a break in the rains, there was a cool, soft breeze blowing. A bird was singing a sweet song among the green trees.
3. He studies in Hindu College.
4. O. Death ! Where is thy sting?
5. I left this place on Sunday, the 9th of October, and returned on Thursday, the 15th of November.
6. “Your son is certainly a boy of ability,” said the Headmaster, “but all depends! upon you whether he is to do well at school.”
“What an extraordinary statement!” said the father, “how can his progress possibly depend upon me ?”
“You can see,” replied the Headmaster, “that he does his homework
“Oh, yes,” said the father, “I can do at least that much.”
7. One day, walking together up a hill, I said to Hemant. “Do you not wish yourself in your own country again ?”
“Yes,” he said.
“What would you do there ?” said I. “Would you turn wild and eat men’s flesh again ?”
He looked full of concern and, shaking his. head, said, “No, no !”
8. A gentleman, thinking he was charged too much by a porter for the delivery of a parcel, asked him what his name was. “My name,” replied the man, “is the same as my father’s.”
9. “No smoking in this compartment!” said the ticket inspector to the traveller. “I am not smoking,” was the traveller’s reply. “But you have got your pipe in your mouth,” answered the inspector. ‘Yes,” was the sharp reply. “I have got my feet in my boots but I am not walking!”
10. ‘You coward !” he said gently, as if to himself. Then with neither hurry nor any particular violence, he struck the man in the mouth. The man sprang to his feet and cried. “A blow ! I would not take a blow from God Almighty.”
11. A blind man, carrying a lantern in his hand and a pitcher on his shoulder, was walking along one night alone when he met a thoughtless young fellow who asked him to explain the use of a lantern to a blind man.
12. “I wish I had lots of money,” said the wife. “If one could get what one wished for, I think I should wish for common sense, not for money,” said the husband. “Naturally, everybody wishes for what he has not got,” said the wife.
13. “Who is the man you speak of ?” asked Rama, leaving his seat, buttoning up his coat, and moving towards the door.
14. The hare said to the tortoise, ‘You bulky fellow ! How slowly you crawl ! I could run a mile while you ran a dozen yards.” The tortoise replied, “O boaster ! Do you really think so ? Let us have a race and we shall see who is faster.”
15. A few years ago, a man named Smith was tried on a charge of entering a house and committing theft there. He had made an opening into which he had thrust the upper part of his body and he had removed the articles he could lay his hands on. His pleader said, “My lord, my client did not end the house; only his upper half went in.”

(2015) – Sets – A, B & C
(A) Do as directed :
(i) Fill in the blanks with suitable determiners :
Chandigarh is …………. capital of Punjab. It is …………. favourite city.
(ii) Fill in the blanks with suitable prepositions :
(a) He took pity …………. the poor man.
(b) He jumped …………. the wall.
(iii) Fill in the blanks with suitable modals :
(a) She worked hard so that she …………. pass………….. (may, might)
(b) You…………. clean your teeth every morning. (could, should)
(iv) Combine the sentences with the given conjunction :
He is very weak. He cannot stand. (So-that)
(v) Identify the Subordinate Clause and name it :
Look before you leap.
(vi) Fill in the blank with the correct form of the non-finite verb given in the bracket :
He is used to ………… (go) to cinema too often.
(vii) Change the voice :
(a) He will do his duty.
(b) What was Sohan doing ?
(viii) Change the narration :
(a) Sita said, “Goodbye, my friend.”
(b) I said to my brother, “Let me study more.”
(ix) Change into Past Indefinite Tense :
He rides a bicycle.
(x) Punctuate the following sentence :
i tell you sir i have read king lear
Answer:
(i) the, my
(ii)
(a) on
(b) over
(iii)
(a) might
(b) should
(iv) He is so weak that he cannot stand.
(v) before you leap – Adverb clause
(vi) going
(vii)
(a) His duty will be done.
(b) What was being done by Soban ?
(viii)
(a) Sita bade her friend goodbye.
(b) I asked my brother to let me study more.
(ix) He rode a bicycle.
