Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class English Book Solutions Chapter 2 The Aged Mother Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Class 8th English Solutions Chapter 2 The Aged Mother Question Answers
The Aged Mother Class 8 Questions and Answers
Activity 1
Look up the following words in a dictionary. You should seek the following information about the words and put them in your WORDS notebook.
1. Meaning of the word as used in the lesson (adjective/noun/verb. etc.)
2. Pronunciation (The teacher may refer to the dictionary or a mobile phone for correct pronunciation.)
3. Spellings.
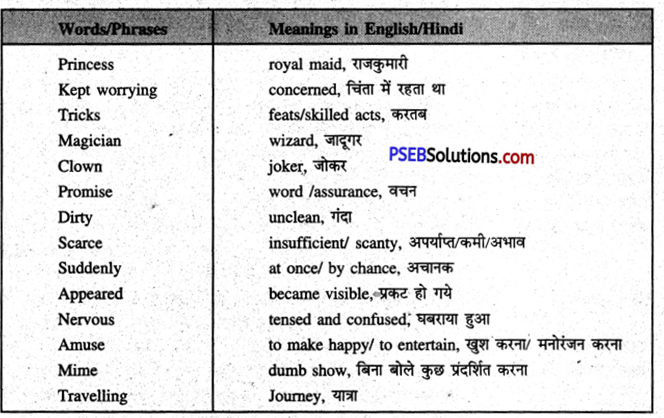
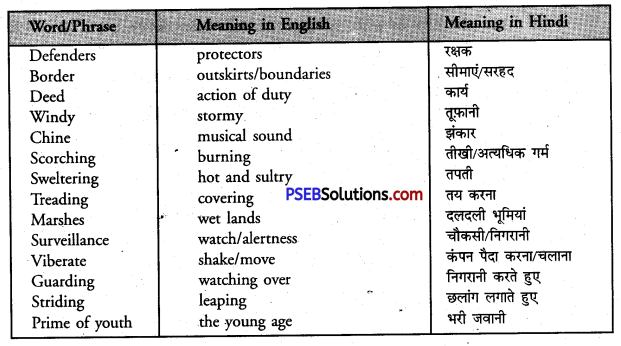
| despotic |
suggestive |
failing |
prompted |
barbarous |
abandoning |
widowed |
| humble |
reckless |
snapped |
. hastened |
blaze |
abolished |
frailty |
Vocabulary Expansion
Activity 2
Put a tick on the option that brings out the meaning of the underlined word.
1. It was governed by a despotic leader.
(a) A person who expects everyone to obey all his orders.
(b) A person who loves his people.

2. He had a great dislike for anything suggestive of failing health and strength.
(a) giving an idea of
(b) typical
3. This prompted him to make a cruel law for the province.
(a) encouraged to do something
(b) made a rule
4. Those were barbarous days.
(a) uncivilized
(b) crude
5. The custom of abandoning old people to die was not uncommon.
(a) to leave or desert
(b) to discontinue
6. The narrow road was crossed and re-crossed by many paths made by the hụnters and the woodcutters.
(a) small width
(b) big
7. She stretched forth her hand and snapped the twigs from bushes.
(a) broke
(b) pulled
8. His demand was that his subjects should present him with a rope of ash.
(a) people
(b) studies

9. That very hour the cruel law was abolished.
(a) came to an end
(b) destroyed
10. He realised that old age meant experience of life and not frailty.
(a) physical weakness
(b) strength
Answer:
1. (a) A person who expects everyone to obey all his orders
2. (a) giving an idea of
3. (a) encouraged to do something
4. (a) uncivilized
5. (a) to leave or desert
6. (a) small width
7. (a) broke
8. (a) people
9. (a) came to an end
10. (a) physical weakness.
Learning to Read and Comprehend
Activity 3:
Rearrange the sentences given below in the correct sequence.
Write the numbers in the given brackets. The first one is done for you.
1. The son decided to take his mother back home.
2. A farmer decided to leave his old mother on the top of a mountain.
3. The governor realized his mistake and abolished the law.
4. Once in Shining, a cruel ruler made a law that all the old people must be put to death.
5. Using the idea of his old and experienced mother, the farmer made a rope of ash.
6. When the farmer turned to go back home, the mother advised him to return home with the help of twigs.
7. Filled with fear, he hid his mother in his home.
8. The mother dropped the small twigs as markers on the way to help her son return home safely.
Answer:
1. Once in Shining, a cruel ruler made a law that all the old people must be put to death.
2. A farmer decided to leave his old mother on the top of a mountain.
3. The mother dropped the small twigs as markers on the way to help her son return home safely.
4. When the farmer turned to go back home, the mother advised him to return home with the help of twigs.
5. The son decided to take his mother back home.
6. Filled with fear, he hid his mother in his home.
7. Using the idea of his old and experienced mother, the farmer made a rope of ash.
8. The governor realized his mistake and abolished the law.

