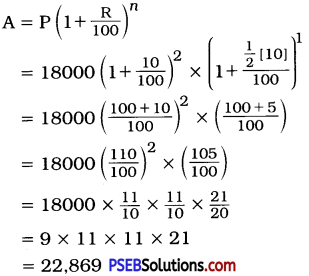
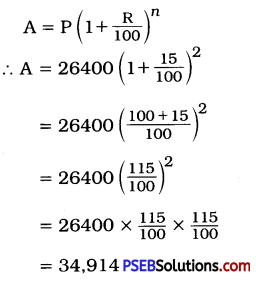
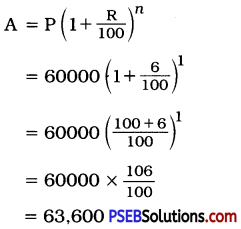
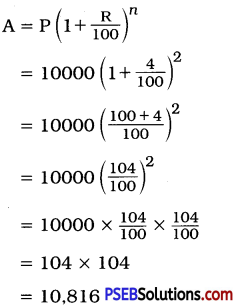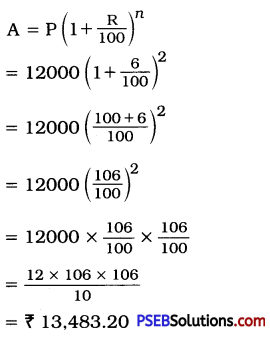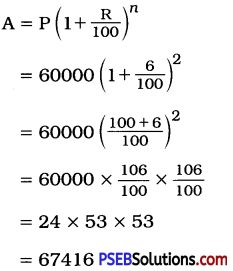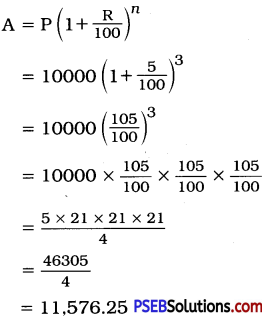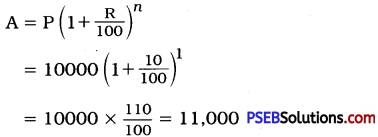Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class Punjabi Book Solutions Chapter 1 ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡਾ Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Punjabi Chapter 1 ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡਾ
(i) ਛੋਟੇ ਉੱਤਰ ਵਾਲੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡੇ ਨੂੰ ਤਿਰੰਗਾ ਕਿਉਂ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਇਸ ਵਿਚ ਤਿੰਨ ਰੰਗ ਹੋਣ ਕਰਕੇ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਹਰਾ ਰੰਗ ਕਿਸ ਗੱਲ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਤੀਕ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਖ਼ੁਸ਼ਹਾਲੀ ਦਾ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਅਮਨ ਦੀ ਨਿਸ਼ਾਨੀ ਕਿਹੜਾ ਰੰਗ ਦਰਸਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਚਿੱਟਾ ਰੰਗ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਕੇਸਰੀ ਰੰਗ ਕਿਸ ਗੱਲ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਤੀਕ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਕੁਰਬਾਨੀ ਦਾ ।
![]()
(ii) ਸੰਖੇਪ ਉੱਤਰ ਵਾਲੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਹਰੇ, ਚਿੱਟੇ ਤੇ ਕੇਸਰੀ ਰੰਗ ਦੀ ਕੀ ਮਹੱਤਤਾ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡੇ ਵਿਚਲਾ ਹਰਾ ਰੰਗ ਦੇਸ਼ ਦੀ ਖ਼ੁਸ਼ਹਾਲੀ, ਚਿੱਟਾ ਰੰਗ ਅਮਨ-ਸ਼ਾਂਤੀ ਤੇ ਕੇਸਰੀ ਰੰਗ ਦੇਸ਼ ਲਈ ਕੁਰਬਾਨੀ ਕਰਨ ਦੀ ਮਹੱਤਤਾ ਨੂੰ ਦਰਸਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਕਵੀ ਨੇ ਕਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਸਤਰਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਭਾਰਤ ਲਈ ਪਿਆਰ ਪ੍ਰਗਟ ਕੀਤਾ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਕਵੀ ਨੇ ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਸਤਰਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਭਾਰਤ ਲਈ ਪਿਆਰ ਪ੍ਰਗਟ ਕੀਤਾ ਹੈ-
ਗੀਤ ਤਿਰੰਗੇ ਦੇ ਰਲ ਕੇ ਗਾਈਏ ।
