Punjab State Board PSEB 6th Class English Book Solutions Chapter 2 The Lake of the Moon Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Class 6th English Solutions Chapter 2 The Lake of the Moon Question Answers
The Lake of the Moon Class 6 Questions and Answers
Activity 1.
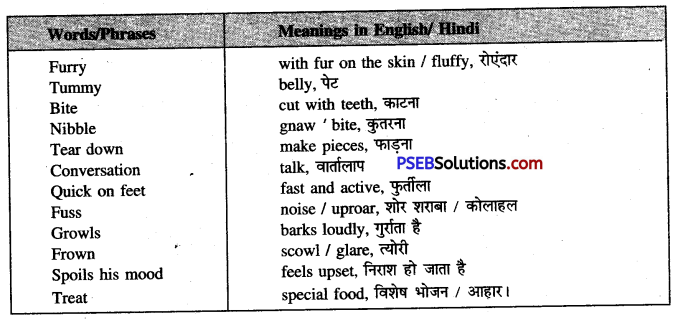
Look up the following words in a dictionary. You should seek the following information about the words and put them in your WORDS notebook. :
1. Meaning of the word as used in the lesson (Adjective, Noun, Verb. etc.)
2. Pronunciation (The teacher may refer to the dictionary or the mobile phone for correct pronunciation.)
3. Spellings
| majestic |
tusker |
severe |
drought |
prevent |
| messenger |
reflect |
protection |
disturb |
to and fro |

Vocabulary Expansion
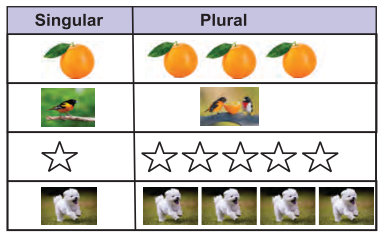
Some animals live or move together. The group of animals have different names. Elephants move in herds, rabbits live in colonies and birds flock together. ‘Herds’ and ‘colonies’ are collective nouns. Collective nouns are names for a ‘collection’ or a ‘number’ of people or things.
कुछ पशु एक साथ समूह में रहते हैं। पशुओं या वस्तुओं के समूह को विभिन्न नाम दिए जाते हैं, जैसे – Herd of elephants (हाथियों का झुंड), Colony of rabbits (खरगोशों की बस्ती), flock of birds (पक्षियों का समूह) Collective Nouns कहलाते हैं।
Let us look at some more collective nouns.
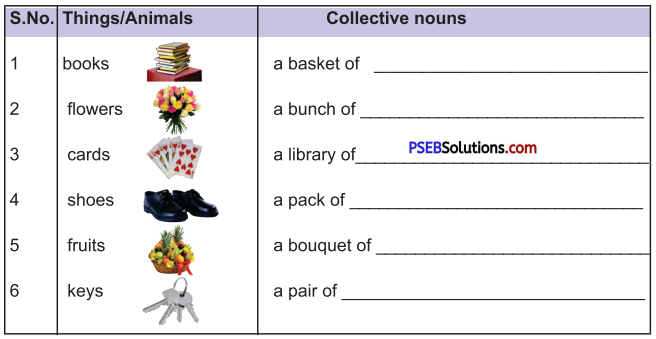
1. Collection of horses – team of horses
2. group of ants – army of ants
3. group of vultures – wake of vultures
4. group of cards – pack of cards
5. group of ladies – bevy of ladies

Activity 2.
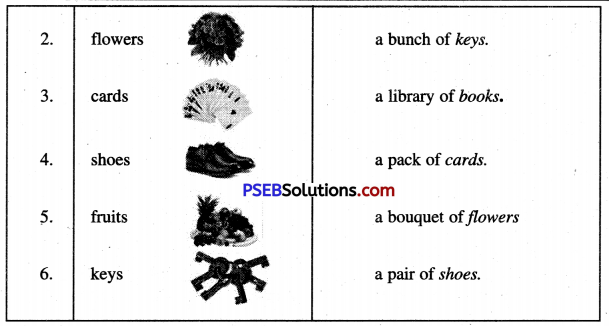
Match the following things with their group name :
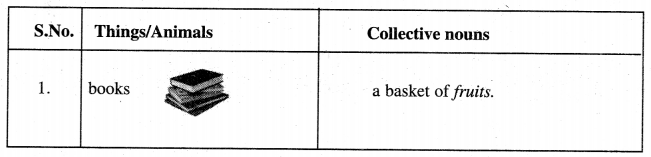
Answer:
Learning to Read and Comprehend
Activity 3.
Choose the correct option and put a tick :
Question 1.
What happened in the area where the elephants lived ?
(a) there were floods
(b) there was no water
(c) there was fire in the jungle.
Answer:
(b) there was no water.

