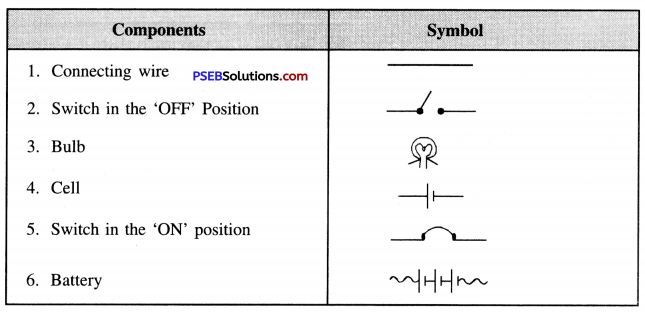
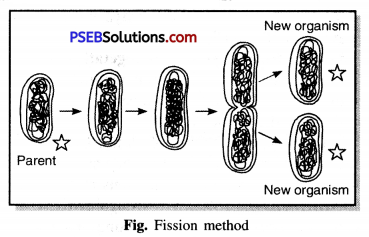
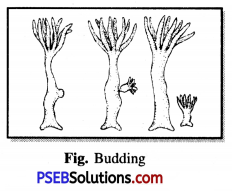
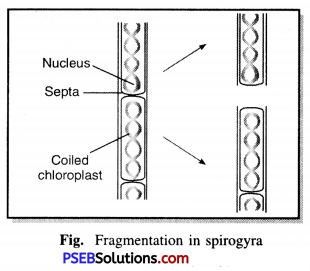
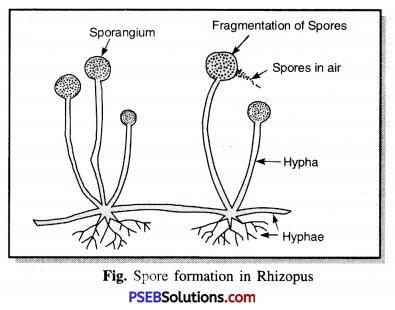
Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class Science Book Solutions Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
PSEB 8th Class Science Guide Stars and the Solar System Textbook Questions and Answers
Exercises
Question 1.
Which of the following is NOT a member of the solar system?
[a] An asteroid
[b] A satellite
[c] A constellation
[d] A comet
Answer:
[d] A comet.
Question 2.
Which of the following is NOT planet of the sun?
[а] Sirius
[b] Mercury
[c] Saturn
[d] Earth
Answer:
[a] Sirius.
Question 3.
Phases of the moon occur because
(a) we can see only that part of the moon which reflects light towards us.
(b) our distance from the moon keeps changing.
(c) the shadow of the earth covers only a part of moon’s surface.
(d) the thickness of the moon’s atmosphere is not constant.
Answer:
(a) We can see only that part of the moon which reflects light towards us.
Question 4.
Fill in the blanks.
(а) The planet which is farthest from the sun is …………………….. .
(b) The planet which appears reddish in colour is …………………… .
(c) A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky is known as a …………………….. .
(d) A celestial body that revolves around a planet is known as ………………………. .
(e) Shooting stars are actually not ………………………………….. .
(f) Asteroids are found between the orbits of ……………………. and …………………………… .
Answer:
(a) Neptune
(b) Mars
(c) Constellation
(d) Satellite
(e) Stars
(f) Mars, Jupiter.
![]()
Question 5.
Mark the following statements as true (T) or false (F) :
(a) Pole star is a member of our solar system. ()
(b) Mercury is the smallest planet of the solar system. ()
(c) Uranus is the farthest planet in the solar system. ()
(d) INSAT is an artificial satellite. ()
(e) There are nine planets in the solar system. ()
(f) Constellation Orion can be seen only with a telescope. ()
Answer:
(a) (T)
(b) (T)
(c) (F)
(d) (T)
(e) (F)
(f) (F).
Question 6.