ਭਾਰਤ ਮਾਂ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਾਨ ਵਧਾਈਏ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਖੇਤਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਖ਼ੁਸ਼ਹਾਲੀ ਕਿਵੇਂ ਟਹਿਕ ਰਹੀ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਖੇਤਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਹਰੀਆਂ-ਭਰੀਆਂ ਬਹੁਮੁੱਲੀਆਂ ਫ਼ਸਲਾਂ ਪੈਦਾ ਹੋਣ ਨਾਲ ਖੁਸ਼ਹਾਲੀ ਟਹਿਕ ਰਹੀ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਤੁਸੀਂ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡੇ ਬਾਰੇ ਹੋਰ ਕੀ ਜਾਣਕਾਰੀ ਰੱਖਦੇ ਹੋ ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡੇ ਵਿਚ ਤਿੰਨ ਰੰਗਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਇਲਾਵਾ ਵਿਚਕਾਰਲੀ ਚਿੱਟੀ ਪੱਟੀ ਵਿਚ ਨੇਵੀ ਬਲਿਊ ਰੰਗ ਦੇ ਅਸ਼ੋਕ ਚੱਕਰ ਦਾ ਚਿੰਨ੍ਹ ਵੀ ਹੈ, ਜਿਸਨੂੰ ਸਾਰਨਾਥ ਵਿਚ ਬਣੇ ਅਸ਼ੋਕ ਥੰਮ ਤੋਂ ਲਿਆ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ, ਜੋ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਤੇ ਤਰੱਕੀ ਦਾ ਚਿੰਨ੍ਹ ਹੈ । 26 ਜਨਵਰੀ ਨੂੰ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰਪਤੀ ਜੀ ਇਸ ਝੰਡੇ ਨੂੰ ਰਾਜ-ਪੱਥ ਉੱਤੇ ਝੁਲਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ ਤੇ 15 ਅਗਸਤ ਨੂੰ ਪ੍ਰਧਾਨ ਮੰਤਰੀ ਜੀ ਇਸਨੂੰ ਲਾਲ ਕਿਲ੍ਹੇ ਉੱਤੇ ਝੁਲਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 5.
‘ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡਾ ਕਵਿਤਾ ਵਿਚ ਮੁੱਖ ਤੌਰ’ ਤੇ ਕੀ ਵਰਣਨ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਇਸ ਕਵਿਤਾ ਵਿਚ ਮੁੱਖ ਤੌਰ ਤੇ ਆਪਣੇ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇਸ਼ ਦੇ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡੇ ਦੀ ਮਹਿਮਾ ਗਾਈ ਗਈ ਹੈ ਤੇ ਇਸ ਦੇ ਤਿੰਨਾਂ ਰੰਗਾਂ ਦੇ ਮਹੱਤਵ ਨੂੰ ਉਜਾਗਰ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਹੀ ਸਾਨੂੰ ਤਿਰੰਗੇ ਝੰਡੇ ਦਾ ਗੀਤ ਗਾਉਣ ਤੇ ਭਾਰਤ ਮਾਂ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਾਨ ਵਧਾਉਣ ਦੀ ਪ੍ਰੇਰਨਾ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਗਈ ਹੈ ।
(iii) ਕੁੱਝ ਹੋਰ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਖ਼ਾਲੀ ਸਥਾਨ ਭਰੋ :
(ੳ) ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡਾ …………… ਪਿਆਰਾ ।
(ਅ) ਹਰੇ ਰੰਗ ਦੀ ਏ ………. !
(ਈ) ………. ਰੰਗ ਹੈ ਚਿੱਟਾ !
(ਸ) ਭਾਰਤ ਮਾਂ ਦੀ ………….. ।
(ਹ) ……….. ਦੇਸ਼ ਦਾ ਸਿਤਾਰਾ ॥
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ਉ) ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡਾ ਤਿਰੰਗਾ ਪਿਆਰਾ ॥
(ਅ) ਹਰੇ ਰੰਗ ਦੀ ਏ ਸ਼ਾਨ ਨਿਰਾਲੀ ।
(ਈ ਅਮਨ ਦੀ ਨਿਸ਼ਾਨੀ ਰੰਗ ਹੈ ਚਿੱਟਾ ।
(ਸ) ਭਾਰਤ ਮਾਂ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਾਨ ਵਧਾਈਏ ।
(ਹ) ਸੂਰਜ ਬਣ ਕੇ ਚਮਕੇ ਦੇਸ਼ ਦਾ ਸਿਤਾਰਾ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਸ਼ਬਦਾਂ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ਣ ਚੁਣੋ :ਤਿਰੰਗਾ, ਖ਼ੁਸ਼ਹਾਲ, ਨਿਸ਼ਾਨੀ, ਗੀਤ, ਸ਼ਾਨ, ਸੂਰਜ ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਤਿਰੰਗਾ
ਖ਼ੁਸ਼ਹਾਲ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਸ਼ਬਦਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਰਲਦੇ ਸ਼ਬਦ ਲਿਖੋ :