Question 2.
The elephant king told the elephant to go to :
(a) different lakes
(b) the moon
(c) different directions
Answer:
(c) different directions
Question 3.
What was close to the lake ?
(a) a big forest
(b) a colony of rabbits
(c) the moon
Answer:
(b) a colony of rabbits.
Question 4.
Why did rabbits panic ?
(a) thousands of rabbits died
(b) elephants would drink all the water in the lake
(c) the moon would get angry
Answer:
(a) thousands of rabbits died.
Question 5.
What did the king of rabbits want other rabbits to find?
(a) water
(b) another place to go
(c) solution
Answer:
(c) solution
Question 6.
What did one little rabbit say?
(a) fight the elephants
(b) hide till the elephants go away
(c) make him a messenger to the elephant king
Answer:
(c) make him a messenger to the elephant king
Question 7.
What did the little rabbit climb?
(a) a mountain
(b) a huge rock
(c) on the back of the elephant king
Answer:
(b) a huge rock
Question 8.
What did the little rabbit say to the Elephant King ?
(a) that he was the messenger of the Moon
(b) he ordered the king to leave their area
(c) that the elephants should be ready for a fight
Answer:
(a) that he was the messenger of the Moon
Question 9.
What message does he give to the King?
(a) that the elephant herd had soiled the water of the holy lake
(b) rabbits, were under the special protection of the moon
(c) both ‘a’ and ‘b’
Answer:
(c) both ‘a’ and ‘b’.

Question 10.
Where does the rabbit take the elephant king ?
(a) a lake
(b) another forest
(c) none of the above
Answer:
(a) a lake.
Activity 4.
Answer the following questions :
Question 1.
What happened to the place where the herd of elephants lived ?
उस स्थान को क्या हुआ जहां हाथियों का झुंड रहता था ?
Answer:
There was a severe drought (भीषण सुखा) and there was no water.
Question 2.
Where was the water found ?
पानी कहां मिला था ?
Answer:
The water was found in a lake in another jungle.
Question 3.
Who became the messenger ?
संदेशवाहक कौन बना?
Answer:
A little rabbit became the messenger.
Question 4.
Why did the water move to and fro ?
पानी इधर-उधर क्यों हिलने लगा ?
Answer:
The water moved to and fro because it was disturbed.
Question 5.
Why did the elephant king believe that the Moon had become angrier ?
राजा हाथी को इस बात का विश्वास क्यों हुआ कि चांद और अधिक क्रोधित हो उठा है ?
Answer:
It was so because the Moon had started moving to and fro.
Learning Language
Noun : Gender
Gender is a type of noun. There are four types of Genders.
1. Masculine Gender : The names of all male persons or animals (सभी नर व्यक्तियों या पशुओं के नाम) are of Masculine Gender. Example : man, uncle, lion, prince, master, etc.
2. Feminine Gender :
The names of all female persons or animals (सभी मादा व्यक्तियों या पशुओं के नाम) are of Feminine Gender. Example : woman, daughter, queen, lioness, etc.
3. Neuter Gender :
Things that do not have life (सभी निर्जीव वस्तुएं) are neither male or female. They belong to the Neuter Gender. Example : knife, computer, tree, chair, table, cycle, etc.

4. Common Gender :
Names that can be used for both males and females (वे नाम जिनका प्रयोग नर तथा मादा दोनों के लिए किया जा सकता है) are of Common Gender. Example : child, teacher, student, parent, leader, etc.
Change of Gender
Activity 5.
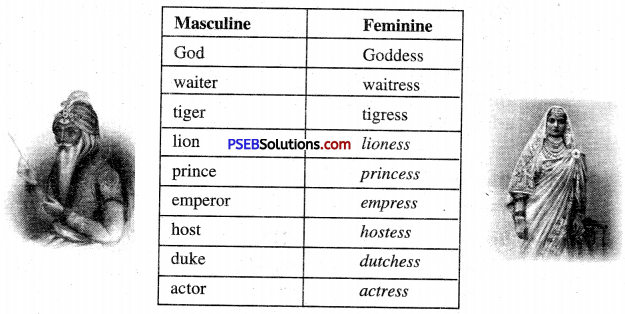
Sometimes the word is slightly changed and-ess is added. Some examples are given in the table.
Complete the ones that have been left blank in the table. (teacher must help] :
Activity 6.
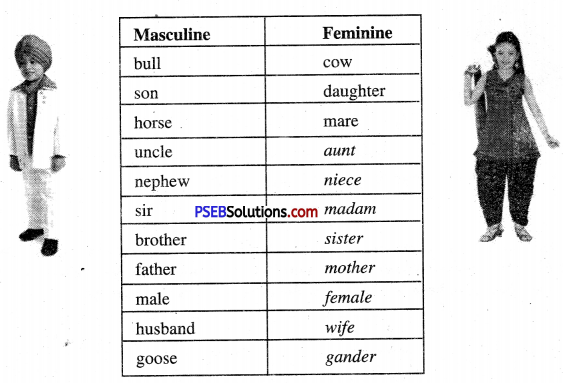
Many nouns have different words for the Masculine and the Feminine. Some examples are done for you. Complete the ones that have been left blank in the table. [teacher must help] :

