Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class Hindi Book Solutions Hindi Grammar samas समास Exercise Questions and Answers, Notes.
PSEB 12th Class Hindi Grammar समास
प्रश्न 1.
समास किसे कहते हैं ? उदाहरण सहित लिखें।
उत्तर:
परस्पर सम्बन्ध रखने वाले दो या दो से अधिक शब्दों को मिलकर बनने वाले एक स्वतन्त्र सार्थक शब्द को समास कहते हैं। जैसे:
राजा और कुमार से मिलकर-राजकुमार
राजा और पुरुष से मिलकर-राजपुरुष
प्रश्न 2.
समास परस्पर सम्बन्ध रखने वाले कौन से शब्दों के मेल से बनता है?
उत्तर:
संज्ञा के साथ संज्ञा का, संज्ञा के साथ विशेषण का, विशेषण के साथ विशेषय का तथा अव्यय के साथ संज्ञा का परस्पर मेल होने से समास बनता है।

प्रश्न 3.
‘समास’ शब्द का अर्थ सोदाहरण स्पष्ट करें।
उत्तर:
‘समास’ शब्द संस्कृत भाषा का है जिसका अर्थ है संक्षेपीकरण अर्थात् संक्षिप्त करना। जैसे ‘कपड़े से छना हुआ’ शब्द समूह का संक्षिप्त रूप होगा कपड़छन।
याद रखें : समास की विशेषता यह है कि यह जिस शब्द समूह का संक्षिप्त रूप होता है उसके अर्थ में किसी प्रकार का परिवर्तन नहीं होता जैसे कि ऊपर दिए गए उदाहरण ‘कपड़छन’ से स्पष्ट होता है।
प्रश्न 4.
समस्तपद या सामासिक शब्द किसे कहते हैं? सोदाहरण लिखें।
उत्तर:
समास करते समय परस्पर मेल होने वाले शब्दों के बीच की विभक्तियों या योजक शब्दों का लोप होकर जो शब्द बनते हैं, उन्हें ‘समस्त पद’ या ‘सामासिक शब्द’ कहते हैं। जैसे-
राम और लक्ष्मण = राम लक्ष्मण
चक्र है पाणि (हाथ) में जिसके = चक्रपाणि
यहाँ ‘राम लक्ष्मण’ तथा ‘चक्रपाणि’ समस्त पद या सामासिक शब्द हैं।
प्रश्न 5.
विग्रह किसे कहते हैं? सोदाहरण स्पष्ट करें।
उत्तर:
किसी शब्द में समास का पता करने के लिए समस्त पद के खण्डों को अलग-अलग करना पड़ता है, उसे विग्रह कहते हैं। अर्थात् समस्त पदों का विग्रह करके ही किसी शब्द का समास जाना जा सकता है। अतः विग्रह की परिभाषा हम इस तरह कर सकते हैं-
समस्त पदों के खण्ड करके विभक्तियाँ आदि लगाकर परस्पर सम्बन्ध दिखलाने की रीति को ‘विग्रह’ कहते हैं। जैसे-
राह-खर्च का विग्रह होगा-रास्ते के लिए खर्च
नीलकमल का विग्रह होगा-नीला है जो कमल
याद रखें: कभी विग्रह के आधार पर एक ही शब्द कई समासों का उदाहरण हो जाता है। जैसे ‘नीलकंठ’ का विग्रह यदि नीला है जो कंठ किया जाएगा तो यह ‘कर्मधारय’ समास होगा। किन्तु यदि इसी शब्द का विग्रह नीला है कंठ जिसका अर्थात् शंकर भगवान् किया जाएगा तो यह ‘बहुब्रीहि’ समास होगा।
समास के सम्बन्ध में कुछ याद रखने वाली बातें
1. हिन्दी में समास प्रायः दो शब्दों से ही बनते हैं जबकि संस्कृत में अनेक शब्दों से बनते हैं। हिन्दी में ‘सुत-वितनारी-भवन-परिवारा’ ही सबसे लम्बा समास है। इसके अतिरिक्त तन-मन-धन, जन-मन-गण, धूप-दीप-नैवैध आदि बहुत थोड़े शब्द हैं जो दो से अधिक शब्दों के मेल से बने हैं।
2. सामासिक शब्द बनते समय परस्पर मिलने वाले दोनों शब्दों की विभक्तियों या योजक शब्दों का लोप हो जाता है। जैसे राम और कृष्ण का समास राम-कृष्ण होने पर ‘और’ योजक शब्द का लोप हो गया है।
3. समास कुछ अपवादों को छोड़कर प्रायः दो सजातीय शब्दों में ही होता है। जैसे रसोई-घर का रसोईशाला नहीं बनेगा अथवा पाठशाला का पाठ घर शब्द नहीं बनेगा।
रेल-गाड़ी, जिला-धीश, धन-दौलत, मनमौजी, दुःख-सुख आदि इनके अपवाद हैं।
4. हिन्दी में मुख्यतः तीन ही प्रकार के शब्दों के सामासिक-शब्द प्रयोग में आते हैं। जैसे-
संस्कृत के-यथा-शक्ति, मनसिज, पुरुषोत्तम, युधिष्ठिर आदि।
हिन्दी के-भरपेट, अनबन, नीलकमल, दही-बड़ा, बैलगाड़ी, अलोना-सलोना आदि।
उर्दू-फ़ारसी के-नालायक, खुशबू, सौदागर, बेशक, चारदीवारी आदि।
इसके अतिरिक्त हिन्दी में कुछ अंग्रेजी शब्दों के मेल से अथवा हिन्दी अंग्रेजी शब्दों के मेल से भी समास बनते हैं। जैसे-
रेलवे स्टेशन, बुकिंग-ऑफिस, टिकट-चैकर, टाइम-टेबल तथा बस-अड्डा, पुलिस-चौकी, दल-बन्दी, पार्टी-बाज़ी आदि।
समास के भेद
प्रश्न 1.
समास के भेद किस आधार पर किये जाते हैं ?
