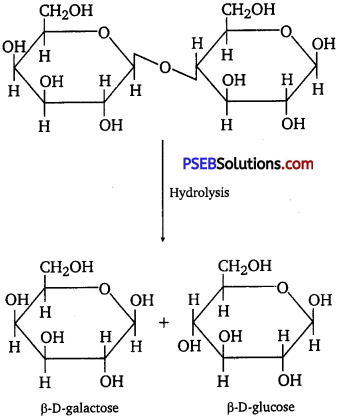
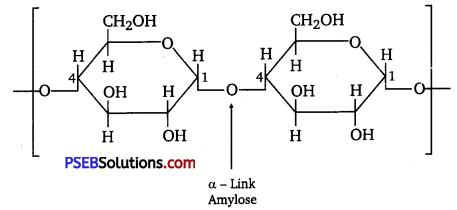
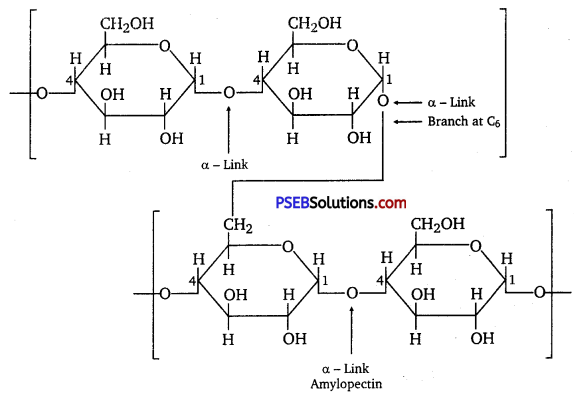
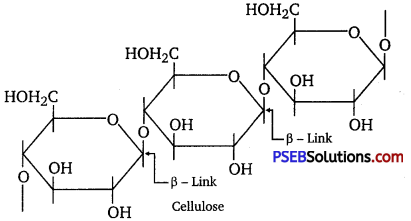
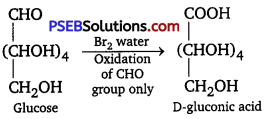
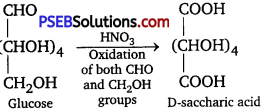
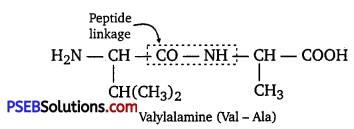
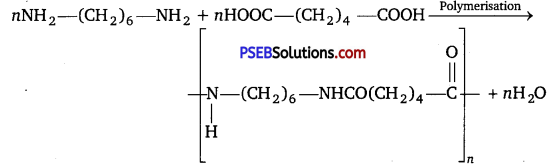
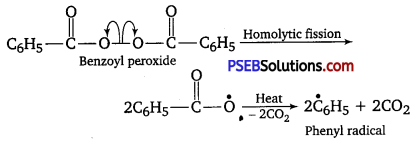
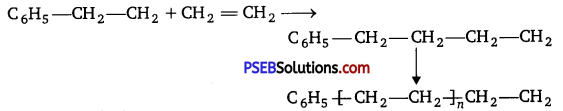
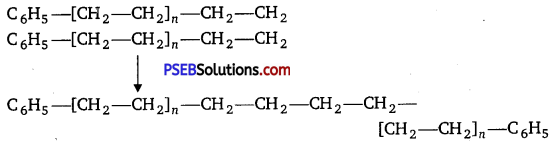
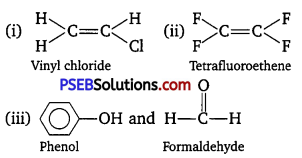
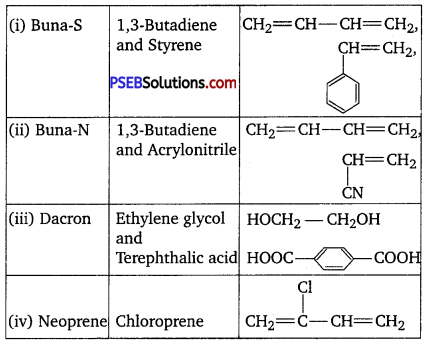
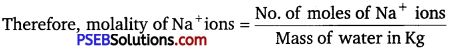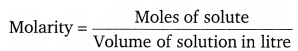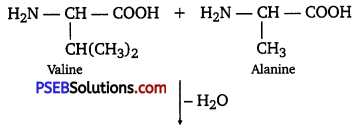Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class Chemistry Book Solutions Chapter 2 Solutions Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Solutions
PSEB 12th Class Chemistry Guide Solutions InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Define the term solution. How many types of solutions are formed? Write briefly about each type with an example.
Answer:
Homogeneous mixtures of two or more than two components are known as solutions. Solute and solvent are two components of a solution.
There are three types of solutions.
(i) Gaseous solution: The solution in which the solvent is a gas is known as a gaseous solution. In these solutions, the solute may be liquid, solid, or gas. For example, a mixture of oxygen and nitrogen gas is a gaseous solution.
(ii) Liquid solution : The solution in which the solvent is a liquid is known as a liquid solution. In these solutions, the solute may be gas, liquid, or solid. For example, a solution of ethanol in water is a liquid solution.
(iii) Solid solution : The solution in which the solvent is a solid is known as a solid solution. In these solution, the solute may be gas, liquid or solid. For example, a solution of copper in gold is a solid solution.

Question 2.
Give an example of a solid solution in which the solute is a gas.
Answer:
In case a solid solution is formed between two substances (one having very large particles and the other having very small particles), an interstitial solid Solution will be formed. For example, a solution of hydrogen in palladium is a solid solution in which the solute is a gas.
Question 3.
Define the following terms:
(i) Mole fraction
(ii) Molality
(iii) Molarity
(iv) Mass percentage.
Answer:
(i) Mole fraction: The mole fraction of a component in a mixture is defined as the ratio of the number of moles of the component (solute or solvent) to the total number of moles of all the components in the mixture.
i.e., Mole fraction of a component

Mole fraction is denoted by ‘χ’
If in a binary solution, the number of moles of the solute and the solvent are nA and nB respectively, then the mole fraction of the solute in the solution is given by,
χA = \(\frac{n_{A}}{n_{A}+n_{B}}\)
Similarly, the mole fraction of the solvent in the solution is given as:
χA = \(\frac{n_{B}}{n_{A}+n_{B}}\)
(ii) Molality: Molality (m) is defined as the number of moles of the solute per kilogram of the solvent. It is expressed as:
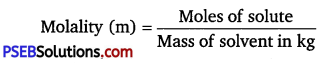
Unit of molality is mol kg-1 or m (molal).
(iii) Molarity: Molarity (M) is defined as the number of moles of the solute dissolved in one litre of the solution.
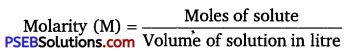
(iv) Mass percentage: The mass percentage of a component of a solution is defined as the mass of the solute in grams present in 100 g of the solution.
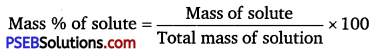

Question 4.
Concentrated nitric acid used in laboratory work is 68% nitric acid by mass in aqueous solution. What should be the molarity of such a sample of the acid if the density of the solution is 1.504gmL -1?
Solution:
68% HNO3 by mass means
Mass of HNO3 (w) = 68 g
Mass of solution = 100 g
Molar mass of nitric acid (HN0),
(M) = 1 × 1 + 1 × 14 + 3 × l6 = 63g mol-1
Then, number of moles of HNO3 = \(\frac{W}{M}\) = \(\frac{68}{63}\) mol
= 1.079 mol
Density of solution = 1.504 g mL-1
∴ Volume of solution = \(\frac{\text { Mass }}{\text { Density }}\) = \(\frac{100}{1.504}\) mL
66.49 mL
66.49 × 10-3 L
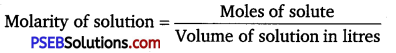
= \(\frac{1.079 \mathrm{~mol}}{66.49 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~L}}\) = 16.23 mol L-1
Question 5.
A solution of glucose in water is labelled as 10% w/w, what would be the molality and mole fraction of each component in the solution? If the density of solution is 1.2 gmL-1, then what shall be the molarity of the solution?
Solution:
10% w/w solution of glucose means 10 g of glucose is present in 100 g of the solution i.e., 90 g of water.
Molar mass of glucose
(C6H12O6) = 6 × 12 + 12 × 1 + 6 × 16 = 180 g mol-1
Then, number of moles of glucose = \(\frac{10}{180}\)mol = 0.056 mol