Activity 7.
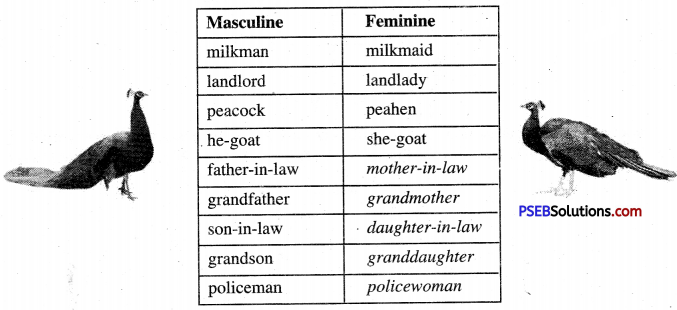
Sometimes half the word that shows gender gets changed. Some examples are done for you. Complete the ones that have been left blank in the table. [teacher must help] :
Masculine milkman
Activity 8.
Some words change but their patterns are different. Some examples are done for you. Complete the ones that have been left blank in the table. [teacher must help] :
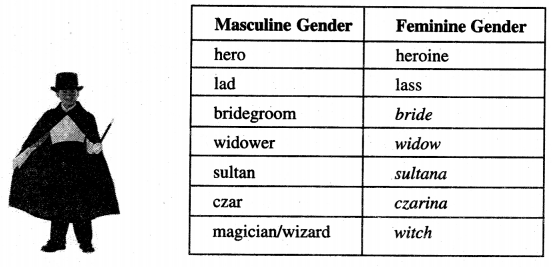
नोट :-Magician वास्तव में Common gender है।
Activity 9.
Some words are common to both genders. These words can be used for both males and females. Such words are called Common Gender. Some examples are done for you. Complete the ones that have been left blanks in the table, [teacher must help]:
| pilot |
friend |
| bird |
parent |
| baby |
teacher |
| doctor |
member |
| child |
candidate |
| president |
shopkeeper |
| artist |
enemy |
| pupil |
player |
Activity 10.
Some words have no gender. Such words are called Neuter gender. Some examples are done for you. Complete the ones that have been left blank in the table, [teacher must help]:
| Neuter Gender |
| chair |
mountain |
| paper |
fan |
| book |
computer |
| school |
camera |
| pencil |
photo |
| map |
table |
| scooter |
rickshaw |

Activity 11.
Fill in the blanks using the correct option:
aunt, cow, queen, uncle, pilot, man, lady, hen, cock, duck
1. A ………………. wears a crown.
2. A …………… flies an aeroplane.
3. My grandmother is an old ……………
4. My father is a very kind and caring ……….
5. A ………….. gives us milk.
6. A ………….. lays eggs.
7. My father’s brother is my ………….
8. My mother’s sister is my
9. A ……………. quacks all day long in the pond.
0. A ………… says cock-a-doodle-doo.
Answer:
1. queen
2. pilot
3. lady
4. man
5. cow
6. hen
7. uncle
8. aunt
9. duck
10. cock
Activity 12
Write the opposite gender.
1. husband — wife
2. master — mistress
3. milkmaid — milkman
4. Peahen — peacock
5. nephew — niece
6. washer man — washer woman
7. president — president
8. queen — king
9. goose — gander
10. princess — prince
Reading a short passage
Activity 13
Read the story and do as directed :
The king was very angry. He ordered his guards to put his minister in prison. The minister had argued with the king on some law and order issue. The minister was put in prison. One day, the emperor went to the prison to see his minister. The king told him. “I will set you free on one condition. You must bring me a horse that is neither white nor black nor brown nor grey”.
The minister was surprised at this demand. However, he agreed to this condition. A week later, the minister came to the palace. “Have you found a horse ?” the King asked. “Yes, my lord”, the minister replied. “But I will show him to you only on a religious day.
The king agreed. Let me know the next religious day. The minister replied, “I will show you the horse on any day other than Sunday, Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday or Saturday.”
The king started laughing. He was cleverly outsmarted by his minister. The minister was set free and promoted to the next higher position.
A. Write the meanings of :
(a) outsmart – outwit,पछाड़ देना
(b) issue – matter,मामला
B. Answer the following:
(a) Why was the King angry ?
Answer:
The King was angry because his minister had argued with him on some law and order issue.
(b) Why was the minister surprised at King’s demand ?
Answer:
The minister was surprised because there was no horse of the colour the king wanted.