ਪਿਆਰਾ – ……………
ਨਿਰਾਲੀ – ……………
ਚਿੱਟਾ – ……………
ਸਿਤਾਰਾ – ……………
ਗਾਈਏ – ……………
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਪਿਆਰਾ – ਨਿਆਰਾ
ਨਿਰਾਲੀ – ਖ਼ੁਸ਼ਹਾਲੀ
ਚਿੱਟਾ – ਮਿੱਠਾ
ਸਿਤਾਰਾ – ਧਾਰਾ
ਗਾਈਏ – ਵਧਾਈਏ ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਸ਼ਬਦਾਂ ਦੀ ਵਾਕਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਕਰੋ :
(ਨਿਰਾਲੀ, ਨਿਸ਼ਾਨੀ, ਖ਼ੁਸ਼ਹਾਲੀ, ਮੇਵਾ, ਧਾਰਾ, ਕੁਰਬਾਨੀ, ਸ਼ਾਨ)
ਉੱਤਰ :
1. ਨਿਰਾਲੀ (ਵੱਖਰੀ, ਦੂਜਿਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਭਿੰਨ, ਅਨੋਖੀ) – ਭਾਰਤ ਮਾਂ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਾਨ ਨਿਰਾਲੀ ਹੈ ।
2. ਨਿਸ਼ਾਨੀ (ਚਿੰਨ੍ਹ) – ਤਿਰੰਗੇ ਝੰਡੇ ਵਿਚਲਾ ਹਰਾ ਰੰਗ ਖ਼ੁਸ਼ਹਾਲੀ ਦੀ ਨਿਸ਼ਾਨੀ ਹੈ ।
3. ਖ਼ੁਸ਼ਹਾਲੀ (ਖ਼ੁਸ਼ੀ ਦਾ ਪਸਾਰ ਹੋਣਾ) – ਜਦੋਂ ਦੇਸ਼ ਸਚਮੁੱਚ ਤਰੱਕੀ ਕਰੇ, ਤਾਂ ਹਰ ਪਾਸੇ ਖ਼ੁਸ਼ਹਾਲੀ ਫੈਲ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ।
4. ਮੇਵਾ (ਸੁੱਕੇ ਮਿੱਠੇ ਫਲ) – ਮੇਵੇ ਵਿਚ ਛੁਹਾਰੇ ਤੇ ਸੌਗੀ ਸ਼ਾਮਿਲ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
5. ਧਾਰਾ (ਵਹਿਣ, ਰੌ) – ਸਾਡੇ ਖੇਤਾਂ ਕੋਲ ਛੋਟੀ ਜਿਹੀ ਨਦੀ ਦੀ ਧਾਰਾ ਵਹਿੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
6. ਕੁਰਬਾਨੀ (ਜਾਨ ਦੇ ਦੇਣੀ) – ਸ਼ਹੀਦ ਭਗਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਦੇਸ਼ ਲਈ ਕੀਤੀ ਕੁਰਬਾਨੀ ਨੂੰ ਕੌਣ ਭੁਲਾ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ ?
7. ਸ਼ਾਨ (ਵਡਿਆਈ) – ਸਾਨੂੰ ਹਮੇਸ਼ਾ ਆਪਣੇ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡੇ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਾਨ ਉੱਚੀ ਰੱਖਣੀ ਚਾਹੀਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 5.
ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੀਆਂ ਸਤਰਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਸੁੰਦਰ ਲਿਖਾਈ ਕਰ ਕੇ ਲਿਖੋ-
ਗੀਤ ਤਿਰੰਗੇ ਦੇ ਰਲ ਗਾਈਏ ।
ਭਾਰਤ ਮਾਂ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਾਨ ਵਧਾਈਏ ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
………………………………………………..
………………………………………………..
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 6.
‘ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡਾ’ ਕਵਿਤਾ ਨੂੰ ਰਲ ਕੇ ਗਾਓ ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ਨੋਟ-ਇਸ ਕਵਿਤਾ ਨੂੰ ਵਿਦਿਆਰਥੀ ਜ਼ਬਾਨੀ ਯਾਦ ਕਰਨ ਤੇ ਰਲ ਕੇ ਗਾਉਣ )
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 7.
‘ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡਾ ਕਵਿਤਾ ਦੀਆਂ ਪੰਜ-ਛੇ ਸਤਰਾਂ ਜ਼ਬਾਨੀ ਲਿਖੋ-
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡਾ ਤਿਰੰਗਾ ਪਿਆਰਾ ।
ਝੱਲੇ ਹਵਾ ਵਿਚ ਲਗਦਾ ਪਿਆਰਾ !
