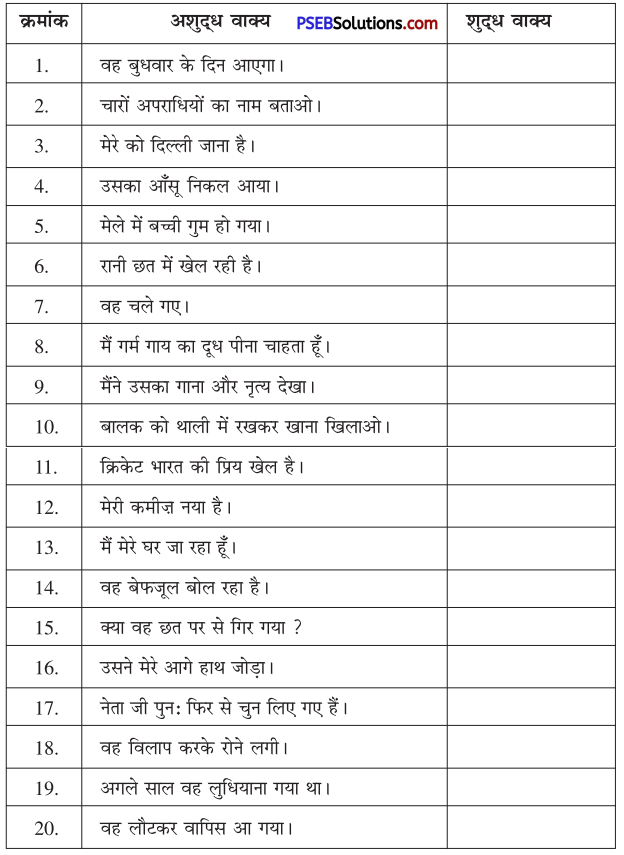
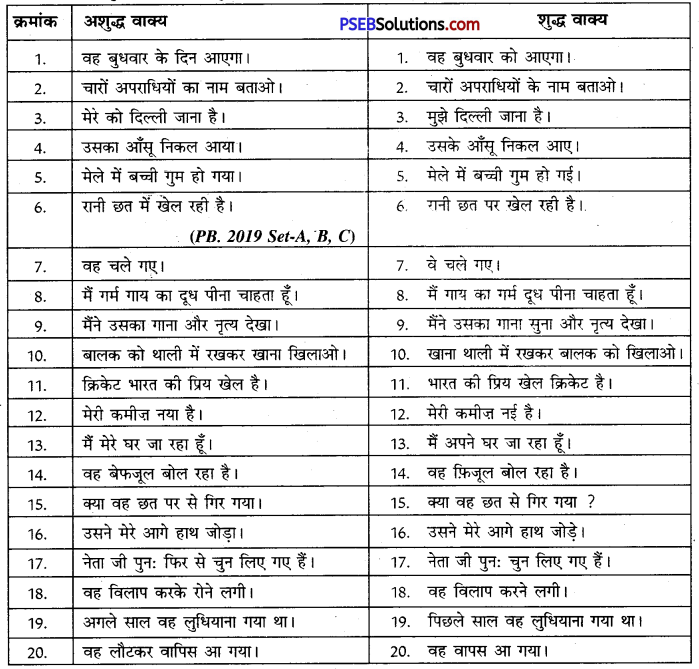
Punjab State Board PSEB 10th Class Hindi Book Solutions Hindi Grammar anuchchhed lekhan अनुच्छेद लेखन Exercise Questions and Answers, Notes.
PSEB 10th Class Hindi Grammar अनुच्छेद लेखन
1. एक आदर्श विद्यार्थी के गुण
संकेत बिंदु : (i) प्रातः जल्दी उठना व नित्य व्यायाम करना (ii) समय पर स्कूल जाना (iii) मन लगाकर पढ़ना (iv) सहपाठियों से मधुर संबंध (v) अनुशासनप्रिय।
एक आदर्श विद्यार्थी के गुण
आदर्श विद्यार्थी अपने सम्मुख सदा एक लक्ष्य रखता है और अपना लक्ष्य स्थिर रखने वाले विद्यार्थी सदा उसके अनुसार अपने जीवन क्रम को दिशा देने का प्रयत्न करता है। निष्ठापूर्वक उस लक्ष्य के अनुसार कार्य करता है। आदर्श विद्यार्थी को समय और अवसर के अनुसार जीवन व्यतीत करना चाहिए। उसे सुबह-सवेरे जल्दी उठकर सैर करनी चाहिए। उसे प्रतिदिन व्यायाम भी करना चाहिए। व्यायाम उसके शरीर को सुदृढ़ बनाने के साथ-साथ उसकी बुद्धि में चिंतन और मनन की क्षमता का विकास करता है। एक आदर्श विद्यार्थी के गुणों में उसका समय पर स्कूल जाना भी आता है। यह आदत उसे समय का महत्त्व समझाती है। समय पर अपने कार्य और जीवन को आगे बढ़ाने का काम करती है।
कक्षा में साथ में पढ़ने वाले विद्यार्थियों के साथ मैत्रीपूर्ण एवं मधुर संबंध बनाए रखने वाला विद्यार्थी एक आदर्श विद्यार्थी कहलाता है। उसके विचार तथा व्यवहार दूसरों को अपनी ओर आकर्षित करने का काम करते हैं। एक आदर्श विद्यार्थी को कौवे के समान प्रयत्नशील, बगुले के समान ध्यानरत, कुत्ते के समान कम और सावधान निद्रा लेने वाला तथा विद्या की शरण लेने वाला होना चाहिए। उसे अपनी विद्या प्राप्ति के लिए खूब मन लगाकर पढ़ना चाहिए। विद्यार्थी जीवन को सुंदर बनाने के लिए अनुशासन का विशेष महत्त्व है। एक अच्छे और गुणी विद्यार्थी के लिए उसका शान्तिपूर्ण अनुशासित होना अति आवश्यक है।

2. जीवन में परिश्रम का महत्त्व
संकेत बिंदु : (i) सफलता का मूल मंत्र : परिश्रम (ii) आलस्य के कारण असफलता व निराशा (iii) परिश्रम से भाग्य का बदलना (iv) पुरुषार्थ से लक्ष्य प्राप्ति।
जीवन में परिश्रम का महत्त्व
जीवन नाम ही परिश्रम का है। इस संसार में जितने भी प्राणी हैं। उन सभी को अपना जीवनयापन करने के लिए परिश्रम करना ही पड़ता है। कर्म अथवा परिश्रम के बिना मानव जीवन की गाड़ी चल ही नहीं सकती है। सच है कि संसार में मनुष्य ने आज तक जितनी उपलब्धियाँ प्राप्त की हैं। वह सब उनके परिश्रम का ही परिणाम है। परिश्रम का परम शत्रु है आलस्य। जिस व्यक्ति में आलस्य या सुस्ती की भावना घर कर जाती है, उसका विकास रुक जाता है। वह उन्नति के पथ पर पिछड़ जाता है। आलस्य के कारण उसे असफलता तथा निराशा का मुँह देखना पड़ता है।
परिश्रम ही छोटे से बड़े बनने का साधन है। परिश्रम करके व्यक्ति उन्नति के शिखर पर पहुँच जाता है। परिश्रम व्यक्ति जीवन और उसके भाग्य को बदलने का काम करता है। परिश्रमी व्यक्ति ही स्वावलम्बी, ईमानदार, सत्यवादी, चरित्रवान और सेवा-भाव से युक्त होता है। वह अपने पुरुषार्थ के बल पर अपने लक्ष्य को प्राप्त करता है। इसी कारण वह अपने परिवार और देश की उन्नति में सहयोग देता है। पुरुषार्थ का रहस्य ही है कि मिट्टी सोना उगलती है।
3. सब्जी मंडी में सब्जी खरीदने का मेरा पहला अनुभव
संकेत बिंदु : (i) घर के पास सब्जी मंडी का लगना (ii) सब्जी मंडी से सब्जी लेने जाना (iii) सब्जियाँ व फल खरीदना (iv) सब्जी मंडी का खट्टा-मीठा अनुभव।
सब्जी मंडी में सब्जी खरीदने का मेरा पहला अनुभव
जीवन में जितनी आवश्यकता काम की है। उससे कहीं ज्यादा महत्त्वपूर्ण उस काम का अनुभव प्राप्त करना है। अनुभव कार्य में गति और प्रगति लाता है। अनुभव के आधार पर किया जाने वाला कार्य श्रेष्ठकर होता है। मेरा घर शहर के सैक्टर आठ क्षेत्र में है। हमारे घर के पास ही सब्जी मंडी लगती है। आस-पास के किसान सब्जी बेचने के लिए यहाँ आते हैं। बड़ी मंडी से भी कुछ छोटे दुकानदार सब्जी बेचने के लिए यहाँ आते हैं। सब्जी लेने और बेचने वालों का कोलाहल देखते ही बनता है। प्रायः वहाँ से सब्जी खरीदने के लिए मंडी मम्मी या बड़ी बहन ही जाते हैं लेकिन गत सप्ताह मैं सब्जी खरीदने वहाँ गया था। वह मेरे जीवन का अलग ही अनुभव था। सब्जी मंडी लोगों की भीड़ से भरी हुई थी।
रेहड़ियों की भीड़ के अतिरिक्त तरह-तरह की सब्जियां बेचने वाले ईंटों के बने फर्श पर बैठ कर अपना काम कर रहे थे। बड़े-बड़े टोकरों और धरती पर बिछाए हुए कपड़ों पर सब्जियों के ढेर लगे हुए थे। लोग दुकानदारों से सब्जियों के मोलभाव कर रहे थे। मैंने भी टमाटर, प्याज, आलू और मटर खरीदने के लिए मोलभाव किया। मैंने स्वयं सब्जियों को चुना और फिर उन्हें तुलवाया। मुझे केले और कीनू भी खरीदने थे। फल अधिकतर रेहड़ियों पर सजे हुए थे। मैंने चार-पाँच रेहड़ियों पर बिकने वाले फलों के दाम पूछे और फिर एक रेहड़ी से फल खरीदे। मुझे यह कार्य करके कुछ अलग प्रकार का संतोष अनुभव हुआ। सब्जियां और फल खरीद कर जब मैं घर पहुंचा तो मुझे ऐसा प्रतीत हो रहा था जैसे मैं कुछ अलग ही काम करके वापस लौटा हूँ।
4. जब मुझे स्कूल के खेल-मैदान से बटुआ मिला
संकेत बिंदु : (i) खेल के मैदान से बटुए का मिलना (ii) बटुए में रुपयों का होना (iii) बटुए को अध्यापक को सौंपना (iv) प्रात:कालीन सभा में ईमानदारी की शाबाशी मिलना (v) मन फूला न समाना।
जब मुझे स्कूल के खेल-मैदान से बटुआ मिला
हमारे विद्यालय में खेल का एक बहुत बड़ा मैदान है। हम सभी आधी छुट्टी में तथा गेम के क्लास में खेलने के लिए खेल के मैदान में जाते हैं। प्रतिदिन की तरह आज भी मैं खेलने के लिए खेल के मैदान में गया। जब मैं अपने दोस्तों के साथ खेल रहा था तो वहीं घास में मुझे एक बटुआ मिला। बटुआ देखने में आकर्षक तथा महंगा लग रहा था। वह भारी भी था। जब बटुए को खोलकर देखा तो उसमें लगभग दो हज़ार रुपये थे। रूपयों को देखकर पलभर के लिए भी मेरा मन विचलित नहीं हुआ। मैंने उसमें पहचान ढूँढ़ने की कोशिश की, ताकि उसे उसके मालिक तक पहुँचाया जा सके।
काफी अथाह परिश्रम के बाद भी जब बटुए से कोई जानकारी नहीं मिली तो तुरंत ही, उस बटुए को मैंने कक्षा अध्यापक को सौंप दिया तथा बटुए के विषय में सारी बातें उन्हें बता दीं। अध्यापक ने मेरी ईमानदारी को देखते हुए अगले दिन प्रात:कालीन सभा में मेरी ईमानदारी का परिचय देते हुए मुझे शाबाशी दी। सभी ने मेरे द्वारा किए कार्य को प्रोत्साहित किया। प्रात:कालीन सभा में सारे स्कूल के सामने शाबाशी और प्रोत्साहन मिलने के कारण मन खूब रोमांचित हो रहा था। दिल में खुशी बढ़ती जा रही थी। मन खुशी से झूम रहा था।
5. परीक्षा से एक घंटा पूर्व
संकेत बिंदु : (i) परीक्षा भवन में एक घंटा पूर्व पहुँचना (ii) परीक्षार्थियों का चिंतित होना (iii) महत्त्वपूर्ण बिंदुओं पर चर्चा से परेशानी दूर होना (iv) सूचना पट्ट पर परीक्षा में बैठने की योजना का लगना (v) परीक्षा भवन में प्रवेश।
परीक्षा से एक घंटा पूर्व
वैसे तो. प्रत्येक मनुष्य परीक्षा से घबराता है किंतु विद्यार्थी इससे विशेष रूप से भयभीत होता है। पराक्षी में पास होना आवश्यक है नहीं तो जीवन का एक बहुमूल्य वर्ष नष्ट हो जाएगा। इसी घबराहट और डर के कारण परीक्षा से पूर्व का एक घंटा उसके लिए अति महत्त्वपूर्ण सिद्ध होता है। परीक्षा शुरू होने से एक घंटा पहले मैं जब परीक्षा भवन पहुँचा तो मेरा दिल धक्-धक् कर रहा था। मैं सोच रहा था कि सारी रात जाग कर जो प्रश्न तैयार किए हैं यदि वे प्रश्न-पत्र में न आए तो क्या होगा ? परीक्षा भवन के बाहर का दृश्य बड़ा विचित्र था। परीक्षा देने आए विद्यार्थी परीक्षा में आने वाले प्रश्नों को लेकर चिंतित दिखाई दे रहे थे। कोई कह रहा था कि उसने सारा पाठ्यक्रम दोहरा लिया है लेकिन कोई प्रश्न घुमा-फिरा कर आ गया तो मुश्किल हो जाएगी। हम कुछ छात्र परीक्षा से पूर्व प्रश्न-पत्र हल करने को लेकर विचार-विमर्श कर रहे थे।
प्रश्नों को हल करने तथा समझने के तरीके एक-दूसरे से सांझा कर रहे थे। एक-दूसरे के विचारों को सुनने के बाद मानसिक तनाव तथा थकान में कमी महसूस हुई। परीक्षा भवन के बाहर विद्यार्थियों का जमघट लगा हुआ था। थोड़ी ही देर में घंटी बजी। परीक्षा भवन का गेट खुला। परीक्षा भवन के बाहर अनुक्रमांक और स्थान देखने के लिए सूचनापट्ट पर सूचनाएं तालिकाओं के रूप में क्रमबद्ध रूप में लगी हुई थीं। सभी विद्यार्थी देखते ही देखते अपना स्थान और अनुक्रमांक सूचना पट्ट में ढूँढ़ने लगे। सूचनापट्ट पर अपना अनुक्रमांक और स्थान देखकर मैं परीक्षा भवन में प्रविष्ट हुआ और अपने स्थान पर जाकर बैठ गया।
6. खुशियाँ और उमंग लाते हैं जीवन में त्योहार
संकेत बिंदु : (i) त्योहारों का महत्त्व (ii) विभिन्न त्योहार (iii) उमंग और जोश से भरे त्योहार (iv) सद्भावना, एकता व प्रेम के प्रतीक (v) सभी को त्योहारों का इंतज़ार।
खुशियाँ और उमंग लाते हैं जीवन में त्योहार
भारत त्योहारों का देश कहा जाता है। ये त्योहार अनेक प्रकार के हैं। कुछ त्योहार धार्मिक महत्त्व रखते हैं तो कुछ राष्ट्रीय त्योहारों के रूप में देश-भर में मनाए जाते हैं। हमारे देश के त्योहार चाहे धार्मिक दृष्टि से मनाए जा रहे हैं या नए वर्ष के आगमन के रूप में सभी अपनी विशेषताओं एवं क्षेत्रीय प्रभाव से मुक्त होने के साथ-साथ देश की राष्ट्रीय एवं सांस्कृतिक एकता और अखण्डता को मज़बूती प्रदान करते हैं। ये त्योहार जहाँ जनमानस में उल्लास, उमंग एवं खुशहाली भर देते हैं, वहीं हमारे अंदर देशभक्ति एवं गौरव की भावना के साथ विश्व-बंधुत्व एवं समन्वय की भावना भी बढ़ाते हैं। भारत में विभिन्न त्योहार मनाए जाते हैं। जैसे-होली, दीपावली, ईद, दशहरा, वैशाखी, रामनवमी, गुरुपर्व, बसंत पंचमी आदि। ये सभी त्योहार हमें समता और भाईचारे का प्रचार करने पर बल देते हैं। भारतीय त्योहार एक अलग अंदाज में एक अलग तरीके से मनाए जाते हैं।
यह हमें प्रसन्न रहने की प्रेरणा देते हैं। हमारे जीवन में उत्साह, उमंग एवं जोश का संचार करते हैं। ये आशा और उम्मीद को जन्म देने का काम भी करते हैं। त्योहार आपसी प्रेमभाव तथा सोहार्द्र को बढ़ाने का काम करते हैं। ये व्यक्ति में नई जागृति और चेतना पैदा करने का काम करते हैं। ये हमें शिक्षा देते हैं कि हमें कभी भी अत्याचार के सामने नहीं झुकना चाहिए। एक-दूसरे को साथ लेकर चलने तथा एकता के प्रसार पर बल देते हैं। हम सभी को बड़ी ही उत्सुकता के साथ त्योहारों का इतंजार रहता है। ये हमारी एकता एवं अखंडता को बनाए रखने का काम करते हैं।
7. नाटक में अभिनय में मेरा पहला अनुभव
संकेत बिन्दु : (i) स्कूल में नाटक मंचन की तैयारी (ii) स्वयं को नाटक में मुख्य रोल के लिए चुना जाना (ii) नाटक मंचन का अभ्यास (iv) मेकअप को लेकर उत्साह (v) मंचन के बाद आत्म-संतुष्टि व लोगों द्वारा सराहना।
नाटक में अभिनय मेरा पहला अनुभव
अभिनय करना एक कला है। इस कला के माध्यम से व्यक्ति अपने अंदर की भावनाओं एवं अनुभूतियों को अभिनय के माध्यम से प्रकट करता है। हमारे विद्यालय में समय-समय अनेक सांस्कृतिक कार्यक्रम होते रहते हैं। बीते दिनों में स्कूल में ‘कन्या भ्रूण हत्या’ विषय को लेकर एक नाटक के मंचन की तैयारी की जाने लगी। मैंने भी बड़े चाव से इस नाटक में भाग लिया। नाटक के प्रति मेरी उत्सुकता तथा मेरे अभिनय कौशल को देखते हुए अध्यापकों ने मुझे नाटक . में मुख्य रोल के लिए चुन लिया। यह मेरे जीवन का सबसे उत्तम और अच्छा पल था। विद्यालय में हमें नाटक मंचन के अभ्यास के लिए प्रतिदिन आखिरी के तीन पीरियड मिले थे। हम सभी पूरे जोश तथा उत्साह के साथ नाटक मंचन के अभ्यास में लगे रहते थे।
हमारे नाटक और उत्साह की सभी ने सराहना भी की थी। अभिनय करने के लिए किया जाने वाला मेकअप हमारे लिए सबसे ज्यादा उत्साहवर्धक काम था। हम सभी चरित्रों तथा उनकी आवश्यकतानुसार मेकअप करने में उत्साह दिखा रहे थे। नाटक में अभिनय करने के बाद मुझे आत्म-संतुष्टि का अनुभव हुआ। मैंने स्वयं को नाटक के चरित्र में डूबो दिया था। मेरी इस अभिनय कला की सभी ने सराहना भी की थी।
1. मेरी माँ की ममता
माँ का रिश्ता दुनिया के सब रिश्तेनातों से ऊपर है, इस बात से कौन इनकार कर सकता है। माँ को हमारे शास्त्रों में भगवान् माना गया है। जैसे भगवान् हमारी रक्षा, हमारा पालन-पोषण और हमारी हर इच्छा को पूरा करते हैं वैसे ही माँ भी हमारी रक्षा, पालन-पोषण और स्वयं कष्ट सहकर हमारी सब इच्छाओं को पूरा करती है। इसलिए कहा गया है कि माँ के कदमों में स्वर्ग है। मुझे भी अपनी माँ दुनिया में सबसे प्यारी है। वह मेरी हर ज़रूरत का ध्यान रखती है। मैं भी अपनी माँ की सेवा करता हूँ। मेरी माँ घर में सबसे पहले उठती है। उठकर वह घर की सफ़ाई करने के बाद स्नान करती है और पूजा-पाठ से निवृत्त होकर हमें जगाती है। जब तक हम स्नानादि करते हैं, माँ हमारे लिए नाश्ता तैयार करने में लग जाती है।
नाश्ता तैयार करके वह हमारे स्कूल जाने के लिए कपड़े निकालकर हमें देती है। जब हम स्कूल जाने के लिए तैयार हो जाते हैं तो वह हमें नाश्ता परोसती है। स्कूल जाते समय वह हमें दोपहर के भोजन के लिए कुछ खाने के लिए डिब्बों में बंद करके हमारे बस्तों में रख देती है। स्कूल में हम आधी छुट्टी के समय मिलकर भोजन करते हैं। कई बार हम अपना खाना एक-दूसरे से भी बाँट लेते हैं। मेरे सभी मित्र मेरी माँ के बनाए भोजन की बहुत तारीफ़ करते हैं। सचमुच मेरी माँ बहत स्वादिष्ट भोजन बनाती है। मेरी माँ हमारे सहपाठियों को भी उतना ही प्यार करती हैं जितना हम से। मेरे सहपाठी ही नहीं हमारे मुहल्ले के सभी बच्चे भी उनका आदर करते हैं। हम सब भाई-बहन अपनी माँ का कहना मानते हैं। छुट्टी के दिन हम घर की सफ़ाई में अपनी माँ का हाथ बँटाते हैं। मेरी माँ इतनी अच्छी है कि मेरी ईश्वर से प्रार्थना है कि उस जैसी माँ सबको मिले।

2. मेले की सैर
भारत एक त्योहारों का देश है। इन त्योहारों को मनाने के लिए जगह-जगह मेले लगते हैं। इन मेलों का महत्त्व कुछ कम नहीं है। किंतु पिछले दिनों मुझे जिस मेले को देखने का सुअवसर मिला वह अपने आप में अलग ही था। भारतीय मेला प्राधिकरण तथा भारतीय कृषि और अनुसंधान परिषद के सहयोग से हमारे नगर में एक कृषि मेले का आयोजन किया गया था। भारतीय कृषि विश्वविद्यालयों का इस मेले में सहयोग प्राप्त किया गया था। इस मेले में विभिन्न राज्यों ने अपने-अपने मंडप लगाए थे। उत्तर प्रदेश, पंजाब, बिहार और महाराष्ट्र के मंडपों में गन्ने और गेहूँ की पैदावार से संबंधित विभिन्न चित्रों का प्रदर्शन किया गया था।
केरल, गोवा के काजू और मसालों, असम में चाय, बंगाल में चावल, गुजरात, मध्य प्रदेश और पंजाब में रूई की पैदावार से संबंधित सामग्री प्रदर्शित की थी। अनेक व्यावसायिक एवं औद्योगिक कंपनियों ने भी अपने अलग-अलग मंडप सजाए थे। इसमें रासायनिक खाद, ट्रैक्टर, डीज़ल पंप, मिट्टी खोदने के उपकरण, हल, अनाज की कटाई और छटाई के अनेक उपकरण प्रदर्शित किए गए थे। यह मेला एशिया में अपनी तरह का पहला मेला था। इसमें अनेक एशियाई देशों ने भी अपने व्यापार को बढ़ाने के लिए मंडप लगाए थे। इनमें जापान का मंडप सबसे विशाल था। इस मंडप को देखकर हमें पता चला कि जापान जैसा छोटा-सा देश कृषि के क्षेत्र में कितनी उन्नति कर चुका है। हमारे प्रदेश के बहुत-से कृषक यह मेला देखने आए थे। मेले में उन्हें अपनी खेती के विकास संबंधी काफ़ी जानकारी प्राप्त हुई।