उत्तर:
समास के भेद उसके पदों की प्रधानता-अप्रधानता के आधार पर किये जाते हैं। अर्थात् समास में कभी पहला पद प्रधान होता है तो कभी दूसरा और कभी-कभी दोनों ही पद प्रधान होते हैं अथवा कोई भी पद प्रधान नहीं होता। जैसे
रमेश गान्धी-भक्त है। यहां गान्धी-भक्त में भक्त प्रधान है क्योंकि रमेश भक्त है गान्धी नहीं।
प्रश्न 2.
समास के कितने भेद हैं?
उत्तर:
समास के मुख्यतः चार भेद माने जाते हैं। जो निम्नलिखित हैं-
1. अव्ययीभाव-इसमें पहला पद प्रधान होता है।
2. तत्पुरुष-इसमें दूसरा पद प्रधान होता है।
3. द्वन्द्व-इसमें दोनों पद प्रधान होते हैं।
4. बहुब्रीहि-इसमें कोई भी पद प्रधान नहीं होता।
कुछ विद्वान् समास के दो अन्य भेद भी मानते हैं-
1. कर्मधारय
2. द्विगु
किन्तु अनेक विद्वान् इन्हें तत्पुरुष समास का ही एक भेद मानते हैं।
इस तरह समास के कुल छः भेद माने जा सकते हैं-
1. अव्ययीभाव
2. तत्पुरुष
3. कर्मधारय
4. द्विगु
5. द्वन्द्व तथा
6. बहुब्रीहि
अव्ययी भाव
प्रश्न 1.
अव्ययीभाव समास की परिभाषा उदाहरण सहित लिखें।
उत्तर:
जिस समास में पहला पद प्रधान हो और समस्त पद अव्यय (क्रिया विशेषण) का काम करे, उसे अव्ययी भाव समास कहते हैं। जैसे-
संस्कृत शब्दों से-यथा शक्ति, प्रतिदिन, यावज्जीवन, व्यर्थ
हिन्दी शब्दों से-भरपेट, हाथों-हाथ, दिनों-दिन, हर घड़ी आदि।
याद रखें-1. अव्ययीभाव समास में समस्त शब्द अव्यय होता है। अतः उसके साथ विभक्ति चिह्न नहीं लगता। जैसे-
यह पुस्तक हाथों हाथ बिक गयी।
वे रातों रात शहर छोड़ कर चले गए।
2. यथा, प्रति, भर तथा आ जिस शब्द के पहले पद होते हैं, वे सब अव्ययीभाव समास कहलाते हैं। जैसा प्रत्येक, प्रतिवर्ष, भरसक, आमरण आदि।
3. द्विरुक्त शब्द बहुधा अव्ययीभाव होते हैं। जैसे-घड़ी-घड़ी, पल-पल, रोज़-रोज़, घर-घर, दर-दर, वन-वन आदि।
4. द्विरुक्त शब्दों के बीच में ‘ही’ अथवा ‘आ’ लगने पर भी अव्ययीभाव ही होता है। जैसे-दिल ही दिल, मन ही मन, साथ ही साथ, एकाएक, मुँहा-मुँह, धड़ाधड़, सरासर आदि।
2. तत्पुरुष
प्रश्न 1.
तत्पुरुष समास की परिभाषा उदाहरण सहित लिखें।
उत्तर:
जिस समास का दूसरा पद प्रधान होता है और दोनों पदों के बीच कर्ता तथा सम्बोधन कारक के अतिरिक्त शेष किसी भी कारक की विभक्ति का लोप हो जाता है। जैसे-
ग्रन्थकार = ग्रन्थ के करने वाला
तुलसीकृत = तुलसी से कृत।
देश-भक्ति = देश के लिए भक्ति
भयभीत = भय से भीत
हिमालय = हिम (बर्फ) का घर
शोकमग्न = शोक में मग्न
ऊपर के उदाहरणों में क्रमशः कर्म, करण, सम्प्रदान, अपादान, सम्बन्ध तथा अधिकरण कारक चिह्नों का लोप हुआ है। इन उदाहरणों में दूसरे पद ही प्रधान हैं। जैसे राज पुरुष में पुरुष प्रधान है क्योंकि यदि हम कहें राज पुरुष पधार रहे हैं तो इसका अर्थ होगा ऐसा पुरुष पधार रहा है जिसका सम्बन्ध राजा से है वह राजा नहीं है।

प्रश्न 2.
तत्पुरुष समास के कितने भेद हैं ? उदाहरण सहित लिखें।
उत्तर:
तत्पुरुष समास में प्रथम पद के साथ जिस कारक की विभक्ति आती है तथा जो समास करते समय लुप्त हो जाती है, उसी कारक के अनुसार तत्पुरुष का नाम भी होता है। जैसे-
- कर्म तत्पुरुष-यशप्राप्त (यश को प्राप्त)
- करण तत्पुरुष-हस्तलिखित (हस्त (हाथ) से लिखित) .