ਹਰੇ ਰੰਗ ਦੀ ਏ ਸ਼ਾਨ ਨਿਰਾਲੀ ।
ਖੇਤਾਂ ਬੰਨੇ ਖੇਡੇ ਖ਼ੁਸ਼ਹਾਲੀ ।
ਸੋਨਾ ਉਪਜੇ ਹਰ ਖੇਤ ਦਾ ਕਿਆਰ ।
ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡਾ ਤਿਰੰਗਾ ਪਿਆਰਾ ॥
ਬਹੁਵਿਕਲਪੀ ਅਤੇ ਬਹੁਤ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਉੱਤਰ ਵਾਲੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ
(ਉ) ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡਾ ਤਿਰੰਗਾ ਪਿਆਰਾ ।
ਭੁੱਲੇ ਹਵਾ ਵਿਚ ਲਗਦਾ ਨਿਆਰਾ ॥
ਹਰੇ ਰੰਗ ਦੀ ਏ ਸ਼ਾਨ ਨਿਰਾਲੀ ॥
ਖੇਤਾਂ ਬੰਨੇ ਖੇਡੇ ਖੁਸ਼ਹਾਲੀ |
ਸੋਨਾ ਉਪਜੇ ਹਰ ਖੇਤ ਦਾ ਕਿਆਰਾ ।
ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡਾ ਤਿਰੰਗਾ ਪਿਆਰਾ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
(i) ਉਪਰੋਕਤ ਕਾਵਿ-ਟੋਟੇ ਦੇ ਭਾਵ-ਅਰਥ ਲਿਖੋ ।
(ii) ਇਹ ਸਤਰਾਂ ਕਿਸ ਕਵਿਤਾ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਹਨ ?
(iii) ਇਹ ਕਵਿਤਾ ਕਿਸੇ ਦੀ ਲਿਖੀ ਹੋਈ ਹੈ ?
(iv) ਸਾਡੇ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡੇ ਦਾ ਕੀ ਨਾਂ ਹੈ ?
(v) ਸਾਡੇ ਝੰਡੇ ਵਿਚ ਹਰਾ ਰੰਗ ਕਿਸ ਗੱਲ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਤੀਕ ਹੈ ?
(vi) ਸਾਡੇ ਖੇਤ ਕੀ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
(i) ਸਾਡਾ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡਾ ਸਾਨੂੰ ਪਿਆਰਾ ਤੇ ਨਿਆਰਾ ਲਗਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਵਿਚਲਾ ਹਰਾ ਰੰਗ ਬਹੁਮੁੱਲੀਆਂ ਫ਼ਸਲਾਂ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰ ਕੇ ਵਰਤੀ ਖ਼ੁਸ਼ਹਾਲੀ ਦਾ ਚਿੰਨ੍ਹ ਹੈ ।
(ii) ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡਾ
(iii) ਡਾ: ਹਰਨੇਕ ਸਿੰਘ ਕਲੇਰ ।
(iv) ਤਿਰੰਗਾ !
(v) ਖ਼ੁਸ਼ਹਾਲੀ ਦਾ ।
(vi) ਬਹੁਮੁੱਲੀਆਂ ਫ਼ਸਲਾਂ ਰੂਪੀ ਸੋਨਾ ।
![]()
(ਅ) ਅਮਨ ਦੀ ਨਿਸ਼ਾਨੀ, ਰੰਗ ਹੈ ਚਿੱਟਾ ।
ਜੀਣ ਤੇ ਜੀਣ ਦਿਓ, ਮੇਵਾ ਹੈ ਮਿੱਠਾ ।
ਵਗਦੀ ਰਹੇ ਸਦਾ ਸ਼ਾਂਤੀ ਦੀ ਧਾਰਾ ।
ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡਾ ਤਿਰੰਗਾ ਪਿਆਰਾ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
(i) ਉਪਰੋਕਤ ਕਾਵਿ-ਟੋਟੇ ਦੇ ਭਾਵ-ਅਰਥ ਲਿਖੋ ।
(ii) ਤਿਰੰਗੇ ਵਿਚਲਾ ਚਿੱਟਾ ਰੰਗ ਕਿਸ ਚੀਜ਼ ਦੀ ਨਿਸ਼ਾਨੀ ਹੈ ?
(iii) ਅਮਨ ਦੀ ਨਿਸ਼ਾਨੀ ਕਿਹੜਾ ਰੰਗ ਹੈ ?
(iv) ਕਿਸ ਮੇਵੇ ਨੂੰ ਮਿੱਠਾ ਕਿਹਾ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ ?
