Punjab State Board PSEB 9th Class Science Important Questions Chapter 6 Tissues Important Questions and Answers.
PSEB 9th Class Science Important Questions Chapter 6 Tissues
Long Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
Define tissue, Differentiate meristematic and permanent tissue, Describe different types of primary meristematic tissue.
Answer:
Tissue, A tissue is a group of similar or dissimilar cells coordinating to perform a specific function.
| Meristematic tissue |
Permanent tissue |
| 1. Cells are thin walled, living, oval or rounded, and isodiametric. |
1. Cells are thin or thick walled, living or dead, oval or rounded or elongated fibre-like. |
| 2. Divide throughout life so help in growth. |
2. Lost the division power, so do not help in growth. |
| 3. Reserve food is absent. |
3. Reserve food may be present. |
| 4. Vacuoles are absent. |
4. Vacuoles are present. |
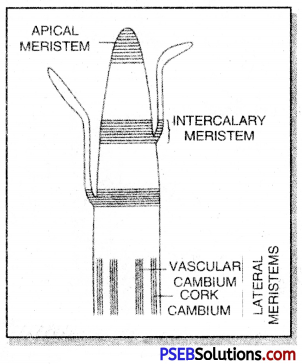
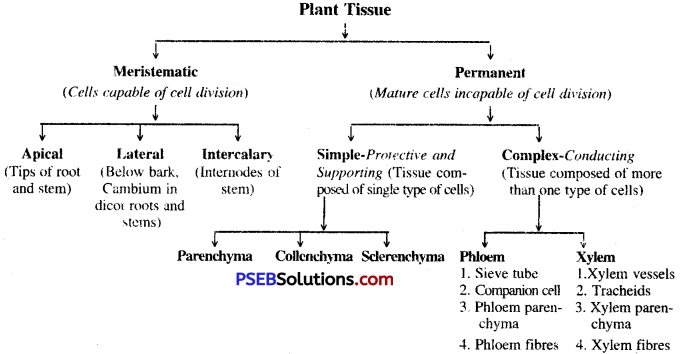
Types of primary meristematic tissues. On the basis of their position, these are of three types:
- Apical meristem lies at shoot and root apices and helps in longitudinal growth.
- Intercalary meristem lies between shoot and root apices and helps in longitudinal growth.
- Lateral meristem lies on lateral sides of stem and root and helps in increase in diameter.

Question 2.
What is permanent tissue? Briefly explain the types of simple permanent tissue.
Answer:
Permanent Tissue: They are composed of mature cells which after undergoing complete growth have assumed a definite shape, size and function. They have lost the power of division. The permanent tissues are of two types i.e. simple tissue and compound tissue.
Kinds of simple tissue:
1. Parenchyma
2. Collenchyma
3. Sclerenchyma
1. Parenchymal tissue is formed of thin walled, living, oval cells having walls formed of only cellulose. It forms cortex, endodermis, pericycie, pith etc. of different parts of plants. It is loosely packed with intercellular spaces. It is modified to form epidermis covering of all the parts of plant body, chlorenchyma for photosynthesis, aerenchyma for floating in the hydrophytes.
2. Collenchyma is formed of thick walled (with pectinised cell wall) and living cells and is found in hypodermis of dicot stem. It provides flexibility to plants.
3. Sclerenchyma is formed of thick walled (with lignified cell wall) and dead cells and forms hypodermis of monocot stem, bark, shells of nuts, etc. It makes the plants hard and stiff. It provides strength to plant parts. It also forms hard covering of seeds and nuts.
Question 3.
What is complex tissue? Explain its types along with diagrams.
Answer:
Complex tissue. The tissue formed of two or more than two kinds of tissue is called complex tissue. It is of two types:
1. Xylem
2. Phloem
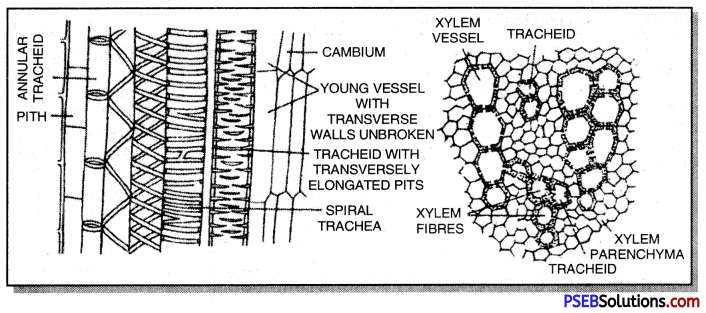
1. Xylem, also called wood, is compound tissue of the plants which primarily helps in conduction of water and minerals from the root system to various parts of shoot system (Ascent of sap).
| Xylem elements |
Function |
| 1. Tracheids
2. Tracheae or vessels
3. Xylem parenchyma
4. Xylem sclerenchyma |
1. Long-distance conduction of water and minerals upward from the root system to various parts of shoot system.
2. Storage and short distance conduction of water and minerals.
3. Mechanical support so helps in resisting strong winds. |
(a) Element of xylem
(b) Kinds of xylem
1. Primary xylem. It is derived from procambium during the formation of primary plant body, developing from embryo.
2. Secondary xylem. It is formed from cambium, during secondary growth of plant development when increase in thickness takes place.
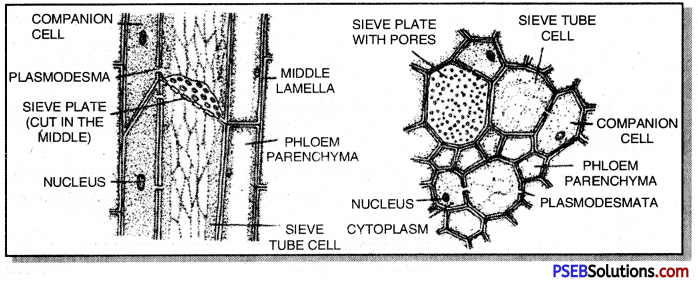
2. Phloem, also called bast, is a compound tissue which helps in downward conduction of food.
| Phloem elements |
Function |
| 1. Sieve tube cells
2. Companion cells
3. Phloem parenchyma
4. Phloem sclerenchyma |
Long-distance conduction of food from the leaves to other parts of plant body.
Control the functioning of dead sieve tube cells.
Storage and short distance conduction of food. Mechanical support. |