Question 6.
How many mL of 0.1 M HCl are required to react completely with lg mixture of Na2CO3 and NaHCO3 containing equimolar amounts of both?
Solution:
Let the mass of Na2CO3 = x g
Mass of mixture = 1.0 g
Then, the mass of NaHCO3 = (1 – x) g
Molar mass of Na2CO3 = 2 × 23 + 1 × 12 + 3 × 16 =106 g mol-1
∴ Number of moles of Na2CO3 = \(\frac{\text { Mass }}{\text { Molar mass }}\) = \(\frac{x}{106}\) = mol
Molar mass of NaHCO3 = 1 × 23 + 1 × 1 + 1 × 12 + 3 × 16 = 84g mol-1
∴ Number of moles of NaHCO3 = \(\frac{\text { Mass }}{\text { Molar mass }}\) = \(\frac{1-x}{84}\) mol
According to the question, the mixture contains equimolar amounts of Na2CO3and NaHCO3
Moles of Na2CO3 = Moles of NaHCO3
\(\frac{x}{106}=\frac{1-x}{84}\)
⇒ 84x =106 -106x
⇒ 190x =106
⇒ x = 0.5579 g
Thus, number of moles of Na2CO3 = \(\frac{0.5579}{106}\) mol = 0.0053 mol
Number of moles of NaHCO3 = \(\frac{1-0.5579}{84}\)mol = 0.0053 mol
To calculate the moles of HCl required
HCl reacts with Na2CO3 and NaHCO3 according to the following equations
2HCl + Na2CO3 → 2NaCl + H2O + CO2
HCl + NaHCO3 → NaCl + H2O + CO2;
1 mol of Na2CO3 reacts with 2 mol of HCl.
Therefore, 0.0053 mol of Na2CO3 reacts with 2 × 0.0053 mol = 0.0106 mol
Similarly, 1 mol of NaHCO3 reacts with 1 mol of HCl.
Therefore, 0.0053 mol of NaHCO3 reacts with 0.0053 mol of HCl.
Total moles of HCl required = (0.0106 + 0.0053) mol
= 0.0159 mol
To calculate the volume of 0.1 MHC1
0.1 mol of 0.1 M HCl present in 1000 mL of HCl
Therefore, 0.0159 mol of HCl will be present in HCl
= \(\frac{1000 \times 0.0159}{0.1}\) mol
= 159 mL
Question 7.
A solution is obtained by mixing 300 g of 25% solution and 400 g of 40% solution by mass. Calculate the mass percentage of the resulting solution.
Solution:
Mass of solute in I solution = \(\frac{25}{100}\) × 300 g = 75 g
Mass of solute in II solution = \(\frac{40}{100}\) × 400 g = 160 g
After mixing both solutions
Total mass of solute = 75 + 160 = 235 g
Total mass of solution = 300 + 400 = 700 g
Therefore, mass percentage (w/w) of the solute in the resulting solution
= \(\frac{235}{700}\) × 100%
= 33.57%
And, mass percentage (w/w) of the solvent in the resulting solution.
= (100 – 33.57)%
= 66.43%

Question 8.
An antifreeze solution is prepared from 222.6 g of ethylene glycol (C2H6O2 ) and 200 g of water. Calculate the molality of the solution. If the density of the solution is 1.072 g mL ‘1, then what shall be the molarity of the solution?
Solution:
To calculate the molality of the solution
Molar mass of ethylene glycol (C2H6O2)
= 2 x 12 + 6 x 1 + 2 x 16 = 62 g mol-1
Mass of ethylene glycol = 222.6 g
Number of moles of ethylene glycol = \(\frac{\text { Mass of ethylene glycol }}{\text { Molar mass of ethylene glycol }}\)
= \(\frac{222.6 \mathrm{~g}}{62 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}}\) = 3.59 mol
Mass of water = 200 g = 0.2 kg
Therefore, molality of the solution \(=\frac{\text { No. of moles of ethylene glycol }}{\text { Mass of solvent in kg }}\)
= \(\frac{3.59 \mathrm{~mol}}{0.200 \mathrm{~kg}}\) = 17.95m
To calculate the molarity of the solution
Density of the solution = 1.072 g mL-1
Mass of solution = Mass of solute + Mass of solvent
222.6 g + 200 g = 422.6 g
∴ Volume of the solution = \(\frac{\text { Mass }}{\text { Density }}\) = \(\frac{422.6 \mathrm{~g}}{1.072 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mL}^{-1}}\)
= 394.22 mL = 0.3942 x 10-3 L
⇒ Molarity of the solution = \(\frac{\text { Moles of ethylene glycol }}{\text { Volume of solution in litre }}\)
= \(\frac{3.59 \mathrm{~mol}}{0.3942 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~L}}\) = 9.1 M
Question 9.
A sample of drinking water was found to be severely contaminated with chloroform (CHCl3) supposed to be a carcinogen. The level of contamination was 15 ppm (by mass):
(i) express this in percent by mass
(ii) determine the molality of chloroform in the water sample.
Solution:
Let the mass of solution be 106 g.
Mass of solute, CHCl3 = 15 g
(i) Therefore, percent by mass of CHCl3 = \(\frac{\text { Mass of } \mathrm{CHCl}_{3}}{\text { Mass of solution }}\) × 100%
\(\frac{15}{10^{6}}\) × 100%
= 1.5 × 10-3%
(ii) Molar mass of chloroform (CHCl3 ) = 1 × 12 + 1 × 1 + 3 × 35.5
= 119.5g mol-1
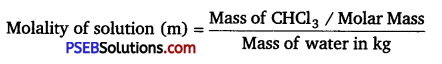
= \(\frac{\frac{15}{119.5} \mathrm{~mol}}{10^{6} \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~kg}}\) = 1.26 × 10 4 mol-4 kg-1
1.26 × 10-4 m

Question 10.
What role does the molecular interaction play in a solution of alcohol and water?
Answer:
In pure alcohol and water, the molecules are held tightly by a strong hydrogen bonding. The interaction between the molecules of alcohol and water is weaker than alcohol-alcohol and water-water interactions. As a result, when alcohol and water are mixed, the intermolecular interactions become weaker and the molecules can easily escape. This increases the vapour pressure of the solution, which in turn lowers the boiling point of the resulting solution.
Question 11.
Why do gases always tend to be less soluble in liquids as the temperature is raised?
Answer:
Solubility of gases in liquids decreases with an increase in temperature. This is because dissolution of gases in liquids is an exothermic process.
Gas + Liquid → Solution + Heat
Therefore, when the temperature is increased, heat is supplied and the equilibrium shifts backwards, thereby decreasing the solubility of gases.
Question 12.
State Henry’s law and mention some important applications?
Answer:
Henry’s law states that partial pressure of a gas in the vapour phase is proportional to the mole fraction of the gas in the solution. If p is the partial pressure of the gas in the vapour phase and % is the mole fraction of the gas, then Henry’s law can be expressed as:
P = KHχ
Where, KH is Henry’s law constant
Some important applications of Henry’s law are mentioned below:
(i) Bottles are sealed under high pressure to increase the solubility of C02 in soft drinks and soda water.
(ii) Henry’s law states that the solubility of gases increases with an increase in pressure. Therefore, when a scuba diver dives deep into the sea, the increased sea pressure causes the nitrogen present in air to dissolve in his blood in great amounts. As a result, when he comes back to the surface, the solubility of nitrogen again decreases and the dissolved gas is released, leading to the formation of nitrogen bubbles in the blood. This results in the blockage of capillaries and leads to a medical condition known as “bends’ or ‘decompression sickness’. Hence, the oxygen tanks used by scuba divers are filled with air and diluted with helium to avoid bends.
(iii) The concentration of oxygen is low in the blood and tissues of people living at high altitudes such as climbers. This is because at high altitudes, partial pressure of oxygen is less than that at ground level. Low-blood oxygen causes climbers to become weak and disables them from thinking clearly. These are symptoms of anoxia.