(v) ਕਿਹੜੀ ਧਾਰਾ ਵਗਦੀ ਰਹਿਣੀ ਚਾਹੀਦੀ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
(i) ਸਾਡੇ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡੇ ਤਿਰੰਗੇ ਵਿਚ ਚਿੱਟਾ ਰੰਗ ਅਮਨ ਦਾ ਚਿੰਨ੍ਹ ਹੈ, ਜਿਹੜਾ ਜੀਓ ਤੇ ਜਿਉਣ ਦਿਓ ਦਾ ਸੁਨੇਹਾ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ, ਤਾਂ ਜੋ ਦੁਨੀਆ ਵਿਚ ਹਮੇਸ਼ਾ ਸ਼ਾਂਤੀ ਦਾ ਵਾਤਾਵਰਨ ਬਣਿਆ ਰਹੇ ।
(ii) ਅਮਨ ਦੀ ।
(iii) ਚਿੱਟਾ ।
(iv) “ਜੀਓ ਅਤੇ ਜੀਣ ਦਿਓ’ ਦੇ ਸਿਧਾਂਤ ਰੂਪ ਮੇਵੇ ਨੂੰ ।
(v) ਸ਼ਾਂਤੀ ਦੀ ।
(ਬ) ਕੇਸਰੀ ਰੰਗ ਹੈ ਕੁਰਬਾਨੀ ਵਾਲਾ ।
ਜੀਵੇ ਸਰਹੱਦਾਂ ਦਾ ਰਖਵਾਲਾ ॥
ਸੂਰਜ ਬਣ ਕੇ ਚਮਕੇ, ਦੇਸ਼ ਦਾ ਸਿਤਾਰਾ ।
ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡਾ ਤਿਰੰਗਾ ਪਿਆਰਾ ॥
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
(i) ਉਪਰੋਕਤ ਕਾਵਿ-ਟੋਟੇ ਦੇ ਭਾਵ-ਅਰਥ ਲਿਖੋ ।
(ii) ਤਿਰੰਗੇ ਵਿਚਲਾ ਕੇਸਰੀ ਰੰਗ ਕਿਸ ਚੀਜ਼ ਦਾ ਚਿੰਨ੍ਹ ਹੈ ?
(iii) ਸਰਹੱਦਾਂ ਦਾ ਰਖਵਾਲਾ ਕੌਣ ਹੈ ?
(iv) ਦੇਸ਼ ਦਾ ਸਿਤਾਰਾ ਕਿਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਚਮਕਣ ਦੀ ਇੱਛਾ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
(i) ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡੇ ਤਿਰੰਗੇ ਵਿਚਲਾ ਕੇਸਰੀ ਰੰਗ ਕੁਰਬਾਨੀ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਤੀਕ ਹੈ । ਅਸੀਂ ਚਾਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਾਂ ਕਿ ਦੇਸ਼ ਦਾ ਰਾਖਾ ਫ਼ੌਜੀ ਸਿਪਾਹੀ ਸਦਾ ਜਿਉਂਦਾ ਰਹੇ, ਤਾਂ ਜੋ ਦੇਸ਼ ਦਾ ਸਿਤਾਰਾ ਸੂਰਜ ਵਾਂਗ ਚਮਕਦਾ ਰਹੇ ।
(ii) ਕੁਰਬਾਨੀ ਦਾ ।
(iii) ਫ਼ੌਜੀ ਸਿਪਾਹੀ ।
(iv) ਸੂਰਜ ਵਾਂਗ ।
(ਸ) ਗੀਤ ਤਿਰੰਗੇ ਦੇ ਰਲ ਕੇ ਗਾਈਏ ।
ਭਾਰਤ ਮਾਂ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਾਨ ਵਧਾਈਏ ।
ਸਿਫ਼ਤਾਂ ਕਰਦਾ ਏ ਜੱਗ ਸਾਰਾ ।
ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡਾ ਤਿਰੰਗਾ ਪਿਆਰਾ ਹੈ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
(i) ਉਪਰੋਕਤ ਕਾਵਿ-ਟੋਟੇ ਦੇ ਭਾਵ-ਅਰਥ ਲਿਖੋ ।
(ii) ਸਾਨੂੰ ਰਲ ਕੇ ਕਿਸਦੇ ਗੀਤ ਗਾਉਣੇ ਚਾਹੀਦੇ ਹਨ ?
(iii) ਸਾਨੂੰ ਕਿਸ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਾਨ ਵਧਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਨਾ ਚਾਹੀਦਾ ਹੈ ?
(iv) ਸਾਰਾ ਜਗਤ ਕਿਸ ਦੀਆਂ ਸਿਫ਼ਤਾਂ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
(i) ਸਾਨੂੰ ਸਭ ਨੂੰ ਰਲ ਕੇ ਆਪਣੇ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡੇ ਤਿਰੰਗੇ ਦੇ ਗੀਤ ਗਾ ਕੇ ਭਾਰਤ ਮਾਂ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਾਨ ਵਧਾਉਣੀ ਚਾਹੀਦੀ ਹੈ । ਸਾਰਾ ਸੰਸਾਰ ਸਾਡੇ ਦੇਸ਼ ਦੀਆਂ ਸਿਫ਼ਤਾਂ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਸਾਨੂੰ ਇਹ ਤਿਰੰਗਾ ਝੰਡਾ ਬਹੁਤ ਪਿਆਰਾ ਹੈ ।
(ii) ਤਿਰੰਗੇ ਦੇ !