- सम्प्रदान तत्पुरुष-गुरुदक्षिणा (गुरु के लिए दक्षिणा)
- अपादान तत्पुरुष-ऋण मुक्त (ऋण से मुक्त)
- सम्बन्ध तत्पुरुष-पवन पुत्र (पवन का पुत्र)
- अधिकरण तत्पुरुष-घुड़सवार (घोड़े पर सवार)
कुछ अन्य प्रश्न
सामासिक शब्द सूची
परीक्षा में प्रायः सामासिक शब्द देकर उनके समास का नाम लिखने को भी कहा जाता है अथवा कभी-कभी कुछ शब्द देकर यह पूछा जाता है कि इस शब्द में समास कौन-सा है। इसी बात को ध्यान में रखते हुए एक विस्तृत सूची यहाँ दी जा रही है।
1. अव्ययीभाव समास
अजानु-जानुओं (घुटनों) तक
अनुगमन-पीछे चलना
अतिकष्ट-बहुत कष्ट
आजीवन-जीवन पर्यन्त
आमरण-मरण पर्यन्त
उपकण्ठ-कण्ठ के समीप
उपकुल-कुल के समीप
उपकृष्ण-कृष्ण के समीप
उपनगर-नगर के समीप
प्रतिदिन-दिन-दिन
अनजाने-जाने बिना
घड़ी-घड़ी-हर घड़ी
घर-घर-हर घर
ज्ञानपूर्वक-ज्ञान के अनुसार
निडर-बिना डर
गली-गली-प्रत्येक गली
प्रत्येक-एक-एक
यथामति–मति के अनुसार
यथा विधि-विधि के अनुसार
यथा शक्ति-शक्ति के अनुसार
यथा शीघ्र-जितना शीघ्र हो सके उतना शीघ्र
यथा संख्य-संख्या के अनुसार
यथा सम्भव-जैसा सम्भव हो
यथा साध्य-जो हो सके
यथा सामर्थ्य-सामर्थ्य के अनुसार
यथोचित -जितना उचित हो
निस्संदेह-संदेह के बिना
बीचों-बीच-ठीक बीच में
भर पेट-पेट भर कर
भरसक-पूरी शक्ति से
हाथों हाथ-हाथ ही हाथ
साफ-साफ-बिलकुल साफ
2. तत्पुरुष
परलोकगमन-परलोक को गमन
यशप्राप्त-यश को प्राप्त
विदेशगत-विदेश को गया हुआ
शरणागत-शरण को आगत (आया हुआ)
स्वर्गगत-स्वर्ग को गत (गया हुआ)
मोक्षप्राप्त-मोक्ष को प्राप्त
कर्म तत्पुरुष-
गंगा प्राप्त-गंगा को प्राप्त
ग्रन्थकार-ग्रन्थ को करने (रचने) वाला
ग्रामगत-ग्राम को गया हुआ
जलपिपासु-जल पीने की इच्छा रखने वाला
जेबकतरा-जेब को कतरने (काटने) वाला
देशगत-देश को गया हुआ
करण तत्पुरुष-
अकाल-पीड़ित-अकाल से पीड़ित
अनुभव-जन्य-अनुभव से जन्य (उत्पन्न)
आचार-हीन-आचार से रहित
ईश्वर-प्रदत्त-ईश्वर से प्रदत्त प्रदत्त (दिया हुआ)
कपड़छन-कपड़े से छना हुआ
कलंकयुक्त-कलंक से युक्त
कष्टसाध्य-कष्ट से साध्य
धनहीन-धन से रहित
प्रेमातुर-प्रेम से आतुर
बाढ़-पीड़ित-बाढ़ से पीड़ित
बाणबिद्ध-बाण से बिद्ध
बिहारी रचित-बिहारी द्वारा रचित
भुखमरा-भूख से मरा हुआ
मदमाता-मद से माता (मस्त)
कीर्तियुक्त-कीर्ति से युक्त
मदाँध-मद से अंधा
गुणयुक्त-गुण से युक्त
मदोन्मत्त-मद से उन्मत्त
गुण हीन-गुण से रहित
मनगढन्त-मन से गढ़ी हुई
गुन भरा-गुण से भरा हुआ
मन चाहा-मन से चाहा
गुरुकृत-गुरु से कृत (किया हुआ)
मन माना-मन से माना हुआ
गुरुदत्त-गुरु से दत्त (दिया हुआ)
मुँह माँगा-मुँह से माँगा हुआ
जन्मरोगी-जन्म से रोगी
रेखांकित-रेखा से अंकित
ज्ञान मुक्त–ज्ञान से मुक्त
रेलयात्रा-रेल से यात्रा
ज्ञान युक्त–ज्ञान से युक्त
वाग्दत्ता-वाक् से दत्ता
तुलसीकृत-तुलसी से कृत
शोकाकुल-शोक से आकुल
दयार्द्र-दया से आर्द्र
श्रीयुक्त-श्री (लक्ष्मी) से युक्त
दर्द भरा-दर्द से भरा हुआ
श्रीहीन–श्री (लक्ष्मी) से हीन
दुःर्खात–दुःख से आर्त (व्याकुल)
हस्तलिखित-हाथ से लिखित
दोषपूर्ण-दोष से पूर्ण

सम्प्रदान तत्पुरुष
आराम कुर्सी-आराम के लिए कुर्सी
प्रयोगशाला-प्रयोग के लिए शाला
क्रीड़ा क्षेत्र-क्रीड़ा के लिए क्षेत्र
बलिपशु-बलि के लिए पशु
कृष्णापर्ण-कृष्ण के लिए अर्पण
मार्गव्यय-मार्ग के लिए व्यय
गुरुदक्षिणा-गुरु के लिए दक्षिणा
यज्ञशाला-यज्ञ के लिए शाला
गौशाला-गौओं के लिए शाला
युद्धक्षेत्र-युद्ध के लिए क्षेत्र
जेब खर्च-जेब के लिए खर्च
युद्धभूमि-युद्ध के लिए भूमि
डाकगाड़ी-डाक के लिए गाड़ी
रसोई घर-रसोई के लिए घर
देवबलि-देवता के लिए बलि
राज्यलिप्सा-राज्य के लिए लिप्सा
देशभक्ति-देश के लिए भक्ति
राहखर्च-राह के लिए खर्च
देशापर्ण देश के लिए अपर्ण
रेलभाड़ा-रेल के लिए भाड़ा
परोपकार-पर (दूसरे) के लिए उपकार
सत्याग्रह-सत्य के लिए आग्रह
पाठशाला-पाठ के लिए शाला
हथकड़ी-हाथ के लिए घड़ी
पुत्रशोक-पुत्र के लिए शोक
हवनसामग्री-हवन के लिए सामग्री
पुत्रहित-पुत्र के लिए हित
अपादान तत्पुरुष
आकाशवाणी-आकाश से आने वाली वाणी