Question 13.
The partial pressure of ethane over a solution containing 6.56 × 10-3g of ethane is 1 bar. If the solution contains 5.00 × 10-2 g of ethane, then what shall be the partial pressure of the gas?
Solution:
According to Henry’s law the mass of the gas dissolved in solution x Partial pressure (p) (At constant temperature)
(6.56 × 10-3g) ∝ 1 bar
(5.00 × 10-2g) ∝ p
or p = \(\frac{5.0 \times 10^{-2} \mathrm{~g}}{6.56 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~g}}\) × 1 bar = 7.62 bar
Question 14.
What is meant by positive and negative deviations from Raoult’s law and how is the sign of Δmix H related to positive and negative deviations from Raoult’s law?
Answer:
Positive deviation: ‘When the vapour pressure of a solution is higher than the predicted value by Raoult’s law, it is called positive deviation’. In such cases intermolecular interactions between solute and solvent particles (A and B) are weaker than those between solute-solute (A – A) and solvent-solvent (B – B). Hence, the molecules of (A or B) will escape more easily from the surface of solution than in their pure state. Therefore, the vapour pressure of the solution will be higher. Characteristics of a solution showing positive deviation :
(i) PA > \(p_{A}^{0}\) χA; PB > \(p_{B}^{0}\) χB
(ii) ΔHmix >0;i.e., + ve
(iii) ΔVmix > 0, i.e., + ve
Examples of solutions showing positive deviation:
(i) Ethyl alcohol and water
(ii) Acetone and carbon disulphide
(iii) Carbon tetrachloride and benzene
(iv) Acetone and benzene
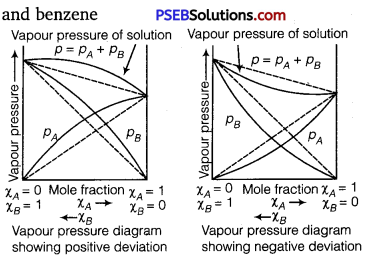
Negative deviation: “When the vapour pressure of a solution is lower than the predicted value by Raoult’s law, it is called negative deviation.’ In case of negative deviation the intermolecular attractive forces between A – A and B – B are weaker than those between A – B. It leads to decrease in vapour pressure resulting in negative deviation.
Characteristics of a solution showing negative deviation:
(i) PA < \(p_{A}^{0}\) χB; PB < \(p_{B}^{0}\) χB
(ii) ΔVmix < 0; i. e., – ve; because weak A – A and B – B bonds are broken
and strong A – B bonds are formed. Heat is consequently released.
(iii) mix<0;i.e.,-ve
Examples of solutions showing negative deviation:
(i) HNO3 and water
(ii) Chloroform and acetone
(iii) Acetic acid and pyridine
(iv) Hydrochloric acid and water

Question 15.
An aqueous solution of 2% non-volatile solute exerts a pressure of 1.004 bar at the normal boiling point of the solvent. What is the molar mass of the solute?
Solution:
Here,
Vapour pressure of the solution at normal boiling point (p1) = 1.004 bar
Vapour pressure of pure water at normal boiling point (\(p_{1}^{0}\)) = 1.013 bar
Mass of solute, (w2) = 2 g
Mass of solvent (water), (w1 ) = 100 – 2 = 98g
Molar mass of solvent (water), (M1) = 18 g mol-1
Molar mass of solute (M2) = ?
According to Raoult’s law,
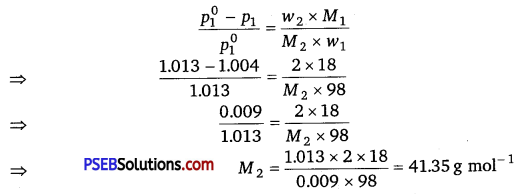
Hence, the molar mass of the solute is 41.35 g mol-1.
Question 16.
Heptane and octane form an ideal solution. At 373 K, the vapour pressures of the two liquid components are 105.2 kPa and 46.8 kPa respectively. What will be the vapour pressure of a mixture of 26.0 g of heptane and 35 g of octane?
Solution:
Vapour pressure of heptane (\(p_{1}^{0}\)) = 105.2 kPa
Vapour pressure of octane (p\(p_{2}^{0}\)) = 46.8 kPa
Mass of heptane = 26.0 g
Mass of octane = 35 g
Molar mass of heptane (C7H16) = 7 × 12 + 16 × 1 = 100 g mol-1;
∴ Number of moles of heptane = \(\frac{26}{100}\) mol = 0.26 mol
Molar mass of octane (C8H18) = 8 × 12 + 18 × 1 = 114g mol-1
∴ Number of moles of octane = \(\frac{35}{114}\) mol = 0.31 mol
Mole fraction of heptane, χ1 = \(\frac{0.26}{0.26+0.31}\) = 0.456
Mole fraction of octane, χ2 = 1 – 0.456 = 0.544
Now, partial pressure of heptane, p1 = χ1 \(p_{1}^{0}\)
= 0.456 × 105.2 = 47.97 kPa
Partial pressure of octane, p2 = χ2\(p_{2}^{0}\)
= 0.544 × 46.8 = 25.46 kPa
Hence, vapour pressure of solution, ptotal = P1 + p2
= 47.97 + 25.46 = 73.43 kPa
Question 17.
The vapour pressure of water is 12.3 kPa at 300 K. Calculate vapour pressure of 1 molal solution of a non-volatile solute in it.
Solution:
1 molal solution means 1 mol of the solute is present in 1000 g of the solvent (water).
Molar mass of water = 18 g mol-1
> Number of moles present in 1000 g of water = \(\frac{1000}{18}\) = 55.56 mol
Therefore, mole fraction of the solute
χ2 = \(\frac{1}{1+55.56}\) = 0.0177
It is given that,
Vapour pressure of water, \(p_{1}^{0}\) = 12.3 kPa
∴ \(\frac{p_{1}^{0}-p_{1}}{p_{1}^{0}}\) = χ2
Applying the relation,
⇒ \(\frac{12.3-p_{1}}{12.3}\) = 0.0177
⇒ 12.3 – p1 = 0.0177 × 12.3
⇒ 12.3 -P1 = 0.2177
⇒ P1 = 12.3 – 0.2177
⇒ p1 = 12.0823
= 12.08 kPa
Hence, the vapour pressure of the solution is 12.08 kPa.

Question 18.
Calculate the mass of a non-volatile solute (molar mass 40 g mol-1) which should be dissolved in 114 g octane to reduce its vapour pressure to 80%.
Solution:
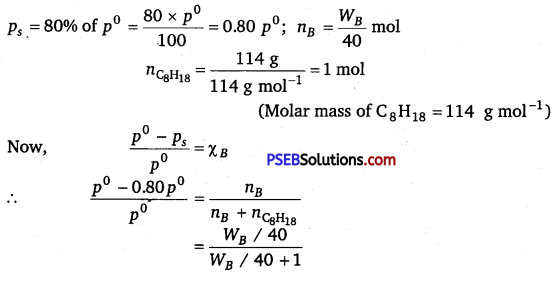
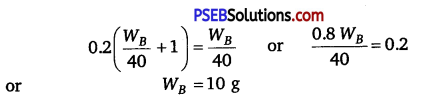
Question 19.
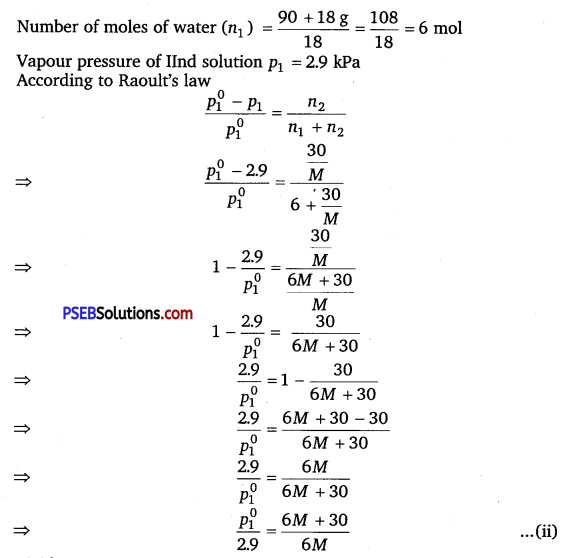
A solution containing 30 g of non-volatile solute exactly in 90 g of water has a vapour pressure of 2.8 kPa at 298 K. Further, 18 g of water is then added to the solution and the new vapour pressure becomes 2.9 kPa at 298 K. Calculate :
(i) molar mass of the solute
(ii) vapour pressure of water at 298 K.
Solution:
(i) Let, the molar mass of the solute be M g mol-1
Now, the no. of moles of solvent (water), = n1 = \(\frac{\text { Mass }}{\text { Molar mass }}\)
= \(\frac{90 \mathrm{~g}}{18 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}}\) = 5mol
And, the no. of moles of solute, n2 = \(\frac{\text { Mass }}{\text { Molar mass }}\)
= \(\frac{30 \mathrm{~g}}{\mathrm{Mg} \mathrm{mol}^{-1}}=\frac{30}{M}\) mol
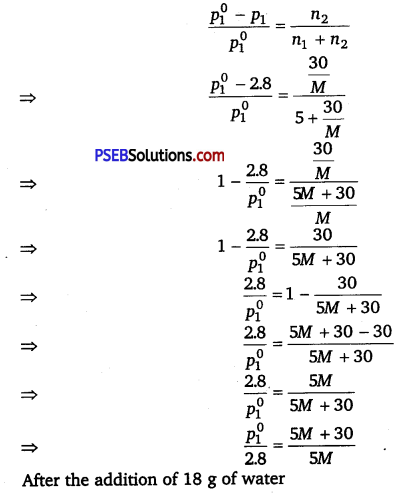
Vapour pressure of I solution
p1 = 2.8 kPa
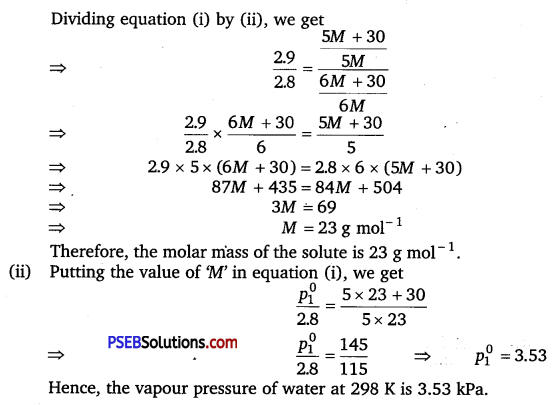
According to Raoult’s law