(x) I tell you, sir, I have read King Lear.
(B) Do as directed :
(i) Fill in the blanks with suitable determiners :
…………… poor peasant went off early in ………….. morning to plough.
(ii) Fill in the blanks with suitable prepositions :
Translation is an art. Good Translation is the result ………….. practice and patience. It requires skill to translate words and ideas …….. a language.
(iii) Fill in the blanks with suitable modals :
(a) Walk fast lest you ………….. miss the train. (should, would)
(b) You ………….. pay your debts. (must, should, can)
(iv) Combine the sentences with the given conjunction :
I cannot stand. I cannot sit. (neither, nor)
(v) Identify the Subordinate Clause and name it :
He is the man who displayed those magic tricks
(vi) Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the non-finite verb given in the bracket :
The children seemed ………. on seeing the giant. (frighten)
(vii) Change the voice :
(a) The peon was ringing the bell.
(b) I know this man.
(viii) Change the narration :
(a) He said, “0, for a glass of water”
(b) I say, “He is an honest man.”
(ix) Change into Past Indefinite Tense :
Mohan helps his father.
(x) Punctuate the following sentence :
harpreet is a student of khalsa college amritsar.
Answer:
(i) The, the
(ii) of, of
(iii)
(a) should
(b) must
(iv) I can neither stand nor sit.
(v) who displayed those magic tricks Adjective clause
(vi) frightened
(vii)
(a) The bell was being rung by the peon.
(b) This man is known to me.
(viii)
(a) he cried for a glass of water.
(b) I say that he is an honest man.
(ix) Mohan helped his father.
(x) Harpreet is la student of Khalsa College, Amritsar.

(C) Do as directed :
(i) Fill in the. blanks with suitable determiners :
In my last summer vacation, I went to ………….. historical place. It was very beautiful place.
(ii) Fill in the blanks with suitable prepositions :
Once there lived a hermit ……….. a forest. He was very kind ……….. others.
(iii) Fill in the blanks with suitable modals :
(a) Candidates ……….. answer all questions. (should, must)
(b) ……….. borrow your pen, Sir ? (may, could, shall)
(iv) Combine the sentences with the given conjunction :
Rajan is kind. He is honest. (both-and)
(v) Identify the Subordinate Clause and name it :
Such students as work hard are liked by all.
(vi) Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the non-finite verb given in the bracket :
It is no use ……… over spilt milk. (cry)
(vii) Change the voice :
(a) They were not selling their books.
(b) Do not make a noise.
(viii) Change the narration :
(a) He said, “What a great misery !”
(b) Sunita says, “ I am doing my homework.”
(ix) Change into Past Indefinite Tense :
We shall help you with money
(x) Punctuate the following sentence :
i tell you sir i have read king lear
Answer:
(i) a, a
(ii) in, to
(iii)
(a) must
(b) could
(iv) Rajan is both kind and honest.
(v) as work hard – Adjective clause
(vi) crying
(vii)
(a) Their books were not being sold by them.
(b) Let a noise not be made,
(viii)
(a) He exclaimed with sorrow that if was a great misery
(b) Sunita I says that she is doing her homework.
(ix) We would help you with money.
(x) I tell you sir, I have to read ‘King Lear’
(2016) – Sets — A, B & C
(A) Do as directed :
(i) Fill in the blanks with suitable determiners,:
She does not want ……….. interference in ……….. lifestyle.
(ii) Fill in the blanks with suitable prepositions :
We belong ……….. a country which is known ……….. its traditions and cultures.
(iii) Fill in the blanks with suitable modals :
(a) A rich man ……….. buy anything he likes. (must, can)
(b) You ……….. do as you are told. (must, should)
(iv) Combine the sentences with the given conjunction :
He worked hard. He fell ill. (so-that)
(v) Identify the Subordinate Clause arid name it :
My fear was that Mohit would reach late.
(vi) Pill in the blank with the correct form of the non-finite verb given in the bracket:
It is no use ……….. over spilt milk. (cry)
(vii) Change the voice :
(a) The teacher will punish the naughty boys.