देशनिर्वासन-देश से निर्वासन
आशातीत-आशा से अधिक
धनहीन-धन से हीन
ईश्वरविमुख-ईश्वर से विमुख
धर्मभ्रष्ट-धर्म से भ्रष्ट
ऋणमुक्त-ऋण से मुक्त
पथभ्रष्ट-पथ से भ्रष्ट
कामचोर-काम से जी चुराने वाला
पदच्युत-पद से च्युत
गुरुभाई-गुरु से पढ़कर भाई
बन्धनमुक्त-बन्धन से मुक्त
जन्मांध-जन्म से अन्धा
भयभीत-भय से भीत
जन्मपूर्व-जन्म से पूर्व
रोगमुक्त-रोग से मुक्त
जलजात-जल से जात (उत्पन्न)
लक्ष्यभ्रष्ट-लक्ष्य से भ्रष्ट
देशनिकाला-देश से निकालना
सर्वोत्तम-सर्व से उत्तम
भवसागर-भव का सागर
भारतरत्न-भारत का रत्न
भारतवासी-भारत के वासी
भ्रातृस्नेह-भ्राता का स्नेह
मृगशावक-मृग का शावक (बच्चा)
यमलोक-यम का लोक
यमुनातट-यमुना का तट
रघुकुलमणि-रघुकुल की मणि
राजकुमार-राजा का कुमार
राजनीतिज्ञ-राजनीति का ज्ञाता
राजपुरुष-राजा का पुरुष
राजवंश-राजा का वंश
रामकहानी-राम की कहानी
लखपति–एक लाख का पति
वनमाली-वन का माली
सम्बन्ध तत्पुरुष
अछूतोद्धार-अछूतों का उद्धार
अमचूर-आम का चूरा
अमृतरस-अमृत का रस
आत्महत्या-आत्मा (अपनी) की हत्या
कनकघट-कनक (सोने) का घट (घड़ा)
कालिदास-काली का दास
कुलदीप-कुल का दीपक
गंगातट-गंगा का तट
गजराज-गजों का राजा
गुरुसेवा-गुरु की सेवा
गौरीपुत्र-गौरी (पार्वती) का पुत्र
घुड़दौड़-घोड़ों की दौड़
जलधारा-जल की धारा
जीवनसाथी-जीवन का साथी
तरणितनूजा-तरणि (सूर्य) की तनूजा (पुत्री)
दिनचर्या-दिन की चर्या
दिनमान-दिन का मान
दीनानाथ-दिनों का नाथ
देवकन्या-देवता की कन्या
देवराज-देवताओं का राजा
देवालय-देव का आलय
देशसेवक-देश का सेवक
परनिन्दा-पर (दूसरे) की निन्दा
पराधीन-पर (दूसरे) के अधीन
पशुपति-पशुओं का पति
प्रजापति-प्रजाओं का पति
प्रेमसागर-प्रेम का सागर
बैलगाड़ी-बैलों की गाड़ी
वायुसेना-वायु की सेना
विचाराधीन-विचार के अधीन
विद्यार्थी-विद्या का अर्थी (इच्छुक)
विद्यालय-विद्या का आलय
विश्वविद्यालय–विश्व की विद्यालय
सचिवालय-सचिवों का आलय
सिरदर्द-सिर का दर्द
सुखसागर-सुख का सागर
सूर्यपुत्र-सूर्य का पुत्र
सेनापति-सेना का पति
हिन्दुस्थान-हिन्दुओं का स्थान
हिमालय-हिम (बर्फ) का घर

अधिकरण तत्पुरुष
आत्मविश्वास-आत्म (अपने) पर विश्वास
आनन्दमग्न-आनन्द में मग्न
आपबीती-अपने पर बीती।
कानाफूसी-कानों में फुसफुसाहट
कलाप्रवीण-कला में प्रवीण
गृहप्रवेश-गृह में प्रवेश
घुड़सवार-घोड़े पर सवार
जनप्रिय-जनता में प्रिय
दानवीर-दान (देने) में वीर
देशाटन-देश में अटन (भ्रमण)
धर्मवीर-धर्म में वीर
रणकौशल-रण में कौशल
लोकप्रिय-लोक में प्रिय
वनवास-वन में वास
शोकमग्न-शोक में मग्न
(क) नञ् तत्पुरुष
निषेध या अभाव के अर्थ में किसी शब्द से पूर्व ‘अ’ या ‘अन्’ लगाने से जो समास बनता है, उसे नञ् तत्पुरुष समास कहते हैं। जैसे-
अहित = न हित
अपूर्ण = न पूर्ण
अधर्म = न धर्म
असंभव = न संभव
अब्राह्मण = न ब्राह्मण
अन्याय = न न्याय
अनुदार = न उदार
अनाश्रित =न आश्रित
अनिष्ट =न इष्ट
अनाचार = न आचार
विशेष-(क) प्रायः संस्कृत शब्दों में जिस शब्द के आदि में व्यंजन होता है, तो ‘नञ्’ समास में उस शब्द से पूर्व ‘अ’ जुड़ता है और यदि शब्द के आदि में स्वर होता है, तो उससे पूर्व ‘अन्’ जुड़ता है, जैसे-
अन् + अन्य = अनन्य
अन् + उत्तीर्ण = अनुत्तीर्ण
अ + वांछित = अवांछित
अ + स्थिर = अस्थिर।
(ख) किंतु उक्त नियम प्रायः तत्सम शब्दों पर ही लागू होता है, हिंदी शब्दों पर नहीं। हिंदी शब्दों में सर्वत्र ऐसा नहीं होता, जैसे-
अन् + चाहा = अनचाहा
अ + काज = अकाज
अन + होनी = अनहोनी है
अन + बन = अनबन
अ + न्याय = अन्याय
अन + देखा = अनदेखा
अ + टूट = अटूट
अ + सुंदर = असुंदर।
(ग) हिंदी और संस्कृत शब्दों के अतिरिक्त ‘गैर’ और ‘ना’ वाले शब्द भी ‘न’ तत्पुरुष के अंतर्गत आ जाते हैं, जैसे-
नागवार नापसंद
गैर हाज़िर नाबालिग
नालायक गैरवाज़िब।
(ख) अलुक् तत्पुरुष
जिस तत्पुरुष समास में पहले पद की विभक्ति का लोप नहीं होता, उसे ‘अलुक्’ तत्पुरुष समास कहते हैं, जैसे-
मनसिज = मन में उत्पन्न
वाचस्पति = वाणी का पति
विश्वंभर = विश्व को भरने वाला
युधिष्ठिर = युद्ध में स्थिर