Question 20.
A 5% solution (by mass) of cane sugar in water has freezing point of 271 K. Calculate the freezing point of 5% glucose in water if freezing point of pure water is 273.15 K.
Solution:
Let the mass of solution = 100 g
∴ Mass of cane sugar (w2) = 5 g
ΔTf = (273.15 – 271) K = 2.15 K
Molar mass of cane sugar (C12H22O11), (M2) = 12 x 12 + 22 x 1 +11 x 16
= 342 g mol-1
Mass of solvent (water), (w1) = 100 – 5 = 95 g

(Molar mass of glucose = 180 g mol-1)
ΔTf = 4.08 K
Freezing point of glucose solution
Tf = \(T_{f}^{0}\) – ΔTf = 273.15 – 4.08 = 269.07 K
Question 21.
Two elements A and B form compounds having formula AB2 and AB4. When dissolved in 20 g of benzene (C6H6, 1 g of AB2 lowers the freezing point by 2.3 K whereas 1.0 g of AB4 lowers it by 1.3 K. The molar depression constant for benzene is 5.1 K kg mol-1. Calculate atomic masses of A and B.
Solution:
We know,
M2 = \(\frac{1000 \times w_{2} \times K_{f}}{\Delta T_{f} \times w_{1}}\)
Then MAB2 = \(\frac{1000 \times 1 \times 5.1}{2.3 \times 20}\) = 110.87 g mol-1
Then MAB2 = \(\frac{1000 \times 1 \times 5.1}{1.3 \times 20}\) = 196.15 g mol-1
Let the atomic masses of A and B be x and y respectively.
Molar mass of AB2 = x + 2 y = 110.87 …………… (i)
Molar mass of AB4 = x + 4y = 196.15 ………… (ii)
Subtracting equation (i) from (ii) , we get
2y=85.28 y = 42.64
Putting the value of ‘/ in equation (i), we get
x + 2 x 42.64 = 110.87
⇒ x = 25.59
Hence, the atomic masses of A and B are 25.59 u and 42.64 u respectively.
Question 22.
At 300 K, 36 g of glucose present in a litre of its solution has an osmotic pressure of 4.98 bar. If the osmotic pressure of the solution is 1.52 bars at the same temperature, what would be its concentration?
Solution:
Here, T = 300 K, π = 1.52 bar, R = 0.083 bar L K-1mol-1
Applying the relation, π = CRT
⇒ C = \(\frac{\pi}{R T}\)
= \(\frac{1.52 \mathrm{bar}}{0.083 \mathrm{bar} \mathrm{L} \mathrm{K}^{-1} \mathrm{~mol}}\)
= 0.061 mol
Since, the volume of the solution is 1 L, the concentration of the solution would be 0.061 M.

Question 23.
Suggest the most important type of intermolecular attractive interaction in the following pairs. .
(i) n-hexane and n-octane
(ii) I2 and CCl4
(iii) NaClO4 and water
(iv) methanol and acetone
(v) acetonitrile (CH3CN) and acetone (C3H6O).
Answer:
(i) Van der Wall’s forces of attraction. (London forces)
(ii) Van der Wall’s forces of attraction. (London forces) .
(iii) Ion-dipole interaction. ‘
(iv) Dipole-dipole interaction.
(v) Dipole-dipole interaction.
Question 24.
Based on solute-solvent interactions, arrange the following in order of increasing solubility in n-octane and explain. Cyclohexane, KCl, CH3OH, CH3CN.
Answer:
(i) Cyclohexane and n-octane both are non-polar.
So, they will mix completely in all proportions.
(ii) KCl is an ionic compound, but n-octane is non-polar.
So, KCl will not dissolve in n-octane.
(iii) CH3OH and CH3CN both are polar but CH3CN is less polar than CH3OH. As the solvent is non-polar CH3CN will dissolve more than CH3OH in n-octane.
Therefore, the order of solubility in n-octane will be KCl < CH3OH < CH3CN < Cyclohexane
Question 25.
Amongst the following compounds, identify which are insoluble, partially soluble and highly soluble in water?
(i) phenol
(ii) toluene
(iii) formic acid
(iv) ethylene glycol
(v) chloroform
(vi) pentanol.
Answer:
(i) Phenol (C6H5OH) has the polar group -OH and non-polar group -C6H5. Thus, phenol is partially soluble in water.
(ii) Toluene (C6H5 – CH3) has no polar groups. Thus, toluene is insoluble in water.
(iii) Formic acid (HCOOH) has the polar group -OH and can form H-bond with water. Thus, formic acid is highly soluble in water.
(iv) Ethylene glycol 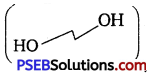 has polar -OH group and can form H-bond. Thus, it is highly soluble in water.
has polar -OH group and can form H-bond. Thus, it is highly soluble in water.
(v) Chloroform is insoluble in water because it cannot form hydrogen bonds with water.
(vi) Pentanol (C5H11OH) has polar -OH group, but it also contains a very bulky non-polar -C5H11 group. Thus, pentanol is partially soluble in water.

Question 26.
If the density of some lake water is 1.25 g mL-1 and contains 92 g of Na+ ions per kg of water, calculate the molality of Na+ ions in the lake.
Solution:
Number of moles present in 92 g of Na+ ions
= \(\frac{92 \mathrm{~g}}{23 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}}\) = 4 mol
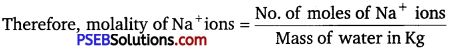
= \(\frac{4 \mathrm{~mol}}{1 \mathrm{~kg}}\) = m
Question 27.
If the solubility product of CuS is 6 × 1016, calculate the maximum molarity of CuS in aqueous solution.
Solution:
Solubility product of CuS, Ksp = 6 × 10-16 .
Let s be the solubility of CuS in mol L-1. Then,

= s × s
= s2
Then we have, K sp s2 = 6 × 10-16
⇒ s = \(\sqrt{6 \times 10^{-16}}\)
= 2.45 x 10-8 mol-1
Hence, the maximum molarity of CuS in an aqueous solution is 2.45 × -8 mol-1.
Question 28.
Calculate the mass percentage of aspirin (C9H8O4) in
acetonitrile (CH3CN) when 6.5 g of C9H8O4 is dissolved in 450 g of CH3CN.
Solution:
Mass of aspirin = 6.5 g
Mass of acetonitrile = 450 g
Then, total mass of the solution = (6.5 + 450) g = 456.5 g
Therefore, mass percentage of C9H8O4 = \(\frac{6.5}{456.5}\) × 100%
= 1.424%
Question 29.
Nalorphene (C19H21NO3), similar to morphine, is used to combat withdrawal symptoms in narcotic users. Dose of nalorphene generally given is 1.5 mg. Calculate the mass of 1.5 × 10-3 m aqueous solution required for the above dose.
Solution:
1.5 × 10-3 m solution means that 1.5 × 10-3 mole of nalorphene is dissolved in 1 kg of water.
Molar mass of C19H21N03
= 19 × 12 + 21 + 14 + 48
= 311 g mol-1
∴ 1.5 × 10-3 mole of nalorphene
= 1.5 × 10-3 × 311 g = 0.467 g
= 467 mg
Mass of solution
= 1000 g + 0.467 g
= 1000.467 g
Thus, for 467 mg of nalorphene solution required 1000.467.
For 1.5 mg nalorphene = \(\frac{1000.467 \times 1.5}{467}\) = 3.21 g