Activity 4.
Answer the following questions in one or two sentences.
Question 1.
What was the cruel announcement made by the despotic leader ?
तानाशाह नेता द्वारा क्या घोषणा की गई ?
Answer:
It was to put all the aged in the province to death.
Question 2.
Why was the farmer sorrowful ?
Answer:
The farmer was sorrowful because he loved his old mother very much. He did not want to leave her.
Question 3.
What things did the farmer carry to the top of the mountain ?
किसान पर्वत की चोटी पर क्या-क्या चीजें ले गया ?
Answer:
The farmer carried some cooked rice and a pot filled with cold water to the top of the mountain.
Question 4.
What made the mother anxious as they climbed up the mountain ?
पहाड़ी पर चढ़ते समय माँ को किस बात ने चिंतित किया?
Answer:
Many paths to the top of the mountain were unknown to the son. This made the mother anxious. She got worried about her son to lose his way on his return.
Question 5.
What did the mother drop along the way?
माँ ने रास्ते के साथ-साथ क्या गिरा दिया ?
Answer:
The mother dropped twigs along the way.

Question 6.
What was the advice given by the farmer’s mother for the safe return of her son ?
किसान की माँ ने अपने पुत्र की सुरक्षित वापिसी के लिए क्या परामर्श दिया ?
Answer:
She adviced her son to follow the path dotted with piles of twigs.
Question 7.
Where did the farmer hide his mother?
किसान ने अपनी माँ को कहाँ छिपाया ?
Answer:
The farmer hide his mother in a walled closet under their kitchen floor.
Question 8.
When did the Governor realize his mistake ?
गवर्नर को अपनी गलती का अहसास कब हुआ ?
Answer:
The governor realized his mistake when he came to know the truth of real wisdom. He realized that real wisdom comes with a growing age.
Activity 5
Identify the underlined character(s).
1. He gave orders for the aged to be put to death.
2. He considered the order to be the kindest mode of death.
3. She quietly dropped some twigs on the way.
4. Together we will follow the path, together we will die.
5. He listened and meditated in silence.
Answer:
1. The governor of Shining
2. the farmer
3. the farmer’s old mother
4. the farmer and his old mother
5. The governor.
The Determiners
To determine’ means to mark, to fix or to limit. Therefore, a determiner is a word which limits or fixes the meaning of a noun. It is also called a Noun-marker.
‘Determine’ का अर्थ है कुछ निर्धारित करना या सीमित करना। इस तरह Determiner वह शब्द है जो Noun के अर्थ को ‘निश्चित करता है या एक सीमा में बांधता है। इसे Noun-marker भी कहा जाता है।
Examples :
1. He helped his friend.
2. My friend gave me a pen.
In sentence 1. ‘his’ is a determiner. It tells us that ‘he’ helped only ‘his friend and no one else. In sentence

2. the word ‘my’ is a determiner.
Note : A determiner limits or fixes only the noun and not any other part of speech.
For example : Veena is a good girl. In this sentence a refers to the noun ‘girl and the adjective ‘good’ makes no difference to the function of a. Kinds of Determiners.
There are five types of determiners :
1. Articles – a, an, the
2. Possessives – my, our, your, his, her, their, its.
3. Numerals – one, two, three, four, first, second, etc.
4. Quantitative – all, any, little, a little, much, some, etc.
5. Demonstratives – this, that, these, those. 1. Articles
There are two types of articles :
1. Indefinite articles – ‘a’, ‘an’
2. Definite article – the
(a) Indefinite articles : ‘A’and ‘an’ are indefinite articles. They are used before a countable common noun in singular number. They are called indefinite articles because they are used with indefinite names.
Examples : a boy, a pencil, an apple, etc.
Use of ‘a’ and ‘an’
1. ‘An’ is generally used with countable common nouns in singular numbers before words beginning with a vowel sound.
For example : an apple, an egg, an MLA, an umbrella, an incident.
2. If a word begins with a silent h, ‘an’ is used before it.
For example : an hour, an honest man.
3. When a word begins with a vowel letter ‘u’ sounding like ‘you’, ‘& is used before ‘it instead of ‘an’.
For example : a university, a union.
4. If a word begins with a vowel letter é sounding like ‘you’, ‘k’ is used instead of ‘an’.
For example : a European.
5. If a vowel gives the sound of ‘w’, ‘a’ is used.
For example : a one-eyed man, a one-rupee coin.

