Punjab State Board PSEB 6th Class Science Book Solutions Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets
Science Guide for Class 6 PSEB Fun with Magnets Intext Questions and Answers
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 135)
Question 1.
Materials attracted by a magnet are called ……………….
(Magnetic/Non-magnetic)
Answer:
Materials attracted by a magnet are called magnetic.
Question 2.
Materials not attracted by a magnet are called ……………..
(Magnetic/Non-magnetic)
Answer:
Materials not attracted by a magnet are called Non-magnetic.
![]()
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 136)
Question 1.
A freely suspended bar magnet always points towards direction:
(a) North-South (b) East-West
Answer:
A freely suspended bar magnet always points towards direction : North-South
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 138)
Question 1.
The poles of a bar magnet are ……………… to its ends. (near/far)
Answer:
The poles of a bar magnet are near to its ends.
Question 2.
Bar magnet has ……………… poles.
Answer:
Bar magnet has two poles.
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 139)
Question 1.
Magnetic compass is a device to find the ……………. of earth, (directions/time)
Answer:
Magnetic compass is a device to find the directions of earth.
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 140)
Question 1.
Like poles of two magnets ……………. each other. (Repel, Attract)
Answer:
Like poles of two magnets repel each other.
Question 2.
Unlike poles of two magnets …………… each other. (Repel, Attract)
Answer:
Unlike poles of two magnets attract each other.
PSEB 6th Class Science Guide Fun with Magnets Textbook Questions and Answers
Exercise – 1
Fill in the Blanks:
(a) Magnetite is ……………… magnet.
Answer:
natural
(b) Plastic is not a ……………… material.
Answer:
magnetic
![]()
(c) A magnet has ………………. poles.
Answer:
two
(d) The poles of a bar magnet are at its ………………
Answer:
ends
(e) ………………. is used for finding directions on earth.
Answer:
Compass
2. Write True or False:
(a) Poles of a magnet can be separated.
Answer:
False
(b) A magnet does not attract glass material.
Answer:
True
(c) Magnet can damage memory devices.
Answer:
True
(d) Magnetic compass always points towards East-West direction.
Answer:
False
(e) Magnets lose their property on hammering.
Answer:
True
![]()
3. Match the Column A with Column B:
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Wood | (a) Repel |
| 2. Iron | (b) Natural Magnet |
| 3. North pole-North pole | (c) Non-magnetic material |
| 4. Magnetite | (d) Attract |
| 5. North pole-South pole | (e) Magnetic material |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Wood | (c) Non-magnetic material |
| 2. Iron | (e) Magnetic material |
| 3. North pole-North pole | (a) Repel |
| 4. Magnetite | (b) Natural Magnet |
| 5. North pole-South pole | (d) Attract |
4. Choose the Correct Answer:
Question (i)
Non-magnetic material is:
(a) Iron
(b) Needle
(c) Paper
(d) None of them.
Answer:
(c) Paper
Question (ii)
Which can be converted into magnet
(a) Eraser
(b) Iron Nail
(c) Wooden bar
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Iron Nail
Exercise – 2
5. Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Question (i)
Write name of any two things used in our daily life that contains magnet.
Answer:
Things containing magnet in daily use : (1) Door Closer (2) Sticker (Chipko).
Question (ii)
When a bar magnet is placed on iron filings, where the filings will be attracted more ?
Answer:
When a bar magnet is placed on iron filings, the iron filings are attracted more at the poles of the magnet. This happens because a magnet has more attractive power at its poles.
Question (iii)
What is a Artificial Magnet ?
Answer:
Artificial Magnet. A magnet made by a man in the laboratory is called Artificial Magnet.
Question (iv)
Write any two properties of magnet ?
Answer:
Properties of Magnet :
- A magnet when freely suspended always sets itself in North-South direction.
- Every magnet has two poles : (a) North pole and the other (b) South pole which cannot be separated.
![]()
6. Short Answer Type Questions:
Question (i)
What is a magnet ? Name the poles of magnet.