(b) Help everybody.
(viii) Change the narration :
(a) He said to his friends, “Please let me study.”
(b) Seema said to me, “My husband does not like me.”
(ix) I am going home. (Change into Future Indefinite Tense)
(x) Punctuate the following sentence :
there are five beds in our school
Answer:
(i) any, her
(ii) to, for
(iii)
(a) can
(b) should
(iv) He worked so hard that he fell in.
(v) that Mohit would reach late – Noun clause
(vi) crying
(vii)
(a) The naughty boys will be punished by the teacher.
(b) Everybody should be helped.
(viii)
(a) He requested his friends to let him study.
(b) Seema told me that her husband did not like her.
(ix) I will go home. til
(x) There are five M.A., B.Eds. in our school.

(B) Do as directed :
(i) Fill in the blanks with suitable determiners :
Mr Gupta went to bazaar and bought ……… honey from ……… shop.
(ii) Fill in the blanks with suitable prepositions :
Now women are conscious ……… their position ……… society.
(iii) Fill in the blanks with suitable modals :
(a) ……… I smoke here ? (may, might)
(b) You ……… be home by 11 o’clock”. (should, must)
(iv) Combine the sentences with the given conjunction :
I was late for school. I missed the first bus. (because)
(v) Identify the Subordinate Clause and name it:
I am glad that you have acted honestly.
(vi) Fill in the blank with the correct form of the non-finite verb given in the bracket:
He dislikes ……….. in the village. (live)
(vii) Change the voice :
(a) She will water the plants.
(b) Learn it by heart.
(viii) Change the narration :
(a) The teacher said to the boy, “Shut the door.”
(b) He said to you, “I have passed the test today.”
(ix) We are locking the door.
(Change into Future Indefinite Tense)
(x) Punctuate the following sentence :
he asked me why i was crying
Answer:
(i) some, a
(ii) of, in
(iii)
(a) May
(b) must
(iv) I was late for school because I missed the first bus.
(v) that you have acted honestly — Adverb clause
(vi) living
(vii)
(a) The plants will be watered by her.
(b) It should be learnt by heart
(viii)
(a) The teacher ordered the boy to shut the door
(b) He told you that he had passed the test that day.
(ix) We shall lock the door
(x) He asked me why I was crying.
(C) Do as directed :
(1) Fill in the blanks with suitable determiners :
He earned …………. money from …………. profession.
(ii) Fill in the blanks with suitable prepositions :
Once there lived a hermit …………. a forest. He was very kind ……….. others.
(iii) Fill in the blanks with suitable modals :
(a) She worked hard so that she ………. pass. (may, might)
(b) You ………….. clean your teeth every morning. (should, could)
(iv) Combine the sentences with the given conjunction :
He was tired. He could hardly stand. (so-that)
(v) Identify the Subordinate Clause and name it :
This is the school that the President visited.
(vi) Fill in the blank with the correct form of the non-finite verb given in the bracket :
She objected to …………. her bicycle. (take)
(vii) Change the Voice :
(a) Nikhil will buy a new house.
(b) Do not make a noise.
(viii) Change the Narration :
(a) Neetu said to Mr Sanjeev, “Please go to the station with him.”
(b) Dinesh said to Simran, “You cannot save me now.”
(ix) I had written a letter. ” (Change into Future Indefinite Tense)
(x) Punctuate the following sentence :
friends romans countrymen lend me your ears
Answer:
(i) much, his
(ii) in, to
(iii)
(a) might
(b) should
(iv) He was so tired that he could hardly stand
(v) that the President visited — Adjective clause
(vi) taking
(vii)
(a) A new, house will be bought by Nikhil.
(b) Let a noise not be made
(viii)
(a) Neetu requested Mr Sanjeev to go to the station with him.
(b) Dinesh told Simran that she could not save him then
(ix) I will write a letter
(x) Friends, Romans, Countrymen, lend me your ears.

(2017) Sets -A, B & C
(A) Do as directed:
(i) Fill in the blanks with suitable determiners :
He opened ………….. bag and spread out …………….. articles.