इस मेले का सबसे बड़ा आकर्षण था मेले में आयोजित विभिन्न प्रांतों के लोकनृत्यों का आयोजन। सभी नृत्य एक से बढ़कर एक थे। मुझे पंजाब और हिमाचल प्रदेश के लोकनृत्य सबसे अच्छे लगे। इन नृत्यों को आमने-सामने देखने का मेरा यह पहला ही अवसर था।
3. प्रदर्शनी अवलोकन
पिछले महीने मुझे दिल्ली में अपने किसी मित्र के पास जाने का अवसर प्राप्त हुआ। संयोग से उन दिनों दिल्ली के प्रगति मैदान में एक अंतर्राष्ट्रीय प्रदर्शनी चल रही थी। मैंने अपने मित्र के साथ इस प्रदर्शनी को देखने का निश्चय किया। शाम को लगभग पाँच बजे हम प्रगति मैदान पहँचे। प्रदर्शनी के मुख्य द्वार पर हमें यह सूचना मिल गई कि इस प्रदर्शनी में लगभग तीस देश भाग ले रहे हैं। हमने देखा की सभी देशों ने अपने-अपने पंडाल बड़े कलात्मक ढंग से सजाए हुए हैं। उन पंडालों में उन देशों की निर्यात की जाने वाली वस्तुओं का प्रदर्शन किया जा रहा था।
अनेक भारतीय कंपनियों ने भी अपने-अपने पंडाल सजाए हुए थे। प्रगति मैदान किसी दुल्हन की तरह सजाया गया था। प्रदर्शनी में सजावट और रोशनी का प्रबंध इतना शानदार था कि अनायास ही मन से वाह निकल पड़ती थी। प्रदर्शनी को देखने के लिए आने वालों की काफ़ी भीड़ थी। हमने प्रदर्शनी के मुख्य द्वार से टिकट खरीदकर भीतर प्रवेश किया। सबसे पहले हम जापान के पंडाल में गए। जापान ने अपने पंडाल में कृषि, दूर-संचार, कंप्यूटर आदि से जुड़ी वस्तुओं का प्रदर्शन किया था। हमने वहाँ इक्कीसवीं सदी में टेलीफ़ोन एवं दूर-संचार सेवा कैसी होगी इसका एक छोटा-सा नमूना देखा। जापान ने ऐसे टेलीफ़ोन का निर्माण किया था जिसमें बातें करने वाले दोनों व्यक्ति एक-दूसरे की फ़ोटो भी देख सकेंगे। वहीं हमने एक पॉकेट टेलीविज़न भी देखा जो माचिस की डिबिया जितना था। सारे पंडाल का चक्कर लगाकर हम बाहर आए। उसके बाद हमने दक्षिण कोरिया, ऑस्ट्रेलिया और जर्मनी के पंडाल देखे। उस प्रदर्शनी को देखकर हमें लगा कि अभी भारत को उन देशों का
मुकाबला करने के लिए काफी मेहनत करनी होगी। हमने वहाँ भारत में बनने वाले टेलीफ़ोन, कंप्यूटर आदि का पंडाल भी देखा। वहाँ यह जानकारी प्राप्त करके मन बहुत खुश हुआ कि भारत दूसरे बहुत-से देशों को ऐसा सामान निर्यात करता है। भारतीय उपकरण किसी भी हालत में विदेशों में बने सामान से कम नहीं थे। हमने प्रदर्शनी में ही बने रेस्टोरेंट में चाय-पान किया और इक्कीसवीं सदी में दुनिया में होने वाली प्रगति का नक्शा आँखों में बसाए विज्ञान और तकनीक के क्षेत्र में होने वाली अत्याधुनिक जानकारी प्राप्त करके घर वापस आ गए।
4. नदी किनारे एक शाम
गर्मियों की छुट्टियों के दिन थे। स्कूल जाने की चिंता नहीं थी और न ही होमवर्क की। एक दिन चार मित्र एकत्र हुए और सभी ने यह तय किया कि आज की शाम नदी किनारे सैर करके बिताई जाए। कुछ तो गर्मी से राहत मिलेगी, कुछ प्रकृति के सौंदर्य के दर्शन करके मन खुश होगा। एक ने कही दूजे ने मानी के अनुसार हम सब लगभग छह बजे के करीब एक स्थान पर एकत्र हुए और पैदल ही नदी की ओर चल पड़े।
दिन अभी ढला नहीं था बस ढलने ही वाला था। ढलते सूर्य की लाल-लाल किरणें पश्चिम क्षितिज पर ऐसे लग रही थीं मानो प्रकृति रूपी युवती लाल-लाल वस्त्र पहने मचल रही हो। पक्षी अपने-अपने घोंसलों की ओर लौटने लगे थे। खेतों में हरियाली छायी हुई थी। ज्यों ही हम नदी किनारे पहुँचे सूर्य की सुनहरी किरणें नदी के पानी पर पड़ती हुई बहुत भली प्रतीत हो रही थीं। ऐसे लगता था मानों नदी के जल में हज़ारों लाल कमल एक साथ खिल उठे हों। नदी तट पर लगे वृक्षों की पंक्ति देखकर ‘तरनि तनूजा तट तमाल तरुवर बहु छाए’ कविता की पंक्ति याद हो आई। नदी तट के पास वाले जंगल से ग्वाले पशु चराकर लौट रहे थे। पशुओं के पैरों से उठने वाली धूलि एक मनोरम दृश्य उपस्थित कर रही थी।
हम सभी मित्र बातें कम कर रहे थे, प्रकृति के रूप रस का पान अधिक कर रहे थे। थोड़ी ही देर में सूर्य अस्ताचल की ओर में जाता हुआ प्रतीत हुआ। नदी का जो जल पहले लाल-लाल लगता था अब धीरे-धीरे नीला पड़ना शुरू हो गया था। उड़ते हुए बगुलों की सफ़ेदसफ़ेद पंक्तियाँ उस धूमिल वातावरण में और भी अधिक सफ़ेद लग रही थीं। नदी तट पर सैर करते-करते हम गाँव से काफ़ी दूर निकल आए थे। प्रकृति की सुंदरता निहारते-निहारते ऐसे खोए थे कि समय का ध्यान ही न रहा। हम सब गाँव की ओर लौट पड़े। नदी तट पर नृत्य करती हुई प्रकृति रूपी नदी की यह शोभा विचित्र थी। नदी किनारे सैर करते हुए बिताई यह शाम हमें जिंदगी-भर नहीं भूलेगी।
5. परीक्षा से पहले
अथवा
परीक्षा से एक घंटा पूर्व
वैसे तो हर मनुष्य परीक्षा से घबराता है किंतु विद्यार्थी इससे विशेष रूप से घबराता है। परीक्षा में पास होना ज़रूरी है नहीं तो जीवन का एक बहुमूल्य वर्ष नष्ट हो जाएगा। अपने साथियों से बिछड़ जाएँगे। ऐसी चिंताएँ हर विद्यार्थी को रहती हैं। परीक्षा शुरू होने से पूर्व जब मैं परीक्षा भवन पहुँचा तो मेरा दिल धक्-धक् कर रहा था। परीक्षा शुरू होने से आधा घंटा पहले मैं वहाँ पहुँच गया था। मैं सोच रहा था कि सारी रात जाग कर जो प्रश्न तैयार किए हैं यदि वे प्रश्नपत्र में न आए तो मेरा क्या होगा? इसी चिंता में मैं अपने सहपाठियों से खुलकर बात नहीं कर रहा था।
परीक्षा भवन के बाहर का दृश्य बड़ा विचित्र था। परीक्षा देने आए कुछ विद्यार्थी बिलकुल बेफ़िक्र लग रहे थे। वे आपस में ठहाके मार-मारकर बातें कर रहे थे। कुछ ऐसे भी विद्यार्थी थे जो अभी तक किताबों या नोट्स से चिपके हुए थे। मैं अकेला ऐसा विद्यार्थी था जो अपने साथ घर से कोई किताब या सहायक पुस्तक नहीं लाया था। क्योंकि मेरे पिताजी कहा करते हैं कि परीक्षा के दिन से पहले की रात को ज्यादा पढ़ना नहीं चाहिए। सारे साल का पढ़ा हुआ भूल नहीं जाता। वे परीक्षा के दिन से पूर्व की रात को जल्दी सोने की भी सलाह देते हैं जिससे सवेरे उठकर विद्यार्थी ताज़ा दम होकर परीक्षा देने जाए न कि थका-थका महसूस करे। परीक्षा भवन के बाहर लड़कों की अपेक्षा लड़कियाँ अधिक खुश नज़र आ रही थीं। उनके खिले चेहरे देखकर ऐसा लगता था मानो परीक्षा के भूत का उन्हें कोई डर नहीं। उन्हें अपनी स्मरण-शक्ति पर पूरा भरोसा था।
थोड़ी ही देर में घंटी बजी। यह घंटी परीक्षा भवन में प्रवेश की घंटी थी। इसी घंटी को सुनकर सभी ने परीक्षा भवन की ओर जाना शुरू कर दिया। हँसते हुए चेहरों पर अब गंभीरता आ गई थी। परीक्षा भवन के बाहर अपना अनुक्रमांक और स्थान देखकर मैं परीक्षा भवन में प्रविष्ट हुआ और अपने स्थान पर जाकर बैठ गया। कुछ विद्यार्थी अब भी शरारतें कर रहे थे। मैं मौन हो धड़कते दिल से प्रश्न-पत्र बँटने की प्रतीक्षा करने लगा।
6. मदारी का खेल
कल मैं बाज़ार सब्जी लेने के लिए घर से निकला। चौराहे के एक कोने पर मैंने कुछ लोगों की भीड़ देखी। दूर से देखने पर मुझे लगा कि शायद यहाँ कोई दुर्घटना हो गई। उत्सुकतावश मैं वहाँ चला गया। वहाँ जाकर मुझे पता चला कि वहाँ एक मदारी तमाशा दिखा रहा था। बच्चों की भीड़ जमा है। बहुत-से युवक-युवतियाँ और बुजुर्ग के लोग भी वहाँ एकत्र थे। जब मैं वहाँ पहँचा तो मदारी अपने बंदर और बंदरिया का नाच दिखा रहा था। मदारी डुगडुगी बजा रहा था और बाँसुरी भी बजा रहा था।
बंदरिया ने घाघरा-चोली पहन रखी थी और सिर पर चुनरी भी ओढ़ रखी थी। बंदर ने भी धोती-कुरता पहन रखा था। बंदरिया ने गले में मोतियों की माला और हाथों में चूड़ियाँ भी पहन रखी थीं। मदारी बंदर से पूछ रहा था कि क्या तुम ने विवाह करवाना है। बंदर हाँ में सिर हिलाता। फिर वह यही प्रश्न बंदरिया से करता। बंदरिया भी हाँ में सिर हिलाती। फिर मदारी ने पूछा कि कैसी लड़की से विवाह करवाएगा। बंदर ने हाव-भाव से बताया। उसके हाव-भाव को देखकर सभी हँसने लगे। फिर बंदर दूल्हा बनकर विवाह करने चला और बंदरिया को ब्याह कर लाया। इस सारे तमाशे में बंदर की हरकतों, बंदरिया के शर्माने के अभिनय को देखकर लोगों ने कई बार तालियाँ बजाईं। मदारी ने डुगडुगी बजाकर नाच समाप्त होने की घोषणा की। बंदर-बंदरिया का नाच दिखाने के बाद मदारी ने एक चौंका देने वाला तमाशा दिखाया।
मदारी ने अपने साथ एक छोटे लड़के को ज़मीन पर लिटाकर उसकी एक तेज़ छुरी से जीभ काट ली। बच्चा खून से लथपथ ज़मीन पर छटपटा रहा था। उस भीड़ में मौजूद स्त्रियाँ यह दृश्य देखकर काँप उठीं। कुछ स्त्रियों ने तो उस मदारी को बुरा-भला भी कहना शुरू कर दिया। मदारी पर उनका कोई प्रभाव न पड़ा। वह शांत बना रहा। उसने लोगों को बताया कि यह तो मात्र एक तमाशा है। क्या कोई अपने बच्चे की जीभ काट सकता है। उसने ज़मीन पर पड़े अपने बच्चे का नाम लेकर पुकारा और लड़का हँसता हुआ उठ खड़ा हुआ। उसने अपना मुँह खोल कर लोगों को दिखाया तो उसकी जीभ सही सलामत थी। यह खेल दिखा कर मदारी ने बंदर और बंदरिया के हाथों में दो टोपियाँ पकड़ाकर लोगों से पैसा माँगने के लिए कहा-बंदर और बंदरिया लोगों के सामने मटकते हुए जाते और उनके आगे अपनी टोपी करते। सभी लोगों ने उनकी टोपी में कुछ-न-कुछ ज़रूर डाला जिन्होंने कुछ नहीं डाला उन्हें बंदरों ने घुड़की मारकर डराया और भागने पर विवश कर दिया। मदारी का तमाशा खत्म हुआ। भीड़ छट गई।

7. अवकाश का दिन
अवकाश के दिन की हर किसी को प्रतीक्षा होती है। विशेषकर विद्यार्थियों को तो इस दिन की प्रतीक्षा बड़ी बेसबरी से होती है। उस दिन न तो जल्दी उठने की चिंता होती है, न स्कूल जाने की। स्कूल में भी छुट्टी की घंटी बजते ही विद्यार्थी कितनी प्रसन्नता से कक्षाओं से बाहर आ जाते हैं। अध्यापक महोदय के भाषण का आधा वाक्य ही उनके मुँह में रह जाता है और विद्यार्थी कक्षा छोड़कर बाहर की ओर भाग जाते हैं। जब यह पता चलता है कि आज दिनभर की छुट्टी है तो विद्यार्थी की खुशी का ठिकाना नहीं रहता। वे उस दिन खूब जी भरकर खेलते हैं, घूमते हैं। कोई सारा दिन क्रिकेट के मैदान में बिताता है तो कोई पतंगबाज़ी में सारा दिन बिता देते हैं।
सुबह के घर से निकले शाम को ही घर लौटते हैं। कोई कुछ कहे तो उत्तर मिलता कि आज तो छुट्टी है। लड़कियों के लिए छुट्टी का दिन घरेलू काम-काज का दिन होता है। छुट्टी के दिन मुझे सुबह-सवेरे उठकर अपनी माताजी के साथ कपड़े धोने में सहायता करनी पड़ती है। मेरी माताजी एक स्कूल में पढ़ाती हैं अतः उनके पास कपड़े धोने के लिए केवल छुट्टी का दिन ही उपयुक्त होता है। कपड़े धोने के बाद मुझे अपने बाल धोने होते हैं, बाल धोकर स्नान करके फिर रसोई में माताजी का हाथ बटाना पड़ता है। इस दिन ही हमारे घर में विशेष व्यंजन पकते हैं। दूसरे दिनों में तो सुबह-सवेरे तो सबको भागम-भाग लगी होती है। किसी को स्कूल जाना होता है तो किसी को दफ़्तर। दोपहर के भोजन के पश्चात् थोड़ा आराम करते हैं। फिर माताजी मुझे लेकर बैठ जाती हैं। कुछ सिलाई, बुनाई या कढ़ाई की शिक्षा देती हैं। उनका मानना है कि लड़कियों को ये सब काम आने चाहिए। शाम होते ही शाम की चाय का समय हो जाता है।
अवकाश के दिन शाम की चाय में कभी समोसे, कभी पकौड़े बनाए जाते हैं। चाय पीने के बाद फिर रात के खाने की चिंता होने लगती है और इस तरह अवकाश का दिन एक लड़की के लिए अवकाश का नहीं बल्कि अधिक काम का दिन होता है।
8. रेलवे प्लेटफ़ॉर्म का दृश्य
एक दिन संयोग से मुझे अपने बड़े भाई को लेने रेलवे स्टेशन जाना पड़ा। मैं प्लेटफॉर्म टिकट लेकर रेलवे स्टेशन के अंदर गया। पूछताछ खिड़की से पता चला कि दिल्ली से आने वाली गाड़ी प्लेटफ़ॉर्म नंबर चार पर आएगी। मैं रेलवे पुल पार करके प्लेटफ़ॉर्म नंबर चार पर पहुँच गया। वहाँ यात्रियों की बड़ी संख्या थी। कुछ लोग अपने प्रियजनों को लेने के लिए आए थे तो कुछ अपने प्रियजनों को गाड़ी में सवार कराने के लिए आए हुए थे। जाने वाले यात्री अपने-अपने सामान के पास खड़े थे।
कुछ यात्रियों के पास कुली भी खड़े थे। मैं भी उन लोगों की तरह गाड़ी की प्रतीक्षा करने लगा। इसी दौरान मैंने अपनी नज़र रेलवे प्लेटफॉर्म पर दौड़ाई। मैंने देखा कि अनेक युवक और युवतियाँ अत्याधुनिक पोशाक पहने इधर-उधर घूम रहे थे। कुछ यात्री टी-स्टाल पर खड़े चाय की चुस्कियाँ ले रहे थे, परंतु उनकी नज़रें बार-बार उस तरफ़ उठ जाती थीं, जिधर से गाड़ी आने वाली थी। कुछ यात्री बड़े आराम से अपने सामान के पास खड़े थे, लगता था कि उन्हें गाड़ी आने पर जगह प्राप्त करने की कोई चिंता नहीं। उन्होंने पहले से ही अपनी सीट आरक्षित करवा ली थी। कुछ फेरीवाले भी अपना माल बेचते हुए प्लेटफॉर्म पर घूम रहे थे। सभी लोगों की नज़रें उस तरफ़ थीं जिधर से गाड़ी ने आना था। तभी लगा जैसे गाड़ी आने वाली हो। प्लेटफॉर्म पर भगदड़-सी मच गई। सभी यात्री अपना-अपना सामान उठाकर तैयार हो गए। कुलियों ने सामान अपने सिरों पर रख लिया। सारा वातावरण उत्तेजना से भर गया। देखतेही-देखते गाड़ी प्लेटफॉर्म पर आ पहुँची।
कुछ युवकों ने तो गाड़ी के रुकने की भी प्रतीक्षा न की। वे गाड़ी के साथ दौड़ते-दौड़ते गाड़ी में सवार हो गए। गाड़ी रुकी तो गाड़ी में सवार होने के लिए धक्कम-पेल शुरू हो गई। हर कोई पहले गाड़ी में सवार हो जाना चाहता था। उन्हें दूसरों की नहीं अपनी केवल अपनी चिंता थी। मेरे भाई मेरे सामने वाले डब्बे में थे। उनके गाड़ी से नीचे उतरते ही मैंने उनके चरण-स्पर्श किए और उनका सामान उठाकर स्टेशन से बाहर की ओर चल पड़ा। चलते-चलते मैंने देखा जो लोग अपने प्रियजनों को गाड़ी में सवार कराकर लौट रहे थे। उनके चेहरे उदास थे और मेरी तरह जिनके प्रियजन गाड़ी से उतरे थे उनके चेहरों पर खुशी थी।
9. सूर्योदय का दृश्य
पूर्व दिशा की ओर उभरती हुई लालिमा को देखकर पक्षी चहचहाने लगते हैं। उन्हें सूर्य के आगमन की सबसे पहले सूचना मिल जाती है। वे अपनी चहचहाहट द्वारा समस्त प्राणी-जगत को रात के बीत जाने की सूचना देते हुए जागने की प्रेरणा देते हैं। सूर्य देवता का स्वागत करने के लिए प्रकृति रूपी नदी भी प्रसन्नता में भरकर नाच उठती है। फूल खिल उठते हैं, कलियाँ चटक जाती हैं और चारों ओर का वातावरण सुगंधित हो जाता है।
सूर्य देवता के आगमन के साथ ही मनुष्य रात भर के विश्राम के बाद ताज़ा दम होकर जाग उठते हैं। हर तरफ़ चहल-पहल नज़र आने लगती है। किसान हल और बैलों के साथ अपने खेतों की ओर चल पड़ते हैं। गृहणियाँ घरेलू काम-काज में व्यस्त हो जाती हैं। मंदिरों एवं गुरुद्वारों में लगे लाउडस्पीकर से भजन-कीर्तन के कार्यक्रम प्रसारित होने लगते हैं। भक्तजन स्नानादि से निवृत्त हो पूजा-पाठ में लग जाते हैं। स्कूली बच्चों की माताएँ उन्हें झिंझोड़-झिंझोड़कर जगाने लगती हैं। दफ्तरों को जाने वाले बाबू जल्दी-जल्दी तैयार होने लगते हैं जिससे समय पर बस पकड़कर अपने दफ्तर पहुँच सकें। थोड़ी देर पहले जो शहर सन्नाटे में लीन था आवाज़ों के घेरे में घिरने लगता है। सड़कों पर मोटरों, स्कूटरों, कारों के चलने की आवाजें सुनाई देने लगती हैं।
ऐसा लगता है मानो सड़कें भी नींद से जाग उठी हों। सूर्योदय के समय की प्राकृतिक सुषमा का वास्तविक दृश्य तो किसी गाँव, किसी पहाड़ी क्षेत्र अथवा किसी नदी तट पर ही देखा जा सकता है। प्रात: वेला में सोये रहने वाले लोग प्रकृति की इस सुंदरता के दर्शन नहीं कर सकते। कौन उन्हें बताए कि सूर्योदय के समय सूर्य के सामने आँखें बंदकर दो-चार मिनट खड़े रहने से आँखों की ज्योति कभी क्षीण नहीं होती।