Question 4.
List various forms of connective tissue and write functions of each.
Answer:
Kinds of connective tissue:
- Proper connective tissue: It joins the body parts, such as blood vessels and nerves.
- Bone: It is the hardest tissue: It forms skeleton and provides shape to body. It protects the body organs.
- Cartilage: It forms parts of endoskeleton. It forms tip of nose, pinna, ends of long bones.
- Blood: It is fluid tissue. It transports materials and gases in the body.
- Tendon: It connects muscles with bone.
- Ligament: It connects bone with bone.
Question 5.
Give an account on types of epithelia.
Answer:
Simple epithelium is unilaminar in which cells are arranged in only one layer. It is found in those parts of body where wear and tear are less. Types of simple epithelial tissues are:
| Type of Epithelium |
Structure |
Positive |
Function |
| 1. Squamous epithelium |
Cells are flat, discoidal and polygonal and fit like the tiles in a floor. |
Alveoli of lung. Bowman’s capsule of nephron. Blood capillaries. |
Exchange of gases. Ultrafiltration. Exchange between body cells and blood. |
| 2. Cuboidal epithelium |
Cells are polygonal and cuboidal with centric and rounded nuclei. |
Proximal part of body of nephron (with micro-villi). In gonads. |
Selective reabsorption of useful materials. Divide by meiosis and form gametes. |
| 3. Columnar epithelium |
Cells are polygonal and pillar-like with oval-shaped nuclei. |
Fallopian tube (cells) with cilia. Mucosa of small intestine (with microvilli). |
Move ovum/zygote. Increased absorption of nutrients. |
| 4. Ciliated epithelium |
Free ends of cells bear cilia. |
Uriniferous tubules, trachea and fallopian tubes. |
Flow of materials |
| 5. Glandular epithelium |
These are cuboidal gland cells. |
Lining of alimentary canal and digestive gland. |
Secretion of useful substances. |
Question 6.
Give an account on the types of animal tissue.
Answer:
- Epithelial tissue is covering and protective tissue and is formed of one or more layers of compactly arranged cells with no intercellular spaces and resting on basement membrane.
- Muscular tissue is formed of highly elongated and useful secretion contractile cells called muscle fibres. It helps in movements of body parts and locomotion.
- Muscular tissue is of three types:
- Striated or skeletal muscular tissue.
- Visceral or smooth or unstriated muscular tissue.
- Cardiac muscular tissue.
- Connective tissue mainly acts as binding tissue and has large amount of matrix.
- Connective tissue is of three types: Connective tissue proper, Skeletal connective tissue and Vascular connective tissue.
- Connective tissue proper: Areolar connective tissue has soft matrix. Yellow fibrous connective tissue (with many elastic fibres and forms ligaments); Adipose connective tissue (with large number of fat-storing adipocytes e.g. below the skin of mammals, fat- bodies of frog, etc.)
- Skeletal connective tissue has dense and mineralised matrix and forms endoskeleton of vertebrates. It includes cartilages and bones.
- Vascular connective tissue has fluidy and fibre-free matrix. It is of two types: Blood and Lymph.
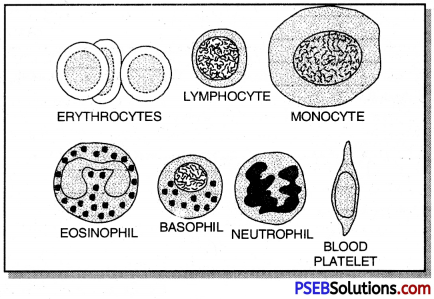
- Blood is red vascular connective tissue and flows inside the blood vessels. It is formed of plasma and blood corpuscles which are of three types: Erythrocytes or RBCs mainly with haemoglobin.
- Leucocytes or WBCs (rounded or amoeboid and nucleated corpuscles and Blood platelets (cytoplasmic fragments and help in blood clotting at the injury’).
- Lymph is white vascular connective tissue and flows inside the lymph-vessels. It is formed of plasma and leucocytes so is called filtered blood. It acts as middle man between body cells and blood.
- Nervous tissue has the properties of excitability and conductivity of nerve impulses.
- Neurons are structural and functional units of nervous tissue. Neurons receive and conduct impulses.
- Each neuron is formed of a nucleated cyton and one or more nerve processes which are of 2 types: Axon or efferent and dendron or afferent.
- When axon (acts as neuraxis) is surrounded by one or more sheath, then it is called nerve fibre.
Nerve fibres are of two types: Medullated nerve fibres and Non-medullated nerve fibres.

Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
What is a tissue? What are its kinds?
Answer:
Tissue: A tissue is a group of cells having a similar origin along with intercellular material and performing a similar function. The different cells of a tissue are usually joined together. The microscopic study of tissues is called histology.
Depending upon the constitution, their structure and arrangement, tissues are of two types-simple and complex (= compound).
A simple tissue is made up of only one type of cells while a complex tissue consists of two or more types of cells.
Question 2.
What are the kinds of meristem depending upon location?
Answer:
Depending upon the position (location) in the plant body, the meristems may be apical, intercalary and lateral.
- Apical meristems are bom at the tips of the stems, roots and their branches.
- Intercalary meristems are the left-out portions of the apical meristems that get separated from the latter by the differentiation of permanent tissues in-between meristems at the base of leaves or inter- nodes.
- Lateral meristems are located along the lateral sides of stems and roots.
Question 3.
How will you prove that growth occurs in certain specific regions of plant?
Answer:
Apical meristem causes growth in length.
Materials: Two jars, two onion bulbs, water, pair, of scissors and measuring scale.
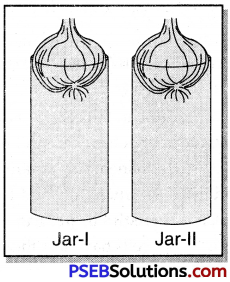
Procedure:
- Take two glass jars and fill them with water.
- Now, take two onion bulbs and place one on each jar as shown in the Fig.
- Observe the growth of roots in both the bulbs for a few days.
- Measure the length of roots on day 1,2 and 3.
- On day 4, cut the root tips of the onion bulb in Jar-II by about 1 cm.
After this, observe the growth of roots in both the jars and measure their lengths each day for five more days and record the observations in tables like the table below:
| Length |
Day 1 |
Day 2 |
Day 3 |
Day 4 |
Day 5 |
| Jar-I |
|
|
|
|
|
| Jar-II |
|
|
|
|
|
Observation:
1. Roots of Jar-1 continue to grow on 5th and 6th day. They stop in case of Jar-II. Conclusion. It is due to the fact that apical meristem remains intact in case of Jar-I which is responsible for growth Thus growth occurs in specific regions.

Question 4.
What are different kinds of animal tissue? Give one example and one function of each type.
Answer:
Types of animal tissues:
| Name of tissue |
Example |
Function |
| Epithelial Tissue |
Internal and external surfaces of body and its organs |
Protection |
| Connective Tissue |
Bone, Cartilage, Areolar tissue, Blood |
Connects two similar or different types of tissues together. |
| Muscular Tissue |
Body wall, Limbs, Tongue, Face. |
Movement and protection. |
| Nervous Tissue |
Brain and Spinal cord. |
Conduction of messages and coordination of various parts of body. |
Question 5.
Describe the salient features of meristematic tissue.
Answer:
Characteristic features of meristematic tissue are as follows:
- They consist of immature cells which are in a state of division and growth.
- They are compactly arranged so that there are no intercellular spaces in between them.
- The cells have thin walls.
- Each cell consists of a prominent nucleus and dense cytoplasm.
- Vacuole in the cells is usually absent, if present it is quite small.
Question 6.
Write characteristics of permanent tissues.
Answer:
Permanent tissues are those tissues whose cells have lost the power of division and become structurally and functionally specialised.
Characteristics of permanent tissue are as follows:
- The cells have lost the power of division.
- They have undergone differentiation into specific types, for a particular function.
- Permanent tissues are of two types:
- Simple permanent tissues, where the tissue is composed of only one type of cells.
- Complex permanent tissues, where the tissue is composed of more than one type of cells.
Question 7.
Differentiate meristematic cells and permanent cells.
Answer:
Differences between meristematic cells and permanent cells:
| Meristematic cells |
Permanent cells |
| 1. These cells do not have large vacuoles.
2. They are thin-walled and isodiametric.
3. These cells can divide and produce new cells. |
1. These cells often have large central vacuoles.
2. They may be thin or thick-walled. They have permanent shape.
3. These cells have lost the power of growth and cell division. |

Question 8.
What are the characteristics of parenchyma? Give two examples of specialized parenchyma cells.
Answer:
Parenchyma. It is the most common type of simple permanent tissue found in almost all the parts of the plant.
Characteristics of parenchyma:
1. It is the main representative of the ground tissue system. It forms a continuous soft tissue, as in the cortex and pith of stems, cortex of roots, ground tissue, petiole, mesophyll of leaves.
2. It is thin-walled.
3. They retain the ability to divide at maturity.
4. The cells of parenchyma vary in their shape, but a typical ground tissue parenchyma cell is equal in length and width.
5. Parenchyma of stems and roots stores nutrients and water.
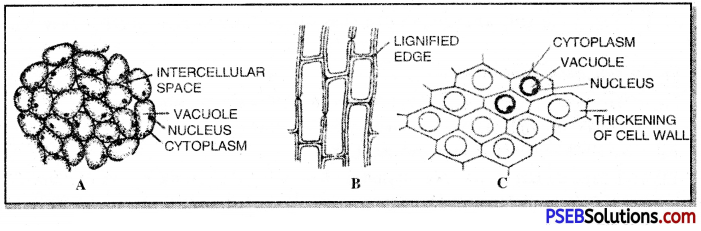
Examples of specialized parenchyma:
- Chlorenchyma. In some cases the parenchyma cells contain chloroplasts and are called as chlorenchyma. These cells are meant for photosynthesis.
- Aerenchyma. In aquatic plants parenchyma cells occur around air cavities, they are called as aerenchyma e.g. in Hydrilla stem. Aerenchyma provides buoyancy to the plants to help them float.
Question 9.
Mention any two functions of parenchyma.
Answer:
Functions of parenchyma:
- It provides rigidity and also stores food in the form of starch, proteins, oil and fats.
- In hydrophytes they have large air spaces to keep up buoyancy of plants.
Question 10.
Explain the structure and functions of collenchyma.
Answer:
Structure of collenchyma. It is a special type of parenchyma having localised thickenings on the cell walls and is found only in the primary body. The cells are longer than ordinary’ parenchyma. It is a soft tissue having a pliable primary wall. Tire thickening of the corners of the cells is due to the addition of cellulose and pectin.
Functions:
- Provide flexibility as allows easy bending in different parts.
- It provides rigidity and strength,
- Chloroplast containing collenchyma takes part in photosynthesis.