Choose the right option.
Question 1.
The argument between the king and the minister was about
(a) law and order issue
(b) religious issue
(c) war issue.
Answer:
(a) law and order issue.
Question 2.
The king ordered his guards to put his minister in prison because the minister had
(a) failed to reach the palace on time.
(b) not obeyed the king’s orders.
(c) argued with him on law and order issue.
Answer:
(c) argued with him on law and order issue.
Question 3.
The minister was surprised at the king’s demand because
(a) all horses are either black or brown or grey or white.
(b) there were no horses in the kingdom.
(c) there was no time to find a horse that the king wanted.
Answer:
(a) all horses are either black or brown or grey or white.
Activity 14(Pairwork):
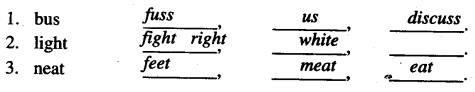
Write as many words as you can think of that rhyme with the following words. One rhyming word is given for each word. And practise speaking them with your partner.

नोट :- विद्यार्थी इन्हें बोलने का अभ्यास करें।
Learning to Write
Letter Writing (Informal)
Writing a letter is an art. It has a set format that must be followed. Given ahead is the format.
Answer:

नोट-विद्यार्थी पत्र लिखते समय इस Format का प्रयोग करें।

Activity 15
Write a letter to your uncle thanking him for the beautiful gift he has sent to you.
Answer:
28 Moti Nagar
Ludhiana
March 29, 20….
My dear Uncle,
Last Monday was my birthday. I received many other gifts too. But your gift was the best one. The watch had a silver dial and a golden chain. All praised this beautiful watch. I felt proud of you. The watch will be very useful to me. It will make my life regular and punctual. I shall never be late for school now. I shall keep this watch with great care. After all, this is a token of your love for me. I celebrated it at home. A big cake was cut. Most of our near and dear ones were present. But you were absent. I missed you very much. However, you did not forget the day. You have sent me a gift.
With regards
Yours lovingly
Ravi
Address :
Shri Manohar Lal
Prem Street
Joginder Nagar
Rohtak.
Comprehension Of Passages
Read the given passages and answer the questions that follow each :
(1) A severe drought hit the area. There was no rain for some years. All the rivers and ponds dried up. Birds and animals started dying of thirst. The wild elephants suffered too due to lack of water. The king of elephants understood that many of them would die of thirst if they did not get water soon. He had to find water for his herd as quick as possible. He told the elephants to go in different directions to look for water.
One of them found a large lake full of water in another jungle far away. The king was happy. He ordered all the elephants to start moving towards the lake. It was a beautiful lake. However close to the lake was a colony of rabbits. The elephants had to pass through that colony. Thousands of rabbits were crushed to death and thousands more were injured. The rabbits were in a state of panic.
(i) What was the effect of drought on birds and animals ?
पशु-पक्षियों पर सूखे का क्या प्रभाव पड़ा ?
(ii) Who found water ? Where was it ?
पानी किसे मिला ? यह कहां था?
(iii) Choose true or false statements and write them in your answer book :
(a) Close to the lake was a colony of rabbits.
(b) The elephants had to pass through the lake.
(iv) Complete the following sentences according to the meaning of the passage.
(a) Thousands of rabbits were crushed ……….
(b) The …………. were in a panic.
Or
Match the words with the meanings :
| (a) panic |
wounded |
| (b) injured |
great fear |
|
captured |
Answer:
(i) The birds and animals started dying of thirst.
(ii) One of the elephants found water. It was in a large lake in another jungle far away.
(iii)
(a) True
(b) False.
(iv)
(a) Thousands of rabbits were crushed to death.
(b) The rabbits were in a panic.
Or
(a) panic — great fear
(b) injured — wounded.