(iii) ਭਾਰਤ ਮਾਂ ਦੀ ।
(iv) ਭਾਰਤ ਮਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ ।
![]()
ਕਾਵਿ-ਟੋਟਿਆਂ ਦੇ ਸਰਲ ਅਰਥ
(ਉ) ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡਾ ਤਿਰੰਗਾ ਪਿਆਰਾ ॥
ਝੱਲੇ ਹਵਾ ਵਿਚ ਲਗਦਾ ਨਿਆਰਾ ।
ਹਰੇ ਰੰਗ ਦੀ ਏ ਸ਼ਾਨ ਨਿਰਾਲੀ ।
ਖੇਤਾਂ ਬੰਨੇ ਖੇਡੇ ਖ਼ੁਸ਼ਹਾਲੀ ॥
ਸੋਨਾ ਉਪਜੇ ਹਰ ਖੇਤ ਦਾ ਕਿਆਰਾ ।
ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡਾ ਤਿਰੰਗਾ ਪਿਆਰਾ ॥
ਔਖੇ ਸ਼ਬਦਾਂ ਦੇ ਅਰਥ : ਨਿਆਰਾ-ਵੱਖਰਾ, ਦੂਜਿਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਖਰਾ । ਨਿਰਾਲੀ-ਵੱਖਰੀ, ਦੁਜਿਆਂ ਨਾਲੋਂ ਭਿੰਨ ( ਬੰਨੇ-ਵਲ, ਬੰਨੇ ਉੱਤੇ । ਉਪਜੇ-ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰੇ । ਕਿਆਰਾ-ਖੇਤ ਦਾ ਛੋਟਾ ਹਿੱਸਾ, ਜੋ ਵੱਟ ਪਾ ਕੇ ਵੱਖਰਾ ਕੀਤਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
(i) ਉੱਪਰ ਲਿਖੇ ਕਾਵਿ-ਟੋਟੇ ਦੇ ਸਰਲ ਅਰਥ ਲਿਖੋ ।
(ii) ਸਾਡੇ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡੇ ਦਾ ਕੀ ਨਾਂ ਹੈ ?
(iii) ਕਿਹੜੀ ਚੀਜ਼ ਪਿਆਰੀ ਲੱਗਦੀ ਹੈ ?
(iv) ਝੰਡੇ ਦਾ ਹਰਾ ਰੰਗ ਕਿਸ ਚੀਜ਼ ਦਾ ਚਿੰਨ੍ਹ ਹੈ ?
(v) ਹਰ ਖੇਤ ਵਿਚ ਕੀ ਪੈਦਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
(i) ਕਵੀ ਕਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਸਾਨੂੰ ਆਪਣੇ ਭਾਰਤ ਦੇਸ਼ ਦਾ ਤਿਰੰਗਾ ਝੰਡਾ ਬਹੁਤ ਪਿਆਰਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਜਦੋਂ ਹਵਾ ਵਿਚ ਭੁੱਲ ਰਿਹਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ, ਤਾਂ ਸਾਨੂੰ ਹੋਰ ਵੀ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਪਿਆਰਾ ਲਗਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਦੇ ਹਰੇ ਰੰਗ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਾਨ ਹੀ ਵੱਖਰੀ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਖੇਤਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਖੇਡ ਰਹੀਆਂ ਹਰੀਆਂ ਫ਼ਸਲਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਪੈਦਾ ਹੋਣ ਵਾਲੀ ਖ਼ੁਸ਼ਹਾਲੀ ਦਾ ਚਿੰਨ੍ਹ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਇਸ ਗੱਲ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਤੀਕ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਇਸ ਦੇਸ਼ ਦੇ ਖੇਤਾਂ ਦਾ ਹਰ ਕਿਆਰਾ ਸੋਨੇ ਵਰਗੀਆਂ ਬਹੁਮੁੱਲੀਆਂ ਫ਼ਸਲਾਂ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਸਾਨੂੰ ਦੇਸ਼ ਦੇ ਖੇਤਾਂ ਵਿਚਲੀ ਹਰਿਆਵਲ ਨੂੰ ਦਰਸਾਉਣ ਵਾਲਾ ਆਪਣਾ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡਾ ਬਹੁਤ ਪਿਆਰਾ ਹੈ ।
(ii) ਤਿਰੰਗਾ ।
(iii) ਹਵਾ ਵਿਚ ਭੁੱਲਦਾ ਤਿਰੰਗਾ ਝੰਡਾ ।
(iv) ਖ਼ੁਸ਼ਹਾਲੀ ਦਾ ।
(v) ਸੋਨੇ ਵਰਗੀਆਂ ਬਹੁਮੁੱਲੀਆਂ ਫ਼ਸਲਾਂ ।
![]()
(ਅ) ਅਮਨ ਦੀ ਨਿਸ਼ਾਨੀ, ਰੰਗ ਹੈ ਚਿੱਟਾ ।
ਜੀਣ ਤੇ ਜੀਣ ਦਿਓ, ਮੇਵਾ ਹੈ ਮਿੱਠਾ ।
ਵਗਦੀ ਰਹੇ ਸਦਾ ਸ਼ਾਂਤੀ ਦੀ ਧਾਰਾ ॥
ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡਾ ਤਿਰੰਗਾ ਪਿਆਰਾ ।
ਔਖੇ ਸ਼ਬਦਾਂ ਦੇ ਅਰਥ : ਮੇਵਾ-ਫਲ, ਸੁੱਕਾ ਮਿੱਠਾ ਫਲ ਧਾਰਾ-ਰੌ, ਵਹਿਣ, ਨਦੀ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
(i) ਉੱਪਰ ਲਿਖੇ ਕਾਵਿ-ਟੋਟੇ ਦੇ ਸਰਲ ਅਰਥ ਲਿਖੋ ।
(ii) ਸਾਡੇ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡੇ ਦਾ ਕੀ ਨਾਂ ਹੈ ?