10. अपना घर
कहते हैं कि घरों में घर अपना घर । सच है अपना घर अपना ही होता है। अपने घर में चाहे सारी सुख-सुविधाएँ न भी प्राप्त हों तो भी वह अच्छा लगता है। जो स्वतंत्रता व्यक्ति को अपने घर में होती है वह किसी बड़े-बड़े आलीशान घर में भी नहीं प्राप्त होती। पराये घर में जो झिझक, असुविधा होती है वह अपने घर में नहीं होती। अपने घर में व्यक्ति अपनी मर्जी का मालिक होता है। दूसरे के घर में उस घर के स्वामी की इच्छानुसार अथवा उस घर के नियमों के अनुसार चलना होता है।
अपने घर में आप जो चाहें करें, जो चाहें खाएँ, जहाँ चाहें बैठें, जहाँ चाहें लेटें पर दूसरे के घर में यह सब संभव नहीं। इसीलिए तो किसी ने कहा है-‘जो सुख छज्जू दे चौबारे वह न बलख, न बुखारे।’ शायद यही कारण है कि आजकल नौकरी करने वाले प्रतिदिन मीलों का सफ़र करके नौकरी पर जाते हैं परंतु रात को अपने घर वापस आ जाते हैं। पुरुष तो पहले भी नौकरी करने बाहर जाते थे। आजकल स्त्री भी नौकरी करने घर से कई मील दूर जाती है परंतु आजकल सभी अपने-अपने घरों को लौटना पंसद करते हैं। मनुष्य ही नहीं पशु-पक्षी तक भी अपने घर के महत्त्व को समझते हैं। सारा दिन जंगल में चरने वाली गाएँ, भैंसें, भेड़, बकरियाँ संध्या होते ही अपने-अपने घरों को लौट आते हैं।
पक्षी भी दिनभर दाना-दुनका चुगकर संध्या होते ही अपने-अपने घोंसलों को लौट आते हैं। घर का मोह ही उन्हें अपने घोंसलों में लौट आने के लिए विवश करता है क्योंकि जो सुख अपने घर में मिलता है वह और कहीं नहीं मिलता। इसीलिए कहा गया है कि घरों में घर अपना घर।
11. जब आँधी आई
मई का महीना था। सूर्य देवता लगता था मानो आग बरसा रहे हों। धरती भट्ठी की तरह जल रही थी। हवा भी गरमी के डर से सहमी हुई थम-सी गई थी। पेड़-पौधे तक भीषण गरमी से घबराकर मौन खड़े थे। पत्ता तक नहीं हिल रहा था। उस दिन हमारे विद्यालय में जल्दी छुट्टी कर दी गई। मैं अपने कुछ सहपाठियों के साथ पसीने में लथपथ अपने घर की ओर लौट रहा था कि अचानक पश्चिम दिशा में कालिमा-सी दिखाई दी।
आकाश में चीलें मँडराने लगीं। चारों ओर शोर मच गया कि आँधी आ रही है। हम सब ने तेज़-तेज़ चलना शुरू किया जिससे आँधी आने से पूर्व सुरक्षित अपनेअपने घर पहुँच जाएँ। देखते-ही-देखते तेज़ हवा के झोंके आने लगे। दूर आकाश धूलि से अट गया लगता था। हम सब साथी एक दुकान के छज्जे के नीचे रुक गए और प्रतीक्षा करने लगे कि आँधी गुज़र जाए तो चलें। पलक झपकते ही धूल का एक बहुत बड़ा बवंडर उठा। दुकानदारों ने अपना सामान सहेजना शुरू कर दिया। आस-पास के घरों की खिड़कियाँ, दरवाज़े ज़ोर-ज़ोर से बजने लगे। धूल भरी उस आँधी में कुछ भी दिखाई नहीं दे रहा था। हम सब आँखें बंद करके खड़े थे जिससे हमारी आँखें धूल से न भर जाएँ। राह चलते लोग रुक गए। स्कूटर, साइकिल और कार चलाने वाले भी अपनी-अपनी जगह रुक गए थे। अचानक सड़क के किनारे लगे एक वृक्ष की एक बहुत बड़ी टहनी टूटकर हमारे सामने गिरी। दुकानों के बाहर लगी कनातें उड़ने लगीं।
बहुत-से दुकानदारों ने जो सामान बाहर सजा रखा था, वह उड़ गया। धूल भरी आँधी में कुछ भी दिखाई न दे रहा था। चारों तरफ़ अफ़रा-तफरी मची हुई थी। आँधी का यह प्रकोप करीब घंटा भर रहा। धीरे-धीरे स्थिति सामान्य होने लगी। यातायात फिर से चालू हो गया। हम भी उस दुकान के छज्जे के नीचे से बाहर आकर अपने-अपने घरों की ओर रवाना हुए। सच ही उस आँधी का दृश्य बड़ा ही डरावना था। घर पहुँचते-पहुँचते मैंने देखा रास्ते में बिजली के कई खंबे, वृक्ष आदि उखड़े पड़े थे। सारे शहर में बिजली भी ठप्प हो गई थी। मैं कुशलतापूर्वक अपने घर पहुँच गया। घर पहुँचकर मैंने सुख की साँस ली।
12. मतदान केंद्र का दृश्य
प्रजातंत्र में चुनाव अपना विशेष महत्त्व रखते हैं। गत 22 फरवरी को हमारे नगर में विधानसभा क्षेत्र के लिए उपचुनाव हुआ। चुनाव से कोई महीना भर पहले विभिन्न राजनीतिक दलों द्वारा बड़े जोर-शोर से चुनाव प्रचार किया गया। धन का खुलकर वितरण किया गया। हमारे यहाँ एक कहावत प्रसिद्ध है कि चुनाव के दिनों में यहाँ नोटों की वर्षा होती है। चुनाव आयोग ने लाख सिर पटका पर ढाक के तीन पात ही रहे। आज मतदान का दिन है।
मतदान से एक दिन पूर्व ही मतदान केंद्रों की स्थापना की गई है। मतदान वाले दिन जनता में भारी उत्साह देखा गया। इस बार पहली बार इलेक्ट्रॉनिक मशीनों का प्रयोग किया जा रहा था। अब मतदाताओं को मतदान केंद्र पर मत-पत्र नहीं दिए जाने थे और न ही उन्हें अपने मत मतपेटियों में डालने थे। अब तो मतदाताओं को अपनी पसंद के उम्मीदवार के नाम और चुनावचिह्न के आगे लगे बटन को दबाना भर था। इस नए प्रयोग के कारण भी मतदाताओं में काफी उत्साह देखने में आया। मतदान प्रात: आठ बजे शुरू होना था किंतु मतदान केंद्रों के बाहर विभिन्न राजनीतिक दलों ने अपने-अपने पंडाल समय से काफ़ी पहले सजा लिए थे। उन पंडालों में उन्होंने अपनी-अपनी पार्टी के झंडे एवं उम्मीदवार के चित्र भी लगा रखे थे। दो-तीन मेजें भी पंडाल में लगाई गई थीं। जिन पर उम्मीदवार के कार्यकर्ता मतदान सूचियाँ लेकर बैठे थे और मतदाताओं को मतदाता सूची में से उनकी क्रम संख्या तथा मतदान केंद्र की संख्या तथा मतदान केंद्र का नाम लिखकर एक पर्ची दे रहे थे।
आठ बजने से पूर्व ही मतदान केंद्रों पर मतदाताओं की लंबी-लंबी पंक्तियाँ लगनी शुरू हो गई थीं। मतदाता खूब सज-धज कर आए थे। ऐसा लगता था कि वे किसी मेले में आए हों। दोपहर होते-होते मतदाताओं की भीड़ में कमी आने लगी। राजनीतिक पार्टियों के कार्यकर्ता मतदाताओं को घेर-घेर कर ला रहे थे। चुनाव आयोग ने मतदाताओं को किसी प्रकार के वाहन में लाने की मनाही की है किंतु सभी उम्मीदवार अपने-अपने मतदाताओं को रिक्शा, जीप या कार में बैठाकर ला रहे थे। सायं पाँच बजते-बजते यह मेला उजड़ने लगा। भीड़ मतदान केंद्र से हटकर उम्मीदवारों के पंडालों में जमा हो गई थी और सभी अपने-अपने उम्मीदवार की जीत के अनुमान लगाने लगे।
13. जब भूचाल आया
गरमियों की रात थी। मैं अपने भाइयों के साथ मकान की छत पर सो रहा था। रात लगभग आधी बीत चुकी थी। गरमी के मारे मुझे नींद नहीं आ रही थी। तभी अचानक कुत्तों के भौंकने का स्वर सुनाई पड़ा। यह स्वर लगातार बढ़ता ही जा रहा था और लगता था कि कुत्ते तेज़ी से इधर-उधर भाग रहे हैं। कुछ ही क्षण बाद हमारी मुरगियों ने दड़बों में फड़फड़ाना शुरू कर दिया। उनकी आवाज़ सुनकर ऐसा लगता था कि जैसे उन्होंने किसी साँप को देख लिया हो। मैं बिस्तर पर लेटा-लेटा कुत्तों के भौंकने के कारण पर विचार करने लगा। मैंने समझा कि शायद वे किसी चोर को या संदिग्ध व्यक्ति को देखकर भौंक रहे हैं।
अभी मैं इन्हीं बातों पर विचार कर ही रहा था कि मुझे लगा जैसे मेरी चारपाई को कोई हिला रहा है अथवा किसी ने मेरी चारपाई को झुला दिया हो। क्षण भर में ही मैं समझ गया कि भूचाल आया है। यह झटका भूचाल का ही था। मैंने तुरंत अपने भाइयों को जगाया और उन्हें छत से शीघ्र नीचे उतरने को कहा। छत से उतरते समय हम ने परिवार के अन्य सदस्यों को भी जगा दिया। तेजी से दौड़कर हम सब बाहर खुले मैदान में आ गए। वहाँ पहुँचकर हमने शोर मचाया कि भूचाल आया है। सब लोग घर से बाहर आ जाओ। सभी गहरी नींद में सोये पड़े थे, हड़बड़ाहट में सभी बाहर की ओर दौड़े। मैंने उन्हें बताया कि भूचाल के झटके कभी-कभी कुछ मिनटों के बाद भी आते हैं। अतः हमें सावधान रहना चाहिए। अभी यह बात मेरे मुँह में ही थी कि भूचाल का एक ज़ोरदार झटका और आया। सारे मकानों की खिड़कियाँ, दरवाज़े खड़-खड़ा उठे।
हमें धरती हिलती महसूस हुई। हम सब धरती पर लेट गए। ‘तभी पड़ोस से मकान ढहने की आवाज़ आई। साथ ही बहुत-से लोगों के चीखने-चिल्लाने की आवाजें भी आईं। हम में से कोई भी डर के मारे अपनी जगह से नहीं हिला। कुछ देर बाद जब हम ने सोचा कि जितना भूचाल आना था आ चुका, हम उस जगह की ओर बढ़े। निकट जाकर देखा तो काफ़ी मकान क्षतिग्रस्त हुए थे। ईश्वर कृपा से जान-माल की कोई हानि न हुई थी। वह रात सारे गाँववासियों ने पुनः भूचाल के आने की अशंका में घरों से बाहर रहकर ही बिताई।

14. मेरी रेल-यात्रा
हमारे देश में रेलवे ही एक ऐसा विभाग है जो यात्रियों को टिकट देकर भी सीट की गारंटी नहीं देता। रेल का टिकट खरीदकर सीट मिलने की बात तो बाद में आती है पहले तो गाड़ी में घुस पाने की समस्या सामने आती है। यदि कहीं आप बाल-बच्चों अथवा सामान के साथ यात्रा कर रहे हों तो यह समस्या और भी विकट हो उठती है। कभी-कभी तो ऐसा भी होता है कि टिकट पास होते हुए भी आप गाड़ी में सवार नहीं हो पाते और ‘दिल की तमन्ना दिल में रह गयी’ गाते हुए या रोते हुए घर लौट आते हैं। रेलगाड़ी में सवार होने से पूर्व गाड़ी की प्रतीक्षा करने का समय बड़ा कष्टदायक होता है।
मैं भी एक बार रेलगाड़ी में मुंबई जाने के लिए स्टेशन पर गाड़ी की प्रतीक्षा कर रहा था। गाड़ी दो घंटे लेट थी। यात्रियों की बेचैनी देखते ही बनती थी। गाड़ी आई तो गाड़ी में सवार होने के लिए जोर आजमाई शुरू हो गयी। किस्मत अच्छी थी कि मैं गाड़ी में सवार होने में सफल हो सका। गाड़ी चले अभी घंटा भर ही हुआ था कि कुछ यात्रियों के मुख से मैंने सुना कि यह डब्बा जिसमें मैं बैठा था अमुक स्थान पर कट जाएगा। यह सुनकर मैं तो दुविधा में पड़ गया। गाड़ी रात के एक बजे उस स्टेशन पर पहुंची जहाँ हमारा वह डब्बा मुख्य गाड़ी से कटना था और हमें दूसरे डब्बे में सवार होना था। उस समय अचानक तेज़ वर्षा होने लगी। स्टेशन पर कोई भी कुली नज़र नहीं आ रहा था।
सभी यात्री अपना-अपना सामान उठाए वर्षा में भीगते हुए दूसरे डब्बे की ओर भागने लगे। मैं अपना अटैची लेकर उतरने लगा कि एकदम से वह डब्बा चलने लगा। मैं गिरते-गिरते बचा और अटैची मेरे हाथ से छूटकर प्लेटफॉर्म पर गिर पड़ी। मैंने जल्दी-जल्दी अपना सामान समेटा और दूसरे डब्बे की ओर बढ़ गया। गरमी का मौसम और उस डब्बे के पंखे बंद थे। गाड़ी चली तो थोड़ी हवा लगी और कुछ राहत मिली।
15. एक दिन बिजली न आई
मनुष्य विकास कर रहा है। वह अपनी सुख-सुविधाओं के साधन भी जुटाने लगा है। बिजली भी उन साधनों में से एक है। आजकल हम बिजली पर किसी हद तक निर्भर हो गए हैं इसका पता मुझे उस दिन चला जब हमारे शहर में सारा दिन बिजली नहीं आई। जून का महीना था। सूर्य देव ने उदय होते ही गरमी बरसानी शुरू कर दी थी। आकाश में धूल-सी चढ़ी हुई थी। सात बजे होंगे कि बिजली चली गई। बिजली जाने के साथ ही पानी भी चला गया। घर में बड़े बुजुर्ग तो स्नान कर चुके थे पर हम तो अभी सोकर ही उठे थे इसलिए हमारा नहाना बीच में ही लटक गया।
घर के अंदर इतनी तपश थी कि खड़ा न हुआ जाता था। बाहर निकलते तो वहाँ भी चैन न था। एक तो धूप की तेज़ी और ऊपर से हवा भी बंद थी। दिन चढ़ता गया और गरमी की प्रचंडता भी बढ़ने लगी। हमने बिजलीघर के शिकायत केंद्र को फ़ोन किया तो पता चला कि बिजली पीछे से ही बंद है। कोई पता नहीं कि कब आएगी। गरमी के मारे सब का बुरा हाल था। छोटे बच्चों की हालत देखी न जाती थी। गरमी के कारण माताजी को खाना पकाने में भी बड़ा कष्ट झेलना पड़ा। गला प्यास के मारे सूख रहा था। खाना खाने से पहले तक कई गिलास पानी पी चुके थे। इसलिए खाना भी ठीक ढंग से नहीं खाया गया। उस दिन हमें पता चला कि हम कितने बिजली पर निर्भर हो चुके हैं। मैं बार-बार सोचता था कि जिन दिनों बिजली नहीं थी तब लोग कैसे रहते होंगे। घर में हाथ से चलाने वाले पंखे भी नहीं थे। हम अखबार या कापी के गत्ते को ही पंखा बनाकर हवा ले रहे थे। सूर्य छिप जाने पर गरमी की प्रचंडता में कुछ कमी तो हुई किंतु हवा बंद होने के कारण बाहर खड़े होना भी कठिन लग रहा था।
हमें चिंता हुई कि यदि बिजली रातभर न आई तो रात कैसे कटेगी। बिजली आने पर लोगों ने घरों के बाहर या छत पर सोना छोड़ दिया था। सभी कमरों में ही पंखों, कूलरों को लगाकर ही सोते थे। बाहर सोने पर मच्छरों के प्रकोप को सहना पड़ता था। रात के लगभग नौ बजे बिजली आई और मुहल्ले के हर घर में बच्चों ने ज़ोर से आवाज़ लगाई–’आ गई, आ गई’ और हम सब ने सुख की साँस ली।
16. परीक्षा भवन का दृश्य
मार्च महीने की पहली तारीख थी। उस दिन हमारी वार्षिक परीक्षाएं शुरू हो रही थीं। परीक्षा शब्द से वैसे सभी मनुष्य घबराते हैं परंतु विद्यार्थी वर्ग इस शब्द से विशेष रूप से घबराता है। मैं जब घर से चला तो मेरा दिल भी धक्– धक् कर रहा था। मैं रातभर पढ़ता रहा था और चिंता थी कि यदि सारी रात के पढ़े में से कुछ भी प्रश्न-पत्र में न आया तो क्या होगा? परीक्षा भवन के बाहर सभी विद्यार्थी चिंतित से नज़र आ रहे थे। कुछ विद्यार्थी किताबें लेकर अब भी उसके पन्ने उलट-पुलट रहे थे। कुछ बड़े खुश-खुश नज़र आ रहे थे। लड़कों से ज़्यादा लड़कियाँ अधिक गंभीर नज़र आ रही थीं।
कुछ लड़कियाँ तो बड़े आत्मविश्वास से भरी दिखाई पड़ रही थीं। लड़कियाँ इसी आत्मविश्वास के कारण परीक्षा में लड़कों से बाज़ी मार जाती हैं। मैं अपने सहपाठियों से उस दिन के प्रश्न-पत्र के बारे में बात कर ही रहा था कि परीक्षा भवन में घंटी बजनी शुरू हो गई। यह संकेत था कि हमें परीक्षा भवन में प्रवेश कर जाना चाहिए। सभी विद्यार्थियों ने परीक्षा भवन में प्रवेश करना शुरू कर दिया। भीतर पहुँचकर हम सब अपने-अपने अनुक्रमांक के अनुसार अपनी-अपनी सीट पर जाकर बैठ गए। थोड़ी ही देर में अध्यापकों द्वारा उत्तर-पुस्तिकाएँ बाँट दी गयीं और हम ने उस पर अपना-अपना अनुक्रमांक आदि लिखना शुरू कर दिया। ठीक नौ बजते ही एक घंटी बजी और अध्यापकों ने प्रश्नपत्र बाँट दिए। कुछ विद्यार्थी प्रश्न-पत्र प्राप्त करके उसे माथा टेकते देखे गए। मैंने भी ऐसा ही किया। माथा टेकने के बाद मैंने प्रश्न-पत्र पढ़ना शुरू किया। मेरी खुशी का कोई ठिकाना न था क्योंकि प्रश्न-पत्र के सभी प्रश्न मेरे पढ़े हुए प्रश्नों में से थे।
मैंने किए जाने वाले प्रश्नों पर निशान लगाए और कुछ क्षण तक यह सोचा कि कौन-सा प्रश्न पहले करना चाहिए और फिर उत्तर लिखना शुरू कर दिया। मैंने देखा कुछ विद्यार्थी अभी बैठे सोच ही रहे थे शायद उनके पढ़े में से कोई प्रश्न न आया हो। तीन घंटे तक मैं बिना इधर-उधर देखे लिखता रहा। मैं प्रसन्न था कि उस दिन मेरा पर्चा बहुत अच्छा हुआ था।
17. साइकिल चोरी होने पर
एक दिन मैं अपने स्कूल में अवकाश लेने का आवेदन-पत्र देने गया। मैं अपनी साइकिल स्कूल के बाहर खड़ी कर के, उसे ताला लगाकर स्कूल के भीतर चला गया। थोड़ी देर में ही मैं लौट आया। मैंने देखा मेरी साइकिल वहाँ नहीं थी जहाँ मैं उसे खड़ी करके गया था। मैंने आसपास देखा पर मुझे मेरी साइकिल कहीं नज़र नहीं आई। मुझे यह समझते देर न लगी कि मेरी साइकिल चोरी हो गयी है। मैं सीधा घर आ गया। घर आकर मैंने अपनी माँ को बताया कि मेरी साइकिल चोरी हो गयी है।
मेरी माँ यह सुनकर रोने लगी। उसने कहा कि बड़ी मुश्किल से तीन हजार रुपया खर्च करके तुम्हें साइकिल लेकर दी थी तुम ने वह भी गँवा दी। मेरी साइकिल चोरी हो गयी है, यह बात सारे मुहल्ले में फैल गयी। किसी ने सलाह दी कि पुलिस में रिपोर्ट अवश्य लिखवा देनी चाहिए। मैं पुलिस से बहुत डरता हूँ। मैं डरता-डरता पुलिस चौकी गया। मैं इतना घबरा गया था, मानो मैंने ही साइकिल चुराई हो। पुलिस वालों ने कहा साइकिल की रसीद लाओ, उसका नंबर बताओ, तब हम तुम्हारी रिपोर्ट लिखेंगे। साइकिल खरीदने की रसीद मुझ से गुम हो गयी थी और साइकिल का नंबर मुझे याद नहीं था। मुझे क्या यह मालूम था कि मेरी साइकिल चोरी हो जाएगी? निराश हो मैं घर लौट आया। लौटने पर पता चला कि मेरी साइकिल चोरी होने का समाचार सारे मुहल्ले में फैल गया है। हमारे देश में शोक प्रकट करने का कुछ ऐसा चलन है कि लोग मामूली-से-मामूली बात पर भी शोक प्रकट करने आ पहुँचते हैं। हर आने वाला मुझ से साइकिल कैसे चोरी हुई ? प्रश्न का उत्तर जानना चाहता था। मैं एक ही उत्तर सभी को देता उकता-सा गया। कुछ लोग मुझे सांत्वना देते हुए कहते-जो होना था सो हो गया।