(2) The rabbits thought and thought. How could they stop the elephants ? One little rabbit stoop up. “Your Majesty,” he said, “if you send me as your messenger to the king of the elephants, I may be able to find a solution.” “Who said these words is not mentioned.”
The little rabbit hurried to the spot where elephants lived. He saw a group elephants returning from the lake. Right in the middle was the king of elephants. To get near him was impossible. “I will be crushed to death,” thought the rabbit. So he climbed up a huge rock.
“O king of the elephants,” he shouted, “Hear me, please.” The king heard his voice and turned towards him.“Who are you ?” he asked. “I am a messenger.” replied the rabbit. “A messenger ? From whom ?” “I am a messenger from the mighty Moon.”
(i) Why did the rabbit not go near the king of elephants ?
खरगोश हथियों के राजा के निकट क्यों न गया ?
(ii) What did he do instead ?
इसकी बजाय उसने क्या किया ?
(iii) Choose true. or false statements and write them in your answer book :
(a) The king did not hear the rabbit.
(b) The king of the elephants was in the middle of the group.
(iv) Complete the following sentences according to the meaning of the passage.
(a) The king heard his voice and ……..
(b) I am a messenger from ………..
Or
Match the words with the meanings :
| (a) spot |
place/site |
| (b) huge |
far away |
|
very big |
Answer:
(i) The rabbit did not go near the king of elephants lest he should be crushed to death.
(ii) He climbed up a huge rock.
(iii)
(a) False
(b) True.
(iv)
(a) The king heard his voice and turned towards him.
(b) I am a messenger from the mighty Moon.
or
(a) spot — place/site
(b) huge – very big.
(3) “Sir, the Moon says,” said the little rabbit, “You, the king of the elephants, have brought your herd to my holy lake. You and your herd have soiled its water. You and your herd have killed thousands of rabbits on your way to the lake.
You must know that rabbits are under my special protection. Everyone knows that the king of the rabbits lives with me. I ask you not to kill any more rabbits. If you do not agree, something bad will happen to you and your herd.” The king of the elephants was shocked.
He looked at the little rabbit. “You are right,” he said. “We may have killed many rabbits on our way to the lake. I shall see that you do not suffer anymore. I shall request the Moon to forgive me for my sins. Please tell me what I should do.”
(i) What was the Moon’s message to the king of elephants ?
हाथियों के राजा के नाम चांद का क्या संदेश था ?
(ii) Who wanted the Moon to foregive him and for what ?
चांद से माफ़ी कौन चाहता था और किस बात के लिए ?
(iii) Choose true or false statements and write them in your answer book :
(a) The elephants had killed thousands of rabbits.
(b) The king of the elephants was happy.
(iv) Complete the following sentences according to the meaning of the passage.
(a) If you do not agree something bad will happen to ………..
(b) I shall see that ……
Or
Match the words with their meanings :
| (a) protection |
punishment |
| (b) sins |
defence |
|
bad deeds |

Answer:
(i) The Moon’s message was not to kill any more rabbits.
(ii) The king of elephants wanted the Moon to forgive him for his sins.
(iii)
(a) True
(b) False
(iv)
(a) If you do not agree something bad will happen to you and your herd.
(b) I shall see that you do not suffer anymore.
Or
(a) protection – defence
(b) sins – bad deeds.
Use Of Words/Phrases In Sentences
1. Huge (very big) —
A palace is a huge building.
महल एक बहुत बड़ा भवन होता है। I
2. Due to (because of —
could not attend the meeting due to illness.
बीमारी के कारण मैं मीटिंग में न जा सका।
3. Look for (search) —
We are looking for our lost bal.
हम अपनी गुम हुई गेंद ढूंढ रहे हैं।
4. Disturb (interrupt) —
Don’t disturb me. I am doing my homework.
मेरे काम में बाधा मत डालो। मैं घर का काम कर रहा हूँ।
5. Severe (acute) —
I have severe pain in my body.
मेरे शरीर में बहुत अधिक दर्द है।
6. To and fro (here and there) —
The swing was moving to and fro.
झूला इधर-उधर आ जा रहा था।
7. Majestic (grand) —
The Taj Mahal is a majestic building.
ताजमहल एक शानदार इमारत है।
8. Prevent (stop) —
I could not prevent him to soil his clothes.
मैं उसे अपने कपड़े गंदे करने से न रोक सका।
9. Reflect (cast back/give back) —
Water reflects light.
पानी प्रकाश को परावर्तित करता है
10. Injured (wounded) —
Many people were injured in the accident.
दुर्घटना में कई लोग घायल हो गए।
11. Occur to (strike one’s mind) —
It did not occur to me that I was running into danger.
मैं यह न समझ सका कि मैं खतरे में पड़ रहा हूं।
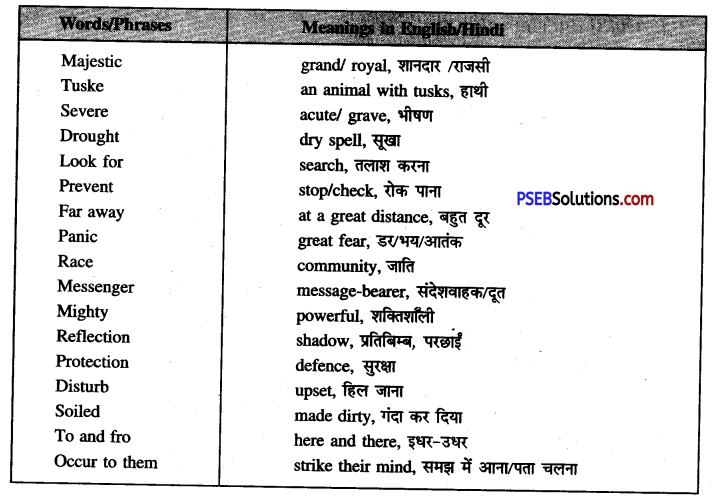
Word Meanings
The Lake of the Moon Summary in Hindi
Once upon a time …………………………. state of panic.
एक समय की बात है, जंगल में हाथियों का एक बहुत बड़ा झुंड रहता था। उनका राजा एक बहुत बड़ा राजसी हाथी था जो अपने झुंड से बहुत प्यार करता था। उस क्षेत्र में भयंकर सूखा पड़ा। कुछ वर्षों से वहाँ वर्षा नहीं हुई थी। सभी नदियां तथा तालाब सूख गए। पक्षी और जानवर प्यास से मरने लगे।
जंगली हाथियों को भी पानी की कमी के कारण मुसीबत का सामना करना पड़ा। हाथियों का राजा समझ गया यदि उन्हें शीघ्र ही पानी नहीं मिला तो उनमें से बहुत से मर जाएंगे। उसे जल्दी से जल्दी अपने झुंड के लिए पानी की तलाश करनी होगी। उसने हाथियों को अलग-अलग दिशा में जाकर पानी ढूंढने के लिए कहा।
उनमें से एक को दूर किसी दूसरे जंगल में पानी से भरी एक बड़ी झील मिली। राजा खुश हुआ। उसने सभी हाथियों को उस झील की ओर चलने का आदेश दिया।झील सुन्दर थी। परन्तु झील के निकट खरगोशों की एक बस्ती थी। हाथियों को उस बस्ती में से होकर जाना पड़ता था। हजारों खरगोश मारे जाते थे और उससे भी कई हजार अधिक खरगोश घायल हो जाते थे। खरगोश आतंकित थे।

