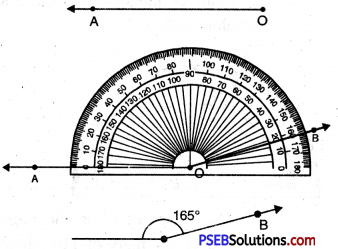
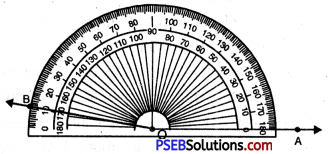
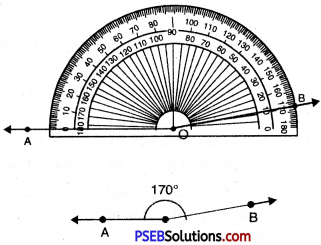
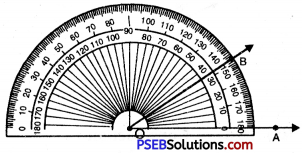
Punjab State Board PSEB 6th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 11 Ratio and Proportion Ex 11.1 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 11 Ratio and Proportion Ex 11.1
1. Express the following ratios in the simplest form:
Question (i)
12 : 32
Solution:
To express this ratio in the simplest form, we shall have to divide both terms by their H.C.F.

So H.C.F. of 12 and 32 = 4
∴ 12 : 32= (12 ÷ 4) : (32 ÷ 4)
= 3 : 8
![]()
Question (ii)
45 : 25
Solution:
To express this ratio in the simplest form, we shall have to divide both terms by their H.C.F.
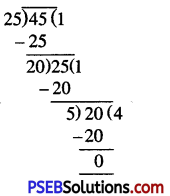
So H.C.F. of 45 and 25 = 5
∴ 45 : 25 = (45 ÷ 5) : (25 ÷ 5)
= 9 : 5
Question (iiii)
91 : 104
Solution:
To express this ratio in the simplest form, we shall have to divide both terms by their H.C.F.

So H.C.F. of 91 and 104 = 13
∴ 91 : 104 = (91 ÷ 13) : (104 ÷ 13)
= 7 : 8
Question (iv)
60 : 72
Solution:
To express this ratio in the simplest form, we shall have to divide both terms by their H.C.F.

So H.C.F. of 60 and 72 = 12
∴ 60 : 72 = (60 + 12) : (62 ÷ 12)
= 5 : 6
![]()
Question (v)
375 : 125.
Solution:
To express this ratio in the simplest form, we shall have to divide both terms by their H.C.F.

So H.C.F. of 375 and 125 = 125
∴ 375 : 125 = (375 ÷ 125) : (125 ÷ 125)
= 3 : 1
2. Write the ratio in the simplest form:
Question (i)
₹ 20 to ₹ 55
Solution:
₹ 20 to ₹ 55
= 20 : 55
= (20 ÷ 5) : (55 ÷ 5)
[Divide both terms by their H.C.F.]
= 4:11
Question (ii)
18 m to 63 m
Solution:
18 m to 63 m
= 18 : 63 [H.C.F. of 18 and 63 = 9]
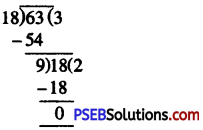
= (18 ÷ 9): (63 ÷ 9)
= 2 : 7
![]()
Question (iii)
40 paise to ₹ 2
Solution:
40 paise to ₹ 2
= 40 paise to 200 paise
(₹ 1 = 100 paise)
= 40 : 200
[H.C.F. of 40 and 200 = 40]

= 1 : 5
Question (iv)
One hour to 36 minutes
Solution:
One hour to 36 minutes
= 60 minutes to 36 minutes
(1 hour = 60 minutes)
= 60 : 36
[H.C.F. of 60 and 36 = 12]
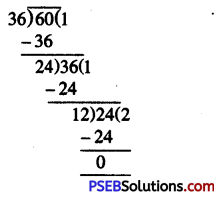
= (60 ÷ 12) : (36 ÷ 12)
= 5 : 3
Question (v)
5 kg to 1200 g.
Solution:
5 kg to 1200 g
= 5000 g : 1200 g
( ∵ 1 kg = 1000 g) [H.C.F. of 5000 and 1200]
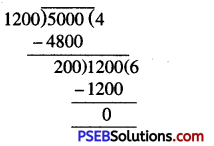
= 5000 : 1200
= (5000 ÷ 200) : (1200 ÷ 200)
= 25 : 6
![]()
3. Simplify the following ratios:
Question (i)
2 years : 14 months
Solution:
2 years : 14 months
= 24 months : 14 months
(∵ 1 year =12 months)
= 24 : 14 [H.C.F. of 24 and 14 = 2]
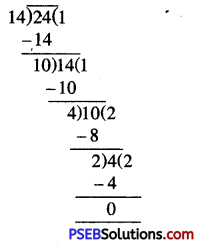
= (24 ÷ 2) : (14 ÷ 2)
= 12 : 7
Question (ii)
28 min : 2 hours
Solution:
28 min : 2 hours
= 28 min : 120 min
(∵ 1 hour = 60 min)
= 28 : 120
[H.C.F. of 28 and 120 = 4]