Match items in column A with one or more items in column B
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) Inner planets | (a) Saturn |
| (ii) Outer planets | (b) Pole star |
| (iii) Constellation | (c) Great Bear |
| (iv) Satellite of the earth | (d) Moon |
| (e) Earth | |
| (f) Orion | |
| (g) Mars |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) Inner planets | (e) Earth |
| (g) Mars | |
| (ii) Outer planets | (a) Saturn |
| (iii) Constellation | (c) Great Bear |
| (f) Orion | |
| (iv) Satellite of the Earth | (d) Moon |
Question 7.
In which part of the sky can you find Venus if it is visible as an evening star?
Answer:
In west part of the sky.
Question 8.
Name the largest planet of the solar system.
Answer:
Jupiter.
Question 9.
What is a constellation? Name any two constellations.
Answer:
Constellations are small groups of stars appearing in the space having specific common shapes. All the stars of a group always stay together and their positions are fixed relative to each other e.g. Ursa Major.
![]()
Question 10.
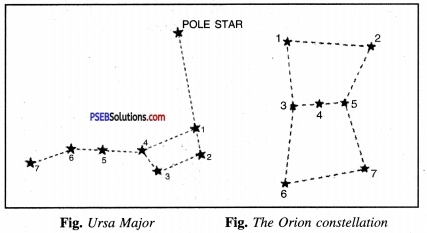
Draw sketches to show the relative positions of prominent stars in
(a) Ursa Major
(b) Orion.
Answer:
Question 11.
Name two objects other than planets which are members of the solar system.
Answer:
Asteroids, Meteors, Natural satellite.
Question 12.
Explain how you can locate the Pole Star with the help of Ursa Major.
Answer:
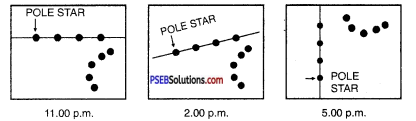
Ursa major changes its position in the sky after every three hours, it appears to revolve around fixed star. This fixed star is pole star.
Question 13.
Do all the stars in the sky move? Explain.
Answer:
All the stars except pole stars, appear to move in the sky from east to west as the earth rotates from west to east about its axis. Pole star is situated in the direction of axis of the earth, so it appears to be stationary.
Question 14.
Why is the distance between stars expressed in light years? What do you understand by the statement that a star is eight light-years away from the earth?
Answer:
Distance between the stars is very large. It is of the order of millions or billions kilometres. So, it is not convenient to express the distance in kilometres. So another larger unit called light-year is used to express distance between the stars. It can be defined as distance travelled by light in one year.
When a star is 8 light-years from the earth it means, light with speed of 3 × 108 m/sec, takes 8 years to cover that distance from earth to that star.
Now 1 light year = 9.46 × 1015 m
.’. 8 light years = 8 × 9.45 × 1015 m
= 75.6 × 1015 m
So, earth is 7.56 x 1016 m away from the given star.
![]()
Question 15.
The radius of Jupiter is 11 times the radius of the Earth. Calculate the ratio of the volumes of Jupiter and the Earth. How many Earths can Jupiter accommodate?
Answer:
Let R be radius of the Earth.
then volume of the Earth = \(\frac{4}{3} \pi \mathrm{R}^{3}\)
and volume of Jupiter = \(\frac{4}{3} \pi \mathrm{R}^{\prime 3}\)
= \(\frac{4}{3} \times \pi(11 \mathrm{R})^{3}\) [as R’= 11R]
Now Ratio = \(\frac{\text { Volume of the Earth }}{\text { Volume of the Jupiter }}=\frac{\frac{4}{3} \pi \mathrm{R}^{3}}{\frac{4}{3} \pi(11 \mathrm{R})^{3}}=\frac{1}{1331}\)
or 1:1331
Question 16.
Bojo made the following sketch of the solar system. Is the sketch correct ?.’If not, correct it.
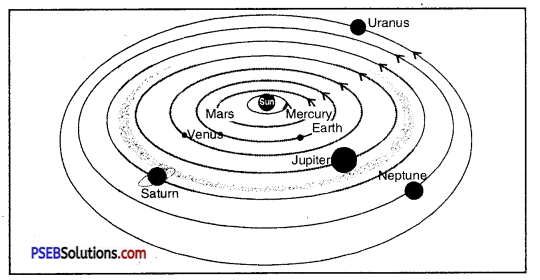
Answer:
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Stars and the Solar System Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Parvinder saw a constellation in the sky in a clear dark night. Name this constellation.