(ii) Fill in the blanks with suitable prepositions :
Trust ….. God and have faith ………. Him.
(iii) Fill in the blanks with suitable modals :
(a) …………………. that I were a minister! (Would/Will)
(b) …………….. you climb up this tree ? (Can/Should)
(iv) Combine the sentences with a suitable conjunction :
(a) The patient had died.
(b) The doctor came afterwards.
(v) Identify the Subordinate Clause and name it :
It know that he is wrong.
(vi) Fill in the blank with the correct form of the non-finite verb given in the bracket :
This pen is not worth ……….. (buy)
(vii) Change the voice :
(a) I play cricket every day.
(b) Who does not want liberty ?
(viii) Change the narration :
(a) He said, “I shall be coming tomorrow.”
(b) Ram said to Sham, “Is the earth round ?
(ix) Change into the Past Indefinite Tense :
She speaks the truth.
(x) Punctuate the following sentence :
he is an ma in english
Answer:
(i) his, the.
(ii) in, in
(iii)
(a) Would
(b) Can
(iv) The patient had died before the doctor came
(v) that he is wrong – Noun clause
(vi) buying,
(vii)
(a) Cricket is played everyday by me.
(b) By whom is liberty not wanted ?
(viii)
(a) He said that ho would be coming the next day.
(b) Ram asked Sham if the earth was round
(ix) She spoke the truth.
(x) He is an M.A. in English.
(B) Do as directed :
(i) Fill in the blank with a suitable determiner :
He looks as stupid as ………………. owl.
(ii) Fill in the blank with a suitable preposition :
He was accused …………… theft.
(iii) Fill in the blanks with suitable modals :
(a) It ………………… rain today. (may/must)
(b) You ……………. follow the traffic rules. (must/can)
(iv) Combine the sentences with a suitable conjunction
(a) The sum is difficult.
(b) We cannot solve it.
(v) Identify the Subordinate Clause and name it :
Life is what you make it.
(vi) Fill in the blank with the correct form of the non-finite verb given in the bracket :
Do you want …………. my address. (know)
(vii) Change the voice :
(a) I know his ways.
(b) He has been punished.
(viii) Change the narration : the narration :
(a) My mother said to me, “Did you break the cup ?
(b) “Why are you sad ?” she said to Naini.
(ix) Change into the Past Idefinite Tense :
She is going to Shimla with me.
(x) Punctuate the following sentence :
harpreet is a student of khalsa college amritsar
Answer:
(i) an
(ii) of
(iii)
(a) may
(b) must
(iv) I he sum is so difficult that we I cannot solve it.
(v) What you make it – Noun Clause
(vi) to know
(vii)
(a) His ways are known to me.
(b) The teacher has punished him.
(viii)
(a) My mother asked me if I had broken the cup.
(b) She asked Naini why she was sad.
(ix) She went to Shimla with me.
(x) Harpreet is a student of Khalsa College, Amritsar.

(C) Do as directed :
(i) Fill in the blanks with a suitable determiner :
Would you like ……………….. coffee ?
(ii) Fill in the blanks with suitable prepositions :
Cholera has broken ………………… ; beware ……………. it.
(iii) Fill in the blanks with suitable modals :
(a) You ……………… Avoid him. He is a liar. (insistence)
(b) It ……………….. rain; it is cloudy. (may/should)
(iv) Combine the sentences with a suitable conjunction :
(a) He is working hard.
(b) He wants to get a scholarship.
(v) Identify the Subordinate Clause and name it :
Go where you came from.
(vi) Fill in the blank with the correct form of the non-finite verb given in the bracket :
He wants …………. (sleep)
(vii) Change the voice :
(a) How do you know him ?
(b) I have finished my work.
(viii) Change the narration :
(a) Rama said, “India won freedom in 1947.”
(b) The doctor said to me, “What can I do for you ?”
(ix) Change into the Past Continuous Tense :
They are taking food.