ईश्वर चाहेंगे तो साइकिल ज़रूर मिल जाएगी। मेरा एक मित्र विशेष रूप से शोक-ग्रस्त था। क्योंकि यदाकदा वह मुझसे साइकिल माँगकर ले जाता था। कुछ लोग मुझे यह भी सलाह देने लगे कि मुझे अब कौन-सी कंपनी की बनी साइकिल खरीदनी चाहिए और किस दुकान से खरीदनी चाहिए तथा रसीद सँभालकर रखनी चाहिए। एक तरफ़ मुझे अपनी साइकिल चोरी हो जाने का दुख था तो दूसरी तरफ़ संवेदना प्रकट करने वालों की ऊल-जलूल बातों से परेशानी हो रही थी।
18. जेब कटने पर
यह घटना पिछले साल की है। परीक्षाएँ समाप्त होने के बाद मैं अपने ननिहाल जाने के लिए बस अड्डे पहुँचा। बस अड्डे पर उस दिन काफ़ी भीड़ थी। स्कूलों में छुट्टियाँ हो जाने पर बहुत-से माता-पिता अपने बच्चों को लेकर कहींन-कहीं छुट्टियाँ बिताने जा रहे थे। मेरे गाँव को जाने वाली बस में काफ़ी भीड़ थी। मैं जब बस में सवार हुआ तो बस में बैठने की कोई जगह खाली न थी। मैं भी अपने सामान का बैग कंधे पर लटकाए खड़ा हो गया। कुछ ही देर में बस खचाखच भर चुकी थी परंतु बस वाले अभी बस चलाने को तैयार नहीं थे। वे और सवारियों को चढ़ा रहे थे।
जब बस के अंदर तिल धरने को भी जगह न रही तो कंडक्टर ने सवारियों को बस की छत पर चढ़ाना शुरू कर दिया। गरमियाँ अभी पूरी तरह से शुरू नहीं हुई थी फिर भी हम बस के अंदर खड़े-खड़े पसीने से लथपथ हो रहे थे। मेरे पीछे एक सुंदर लड़की खड़ी थी। बस चलने से कुछ देर पहले वह लड़की यह कहकर बस से उतर गई कि यहाँ तो खड़ा भी नहीं हुआ जाता। मैं अगली बस से चली जाऊँगी। बड़ी मुश्किल से बस ने चलने का नाम लिया। बस चलने के बाद कंडक्टर ने टिकटें बाँटना शुरू किया। थोड़ी देर में ही पीछे खड़े यात्रियों में से दो यात्रियों ने शोर मचाया कि उनकी किसी ने जेब काट ली है। कंडक्टर ने उन्हें बस रोककर बस से उतार दिया। कंडक्टर जब मेरे पास आया तो मैंने पैंट की पिछली जेब से जैसे ही बटुआ निकालने के लिए हाथ बढ़ाया। मैंने अनुभव किया कि मेरी जेब में बटुआ नहीं है। मैंने कंडक्टर को बताया कि मेरी जेब भी किसी ने काट ली है। सौभाग्य से मेरी दूसरी जेब में इतने पैसे थे कि मैं टिकट के पैसे दे. सकता।
कंडक्टर ने मुझे टिकट देते हुए कहा तुम फ़ैशन के मारे बटुए पैंट की पिछली जेब में रखोगे तो जेब कटेगी ही। मैं थोड़ा शर्मिंदा अनुभव कर रहा था। दूसरे यात्री हँस रहे थे कि मैं बस से उतारे जाने से बच गया। मुझे यह समझते देर न लगी कि जो फैशनेबल-सी लड़की मेरे पीछे खड़ी थी उसी ने मेरी जेब साफ़ की है। मेरी ही नहीं बल्कि दूसरे यात्रियों की जेबों की वही सफ़ाई कर गई है। मैं सोचने लगा कि बस अड्डे पर तो सरकार ने लिखा है कि जेबकतरों से सावधान रहें बसों में भी ऐसे बोर्ड लगवा देने चाहिए या फिर बस चालक गिनती से अधिक सवारियाँ बस में न चढ़ाएँ। इतनी भीड़ में तो किसी की भी जेब कट सकती है।

19. जीवन की अविस्मरणीय घटना
आज मैं दसवीं कक्षा में हूँ। माता-पिता कहते हैं कि अब तुम बड़े हो गए हो। मैं भी कभी-कभी सोचता हूँ कि क्या मैं सचमुच बड़ा हो गया हूँ। हाँ, मैं सचमुच बड़ा हो गया हूँ। मुझे बीते दिनों की कुछ बातें आज भी याद हैं जो मेरा मार्गदर्शन कर रही हैं। एक घटना ऐसी है जिसे मैं आज भी याद करके आनंद-विभोर हो उठता हूँ। घटना कुछ इस तरह से है। कोई दो-तीन साल पहले की घटना है। मैंने एक दिन देखा कि हमारे आँगन में लगे वृक्ष के नीचे एक चिड़िया का बच्चा घायल अवस्था में पड़ा है।
मैं उस बच्चे को उठा कर अपने कमरे में ले आया। मेरी माँ ने मुझे रोका भी कि इसे इस तरह न उठाओ यह मर जाएगा किंतु मेरा मन कहता था कि इस चिड़िया के बच्चे को बचाया जा सकता है। मैंने उसे चम्मच से पानी पिलाया। पानी मुँह में जाते ही उस बच्चे ने जो बेहोश-सा लगता था पंख फड़फड़ाने शुरू कर दिए। यह देख कर मैं प्रसन्न हुआ। मैंने उसे गोद में लेकर देखा कि उसकी टाँग में चोट आई है। मैंने अपने छोटे भाई को माँ से मरहम की डिबिया लाने के लिए कहा। वह तुरंत मरहम की डिबिया ले आया। उसमें से थोड़ी-सी मरहम मैंने उस चिड़िया के बच्चे की चोट पर लगाई। मरहम लगाते ही मानो उसकी पीड़ा कुछ कम हुई। वह चुपचाप मेरी गोद में ही लेटा था। मेरा छोटा भाई भी उसके पंखों पर हाथ फेरकर खुश हो रहा था। कोई घंटा भर मैं उसे गोद में ही लेकर बैठा रहा। मैंने देखा कि बच्चा थोड़ा उड़ने की कोशिश करने लगा था।
मैंने छोटे भाई से रोटी मँगवाई और उसकी चूरी बनाकर उसके सामने रखी। वह उसे खाने लगा। हम दोनों भाई उसे खाते हुए देखकर खुश हो रहे थे। मैंने उसे अब अपनी पढ़ाई की मेज़ पर रख दिया। रात को एक बार फिर उस के घाव पर मरहम लगाई। दूसरे दिन मैंने देखा चिड़िया का वह बच्चा मेरे कमरे में इधर-उधर फुदकने लगा है। वह मुझे देख चींची करके मेरे प्रति अपना आभार प्रकट कर रहा था। एक-दो दिनों में ही उसका घाव ठीक हो गया और मैंने उसे आकाश में छोड़ दिया। वह उड़ गया। मुझे उस चिड़िया के बच्चे के प्राणों की रक्षा करके जो आनंद प्राप्त हुआ उसे मैं जीवनभर नहीं भुला पाऊँगा।
20. आँखों देखा हॉकी मैच
भले ही आज लोग क्रिकेट के दीवाने बने हुए हैं परंतु हमारा राष्ट्रीय खेल हॉकी ही है। लगातार कई वर्षों तक भारत हॉकी के खेल में विश्वभर में सबसे आगे रहा किंतु खेलों में भी राजनीतिज्ञों के दखल के कारण हॉकी के खेल में हमारा स्तर दिनोंदिन गिर रहा है। 70 मिनट की अवधि वाला यह खेल अत्यंत रोचक, रोमांचक और उत्साहवर्धक होता है। मेरा सौभाग्य है कि मुझे ऐसा ही एक हॉकी मैच देखने को मिला। यह मैच सुभाष एकादश और चंद्र एकादश की टीमों के बीच चेन्नई के खेल परिसर में खेला गया। दोनों टीमें अपने-अपने खेल के लिए देशभर में जानी जाती हैं।
दोनों ही टीमों में राष्ट्रीय-स्तर के खिलाड़ी भाग ले रहे थे। चंद्र एकादश की टीम क्योंकि अपनी घरेलू मैदान पर खेल रही थी इसलिए उसने सुभाष एकादश को मैच के आरंभिक दस मिनटों में दबाए रखा। उसके फॉरवर्ड खिलाड़ियों ने दो-तीन बार विरोधी गोल पर आक्रमण किए। सुभाष एकादश का गोलकीपर बहुत ही चुस्त और होशियार था उसने अपने विरोधियों के सभी आक्रमणों को विफल बना दिया। जब सुभाष एकादश ने तेजी पकड़ी तो देखते-ही-देखते चंद्र एकादश के विरुद्ध एक गोल दाग दिया। गोल होने पर चंद्र एकादश की टीम ने एक-जुट होकर दो-तीन बार सुभाष एकादश पर कड़े आक्रमण किए परंतु उनका प्रत्येक आक्रमण विफल रहा। इसी बीच चंद्र एकादश को दो पेनल्टी कार्नर भी मिले पर वे इसका लाभ न उठा सके। सुभाष एकादश ने कई अच्छे मूव बनाए। उनका कप्तान बलजीत सिंह तो जैसे बलबीर सिंह ओलंपियन की याद दिला रहा था।
इसी बीच सुभाष एकादश को भी एक पेनल्टी कार्नर मिला जिसे उन्होंने बड़ी खूबसूरती से गोल में बदल दिया। इससे चंद्र एकादश के खिलाड़ी हताश हो गए। चेन्नई के दर्शक भी उनके खेल को देखकर कुछ निराश हुए। मध्यांतर के समय सुभाष एकादश दो शून्य से आगे थी। मध्यांतर के बाद खेल बड़ी तेजी से शुरू हुआ। चंद्र एकादश के खिलाड़ी बड़ी तालमेल से आगे बढ़े और कप्तान हरजीत सिंह ने दाएँ कोण से एक बढ़िया हिट लगाकर सुभाष एकादश पर एक गोल कर दिया। इस गोल से चंद्र एकादश के जोश में ज़बरदस्त वृद्धि हो गई। उन्होंने अगले पाँच मिनटों में दूसरा गोल करके मैच बराबरी पर ला दिया। दर्शक खुशी से नाच उठे। मैच समाप्ति की सीटी के बजते ही दर्शकों ने खिलाड़ियों को मैदान में जाकर शाबाशी दी। मैच का स्तर इतना अच्छा था कि मैच देखकर आनंद आ गया।
21. पत्थर तोड़ती मज़दूरिन
जून का महीना था। गरमी इतनी प्रचंड पड़ रही थी कि मनुष्य तो क्या पशु-पक्षी तक सभी घबरा उठे थे। दूरदर्शन पर बीती रात बताया गया था कि गरमी का प्रकोप 46 डिग्री तक बढ़ जाने का अनुमान है। सड़कें सूनी हो गई थीं। यातायात भी मानो रुक गया हो। लगता था वृक्षों की छाया भी गरमी की भीषणता से घबराकर छाया तलाश रही थी। ऐसे में हमारे मुहल्ले के कुछ लड़के वृक्षों की छाया में क्रिकेट खेल रहे थे। उनमें मेरा छोटा भाई भी था।
मेरी माँ ने कहा उसे बुला लाओ कहीं लू न लग जाए। मैं उसे लेने के लिए घर से निकला तो मैंने कड़कती धूप और भीषण गरमी में एक मज़दूरिन को एक नए बन रहे मकान के पास पत्थर तोड़ते देखा। जहाँ वह स्त्री पत्थर तोड़ रही थी वहाँ आसपास कोई वृक्ष भी नहीं था। वह गरमी की भयंकरता की परवाह न करके भी हथौड़ा चलाए जा रही थी। उसके माथे से पसीना टपक रहा था। कभी-कभी वह उदास नज़रों से सामने वाले मकानों की ओर देख लेती थी। जिनके अमीर मालिक गरमी को भगाने के पूरे उपाय करके अपने घरों में आराम कर रहे थे। उसे देखकर मेरे मन में आया कि विधि की यह कैसी बिडंबना है कि जो लोग मकान बनाने वाले हैं वे तो कड़कती दुपहरी में काम कर रहे हैं और जिन लोगों के मकान बन रहे हैं वे इस कष्ट से दूर हैं।
मेरी सहानुभूति भरी नज़र को देखकर वह मज़दूरिन पहले तो कुछ ठिठकी किंतु फिर कुछ ध्यान कर अपने काम में व्यस्त हो गयी। उसकी नज़रें मुझे जैसे कह रही हों काम नहीं करूँगी तो रात को रोटी कैसे पकेगी। मैं वेतन भोगी नहीं दिहाड़ीदार मज़दूर हूँ। इस सामाजिक अन्याय को देखकर मेरा हृदय चीत्कार कर उठा। काश ! मैं इन लोगों के लिए कुछ कर सकता।
22. आँखों देखी दुर्घटना
रविवार की बात है मैं अपने मित्र के साथ सुबह-सुबह सैर करने माल रोड पर गया। वहाँ बहत-से स्त्री-पुरुष और बच्चे भी सैर करने आए हुए थे। जब से दूरदर्शन पर स्वास्थ्य संबंधी कार्यक्रम आने लगे हैं अधिक-से-अधिक लोग प्रातः भ्रमण के लिए इन जगहों पर आने लगे हैं। रविवार होने के कारण उस दिन भीड़ कुछ अधिक थी। तभी मैंने वहाँ एक युवा दंपति को अपने छोटे बच्चे को बच्चागाड़ी में बैठाकर सैर करते देखा।
अचानक लड़कियों के स्कूल की ओर से एक ताँगा आता हुआ दिखाई दिया। उस में चार-पाँच सवारियाँ भी बैठी थीं। बच्चागाड़ी वाले दंपति ने ताँगे से बचने के लिए सड़क पार करनी चाही। जब वे सड़क पार कर रहे थे तो दूसरी तरफ़ से बड़ी तेज़ गति से आ रही एक कार उस ताँगे से टकरा गई। ताँगा चलाने वाला और दो सवारियाँ बुरी तरह से घायल हो गये थे। बच्चागाड़ी वाली स्त्री के हाथ से बच्चागाड़ी छूट गई। किंतु इस से पूर्व कि वह बच्चे समेत ताँगे और कार की टक्कर वाली जगह पर पहुँचकर उनसे टकरा जाती, मेरे साथी ने भागकर उस बच्चागाड़ी को सँभाल लिया। कार चलाने वाले सज्जन को भी काफ़ी चोटें आई थीं पर उसकी कार को कोई खास क्षति नहीं पहुंची थी। माल रोड पर गश्त करने वाले पुलिस के तीन-चार सिपाही तुरंत घटना-स्थल पर पहुँच गए। उन्होंने वायरलैस द्वारा अपने अधिकारियों और हस्पताल को फ़ोन किया।
चंद मिनटों में वहाँ ऐंब्युलेंस गाड़ी आ गई। हम सब ने घायलों को उठाकर ऐंब्युलेंस में लिटाया। पुलिस के वरिष्ठ अधिकारी भी तुरंत वहाँ पहुँच गए। उन्होंने कार चालक को पकड़ लिया था। प्रत्यक्षदर्शियों ने पुलिस को बताया कि सारा दोष कार चालक का था। इस सैर-सपाटे वाली सड़क पर वह 100 कि० मी० की स्पीड से कार चला रहा था और ताँगा सामने आने पर ब्रेक न लगा सका। दूसरी तरफ़ बच्चे को बचाने के लिए मेरे मित्र द्वारा दिखाई फुर्ती और चुस्ती की भी लोग सराहना कर रहे थे। उस दंपति ने उसका विशेष धन्यवाद किया।
23. हम ने मनाई पिकनिक
पिकनिक एक ऐसा शब्द है जो थके हुए शरीर एवं मन में एकदम स्फूर्ति ला देता है। मैंने और मेरे मित्र ने परीक्षा के दिनों में बड़ी मेहनत की थी। परीक्षा का तनाव हमारे मन और मस्तिष्क पर विद्यमान था। उस तनाव को दूर करने के लिए हम दोनों ने यह निर्णय किया कि क्यों न किसी दिन माधोपुर हैडवर्क्स पर जाकर पिकनिक मनायी जाए। अपने इस निर्णय से अपने मुहल्ले के दो-चार और मित्रों को अवगत करवाया तो वे भी हमारे साथ चलने को तैयार हो गए। माधोपुर हैडवर्क्स हमारे नगर से दस कि० मी० दूरी पर था। हम सब ने अपने-अपने साइकिलों पर जाने का निश्चय किया।
पिकनिक के लिए रविवार का दिन निश्चित किया गया। रविवार को हम सब ने नाश्ता करने के बाद अपन-अपने लंच बॉक्स तैयार किए तथा कुछ अन्य खाने का सामान अपने अपने साइकिलों पर रख लिया। मेरे मित्र के पास एक छोटा सी०डी० प्लेयर भी था उसे भी अपने साथ ले लिया तथा साथ में कुछ अपने मनपंसद गानों की सी०डी० भी रख ली। हम सब अपनी-अपनी साइकिल पर सवार होकर, हँसते-गाते एक-दूसरे को चुटकले सुनाते पिकनिक स्थल की अनुच्छेद लेखन ओर बढ़ चले। लगभग 45 मिनट में हम सब माधोपुर हैडवर्क्स पर पहुंच गए। वहाँ हम ने प्रकृति को अपनी संपूर्ण सुषमा के साथ विराजमान देखा।
चारों तरफ़ रंग-बिरंगे फूल खिले हुए थे, शीतल और मंद-मंद हवा बह रही थी। हम ने एक ऐसी जगह चुनी जहाँ घास की प्राकृतिक कालीन बिछी हुई थी। हमने वहाँ एक दरी बिछा दी। साइकिल चलाकर हम थोड़ा थक गए थे, अतः हमने पहले थोड़ी देर विश्राम किया। हमारे एक साथी ने हमारी कुछ फ़ोटो उतारी। थोड़ी देर सुस्ता कर हमने सी०डी० प्लेयर चला दिया और उसने गीतों की धुन पर मस्ती में भर कर नाचने लगे। कुछ देर तक हम ने इधर-उधर घूमकर वहाँ के प्राकृतिक दृश्यों का नजारा किया। दोपहर को हम सब ने अपने-अपने टिफ़न खोले और सबने मिल-बैठकर एक-दूसरे का भोजन बाँटकर खाया। उसके बाद हम ने वहाँ स्थित कैनाल रेस्ट हाउस रेस्टोराँ में जाकर चाय पी।
चाय-पान के बाद हम ने अपने स्थान पर बैठकर अंताक्षरी खेलनी शुरू की। इसके बाद हमने एकदूसरे को कुछ चुटकले और कुछ आप बीती हँसी-मज़ाक की बातें बताईं। समय कितनी जल्दी बीत गया इसका हमें पता ही न चला। जब सूर्य छिपने को आया तो हम ने अपना-अपना सामान समेटा और घर की तरफ चल पड़े।
24. पर्वतीय यात्रा
आश्विन महीने के नवरात्रों में पंजाब के अधिकतर लोग देवी दुर्गा माता के दरबार में हाजिरी लगवाने और माथा टेकने जाते हैं। पहले हम हिमाचल प्रदेश में स्थित माता चिंतपूर्णी और माता ज्वाला जी के मंदिरों में माथा टेकने जाया करते थे। इस बार हमारे मुहल्लेवासियों ने मिलकर जम्मू-क्षेत्र में स्थित माता वैष्णो देवी के दर्शनों को जाने का निर्णय किया। हमने एक बस का प्रबंध किया था जिसमें लगभग पचास के करीब बच्चे-बूढ़े और स्त्री-पुरुष सवार होकर जम्मू के लिए रवाना हुए। सभी परिवारों ने अपने साथ भोजन आदि सामग्री भी ले ली थी। पहले हमारी बस पठानकोट पहुँची वहाँ कुछ रुकने के बाद हम ने जम्मू-क्षेत्र में प्रवेश किया। हमारी बस टेढ़े-मेढ़े पहाड़ी रास्ते को पार करती हुई जम्मूतवी पहुँच गयी।
सारे रास्ते में दोनों तरफ़ अद्भुत प्राकृतिक दृश्य देखने को मिले जिन्हें देखकर हमारा मन प्रसन्न हो उठा। बस में सवार सभी यात्री माता की भेटें गा रहे थे और बीच में माँ शेरावाली का जयकारा भी बुला रहे थे। प्रातः सात बजे हम कटरा पहुँच गए। वहाँ एक धर्मशाला में हम ने अपना सामान रखा और विश्राम किया और वैष्णो देवी जाने के लिए टिकटें प्राप्त की। दूसरे दिन सुबह-सवेरे हम सभी माता की जय पुकारते हुए माता के दरबार की ओर चल पड़े। कटरा से भक्तों को पैदल ही चलना पड़ता है। कटरे से माता के दरबार तक जाने के दो मार्ग हैं। एक सीढ़ियों वाला मार्ग तथा दूसरा साधारण। हमने साधारण मार्ग को चुना। इस मार्ग पर कुछ लोग खच्चरों पर सवार होकर भी यात्रा कर रहे थे। मार्ग में हमने बाण-गंगा में स्नान किया। पानी बर्फ़-सा ठंडा था फिर भी सभी यात्री बड़ी श्रद्धा से स्नान कर रहे थे। कहते हैं यहाँ माता वैष्णो देवी ने हनुमान जी की प्यास बुझाने के लिए बाण चलाकर गंगा उत्पन्न की थी।