धनंजय = धन को जय करने वाला
खेचर = आकाश में विचरने वाला।
(ग) उपपद तत्पुरुष
जिस तत्पुरुष समास का स्वतंत्र रूप में प्रयोग नहीं किया जा सकता, ऐसे सामासिक शब्दों को ‘उपपद’ तत्पुरुष समास कहते हैं, जैसे-
जलज = जल + ज (‘ज’ का अर्थ उत्पन्न अर्थात् पैदा होने वाला है, पर इस शब्द को अलग से प्रयोग नहीं किया जा सकता है।)
इसी प्रकार
तटस्थ = तट + स्थ
गृहस्थ = गृह + स्थ
पंकज = पंक + ज
जलद = जल + द
कृतघ्न = कृत + न
उरग = उर + ग
तिलचट्टा = तिल + चट्टा
लकड़फोड़ = लकड़ + फोड़
बटमार = बट + मार
घरघुसा = घर + घुसा
पनडुब्बी = पन + डुब्बी
घुड़चढ़ी = घुड़ + चढ़ी
कलमतराश = कलम + तराश
सौदागर = सौदा + गर
ग़रीबनिवाज़ = ग़रीब + निवाज़
चोबदार = चोब + दार।

3. कर्मधारय
जिस समास के दोनों पदों के बीच विशेष्य-विशेषण अथवा उपमेय-उपमान का संबंध हो और दोनों पदों में एक ही कारक (कर्ता कारक) की विभक्ति आए, उसे कर्मधारय समास कहते हैं, जैसे-
नीलकमल = नीला है जो कमल
लाल-मिर्च = लाल है जो मिर्च
पुरुषोत्तम = पुरुषों में है जो उत्तम
महाराजा = महान् है जो राजा
चंद्रमुख = चंद्र के समान है जो मुख
पुरुषसिंह = सिंह के समान है जो पुरुष
नील-कंठ = नीला है जो कंठ
महाजन = महान् है जो जन
पीतांबर = पीत है जो अंबर
सज्जन = सत् (अच्छा) है जो जन
भलामानस = भला है जो मानस (मनुष्य)
सद्गुण = सद् (अच्छे) हैं जो गुण
शुभागमन = शुभ है जो आगमन
नीलांबर = नीला है जो अंबर
महाविद्यालय = महान् है जो विद्यालय
काला-पानी = काला है जो पानी
चरण-कमल = कमल रूपी चरण
प्राण-प्रिय = प्राणों के समान प्रिय
वज्र-देह = वज्र के समान देह
विद्या धन = विद्या रूपी धन
देहलता = देह रूपी लता
घनश्याम = घन के समान श्याम
काली-मिर्च = काली है जो मिर्च
महारानी = महान् है जो रानी
नील-गाय = नीली है जो गाय
कर-कमल = कमल के समान
कर मुखचंद्र = मुख रूपी चंद्र
नरसिंह = सिंह के समान है जो नर
भव-सागर = भव रूपी सागर
बुद्धिबल = बुदधि रूपी बल
गुरुदेव = गुरु रूपी देव
कर-पल्लव = पल्लव रूपी कर
कमल-नयन = कमल के समान नयन
कनक-लता = कनक की सी लता
चंद्रमुख = चंद्र के समान मुख
मृगनयन = मृग के नयन के समान नयन
कुसुम-कोमल = कुसुम के समान कोमल
सिंह-नाद = सिंह के नाद के समान नाद
जन्मांतर = अंतर (अन्य) जन्म
नराधम = अधम है जो नर
दीनदयालु = दीनों पर है जो दयालु
मुनिवर = मुनियों में है जो श्रेष्ठ
मानवोचित = मानवों के लिए है जो उचित
पुरुष-रत्न = पुरुषों में है जो रत्न
घृतांत = घृत में मिला हुआ अन्न
पर्णशाला = पर्ण (पत्तों से) निर्मित शाला
छाया-तरु = छाया-प्रधान तरु
वन-मानुष = वन में निवास करने वाला मानुष
गुरु-भाई = गुरु के संबंध से भाई
बैलगाड़ी = बैलों से खींची जाने वाली गाड़ी
माल-गाड़ी = माल ले जाने वाली गाड़ी
गुडंबा = गुड से पकाया हुआ आम
दही-बड़ा = दही में डूबा हुआ बड़ा
जेब-घड़ी = जेब में रखी जाने वाली घड़ी
पन-चक्की = पानी से चलने वाली चक्की
4. द्विगु
जिस समास में पहला पद संख्यावाचक हो और समस्त समूह या समाहार का ज्ञान कराए, उसे द्विगु समास कहते हैं, जैसे-
शताब्दी = शत (सौ) अब्दों (वर्षों) का समूह
सतसई = सात सौ दोहों का समूह
चौराहा = चार राहों (रास्तों) का समाहार
चौमासा = चार मासों का समाहार
अठन्नी = आठ आनों का समूह
पंसेरी = पाँच सेरों का समाहार
दोपहर = दो पहरों का समाहार
त्रिफला = तीन फलों का समूह
चौपाई = चार पदों का समूह
नव-रत्न = नौ रत्नों का समूह
त्रिवेणी = तीन वेणियों (नदियों) का समाहार
सप्ताह = सप्त (सात) अह (दिनों) का समूह
सप्तर्षि = सात ऋषियों का समूह
अष्टाध्यायी = अष्ट (आठ) अध्यायों का समूह
त्रिभुवन = तीन भुवनों (लोकों) का समूह
पंचवटी = पाँच वट (वृक्षों) का समाहार
नवग्रह = नौ ग्रहों का समाहार
चतुर्वर्ण = चार वर्णों का समूह
चतुष्पदी = चार पदों का समाहार
पंचतत्व = पाँच तत्वों का समूह।
बहब्रीहि समास
बहुब्रीहि समास की परिभाषा उदाहरण सहित लिखें।
उत्तर:
जिस समास का कोई भी पद प्रधान नहीं होता और दोनों पद किसी अन्य शब्द (संज्ञा) के विशेषण होते हैं, उसे बहुब्रीहि समास कहते हैं। जैसे-