(x) Punctuate the following sentence :
sita bought pens books pencils and notebooks
Answer:
(i) some
(ii) out: of
(iii)
(a) must
(b) may
(iv) He is working hard because he wants to get a scholarship
(v) Where you came from-Adverb clause
(vi) to sleep
(vii)
(a) How is he known to you ?
(b) My work has been finished by me.
(viii)
(a) Rama said that India won freedom in 1947.
(b) The doctor asked me what he could do for me.
(ix) They were taking food
(x) Sita bought pens, books, pencils and notebooks.
(2018) — All Sets
Note : All the questions in all sets are the same.
1. Do as directed :
(i) Fill in the blanks with suitable determiners :
My grandmother was ………. old lady ………… parents left me with her.
(ii) Fill in the blanks with suitable prepositions :
Dreams have been the topic …………. discussion with men …………. centuries.
(iii) Fill in the blanks with suitable modals :
(a) If I were the Prime Minister, I ………… fight corruption. (will, would)
(b) How …………. you abuse your elder brother ? (could, should)
(iv) Combine the sentences with, suitable conjunctions :
Mohan is honest. He is sincere. (both-and)
(v) Identify the Subordinate Clause and name it :
This is the doctor who treated me.
(vi) Fill in he blank with the correct form of the non-finite verb given in the bracket
Every miser hates …………. money………… (spend)
(vii) Change the voice :
(a) Who had been fined ?
(b) Sit down, please.
(viii) Change the narration :
(a) “Stand up on the benches”, I said to the children.
(b) My mother said to me, “Did you break the slate ?
(ix) Change into the Past Indefinite Tense :
I shall go to Delhi.
(x) Punctuate the following sentence :
i like the poems of amrita Pritam
2. Answer the following objective type questions :
(i) Walk slowly lest you …………….. fall.
(Fill in the blank with a suitable modal from the options given below.)
(a) might
(b) should
(c) might
(d) would.
(ii) Fill in the blank with the Future Continuous form of the verb given in the brackets.
He …………… not ……………….. his friends. (cheat)
Answer:
1. (i) an, my
(ii) of, for
(iii)
(a) would
(b) could
(iv) Mohan is both honest and sincere
(v) who treated me – Adjective clause
(vi) spending
(vii)
(a) Whom had the teacher fined ?
(b) You are requested to sit down
(viii)
(a) I ordered the children to stand up on the benches
(b) My mother asked me whether I had broken the slate
(ix) I went to Delhi
(x) I like the poems of Amrita Pritam.
2. (i) (b)
(ii) will (not) be cheating.

(2019 – All Sets)
1. Do as directed :
(i) Fill in the blanks with suitable determiners :
……………. Ganga is ………….. sacred river.
(ii) Mr. Smith is known ……….. me.
He is a man ……….. letters. (Use Prepositions)
(iii) Fill in the blanks with suitable modals ?
(a) Duty …………. be done. (must, should)
(b) Rita …………… speak English fluently. (can, need)
(iv) Combine the following sentences :
I cannot stand. I cannot sit. (Use neither … nor)
(v) I know that she loves music. (Identify the Subordinate Clause and name it)
(vi) Use the correct form of the non-finite verb to fill in the blank:
She bade us ……….. away. (go)
(vii) Change the voice :
(a) Quinine tastes bitter.
(b) I like music.
(viii) Change the narration :
(a) Rashmi says, “I am doing my homework.”
(b) The teacher said to the boy, “Honesty is the best policy.”
(ix) Change into Future Indefinite Tense :
He helps his father.
(x) Punctuate the following sentence :
we bought apples oranges peaches and bananas
Answer:
(i) The, a
(ii) to, of
(iii)
(a) must
(b) can
(iv) I can neither stand nor sit.
(v) that she loves music—Noun Clause
(vi) go
(vii)
(a) Quinine is bitter when tasted
(b) Music is liked by me.
(viii)
(a) Rashmi says that she is doing her homework
(b) The teacher told the boy that honesty is the best policy
(ix) He will help his father
(x) We bought apples, oranges, peaches, and bananas.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()



![]()