6. ‘A’ and an’ are used in expressions denoting price, speed, ratio etc.
For example : thirty miles an hour
twenty rupees a day
two of a trade
7. ‘A’ is used in some numerical expressions.
For example :
a great deal, a lot of, a dozen, a hundred
8. ‘A’ is used with few’ and ‘little’.
For example :
I borrowed a few books from him.
A little knowledge is a dangerous thing.
(b) Definite Article :
“The’ is called the definite article because it points out to a definite person or a thing.
1. I met a boy.
2. The boy told me a story.
3. The story was very interesting.
In the first sentence ‘a boy’ means any boy and not a particular person.
In the second sentence, ‘the boy’ refers to a particular person. Similarly, in the second sentence ‘a story’ means any story. But in the third sentence ‘the story’ means a particular story.
Use of ‘the’
“The’ is used to denote a particular person, place or thing.
For example:
1. He is the boy who won the prize.
2. She has gone to the bus stop.
“The’ is used when a person, place or thing has already been mentioned.
For example :
I bought a bicycle. The bicycle cost me ₹5000.
‘The’ is used to denote the whole class or community.
For example : The dog runs fast.
Special ‘use of the’ :
1. Before the names of rivers, mountain ranges, oceans, groups of islands, bays, descriptive names of states and countries :
the Ganges
the Ravi/Beas
the Shivaliks
the Indian Ocean
the Andaman and Nicobar Islands
the Bay of Bengal
the USA

2. Before the names of newspapers, magazines, companies, corporations, organizations :
The Tribune
The Hindustan Times
The Life Insurance
The National Book Trust
The Punjab Roadways
3. Before the names of sacred books :
the Ramayana/the Gita
the Guru Granth Sahib
the Quran
the Vedas
the Bible
4. Before musical instruments :
the sitar
the veena
5. Before the names of unique things :
the sun the moon
the stars
6. Before adjectives in superlative degree :
He is the best doctor of the college.
Mumbai is the biggest city in India.
7. Before adjectives used as nouns :
the sick
the poor
8. As part of the phrase made of the comparative degrees :
The higher we go, the colder it gets.
9. When a family name is used to refer to the whole family:
The Malhotras are a happy family.
The position of the Article
Generally the article is placed before the noun it refers to. But when an adjective or an adverb appears before a noun, the article comes before the adjective or the adverb.
For example :
She is a teacher. (before a noun)
She is a good teacher. (before an adjective)
She is a very good player. (before an adverb)
But when the adjective is preceded by “as,’ ‘so’, ‘too’ and ‘how’, the article is used between :the noun and the adjective.

For example:
so beautiful a house
too hot a day
When the noun is preceeded by ‘such’, both’ and ‘all, the article is placed after them.
For example :
I have not seen such a fool.
Both the brothers were present.
All the boys had left.
2. Possessives
(सम्बन्धवाचक शब्द) my, her, your,his, its, our, their सम्बन्धवाचक सर्वनाम है और इनका प्रयोग एक वचन और बहुवचन दोनों प्रकार को संज्ञाओं के साथ किया जाता है जैसे
These determiners are possessive forms of personal pronouns. They can be used both before singular and plural nouns.
For example :
1 I do not lend my books to anyone.
2. We love our teacher.
3. One should do one’s duty.
4. My mother is a doctor.
3. Numerals
Numerals are words that relate to numbers. There are three types of numerals :
Definite Numerals : They refer to a definite or exact number.
The definite numerals are further divided into two kinds:
a. Cardinals : one, two, three, five, etc.
These words can be used before nouns which are countable :
1. Please bring one pen for me.
2. He gave him ten coins.
b. Ordinals : first, second, third, etc.
These words are used to indicate order:
1. The first book was very boring.
2.He was the last man to come.
Indefinite Numerals : They refer to vague or indefinite number such as “many’, ‘few’;’a . few’, ‘the few’, ‘several, ‘all’, etc.
1. I have many things to do.
2. Several people witnessed the accident.
3. He has few friends in the city. (almost none)
4. He does have a few friends in the city. (a small number)
5. The few friends he has are loyal to him. (whatever small number)