Question 11.
What is sclerenchyma? What are its two main kinds?
Answer:
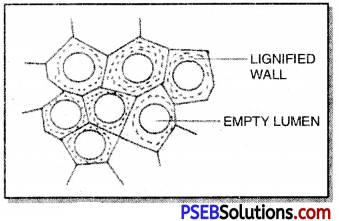
Sclerenchyma: The cells of this tissue have very thick cell walls. Most of these cells may be dead. They are long and narrow as walls are thickened due to lignin. They provide mechanical support to the plants and parts. Sclerenchyma cells are generally of two types i.e. Fibres and sclereids.
Question 12.
State the location and one function of each of the following tissues: Parenchyma, Sclerenchyma and Collenchyma.
Answer:
| Name of tissue |
Location |
Function |
| 1. Parenchyma |
Soft parts |
Store food |
| 2. Sclerenchyma |
Stems and veins |
Strength to the plant |
| 3. Collenchyma |
Leaf stalk and below epidermis of leaf |
Support and Photosynthesis |
Question 13.
Differentiate parenchyma and collenchyma.
Answer:
Differences between parenchyma and collenchyma:
| Parenchyma |
Collenchyma |
| 1. The cell walls are uniformly thickened. |
1. The ceil walls get extra thickened at places. |
| 2. Parenchyma does not have any permanent mechanical function except when its cells are turgid. |
2. Tt is a living mechanical tissue. |
| 3. Parenchyma is formed both in the outer and inner parts of plant organs. |
3. It is mostly restricted to outer parts of plant organs. |
Question 14.
Write functions of xylem and phloem.
Answer:
Functions of xylem:
- It is mainly responsible for conduction of water and minerals.
- Provides mechanical strength.
Functions of phloem:
- Phloem transports food from leaves to other parts.
- Phloem parenchyma helps in storage of food.
- Materials can move in both directions.

Question 15.
Differentiate skeletal and smooth muscles.
Answer:
Differences between skeletal (striped) and smooth muscles (unstriped)
| Skeletal muscles (striped) |
Smooth muscles (unstriped) |
| 1. Muscle fibres are cylindrical and unbranched.
2. Multiruicleate and nuclei lie in the peripheral region.
3. Striated due to presence of dark and light bands. |
1. Fibres are spindle-shaped and unbranched.
2. Uninucleate and nucleus lies in the middle.
3. Non-stria ted. |
Question 16.
List the functions of bone.
Answer:
Functions of bone:
- It forms framework of the body.
- It provides definite shape to the body.
- It protects the internal organs of body such as brain, spinal cord, heart and lungs.
- It provides solid surface for attachment of muscles so that they may act as system of levers in motion and locomotion.
- Skeleton stores certain mineral reserves.
- R.B.Cs. are formed in the bone marrow.
Question 17.
Write a note on blood.
Answer:
Blood. It consists of plasma, red blood corpuscles, white blood corpuscles and platelets, circulates in blood vessels. Red corpuscles are circular, biconcave and enucleated in mammals, carry O2 and CO2. White corpuscles are nucleated, have granular or non-granular cytoplasm, and defend the body. Platelets help in blood clotting. Plasma transports materials and contains proteins that maintain osmotic pressure, help in blood clotting and act as antibodies.
Question 18.
Explain the structure of xylem elements.
Answer:
Structural elements of xylem
(a) Tracheids are elongated, dead cells with large cavities and possess highly lignified thick-walls. Depending upon the kind of thickenings, tracheids may be annular, spiral, reticulate, scleriform and pitted.
(b) Vessels are broader as compared to the tracheids. These are composed of many cells joined end to end with their walls perforated to give it a tube-like appearance. They also show thickenings like the tracheids.
(c) Xylem Parenchyma (= Wood Parenchyma). It is parenchyma present in xylem. The cells are, however smaller and thick-walled. Xylem parenchyma stores food and helps in lateral conduction of sap or water.
(d) Xylem Fibres (= Wood Fibres). They represent sclerenchyma fibres present in xylem. The fibres are mechanical in function.

Question 19.
Give a brief account of components of phloem.
Answer:
Phloem. It is a complex permanent tissue which conducts organic materials inside the plant. Phloem consists of four types of cells-sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma and phloem fibres. Except for phloem fibres, phloem cells are living cells.
(a) Companion Cells. They are narrow, elongated, nucleated cells which are connected to sieve tube cells.
(b) Phloem Parenchyma. It is parenchyma associated with phloem. The cells store food and take part in slow lateral conduction of the same.
(c) Phloem Fibres. Sclerenchyma fibres found in phloem are known as phloem or bast fibres. They provide mechanical strength.
(d) Sieve Tubes. They are tubular cells with perforated walls. They are tubular channels which are formed by end to end arrangement of a number of cells called sieve tube cells or sieve elements. They bear a number of small sieve pores. Due to the presence of sieve pores, the end walls are also called sieve plates.
Question 20.
Make a list of functions of blood.
Answer:
Functions of Blood:
- It delivers the nutrients to the tissue and carries the waste products away from tissue.
- It transports carbon dioxide from various organs to lungs.
- It transports hormones.
- Its components act as carrier of antibodies and antitoxic substances.
- It conducts heat of skin for dissipation.
- It acts as carrier of nitrogenous waste material like urea etc. to kidneys for elimination.
- It maintains water balance in the body.
- It maintains constant temperature in body after distributing heat within the body.
Functions of RBC:
- They transport O2 to tissues from respiratory organs as oxyhaemoglobin.
- Erythrocytes also participate in transport of C02 Mainly C02 is carried as bicarbonate.
- Function of WBC. Act as soldiers.
Question 21.
What is muscular tissue?
Answer:
Muscular Tissue:
The muscular tissue is a contractile tissue consisting of very large cells. Excitability and contractility are properties of protoplasm called sarcoplasm which is very well developed in these tissues. These cells bring about locomotion and movement of internal organs. Based on structural and functional differences, three types of muscles are recognised. They are unstriated, striated and cardiac muscles.