Answer:
Magnet. A substance which attracts iron and substances made of iron towards itself, is called Magnet. Every magnet has two poles : (1) North pole and (2) South pole. These two poles cannot be separated.
Question (ii)
Give three reasons by which a magnet loses its property.
Answer:
Reasons by which a magnet loses its property :
- By heating a magnet
- By striking a magnet with hammer
- Dropping a magnet from height
- By not properly storing a magnet.
Question (iii)
What is a compass ? For what purpose it is used ?
Answer:
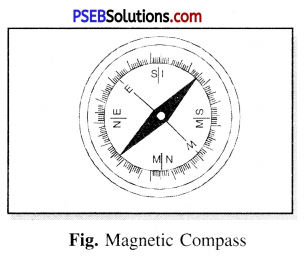
Magnetic compass.
It is an instrument which is used to determine the geographical directions of earth. It has a small magnetic needle enclosed in a plastic or aluminium circular box and is supported on a vertical axis. The needle can freely rotate in a horizontal direction freely.
The north pole of the needle is painted red to distinguish it from the other pole.
Geographical direction are marked on the dial of the compass.
Question (iv)
What are magnetic and non-magnetic materials ? Give examples.
Answer:
Magnetic materials.
Those substances which are attracted towards magnet, are called magnetic materials. As for example Iron, Cobalt and Nickle.
Non-magnetic materials.
Those materials which are not attracted towards magnet are called Non-magnetic materials e.g. Wood, Plastic, Paper and Cloth.
7. Long Answer Type Question:
Question (i)
How will you make your own magnet from a given strip of iron ? Describe.
Answer:
Method of making Iron strip a magnet (By Rubbing)
Take an iron strip. Place it on a table. Now take a bar magnet and place one of its pole on one end of the strip. Now without lifting the magnet rub it gently along the length of the strip to its other end. Now lift the magnet and bring the same pole of the magnet to the previous end of the strip. Rub the magnet as before. Repeat this process 30-40 times. Now to test whether the iron strip has become magnet or not, bring some alpins or some iron filings near one of its ends. If alpins/iron filings are attracted then the given iron strip has become magnet otherwise not. If not, then continue the process of rubbing till it acquires magnetism. Note that the rubbing pole and the direction of rubbing the strip does not change.
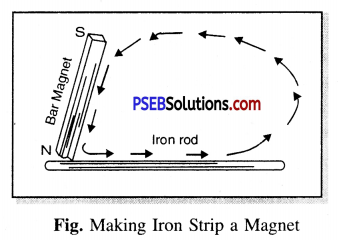
Precautions : (1) The direction of rubbing with magnet has to be the same.
(2) While rubbing the pole of the magnet should remain the same everytime.
![]()
Question (ii)
Give some uses of magnets in our daily life.
Answer:
Uses of magnets in daily life :
- Magnet is used in hard disc of computers which we use daily.
- Magnets are used in TV, speakers and radios magnet and coil used in speakers convert electric signals into sound.
- These are used in generators which change mechanical energy into electric energy. In some other type of motors magnets are used to convert electric energy into mechanical energy.
- Electrically charged magnets in cranes help to lift heavy iron loads and carry them from one place to another place which cannot be done by human labour.
- Magnets are used in filter machines where are is separated from crushed rock pieces.
PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Science Fun with Magnets Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question (i)
A magnet has poles :
(a) Three
(b) One
(c) Two
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Two
Question (ii)
A magnet attracts :
(a) Iron
(b) Rubber
(c) Glass
(d) Wood.
Answer:
(a) Iron
Question (iii)
On suspending a magnet freely it always stays in:
(a) North-West direction
(b) North-East direction
(c) North-South direction
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) North-South direction
Question (iv)
A magnet made from iron is called:
(a) Artificial magnet
(b) Natural magnet
(c) Spherical ended magnet
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Artificial magnet
Question (v)
To preserve the properties of a magnet the pairs of magnet should be with:
(a) similar poles near each other
(b) dissimilar poles near each other
(c) poles struck with hammer
(d) none of these.