यात्रियों को बाण-गंगा में नहाना ज़रूरी माना जाता है अन्यथा कहते हैं कि माता के दरबार की यात्रा सफल नहीं होती। चढ़ाई बिलकुल सीधी थी। चढ़ाई चढ़ते हुए हमारी साँस फूल रही थी परंतु सभी यात्री माता की भेटें गाते हुए और माता की जय-जयकार करते हुए बड़े उत्साह से आगे बढ़ रहे थे। सारे रास्ते में बिजली के बल्ब लगे हुए थे और जगह-जगह पर चाय की दुकानें और पीने के पानी का प्रबंध किया गया था। कुछ ही देर में हम आदक्वारी नामक स्थान पर पहुँच गए। मंदिर के निकट पहुँचकर हम दर्शन करने वाले भक्तों की लाइन में खड़े हो गए। अपनी बारी आने पर हम ने माँ के दर्शन किए। श्रद्धापूर्वक माथा टेका और मंदिर से बाहर आ गए। आजकल मंदिर का सारा प्रबंध जम्मू-कश्मीर की सरकार एवं एक ट्रस्ट की देख-रेख में होता है। सभी प्रबंध बहुत अच्छे एवं सराहना के योग्य थे। घर लौटते तक हम सभी माता के दर्शनों के प्रभाव का अनुभव करते रहे।

25. ऐतिहासिक यात्रा
यह बात पिछली गरमियों की है। मुझे मेरे मित्र का पत्र प्राप्त हुआ जिसने मुझे कुछ दिन उसके साथ आगरा में बिताने का निमंत्रण दिया गया था। यह निमंत्रण पाकर मैं बहुत प्रसन्न हुआ। किसी महत्त्वपूर्ण ऐतिहासिक स्थान को देखने का मुझे अवसर मिल रहा था। मैंने अपने पिता से बात की तो उन्होंने खुशी-खुशी मुझे आगरा जाने की अनुमति दे दी। मैं रेल द्वारा आगरा पहुँचा। मेरा मित्र मुझे स्टेशन पर लेने आया हुआ था। वह मुझे अपने घर ले गया। उस दिन पूर्णिमा थी और कहते हैं पूर्णिमा की चाँदनी में ताजमहल को देखने का आनंद ही कुछ और होता है। रात के लगभग नौ बजे हम घर से निकले। दूर से ही ताजमहल के मीनारों और गुंबदों का दृश्य दिखाई दे रहा था।
हमने प्रवेश-द्वार से टिकट खरीदे और अपनी बारी की प्रतीक्षा करने लगे। भारत सरकार ने ताजमहल को प्रदूषण से बचाने के लिए कई उपाय किए हैं जिनमें यात्रियों की संख्या को नियंत्रित करना भी एक है। ताजमहल के चारों ओर लाल पत्थर की दीवारें हैं जिसमें एक बहुत बड़ा सुंदर उद्यान है जिसकी सजावट और हरियाली देखकर मन मोहित हो उठता है। हमने ताजमहल परिसर में जब प्रवेश किया तो देखा कि अंदर देशी कम विदेशी पर्यटक अधिक थे। ताजमहल तक जाने के लिए सबसे पहले एक बहुत ऊँचे और सुंदर द्वार से होकर जाना पड़ता है। ताजमहल उद्यान के एक ऊँचे चबूतरे पर बनाया गया है जो सफ़ेद संगमरमर का बना है। इसका गुंबद बहुत ऊँचा है उसके चारों ओर बड़ी-बड़ी मीनारें हैं। ताजमहल के पश्चिम की ओर यमुना नदी बहती है। यमुना जल में ताज की परछाईं बहुत सुंदर और मोहक लग रही थी। हम ने ताजमहल के भीतर प्रवेश किया। सबसे नीचे के भवन में मुगल सम्राट शाहजहाँ और उसकी पत्नी और प्रेमिका मुमताज महल की कब्रे हैं।
उन पर अरबी भाषा में कुछ लिखा हुआ है और बहुत-से रंग-बिरंगे बेलबूटे बने हुए हैं। इस कमरे के ठीक ऊपर एक ऐसा ही भाग है। सौंदर्य की दृष्टि से भी उसका विशेष महत्त्व है। कहते हैं इसमें बनी संगमरमर की जाली की जगह पहले सोने की बनी जाली थी जिसे औरंगजेब ने हटवा दिया था। कहते हैं कि ताजमहल के निर्माण में बीस वर्ष लगे थे और उस युग में तीस लाख रुपये खर्च हुए थे। इसे बनाने में तीस हज़ार मजदूरों ने योगदान किया था। यह स्मारक बादशाह ने अपनी पत्नी की याद में बनवाया था। इसे संसार के सात आश्चर्यों में भी गिना जाता है। दुनियाभर से हर वर्ष लाखों लोग इसे देखने के लिए आते हैं।
26. जैसी संगति बैठिए तैसोई फल होत
मनुष्य एक सामाजिक प्राणी है। जब तक वह समाज से संपर्क स्थापित नहीं करता तब तक उसके जीवन की गाड़ी नहीं चल सकती। समाज में कई प्रकार के लोग होते हैं। कुछ सदाचारी हैं तो कुछ दुराचारी। हमें ऐसे लोगों की संगति करनी चाहिए जो हमारे जीवन को उन्नत एवं निर्मल बनाएँ। अच्छी संगति का प्रभाव अच्छा तथा बुरी संगति का प्रभाव बुरा होता है। क्योंकि ‘जैसी संगति बैठिए तैसोई फल होत’ कहा भी है कि किसी व्यक्ति के आचरण को जानने के लिए उसकी संगति को जानना चाहिए। क्योंकि दुष्टों के साथ रहने वाला व्यक्ति भला हो ही नहीं सकता। संगति का प्रभाव जाने अथवा अनजाने अवश्य पड़ता है। बचपन में जो बालक परिवार अथवा मुहल्ले में जो कुछ सुनते हैं, प्रायः उसी को दोहराते हैं।
कहा गया है “दुर्जन यदि विद्वान् भी हो तो उसकी संगति छोड़ देना चाहिए। मणि धारण करने वाला साँप क्या भयंकर नहीं होता?” सत्संगति का हमारे चरित्र के निर्माण में बड़ा हाथ रहता है। अच्छी पुस्तकों का अध्ययन भी सत्संग से कम नहीं। विद्वान् लेखक अपनी पुस्तक रूप में हमारे साथ रहता है। अच्छी पुस्तकें हमारी मित्र एवं पथप्रदर्शक हैं। महान् व्यक्तियों के संपर्क ने अनेक व्यक्तियों के जीवन को कंचन के समान बहुमूल्य बना दिया। दुष्टों एवं दुराचारियों का संग मनुष्य को पतन की ओर ले जाता है। मनुष्य को विवेक प्राप्त करने के लिए सत्संगति का आश्रय लेना चाहिए। अपनी और समाज की उन्नति के लिए सत्संग से बढ़कर दूसरा साधन नहीं है। अच्छी संगति आत्म-बल को बढ़ाती है तथा सद्मार्ग पर चलने की प्रेरणा देती है।
27. सब दिन होत न एक समान
जीवन को जल की संज्ञा दी गई है। जल कभी सम भूमि पर बहता है तो कभी विषम भूमि पर। कभी रेगिस्तान की भूमि उसका शोषण करती है तो कभी वर्षा की धारा उसके प्रवाह को बढ़ा देती है। मानव-जीवन में भी कभी सुख का अध्याय जुड़ता है तो कभी दुख अपने पूरे दल-बल के साथ आक्रमण करता है। प्रकृति में दुख-सुख की धूप-छाया के दर्शन होते हैं। प्रात:काल का समय सुख का प्रतीक है तो रात्रि दुख का। विभिन्न ऋतुएँ भी जीवन के विभिन्न पक्षों की प्रतीक हैं। राष्ट्रकवि श्री मैथिलीशरण गुप्त ने ठीक ही कहा है-
संसार में किसका समय है एक सा रहता सदा,
है निशा दिवा सी घूमती सर्वत्र विपदा-संपदा।
संसार के बड़े-बड़े शासकों का समय भी एक-सा नहीं रहा है। अंतिम मुगल सम्राट बहादुरशाह जफ़र का करुण अंत इस बात का प्रमाण है कि मनुष्य का समय हमेशा एक-सा नहीं रहता। जो आज दीन एवं दुखी है वह कल वैभव के झूले में झूलता दिखाई देता है। जो आज सुख-संपदा एवं ऐश्वर्य में डूबा हुआ है, संभव है भाग्य के विपरीत होने के कारण उसे दर-दर की ठोकरें खाने पर विवश होना पड़े। जो वृक्ष, लताएँ एवं पौधे वसंत ऋतु में वातावरण को मादकता प्रदान करते हैं, वही पतझड़ में वातावरण को नीरस बना देते हैं। जीवन सुख-दुख, आशा-निराशा एवं हर्ष-विषाद का समन्यव है। एक ओर जीवन का उदय है तो दूसरी ओर जीवन का अस्त। अतः ठीक ही कहा गया है-‘सब दिन होत न एक समान।’
28. जननी जन्मभूमिश्च स्वर्गादपिगरीयसी
इस कथन का भाव है, “जननी और जन्मभूमि का स्थान स्वर्ग से भी ऊँचा है।” जो व्यक्ति अपनी माँ से और भूमि से प्रेम नहीं करता, वह मनुष्य कहलाने का अधिकारी नहीं है। देश-द्रोह एवं मातृद्रोह से बड़ा अपराध कोई और नहीं है। यह ऐसा अपराध है जिसका प्रायश्चित्त संभव ही नहीं है। देश-प्रेम की भावना ही मनुष्य को यह प्रेरणा देती है कि जिस भूमि से उसका भरण-पोषण हो रहा है, उसकी रक्षा के लिए उसे अपना सब कुछ अर्पित कर देना उसका परम कर्तव्य है। जननी एवं जन्मभूमि के प्रति प्रेम की भावना जीवधारियों की स्वाभाविक प्रवृत्ति है। मनुष्य संसार का सर्वश्रेष्ठ प्राणी है। अतः उसके हृदय में देशानुराग की भावना का उदय स्वाभाविक है। मरुस्थल में रहने वाले लोग हाँफ-हाँफ कर जीते हैं, फिर भी उन्हें अपनी जन्मभमि से अगाध प्रेम है। ध्रववासी अत्यंत शीत के कारण अंधकार तथा शीत में काँप-काँप कर तो जीवन व्यतीत कर लेते हैं, पर अपनी मातृभूमि का बाल-बाँका नहीं होने देते। मुग़ल साम्राज्य के अंतिम दीप सम्राट् बहादुरशाह जफ़र की रंगून के कारागार से लिखी ये पंक्तियाँ कितनी मार्मिक हैं-
कितना है बदनसीब ज़फ़र दफ़न के लिए,
दो गज़ ज़मीन भी न मिली कूचा-ए-यार में।
जिस देश के लोग अपनी मातृ-भूमि से जितना अधिक स्नेह करते हैं, वह देश उतना ही उन्नत माना जाता है। देशप्रेम की भावना ने ही भारत की पराधीनता की जंजीरों को काटने के लिए देश-भक्तों को प्रेरित किया है। स्वतंत्रता प्राप्ति के बाद देश के प्रति हमारा कर्त्तव्य और भी बढ़ गया है। इस कर्त्तव्य की पूर्ति हमें जी-जान लगाकर करनी चाहिए।
29. नेता नहीं, नागरिक चाहिए
लोगों के नेतृत्व करने वाले व्यक्ति को नेता कहते हैं। आदर्श नेता एक मार्ग-दर्शक के समान है जो दूसरों को सुमार्ग की ओर ले जाता है। आदर्श नागरिक ही आदर्श नेता बन सकता है। आज के नेताओं में सद्गुणों का अभाव है। वे जनता के शासक बनकर रहना चाहते हैं, सेवक नहीं। उनमें अहं एवं स्पर्धा का भाव भी पाया जाता है। वर्तमान भारत की राजनीति इस तथ्य की परिचायक है कि नेता बनने की होड़ ने आपसी राग-द्वेष को ही अधिक बढ़ावा दिया है। इसीलिए यह कहा गया है-नेता नहीं नागरिक चाहिए। नागरिक को अपने कर्त्तव्य एवं अधिकारों के बीच समन्वय रखना पड़ता है। यदि नागरिक अपने समाज के प्रति अपने कर्त्तव्य का समुचित पालन करता है तो राष्ट्र किसी संकट का सामना कर ही नहीं सकता।
नेता बनने की तीव्र लालसा ने नागरिकता के भाव को कम कर दिया है। नागरिक के पास राजनीतिक एवं सामाजिक दोनों अधिकार रहते हैं। अधिकार की सीमा होती है। हमारे ही नहीं दूसरे नागरिकों के भी अधिकार होते हैं। अतः नागरिक को अपने कर्तव्यों की ओर विशेष ध्यान देना चाहिए। नेता अधिकारों की बात ज़्यादा जानता है, लेकिन कर्त्तव्यों के प्रति उपेक्षा भाव रखता है। उत्तम नागरिक ही उत्तम नेता होता है। अतः प्रत्येक व्यक्ति का यह परम कर्त्तव्य है कि वह अपने आपको एक अच्छा नागरिक बनाए। नागरिक में नेतृत्व का भाव स्वयंमेव आ जाता है। नेता का शाब्दिक अर्थ है जो दूसरों को आगे ले जाए अर्थात् अपने साथियों के प्रति सहायता एवं सहानुभूति का भाव अपनाए। अतः देश को नेता नहीं नागरिक चाहिए।
30. आलस्य दरिद्रता का मूल है
जो व्यक्ति श्रम से पलायन करके आलस्य का जीवन व्यतीत करते हैं वे कभी भी सुख-सुविधा का आनंद प्राप्त नहीं कर सकते। कोई भी कार्य यहाँ तक कि स्वयं का जीना भी बिना काम किए संभव नहीं। यह ठीक है कि हमारे जीवन में भाग्य का बड़ा हाथ है। दुर्भाग्य के कारण संभव है मनुष्य को विकास और वैभव के दर्शन न हों पर परिश्रम के बल पर वह अपनी जीविका के प्रश्न को हल कर ही सकता है। यदि ऐसा न होता तो श्रम के महत्त्व का कौन स्वीकार करता। कुछ लोगों का विचार है कि भाग्य के अनुसार ही मनुष्य सुख-दुख भोगता है। दाने-दाने पर मोहर लगी है, भगवान् सबका ध्यान रखता है। जिसने मुँह दिया है, वह खाना भी देगा। ऐसे लोग यह भूल जाते हैं कि भाग्य का निर्माण भी परिश्रम द्वारा ही होता है। राष्ट्रकवि दिनकर ने ठीक ही कहा है-
ब्रह्मा ने कुछ लिखा भाग्य में, मनुज नहीं लाया है।
उसने अपना सुख, अपने ही भुजबल से पाया है।
भगवान् ने मुख के साथ-साथ दो हाथ भी दिए हैं। इन हाथों से काम लेकर मनुष्य अपनी दरिद्रता को दूर कर सकता है। हाथ पर हाथ धरकर बैठे रहने वाला व्यक्ति आलसी होता है। जो आलसी है वह दरिद्र और परावलंबी है क्योंकि आलस्य दरिद्रता का मूल है। आज इस संसार में जो कुछ भी दिखाई दे रहा है, वह श्रम का ही परिणाम है। यदि सभी लोग आलसी बने रहते तो ये सड़कें, भवन, अनेक प्रकार के यान, कला-कृतियाँ कैसे बनती? श्रम से उगले मिट्टी सोना परंतु आलस्य से सोना भी मिट्टी बन जाता है। अपने परिवार, समाज और राष्ट्र की दरिद्रता दूर करने के लिए आलस्य को परित्याग कर परिश्रम को अपनाने की आवश्यकता है। हमारे राष्ट्र में जितने हाथ हैं, यदि वे सभी काम में जुट जाएँ तो सारी दरिद्रता बिलख-बिलखकर विदा हो जाएगी। आलस्य ही दरिद्रता का मूल है।
31. मन के हारे हार है, मन के जीते जीत
मानव-शरीर यदि रथ के समान है तो यह मन उसका चालक है। मनुष्य के शरीर की असली शक्ति उसका मन है। मन के अभाव में शरीर का कोई अस्तित्व ही नहीं। मन ही वह प्रेरक शक्ति है जो मनुष्य से बड़े-से-बड़े काम करवा लेती है। यदि मन में दुर्बलता का भाव आ जाए तो शक्तिशाली शरीर और विभिन्न प्रकार के साधन व्यर्थ हो जाते हैं। उदाहरण के लिए एक सैनिक को लिया जा सकता है। यदि उसने अपने मन को जीत लिया है तो वह अपनी शारीरिक शक्ति एवं अनुमान से कहीं अधिक सफलता दिखा सकता है। यदि उसका मन हार गया तो बड़े-बड़े मारक अस्त्र-शस्त्र भी उसके द्वारा अपना प्रभाव नहीं दिखा सकते। मन की शक्ति के बल पर ही मनुष्य ने अनेक आविष्कार किए हैं।
मन की शक्ति मनुष्य को अनवरत साधना की प्रेरणा देती है और विजयश्री उनके सामने हाथ जोड़कर खड़ी हो जाती है। जब तक मन में संकल्प एवं प्रेरणा का भाव नहीं जागता तब तक हम किसी भी कार्य में सफलता प्राप्त नहीं कर सकते। एक ही काम में एक व्यक्ति सफलता प्राप्त कर लेता है और दूसरा असफल हो जाता है। इसका कारण दोनों के मन की शक्ति की भिन्नता है। जब तक हमारा मन शिथिल है तब तक हम कुछ भी नहीं कर सकते। अत: ठीक ही कहा गया है-“मन के हारे हार है मन के जीते जीत।”
32. बादलों से घिरा आकाश
आकाश की शोभा बादल हैं। बादलों के बिना आकाश शून्य है। जब आकाश में बादल घिरते हैं तो आकाश का रूप । अत्यंत मोहक एवं आकर्षक बन जाता है। जब आकाश में बादल इधर-उधर विचरते हैं तो ऐसा प्रतीत होता है मानो हाथी मस्त होकर झूम रहे हों। बादलों की गर्जन वातावरण में संगीत भर देती है। बीच-बीच में बिजली की कौंध भी आकर्षक प्रतीत होती है। श्याम बादलों की छाया में प्राणी का हृदय आनंदित हो उठता है। ग्रीष्म ऋतु की झुलसा देने वाली लू से छुटकारा दिलाने वाला पावन ऋतु बादलों की रानी है। विज्ञान ने मानव की सेवा में अनेक साधन जुटाए हैं, लेकिन जो वरदान प्रकृति के पास है वह विज्ञान के पास कहाँ? जब प्रकृति प्रसन्न होती है तो स्वर्ग-सा दृश्य बन जाता है।
फूल महकने लगते हैं। भ्रमर गूंजने लगते हैं। बादलों से घिरा आकाश मनुष्य के हृदय को ही उल्लासित नहीं करता, पशु-पक्षी तक प्रसन्नता से झूमने लगते हैं। बादलों के बरस जाने के बाद तो दृश्य ही बदल जाता है। संतप्त धरा शांत हो जाती है। पेड़-पौधों में नव-जीवन का संचार होने लगता है। सर्वत्र हरियाली का दृश्य छा जाता है। शीतल हवा के झोंके शरीर को सुखद प्रतीत होते हैं। धरती से मीठी-मीठी सुगंध उठने लगती है। किसान बीज बोने की तैयारी करने लगते हैं। वर्षा का जल तो ईश्वरीय कृपा का जल है।

33. सबै सहायक सबल के
यह संसार शक्ति का लोहा मानता है। लोग चढ़ते सूर्य की पूजा करते हैं। शक्तिशाली की सहायता के लिए सभी तत्पर रहते हैं लेकिन निर्बल को कोई नहीं पूछता। वायु भी आग को तो भड़का देती है, पर दीपक को बुझा देती है। दीपक निर्बल है, कमज़ोर है, इसलिए वायु का उस पर पूर्ण अधिकार है। व्यावहारिक जीवन में भी हम देखते हैं कि जो निर्धन है, वे और निर्धन बनते जाते हैं, और जो धनवान हैं उनके पास और धन चला आ रहा है। इसका एकमात्र कारण यही है कि सबल की सभी सहायता कर रहे हैं और निर्धन उपेक्षित हो रहा है। सर्वत्र जिसकी लाठी उसकी भैंस वाली कहावत चरितार्थ हो रही है। सामाजिक जीवन से लेकर अंतर्राष्ट्रीय जीवन तक यह भावना काम कर रही है।