नीलकण्ठ-नीला है कण्ठ जिसका अर्थात् शिव
दिगम्बर-दिशाएं ही हैं वस्त्र जिसके अर्थात् नग्न
चन्द्रमुखी-चन्द्र के समान है मुख है जिसका (कोई स्त्री)
मनचला-मन रहता हो चंचल जिसका
दशानन-दश है आनन (मुख) जिसके अर्थात् रावण

द्वन्द्व समास
द्वन्द्व समास की परिभाषा उदाहरण सहित लिखें।
उत्तर:
जिस समस्त पद के दोनों पद प्रधान हों तथा विग्रह (अलग-अलग) करने पर दोनों पदों के बीच ‘और’, ‘तथा’, ‘अथवा’, ‘या’ आदि योजक शब्द लगें, उन्हें द्वन्द्व समास कहते हैं। जैसे-
पाप-पुण्य-पाप अथवा पुण्य।
पति-पत्नी-पति और पत्नी।
अन्न-जल-अन्न और जल
भीम-अर्जुन-भीम और अर्जुन।
राधा-कृष्ण-राधा और कृष्ण
सीता-राम-सीता और (राम)
निशि-वासर-निशि और वासर
दालभात-दाल और भात
देश-विदेश-देश और विदेश
जल-थल-जल और थल
दीन-ईमान-दीन और ईमान
पूर्वपश्चिम-पूर्व और पश्चिम।
सामासिक शब्द सूची
बहब्रीहि समास
अंशुमाली–अंशु (किरणें) है माला जिसकी-सूर्य
अजातशत्रु-अजात (नहीं पैदा हुआ हो) है शत्रु जिसका
अजानुबाहु-अजानु (घुटनों तक लम्बी) है भुजाएं जिसकी-अवतारी पुरुष
अनहोनी-न होने वाली घटना
उदारहृदय-उदार हृदय है जिसका
कनकटा-कान कटा हुआ है जिसका
कनफटा-कान फटे हुए हैं जिसके
कुसुमाकर-कुसमों का खजाना है जो-वसंत ऋतु।
गजानन-गज का मुख है जिसका गणेश
विषधर-विष को धारण करने वाला सर्प।
कुसुमाकर-कुसुमों का आकार (समूह) है जो-बसन्त ऋतु
गिरिधर-गिरि (पर्वत) को धारण करने वाला-श्रीकृष्ण
घनश्याम-घन के समान श्याम (काला) है जो-श्रीकृष्ण
चन्द्रमुखी-चन्द्रमा के समान मुख है जिसका।
चन्द्रवदनि-चन्द्रमा के समान बदन (मुख) है जिसका
चन्द्रशेखर-शेखर (मस्तक) पर है चन्द्र जिसके-शिवजी
चक्रपाणि-चक्र है पाणि (हाथ) में जिसके-विष्णु
चतुर्भुज-चार भुजाएं हैं जिसकी-विष्णु
चारपाई-चार हैं पैर जिसके-खाट
तिमंजिला-तीन हैं मंजिल जिसकी
त्रिनेत्र-तीन हैं नेत्र जिसके अर्थात् शिव।
दशानन–दश हैं आनन (मुख) जिसके-रावण
दिगम्बर-दिशाएं हैं वस्त्र जिसके-शिवजी
दुरात्मा-दुष्ट (बुरी) आत्मा वाला
धर्मात्मा-धर्म में आत्मा वाला
नीलकण्ठ-नीला है कण्ठ जिसका-शिवजी
पंकज-पंक (कीचड़) में पैदा हुआ है जो-कमल
पंचानन–पाँच हैं मुख जिसके-ब्रह्मा जी
पंचवटी-पाँच हैं वट (वृक्ष) जहाँ
पद्मासना-पद्म (कमल) है आसन जिसका-सरस्वती
पीताम्बर-पीले हैं अम्बर (कपड़े) जिसके-श्रीकृष्ण, विष्णु
प्रधानमन्त्री–मन्त्रियों में प्रधान है जो
बड़बोला-बड़े बोल बोलने वाला
मनचला-मन है चलायमान (चंचल) जिसका
मयूरवाहन-मयूर (मोर) है वाहन जिसका-शिवजी पुत्र कार्तिकेय
महावीर-महान् है वीर जो-हनुमान जी
मीनाक्षी-मीन (मछली) जैसी आँखें हैं जिसकी
मृगाक्षी/मृगनयनी-मृग की आँखों जैसी आँखें हैं जिसकी स्त्री विशेष।
मृगेन्द्र-मृगों का इन्द्र (राजा) है जो-सिंह
मृत्युञ्जय-मृत्यु को जीतने वाला है जो-शिवजी
मेघनाद-मेघ के समान नाद है जिसका-रावण पुत्र इन्द्रजीत
लम्बोदर-लम्बा है उदर जिसका-गणेश
महादेव-महान् है जो देव-शिव।
त्रिलोचन-तीन हैं नेत्र जिसके-शिव
बारहसिंगा-बारह है सींग जिसके (वह हिरन)
वीणापाणि-वीणा है पाणि (हाथ) में जिसके-सरस्वती
चक्रधर-चक्र को धारण करने वाला-विष्णु
सहस्रबाहु-सहस्र (हज़ार) भुजाओं वाला-एक रक्षक का नाम
सिरकटा-सिर है कटा हआ जिसका।
सुलोचना-सुन्दर है लोचन जिस (स्त्री) के
षटकोण-षट (छ:) है जिसके कोण
षडानन-छ: मुख हैं जिसके
पतझड़-झड़ते हैं पत्ते जिसमें वह ऋतु
अष्टाध्यायी-आठ अध्यायों वाला (पणिनी व्याकरण)
महात्मा-महान् है आत्मा जिसकी
गुरुद्वारा-गुरु का द्वारा है जो (सिक्ख धर्म का परम-पवित्र धार्मिक स्थल)
द्वन्द्व समास
अन्न-जल-अन्न और जल
नमक-मिर्च-नमक और मिर्च
अमीर-गरीब-अमीर और ग़रीब
नर-नारी-नर और नारी
आचार-व्यवहार-आचार और व्यवहार
नाच-रंग-नाच और रंग
आब-हवा-आब (पानी) और हवा
नाम-निशान-नाम और निशान
ऊँचा-नीचा-ऊँचा और नीचा
निशि-वासर-निशि (रात) और वासर (दिन)
खरा-खोटा-खरा और खोटा
रुपया-पैसा-रुपया और पैसा
गुण-दोष-गुण और दोष
नोन-तेल-नोन और तेल
चाल-चलन-चाल और चलन
पाप-पुण्य-पाप और पुण्य
जन्म-मरण-जन्म और मरण