Thinking …………..not mentioned.
उनके राजा ने एक सभा बुलाई। उसने कहा, “जंगली हाथियों का एक झुंड हमारी बस्ती में से निकलता है। उन्होंने हमें हजारों की संख्या में पहले ही मार डाला है और कई हजार घायल हो गए हैं। हमें शीघ्र ही जरूरी कदम उठा कर और अधिक मौतों को रोकना होगा। मैं चाहता हूँ कि तुम सब अपनी जाति की सुरक्षा के लिए किसी तरीके पर विचार करो” खरगोशों ने बार-बार सोचा। हाथियों को कैसे रोका जाए? एक छोटा सा खरगोश उठ खड़ा हुआ। उसने कहा, “महाराज, यदि आप मुझे हाथियों के राजा के पास अपना दूत बनाकर भेजे तो मैं कोई समाधान निकाल पाऊँगा।”
The little Rabbit ………………………. I should do.”
छोटा खरगोश तेज़ी से उस स्थान की ओर गया जहाँ हाथी रहते थे। उसने हाथियों के एक समूह को झील से वापिस आते देखा। उनके बिल्कुल बीच हाथियों का राजा था। उसके पास पहुँचना असंभव था ( खरगोश ने सोचा, “मैं तो कुचलकर मारा जाऊँगा।” इसलिए वह एक बहुत बड़ी चट्टान पर चढ़ गया। वह चिल्लाया, ” ओ, हाथियों के राजा कृपया मेरी बात सुनें।” राजा ने आवाज़ सुनी और उसकी ओर मुड़ा। उसने कहा, “कौन हो तुम ?” खरगोश ने उत्तर दिया, “मैं एक दूत हूँ।” “एक दूत ? किसके यहाँ से ?” “मैं शक्तिशाली चंद्रमा का दूत हूँ।” “सच में ? तुम क्या चाहते हो? क्या मेरे लिए चंद्रमा का कोई संदेश है?”
“हाँ, हाँ महाराज, परन्तु तुम मुझसे क्रोधित मत होना। मैं तो केवल एक दूत हूँ। मैं तो केवल अपना कर्त्तव्य निभा रहा हूँ।” राजा हाथी ने कहा, “बिल्कुल ठीक, एक दूत को उसके कुछ भी कहने के लिए दण्डित नहीं किया जाता। तुम कहो जो भी कहने के लिए आए हो। मैं तुम्हें कोई हानि नहीं पहुँचाऊंगा। तुम तो केवल अपना कर्तव्य निभा रहे हो।” छोटे से खरगोश ने कहा, “श्री मानजी, चंद्रमा कहता है “हाथियों के राजा, तुम अपने झुंड को मेरी पवित्र झील पर लाए हो। तुमने और तुम्हारे झंड ने मेरे जल को गंदा कर दिया है। तुमने और तुम्हारे झंड ने झील की ओर जाते हुए हजारों खरगोशों को मार डाला है। तुम्हें पता होना चाहिए कि खरगोश मेरे विशेष संरक्षण में हैं। सभी जानते हैं कि खरगोशों का राजा मेरे साथ रहता है।
मैं तुम्हें कह रहा हूँ कि अव और खरगोशों को मत मारना। यदि तुम नहीं मानोगे तो तुम्हें और तुम्हारे झुंड के साथ कुछ बुरा होगा।” राजा को दुख पहुँचा। उसने छोटे से खरगोश की ओर देखा। “तुम ठीक कह रहे हो।” उसने कहा हो सकता है, “हमने झील के रास्ते में बहुत से खरगोशों को मार डाला हो। मैं इस बात का ध्यान रखूगा कि तुम्हें अब और अधिक कष्ट न उठाना पड़े। मैं चंद्रमा से निवेदन करूंगा कि वह मुझे मेरे पापों के लिए क्षमा कर दें। कृपया मुझे बताओ कि मुझे क्या करना चाहिए।”
“Come with me ………………….. fooled or befooled ?