= (28 ÷ 4) : (120 ÷ 4)
= 7 : 30
![]()
Question (iii)
125 ml: 21
Solution:
125 ml : 2 l
= 125 ml : 2000 ml
(∵ 1 l = 1000 ml)
= 125 : 2000
[H.C.F. of 125 and 2000 = 125]

= (125 ÷ 125) : (2000 ÷ 125)
= 1 : 16
Question (iv)
4 m 20 cm : 80 cm
Solution:
4 m 20 cm : 80 cm
= 420 cm : 80 cm
(∵ 1 m = 100 cm)
= 420 : 80
[H.C.F. of 420 and 80 = 20]

= (420 ÷ 20) : (80 ÷ 20)
= 21 : 4
Question (v)
3 dozen : 12 pieces.
Solution:
3 dozen : 12 pieces
= 36 pieces : 12 pieces
(∵ 1 dozen =12 pieces)
= 36 : 12
[H.C.F. of 36 and 12 = 12]

= (36 ÷ 12) : (12 ÷ 12)
= 3 : 1
![]()
4. Find two equivalent ratios for each given ratio:
Question (i)
4:1
Solution:
4 : 1
4 × 2 : 1 × 2 = 8 : 2
(Multiply both terms by 2)
or 4 × 3 : 1 × 3 = 12 : 3
(Multiply both terms by 3)
∴ 8 : 2 and 12 : 3 are two equivalent ratios
Question (ii)
3:5
Solution:
3 : 5
3 × 2 : 5 × 2 = 6 : 10
(Multiply both terms by 2)
or 3 × 3 : 5 × 3 = 9 : 15
(Multiply both terms by 3)
Thus two equivalent ratios for 3 : 5 are 6 : 10 and 9 : 15
Question (iii)
5 : 12.
Solution:
5 : 12
5 × 2 : 12 × 2 = 10 : 24
(Multiply both terms by 2)
or 5 × 3 : 12 × 3 = 15 : 36
(Multiply both terms by 3)
Thus two equivalent ratios of 5 : 12 are 10 : 24 and 15 : 36
5. The number of boys and girls in a class are 60 and 52 respectively. Find the ratio of number of boys to the number of girls.
Solution:
We have number of boys = 60
and number of girls = 52
Ratio of number of boys to the number of girls = 60 : 52
(Divide both by their H.C.F. = 4)
= 15 : 13
![]()
6. Pankaj has 23 pens and 42 pencils. Find the ratio of pens to pencils.
Solution:
Number of pens = 23
Number of pencils = 42
∴ Ratio of pens to pencils = 23 : 42
7. In a year, Harjot earns ₹ 2,80,000 and saves ₹ 60,000. Find the ratio of money:
Question (i)
He saves to the money he spends.
Solution:
Harjot’s income = ₹ 2,80,000
Haijot’s savings = ₹ 60,000
Haijot’s spendings = ₹ 2,80,000 – ₹ 60,000
= ₹ 2,20,000
Ratio of Harjot’s savings of Haijot’s spendings = 60,000 : 2,20,000 (Divide both terms by their H.C.F.
= 20,000)
= 3:11
Question (ii)
He earns to the money he saves.
Solution:
Ratio of Haijot’s income to Haijot’s savings = ₹ 2,80,000 : ₹ 60,000
(Divide both terms by their H.C.F. = 20,000)
= 14 : 3
Question (iii)
He spends to the money he earns.
Solution:
Ratio of Haijot’s spendings to Haijot’s income = 2,20,000 : 2,80,000
(Divide both terms by their H.C.F. = 20,000)
= 11 : 14
![]()
8. In a school, there are 175 boys, 205 girls students and 20 teachers. Find the ratio of the number of:
Question (i)
Boys to the number of teachers.
Solution:
Number of boys = 175
Number of girls = 205
Number of teachers = 20
Number of total persons in the school = 175 + 205 + 20 = 400.
Ratio of number of boys to the number of teachers = 175 : 20
(Divide both terms by their H.C.F. = 5)
= 35 : 4
Question (ii)
Girls to the number of boys.
Solution:
Ratio of number of girls to the number of boys = 205 : 175
(Divide both terms by their H.C.F. = 5)
= 41 : 35
Question (iii)
Teachers to the number of total persons in the school.
Solution:
Ratio of number of teachers to the number of total persons in the school = 20 : 400
(Divide both terms by their H.C.F. = 20)
= 1 : 20
![]()
9. Out of 144 students in a school, 48 play cricket, 28 play kabaddi, 40 play volleyball and the remaining play kho-kho. Find the ratio of:
Question (i)
Number of students play kabaddi to the number of students play kho- kho.
Solution:
Total number of students in the school = 144
Number of students play cricket = 48
Number of students play kabaddi = 28
Number of students play volley ball = 40
Number of students play kho-kho
= 144 – (48 + 28 + 40)
= 144 – 116
= 28
Ratio of number of students play kabaddi to the number of students play kho-kho