Distributive Numerals :
These words refer to each of a group, such as ‘each’, ‘every’, “either’, ‘neither’ etc.
1. Each of us must do so.
2. Each of the boys must do his duty.
3. Either Gurpreet or Harpreet has won the prize.
4. Quantitatives
Words like some’, ‘any’, ‘little’, ‘much etc. are determiners of quantity.
(a) Some and Any: ‘Some’ has positive implications and any’ has negative implications. · Questions with negative implications also take any’. But questions with positive
implications take ‘some’.
Examples :
1. I want some milk. Is there any milk in the house ?
2. I spent some holidays with my uncle.
3. There is hardly any milk.
4. Did you hear any noise ?
5. Do you want books ? We have some very good books.
6. I don’t have any money with me.
7. I have hardly any money.
8. There was hardly any boy in the school.
9. I can lend you some money.
(b) Much : ‘Much’ is used to denote quantity.
He has much money.
Don’t think about it too much.
(c) Little, a little, the little : ‘Little’ has a negative implication. It means ‘hardly any’. A little means ‘some’. “The little means whatever little exists, but the whole of it.
I want to have some water. But there is little water in the pitcher.
However, there is a little in the bucket.
I have drunk the little water the jug had.

5. Demonstratives
This’, ‘that’, ‘these and those are called Demonstrative determiners. They point out the object denoted by the nouns that follow them. “This and that are singular; ‘these and ‘those are plural. They show which person, place or thing is being talked about.
For example :
1. This book is mine and that is yours.
2. These men are hardworking.
3. Those girls sing very well.
Activity 6
Fill in the blanks with suitable determiners.
1. I went to …………….. window which commanded a large green garden.
2. I have …………………. work to do…
3. Lookout of the window for ………………… minute.
4. …………… shirt is costly but ……………….. shirt is cheap.
5. ………………….. books she had were all lost.
6. ………………… pen costs two rupees.
7. But I had …………………. idea of all this.
8. He didn’t make . …………….. mistakes in the essay.
9. I borrowed ……………….. books from him.
10. It educates both ……………….. blind and the helpers.
11. We should look into ………………….. depth of the problem.
12. It was ………………….. daring idea.
13. ………………….. boys attended the class.
14. This is …………….. good home for him.
15. ………………… teachers were asked to be present on Sunday.
16. …………………. sum cannot be solved by ……….. silly boys.
17. Besides them stood Pasteur, holding a narrow tube in … ………… hand.
18. They took samples from ………………. brain of a dog that had died.
19. ………….. little knowledge is …………….. dangerous thing.
20. He takes ……………… interest in me.
Answer:
1. the
2. much
3. a
4. this, that/ my, your
5. The
6. My
7. no
8. any
9. some
10. the
11. the
12. a
13. only, A few
14. a
15. only
16. This, the,
17. his
18. the
19. A, a
20. no.

Activity 7 :
Rewrite the following sentences after correcting them by adding/deleting a word wherever necessary in each sentence :
Question 1.
Only few men are honest.
Answer:
Only a few men are honest.
Question 2.
The man is mortal.
Answer:
Man is mortal.
Question 3.
He acted like man.
Answer:
He acted like a man.
Question 4.
Beas flows in Punjab.
Answer:
The Beas flows in the Punjab.
Question 5.
You are in wrong but he is in right.
Answer:
You are in the wrong but he is in the right.
Question 6.
He is by far ablest boy.
Answer:
He is by far the ablest boy.
Question 7.
Nobody likes a person with bad temper.
Answer:
Nobody likes a person with a bad temper.
Question 8.
The iron is useful metal.
Answer:
Iron is a useful metal.
Question 9.
Not word was said.
Answer:
Not a word was said.
Question 10.
He has too high a opinion of you.
Answer:
He has too high an opinion of you.
Question 11.
Learn this poem by the heart.
Answer:
I learn this poem by heart.

Question 12.
Never tell lie.
Answer:
Never tell a lie.
Leaning to Listen
Activity 8.
Listen to your teacher carefully. She/he will tell you a story. Write the story in the given space as you hear it. Listen carefully to the pauses and tone and use appropriate punctuation marks.
Answer:
The Lion and the Boar
It was a hot summer day. A lion and a boar reached a small water body for a drink. They began arguing and fighting about who would drink first. After a while they were tired and stopped for breath, when they noticed vultures above. Some. they realized that the vultures are waiting for one or both of them to fall, to feast on them. The lion and the boar then decided that it were best to make up and be friends than fight and become food for vultures. They drank the water together and went their own ways.