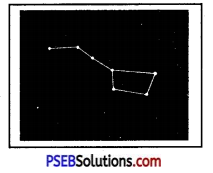
(a) Saptarishi
(b) Orion
(c) Cassiopia
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(a) Sapatrishi.
Question 2.
The planet which is nearest to the sun?
(a) Earth
(b) Mercury
(c) Saturn
(d) Venus
Answer:
(b) Mercury.
![]()
Question 3.
Which planet is called red planet?
(a) Mars
(b) Mercury
(c) Venus
(d) Jupiter
Answer:
(a) Mars
Question 4.
Which is the brightest planet at night?
(a) Mercury
(b) Earth
(c) Venus
(d) Mars
Answer:
(c) Venus.
Question 5.
The planet which is farthest from the Sun is :
(a) Neptune
(b) Jupiter
(c) Mercury
(d) Earth
Answer:
(a) Neptune.
Question 6.
Name the first Indian Artificial satellite.
(a) INSAT
(b) IRS
(c) Arya Bhatta
(d) Kalpana-I
Answer:
(c) Arya Bhatta.
![]()
Question 7.
Name the planet of the solar system where life exists.
(a) Mercury
(b) Earth
(c) Mars
(d) Saturn
Answer:
(b) Earth.
Question 8.
Which of the following is not the member of solar system?
(a) An asteroid
(b) A satellite
(c) A constellation
(d) A comet
Answer:
(c) A constellation.
Question 9.
Which of the following is not planet of the solar system?
(a) Sirius
(b) Mercury
(c) Saturn
(d) Earth
Answer:
(a) Sirius.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name the star closest to earth other than sun.
Answer:
Alpha century.
Question 2.
How much time does light take to reach us from Alpha century.
Answer:
4.3 years.
Question 3.
Which constellation looks like a big kite with a tail?
Answer:
Ursa-major constellation.
Question 4.
Name the constellation which looks like a cluster of twinkling gems in the night sky.
Answer:
Pleides constellation.
![]()
Question 5.
Define a light year.
Answer:
Light year. It is the distance travelled by light with a speed of 3,00,000 km/ hr in one year.
1 light year = 9.46 × 1012 km.
Question 6.
How far is the sun from the earth?
Answer:
The sun is at a distance of 1.5 × 108 km from the earth.
Question 7.
Which planet is known as the red planet?
Answer:
Mars.
Question 8.
Which planet rotates on its axis from East to West?
Answer:
Uranus.
Question 9.
Which force hold the planets in their orbits around the sun?
Answer:
Gravitational force of the sun holds the planets in their orbits around the sun.
Question 10.
What are Asteroids?
Answer:
Asteroids. The small solid objects made up of rocks and minerals, which move in the gap between the orbits of the Mars and Jupiter are called Asteroids.
![]()
Question 11.
What are meteorites?
Answer:
Meteorites are small chunks of rock or metal that are leftovers of broken comets. They are called meteors while falling through the atmosphere and appearing as streak of light. But those meteors that fall on the earth surface are called meteorites.
Question 12.
What are phases of moon?
Answer:
The shape of the bright part of the moon changes slightly every day. These are called phases of moon.
Question 13.
What is an artificial satellite?
Answer:
Artificial Satellite. It is an object which is made to revolve around the earth or any object.
Question 14.
Write two uses of artificial satellites.
Answer:
Uses of Artificial Satellites. Artificial satellites are used for long-distance communication, research, remote sensing and defence.
Question 15.
Which planet has maximum of satellites?
Answer:
Jupiter.
Question 16.
Why is Pole star stationary?
Answer:
It is because pole star is situated on the axis of the earth.
Question 17.
Which is natural satellite of the earth?
Answer:
Moon.
Question 18.
Why can’t Moon surface be used for communication?
Answer:
It is because moon has no atmosphere.
![]()
Question 19.