(iii) ਝੰਡੇ ਵਿਚਲਾ ਚਿੱਟਾ ਰੰਗ ਕਿਸ ਗੱਲ ਦੀ ਨਿਸ਼ਾਨੀ ਹੈ ?
(iv) “ਮਿੱਠਾ ਮੇਵਾ ਕਿਸਨੂੰ ਕਿਹਾ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ ?
(v) ਕਿਹੜੀ ਧਾਰਾ ਸਦਾ ਵਗਦੀ ਰਹਿਣੀ ਚਾਹੀਦੀ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
(i) ਕਵੀ ਕਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਸਾਡੇ ਦੇਸ਼ ਦੇ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡੇ ਤਿਰੰਗੇ ਵਿਚਲਾ ਚਿੱਟਾ ਰੰਗ ਅਮਨ ਦਾ ਚਿੰਨ੍ਹ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਸਾਨੂੰ ਸੰਦੇਸ਼ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਸਾਨੂੰ ਆਪ ਵੀ ਅਮਨ-ਸ਼ਾਂਤੀ ਵਿਚ ਜਿਉਣਾ ਚਾਹੀਦਾ ਹੈ ਤੇ ਦੂਜਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਵੀ ਜਿਉਣ ਦੇਣਾ ਚਾਹੀਦਾ ਹੈ | ਅਮਨ ਤੇ ਪ੍ਰੇਮ-ਪਿਆਰ ਨਾਲ ਰਹਿਣ ਦਾ ਸੁਆਦ ਮਿੱਠੇ ਮੇਵੇ ਵਰਗਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ | ਸਾਡੇ ਤਿਰੰਗੇ ਝੰਡੇ ਵਿਚਲਾ ਚਿੱਟਾ ਰੰਗ ਸਾਨੂੰ ਸਦਾ ਅਮਨ ਤੇ ਸ਼ਾਂਤੀ ਦੀ ਧਾਰਾ ਵਗਦੀ ਰੱਖਣ ਦੀ ਇੱਛਾ ਕਰਨ ਦਾ ਸੰਦੇਸ਼ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸੇ ਕਰਕੇ ਸਾਨੂੰ ਆਪਣਾ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡਾ ਤਿਰੰਗਾ ਬਹੁਤ ਪਿਆਰਾ ਹੈ ।
(ii) ਤਿਰੰਗਾ ।
(iii) ਅਮਨ ਦੀ ।
(iv) ‘ਆਪ ਜੀਉ ਤੇ ਦੂਜਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਜਿਊਣ ਦਿਓ’ ਦੇ ਵਿਚਾਰ ਨੂੰ ।
(v) ਸ਼ਾਂਤੀ ਦੀ ।
(ਇ) ਕੇਸਰੀ ਰੰਗ ਹੈ ਕੁਰਬਾਨੀ ਵਾਲਾ ॥
ਜੀਵੇ ਸਰਹੱਦਾਂ ਦਾ ਰਖਵਾਲਾ ॥
ਸੂਰਜ ਬਣ ਕੇ ਚਮਕੇ, ਦੇਸ਼ ਦਾ ਸਿਤਾਰਾ ।
ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡਾ ਤਿਰੰਗਾ ਪਿਆਰਾ ।
ਔਖੇ ਸ਼ਬਦਾਂ ਦੇ ਅਰਥ : ਸਰਹੱਦਾਂ ਦਾ ਰਖਵਾਲਾ-ਫ਼ੌਜ ਦਾ ਸਿਪਾਹੀ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
(i) ਉੱਪਰ ਲਿਖੇ ਕਾਵਿ-ਟੋਟੇ ਦੇ ਸਰਲ ਅਰਥ ਲਿਖੋ ।
(ii) ਕੇਸਰੀ ਰੰਗ ਕਿਸ ਚੀਜ਼ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਤੀਕ ਚਿੰਨ ਹੈ ?
(iii) ਸਰਹੱਦਾਂ ਦਾ ਰਖਵਾਲਾ ਕੌਣ ਹੈ ?
(iv) ਦੇਸ਼ ਦਾ ਸਿਤਾਰਾ ਕਿਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਚਮਕਣਾ ਚਾਹੀਦਾ ਹੈ ?