Learning to Speak
Role Play
Making Telephone Calls in Emergency
There are special emergency numbers that you can dial in an emergency. For example, to call the police you need to dial 100 from your phone. Other emergency calls could be made to the ambulance service, fire station, trauma centres, etc. When making such calls, we must give quick and adequate information. Our address or location and our contact details are most important. We must also be able to tell them the reason for our call i.e. what kind of emergency we are dealing with.
Look at the following conversation for proper understanding :
Police station : Hello, this is Mullanpur Police Station.
You : Hello, there is a hit and run case. A boy is lying injured on the road.
Police station : Please give us your location details.
You : I am standing near the main office of Omaxe Township. I will send you my mobile location.
Police station : That will be very helpful!
You : Can you also call an ambulance please ? He needs immediate medical attention.
Activity 9.
Create a dialogue between yourself and the Fire station informing them about the fire near your house. Once you have written the dialogue in your notebooks, practise it with your partner. You must take turn to play both roles.
Answer:
I : Hurry up ! There is a big fire in Sector 11.
Fire station : What is the location ?
I : It is just behind the Rose Model School Building.
Fire station : Worry not! The Fire Brigade reaches within five minutes.
I : How can we help you?
Fire station : Look ! Try to keep the traffic away from the road.
Story Writting
Activity 10
Write a short story. You may use some of the following words and phrases :
- felt scared
- heard the sound in the cupboard
- thought it must be a thief
- might be a killer
- lay still
- could hardly breathe
- felt someone touched my foot
- shouted with fear
- parents came and switched on light
- saw a rat
Begin your story with :
Suddenly, I woke up. It was very dark. I felt there was someone in my room. I tried to guess who it could be. It might be a thief. It could be a killer. I got scared and lay still. I could hardly breathe, out of fear. I felt someone touching my foot. I shouted loudly. At that very moment, my parents came and switched on the light. We all burst into laughter when we saw a rat close to my bed.

Learning to Use the language (Grop Work)
Activity 11
Suppose your classroom has been attacked by a swarm of bees. It is time to go back home. Get into groups of five and think of how you will take your bags from the classroom full of bees. You will get 5 minutes to discuss.
Answer:
When you have finished discussing, your chosen group leader will present your ideas in front of the class. The teacher will observe and discuss good, practical and impractical points.
Group leader : We are going to cover our body with blankets, lying in the emergency room. We will produce smoke by burning a rags. It will make the bees fly away. We will quickly pick up our bags and come out of the room.
Teacher : This method may work successfully. But some bees may not fly away. You must: keep this point in mind.
Comprehension of passage
Read the following passages and answer the questions given below each :
(1) Long, long ago there was a province in Japan called Shining. It was governed by a despotic leader. He was a good warrior but he had a great dislike for anything suggestive of failing health and strength. This prompted him to make a cruel law for the province. The entire province was given strict orders to immediately put all the aged people to death. Those were barbarous days and the custom of abandoning old people to die was not uncommon.
In the same province lived a poor farmer and his aged widowed mother at the foot of the mountain. They owned a bit of land which supplied them with food. They were humble, peaceful and happy. The poor farmer loved his aged mother and dealt with her very tenderly. The order by the despot filled his heart with sorrow. Other people did not think twice about obeying the order of the governor but this farmer was very unhappy. However, he had to obey the order so the farmer prepared for what at that time was considered the kindest way of death.
1. What prompted him to make a cruel law ?
उसे किस बात ने क्रूर कानून बनाने के लिए प्रोत्साहित किया ?
2. What was the order given to the people ?
लोगों को क्या आदेश दिया गया
3. Choose true and false statements and write them in your answer-book :
(a) The order by the despot filled the heart of the farmer with delight.
(b) The mother and the son were humble and peaceful.
4. Complete the following sentences according to the meaning of the passage :
(a) The custom of abandoning old people to die was …….
(b) They owned a bit of land which …
Or
Match the words with their meaning :
| (i) entire |
whole |
| (ii) barbarous |
beautiful |
|
cruel |
Answer:
1. He disliked failing health and strength. This prompted him to make a cruel law.
2. The people were ordered to put all the aged people to death immediately.
3. (a) False, (b) True.
4. (a) The custom of abandoning old people to die was not uncommon.
(b) They owned a bit of land which supplied them with food.
Or
(i) entire — whole
(ii) barbarous — cruel.