एक शक्तिशाली राष्ट्र दूसरे शक्तिशाली राष्ट्र की सहायता सहर्ष करता है जबकि निर्धन देशों को शक्ति संपन्न देशों के आगे गिड़गिड़ाना पड़ता है। परिवार जैसे सीमित क्षेत्र में भी प्राय: यह देखने को मिलता है कि जो धनवान हैं, उनके प्रति सत्कार एवं सहायता की भावना अधिक होती है। घर में जब कभी कोई धनवान आता है तो उसकी खूब सेवा की जाती है, लेकिन जब द्वार पर भिखारी आता है तो उसको दुत्कार दिया जाता है। निर्धन ईमानदारी एवं सत्य के पथ पर चलता हुआ भी अनेक कष्टों का सामना करता है जबकि शक्तिशाली दुराचार एवं अन्याय के पथ पर बढ़ता हुआ भी दूसरों की सहायता प्राप्त करने में समर्थ होता है। इसका कारण यही है कि उसके पास शक्ति है तथा अपने कुकृत्यों को छिपाने के लिए साधन हैं। अत: वृंदकवि का यह कथन बिलकुल सार्थक प्रतीक होता है-सबै सहायक सबल के, कोऊ न निबल सहाय।
34. सच्चे मित्र से जीवन में सौंदर्य आता है
मनुष्य एक सामाजिक प्राणी है। समाज के अभाव में उसका जीवन-निर्वाह संभव नहीं। सामाजिकों के साथ हमारे संबंध अनेक प्रकार के हैं। कुछ हमारे संबंधी हैं, कुछ परिचित तथा कुछ मित्र होते हैं। मित्रों में भी कुछ विशेष प्रिय होते हैं। जीवन में यदि सच्चा मित्र मिल जाए तो समझना चाहिए कि हमें बहुत बड़ी निधि मिल गई है। सच्चा मित्र हमारा मार्ग प्रशस्त करता है। वह दिन प्रतिदिन हमें उन्नति की ओर ले जाता है। उसके सद्व्यवहार से हमारे जीवन में निर्मलता का प्रसार होता है। दुख के दिनों में वह हमारे लिए विशेष सहायक होता है। जब हम निरुत्साहित होते हैं तो वह हम में उत्साह भरता है। वह हमें कुमार्ग से हटाकर सुमार्ग की ओर चलने की प्रेरणा देता है। सुदामा एवं कृष्ण की तथा राम एवं सुग्रीव की आदर्श मित्रता को कौन नहीं जानता। श्रीकृष्ण ने अपने दरिद्र मित्र सुदामा की सहायता कर उसके जीवन को ऐश्वर्यमय बना दिया था। राम ने सुग्रीव की सहायता कर उसे सब प्रकार के संकट से मुक्त कर दिया।
सच्चा मित्र कभी एहसान नहीं जतलाता। वह मित्र की सहायता करना अपना कर्तव्य समझता है। वह अपनी दरिद्रता एवं अपने दुख की परवाह न करता हुआ अपने मित्र के जीवन में अधिक-से-अधिक सौंदर्य लाने का प्रयत्न करता है। सच्चा मित्र जीवन के बेरंग खाके में सुखों के रंग भरकर उसे अत्यंत आकर्षक बना देता है, अत: ठीक ही कहा गया है “सच्चे मित्र से जीवन में सौंदर्य आता है।”
35. जीवन का रहस्य निष्काम सेवा है
प्रत्येक मनुष्य अपनी रुचि के अनुसार अपना जीवन लक्ष्य निर्धारित करता है। कोई व्यापारी बनना चाहता है तो कोई कर्मचारी, कोई इंजीनियर बनने की लालसा से प्रेरित है तो कोई डॉक्टर बनकर घर भरना चाहता है। स्वार्थ पूर्ति के लिए किया गया काम उच्चकोटि की संज्ञा नहीं पा सकता। स्वार्थ के पीछे तो संसार पागल है। लोग भूल गए हैं कि जीवन का रहस्य निष्काम सेवा है। जो व्यक्ति काम-भावना से प्रेरित होकर काम करता है, वह कभी भी सुपरिणाम नहीं ला सकता। उससे कोई लाभ हो भी तो वह केवल व्यक्ति विशेष को ही होता है। समाज को कोई लाभ प्राप्त नहीं होता। निष्काम सेवा के द्वारा ही मनुष्य समाज के प्रति अपना उत्तरदायित्व निभा सकता है। कबीरदास ने भी अपने एक दोहे में यह स्पष्ट किया है-
जब लगि भक्ति सकाम है, तब लेगि निष्फल सेव।
कह कबीर वह क्यों मिले निहकामी निज देव॥
निष्काम सेवा के द्वारा ही ईश्वर को प्राप्त किया जा सकता है। समाज एवं देश को उन्नति की ओर ले जाने का श्रेष्ठतम तथा सरलतम साधन निष्काम सेवा है। हमारे संत कवियों तथा समाज-सुधारकों ने इसी भाव से प्रेरित होकर अपनी चिंता छोड़ देश और जाति के कल्याण की। इसलिए वे समाज और राष्ट्र के लिए कुछ कर सके। अपने लिए तो सभी जीते हैं। जो दूसरों के लिए जीता है, उसका जीवन अमर हो जाता है। तभी तो गुप्तजी ने कहा है-‘वही मनुष्य है जो मनुष्य के लिए मरे।”
36. भीड़ भरी बस की यात्रा का अनुभव
वैसे तो जीवन को ही यात्रा की संज्ञा दी गई है पर कभी-कभी मनुष्य को एक स्थान से दूसरे स्थान पर जाने के लिए गाड़ी अथवा बस का भी सहारा लेना पड़ता है। बस की यात्रा का अनुभव भी बड़ा विचित्र है। भारत जैसे जनसंख्या प्रधान देश में बस की यात्रा अत्यंत असुविधानजनक है। प्रत्येक बस में सीटें तो गिनती की हैं पर बस में चढ़ने वालों की संख्या निर्धारित करना एक जटिल कार्य है। भले ही बस हर पाँच मिनट बाद चले पर चलेगी पूरी तरह भर कर। गरमियों के दिनों में तो यह यात्रा किसी भी यातना से कम नहीं। भारत के नगरों की अधिकांश सड़कें सम न होकर विषम हैं। खड़े हुए यात्री की तो दुर्दशा हो जाती है, एक यात्री दूसरे यात्री पर गिरने लगता है। कभी-कभी तो लड़ाई-झगड़े की नौबत पैदा हो जाती है। लोगों की जेबें कट जाती हैं। जिन लोगों के कार्यालय दूर हैं, उन्हें प्रायः बस का सहारा लेना ही पड़ता है।
बस-यात्रा एक प्रकार से रेल-यात्रा का लघु रूप है। जिस प्रकार गाड़ी में विभिन्न जातियों एवं प्रवृत्तियों के लोगों के दर्शन होते हैं, उसी प्रकार बस में भी अलग-अलग विचारों के लोग मिलते हैं। इनसे मनुष्य बहुत कुछ सीख भी सकता है। भीड़ भरी बस की यात्रा जीवन की कठिनाइयों का सामना करने का छोटा-सा शिक्षालय है। यह यात्रा इस तथ्य की परिचायक है कि भारत अनेक क्षेत्रों में अभी तक भरपूर प्रगति नहीं कर सका। जो व्यक्ति बसयात्रा के अनुभव से वंचित है, वह एक प्रकार से भारतीय जीवन के बहुत बड़े अनुभव से ही वंचित है।
37. हानि-लाभ, जीवन-मरण, यश-अपयश विधि हाथ
इस संसार में जो कुछ भी हो रहा है, उस सबके पीछे विधि का प्रबल हाथ है। मनुष्य के भविष्य के विषय में बड़े-बड़े ज्योतिषी भी सही अनुमान नहीं लगा सकते। भाग्य रूपी नर्तकी के क्रिया-कलाप बड़े विचित्र हैं। विधि के विधान पर भले कोई रीझे अथवा शोक मनाए पर होनी होकर और अपना प्रभाव दिखाकर रहती है। मनुष्य तो विधि के हाथ का खिलौना मात्र है। हमारे भक्त कलाकारों ने विधि की प्रबल शक्ति के आगे नत-मस्तक होकर जीवन की प्रत्येक स्थिति पर संतोष प्रकट करने की प्रेरणा दी है। उक्त उक्ति जीवन संबंधी गहन अनुभव का निष्कर्ष है।
जो व्यक्ति जीवन के सुखद एवं दुखद अनुभवों का भोक्ता बन चुका है, वह बिना किसी तर्क के इस उक्ति का समर्थन करेगा-“हानिलाभ, जीवन-मरण, यश-अपयश विधि हाथ” मनुष्य सोचता कुछ है पर विधाता और भाग्य को कुछ और ही स्वीकार होता है। मनुष्य लाभ के लिए काम करता है, दिन-रात परिश्रम करता है, वह काम की सिद्धि के लिए एड़ीचोटी का पसीना एक कर देता है, लेकिन परिणाम उसकी आशा के सर्वथा विपरीत भी हो सकता है। मनुष्य जीने की लालसा में न जाने क्या कुछ करता है पर जब मौत अनायास ही अपने दल-बल के साथ आक्रमण करती है तो सब कुछ धरे का धरा रह जाता है। मनुष्य समाज में प्रतिष्ठा प्राप्त करने के लिए अपना सर्वस्व अर्पित कर देता है, पर उसे मिलती है बदनामी और निराशा। इतिहास में असंख्य उदाहरण हैं जो उक्त कथन के साक्षी रूप में प्रस्तुत किए जा सकते हैं।
राम, कृष्ण, जगत जननी सीता एवं सत्य के उपासक राजा हरिश्चंद्र तक विधि की विडंबना से नहीं बच सके। तब सामान्य मनुष्य की बात ही क्या है? वह व्यर्थ में ही अपनी शक्ति एवं साधनों की डींगे हाँकता है। उक्त उक्ति में यह संदेश निहित है कि मनुष्य को अपने जीवन में आने वाली प्रत्येक आपदा का सामना करने के लिए तत्पर रहना चाहिए। कबीरजी ने भी कहा है कि-“करम गति टारे नाहिं टरे।”
38. दैव दैव आलसी पुकारा
इस उक्ति का अर्थ है कि आलसी व्यक्ति ही भाग्य की दुहाई देता है। वह भाग्य के भरोसे ही जीवन बिता देना चाहता है। सुख प्राप्त होने पर वह भाग्य की प्रशंसा करता है और दुख आने पर वह भाग्य को कोसता है। यह ठीक है कि भाग्य का भी हमारे जीवन में महत्त्व है, लेकिन आलसी बनकर बैठे रहना तथा असफलता प्राप्त होने पर भाग्य को दोष देना किसी प्रकार भी उचित नहीं। प्रयास और परिश्रम की महिमा कौन नहीं जानता? परिश्रम के बल पर मनुष्य भाग्य की रेखाओं को बदल सकता है। परिश्रम सफलता की कुंजी है। कहा भी है-“यदि पुरुषार्थ मेरे दाएँ हाथ में है तो विजय बाएँ हाथ में।” परिश्रम से मिट्टी भी सोना उगलती है। आलसी एवं कामचोर व्यक्ति ही भाग्य के लेख पढ़ते हैं।
वही ज्योतिषियों का दरवाजा खटखटाते हैं। कर्मठ व्यक्ति तो बाहबल पर भरोसा करते हैं। परिश्रमी व्यक्ति स्वावलंबी, ईमानदार, सत्यवादी एवं चरित्रवान होता है। आलसी व्यक्ति जीवन में कभी प्रगति नहीं कर सकता। आलस्य जीवन को जड़ बनाता है। आलसी परावलंबी होता है। वह कभी भी पराधीनता के बंधन से मुक्त नहीं हो सकता। वह भाग्य के भरोसे रहकर जीवन-भर दुख भोगता रहता है।
39. आवश्यकता आविष्कार की जननी है
आवश्यकता अनेक आविष्कारों को जन्म देती है। शारीरिक तथा बौद्धिक दोनों प्रकार के बल का उपयोग करके मनुष्य ने अपने लिए अनेक सुविधाएँ जुटाई हैं। इन्हीं आविष्कारों के बल पर मनुष्य आज सुख-सुविधा के झूले में झूल रहा है। जब उसने अनुभव किया कि बैलगाड़ी की यात्रा न सुविधाजनक है और न ही इससे समय की बचत होती है। तो उसने तेज़ गति से चलने वाले वाहनों का आविष्कार किया। रेल, कार तथा वायुयान आदि उसकी आवश्यकता की पूर्ति करने वाले साधन हैं। बिजली के अनेक चमत्कार, टेलीफ़ोन आदि भी मनुष्य की आवश्यकता की पूर्ति करने वाले साधन हैं। इन आविष्कारों की कोई सीमा नहीं। जैसे-जैसे मानव-जाति की आवश्यकता बढ़ती है वैसे-वैसे नए आविष्कार हमारे सामने आते हैं। मनुष्य की बुद्धि के विकास के साथ ही आविष्कारों की भी संख्या बढ़ती जाती है। अत: यह ठीक ही कहा है कि ‘आवश्यकता आविष्कार की जननी है।’

40. आत्म-निर्भरता
आत्म-निर्भरता अथवा स्वावलंबन का अर्थ है-अपना सहारा आप बनना। बिना किसी की सहायता लिए अपना कार्य सिद्ध कर लेना आत्म-निर्भरता कहलाता है। आत्म-निर्भरता का यह अर्थ कदापि नहीं कि मनुष्य हर काम में मनमर्जी करे। आवश्यकतानुसार उसे दूसरों से परामर्श भी लेना चाहिए। आत्म-निर्भरता का गुण साधन एवं परिश्रम से आता है। आत्मविश्वास आत्म-निर्भरता का मूल आधार है। आत्मविश्वास के अभाव में आत्म-निर्भरता का गुण नहीं आता। आत्मनिर्भरता का गुण मनुष्य का एकमात्र सच्चा मित्र है। अन्य मित्र तो विपत्ति में साथ छोड़ सकते हैं, पर इस मित्र के बल पर मनुष्य चाहे तो विश्व-विजय का सपना साकार कर सकता है। आत्मनिर्भर व्यक्ति स्वाभिमानी एवं स्वतंत्रता-प्रिय होता है। वह अपने उद्धार के साथ-साथ देश और जाति का उद्धार करने में भी समर्थ होता है। जिस देश के प्रत्येक नागरिक में आत्म-निर्भरता का गुण होता है, वह प्रत्येक क्षेत्र में भरपूर उन्नति कर सकता है।
41. करत-करत अभ्यास के जड़मत होत सुजान
निरंतर अभ्यास से मूर्ख मनुष्य भी मेधावी बन सकता है। जिस प्रकार रस्सी के निरंतर आने-जाने से शिला पर निशान पड़ जाते हैं। उसी प्रकार अभ्यास से मनुष्य जड़मति से सुजान हो जाता है। यह ठीक है कि गधे को पीट-पीटकर घोड़ा तो नहीं बनाया जा सकता, किंतु निरंतर अभ्यास और प्रयत्न से अनेकानेक गुणों का विकास किया जा सकता है। उदाहरणार्थ, कवियों में कविता करने की शक्ति ईश्वर-प्रदत्त होती है, परंतु निरंतर अभ्यास से भी कविता संपादित की जा सकती है। सच तो यह है कि अभ्यास सबके लिए आवश्यक है। कोई भी कलाकार बिना अभ्यास के सफलता की चरम-सीमा को नहीं छू सकता। परिपक्वता अभ्यास से ही आती है। जब हम किसी भी काम को सीखना चाहते हैं तो उसके लिए अभ्यास अनिवार्य है। एक अच्छा खिलाड़ी बनने के लिए नित्य प्रति खेलने का अभ्यास आवश्यक है तो एक अच्छा संगीतकार बनने के लिए निरंतर स्वर-साधना का अभ्यास अपेक्षित है।
42. अधजल गगरी छलकत जाय
जल से आमुख भरी गगरी चुपचाप बिना उछले चलती है। आधी भरी हुई जल की मटकी उछल-उछलकर चलती है। ठीक यही स्वभाव मानव मन का भी है। वास्तविक विद्वान् विनम्र हो जाते हैं। नम्रता ही उनकी शिक्षा का प्रतीक होता है। दूसरी ओर जो लोग अर्द्ध-शिक्षित होते हैं अथवा अर्द्ध-समृद्ध होते हैं, वे अपने ज्ञान अथवा धन की डींग बहुत हाँकते हैं। अर्द्ध-शिक्षित व्यक्ति का डींग हाँकना बहुत कुछ मनोवैज्ञानिक भी है। वे लोग अपने ज्ञान का प्रदर्शन करके अपनी अपूर्णता को ढकना चाहते हैं। उनके मन में अपने अधूरेपन के प्रति एक प्रकार की हीनता का मनोभाव होता है जिसे वे प्रदर्शन के माध्यम से झूठा प्रभाव उत्पन्न करके समाप्त करना चाहते हैं।
यही कारण है कि मध्यमवर्गीय व्यक्तियों के जीवन जितने आडंबरपूर्ण, प्रपंचपूर्ण एवं लचर होते हैं उतने निम्न या उच्चवर्ग के नहीं। उच्चवर्ग में शिक्षा, धन और समृद्धि रच जाती है। इस कारण ये चीजें महत्त्व को बढ़ाने का साधन नहीं बनती। मध्यमवर्गीय व्यक्ति अपनी हर समृद्धि को, अपने गुण को, अपने महत्त्व को हथियार बनाकर चलाता है। प्रायः यह व्यवहार देखने में आता है कि अंग्रेज़ी की शिक्षा से अल्प परिचित लोग अंग्रेजी बोलने तथा अंग्रेजी में निमंत्रण-पत्र छपवाने में अधिक गौरव अनुभव करते हैं। अत: यह सत्य है कि अपूर्ण समृद्धि प्रदर्शन को जन्म देती है अर्थात् अधजल गगरी छलकत जाय।
43. निज भाषा उन्नति अहै, सब उन्नति को मूल
अपनी भाषा के उत्थान के बिना व्यक्ति उन्नति ही नहीं कर सकता। भाषा अभिव्यक्ति का प्रमुख माध्यम है। भाषा सामाजिक जीवन का अपरिहार्य अंग है। इसके बिना समाज की कल्पना भी नहीं की जा सकती। अपनी भाषा में अपने मन के विचारों को प्रकट करने में सुविधा रहती है। विदेशी भाषा कभी भी हमारे भावों को उतनी गहरी अभिव्यक्ति नहीं दे सकती जितनी हमारी मातृभाषा। महात्मा गांधीजी ने भी इसी बात को ध्यान में रखकर मातृ-भाषा को शिक्षा का माध्यम बनाने पर बल दिया था। हमारे देश में अंग्रेज़ी के प्रयोग पर इतना अधिक बल दिए जाने के उपरांत भी अपेक्षित सफलता इसी कारण नहीं मिल पा रही है क्योंकि इसके द्वारा हम अपने विचारों को पूर्ण अभिव्यक्ति नहीं दे सकते। हम हीनता की भावना का शिकार हो रहे हैं। अंग्रेज़ी-परस्तों द्वारा दिया जाने वाला यह तर्क भ्रमित कर रहा है कि, “अंग्रेज़ी ज्ञान का वातायन है।” अपनी भाषा के बिना मानव की मानसिक भूख शांत नहीं हो सकती। निज भाषा की उन्नति से ही समाज की उन्नति होती है। निज भाषा जननी तुल्य है। अतः कहा गया है कि-
निज भाषा उन्नति अहै, सब उन्नति को मूल।
बिना निज भाषा ज्ञान के, मिटत न हिय को सूल॥
44. वीर भोग्या वसुंधरा
वीर लोग ही वसुंधरा का भोग करते हैं। जयशंकर प्रसाद के नाटक ‘स्कंदगुप्त’ में भटार्क नामक पात्र कहता है ‘वीर लोग एक कान से तलवार का तथा दूसरे से नूपुर की झंकार सुना करते हैं।’ यह सत्य उक्ति है कि वीरता और भोग परस्पर पूरक हैं। वीरता भोगप्रिय होती है। विजय पाने के लिए प्रेरणा चाहिए, उत्साह चाहिए, पौरुष और सामर्थ्य चाहिए। भोग . करने के लिए स्वस्थ, उमंगपूर्ण, उत्साहित एवं शक्तिशाली शरीर चाहिए। बूढ़े लोग कभी भोग नहीं कर सकते। हर गहरे भोग के लिए अंत:स्थल में जोश और आवेग होना चाहिए, जो वीरों में ही होता है। हिंदी साहित्य का आदिकाल इस प्रकार के उदाहरणों से भरा पड़ा है। तत्कालीन राजा लड़ते थे, भोगते थे, मर जाते थे।