Question 22.
What are main functions of muscular tissue? Name the three kinds of muscular tissue.
Answer:
Functions:
- The muscular tissues help in protection of body.
- The muscles bring about various kinds of movements.
Types of muscular tissue:
The muscular tissue is of three kinds:
- Unstriated or visceral muscle fibres.
- Striated or skeletal muscle fibres.
- Cardiac muscle fibres.
Question 23.
1. Write the similarities between cardiac muscles and striped muscles.
2. Outline two similarities between smooth and cardiac muscles.
Answer:
1. Similarities of cardiac muscles with striped muscles:
- Both are striated and bear dark and light bands.
- Both are cylindrical in shape.
- Blood supply is abundant.
2. Similarities between smooth and cardiac muscles:
- Nucleus is present centrally in both muscles.
- Both are involuntary muscles.
Question 24.
Differentiate tendon and ligament.
Answer:
Differences between tendon and ligament:
| Tendon |
Ligament |
| 1. It is an inelastic band.
2. Tendon connects a muscle with a bone.
3. Yellow fibres are absent.
4. Bundle of white fibres occur in parallel series. |
1. It is an elastic band.
2. Ligament connects one bone with another bone.
3. Yellow fibres are present.
4. Bundles of white fibres run in different directions. |

Question 25.
Bring out two points of differences between Bone and Cartilage.
Answer:
Differences between bone and cartilage:
| Cartilage |
Bone |
| 1. It is a soft tissue. Perichondrium, covers the cartilage externally. |
1. It is hard. It is covered by periosteum. |
| 2. Matrix is not arranged in lamellae. |
2. Matrix is arranged in concentric layers called lamellae. |
| 3. Marrow cavity and bone marrow absent. |
3. In the centre of bone, marrow cavity is present. Marrow cavity is filled with bone marrow. |
Question 26.
What is nervous tissue?
Answer:
Nervous Tissue. It forms the nervous system. It is made up of neurons, nerve cells and neuroglia cells. Nerve cell (neuron) consists of a cell body or cyton containing nucleus, one long process called axon and many short branched processes called dendrites. Nervous system is concerned with responsiveness of animals.
Question 27.
Describe neuron.
Answer:
Nerve Cells (Neurons): May be unipolar, bipolar or multipolar, with one axon and one or more dendrons. Dendrites carry nerve impulses towards the cell body and axon away from it. Cell body has Nissl’s granules in the cytoplasm, Axons form synapses with the dendrites and cell body or axon of some other neuron.
Question 28.
What is nerve fibre? Name the two main types.
Answer:
Nerve Fibres. These are extended axons or dendrites. There are two types:
- Medulliated Nerve Fibres. These have thick myelin sheath, occur in white matter of brain and spinal cord and in cranial and spinal nerves.
- Non-medullated Nerve Fibres. These have very thin myelin sheath, occur in sy mpathetic nerves.
Question 29.
What is white fibrous connective tissue? Explain tendon and ligament.
Answer:
White Fibrous Connective Tissue. It is a silvery white connective tissue which contains abundant white fibres. Yellow fibres are rare. The tissue occurs at the joints of sk ull bones and covering sheaths of hone, cartilage, muscles, etc.
1. Tendoin, It is a connective tissue which binds skeletal muscles to the bones. The tissue occurs; in small bands. It contains abundant parallel bundles of white fibres with flattened tendon cells of fibroblasts found in rows in between them.
2. Ligament. It is an. elastic connective tissue which connects one bone with another. In temaliy it contains bundles of white fibres running in different directions and scattered yellow fibres. Fibroblasits occur in between the bundles of white fibres.
Question 30.
Differentiate R.B.C. and W.B.C.
Answer:
Differences between RBC (erythrocytes) and WBC (leucocytes)
| Red blood cells (Erythrocytes) |
White blood cells (Leucocytes) |
| 1. Circular, biconvex in shape.
2. Coloured red due to pigment haemoglobin.
3. Occur in very large numbers (approx. 4 to 6 million per cubic mm).
4. Concerned with oxygen transport. |
1. Irregular or amoeboid in shape.
2. Colourless due to absence of pigments.
3. Less numerous than R.B.C.s (approx. 5,000-7,000 per cubic mm).
4. Protect body against infections. |