Answer:
(b) dissimilar poles near each other
Question (vi)
For ascertaining direction is used :
(a) Magnous rod
(b) Non-magnetic substances
(c) Compass
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Compass
Question (vii)
In which part of the magnet, the force of attraction is maximum ?
(a) At the ends
(b) In the middle
(c) Between the end and the centre of magnet
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) At the ends
![]()
Question (viii)
The similar poles of the magnet mutually :
(a) attract each other
(b) repel each other
(c) neither attract nor repel
(d) none of these.
Answer:
(b) repel each other
Question (ix)
Between dissimilar poles of a magnet there is :
(a) Attraction
(b) Repulsion
(c) Neither attraction nor repulsion
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Attraction
Fill in the Blanks:
(a) Artificial magnets are made in different shapes such as …………….. , …………… and ……………..
Answer:
bar magnets, horse-shoe magnet, cylindrical,
(b) The materials which are attracted towards magnet are called ………………
Answer:
Magnetic materials
(c) Paper is not a ……………. material.
Answer:
Magnetic
(d) In olden days, sailor used to find direction by suspending a piece of ………………
Answer:
Natural magnet (load stone)
(e) A magnet always has ……………… poles.
Answer:
two
Write (T) against true and (F) against false Statements:
(a) A cylindrical magnet has only one pole.
Answer:
False
![]()
(b) Artificial magnets were discovered in Greece.
Answer:
False
(c) Similar poles of a magnet repel each other.
Answer:
True
(d) Maximum iron filings stick in the middle of a bar magnet when it is brought near them.
Answer:
False
(e) Bar magnet always point towards North-South direction.
Answer:
True
(f) A compass can be used to find East-West direction at any place.
Answer:
True
(g) Rubber is a magnetic material.
Answer:
False
Matching Match the following:
| Column A | Column B |
| (1) To find geographical direction at a place | Natural magnet |
| (2) Two dissimilar poles | Rubbing with a permanent magnet |
| (3) Freely suspended magnet stays | Magnetic compass |
| (4) An iron needle becomes megnet | Attract |
| (5) Magnetite | North-South direction |
Answer:
(1) – Natural magnet,
(2) – Rubbing with a permanent magnet.
(3) – Magnetic compass,
(4) – Attract,
(5) – North-South direction
![]()
Very short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Where are stickers (Chipko) generally used ?
Answer:
Stickers are generally used in steel almirahs or refrigerators so that these do not open when not required.
Question 2.
Name some four common things which have magnet in them.
Answer:
- Pin holder,
- Pencil box,
- Tape recorder and
- Radio.
Question 3.
Name the shepherd who first discovered natural magnet.
Answer:
Magnus.
Question 4.
What is natural magnet ?
Answer:
Natural magnet. Natural rock of magnetite found in the form of magnet is called natural magnet.
Question 5.
Name three magnetic substances.
Answer:
- Iron
- Nickle
- Cobalt.
Question 6.
List four non-magnetic substances.
Answer:
- Plastic
- Cloth
- Paper
- Wood.
Question 7.
How iron particles separated from a mixture of iron, sand and dust ?
Answer:
Iron particles can be separated from the mixture with the help of a magnet.
![]()
Question 8.
Where do iron particles stick more at the middle of the poles of a magnet ?
Answer:
Iron particles stick more at the poles of a magnet than in the middle.
Question 9.
In which direction a freely suspended magnet stays ?
Answer:
A freely suspended magnet always stays in the North-South direction.
Question 10.
What is North pole of a magnet ?
Answer:
The end of a freely suspended magnet which points towards the geographical North is called North pole of magnet.
Question 11.
What is South pole of a magnet ?
Answer:
That end of a freely suspended magnet which points towards geographical South pole is called South pole of magnet.
Question 12.
Which property of magnet is used to determine the direction ?
Answer:
A freely suspended magnet always points in N-S direction. This property is used to determine the direction.