(2) Just at sunset, when his day’s work ended, he took some unwhitened rice which was the main food for the poor and cooked it, dried it and tied it in a cloth which he swung in a bundle around his neck along with a pot filled with cool water. Then he lifted his helpless old mother on his back and started on his painful journey up the mountain. The road was long and steep. The narrow road was crossed and re-crossed by many paths made by the hunters and the woodcutters. At some places, they got lost and confused but he did not think about it. He was about to abandon his dear mother so it did not matter. which path he took to reach the mountain top. On he went, climbing blindly upward-ever upward towards the high bare summit known as Obatsuyama, the mountain where the aged were abandoned.
1. Where did he take his old mother?
2. Why was the journey painful ?
3. Choose true and false statements and write them in your answer-book :
(a) The name of the high bare summit was Shining.
(b) Unpolished rice was the main food for the people.
4. Complete the following sentences according to the meaning of the passage :
(a) In this bundle, along with rice there was a pot ……..
(b) The summit where …………… was known as obatsuyama.
Or. Write the meaning of the following words in English : (Any two)
helpless, summit, puzzled.
Answer:
1. He took his old mother to the top of a mountain.
2. The journey was painful because it lay through a mountain. The road was long and steep. Beside, the son was carrying his helpless old mother on his back.
3. (a) False
(b) True.
4. (a) In the bundle, along with rice, there was a pot filled with cool water.
(b) The summit where the aged were abandoned was known as obatsuyama.
Or
poor, top, confused.
(3) The eyes of the old mother were not so dim that they could not notice the reckless hastening from one path to another and her loving heart grew anxious. Her son did not know many paths of the mountain and his return might be dangerous so she stretched forth her hand and snapped twigs from bushes as they passed. She quietly dropped a handful every few steps of the way so that as they climbed, the narrow path behind them was dotted with tiny piles of twigs. At last, the summit was reached. Weary and heartsick, the youth gently released his burden and silently prepared a place of comfort as his last duty to the loved one. Gathering fallen pine needles, he made a soft cushion and tenderly lifted his old mother onto it. He wrapped her padded coat more closely about her stooping shoulders and with tearful eyes and an aching heart, he had farewell to his mother.

1. Why did the old mother grow anxious ?
वृद्ध मोँ चिंता में क्यों पड़ गई
2. Why did he prepare a place of comfort ?
उसने आरामदायक स्थान क्यों तैयार किया ?
3. Choose true and false statements and write them in your answer-book :
(a) The summit was reached easily.
(b) He had farewell to his mother with tearful eyes.
4. Complete the following sentences according to the meaning of the passage :
(a) Gathering fallen pine needles, he made a
(b) The narrow path behind them was dotted with …
Or
Match the words with their meaning :
| (i) Weary |
softly and slowly |
| (ii) tenderly |
heavy |
|
tired |
Answer:
1. The old mother grew anxious because her son did not know many paths of mountain. So his return might be dangerous.
2. He prepared a place of comfort for his old mother. It was a symbol of his last duty to his loved mother.
3. (a) False
(b) True.
4. (a) Gathering fallen pine needles, he made a soft cushion.
(b) The narrow path behind them was dotted with tiny piles of twigs.
Or
tired
(i) Weary — tired
(ii) Tenderly — softly and slowly.