Question 30.
Calculate the amount of benzoic acid (C6H5COOH) required for preparing 250 mL of 0.15 M solution in methanol.
Solution:
Molarity = 0.15 M or 0.15 mol L-1
Volume of solution = 250 mL = 0.25 L
Molar mass of benzoic acid (C6H5COOH) = 7 × 12 + 6 × 1 + 2 × 16
= 122 g mol-1
Molality \(\frac{\text { Mass }}{\text { Molar mass }}\) × \(\frac{1}{\text { Volume (L) }}\)
0.15 mol L-1 = \(\frac{w}{122 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}}\) × \(\frac{1}{0.25 \mathrm{~L}}\)
Mass of solute = (0.15 × 122 × 0.25) g = 4.575 g
Question 31.
The depression in freezing point of water observed for the same amount of acetic acid, trichloroacetic acid and trifluoroacetic acid increases in the order given above. Explain briefly.
Answer:
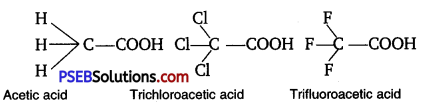
Among H, Cl, and F, H is least electronegative while F is most electronegative. Then, F can withdraw electrons towards itself more than Cl and H. Thus, trifluoroacetic acid can easily lose H+ ions i.e., trifluoroacetic acid ionises to the largest extent. Now, the more ions produced, the greater is the depression of the freezing point. Hence, the depression in the freezing point increases in the order:
Acetic acid < trichloroacetic acid < trifluoroacetic acid
Question 32.
Calculate the depression in the freezing point of water when 10 g of CH3CH2CHClCOOH is added to 250 g of water, Ka = 1.4 × 10-3, Kf = 1.86 K kg mol-1.
Solution:
Mass of solute (CH3CH2CHClCOOH) = 10 g
Molar mass of
CH3CH2CHClC00H = 4 × 12 + 7 × 1 + 1 × 35.5 + 2 × 16 = 48 + 7 + 35.5 + 32
= 122.5 g mol-1
\frac{\text { Mass / Molar mass }}{\text { Mass of solvent (Kg) }} = \(\frac{\text { Mass / Molar mass }}{\text { Mass of solvent (Kg) }}[latex/latex]
= [latex]\frac{10 \mathrm{~g}}{\left(122.5 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}\right) \times(0.25 \mathrm{Kg})}\)
= 0.326 m
Let α be the degree of dissociation of CH3CH2CHClCOOH then
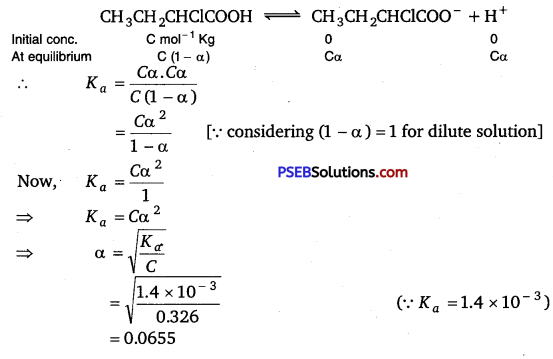

Total no. of moles after dissociation = 1 – α + α + α
= 1 + α
Van’t Hoff factor
Total no. of moles after dissociation

∴ i = \(\frac{1+\alpha}{1}\)
= 1 + α
= 1 + 0.0655
= 1.0655
Hence, the depression in the freezing point of water is given as:
ΔTf = i.Kfm
= 1.0655 × 1.86 kg mol-1 × 0.326 mol kg-1
= 0.65K

Question 33.
19.5 g of CH2FCOOH is dissolved in 500 g of water. The depression in the freezing point of water observed is 1.0°C. Calculate the van’t Hoff factor and dissociation constant of fluoroacetic acid.
Solution:
Calculation of Van’t Hoff factor (i)
Given, w1 = 500 g = 0.5 kg, w2 = 19.5 g, Kf = 1.86 K kg mol-1, ΔTf = 1 K
Molar mass of CH2FCOOH (M2)
= 2 × 12 + 3 × 1 + 1 × 19 + 2 × 16
= 24 + 3 + 19 + 32
= 78 g mol-1
ΔTf = i Kf m
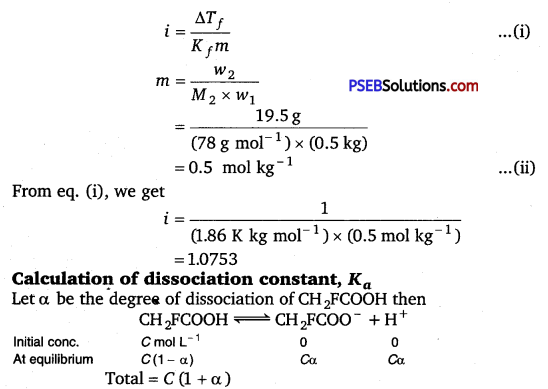

Question 34.
Vapour pressure of water at 293 K is 17.535 mm Hg. Calculate the vapour pressure of water at 293 K when 25 g of glucose is dissolved in 450 g of water.
Solution:
Vapour pressure of water, \(\) = 17.535 mm Hg
Mass of glucose, w2 = 25 g
Mass of water, w1 = 450 g
Molar mass of glucose (C6H12O6), M2 = 6 × 12 + 12 × 1 + 6 × 16
= 180 g mol-1

we know that
\(\frac{p_{1}^{0}-p_{1}}{p_{1}^{0}}\) = \(\frac{n_{2}}{n_{2}+n_{1}}\)
⇒ \(\frac{17.535-p_{1}}{17.535}\) = \(\frac{0.139}{0.139+25}\)
⇒ 17.535 – p1 = \(\frac{0.139 \times 17.535}{25.139}\)
⇒ 17.535 – p1 = 0.097
⇒ P1 = 17.44 mm Hg
Hence, the vapour pressure of water is 17.44 mm Hg.

Question 35.
Henry’s law constant for the molality of methane in benzene at 298 K is 4.27 x 105 mm Hg. Calculate the solubility of methane in benzene at 298 K under 760 mm Hg.
Solution:
Here, p = 760 mm Hg, KH = 4.27 × 105 mm Hg (at 298 K)
According to Henry’s law, p = KHχ
χ = \(\frac{p}{k_{\mathrm{H}}}\)
= \(\frac{760 \mathrm{~mm} \mathrm{Hg}}{4.27 \times 10^{5} \mathrm{~mm} \mathrm{Hg}}\)
= 177.99 × 10-5
= 178 × 10-5
Hence, the mole fraction of methane in benzene is 178 × 10-5.
Question 36.
100 g of liquid A (molar mass 140 g mol-1) was dissolved in 1000 g of liquid B (molar mass 180 g mol-1). The vapour pressure of pure liquid B was found to be 500 torr. Calculate the vapour pressure of pure liquid A and its vapour pressure in the solution if the total vapour pressure of the solution is 475 Torr.
Solution:
Number of moles of liquid A, nA = \(\frac{w_{1}}{M_{1}}\) = \(\frac{100}{140}\) mol = 0.714 mol
Number of moles of liquid B,nB = \(\frac{w_{2}}{M_{2}}\) = \(\frac{1000}{180}\) mol = 5.556 mol
Then, mole fraction of A, χA = \(\frac{n_{A}}{n_{A}+n_{B}}\)
= \(\frac{0.714 \mathrm{~mol}}{(0.714+5.556) \mathrm{mol}}\) = 0.114
Mole fraction of B, χB = 1 – 0.114 = 0.886
Vapour pressure of pure liquid B, \(p_{B}^{0}\) = 500 torr
Therefore, vapour pressure of liquid B in the solution,
PB = \(p_{B}^{0}\)χB
= 500 × 0.886
= 443 torr
Total vapour pressure of the solution, ptotal = 475 torr
∴ Vapour pressure of liquid A in the solution,
PA = Ptotal – PB
= 475 – 443 = 32 torr
Now, PA = \(p_{A}^{0}\)χA
⇒ \(\frac{p_{A}}{\chi_{A}}\) = \(\frac{32}{0.114}\)
= 280.7 torr
Hence, the vapour pressure of pure liquid A is 280.7 torr.
Question 37.
Vapour pressures of pure acetone and chloroform at 328 K are 741.8 mm Hg and 632.8 nun Hg respectively. Assuming that they form ideal solution over the entire range of composition, plot
Ptotal’ Pchloroform and Pacetone as a function of xacetone experimental data observed for different compositions of mixture is
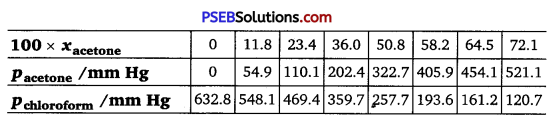
Plot this data also on the same graph paper. Indicate whether it has positive deviation or negative deviation from the ideal
solution.
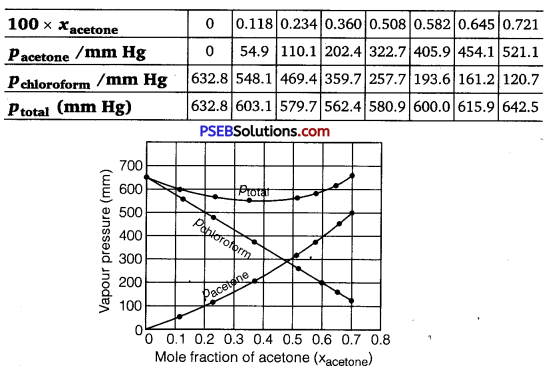
It can be observed from the graph that the plot for the ptotai of the solution curves downwards. Therefore, the solution shows negative deviation from the ideal behaviour.