खरगोश ने उत्तर दिया, “मेरे साथ अकेले आओ। आओ, मैं तुम्हें चंद्रमा के पास ले चलता हूँ।” छोटा खरगोश भारी भरकम हाथी को झील पर ले गया। वहाँ उन्होंने शांत (ठहरे हुए) जल में चांद का प्रतिबिंब (परछाईं) देखा। छोटे झील सुन्दर थी। परन्तु झील के निकट खरगोशों की एक बस्ती थी। हाथियों को उस बस्ती में से होकर जाना पड़ता था। हजारों खरगोश मारे जाते थे और उससे भी कई हजार अधिक खरगोश घायल हो जाते थे। खरगोश आतंकित थे।
Thinking …….. not mentioned.
उनके राजा ने एक सभा बुलाई। उसने कहा, “जंगली हाथियों का एक झुंड हमारी बस्ती में से निकलता है। उन्होंने हमें हजारों की संख्या में पहले ही मार डाला है और कई हजार घायल हो गए हैं। हमें शीघ्र ही जरूरी कदम उठा कर और अधिक मौतों को रोकना होगा। मैं चाहता हूँ कि तुम सब अपनी जाति की सुरक्षा के लिए किसी तरीके पर विचार करो” खरगोशों ने बार-बार सोचा। हाथियों को कैसे रोका जाए? एक छोटा सा खरगोश उठ खड़ा हुआ। उसने कहा, “महाराज, यदि आप मुझे हाथियों के राजा के पास अपना दूत बनाकर भेजे तो मैं कोई समाधान निकाल पाऊँगा।”
The little Rabbit …………. ……………. I should do.
” छोटा खरगोश तेज़ी से उस स्थान की ओर गया जहाँ हाथी रहते थे। उसने हाथियों के एक समूह को झील से वापिस आते देखा। उनके बिल्कुल बीच हाथियों का राजा था। उसके पास पहुँचना असंभव था ( खरगोश ने सोचा, “मैं तो कुचलकर मारा जाऊँगा।” इसलिए वह एक बहुत बड़ी चट्टान पर चढ़ गया।
वह चिल्लाया, ” ओ, हाथियों के राजा कृपया मेरी बात सुनें।” राजा ने आवाज़ सुनी और उसकी ओर मुड़ा। उसने कहा, “कौन हो तुम ?” खरगोश ने उत्तर दिया, “मैं एक दूत हूँ।” “एक दूत ? किसके यहाँ से ?” “मैं शक्तिशाली चंद्रमा का दूत हूँ।” “सच में ? तुम क्या चाहते हो? क्या मेरे लिए चंद्रमा का कोई संदेश है?”
“हाँ, हाँ महाराज, परन्तु तुम मुझसे क्रोधित मत होना। मैं तो केवल एक दूत हूँ। मैं तो केवल अपना कर्त्तव्य निभा रहा हूँ।” राजा हाथी ने कहा, “बिल्कुल ठीक, एक दूत को उसके कुछ भी कहने के लिए दण्डित नहीं किया जाता। तुम कहो जो भी कहने के लिए आए हो। मैं तुम्हें कोई हानि नहीं पहुँचाऊंगा। तुम तो केवल अपना कर्तव्य निभा रहे हो।
” छोटे से खरगोश ने कहा, “श्री मानजी, चंद्रमा कहता है “हाथियों के राजा, तुम अपने झुंड को मेरी पवित्र झील पर लाए हो। तुमने और तुम्हारे झंड ने मेरे जल को गंदा कर दिया है। तुमने और तुम्हारे झंड ने झील की ओर जाते हुए हजारों खरगोशों को मार डाला है। तुम्हें पता होना चाहिए कि खरगोश मेरे विशेष संरक्षण में हैं।
सभी जानते हैं कि खरगोशों का राजा मेरे साथ रहता है। मैं तुम्हें कह रहा हूँ कि अव और खरगोशों को मत मारना। यदि तुम नहीं मानोगे तो तुम्हें और तुम्हारे झुंड के साथ कुछ बुरा होगा।” राजा को दुख पहुँचा। उसने छोटे से खरगोश की ओर देखा। “तुम ठीक कह रहे हो।” उसने कहा हो सकता है, “हमने झील के रास्ते में बहुत से खरगोशों को मार डाला हो। मैं इस बात का ध्यान रखूगा कि तुम्हें अब और अधिक कष्ट न उठाना पड़े। मैं चंद्रमा से निवेदन करूंगा कि वह मुझे मेरे पापों के लिए क्षमा कर दें। कृपया मुझे बताओ कि मुझे क्या करना चाहिए।”