(4) The entire province of Shining trembled with fear. The order had to be obeyed but how could any one make a rope of ash ? One night, in great distress, the son whispered the news to his hidden’ mother. “Wait”, she said, “Let me think … Let me think”. On the second day, she told him what to do, “Make a rope of twisted straw.” she said. “Then stretch it upon a row of flat stones and burn it on a windless night.” He called the people together and did as she had said. When the blaze died down, there upon the stones, with every twist and fiber showing perfectly, lay a rope of ash.
The governor was pleased at the wit of the youth and praised greatly but he demanded to know where he had obtained his wisdom from. “Alas! Alas!” cried the farmer, “the truth must be told!” and with deep bows, he narrated his story. The governor listened and then meditated is silence. Finally, he lifted his head. “Shining needs more than the strength of youth,” he said gravely. “Ah, how could I have forgotten the well-known saying, “With the crown of snow, there cometh wisdom !” That very hour, the cruel law was abolished as he realised that old age means experience of life and not frailty.
1. What was the order given to the people of Shining ?
Shining के लोगों को क्या आदेश दिया गया था?
2. Who made the rope and how ?
रस्सी किसने बनाई और कैसे ?
3. Choose true and false statements and write them in your answer-book :
(a) The entire province of Shining jumped with joy.
(b) “With the crown of snow, there cometh wisdom” is a well-known saying.
4. Complete the following sentences according to the meaning of the passage :
(a) Shining needs more than the …………..
(b) That very hour, the cruel law …………….
Or Write the meanings of the following words in English : (Any two) wit, meditated, gravely.
Answer.
1. The people of Shining given the order of making a rope of ash.
2. The young farmer made the rope. He made it by burning some twisted straw on a windless night.
3. (a) False
(b) True.
4. (a) Shining needs more than the strength of youth.
(b) That very hour, the cruel law was abolished.
Or wit—wisdom, meditated—thought over something deeply, gravely—-seriously.
Use Of Words And Phrases in Sentences
1. Warrior – Arjuna was a great warrior.
2. Abolish – The British government abolished the salt law.
3. Prompt – His cruel nature prompted him to tease the poor beggar.
4. Humble – My father is very humble at heart.
5. Peaceful – The villagers are very peaceful.
6. Boast of – Never boast of your wealth.
7. Summit – The Himalayas have many high summits.
8. Distress – He is in great distress these days.
9. Pleased at – I am pleased at his honesty.
10. Blaze – The sudden blaze almost blinded him.
Word Meaning
The Aged Mother Summary in Hindi
Long, long ago …………………… aged were abandoned.
बहुत समय पहले जापान में शीनिंग (Shining) नामक एक प्रांत था। वहाँ पर एक निरंकुश नेता का शासन था। वह एक अच्छा योद्धा था परन्तु उसे गिरते स्वास्थ्य और ताकत के बारे में कोई भी बात अच्छी नहीं लगती थी। इस बात ने उसे प्रांत के लिए एक क्रूर कानून बनाने के लिए उकसाया। पूरे प्रांत में सभी वृद्धों को तुरन्त मार डालने के सख्त आदेश जारी कर दिए गए। ये बर्बरता के दिन थे और वृद्ध लोगों को मरने के लिए छोड़ देना कोई असामान्य बात नहीं थी। . इसी प्रांत में पहाड़ी के तल पर एक ग़रीब किसान अपनी बूढ़ी विधवा माँ के साथ रहता था। उनके पास भूमि का एक छोटा सा टुकड़ा था जिससे वे जीवनयापन करते थे।
वे विनम्र, शांतिप्रिय तथा खुश थे। गरीब किसान अपनी वृद्ध माँ को बहुत प्यार करता था और वह उसके साथ बहुत ही नम्रतापूर्वक व्यवहार करता था। तानाशाह के आदेश से उसका मन दु:खी हो गया। अन्य लोगों ने शासक के आदेश का पालन करने पर एक बार भी पुनः विचार नहीं किया। परन्तु किसान बहुत ही अप्रसन्न था। फिर भी उसे आदेश का पालन करना था इसलिए किसान ने वह तरीका अपनाने की तैयारी कर ली जो उस काल में मृत्यु का सबसे दयापूर्ण तरीका माना जाता था।