Question 38.
Benzene and toluene form ideal solution over the entire range of composition. The vapour pressure of pure benzene and toluene at 300 K are 50.71 mm Hg and 32.06 mm Hg respectively.
Calculate the mole fraction of benzene in vapour phase if 80 g of benzene is mixed with 100 g of toluene.
Solution:
Molar mass of benzene (C6H6) = 6 × 12 + 6 × 1 = 78g mol-1
Molar mass of toluene (C6H5CH3 ) = 7 × 12 + 8 × 1 = 92 g mol-1
No. of moles present in 80 g of benzene = \(\frac{80}{78}\) mol = 1.026 mol
No. of moles present in 100 g of toluene = \(\frac{100}{92}\) mol = 1.087 mol
Mole fraction of benzene, χC6H6, = \(\frac{1.026}{1.026+1.087}\) = 0.486
∴ Mole fraction of toluene,χC6H5CH35013 = 1 – 0.486 = 0.514
It is given that vapour pressure of pure benzene, \(p_{\mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{6}}^{0}\) = 50.71 mm Hg
Vapour pressure of pure toluene, \(p_{\mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{5} \mathrm{CH}_{3}}^{0}\) = 32.06 mm Hg
Therefore, partial vapour pressure of benzene,
Ptotal = χC6H6 × \(p_{\mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{6}}^{0}\)
= 0.486 × 50.71
= 24.645 mm Hg
Partial vapour pressure of toluene, PC6H5CH3 = χC6H5CH3 × \(P_{\mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{5} \mathrm{CH}_{3}}^{0}\)
= 0.514 × 32.06
= 16.479 mm Hg
Total vapour pressure of solution (p) = 24.645 + 16.479
= 41.124 mm Hg
Mole fraction of benzene in vapour phase
= \(\frac{\chi_{\mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{6}} \times p_{\mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{6}}^{0}}{p_{\text {total }}}\)
= \(\frac{0.486 \times(50.71) \mathrm{mm}}{(41.124) \mathrm{mm}}\)
= 0.599 ≅ 0.6
Question 39.
The air is a mixture of a number of gases. The mqjor components are oxygen and nitrogen with approximate proportion of 20% is to 79% by volume at 298 K. The water is in equilibrium with air at a pressure of 10 atm. At 298 K if the Henry’s law constants for oxygen \md nitrogen are 330 × 107 mm and 6.51 × 107 mm respectively, calculate the composition of these gases in water.
Solution:
Percentage of oxygen (O2) in air = 20%
Percentage of nitrogen (N2) in air = 79%
Also, it is given that water is in equilibrium with air at a total pressure of 10 atm that is, (10 × 760) mm = 7600 mm
Therefore, partial pressure of oxygen,
PO2 = \(\frac{20}{100}\) x 7600 mm
= 1520 mm Hg
Partial pressure of nitrogen, pN2 = \(\frac{79}{100}\) x 7600 mm
= 6004 mm Hg
Now, according to Henry’s law,
p = KH.χ
For oxygen:
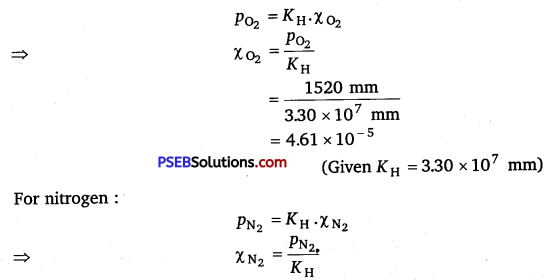
\(\frac{6004 \mathrm{~mm}}{6.51 \times 10^{7} \mathrm{~mm}}\)
(Given KH = 6.51 × 107 mm)
= 9.22 × 10-5
Hence, the mole fractions of oxygen and nitrogen in water are 4.61 × 10-5 and 9.22 × 10-5 respectively.

Question 40.
Determine the amount of CaCl2 (i = 2.47) dissolved in 2.5 litre of water such that its osmotic pressure is 0.75 atm at 27°C.
Solutio:
We know that,
π = i \(\)RT
⇒ π = i \(\)RT
⇒ w = \(\)
Given,
π = 0.75 atm
V = 2.5L
i = 2.47
T = (27 + 273)K = 300K
R = 0.0821 L atm K-1mol–
Molar mass of CaCl2(M) = 1 × 40 + 2 × 35.5 = 111 g mol -1
Therefore, w = \(\frac{0.75 \times 111 \times 2.5}{2.47 \times 0.0821 \times 300}\) = 3.42g
Hence the required amount of CaCl2 is3.42g
Question 41.
Determine the osmotic pressure of a solution prepared by dissolving 25 mg of K2SO4 in 2 litre of water at 25° C, assuming that it is completely dissociated.
Solution:
When K2SO4 is dissolved in water, K+ and \(\mathrm{SO}_{4}^{2-}\) ions are produced.
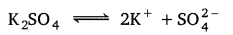
Total number of ions produced = 3
∴ i = 3
Given, w = 25 mg = 0.025 g, V = 2 L
T = 25°C = (25 + 273) K = 298 K
Also, we know that R = 0.0821 L atm K-1 mol-1
Molar Mass of K2SO4 (M) = (2 × 39) + (1 × 32) + (4 × 16) = 174 g mol-1
Applying the following relation,
π = i \(\frac{n}{V}\) RT = i \(\frac{w}{M} \frac{1}{V}\) RT
= 3 × \(\frac{0.025}{174}\) × 1 × 0.0821 × 298 = 5.27 × 10-3 atm
Chemistry Guide for Class 12 PSEB Solutions Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Calculate the mass percentage of benzene (C6H6) and carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) if 22 g of benzene is dissolved in 122 g of carbon tetrachloride.
Solution:
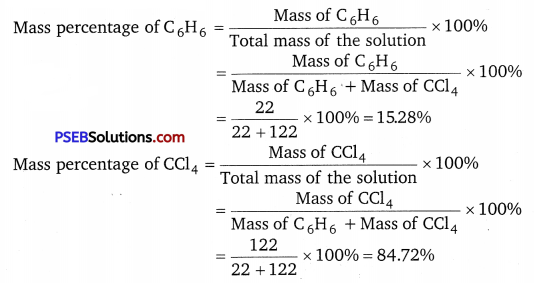
Alternatively,
Mass percentage of CCl4 = (100 – 15.28)% = 84.72%