Question 31.
What is connective tissue? List the different kinds of connective tissue.
Answer:
Connective Tissue:
As the name suggests, it connects or binds the similar or different kinds of tissues. Cells are scattered and intercellular space is filled with matrix. Cells of connective tissue characteristically secrete ground substance called matrix. In the matrix are present cells and fibres.
The nature and function of each connective tissue is determined by the nature of the matrix. Connective tissue is of following types:
(a) Proper connective tissue (jelly-like matrix).
(b) Skeletal (matrix-tough impregnated with salts)-Bone and cartilage.
(c) Vascular tissue (fluid-matrix)-Blood and lymph.
Question 32.
Differentiate cardiac muscles and striated muscles.
Answer:
Differences between cardiac muscle and striated muscles:
| Cardiac muscles |
Striated muscles |
| 1. These are also called involuntary muscles.
2. These are exclusively present in the heart.
3. Sarcolemma is absent in cardiac muscle.
4. Light and dark bands are absent. |
1. These are also called voluntary muscles.
2. These are mostly attached to bones by tendons.
3. Sarcolemma is present in striated muscle.
4. Alternate light and dark bands are present in striated muscles. |
Question 33.
Describe the structure of a neuron.
Answer:
A neuron is longest cell of body (about 1 metre) and is structural and functional unit of nervous system. It is formed of two parts:
1. Cyton or cell body.
2. Nerve processes.
1. Cyton or cell body: It is the nucleated part of neuron whose cytoplasm is called neuroplasm and has fine threads called neurofibrils (for conduction of nerve impulses), RER-rich Nissl’s granules (for protein synthesis) and many mitochondria but no centriole.
2. Nerve processes. There are protoplasmic processes arising from the cyton and are of two types: Axon and dendron.

Question 34.
Differentiate axon and dendron.
Answer:
Differences between axon and dendron
| Characters |
Axon |
Dendron |
| 1. Number |
Always single. |
Maybe one or more. |
| 2. Size |
Long sized and may or may not be branched. |
Small-sized and always branched. |
| 3. Function |
These conduct nerve impulses away from cyton so are efferent in nature. |
Conduct the nerve impulses towards the cyton so are afferent in nature. |
Question 35.
Draw diagrams showing:
(a) Squamous epithelium
(b) Cuboidal epithelium
(c) Columnar epithelium
Answer:
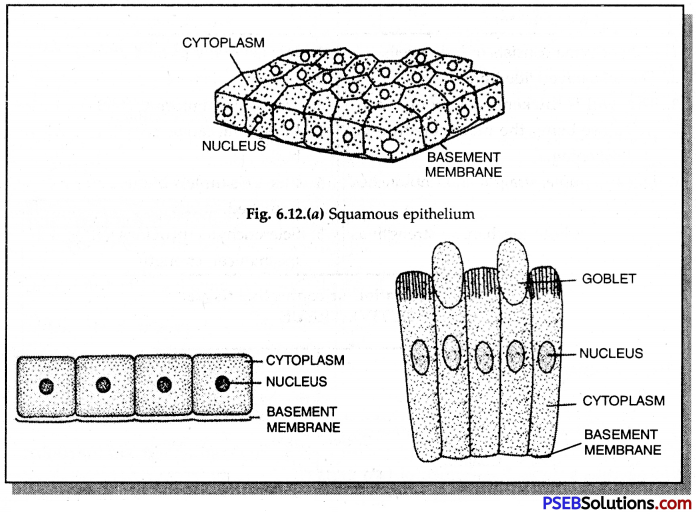
Question 36.
Name three types of connective tissues on the basis of nature of matrix.
Answer:
- Connective tissue proper with soft matrix.
- Skeletal connective tissue with dense and mineralised matrix.
- Vascular connective tissue with fluidity and fibre-free matrix.

Question 37.
What is the main difference in the matrix of cartilage and bone?
Answer:
Matrix of cartilage is formed of proteins and sugars but generally lacks calcium salts. Matrix of bone is formed of protein and is deposited with salts of phosphates of calcium and magnesium.
Question 38.
List two typical features of plant tissues with regard to functions.
Answer:
Features of plant tissue:
- Supportive which provide them with structural strength.
- Presence of meristematic tissues localised in certain selected region.
Question 39.
Why are most of tissues of animals are living as compared to plants?
Answer:
The animals move around in search of food, mates and shelter and consume more energy as compared to plants. Thus they are living.
Question 40.
Differentiate collenchyma and sclerenchyma.
Answer:
Differences between collenchyma and sclerenchyma:
| Collenchyma |
Sclerenchyma |
| 1. Collenchyma consists of living cells.
2. The cells have wide lumen.
3. The wall is thickened unevenly with cellulose being the main constituent of thickening.
4. Pits are simple, straight and unbranched.
5. It provides both mechanical strength as well as elasticity. |
1. It is generally formed of dead cells.
2. Lumen is narrow.
3. The wall is uniformly thickened. The thickening can be cellulose, lignin or both.
4. Pits are simple, oblique and may be branched.
5. Sclerenchyma provides stiffness or mechanical strength. |