Which is the biggest planet of the solar system?
Answer:
Jupiter.
Question 20.
Which is the nearest planet of the earth?
Answer:
Mars.
Question 21.
In which part of the sky and at what time of the year are the following constellations seen? Scorpio, Great Bear, Pole Star and the Orion.
Answer:
1. Scorpio is visible in summer.
2. Great bear (Saptarishi) is visible in autumn.
- Pole star is visible in north throughout the year.
- Orion (Vyadha) is visible in winter in southern sky only.
Question 22.
When was Halley’s comet last seen?
Answer:
In 1986.
Question 23.
Name the nearest and the farthest planet from the sun.
Answer:
The nearest planet from the sun is Mercury and the farthest planet is Neptune.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How can you identify Ursa Major?
Answer:
Identification of Ursa Major. It is a group of seven bright stars. It appears like a large ladle or a question mark. The two stars marked 1 and 2 at the top of the ladle are called Pointers, as the line joining them points towards the polar star.
Question 2.
What are planets? How many planets are there in the solar system? Name them.
Answer:
Planets. The bright objects in the night sky which don’t twinkle like the stars and appear to change their positions with respect to the stars are called planets. In the solar system, there are nine planets. These are: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Pluto and Neptune.
![]()
Question 3.
Give three points of difference between a star and planet.
Answer:
Differences between star and planet.
| Star | Planet |
| 1. They are very hot. | 1. They are not very hot. |
| 2. They emit their own heat and light. | 2. They reflect the sun’s energy falling over them. |
| 3. They twinkle. | 3. They don’t twinkle. |
| 4. They are dot-shaped. | 4. They are disc-shaped. |
| 5. They travel in the sky from East to West. | 5. They travel in sky around the sun from West to East. |
Question 4.
Why is life possible of the earth?
Answer:
The earth has sufficient oxygen and water necessary for life. The temperature on earth is suitable for the existence of life. Also there is an ozone layer around earth which prevents the habitants from the harmful solar radiations. Therefore, all the conditions for the evolution of life are fulfilled on the earth.
Question 5.
Do all the stars of a constellation lie really close together?
Answer:
The various stars forming a constellation are rarely close to each other in space. The stars are in the same direction but at quite different distances from us. They appear to our eye was close together, although they are not really so.
Question 6.
Name the planets which can be identified with naked eye.
Answer:
Besides our own earth, we can identify only five other planets with naked eye. These planets are Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn.
Question 7.
What is the solar system? Name the planets situated between the sun and the earth.
Answer:
Solar System. The sun and its family i.e. planets, satellites, asteroids, comets, etc. is called as solar system. The sun is at the centre of the solar system and all members of the solar system are revolving around the sun in elliptical paths, called orbits. The planets situated between the sun and the earth are Mercury and Venus.
![]()
Question 8.
What is pole star and why is it important?
Answer:
Pole Star. All the stars except one, appear to be shifting their positions in the sky. There is only one star called pole star, which does not shift its position. It is lying in North above the north pole on the axis of rotation of the earth. It is used as a direction finder by sailors and those working in, offshore drilling operations.
Question 9.
Differentiate between a star and a shooting star.
Answer:
Differences between a star and a shooting star :
| Star | Shooting Star |
| 1. A star is made up of hot gases such as hydrogen and helium. | 1. A shooting star is made up of rock and metal particles. |
| 2. A star emits light due to the nuclear reaction taking place in it. | 2. A shooting star emits light due to the heat produced by friction on entering the atmosphere. |
| 3. The size of a star is very big. | 3. The size of a shooting star is very small. It may be as small as a dust particle. |
Question 10.
What are meteors or the shooting stars?
Answer:
Meteors or the Shooting Stars. You must have seen certain objects which appear to fall from the sky leaving a streak of light. They are also called shooting stars. Word ‘STAR’ is in fact misleading since they are neither themselves stars nor in any way connected with stars. These are pieces of rock floating in space.
When these floating rocks enter the earth’s atmosphere, they experience a lot of friction of air and get burnt. They appear as a ball of fire falling towards earth emitting intense light. Most of these burn up in atmosphere. When a meteor is very large, it does not burn up completely and reaches the earth. This piece reaching the earth and sea is called Meteorite.