शाम के समय जब दिनभर का कार्य समाप्त हो गया, उसने कुछ कच्चे चावल जो गरीबों का मुख्य भोजन था लिये और उन्हें पकाया। उसने चावलों को सुखाकर एक कपड़े में इनकी गठरी बना कर उसने इन्हें अपने गले में लटका लिया। उसने ठण्डे पानी से भरा एक, बर्तन भी उनके साथ लटका लिया। तब उसने अपनी लाचार बूढ़ी माँ को अपनी पीठ पर उठा लिया और पहाड़ी पर अपनी कष्टभरी यात्रा के लिए चल पड़ा। सड़क लम्बी और सीधी खड़ी थी। संकरी सड़क को जगह-जगह पर शिकारियों और लकड़हारों द्वारा बनाए गए रास्ते काटते रहे।
कुछ स्थानों पर वे उलझ गए और भटक गए परन्तु उसने इस बारे में नहीं सोचा। उसे तो अपनी प्रिय माँ को त्यागना था, इसलिए इस बात का कोई महत्त्व नहीं था कि वह किस रास्ते से पहाड़ की चोटी पर पहुँचे। वह अन्धा-धुंध ऊपर की ओर चढ़ता गया और अधिक ऊपर उस वनस्पति हीन शिखर की ओर जो Obatsuyama के नाम से जाना जाता था। यह वह पर्वत था जहाँ वृद्धों को त्यागा (छोड़ा) जाता था। .
The eyes of the old……….. we will die !”
वृद्ध माँ की आँखें इतनी धुंधली नहीं हुईं थीं कि वे लापरवाही से एक मार्ग से दूसरे मार्ग पर जाते हुए कदमों को न भांप सकें। उसका प्रेम भरा मन चिंतित हो उठा। उसके पुत्र को पर्वत के बहुत से मार्गों की जानकारी नहीं थी और इससे उसकी वापसी खतरनाक हो सकती थी। इसलिए आगे बढ़ते हुए उसने अपने हाथों को फैला लिया और झाड़ियों की टहनियां तोड़ती गई। वह ऊपर चढ़ते हुए थोड़ी-थोड़ी दूरी पर चुपचाप मुट्ठी भर गिराती रही। उनके पीछे के संकरे मार्ग पर टहनियों के छोटे-छोटे ढेर लग गए थे।
अंत में वे शिखर पर पहुँच गए। थके हुए और मायूस नवयुवक ने धीरे से अपने बोझ को उतारा और चुपचाप अपने अंतिम कर्त्तव्य के लिए आराम भरे एक स्थान को तैयार करने लगा। उसने चीड़ के पेड़ की नुकीली पत्तियों को इकट्ठा करके एक मुलायम गद्दी बनाई और अपनी वृद्ध माता को उस पर बिठा दिया। उसने उसके नर्म कोट को उसके झुके कंधों के और अधिक निकट तक कर दिया और रोते हुए तथा दुःखी मन से अपनी माता से अलविदा कहा।
उसकी माँ ने कांपती आवाज़ तथा नि:स्वार्थ प्यार से उसे अंतिम निर्देश दिए। उसने कहा, “पुत्र अपनी आँखें बंद न होने देना । पर्वत का रास्ता खतरों से भरा हुआ है। ध्यानपूर्वक देखना और उस मार्ग पर चलना जहाँ तुम्हें टहनियों के ढेर दिखें। वे तुम्हें और नीचे जाने के परिचित मार्ग पर ले जाएंगे।” पुत्र ने हैरानी भरी नज़रों से पीछे मार्ग की ओर देखा और फिर अपनी लाचार वृद्ध माँ के थके-हारे हाथों को देखा जिनमें उसके प्यार भरे कार्य के कारण खरोंचें आई हुई थीं और जो मैले हो गए थे।
गवर्नर नवयुवक की बुद्धिमता पर खुश था और उसने उसकी भरपूर प्रशंसा की। परन्तु उसने यह जानने की माँग रखी कि उसने यह बुद्धिमता कहाँ से प्राप्त की। किसान चिल्लाया, “अरे मर गए !’ सच्चाई तो बतानी पड़ेगी !” पूरी तरह झुकते हुए उसने सारी कहानी कह सुनाई। शासक ने सुना और फिर खामोश होकर सोचने लगा। अंततः उसने अपना सिर उठाया। उसने गंभीरता से कहा, “शीनिंग (Shining) को नवयुवकों की ताकत से ज्यादा कुछ और चाहिए।”आह, मैं इतनी प्रसिद्ध कहावत कैसे भूल गया कि बुद्धिमता सफ़ेद बालों (उम्र) के साथ आती है।” उसी क्षण उसने क्रूर कानून को समाप्त कर दिया। उसे आभास हो गया कि बुढ़ापा जीवन का अनुभव है न कि निर्बलता।
Retranslation From English to Hindi
वहां पर एक निरंकुश नेता का शासन था। उनके पास भूमि का एक छोटा सा टुकड़ा था जिससे वे जीवनयापन करते थे। वे विनम्र, शांतिप्रिय तथा खुश थे।
1. It was governed by a deposite leader. —- वहां पर एक निरंकुश नेता का शासन था।
2. They owned a bit of land which supplied them with food. —- उनके पास भूमि का एक छोटा सा टुकड़ा था जिससे वे जीवनयापन करते थे।
3. They were humble, peaceful and happy. —- वे विनम्र, शांतिप्रिय तथा खुश थे।
4. The poor farmer loved his aged mother. —- ग़रीब किसान अपनी वृद्ध माँ से बहुत प्यार करता था।
5. However, he had to obey the order. —- फिर भी उसे आदेश का पालन करना था।
6. The road was long and steep. —- सड़क लम्बी और सीधी खड़ी थी।
7. They got lost and confused. —- वे उलझ गए और भटक गए।
8. He was about to abandon his dear mother. —- वह अपनी प्रिय माँ को त्यागने ही वाला था।
9. Her son did not know many paths of mountain.—- उसके पुत्र को पर्वत के बहुत से मार्गों की जानकारी नहीं थी।
10. The youth gently released his burden. —- नवयुवक ने धीरे से अपना बोझ उतारा
11. He wrapped her padded coat more closely. —- उसने उसके नर्म कोट को और अधिक निकट तक कर दिया।
12. The mountain road is full of dangers. —- पर्वत का रास्ता खतरों से भरा हुआ है।
13. The son hid his mother. —- पुत्र ने अपनी माँ को छिपा लिया।
14. The governor was pleased at the wit the youth. —- गवर्नर नवयुवक की बुद्धिमता पर खुश था।
15. Finally, he lifted his head. —- अंतत: उसने अपना सिर उठाया।
16. The cruel law was abolished.—- क्रूर कानून को समाप्त कर दिया गया।
English Guide for Class 8 PSEB Prose
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()