इतिहास साक्षी है कि भोग के साधनों को उसी जाति या राजा ने विपुल मात्रा में जुटाया जो जूझारू थे, संघर्षशील थे। यह सामान्य मानव-प्रकृति है कि व्यक्ति युवावस्था में सांसारिक द्रव्यों के पीछे भागता है, उन्हें एकत्र करता है, किंतु वृद्धावस्था में उन्हीं द्रव्यों को मायामय कहकर तिरस्कृत करने लगता है। उस तिरस्कार के पीछे द्रव्य का मायामय हो जाना नहीं, अपितु उसकी भोग की इच्छा का शिथिल पड़ जाना है, उसकी पाचन-शक्ति मंद पड़ जाना है। युवावस्था में शरीर हर प्रकार की तेजस्विता से संपन्न होता है, इसलिए उस समय भोग की इच्छा सर्वाधिक उठती है। अतः यह प्रमाणित सत्य है कि वीर लोग ही धरती का तथा धरती के समस्त भोगों का रसपान करते हैं, कर पाते हैं।
45. मन चंगा तो कठौती में गंगा
संत रविदास का यह वचन एक मार्मिक सत्य का उद्घाटन करता है। मानव के लिए मन की निर्मलता का होना आवश्यक है। जिसका मन निर्मल होता है, उसे बाहरी निर्मलता ओढ़ने या गंगा के स्पर्श से निर्मलता प्राप्त करने की आवश्यकता नहीं पड़ती। जिनके मन में मैल होती है, उन्हें ही गंगा की निर्मलता अधिक आकर्षित करती है। स्वच्छ एवं निष्पाप हृदय का व्यक्ति बाह्य आडंबरों से दूर रहता है। अपना महत्त्व प्रतिपादित करने के लिए वह विभिन्न प्रपंचों का सहारा नहीं लेता। प्राचीन भारत में ऋषि-मुनि घर-बार सभी त्याग कर सभी भौतिक सुखों से रहित होकर भी परमानंद की प्राप्ति इसीलिए कर लेते थे कि उनकी मन-आत्मा पर व्यर्थ के पापों का बोझ नहीं होता था। बुरे मन का स्वामी चाहे कितना भी प्रयास कर ले कि उसे आत्मिक शांति मिले, परंतु वह उसे प्राप्त नहीं कर सकता। भक्त यदि परमात्मा को पाना चाहते हैं तो भगवान् स्वयं भी उसकी भक्ति से प्रभावित हो उसके निकट आना चाहता है। वह भक्त के निष्कपट, निष्पाप और निष्कलुष हृदय में मिल जाना चाहता है।
46. व्यक्ति और समाज
व्यक्ति एवं समाज का आपस में गहरा संबंध है। व्यक्तियों के समूह से ही समाज बनता है। व्यक्ति और समाज दोनों एक-दूसरे के अस्तित्व के परिचायक हैं। व्यक्ति के समाज के प्रति अनेक कर्त्तव्य हैं। उसे समाज के नियमों का पालन करना पड़ता है। राज्य के आदेशों को स्वीकार करना पड़ता है, समाज में रहते हुए व्यक्ति को अपनी बात कहने का, स्वतंत्रतापूर्वक एक-दूसरे से मिलने-जुलने का अधिकार रहता है। व्यक्ति का यह कर्त्तव्य है कि वह कोई भी काम ऐसा न करे जिससे समाज की व्यवस्था में बाधा पड़े। व्यक्ति का निर्माण समाज का निर्माण है। यदि सभी व्यक्ति अलगअलग से अपने चरित्र को संपन्न बना लें तो उनसे आदर्श समाज का निर्माण होगा। व्यक्ति कारण है तो समाज कार्य है।
अत: जिस समाज में रहने वाले व्यक्ति जितने सभ्य होंगे, वह समाज उतना ही सभ्य माना जाएगा। उत्तम नागरिक वही है जो कर्तव्यों का तत्परता से पालन करे और दूसरों की सुविधा का ध्यान रखे। व्यक्ति को केवल अपने लिए ही जीवित नहीं रहना होता बल्कि समाज के प्रति भी अपने दायित्व को निभाना होता है। व्यक्ति को अपनी अपेक्षा समाज को प्राथमिकता देनी चाहिए। राष्ट्र कवि मैथिलीशरण गुप्त ने इसी भावना पर बल देते हुए कहा है-“समष्टि के लिए व्यष्टि हों बलिदान।” अर्थात् समाज की मान-मर्यादा की रक्षा के लिए व्यक्ति को त्याग एवं बलिदान के पथ पर बढ़ते रहना चाहिए। इस बात का हमेशा ध्यान रहे कि व्यक्तियों के समूह का नाम समाज नहीं। समाज बनता है आपसी संबंधों से। समूह में तो जानवर भी रहते हैं, पर उनके समूह को समाज की संज्ञा नहीं दी जाती। अतः व्यक्ति एवं समाज में समन्वय की नितांत आवश्यकता है।
47. तेते पाँव पसारिए जेती लांबी सौर
जीवन में अनेक दुख मनुष्य स्वयं मोल लेता है। इन दुखों का कारण उसके चरित्र में छिपी दुर्बलता होती है। अपव्यय की आदत भी एक ऐसी ही दुर्बलता है। जीवन में सुखी बनने के लिए अपनी आय एवं व्यय के बीच संतुलन रखना अत्यंत आवश्यक है। अपनी इच्छाओं पर अंकुश रखे बिना मनुष्य जीवन में सफल नहीं हो सकता। आय के अनुसार व्यय की आदत डालना जीवन में संयम, व्यवस्था एवं स्वावलंबन जैसे गुण लाती है।
आय के अनुरूप खर्च करना किसी प्रकार से भी कंजूसी नहीं कहलाता। कंजूस की संज्ञा तो वह पाता है जो धन के होते हुए भी जीवन के लिए आवश्यक कार्यों में भी धन खर्च नहीं करता। अल्प व्यय के गुण को लक्ष्य करके ही वृंद कवि ने कहा था कि “तेते पाँव पसारिए जेती लांबी सौर”।
यदि संसार के अधिकांश व्यक्ति अपव्ययी होते तो इस संसार का निर्माण भी संभव न होता। सरकार का भी कर्तव्य है कि वह व्यय करने में अपनी आय की मर्यादा का उल्लंघन न करे अन्यथा जनता को संतुलित रखने के लिए स्वयं को असंतुलित बनाना पड़ेगा। आय के अनुरूप व्यय करने से मनुष्य को कभी आर्थिक संकट का सामना नहीं करना पडता। मितव्ययिता के अभ्यास द्वारा उसका भविष्य भी सुरक्षित हो जाता है। उसे किसी की खुशामद नहीं करनी पड़ती। मितव्ययी बनने के लिए आवश्यक है कि अपना हर एक काम योजना बनाकर किया जाए। कहीं भी आवश्यकता से अधिक व्यय न करें। अपनी आय के अनुसार खर्च करने वाला व्यक्ति स्वयं भी आनंद उठाता है और उसका परिवार भी प्रसन्नचित्त दिखाई देता है। यह आदत समाज में प्रतिष्ठा दिलाती है। अतः प्रत्येक को अधोलिखित सूक्ति के अनुसार अपने जीवन को ढालने का प्रयत्न करना चाहिए।
तेते पाँव पसारिए जेती लंबी सौर।
48. जहाँ चाह वहाँ राह
मनुष्य एक सामाजिक प्राणी है। समाज में प्रतिष्ठापूर्वक जीवन-यापन करने के लिए उसे निरंतर संघर्षशील रहना पड़ता है। इसके लिए वह नित्य नवीन प्रयास करता है जिससे उसकी प्रतिष्ठा बनी रहे तथा वह नित्य प्रति उन्नति करता रहे। यदि मनुष्य के मन में उन्नति करने की इच्छा नहीं होगी तो वह कभी उन्नति कर ही नहीं सकता। अपनी इच्छा की पूर्ति के लिए मनुष्य अनेक प्रयत्न करता है तब कहीं अंत में उसे सफलता मिलती है। सबसे पहले मन में किसी कार्य को करने की इच्छा होनी चाहिए, तभी हम कार्य करते हैं और सफलता प्राप्त करते हैं। संस्कृत में एक कथन है कि ‘उद्यमेनहि सिद्धयंति कार्याणि न मनोरथः’ अर्थात् परिश्रम से ही कार्य की सिद्धि होती है। परिश्रम मनुष्य तब करता है जब उसके मन में परिश्रम करने की इच्छा उत्पन्न होती है। जिस मनुष्य के मन में कार्य करने की इच्छा ही नहीं होगी वह कुछ भी नहीं कर सकता। जैसे पानी पीने की इच्छा होने पर हम नल अथवा कुएँ से पानी लेकर पीते हैं। यहाँ पानी पीने की इच्छा ने पानी को प्राप्त करने के लिए हमें नल अथवा कुएँ तक जाने का मार्ग बनाने की प्रेरणा दी। अत: कहा जाता है कि जहाँ चाह वहाँ राह।

49. का वर्षा जब कृषि सुखाने
गोस्वामी तुलसीदास की इस सूक्ति का अर्थ है-जब खेती ही सूख गई, तब पानी के बरसने का क्या लाभ है? जब ठीक अवसर पर वांछित वस्तु उपलब्ध न हुई तो बाद में उस वस्तु का मिलना बेकार ही है। साधन की उपयोगिता तभी सार्थक हो सकती है, जब वे समय पर उपलब्ध हो जाएँ। अवसर बीतने पर सब साधन व्यर्थ पड़े रहते हैं। अंग्रेज़ी में एक कहावत है-लोहे पर तभी चोट करो जबकि वह गर्म हो अर्थात् जब लोहा मुड़ने और ढलने को तैयार हो, तभी उचित चोट करनी चाहिए। उस अवसर को खो देने पर केवल लोहे की टन-टन की आवाज़ के अतिरिक्त कुछ लाभ नहीं मिल सकता।
अतः मनुष्य को चाहिए कि वह उचित समय की प्रतीक्षा में हाथ-पर-हाथ धरकर न बैठा रहे, अपितु समय की आवश्यकता को पहले से ध्यान करके उसके लिए उचित तैयारी करे। हमारे शास्त्रों में भी कहा गया है कि समय एक ऐसी स्त्री है जो अपने लंबे बाल मुँह के आगे फैलाए हुए निरंतर दौड़ती चली जा रही है। जिसे भी समय रूपी उस स्त्री को वश में करना हो, उसे चाहिए कि वह समय के आगे-आगे दौड़कर उस स्त्री के बालों से उसे पकड़े। उसके पीछे-पीछे दौड़ने से मनुष्य उसे नहीं पकड़ पाता। आशय यह है कि उचित समय पर उचित साधनों का होना ज़रूरी है। जो लोग आग लगाने पर कुआँ खोदते हैं, वे आग में अवश्य झुलस जाते हैं। उनका कुछ भी शेष नहीं बचता।
50. परिश्रम सफलता की कुंजी है
संस्कृत की प्रसिद्ध सूक्ति है–’उद्यमेनहि सिद्धयंति कार्याणि न मनोरथः’ अर्थात् परिश्रम से ही कार्य सिद्धि होती है, मात्र इच्छा करने से नहीं। सफलता प्राप्त करने के लिए परिश्रम ही एकमात्र मंत्र है। श्रमेव जयते’ का सूत्र इसी भाव की ओर संकेत करता है। परिश्रम के बिना हरी-भरी खेती सूखकर झाड़ बन जाती है जबकि परिश्रम से बंजर भूमि को भी शस्य-श्यामला बनाया जा सकता है। असाध्य कार्य भी परिश्रम के बल पर संपन्न किए जा सकते हैं। बुद्धिमान व्यक्ति कितने ही प्रतिभाशाली हों, किंतु उन्हें लक्ष्य में सफलता तभी मिलती है जब वे अपनी बुद्धि और प्रतिभा को परिश्रम की सान पर तेज़ करते हैं। न जाने कितनी संभावनाओं के बीज पानी, मिट्टी, सिंचाई और जुताई के अभाव में मिट्टी बन जाते हैं, जबकि ठीक संपोषण प्राप्त करके कई बीज सोना भी बन जाते हैं।
कई बार प्रतिभा के अभाव में परिश्रम ही अपना रंग दिखलाता है। प्रसिद्ध उक्ति है कि निरंतर घिसाव से पत्थर पर भी चिह्न पड़ जाते हैं। जड़मति व्यक्ति परिश्रम द्वारा ज्ञान उपलब्ध कर लेता है। जहाँ परिश्रम तथा प्रतिभा दोनों एकत्र हो जाते हैं वहाँ किसी अद्भुत कृति का सृजन होता है। शेक्सपीयर ने महानता को दो श्रेणियों में विभक्त किया है-जन्मजात महानता तथा अर्जित महानता। यह अर्जित महानता परिश्रम के बल पर ही अर्जित की जाती है। अत: जिन्हें ईश्वर का आशीर्वाद प्राप्त नहीं है, उन्हें अपने श्रम-बल का भरोसा रखकर कर्म में जुटना चाहिए। सफलता अवश्य ही उनकी चेरी बनकर उपस्थित होगी।
51. पशु न बोलने से और मनुष्य बोलने से कष्ट उठाता है
मनुष्य को ईश्वर की ओर से अनेक प्रकार की शक्तियाँ प्राप्त हुई हैं। इनमें वाणी अथवा वाक्-शक्ति का गुण सबसे महत्त्वपूर्ण है। जो व्यक्ति वाणी का सदुपयोग करता है, उसके लिए तो यह वरदान है और जिसकी जीभ कतरनी के समान निरंतर चलती रहती है, उसके लिए वाणी का गुण अभिशाप भी बन जाता है। भाव यह है कि वाचालता दोष है। पशु के पास वाणी की शक्ति नहीं, इसी कारण जीवन-भर उसे दूसरों के अधीन रहकर कष्ट उठाना पड़ता है। वह सुखदुख का अनुभव तो करता है पर उसे व्यक्त नहीं कर सकता। उसके पास वाणी का गुण होता तो उसकी दशा कभी दयनीय न बनती। कभी-कभी पशु का सद्व्यवहार भी मनुष्य को भ्रांति में डाल देता है।
अनेक कहानियाँ ऐसी हैं जिनके अध्ययन से पता चलता है कि पशुओं ने मनुष्य-जाति के लिए अनेक बार अपने बलिदान और त्याग का परिचय दिया है पर वाक्-शक्ति के अभाव के कारण उसे मनुष्य के द्वारा निर्मम मृत्यु का भी सामना करना पड़ा है। इसके विपरीत मनुष्य अपनी वाणी के दुरुपयोग के कारण अनेक बार कष्ट उठाता है। रहीम ने अपने दोहे में व्यक्त किया है कि जीभ तो अपनी मनचाही बात कहकर मुँह में छिप जाती है पर जूतियाँ का सामना करना पड़ता है बेचारे सिर को। अभिप्राय यह है कि मनुष्य को अपनी वाणी पर संयम रखना चाहिए। इस संसार में बहुत-से झगड़ों का कारण वाणी का दुरुपयोग है। एक नेता के मुख से निकली हुई बात सारे देश को युद्ध की ज्वाला में झोंक सकती है। अतः यह ठीक ही कहा गया है कि पशु न बोलने से कष्ट उठाता है और मनुष्य बोलने से। कोई भी बात कहने से पहले उसके परिणाम पर विचार कर लेना चाहिए।
52. कारज धीरे होत हैं, काहे होत अधीर
जिसके पास धैर्य है, वह जो इच्छा करता है, प्राप्त कर लेता है। प्रकृति हमें धीरज धारण करने की सीख देती है। धैर्य जीवन की लक्ष्य प्राप्ति का द्वारा खोलता है। जो लोग ‘जल्दी करो, जल्दी करो’ की रट लगाते हैं, वे वास्तव में ‘अधीर मन, गति कम’ लोकोक्ति को चरितार्थ करते हैं। सफलता और सम्मान उन्हीं को प्राप्त होता है, जो धैर्यपूर्वक काम में लगे रहते हैं। शांत मन से किसी कार्य को करने में निश्चित रूप से कम समय लगता है। बचपन के बाद जवानी धीरे-धीरे आती है। संसार के सभी कार्य धीरे-धीरे संपन्न होते हैं। यदि कोई रोगी डॉक्टर से दवाई लेने के तुरंत पश्चात् पूर्णतया स्वस्थ होने की कामना करता है, तो यह उसकी नितांत मूर्खता है। वृक्ष को कितना भी पानी दो, परंतु फल प्राप्ति तो समय पर ही होगी। ससार के सभी महत्त्वपूर्ण विकास कार्य धीरे-धीरे अपने समय पर ही होते हैं। अत: हमें अधीर होने की बजाय धैर्यपूर्वक अपने कार्य में संलग्न होना चाहिए।
53. दूर के ढोल सुहावने
इस उक्ति का अर्थ है कि दूर के रिश्ते-नाते बड़े अच्छे लगते हैं। जो संबंधी एवं मित्रगण हम से दूर रहते हैं, वे पत्रों के द्वारा हमारे प्रति कितना अगाध स्नेह प्रकट करते हैं। उनके पत्रों से पता चलता है कि वे हमारे पहुँचने पर हमारा अत्यधिक स्वागत करेंगे। हमारी देखभाल तथा हमारे आदर-सत्कार में कुछ कसर न उठा सकेंगे। लेकिन जब उनके पास पहँचते हैं तो उनका दूसरा ही रूप सामने आने लगता है। उनके व्यवहार में यह चरितार्थ हो जाता है कि दूर के ढोल सुहावने होते हैं। दूर बजने वाले ढोल की आवाज़ भी तो कानों को मधुर लगती है। पर निकट पहुँचते ही उसकी ध्वनि कानों को कटु लगने लगती है। दूर से झाड़-झंखाड़ भी सुंदर दृश्य प्रस्तुत करता है पर निकट जाने पर पाँवों के छलनी हो जाने का डर उत्पन्न हो जाता है। ठीक ही कहा है-दूर के ढोल सुहावने।
54. लोभ पाप का मूल है
संस्कृत के किसी नीतिकार का कथन है कि लोभ पाप का मूल है। मन का लोभ ही मनुष्य को चोरी के लिए प्रेरित करता है। लोभ अनेक अपराधों को जन्म देता है। लोभ, अत्याचार, अनाचार और अनैतिकता का कारण बनता है। महमूद गज़नवी जैसे शासकों ने धन के लोभ में आकर मनमाने अत्याचार किए। औरंगज़ेब ने अपने तीनों भाइयों का वध कर दिया और पिता को बंदी बना लिया। ज़र, जोरू तथा ज़मीन के झगड़े भी प्रायः लोभ के कारण होते हैं। लोभी व्यक्ति का हृदय सब प्रकार की बुराइयों का अड्डा होता है। महात्मा बुद्ध ने कहा है कि इच्छाओं का लोभ ही चिंताओं का मूल कारण है। लालची व्यक्ति बहुत कुछ अपने पास रखकर भी कभी संतुष्ट नहीं होता। उसकी दशा तो उस मूर्ख लालची के समान हो जाती है जो मुरगी का पेट फाड़कर सारे अंडे निकाल लेना चाहता है। लोभी व्यक्ति अंत में पछताता है। लोभी किसी पर उपकार नहीं कर सकता। वह तो सबका अपकार ही करता है। इसलिए अगर कोई पाप से बचना चाहता है तो वह लोभ से बचे।
55. पराधीन सपनेहुँ सुख नाहिं
‘पराधीन सपनेहुँ सुख नाहिं’ उक्ति का अर्थ है कि पराधीन व्यक्ति सपने में भी सुख का अनुभव नहीं कर सकता। पराधीन और परावलंबी के लिए सुख बना ही नहीं। पराधीनता एक प्रकार का अभिशाप है। मनुष्य तो क्या पशु-पक्षी तक पराधीनता की अवस्था में छटपटाने लगते हैं। पराधीन हमेशा शोषण की चक्की में पिसता रहता है। उसका स्वामी उसके प्रति जैसे भी अच्छा-बुरा व्यवहार चाहे कर सकता है। पराधीन व्यक्ति अथवा जाति अपने आत्म-सम्मान को सुरक्षित नहीं रख सकते। किसी भी व्यक्ति, जाति अथवा देश की पराधीनता की कहानी दुख एवं पीड़ा की कहानी है। स्वतंत्र व्यक्ति दरिद्रता एवं अभाव में भी जिस सुख का अनुभव कर सकता है, पराधीन व्यक्ति उस सुख की कल्पना भी नहीं कर सकता। अत: ठीक ही कहा गया है-‘पराधीन सपनेहुँ सुख नाहिं।’
56. पर उपदेश कुशल बहुतेरे
दूसरों को उपदेश देना अर्थात् सब प्रकार से आदर्शों का पालन करने की प्रेरणा देना सरल है। जैसे कहना सरल तथा करना कठिन है, उसी प्रकार स्वयं अच्छे पथ पर चलने की अपेक्षा दूसरों को अच्छे काम करने का संदेश देना सरल है। जो व्यक्ति दूसरों को उपदेश देता है, वह स्वयं भी उन उपदेशों का पालन कर रहा है, यह जरूरी नहीं। हर व्यापारी, अधिकारी तथा नेता अपने नौकरों, कर्मचारियों तथा जनता को ईमानदारी, सच्चाई तथा कर्मठता का उपदेश देता है जबकि वह स्वयं भ्रष्टाचार के पथ पर बढ़ता रहता है। नेता मंच पर आकर कितनी सारगर्भित बातें कहते हैं, पर उनका आचरण हमेशा उनकी बातों के विपरीत होता है। माता-पिता तथा गुरुजन बच्चों को नियंत्रण में रहने का उपदेश देते हैं-पर वे यह भूल जाते हैं कि उनका अपना जीवन अनुशासनबद्ध एवं नियंत्रित ही नहीं।