Question 41.
Give broad outline classification of connective tissue.
Answer:
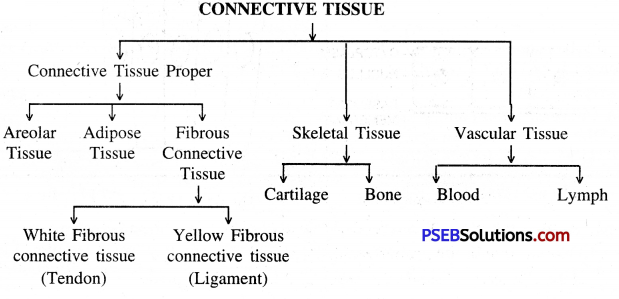
Question 42.
Differentiate muscle fibres and nerve cells.
Answer:
Differences between muscle fibre and nerve cell
| Muscle fibre |
Nerve cell |
| 1. The muscle cells are elongated in the Torm of fibres and are contractile. |
1. Irregular in shape with one long process. |
| 2. Cytoplasm is called sarcoplasm and fibre may be surrounded by sarcolemma. |
2, Cytoplasm is called neuroplasm and neurilemma absent. |
| 3. May have single nucleus or many nuclei. |
3. Uninucleated. |
| 4. Dark and light bands may be present. |
4. Absent. |
| 5. No protoplasmic processes are given out. |
5. Protoplasmic processes called dendrites and axon are given out from the cell body. |
| 6. They are concerned with movement and protection. |
6. They form part of tire nervous system and bring about co-ordination. |
Question 43.
Write a note on areolar tissue. Sketch the type of cells present in it.
Answer:
Areolar tissue. It is a typical connective tissue. It consists of a non-living ground substance called matrix. In the matrix are present cells. The cells are of three types:
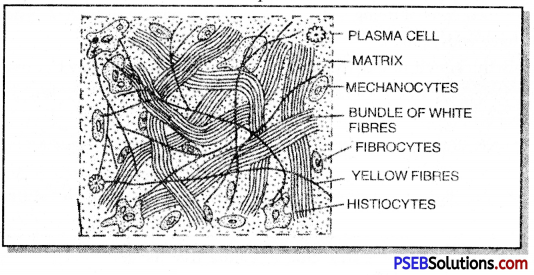
(a) Oval shaped mast cells, they secrete matrix and contain histamine,
(b) Fibroblasts are irregularly shaped flat cells with long protoplasmic processes which form fibres and
(c) Macrophages. They are amoeboid shaped and engulf the foreign particles by phagocytosis.

Question 44.
Compare xylem and phloem.
Answer:
Differences between xylem and phloem
| Xylem |
Phloem |
| 1. The conducting cells are vessels.
2. Xylem conducts water and minerals.
3. Xylem lies deeper in plant organs.
4. Xylem also provides mechanical strength.
5. There is one way conduction of materials. |
1. The conducting cells are phloem sieve tubes.
2. Phloem translocates organic food.
3. Phloem is situated towards outer side.
4. Phloem has no mechanical function.
5. Materials can move in both directions. |
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
Define tissue. Name two types of plant tissues.
Answer:
Tissue is a group of similar or dissimilar cells coordinating to perform a specific function so as to give highest possible efficiency.
Tvto types of plant tissues are: Meristematic and Permanent tissue.
Question 2.
Name two types of plant tissue.
Answer:
- Meristematic tissue
- Permanent tissue.
Question 3.
Give the term for a group of cells capable of division throughout life.
Answer:
Meristem.

Question 4.
Name three types of meristematic tissues.
Answer:
- Apical meristem
- Intercalary meristem
- Lateral meristem.
Question 5.
What is apical meristem?
Answer:
Meristem present at the tips of root and stem and their branches.
Question 6.
How is permanent tissue formed from meristematic tissue?
Answer:
Cells take up specific role and lose ability to divide, it is termed differentiation.
Question 7.
What are two kinds of permanent tissue?
Answer:
1. Simple permanent tissue
2. Complex tissue.
Question 8.
What is simple tissue?
Answer:
The tissue formed of only one kind of cells is called simple tissue.
Question 9.
Name three kinds of simple tissue.
Answer:
- Parenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma.
Question 10.
What is the function of parenchyma?
Answer:
Storage of food, photosynthesis, and short distance conduction.

Question 11.
Give the function of collenchyma.
Answer:
Mechanical support and may become photosynthetic.
Question 12.
What is function of sclerenchyma?
Answer:
Sclerenchyma is chief mechanical supporting tissue.
Question 13.
What is complex tissue?
Answer:
Tissue formed of two or more than two kinds of tissue is called complex tissue.
Question 14.
What are two kinds of complex tissue?
Answer:
1. Xylem 2. Phloem.
Question 15.
Name four elements of xylem.
Answer:
- Xylem parenchyma
- Tracheid
- Vessels
- Xylem fibres.
Question 16.
List four elements of phloem.
Answer:
- Sieve tubes
- Phloem parenchyma
- Companion cells
- fibres.

Question 17.
What are four kinds of animal tissue?
Answer:
- Epithelial tissue
- Muscular tissue
- Connective tissue
- Nervous tissue.
Question 18.
Differentiate two types of epithelial tissue.
Answer:
Simple epithelial tissue is unilaminar, while compound epithelial tissue is multilaminar.
Question 19.
Name three kinds of muscle fibres.
Answer:
- Smooth muscle fibres
- Striped muscle fibres
- Cardiac muscle fibres.
Question 20.
Which type of muscle fibres show rhythmic contraction?
Answer:
Cardiac muscle fibres.
Question 21.
Write two functions of connective tissue.
Answer:
1. Connect different organs.
2. Protection of internal organs.

Question 22.
Write names of different types of connective tissue.
Answer:
- Bone
- Cartilage
- Blood
- Tendon
- Ligament.
Question 23.
What are the smallest unit of living organisms?
Answer:
Cells.
Question 24.
Give the function of stratified epithelium.
Answer:
Protection of the body organs from mechanical injuries, entry of germs and evaporation of water.
Question 25.
List two functional peculiarities of muscle fibres.
Answer:
1. Excitability
2. Conductivity
Question 26.
Why are the smooth muscle fibres called visceral muscle fibres?
Answer:
These are present in layers in the wall of visceral organs of body.
Question 27.
Why are the striated muscle fibres called voluntary muscle fibres?
Answer:
Because these are under the will of an animal.