“Come with me ………………….. fooled or befooled ?
खरगोश ने उत्तर दिया, “मेरे साथ अकेले आओ। आओ, मैं तुम्हें चंद्रमा के पास ले चलता हूँ।” छोटा खरगोश भारी भरकम हाथी को झील पर ले गया। वहाँ उन्होंने शांत (ठहरे हुए) जल में चांद का प्रतिबिंब (परछाईं) देखा। छोटे
खरगोश ने कहा, “महाराज, चांद से मिलें।” हाथी ने अपनी सूंड को जल में डुबोया और कहा, “कृपया मुझे चांद की पूजा करने दो।” जैसे ही पानी को छेड़ा गया पानी में चांद इधर-उधर हिलने लगा। खरगोश ने कहा, ” अब, चाँद पहले से भी अधिक क्रोधित है।” राजा हाथी ने पूछा, ” क्यों ? मैंने ऐसा क्या किया ?” खरगोश ने उत्तर दिया, “आपने झील के पवित्र जल को छुआ है।” हाथी ने अपना सिर झुका लिया।
“कृपया चंद्रमा से कहो मुझे माफ कर दें। हम आगे से कभी भी इस झील के पवित्र जल को नहीं छुएंगे न ही हम फिर कभी उन खरगोशों को हानि पहुँचाएंगे जो चांद के सबसे प्रिय हैं।” इस तरह राजा और उसका झुंड वहां से चले गए। शीघ्र ही वर्षा होने लगी और हाथी खुशी से रहने लगे। उन्हें यह कभी भी नहीं पता चला कि एक छोटे से खरगोश ने उन्हें मूर्ख बनाया है या चकमा दिया है।
Retranslation Of Isolated Sentences
1. Once upon a time, a large herd of elephants lived in a jungle. .
एक समय की बात है जंगल में हाथियों का एक बहुत बड़ा झुंड रहता था।
2. There was no rain for some years.
कुछ वर्षों से वर्षा नहीं हुई थी।
3. The wild elephants suffered too due to lack of water.
जंगली हाथियों को भी पानी की कमी के कारण मुसीबत का सामना करना पड़ा।
4. He had to find water for his herd as quickly as possible.
उसे जल्दी से जल्दी अपने झुंड के लिए पानी की तलाश करनी थी।
5. It was a beautiful lake.
झील सुंदर थी।
6. The rabbits were in a state of panic.
खरगोश आतंकित/भयभीत थे।
7. They have already killed thousands of us.
उन्होंने हमें हजारों की संख्या में पहले ही मार डाला है।
8. The rabbits thought and thought.
खरगोशों ने बार-बार सोचा।
9. Who said these words is not mentioned.
ये शब्द किसने कहे इसका कोई पता नहीं।
10. I will be crushed to death..
मैं तो कुचल (रौंद) कर मारा जाऊँगा।
11. I am a messenger from mighty moon.
मैं शक्तिशाली चंद्रमा का दूत हूँ।
12. You and your herd have soiled its water.
तुमने और तुम्हारे झुंड ने इसके जल को गंदा कर दिया है।

13. The king of the elephants was shocked.
हाथियों का राजा दुखी हो उठा।
14. Please ask the Moon to forgive me.
कृपया चद्रंमा से कहो कि वह मुझे माफ कर दें।
English Class 6 Solutions PSEB Prose
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()