पास-पड़ोस-पास और पड़ोस
जञान-विज्ञान-ज्ञान और विज्ञान
बीस-पच्चीस-बीस और पच्चीस
तिल-चावल-तिल और चावल
भूखा-प्यासा-भूखा और प्यासा
थोड़ा बहुत-थोड़ा और बहुत
माँ-बाप-माँ और बाप
दस-बीस-दस और बीस
राजा-रंक-राजा और रंक
दाल-रोटी-दाल और रोटी
रात-दिन-रात और दिन
दीन-ईमान-दीन और ईमान
राम-कृष्ण-राम और कृष्ण
आचार-व्यवहार-आचार और व्यवहार
राम-लक्ष्मण–राम और लक्ष्मण
दो-चार-दो और चार
लूट-मार-लूट और मार
धनी-निर्धन-धनी और निर्धन
वेद-पुराण-वेद और पुराण
धर्म-अधर्म-धर्म और अधर्म
सुख-दुःख-सुख और दुःख
नदी-नाले-नदी और नाले
राजा-रानी-राजा और रानी।
गंगा-यमुना-गंगा और यमुना
माता-पिता-माता और पिता,
धूप-दीप-धूप और दीप।।
लोभ-मोह-लोभ और मोह।

बोर्ड परीक्षा में पूछे गए प्रश्न
किन्हीं पाँच के समास/समास विग्रह कीजिए।
1. यथा शक्ति, आजीवन, देश निकाला, राह के लिए खर्च, राजा का कुमार।
2. विधि के अनुसार, हाथ ही हाथ में, सेनापति, सिरदर्द, चतुर्भुज।
3. जन्म से लेकर, प्रत्येक गली, रोजगार के बिना, मधुमक्खी, पदच्युत।
4. पति-पत्नी, मेघनाद महात्मा, पूर्व-पश्चिम, लम्बा है उदर जिसका, आचार और व्यवहार, दश हैं आनन जिसके, गंगा और यमुना।
5. महान है आत्मा जिसकी, अन्न और जल, झड़ते हैं पत्ते जिसमें, नर और नारी, गणेश, मृत्युंजय, सीता-राम, ‘ भीम-अर्जुन।
6. रात और दिन, पीत है अम्बर जिसका, सुख और दुःख, कुसुमों का खजाना है, जो धूप-दीप, पंकज, दालभात, चक्रधर।
7. धनहीन, महात्मा, त्रिलोकी, नवरत्न, सत्य के लिए आग्रह, पथ से भ्रष्ट, राजा की नीति, दूध और दही।
8. कुरूप, घनश्याम, पंचवटी, पञ्चानन, महान् है जो देव, न होने वाली घटना, तीन हैं मंज़िल जिसकी, गिरि को धारण करने वाला।
9. चौमासा, अनन्त, दोपहर, विद्यासागर, आठ अध्यायों का समाहार, राह के लिए खर्चे, गणों का पति, पीत हैं अम्बर जिसके।
10. आचार और व्यवहार, मेघ के समान है नाद, सात दिनों का समूह, मालगाड़ी, हस्तलिखित, विद्यालय।
11. जल और थल, महान् है आत्मा जिसकी, तीन रंगों का समूह आजीवन, धनहीन, घुड़सवार।
12. सीता और गीता, झड़ते हैं पत्ते जिसमें, चार भुजाओं का समूह, धर्मवीर, बेखटके, पीताम्बर।
13. पूर्व और पश्चिम, पीला है जो अम्बर, चार भुजाओं वाला, दशानन, यथाशक्ति, अमीर-ग़रीब।
14. देश और विदेश, माल ढोने वाली गाड़ी, नौ ग्रहों का समूह, राजकमार, यथानियम, अन्न-जल।
15. गंगा और यमुना, रेल पर चलने वाली गाड़ी, जन्म से लेकर, सत्याग्रह, गुरुदक्षिणा, पति-पत्नी।
16. शक्ति के अनुसार, महान है आत्मा जिसकी, सिर में दर्द, धनहीन, अन्न-जल, चतुर्भुज।
17. तीन फलों का समूह, रात और दिन, झड़ते हैं पले जिसमें, यथानियम, गौशाला, राष्ट्रपति।
18. रुचि के अनुसार, राजा और रानी, नौ ग्रहों का समूह, गिरिधर , देशवासी नीलाम्बर।
19. नर और नारी, महान है जो देव, सात दिनों का समूह, पतझड़, यथानियम, पाप-पुण्य।
20. भीम और अर्जुन, लाल है जो रूमाल, दो पहरों का समूह, रामभक्ति, यथाकाल, माता-पिता।
21. दाल और भात, महान है जो जन, जन्म से लेकर, बाढ़ पीड़ित, राह खर्च, धूप-दीप।
बोर्ड परीक्षा में पूछे गए प्रश्न
Set-A
निम्नलिखित पदों का समास करें
I. माता और पिता का समास करें।
II. ‘रसोई घर’ के निम्नलिखित विकल्पों में से सही समास-विग्रह विकल्प को चुनें:
(क) रसोई का घर (ख) रसोई के लिए घर (ग) रसोई में घर (घ) रसोई से घर।
III. निम्नलिखित कथने में सही अथवा ग़लत लिखें:
‘तिरंगा’ शब्द का समास विग्रह होगा-‘तीन रंगों का समूह’।
Set-B
I. ‘उत्तर और दक्षिण’ का समास करें।
II. ‘राह खर्च’ पद के निम्नलिखित विकल्पों में से सही समास विकल्पों में से सही समास-विग्रह को चुनें
(क) राह में खर्च (ख) राह को खर्च (ग) राह से खर्च (घ) राह के लिए खर्च।
III. ‘त्रिनेत्र’ शब्द का समास विग्रह होगा-तीन हैं नेत्र जिसके अर्थात् शिव
Set-C
I. निम्नलिखित पदों का समास करें। राजा का कुमार।
II. ‘यथानियम’ पद के निम्नलिखित विकल्पों में से सही समास-विग्रह विकल्प को चुनें:
(क) यथा का नियम (ख) नियम के अनुसार (ग) यथा और नियम (घ) यथा के नियम। .