Question 13.
Which instrument is used to find direction ?
Answer:
Magnetic compass.
Question 14.
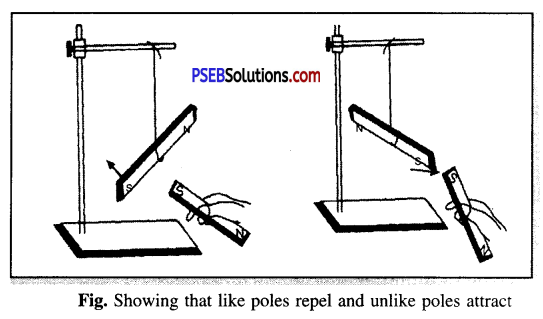
Do the like poles of two magnets attract or repel each other ?
Answer:
Like poles of two magnets repel each other.
Question 15.
Do unlike poles of two magnets attract or repel each other ?
Answer:
Unlike-poles of two magnets attract each other.
![]()
Question 16.
Where are poles of bar magnet situated ?
Answer:
Poles of bar magnet are situated near its ends.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How was natural magnet discovered ?
Answer:
It is believed that there was a shepherd named Magnes, who lived in ancient Greece. He used to take his herd of sheep and goats to the nearby mountains, for grazing. He would take a stick with him to control his herd. At one end of the stick there was a small piece of iron attached. One day while sitting on a rock, he was surprised to find that he had to pull hard to free his stick from that rock. He felt as if the stick was being attracted by the rock. Actually the rock was a natural magnet. This is how natural magnet was discovered. It was given the name magnetite after his own name.
Question 2.
What is magnet ? What are its different types ?
Answer:
Magnet. A magnet is a substance which attracts iron and iron made things towards it. When freely suspended it points in the North-South direction.
Types of Magnets. Mainly it is of two types.
(i) Natural magnet and
(ii) Artificial magnet
(i) Natural magnet. A magnet found in the nature is called natural magnet. Magnetite is a natural magnet.
(ii) Artificial magnet. A man made magnet is called Artificial magnet. Artificial magnets are made in different shapes. For example Bar magnet, Horse-shoe shaped magnet, Ring magnet, cylinderical magnet, Ball ended magnet.
Question 3.
It was observed that a pencil sharpener gets attracted by both the poles of a magnet although its body is made of plastic. Name a material that might have been used to make some part of it.
Answer:
The blade of sharpener is made of iron which is a magnetic material. Therefore, it is attracted by both poles of a magnet.
Question 4.
How will you separate iron particles from the sand or soil ?
Answer:
Spread mixture of sand and iron particles on a piece of paper. Move a magnet through the mixture. Iron particles will stick to the magnet. In this way, iron particles can be separated from sand or soil.
Question 5.
Show that the strength of a magnet is more at the poles that in the middle.
Answer:
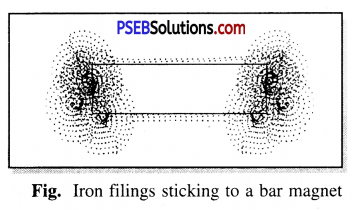
Take a bar magnet and some iron fillings. Now spread iron filings on a sheet of a paper and then put the bar magnet on the filings. We will observe that iron filings are attracted by magnet most on the both ends of the magnet as shown in the figure.
This activity shows that the strength of the magnet is more at the poles than in the middle of it
![]()
Question 6.
Column I shows different positions in which one pole of magnet is placed near that of other. Column II indicates the resulting action between them for each situation. Fill in the blanks.
| Column I | Column II |
| N – N | ……………… |
| N ………… | Attraction |
| S – N | ………….. |
| …….. S | Repulsion |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| N – N | Repulsion |
| N – S | Attraction |
| S – N | Attraction |
| S – S | Repulsion |
Question 7.
A bar magnet has no marking to indicate its poles. How would you find out near which end is its north pole located ?