Question 11.
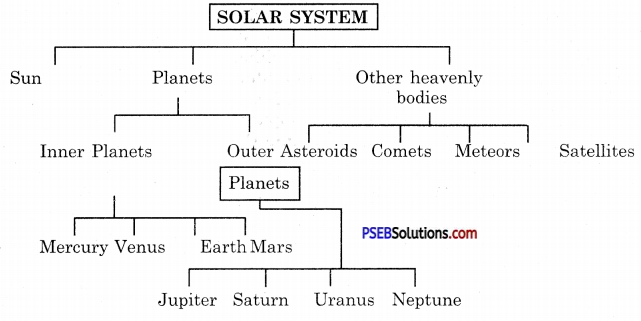
Represent Solar system in a tabular form.
Answer:
Solar system can be represented as
Question 12.
What is light year? How is it expressed in meters.
Answer:
Light year. We know that light travels nearly a distance of 3 × 108 m in one second or 3,00,000 km in one second. Light year is the distance travelled by light in
1 year or in 365\(\frac{1}{4}\) days.
∴1 light year = 365 \(\frac{1}{4}\) × 24 × 60 × 60 × 3 × 108 m/s
or 1 Light year = 9.46 × 1015 m
![]()
Question 13.
Why do the heavenly bodies seem to move from east to west?
Answer:
The heavenly bodies seem to be moving from east to west because earth rotates on its imaginary axis from west to east whereas it appears to us that earth is stationary. That is why various heavenly bodies appear to us moving from east to west. Earth completes one round on its axis in 24 hours.
Question 14.
Define the following terms :
1. Planet
2. Satellite
3. Period of rotation.
Answer:
1. Planet. The celestial bodies which revolve around the sun are called planets, e.g., Mercury, Earth and Venus.
2. Satellite. The celestial bodies which revolve around the planets are called satellites. Moon is a satellite of earth. Some other bodies also have satellites.
3. Period of rotation. The time taken by a planet to complete one rotation on its axis is called period of rotation.
Question 15.
Which is the brightest among all the planets and why?
Answer:
Venus is the brightest planet among all the planets. The bright appearance of Venus is due to its cloudy atmosphere, which reflects almost three-fourth of the sunlight that falls on it.
Question 16.
There is very much difference between the temperatures of Mercury and Venus planets, while there is not so on the earth and the Mars planets. Why?
Answer:
Mercury and Venus are the nearest neighbours of the sun. There is no thick atmospheric cover around them that can work like a heat cover. But these planets are so nearest to the sun that they cannot save themselves from the sunlight and are heated very much. They become most coolest after the sunset.
Only the Earth and Mars are such planets where there is a balance between the atmospheric cover and their distance from the sun. Therefore, there is not much difference in the day and night temperatures of both the planets due to this balance.
Question 17.
Why are the Mercury and the Venus known as morning or evening stars?
Answer:
The Mercury and the Venus are known as morning or evening stars because both can be seen near the horizon immediately before the sunrise and after the sunset. At this time, these appear like the brightest star.
Question 18.
What are the conditions favouring life to flourish on earth?
Answer:
Following are the conditions that favour life to flourish on earth :
- Oxygen is present in the atmosphere of the earth which is necessary for respiration for all the organisms.
- Presence of water for the biological process on the earth.
- Due to proper distance of the earth from the sun, there is proper temperature on the earth.
- Presence of protective ozone layer around the earth which protects us from the ultraviolet radiations of the Sun.
![]()
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is a solar system?
Answer:
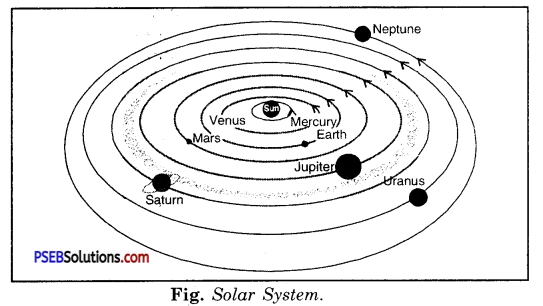
Solar System: Solar system consists of the Sun, a large number of asteroids between Mars and Jupiter. There are large number of comets or shooting stars which move in highly elliptical paths. The planet nearest to the sun is Mercury followed by Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune. Whereas mercury is the smallest planet, Jupiter is the largest one.