Question 2.
Calculate the mole fraction of benzene in solution containing 30% by mass in carbon tetrachloride.
Solution:
Let the total mass of the solution be 100 g and the mass of benzene be 30 g.
∴ Mass of carbon tetrachloride = (100 – 30) g = 70 g
Molar mass of benzene (C6H6) = (6 × 12 + 6 × 1) g
∴ mol-1 = 78 g mol-1
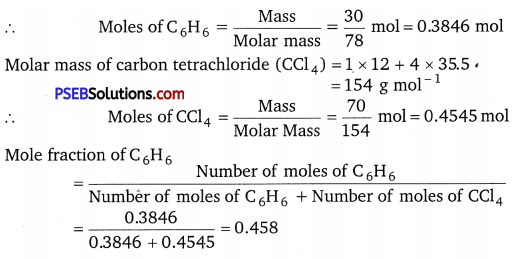
Question 3.
Calculate the molarity of each of the following solutions:
(a) 30 g of CO(NO3) 2.6H2O in 4.3 L of solution
(b) 30 mL of 0.5 M H2SO4diluted to 500 mL.
Solution:
Molarity is given by
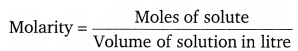
(a) Molar mass of CO (NO3)2.6H2O = 59 + 2 (14 + 3 × 16) + 6 × 18
= 291 g mol-1
∴ Moles of Co (NO3)2.6H2O = \(\frac{30}{291}\) mol = 0.103 mol
Volume of solution = 4.3 L
Therefore, molarity = \(\frac{0.103 \mathrm{~mol}}{4.3 \mathrm{~L}}\) = 0.023 M
(b) Number of moles present in 1000 mL of 0.5 M H2SO4 = 0.5 mol
∴ Number of moles present in 30 mL of 0.5 M H2SO4
= \(\frac{0.5 \times 30}{1000}\) mol
= 0.015 mol
Volume of solution = 500 mL = 0.5 L
Therefore, molarity = \(\frac{0.015}{0.5 \mathrm{~L}}\) mol = 0.03M
Question 4.
Calculate the mass of urea (NH2CONH2) required in making 2.5 kg of 0.25 molal aqueous solution.
Solution:
Mass of required aqueous solution = 2.5 kg = 2500 g
Molar mass of urea (NH2CONH2) = 2 (1 × 14 + 2 × 1) + 1 × 12 +1 × 16
= 60 g mol-1
0.25 molal aqueous solution of urea means 0.25 mole of urea is dissolved in 1000 g of water.
Mass of water = 1000 g
Moles of urea = 0.25 mol
Mass of urea = No. of moles of urea × Molar mass of urea
∴ Mass of 0.25 moles of urea = 0.25 × 60 = 15 g
Mass of solution = 1000 + 15 = 1015 g
1015 g of aqueous solution contains urea = 15 g
∴ 2500 g of aqueous solution will require urea
= \(\frac{15 g}{1015 g}\) × 2500 g = 36.95 g

Question 5.
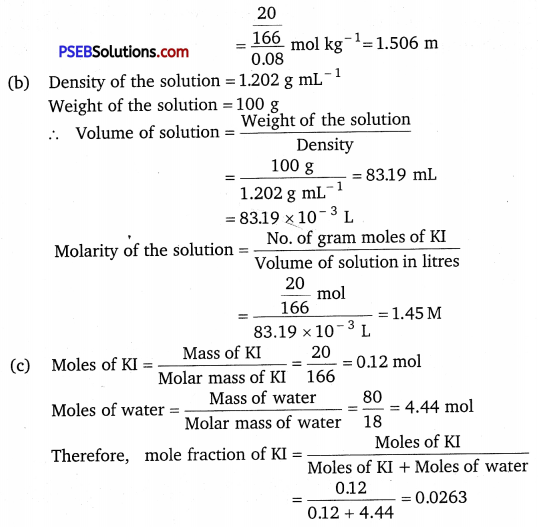
Calculate (a) molality (b) molarity and (c) mole fraction of KI. If the density of 20% (mass/mass) aqueous KI is 1.202 g mL-1.
Solution:
(a) Molar mass of KI = 39 +127 = 166 g mol-1
20% (mass/mass) aqueous solution of KI means 20 g of KI is present in 100 g of solution.
∴ 20 g of KI is present in (100 – 20) g of water = 80 g of water

Question 6.
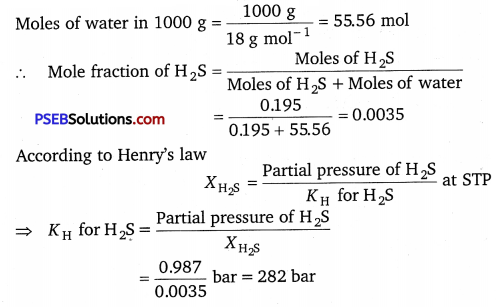
H2S, a toxic gas with rotten egg like smell, is used for the qualitative analysis. If the solubility of H2S in water at STP is 0.195 m, calculate Henry’s law constant.
Solution:
It is given that the solubility of H2S in water at STP is 0.195 m, i.e., 0.195 mol of H2S is dissolved in 1000 g of water.

Question 7.
Henry’s law constant for CO2 in water is 1.67 × 108 Pa at 298 K.
Calculate the quantity of CO2 in 500 mL of soda water when packed under 2.5 atm COa pressure at 298 K.
Solution:
Given, KH = 1.67 × 108 Pa, pCO2 = 2.5 atm = 2.5 × 105 Pa
According to Henry’s law
pCO2 = KHχCO2 = \(\frac{P_{\mathrm{CO}_{2}}}{K_{\mathrm{H}}}\)
\(\frac{2.5 \times 10^{5}}{1.67 \times 10^{8}}\) = 1.5 × 10-3 ……….. (i)
Mass of water = Density of water × Volume of water
= 1 g/mL × 500 mL = 500 g
Number of moles of water, (nH2O)
= \(\frac{\text { Mass of water }}{\text { Molar mass }}=\frac{500 \mathrm{~g}}{18 \mathrm{~g} / \mathrm{mol}}\)
= 27.78 mol
χCO2 = \(\frac{n_{\mathrm{CO}_{2}}}{n_{\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}}+n_{\mathrm{CO}_{2}}}=\frac{n_{\mathrm{CO}_{2}}}{n_{\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}}}\)
⇒ nCO2 = χCO2nH2O
= 1.5 × 10-3 × 27.78 mol
= 41.67 × 10-3 mol
Mass of CO2 = No. of moles of CO2 × Molar mass
= 41.67 × 10-3 × 44 =1.834 g
Question 8.
The vapour pressure of pure liquids A and B are 450 and 700 mm Hg respectively, at 350 K. Find out the composition of the liquid mixture if total vapour pressure is 600 mm Hg. Also find the composition of the vapour phase.
Solution:
Given, p\(p_{A}^{0}\) = 450 mm Hg, \(p_{B}^{0}\) = 700 mm Hg,
Ptotal = 600 mm Hg
According to Raoult’s law
PA = \(p_{A}^{0}\)χA
PB = \(p_{B}^{0}\)χB – \(p_{A}^{0}\) (1 – χA )
Therefore, total pressure, ptotal = pA + pB
⇒ ptotal = \(p_{A}^{0}\)χA + \(p_{B}^{0}\) (1 – χA)
⇒ ptotal = \(p_{A}^{0}\)χA + \(p_{B}^{0}\) – \(p_{B}^{0}\)χA
⇒ ptotal = \(p_{A}^{0}\) – \(p_{B}^{0}\) χA + \(p_{B}^{0}\)
⇒ 600 = (450 – 700)χA + 700
⇒ -100 = -250χA
⇒ χA = 0.4
Mole fraction of A (χA) = 0.4
Mole fraction of B (χB) = 1 – 0.4 = 0.6
Now, PA = PAχA = 450 × 0.4
= 180 mm Hg
PB = \(p_{B}^{0}\)χB
= 700 × 0.6
= 420 mm Hg
Now, in the vapour phase:
Mole fraction of liquid A = \(\frac{p_{A}}{p_{A}+p_{B}}\)
\(\frac{180}{180+420}=\frac{180}{600}\) = 0.30
And, mole fraction of liquid B = 1 – 0.30 = 0.70

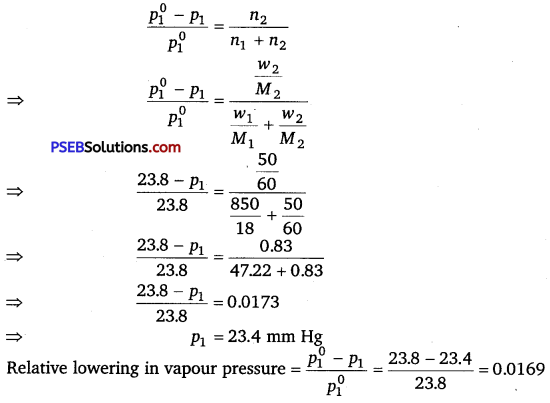
Question 9.
Vapour pressure of pure water at 298 K is 23.8 mm Hg. 50 g of urea (NH2CONH2) dissolved in 850 g of water. Calculate the vapour pressure of water for this solution and its relative lowering.
Solution:
Given, vapour pressure of water, \(p_{1}^{0}\) = 23.8 mm Hg
Weight of water w1, = 850 g
Weight of urea, w2 = 50 g
Molecular weight of water, M1 = 18 g mol-1
Molecular weight of urea, M2 = 60 g mol-1
Now, we have to calculate vapour pressure of water in the solution. We take vapour pressure as p1.
Now, from Raoult’s law, we have
Question 10.
Boiling point of water at 750 mm Hg is 99.63°C. How much sucrose is to be added to 500 g of water such that it boils at 100°C.
Solution:
Here, elevation in boiling point ΔTb = (100 + 273) – (99.63 + 273)
= 0.37 K
Mass of water, w1 = 500 g
Molar mass of sucrose (C12H22O11), M2 = 12 × 12 + 22 × 1 + 11 × 16
= 342 g mol-1
Molal elevation constant, Kb = 0.52 K kg mol-1
We know that,
ΔTb = \(\frac{K_{b} \times 1000 \times w_{2}}{M_{2} \times w_{1}}\)
⇒ w2 = \(\frac{\Delta T_{b} \times M_{2} \times w_{1}}{K_{b} \times 1000}\)
= \(\frac{0.37 \times 342 \times 500}{0.52 \times 1000}\)
= 121.67 g
Hence, 121.67 g of sucrose is to be added. ’