III. निम्नलिखित कथन में सही अथवा ग़लत लिखें
‘पीताम्बर’ शब्द का समास विग्रह होगा-पी लिया है अम्बर जिसने।
Set-A, B, C
(i) निम्नलिखित पदों का समास करें: लोभ और मोह।
(ii) ‘घनश्याम’ पद के निम्नलिखित में से सही समास-विग्रह विकल्प को चुनें :
(अ) घन के लिए श्याम (ब) घन के समान श्याम (स) घन से श्याम (द) घन से श्याम।
(iii) निम्नलिखित कथन में सही अथवा ग़लत लिखें :
‘त्रिफला’ शब्द का समास विग्रह होगा-‘तीन फलों का समूह’।
Set-A, B, C
(i) ‘गुरु दक्षिणा’ के लिए विग्रह का सही विकल्प चुनकर लिखें:
(क) गुरु और दक्षिणा (ख) गुरु के लिए दक्षिणा (ग) गुरु की दक्षिणा (घ) गुरु द्वारा दक्षिणा।
(ii) ‘जन्माध’ का विग्रह होगा-‘जन्म से अंधा’, सही या गलत लिखकर उत्तर दें।
Set-A, B, C
I. निम्नलिखित पदों का समास करें
देश का वासी।
II. ‘रसोई घर’ पद के निम्नलिखित विकल्पों में से सही समास-विग्रह विकल्प को चुनें :
(क) रसोई घर (ख) रसोई के लिए घर (ग) रसोई में घर (घ) रसोई से घर।
III. ‘मालगाड़ी’ शब्द का समास विग्रह होगा-‘माल की गाड़ी’।
बहुविकल्पीय प्रश्नोत्तर
प्रश्न 1.
जिस समास में पूर्व और उत्तर दोनों पद प्रधान होते हैं उसे कहते हैं?
(क) द्विगु
(ख) द्वन्द्व
(ग) कर्मधारय
(घ) अव्ययीभाव।
उत्तर:
(ख) द्वन्द्व
प्रश्न 2.
जिसमें अन्य पद प्रधान हो उसे कहते हैं?
(क) अव्ययीभाव
(ख) बहुव्रीहि
(ग) तत्पुरुष
(घ) द्विगु।
उत्तर:
(ख) बहुब्रीहि
प्रश्न 3.
‘आजीवन’ में कौन-सा समास है?
(क) तत्पुरुष
(ख) कर्मधारय
(ग) बहुव्रीहि
(घ) अव्ययीभाव।
उत्तर:
(घ) अव्ययीभाव
प्रश्न 4.
‘आबोहवा’ में निहित समास है
(क) द्विगु
(ख) कर्मधारय
(ग) द्वन्द्व
(घ) तत्पुरुष।
उत्तर:
(ग) द्वन्द्व

प्रश्न 5.
‘सत् जो जन’ में कौन-सा समास निहित है?
(क) कर्मधारय
(ख) बहुब्रीहि
(ग) अव्ययीभाव
(घ) द्वन्द्व।
उत्तर:
(क) कर्मधारय।
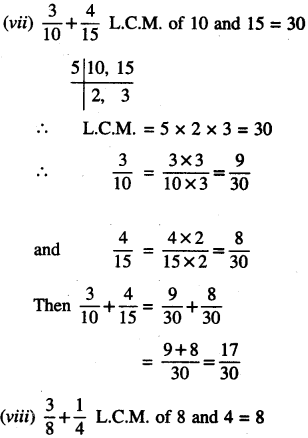

![]()
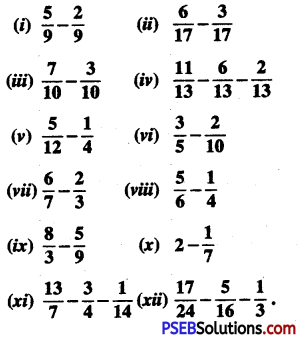
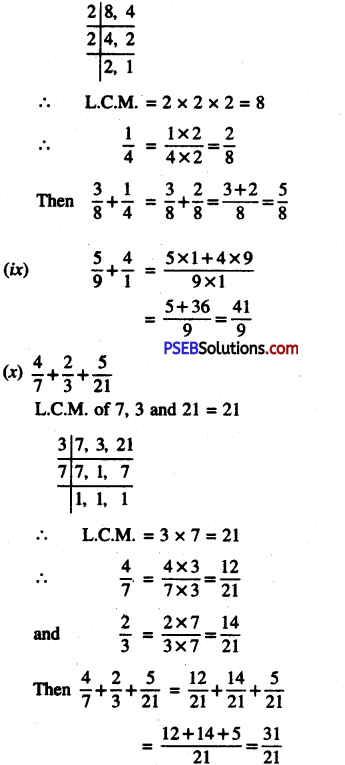
![]()


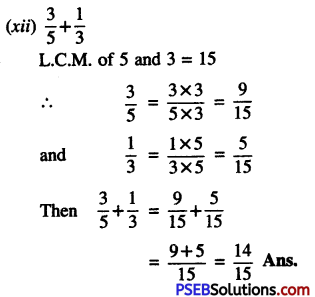
![]()
![]()