= 28 : 28
= 1 : 1
Question (ii)
Number of students play cricket to the number of students play volleyball.
Solution:
Ratio of number of students play cricket to the number of students play volleyball = 48 : 40
(Divide both terms by their H.C.F. = 8)
= 6 : 5
Question (iii)
Number of students who play kho- kho to the total students of school.
Solution:
Ratio of number of students who play kho-kho to the total students of school = 28 : 144
(Divide both terms by their H.C.F. = 4) = 7 : 36
![]()
10. The present age of Kush and Shelly are 22 years and 16 years respectively. Find the ratio of:
Question (i)
Their present ages.
Solution:
Ratio of present age of Kush to the present age of Shelly = 22 : 16
(Divide both terms by their H.C.F. = 2)
= 11 : 8
Question (ii)
Kush’s age to Shelly’s age after 4 years.
Solution:
After four years Kush’s age
= 22 + 4 = 26 years
After four years Shelly’s age
= 16 + 4 = 20 years
Ratio of Kush’s age to Shelly’s age after four years
= 26 : 20
(Divide both terms by their H.C.F. = 2)
= 13 : 10
Question (iii)
Shelly’s age to Kush’s age before 5 years.
Solution:
Ratio of Shelly’s age to Kush’s age before 5 years
= 17 : 11
![]()
Question (iv)
Kush’s present age to Shelly’s age after 6 years.
Solution:
Ratio of Kush’s present age to Shelly’s age after 6 years
= 22 : 22
(Divide both terms by their H.C.F. = 22)
= 1 : 1
11. In a pencil box there are 150 pencils. Out of which 40 are red, 60 are black and the rest are blue pencils. Find the ratio of:
Question (i)
Red pencils to the black pencils.
Solution:
Total pencils = 150
Red pencils = 40
Black pencils = 60
Blue pencils = 150 – (40 + 60)
= (150 – 100)
= 50
Ratio of Red pencils to the black pencils = 40 : 60
(Divide both terms by their H.C.F. = 20)
= 2 : 3
Question (ii)
Blue pencils to the total number of pencils.
Solution:
Ratio of Blue pencils to the total number of pencils = 50 : 150
(Divide both terms by their H.C.F. = 50)
= 1 : 3
Question (iii)
Total pencils to the red pencils.
Solution:
Ratio of total pencils to the red pencils = 150 : 40
(Divide both terms by their H.C.F. = 10)
= 15 : 4
![]()
12. Divide ₹ 175 in ratio 4 : 3 between Preet and Sukhi.
Solution:
Total Amount = ₹ 175
Ratio =4 : 3
Let Preet’s share = 4 x
and Sukhi’s share = 3 x
Acc. to Question
Preet’s share + Sukhi’s share = ₹ 175
⇒ 4x + 3x = 175
⇒ 7x = 175
x = \(\frac {175}{7}\) = 25
∴ Preet’s share = 4x
= 4 × 25
= ₹ 100
Sukhi’s share = 3x
= 3 × 25
= ₹ 75
13. Two numbers are in the ratio 3:7 and their sum is 140. Find the numbers.
Solution:
Sum of numbers = 140
Ratio = 3 : 7
Let first number = 3x
and second number = 4x
Acc. to Question
(First number) + (Second number)
= 140
⇒ 3x + 7x = 140
⇒ 10 x = 140
x = \(\frac {140}{10}\) = 14
∴ First number = 3x
= 3 × 14
= 42
and Second number = 7x
= 7 × 14
= 98
![]()
14. The angles of a triangle are in the ratio 1 : 2 : 3. Find the measure of each angle.
Solution:
Sum of the angles of the triangle = 180°
Ratio of angles = 1 : 2 : 3
Let First angle = x
Second angle = 2x
Third angle = 3x
Acc. to Question
Sum of three angles = 180°
x + 2x + 3x = 180°
6x = 180°
x = \(\frac {180°}{6}\) = 30°
∴ First angle = x = 30°
Second angle = 2x
= 2 × 30° = 60°
Third angle = 3x
= 3 × 30° = 90°
Thus, the angles of triangle are 30°, 60°, 90°
15. A pipe of length 4 m 16 cm is cut into two pieces in ratio 3:5. Find the length of each piece of the pipe.
Solution:
Length of pipe = 4 m 16 cm
= 416 cm (1 m = 100 cm)
Ratio of two parts = 3 : 5
Let length of first part = 3x
and length of second part = 5x
Acc. to Question
3x + 5x = 416
8x = 416
x = \(\frac {416}{8}\) = 52
∴ Length of first part = 3x
= 3 × 52
= 156 cm
= 1.56 m.
Length of second part = 5x
= 5 × 52
= 260 cm
= 2.60 m