Question 11.
Calculate the mass of ascorbic acid (Vitamin C, C6H8O6) to be dissolved in 75 g of acetic acid to lower its melting point by 1.5°C. Kf = 3.9 Kkg mol-1.
Solution:
Mass of acetic acid, w1 = 75 g
Molar mass of ascorbic acid (C6H8O6), M = 6 × 12 + 8 × 1 + 6 × 16
= 176 g mol-1
Depression in melting point (ATf ) = 1.5 K
Molal depression constant (Kf ) = 3.9 K kg mol-1
We know that,
ΔTb = \(\frac{K_{f} \times w_{2} \times 1000}{M_{2} \times w_{1}}\)
⇒ w2 = \(\frac{\Delta T_{f} \times M_{2} \times w_{1}}{K_{f} \times 1000}\)
= \(\frac{1.5 \times 176 \times 75}{3.9 \times 1000}\)
= 5.08 g
Hence, 5.08 g of ascorbic acid is needed to be dissolved.
Question 12.
Calculate the osmotic pressure in pascals exerted by a solution prepared by dissolving 1.0 g of polymer of molar mass 185,000 in 450 mL of water at 37°C. ,
Solution:
It is given that,
Volume of water, V = 450 mL = 0.45 L
Temperature, T = (37 + 273) K = 310 K
R = 8.314 K Pa L K-1 mol-1
= 8.314 × 103 Pa LK-1 mol-1
Number of moles of the polymer, n = \(\frac{1}{185000}\) mol
We know that,
Osmotic pressure, n = \(\frac{n}{V}\)RT
= \(\frac{1}{185000}\) mol × \(\frac{1}{0.45 \mathrm{~L}}\) × 8.314 × 103 Pa LK-1 mol-1 × 310 K
= 30.98 Pa


![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()



![]()
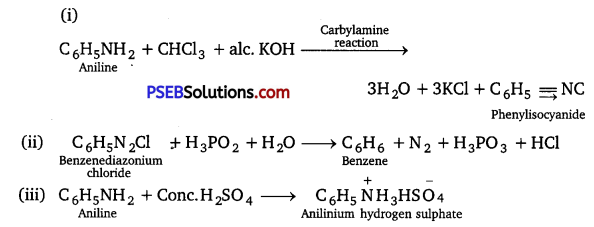
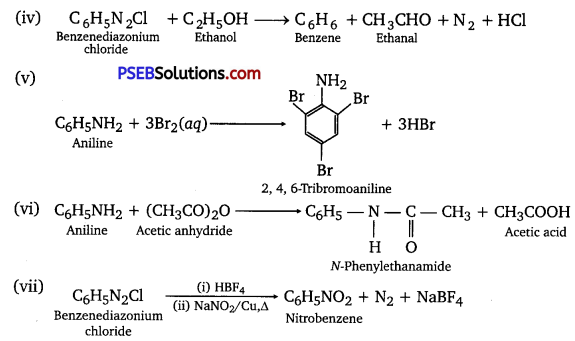

![]()
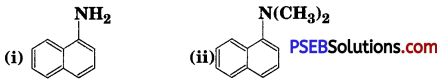


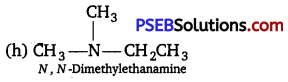
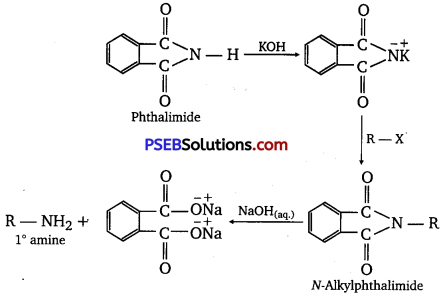
![]()
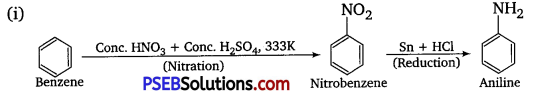
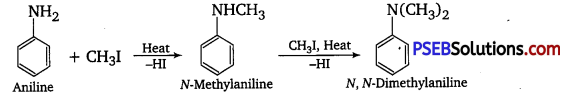
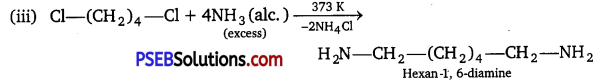
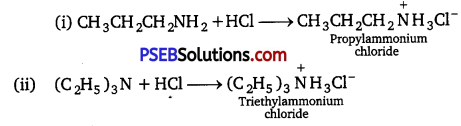
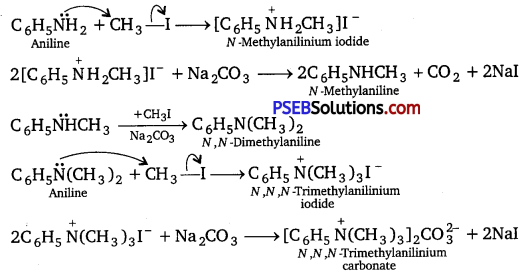
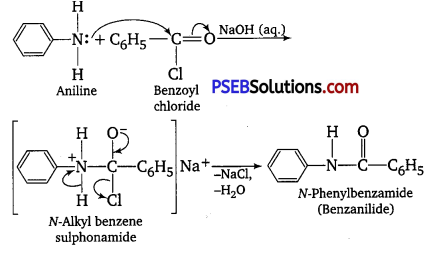

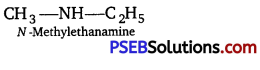

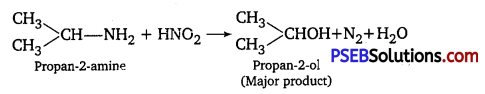
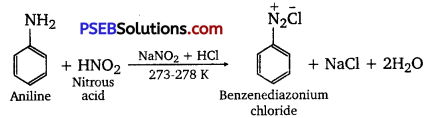
![]()
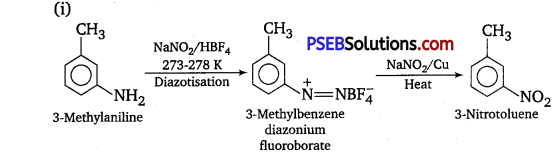
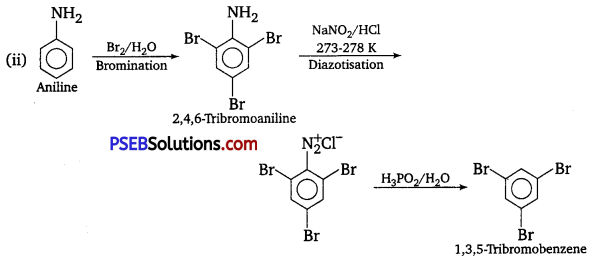

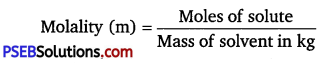
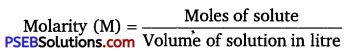
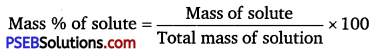
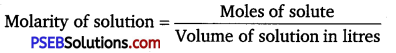

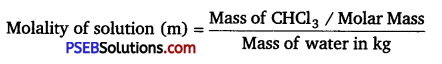



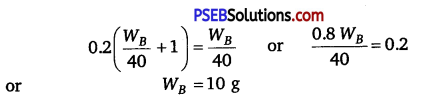




 has polar -OH group and can form H-bond. Thus, it is highly soluble in water.
has polar -OH group and can form H-bond. Thus, it is highly soluble in water.