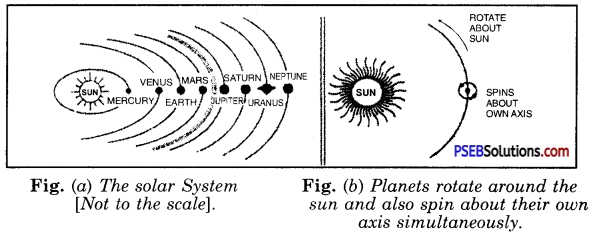
The planets rotate about the sun in elliptical path as well as spin about their own axis [Fig. (6)]. The nearest star to our solar system is Alpha Centauri and is about 4.3 light-years away from us. Brightest star Sirius is about 8.7 light-year from us.
Fig. (a) shows the motion of different planets around the sun (not to the scale). Shape of solar system resembles an inverted saucer with all planets. Sun dominates the solar system and accounts for 99.9% of total matter of the whole system. The sun is the source of all the energy in solar system. Earth receives almost all the energy from the sun.
Question 2.
What is meant by Uttrayan and Dakshinayan?
Answer:
Uttrayan and Dakshinayan. We generally say that the Sun rises in the east and sets in the west. This is only partially correct because the position of rising sun changes every day. Let us perform a time-consuming experiment to stress our point. Note down the direction of rising sun on the sky.
Repeat the observation every week. A continuous change will be observed. From summer solstice (around June 21), the point of the sun shifts towards south. The sun is said to be in dakshinayan (moving south). This continues till winter (around December 22). After this sunrise changes its direction and stars move towards north. Now it is said to be in Uttaryan (moving north). Only on March 21 and September 23, the sunrise in the east and sets in the west.
Question 3.
What are terrestrial and Jovian Planets?
Answer:
Terrestrial planets. Four planets near to the Sun i.e. mercury, venus, earth and mars are called terrestrial planets. Their structure is similar to that of the earth. These are small planets and have a thin atmosphere on them.
Jovian planets are larger in size than terrestrial planets.
These planets are made of mainly hydrogen and helium. These planets, namely Jupiter, Saturn and Neptune are so-called because their structure is similar to Jupiter. They have a number of moons around them and some have rings around them. Their temperature, gravity etc. are such that life can never be possible on them.
![]()
Question 4.
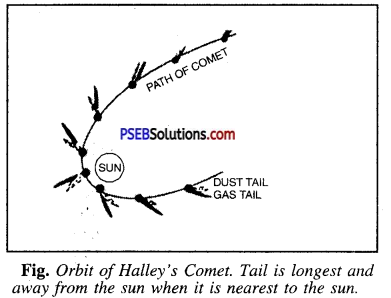
Write a short note on ‘Comets’.
Answer:
Comets: Comets are heavenly bodies which revolve around the Sun in highly elliptical path. Comets appear in the sky as a ball of fire with a tail. Tail always points away from the sun. Lesser the distance it has from the sun, longer is the tail. Comets are composed of rock-like material surrounded by large masses of easily vaporised substances like water, ammonia, methane etc. When comets approach the sun, some of its material is vaporised due to heat of the sun. Light of the sun exerts pressure on these vapours and force them away Tail is longest and from the comet in the form of a tail.
Question 5.
Write various uses of artificial satellites.
Answer:
Uses of Artificial Satellites. Various uses of artificial satellites are as follows :
- They can be used to forecast weather.
- They facilitate radio and television programme transmission.
- Artificial satellites enable long-distance telephone communication.
- They help to locate mineral and metal deposits.
- Artificial satellites fitted with telescopes and software programmes gather and process data on space phenomena, thus enhancing our knowledge and understanding of the universe.