Question 28.
Which structures are responsible for flexibility of plants?
Answer:
Presence of collenchyma.
Question 29.
Meristematic tissue is associated with which kind of organisms?
Answer:
Plants.
Question 30.
Which tissue is responsible for conduction of food in plants?
Answer:
Phloem.
Question 31.
Write function of xylem.
Answer:
Conduction of water and minerals.
Question 32.
Name the peripheral and water proof dead tissue of old stem of woody trees.
Answer:
Cork.
Question 33.
What is source of cork?
Answer:
Cork is obtained from the stem of oak plant.
Question 34.
Name the protective tissue.
Answer:
1. Single layered epidermis
2. Cork
Question 35.
Name the only living cells of phloem.
Answer:
Phloem parenchyma.
Question 36.
What is the function of phloem?
Answer:
Pholem helps in conduction of food within the plant body.
Question 37.
Which kind of cells lack vessels in plants?
Answer:
Meristematic tissue.

Question 38.
What is the function of aerenchyma?
Answer:
Aerenchyma provide buoyancy to the aquatic plants.
Question 39.
Name the tissue which provide flexibility to plants.
Answer:
Collenchyma.
Question 40.
What is collenchyma?
Answer:
It is formed of thick-walled living cells which provide flexibility.
Question 41.
What is sclerenchyma?
Answer:
It is formed of cells with thick lignified cell wall.
Question 42.
Coconut fibres are formed of which tissue.
Answer:
Sclerenchyma.
Question 43.
What are stomata?
Answer:
Small pores in the epidermis of leaf.
Question 44.
What are guard cells?
Answer:
Stomata are enclosed by two kidney-shaped guard cell.
Question 45.
List two functions of stomata.
Answer:
1. Transpiration and
2. Exchange of gases.
Question 46.
What is epithelial tissue?
Answer:
Epithelial Tissue. Cells are arranged into single or multilayered sheet with no intercellular spaces.

Question 47.
What are two kinds of epithelium?
Answer:
1. Simple epithelium
2. Compound epithelium.
Question 48.
Write two functions of epithelium.
Answer:
1. Protection
2. Absorption of material and gases.
Question 49.
What is cartilage?
Answer:
It is a non-porous tissue in which intercellular matrix is abundant and composed of proteins with cells called chondroblasts.
Question 50.
What is connective tissue?
Answer:
Connective tissue connects or binds the similar or different kinds of tissue. Cells are scattered and intercellular spaces are filled with matrix.
Question 51.
Name the most abundant tissue found in the human body. Give its function.
Answer:
Connective tissue. It acts as packaging tissue.
Question 52.
Where is fat stored in the body?
Answer:
Fat is stored in adipose tissue found below the skin and around internal organs.

Question 53.
What is the colour of human blood?
Answer:
It is bright-red coloured when oxygenated and purple-red coloured when deoxy- genated.
Question 54.
Which blood corpuscles of human blood are involved in blood clotting at the injury?
Answer:
Blood platelets.
Question 55.
What is serum?
Answer:
Serum is blood plasma which lacks blood clotting proteins so cannot cause blood clotting.
Question 56.
Name three types of blood corpuscles.
Answer:
Erythrocytes (RBCs), Leucocytes (WBCs) and Blood platelets.
Question 57.
What are functions of RBCs?
Answer:
1. Transportation of oxygen as well as carbon dioxide.
2. pH constancy as haemoglobin acts as a buffer protein.

Question 58.
Give the function of lymph.
Answer:
Lymph acts as middle man so helps in exchange of materials between blood and body cells.
Question 59.
What is the life span of human RBCs?
Answer:
115-120 days.
Question 60.
Name the structural and functional units of nervous tissue.
Answer:
Neurons.
Question 61.
How is a nerve formed?
Answer:
Many nerve fibres bound together by connective tissue to form a nerve.

Question 62.
Name the two types of nerve processes of a neuron.
Answer:
Dendrites and Axon.
Question 63.
Name the components of blood.
Answer:
- Plasma
- RBCs
- WBCs
- Blood Platelets.
Question 64.
Name the minerals present in bones.
Answer:
Calcium and Phosphorus.
Question 65.
What is the function of ligament?
Answer:
Ligament connects bone with bone.
Question 66.
What is the function of tendon?
Answer:
Tendon connects bone with muscles.

Question 67.
Write location of cartilage.
Answer:
Ear lobes, tip of nose, wall of trachea.
Question 68.
What is the shape of smooth muscle fibres?
Answer:
Spindle-shaped.
Question 69.
Name the involuntary muscle fibres.
Answer:
Smooth muscle fibres.
Question 70.
Name the voluntary muscle fibres.
Answer:
Striped (skeletal) muscle fibre.
Question 71.
What is neuron?
Answer:
Neuron is the structural and functional unit of nervous tissue.
Question 72.
Give the location and function of cuboidal epithelium.
Answer:
In the germinal epithelium of gonads (testes and ovaries). Cells divide by meiosis to form gametes (sperms and ova).
Question 73.
Which type of epithelium is located in the mucosa of intestine?
Answer:
Columnar epithelium in which cells have microvilli.
Question 74.
What is the function of vascular tissue in plants?
Answer:
Vascular tissue conducts water and food from one part of plant to the other parts.
Question 75.
What is the advantage of dead cells in plants?
Answer:
Dead cells in plants provide structural strength and need less maintenance.
Question 76.
What is histology?
Answer:
Microscopic study of tissues is called histology.

Question 77.
What are unicellular organisms?
Answer:
Unicellular organisms. The body is comprised of one cell which performs all the functions.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()