(v) ਤਿਰੰਗੇ ਦੇ ਕਿੰਨੇ ਰੰਗ ਹਨ ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
(i) ਕਵੀ ਕਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਸਾਡੇ ਦੇਸ਼ ਦੇ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡੇ ਤਿਰੰਗੇ ਵਿਚਲਾ ਕੇਸਰੀ ਰੰਗ ਕੁਰਬਾਨੀ ਦਾ ਚਿੰਨ੍ਹ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਸਾਨੂੰ ਦੇਸ਼ ਦੀ ਅਜ਼ਾਦੀ ਲਈ ਜਾਨਾਂ ਵਾਰਨ ਵਾਲੇ ਦੇਸ਼ਭਗਤਾਂ ਤੇ ਦੇਸ਼ ਦੀਆਂ ਸਰਹੱਦਾਂ ਉੱਤੇ ਇਸ ਦੇ ਦੁਸ਼ਮਣਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਇਸ ਦੀ ਰਾਖੀ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਹਿੱਕਾਂ ਡਾਹ ਕੇ ਕੁਰਬਾਨੀਆਂ ਕਰਨ ਵਾਲੇ ਫ਼ੌਜ ਦੇ ਸਿਪਾਹੀਆਂ ਦੀ ਯਾਦ ਦੁਆਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਸਾਨੂੰ ਦੇਸ਼ ਦੇ ਸਿਤਾਰੇ ਨੂੰ ਦੁਨੀਆ ਵਿਚ ਚਮਕਦਾ ਰੱਖਣ ਲਈ ਕੁਰਬਾਨੀਆਂ ਕਰਨ ਦੀ ਪ੍ਰੇਰਨਾ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਅਜਿਹਾ ਮਹਾਨ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡਾ ਤਿਰੰਗਾ ਸਾਨੂੰ ਬਹੁਤ ਪਿਆਰਾ ਹੈ !
(ii) ਕੁਰਬਾਨੀ ਦਾ ।
(iii) ਫ਼ੌਜੀ ਜਵਾਨ ।
(iv) ਸੂਰਜ ਵਾਂਗ ।
(v) ਤਿੰਨ-ਹਰਾ, ਚਿੱਟਾ ਤੇ ਕੇਸਰੀ ।
![]()
(ਸ) ਗੀਤ ਤਿਰੰਗੇ ਦੇ ਰਲ ਕੇ ਗਾਈਏ ।
ਭਾਰਤ ਮਾਂ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਾਨ ਵਧਾਈਏ ।
ਸਿਫ਼ਤਾਂ ਕਰਦਾ ਏ ਜੱਗ ਸਾਰਾ ॥
ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡਾ ਤਿਰੰਗਾ ਪਿਆਰਾ ।
ਔਖੇ ਸ਼ਬਦਾਂ ਦੇ ਅਰਥ : ਜੱਗ-ਦੁਨੀਆ, ਜਗਤ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
(i) ਉਪਰੋਕਤ ਕਾਵਿ-ਟੋਟੇ ਦੇ ਸਰਲ ਅਰਥ ਲਿਖੋ ।
(ii) ਸਾਨੂੰ ਰਲ ਕੇ ਕਿਸ ਦੇ ਗੀਤ ਗਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਕਿਹਾ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ ?
(iii) ਭਾਰਤ ਮਾਂ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਾਨ ਕਿਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਵਧਦੀ ਹੈ ?
(iv) ਕਿਸ ਦੀਆਂ ਸਾਰਾ ਸੰਸਾਰ ਸਿਫ਼ਤਾਂ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
(i) ਕਵੀ ਕਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਸਾਨੂੰ ਸਭ ਨੂੰ ਰਲ਼ ਕੇ ਆਪਣੇ ਦੇਸ਼ ਦੇ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡੇ ਤਿਰੰਗੇ ਦੀ ਮਹਿਮਾ ਦੇ ਗੀਤ ਗਾਉਂਦੇ ਰਹਿਣਾ ਚਾਹੀਦਾ ਹੈ ਤੇ ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਭਾਰਤ ਮਾਂ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਾਨ ਨੂੰ ਵਧਾਉਣਾ ਚਾਹੀਦਾ ਹੈ । ਸਾਰਾ ਸੰਸਾਰ ਸਾਡੇ ਦੇਸ਼ ਦੀ ਸੁੰਦਰਤਾ ਤੇ ਬਰਕਤਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਸਿਫ਼ਤਾਂ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸੇ ਕਰਕੇ ਸਾਨੂੰ ਸਾਡਾ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡਾ ਤਿਰੰਗਾ ਬਹੁਤ ਪਿਆਰਾ ਲਗਦਾ ਹੈ ।
(ii) ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡੇ ਤਿਰੰਗੇ ਦੇ ।
(iii) ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡੇ ਤਿਰੰਗੇ ਦੇ ਗੀਤ ਗਾਉਣ ਨਾਲ ।
(iv) ਸਾਡੇ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਝੰਡੇ ਤਿਰੰਗੇ ਦੀਆਂ ।