Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life Important Questions and Answers.
PSEB 12th Class Physics Important Questions Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Where are receptors located? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Receptors are embedded in cell membrane.
Question 2.
Which site of an enzyme is called allosteric site? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Sites different from active site of enzyme where a molecule can bind and affect the active site is called allosteric site.
Question 3.
What is the harmful effect of hyperacidity? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Ulcer development in stomach.
Question 4.
Write the name of an antacid which is often used as a medicine.
Answer:
Ranitidine (Zantac).
![]()
Question 5.
What is the medicinal use of narcotic drugs? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Since narcotic drugs relieve pain and produce sleep, these are chiefly used for the relief of post-operative pain, cardiac pain and pain of terminal cancer and in childbirth.
Question 6.
Which type of drugs come under antimicrobial drugs? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Antiseptics, antibiotics and disinfectants.
Question 7.
What is the mode of action of antimicrobial drugs? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Antimicrobial drugs can kill the microorganism such as bacteria, virus, fungi or other parasites. They can, alternatively, inhibit the pathogenic action of microbes.
Question 8.
Which one of the following drugs is an antibiotic? Morphine, Equanil, Chloramphenicol, Aspirin
Answer:
Chloramphenicol.
Question 9.
What is meant by ‘narrow-spectrum antibiotics’?
Answer:
Antibiotics which are mainly effective against Gram-positive or Gram-negative bacteria are known as narrow-spectrum antibiotics. For , example, penicillin G.
Question 10.
Define the limited spectrum antibiotics.
Answer:
Antibiotics which are mainly effective against a single organism or disease, are called as limited spectrum antibiotics.
Short answer type questions
Question 1.
Why are certain drugs called enzyme inhibitors?[NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Enzymes have active sites that bind the substrate for effective and quick chemical reactions. The functional groups present at the active site of enzyme interact with functional groups of substrate via ionic bonding, hydrogen bonding, van der Waal’s interaction, etc. Some drugs interfere with this interaction by blocking the binding site of enzyme and prevent the binding of actual substrate with enzyme. This inhibits the catalytic activity of the enzyme, therefore, these are called inhibitors.
Question 2.
Sodium salts of some acids are very useful as food preservatives. Suggest a few such acids. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
A preservative is naturally occurring or synthetically produced substance that is added to foods to prevent decomposition by microbial growth or by undesirable chemical changes. Sodium salts of some acids are very useful as food preservatives.
Some examples of such acids are as follows :
- Benzoic acid in the form of its sodium salts constitutes one of the most common food preservatives. Sodium benzoate is a common preservative in acid or acidified foods such as fruit, juices, pickles etc. Yeasts are inhibited by benzoate to a greater extent than are moulds and bacteria.
- Sorbic acid and its salts (sodium, potassium, and calcium) also have preservative activities but the applications of -sodium sorbate (C6H7NaO2) are limited compared to that for potassium salt.
- Sodium erythorbate (C6H7NaO6) is a food additive used predominate in meats, poultry and soft drinks.
- Sodium propanoate[Na(C2H5COO)] is used in bakery products as mould inhibitor.
Question 3.
What is the side product of soap industry? Give reactions showing soap formation. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Soaps are sodium or potassium salts of long-chain fatty acids such as stearic acid, oleic acid and palmitic acid. Soaps containing sodium salts are formed by heating fat (i. e., glyceryl ester of fatty acid) with aqueous sodium hydroxide solution.
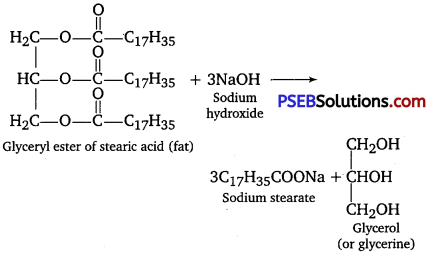
This reaction is known as saponification. In this reaction, esters of fatty acids are hydrolyzed and the soap obtained remains in colloidal form. It is precipitated from the solution by adding NaCl. The solution left after removing the soap contains glycerol as side product.
![]()
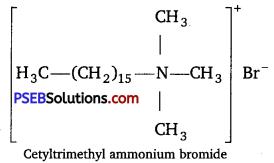
Question 4.
Hair shampoos belong to which class of synthetic detergent? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Hair shampoos are made up of cationic detergents. These are quaternary ammonium salts of amines with acetates, chlorides or bromides as anions, e. g., cetyltrimethylammonium bromide.
Question 5.
Explain why sometimes foaming is seen in river water near the place where sewage water is poured after treatment?
[NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Detergents have long hydrocarbon chains. If their hydrocarbon chain is highly branched, then bacteria cannot degrade this easily. Such detergents are non-biodegradable. Slow degradation of detergents leads to their accumulation.
These non-biodegradable detergents persist in water even after sewage treatment and cause foaming in rivers, ponds and their water get polluted. In order to overcome this issue branching of the hydrocarbon chain is controlled and kept to a minimum.
Long answer type questions
Question 1.
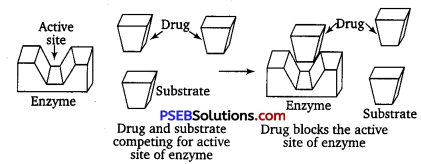
What are enzyme inhibitors? Classify them on the basis of their mode of attachment on the active site of enzymes. With the help of diagrams explain how do inhibitors inhibit the enzymatic activity? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Enzymes are responsible to hold the substrate molecule for a chemical reaction and they provide functional groups which will attack the substrate to carry out the chemical reaction. Drugs which inhibit any of the two activities of enzymes are called enzyme inhibitors.
Enzyme inhibitors can block the binding site thereby preventing the binding of the substrate to the active site and hence inhibiting the catalytic activity of the enzyme.
Drugs inhibit the attachment of natural substrate on the active site of enzymes in two different ways as explained below :
(i) Drugs which compete with natural substrate for their attachment on the active sites of enzymes are called competitive inhibitors.
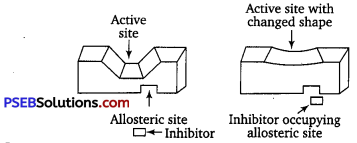
(ii) Some drugs, however, do not bind to the active site but bind to a different site of the enzyme which is called allosteric site. This binding of the drug at allosteric site changes the shape of the active site of the enzyme in such a way that the natural substrate cannot recognize it. Such enzymes are called non-competitive inhibitors.
Question 2.
In what respect to prontosil and salvarsan resemble? Is there any resemblance between azo dye and prontosil? Explain. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Prontosil, also called sulfamide chrysoidine, trade name of the first synthetic drug used in the treatment of general bacterial infections in humans. Prontosil resulted from research, directed by German chemist and pathologist Gerhard Domagk, on the antibacterial action of azo dyes. A red azo dye of low toxicity, prontosil was shown by Domagk to prevent mortality in mice infected with Streptococcus bacteria.
The dye was also effective in controlling staphylococcus infections in rabbits. Within a relatively short period, it was demonstrated that prontosil was effective not only in combating experimental infections in animals but also against Streptococcal disease in humans, including meningitis and puerperal sepsis. Structural formula of prontosil is as follows :
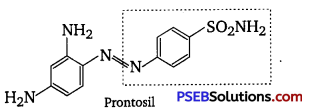
From the structure of prontosil, it is very clear that it has -N = N- linkage. It was discovered that the part of the structure of prontosil molecule shown inbox, i.e., p-amino benzene sulphonamide has antibacterial activity.
Salvarsan is also known as arsphenamine. It was introduced at the beginning of 1910s as the first effective treatment for syphilis. It is an organoarsenic molecule and has -As = As- double bond.
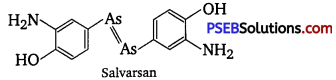
Salvarsan and prontosil show similarity in their structure. Both of these drugs are antimicrobials. Salvarsan contains -As = As- linkage whereas prontosil has —N = N— linkage.
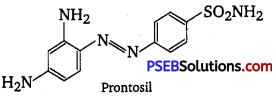
Prontosil (a red azo dye) and azo dye both have -N = N- linkage.
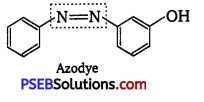
![]()
Question 3.
Ashwin observed that his friend Shubhain was staying aloof, not playing with friends, and becoming easily irritable for some weeks. Ashwin told his teacher about this, who, in turn, called Shubham’s parents and advised them to consult a doctor. The doctor after examining Shubham prescribed antidepressant drugs for him.
After reading the above passage, answer the following questions:
(i) Name two antidepressant drugs.
(ii) Mention the values shown by Ashwin.
(iii) How should Shubham’s family help him other than providing medicine?
(iv) What is the scientific explanation for the feeling of depression?
Answer:
(i) Equanil, Iproniazid, phenelzine (any two)
(ii) Empathetic, caring, sensitive.
(iii) They should talk to him, be a patient listener, can discuss the matter with the psychologist.
(iv) If the level of noradrenaline is low, then the signal sending activity becomes low and the person suffers from depression.