Answer:
Identifying poles of a magnet. Take a bar magnet with poles marked on it. Suspend it freely with a thread from a wooden stand. Now take the unmarked bar magnet. Bring its one pole towards the north pole of the magnet suspended from the wooden stand. If it attracts then -it is south pole otherwise it is north pole and the other pole will be south pole.
Question 8.
Write any four properties of a magnet.
Answer:
Properties of a magnet.
- Magnet has two poles, which cannot be isolated.
- Magnet always rests in North-south direction when suspended freely.
- Like poles of a magnet repel each other while unlike pole attract each other.
- Magnet attracts magnetic substances like iron, cobalt, nickel etc.
- When a magnetic substance is rubbed with magnet, it also becomes a magnet.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is artificial magnet ? Give one method of making an artificial magnet.
Answer:
Artificial magnet. A magnet made by man is called artificial magnet. It can be of different shapes e.g.
(i) Bar magnet (ii) Horse shoe shaped (U-shaped) magnet (iii) cylinderical magnet.
Method of making an artificial magnet.
Method of making Iron strip a magnet (By Rubbing)
Take an iron strip. Place it on a table. Now take a bar magnet and place one of its pole on one end of the strip. Now without lifting the magnet rub it gently along the length of the strip to its other end. Now lift the magnet and bring the same pole of the magnet to the previous end of the strip. Rub the magnet as before. Repeat this process 30-40 times. Now to test whether the iron strip has become magnet or not, bring some alpins or some iron filings near one of its ends. If alpins/iron filings are attracted then the given iron strip has become magnet otherwise not. If not, then continue the process of rubbing till it acquires magnetism. Note that the rubbing pole and the direction of rubbing the strip does not change.

Precautions : (1) The direction of rubbing with magnet has to be the same.
(2) While rubbing the pole of the magnet should remain the same everytime.
![]()
Question 2.
Show experimentally that like poles repel and unlike poles attract each other.
Answer:
Experiment to show like poles repel and unlike poles attract each other. Take two bar magnets. Suspend one of these bar magnets by a string at some distance away from the other magnet and mark its north and south poles. Now, hold the first magnet in your hand and brings its north pole close to each pole of the suspended magnet, one by one. Repeat the same experiment now with the south pole of the bar magnet held in your hand. You will observe that the north poles of the two magnets, repel one another. The same is true for their south poles. However, the north pole of one magnet attracts the south pole of the other and vice-versa.
The observations can be summarised in the following way:
Like poles repel each other and unlike poles attract each other.
Question 3.
What is a magnetic compass ? Explain it.
Answer:
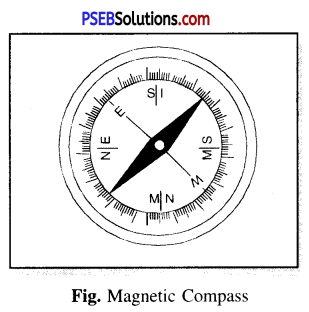
Compass.
This is a device which is used to find the directions. It is based on principle that a magnet always rests in North-South direction when suspended freely.
Construction.
A magnetic compass consists of a small magnet pivoted at its centre so that it can rotate freely about that pointed in the horizontal plane. Its north pole is generally paintd red and is enclosed in a small box of aluminium having a glass cover. Its needle always comes to rest in north-south direction. It is used to find directions at any place. Fig. Magnetic Compass
Question 4.
How are magnets’ safety preserved?
Answer:
If the magnets are not kept properly, they get weaken with time. To store magnets safely the following arrangement should be made.
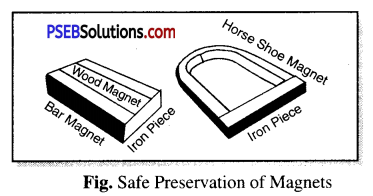
1. The opposite poles should be kept near each other with a strip of wood in between them and also place some soft iron pieces near their ends.
2. To store a horseshoe magnet place a soft iron piece in between its poles.
Keep your magnets away from Cassettes Mobiles, Televisions, Music systems, CDs, Computer, etc.