57. जैसा करोगे वैसा भरोगे
जैसा करोगे वैसा भरोगे’ उक्ति का अर्थ है कि मनुष्य अपने जीवन में जैसा कर्म करता है, उसी के अनुरूप ही उसे फल मिलता है। मनुष्य जैसा बोता है, वैसा ही काटता है। सुकर्मों का फल अच्छा तथा कुकर्मों का फल बुरा होता है। दूसरों को पीड़ित करने वाला व्यक्ति एक दिन स्वयं पीड़ा के सागर में डूब जाता है। जो दूसरों का भला करता है, ईश्वर उसका भला करता है। कहा भी है, ‘कर भला हो भला’। पुण्य से परिपूर्ण कर्म कभी भी व्यर्थ नहीं जाते। जो दूसरों का शोषण करता है, वह कभी सुख की नींद नहीं सो सकता। ‘जैसी करनी वैसी भरनी’ वाली बात प्रसिद्ध है। मनुष्य को हमेशा अच्छे कर्मों में रुचि लेनी चाहिए। दूसरों का हित करना तथा उन्हें संकट से मुक्त करने का प्रयास मानवता की पहचान है। मानवता के पथ पर बढ़ने वाला व्यक्ति मानव तथा दानवता के पथ पर बढ़ने वाला व्यक्ति दानव कहलाता है। मानवता की पहचान मनुष्य के शुभ कर्म हैं।

58. समय का महत्त्व/समय सबसे बड़ा धन है
दार्शनिकों ने जीवन को क्षणभंगुर कहा है। इनकी तुलना प्रभात के तारे और पानी के बुलबुले से की गई है। अतः यह प्रश्न उठाना स्वाभाविक है कि हम अपने जीवन को सफल कैसे बनाएँ। इसका एकमात्र उपाय समय का सदुपयोग है। समय एक अमूल्य वस्तु है। इसे काटने की वृत्ति जीवन को काट देती है। खोया समय पुनः नहीं मिलता। दुनिया में कोई भी शक्ति नहीं जो बीते हुए समय को वापस लाए। हमारे जीवन को सफलता-असफलता के सदुपयोग तथा दुरुपयोग पर निर्भर करती है। कहा भी है-क्षण को क्षुद्र न समझो भाई, यह जग का निर्माता है। हमारे देश में अधिकांश लोग समय का मूल्य नहीं समझते। देर से उठना, व्यर्थ की बातचीत करना, खेल, शतरंज आदि में रुचि का होना आदि के द्वारा समय का नष्ट करना।
यदि हम चाहते हैं तो पहले अपना काम पूरा करें। बहुतसे लोग समय को नष्ट करने में आनंद का अनुभव करते हैं। मनोरंजन के नाम पर समय नष्ट करना बहुत बड़ी भूल है। समय का सदुपयोग करने के लिए आवश्यक है कि हम अपने दैनिक कार्य को करने का समय निश्चित कर लें। फिर उस कार्य को उसी काम में करने का प्रयत्न करें। इस तरह का अभ्यास होने से समय का मूल्य समझ जाएँगे और देखेंगे कि हमारा जीवन निरंतर प्रगति की ओर बढ़ता जा रहा है। समय के सदुपयोग से ही जीवन का पथ सरल हो जाता है। महान् व्यक्तियों के महान् बनने का रहस्य समय का सदुपयोग ही है। समय के सदुपयोग के द्वारा ही मनुष्य अमर कीर्ति का पात्र बन सकता है। समय का सदुपयोग ही जीवन का सदुपयोग है। इसी में जीवन की सार्थकता है–“कल करै सो आज कर, आज करै सो अब, पल में परलै होयगी, बहुरि करोगे कब।”
59. स्त्री-शिक्षा का महत्त्व
विद्या हमारी भी न तब तक काम में कुछ आएगी।
अर्धांगनियों को भी सुशिक्षा दी न जब तक जाएगी।
आज शिक्षा मानव-जीवन का एक अंग बन गई है। शिक्षा के बिना मनुष्य ज्ञान पंगु कहलाता है। पुरुष के साथ-साथ नारी को भी शिक्षा की आवश्यकता है। नारी शिक्षित होकर ही बच्चों को शिक्षा प्रदान कर सकती है। बच्चों पर पुरुष की अपेक्षा नारी के व्यक्तित्व का प्रभाव अधिक पड़ता है। अतः उसका शिक्षित होना ज़रूरी है। ‘स्त्री का रूप क्या हो?’-यह प्रश्न उठना स्वाभाविक है। इतना तो स्वीकार करना ही पड़ेगा कि नारी और पुरुष के क्षेत्र अलगअलग हैं। पुरुष को अपना अधिकांश जीवन बाहर के क्षेत्र में बिताना पड़ता है जबकि नारी को घर और बाहर में समन्वय स्थापित करने की आवश्यकता होती है।
सामाजिक कर्त्तव्य के साथ-साथ उसे घर के प्रति भी अपनी भूमिका का निर्वाह करना पड़ता है। अत: नारी को गृह-विज्ञान की शिक्षा में संपन्न होना चाहिए। अध्ययन के क्षेत्र में भी वह सफल भूमिका का निर्वाह कर सकती है। शिक्षा के साथ-साथ चिकित्सा के क्षेत्र में भी उसे योगदान देना चाहिए। सुशिक्षित माताएँ ही देश को अधिक योग्य, स्वस्थ और आदर्श नागरिक दे सकती हैं। स्पष्ट हो जाता है कि स्त्री-शिक्षा का प्रचार एवं प्रसार होना चाहिए। नारी को फ़ैशन से दूर रहकर सादगी के जीवन का समर्थन करना चाहिए। उसकी शिक्षा समाजोपयोगी हो।
60. स्वास्थ्य ही जीवन है
जीवन का पूर्ण आनंद वही ले सकता है जो स्वस्थ है। स्वास्थ्य के अभाव में सब प्रकार की सुख-सुविधाएँ व्यर्थ प्रमाणित होती हैं। तभी तो कहा है-‘शरीरमाद्यं खलु धर्मसाधनम्’ अर्थात् शरीर ही सब धर्मों का मुख्य साधन है। स्वास्थ्य जीवन है और अस्वस्थता मृत्यु है। अस्वस्थ व्यक्ति का किसी भी काम में मन नहीं लगता। बढ़िया-से-बढ़िया खाद्य-पदार्थ उसे विष के समान लगता है। वस्तुतः उसमें काम करने की क्षमता ही नहीं होती। अतः प्रत्येक व्यक्ति का यह कर्त्तव्य है कि वह अपने स्वास्थ्य को अच्छा बनाए रखने के लिए प्रयत्नशील रहे। स्वास्थ्य-रक्षा के लिए नियमितता तथा संयम की सबसे अधिक ज़रूरत है। समय पर भोजन, समय पर सोना और जागना अच्छे स्वास्थ्य के लक्षण हैं। शरीर की सफ़ाई की तरफ़ भी पूरा ध्यान देने की ज़रूरत है।
सफ़ाई के अभाव से तथा असमय खाने-पीने से स्वास्थ्य बिगड़ जाता है। क्रोध, भय आदि भी स्वास्थ्य को हानि पहुँचाते हैं। नशीले पदार्थों का सेवन तो शरीर के लिए घातक साबित होता है। स्वास्थ्य बनाए रखने के लिए पौष्टिक एवं सात्विक भोजन भी ज़रूरी है। स्वास्थ्य रक्षा के लिए व्यायाम का भी सबसे अधिक महत्त्व है। व्यायाम से बढ़कर न कोई औषधि है और न कोई टॉनिक। व्यायाम से शरीर में स्फूर्ति आती है, शक्ति, उत्साह एवं उल्लास का संचार होता है। शरीर की आवश्यकतानुसार विविध आसनों का प्रयोग भी बड़ा लाभकारी होता है। खेल भी स्वास्थ्य लाभ का अच्छा साधन है। इनसे मनोरंजन भी होता है और शरीर भी पुष्ट तथा चुस्त बनता है। प्रायः भ्रमण का भी विशेष लाभ है। इससे शरीर का आलस्य भागता है, काम में तत्परता बढ़ती है। जल्दी थकान का अनुभव नहीं होता।
61. मधुर-वाणी
वाणी ही मनुष्य का सर्वश्रेष्ठ अलंकार है। वाणी के द्वारा ही मनुष्य अपने विचारों का आदान-प्रदान दूसरे व्यक्तियों से करता है। वाणी का मनुष्य के जीवन पर सर्वाधिक प्रभाव पड़ता है। सुमधुर वाणी के प्रयोग से लोगों के साथ आत्मीय संबंध बन जाते हैं, जो व्यक्ति कर्कश वाणी का प्रयोग करते हैं, उनसे लोगों में कटुता की भावना व्याप्त हो जाती है। जो लोग अपनी वाणी का मधुरता से प्रयोग करते हैं उनकी सभी लोग प्रशंसा करते हैं। सभी लोग उनसे संबंध बनाने के इच्छुक रहते हैं। वाणी मनुष्य के चरित्र को भी स्पष्ट करने में सहायक होती है। जो व्यक्ति विनम्र और मधुरवाणी से लोगों के साथ व्यवहार करते हैं, उसके बारे में लोग यही समझते हैं कि इनमें सद्भावना विद्यमान है।
मधुरवाणी मित्रों की संख्या में वृद्धि करती है। कोमल और मधुर वाणी से शत्रु के मन पर भी विजय प्राप्त की जा सकती है। वह भी अपनी द्वेष और ईर्ष्या की भावना को विस्तृत करके मधुर संबंध बनाने के इच्छुक हो जाता है। यदि कोई अच्छी बात भी कठोर और कर्कश वाणी में कही जाए तो लोगों पर उसकी प्रतिक्रिया विपरीत होती है। लोग यही समझते हैं कि यह व्यक्ति अहंकारी है। इसलिए वाणी मनुष्य का सर्वश्रेष्ठ अलंकार है तथा उसे उसका सदुपयोग करना चाहिए।
62. नारी शक्ति
नारी त्याग, तपस्या, दया, ममता, प्रेम एवं बलिदान की साक्षात मूर्ति है। नारी तो नर की जन्मदात्री है। वह भगिनी भी और पत्नी भी है। वह सभी रूपों में सुकुमार, सुंदर और कोमल दिखाई देती है। हमारे प्राचीन ग्रंथों में भी नारी को पूज्य माना गया है। कहा गया है कि जहाँ नारी की पूजा होती है, वहाँ देवता निवास करते हैं। उसके हृदय में सदैव स्नेह की धारा प्रवाहित होती रहती है। नर की रुक्षता, कठोरता एवं उदंडता को नियंत्रित करने में भी नारी की महत्त्वपूर्ण भूमिका है। वह धात्री, जन्मदात्री और दुखहीं है। नारी के बिना नर अपूर्ण है। नारी को नर से बढ़कर कहने में किसी भी प्रकार की अतिशयोक्ति नहीं है। नारी प्राचीनकाल से आधुनिक काल तक अपनी महत्ता एवं श्रेष्ठता प्रतिपादित करती आई है।
नारियाँ ज्ञान, कर्म एवं भाव सभी क्षेत्रों में अग्रणी रही हैं। यहाँ तक कि पुरुष वर्ग के लिए आरक्षित कहे जाने वाले कार्यों में भी उसने अपना प्रभुत्व स्थापित किया है। चाहे एवरेस्ट की चोटी ही क्यों न हो, वहाँ भी नारी के चरण जा पहुँचे हैं। एंटार्कटिका पर भी नारी जा पहुँची है। प्रशासनिक क्षमता का प्रदर्शन वह अनेक क्षेत्रों में सफलतापूर्वक कर चुकी है। आधुनिक काल की प्रमुख नारियों में श्रीमती इंदिरा गांधी, विजयलक्ष्मी पंडित, सरोजिनी नायडू, बचेंद्री पाल, सानिया मिर्जा आदि का नाम गर्व के साथ लिया जा सकता है।
63. चाँदनी रात में नौका विहार
ग्रीष्मावकाश में हमें पूर्णिमा के अवसर पर यमुना नदी के नौका विहार का अवसर प्राप्त हुआ। चंद्रमा की चाँदनी से आकाश शांत, तर एवं उज्ज्वल प्रतीत हो रहा था। आकाश में चमकते तारे ऐसे प्रतीत हो रहे थे मानो वे आकाश के नेत्र हैं जो अपलक चाँदनी से स्नात पृथ्वी के सौंदर्य को देख रहे हैं। तारों से जड़े आकाश की शोभा यमुना के जल में द्विगुणित हो गई थी। इस रात-रजनी के शुभ प्रकाश में हमारी नौका धीरे-धीरे चलती है जो ऐसी लगती है मानो कोई सुंदर परी धीरे-धीरे चल रही हो।
जब नौका नदी के मध्य में पहुँच जाती है तो चाँदनी में चमकता हुआ पुलिन आँखों से ओझल हो जाता है तथा यमुना के किनारे खड़े हुए वृक्षों की पंक्ति भृकुटि-सी वक्र लग रही थी। नौका के चलने से जल में उत्पन्न लहरों के कारण उसमें चंद्रमा एवं तारक वृंद ऐसे झिलमिला रहे थे मानो तरंगों की लताओं में फूल खिले हों। रजत सर्पो-सी सीधी तिरछी नाचती हुई चाँदनी की किरणों की छाया चंचल लहरों में ऐसी प्रतीत होती थी मानो जल में आड़ी-तिरछी रजत रेखाएँ खींच दी गई हों। नौका के चलते रहने से आकाश के ओर-छोर भी हिलते हुए लगते थे। जल में तारों की छाया ऐसी प्रतिबिंबित हो रही थी मानो जल में दीपोत्सव हो रहा हो। ऐसे में हमारे एक मित्र ने मधुर राग छेड़ दिया जिससे वातावरण और भी अधिक उन्मादित हो गया। धीरे-धीरे हम नौका को किनारे की ओर ले आए।
डंडों से नौका को खेने पर जो फेन उत्पन्न होती थी वह भी चाँदनी के प्रभाव से मोतियों की ढेर-सी प्रतीत होती थी जिसे डंडों रूपी हथेलियों ने जल में बिखेर दिया हो। समस्त दृश्य अत्यंत दिव्य, अलौकिक एवं अपार्थिव ही लगता था।
64. राष्ट्रीय एकता
आज देश के विभिन्न राज्य क्षेत्रीयता के मोह में ग्रस्त हैं। सर्वत्र एक-दूसरे से बिछुड़कर अलग होने तथा अपना-अपना मनोराज्य स्थापित करने की होड़ लगी हुई है। यह स्थिति देश की एकता के लिए अत्यंत घातक है क्योंकि राष्ट्रीय एकता के अभाव में देश का अस्तित्व ही समाप्त हो जाता है। राष्ट्र से तात्पर्य किसी भौगोलिक भू-खंड मात्र अथवा उस भू-खंड में सामूहिक रूप से रहने वाले व्यक्तियों से न होकर उस भू-खंड में रहने वाली संवेदनशील अस्तित्व से युक्त जनता से होता है। अत: राष्ट्रीय एकता वह भावना है जो किसी एक राष्ट्र के समस्त नागरिकों को एकता के सूत्र में बाँधे रखती है। राष्ट्र के प्रति ममत्व की भावना से ही राष्ट्रीय एकता की भावना का जन्म होता है।
भारत की प्राकृतिक, भाषायी, रहन-सहन आदि की दृष्टि से अनेक रूप वाला. होते हुए भी राष्ट्रीय स्वरूप में एक है। पर्वतराज हिमालय एवं सागर इसकी प्राकृतिक सीमाएँ हैं, समस्त भारतीय धर्म एवं संप्रदाय के आवागमन में आस्था रखते हैं। भाषाई भेद-भाव होते हुए भी भारतवासियों की भाव-धारा एक है। यहाँ की संस्कृति की पहचान दूर से ही हो जाती है। भारत की एकता का सर्वप्रमुख प्रमाण यहाँ का एक संविधान का होना है। भारतीय संसद की सदस्यता धर्म, संप्रदाय, जाति, क्षेत्र आदि के भेद-भाव से मुक्त है। इस प्रकार अनेकता में एकता के कारण भारत की राष्ट्रीय एकता सदा सुदृढ़ है।

65. जब मैं अकेली होती हूँ
जब कभी मैं अकेली होती हूँ मेरा मन न जाने कहाँ-कहाँ भटकने लगता है। मुझे अपने आस-पास सब कुछ व्यर्थ लगने लगता है। उपन्यास, कहानी, पत्र-पत्रिकाएँ आदि व्यर्थ लगने लगती हैं। मैं रेडियो चलाकर गाने सुनने लगती हूँ। जब उनसे मेरा मन भर जाता है तो सी० डी० प्लेयर पर मन-पसंद दुख भरे गाने सुनने लगती हूँ। इनसे भी ऊब होने पर घर की हो चुकी सफ़ाई की पुनः सफ़ाई करने में जुट जाती हूँ, इतने से जब अकेलापन नहीं दूर होता तो चित्रकारी करने बैठ जाती हूँ। रेखांकन के पश्चात् जब रंग भरने लगती हूँ तो पुनः अकेलेपन का एहसास जाग उठता है तथा रंग भरने का उत्साह भी समाप्त हो जाता है। मुझे लगता है, यह अकेलापन मुझे पागल बना देगा। मैं जब भी अकेली होती हूँ मुझे अकेलेपन का एहसास चारों ओर से घेर कर ऐसा चक्रव्यूह बना लेता है जिससे निकलने के समस्त प्रयास करते-करते जब पराजित हो जाती हूँ तो अंत में निद्रा देवी की गोद में जाकर अकेलेपन से उबरने का प्रयास करती हूँ।
66. बारूद के इक ढेर पे बैठी है यह दुनिया
आधुनिक युग विज्ञान का युग है। मनुष्य ने अपने भौतिक सुखों की वृद्धि के लिए इतने अधिक वैज्ञानिक उपकरणों का आविष्कार कर लिया है कि एक दिन वे सभी उपकरण मानव सभ्यता के विनाश का कारण भी बन सकते हैं। एक-दूसरे देश को नीचा दिखाने के लिए अस्त्र-शस्त्रों, परमाणु बमों, रासायनिक बमों के निर्माण ने जहाँ परस्पर प्रतिद्वंद्विता पैदा की है वहीं इनका प्रयोग केवल प्रतिपक्षी दल को ही नष्ट नहीं करता अपितु प्रयोग करने वाले देश पर भी इनका प्रभाव पड़ता है। नए-नए कारखानों की स्थापना से वातावरण प्रदूषित होता जा रहा है। भोपाल गैस दुर्घटना के भीषण परिणाम हम अभी भी सहन कर रहे हैं। देश में एक कोने से दूसरे कोने तक ज़मीन के अंदर पेट्रोल तथा गैस की नालियाँ बिछाई जा रही हैं जिनमें आग लगने से सारा देश जलकर राख हो सकता है। घर में गैस के चूल्हों से अकसर दुर्घटनाएं होती रहती हैं। पनडुब्बियों के जाल ने सागर-तल को भी सुरक्षित नहीं रहने दिया है। धरती का हृदय चीर कर मेट्रो-रेल बनाई गई है। इसमें विस्फोट होने से अनेक नगर ध्वस्त हो सकते हैं। इस प्रकार आज की मानवता बारूद के एक ढेर पर बैठी है जिसमें छोटी-सी चिंगारी लगने मात्र से भयंकर विस्फोट हो सकता है।
67. जिस दिन समाचार-पत्र नहीं आता
समाचार-पत्र का हमारे आधुनिक जीवन में बहुत महत्त्व है। देश-विदेश के क्रिया-कलापों का परिचय हमें समाचारपत्र से ही प्राप्त होता है। कुछ लोग तो प्रायः अपना बिस्तर ही तभी छोड़ते हैं जब उन्हें चाय का कप और समाचारपत्र प्राप्त हो जाता है। जिस दिन समाचार-पत्र नहीं आता उस दिन इस प्रकार के व्यक्तियों को यह प्रतीत होता है कि मानो दिन निकला ही न हो कुछ लोग अपने घर के छज्जे आदि पर चढ़कर देखने लगते हैं कि कहीं समाचार-पत्र वाले ने समाचार-पत्र इतनी ज़ोर से तो नहीं फेंका कि वह छज्जे पर जा गिरा हो। वहाँ से भी जब निराशा हाथ लगती है तो वह आस-पास के घर वालों से पूछते हैं कि क्या उनका समाचार-पत्र आ गया है ? यदि उनका समाचार-पत्र आ गया हो तो वे अपने समाचार-पत्र वाले को कोसने लगते हैं।
उन्हें लगता है आज का उनका दिन अच्छा नहीं व्यतीत होगा। उनका अपने काम पर जाने का मन भी नहीं होता। वे पुराना अखबार उठाकर पढ़ने का प्रयास करते हैं किंतु पढ़ा हुआ होने पर उसे फेंक देते हैं तथा समाचार-पत्र वाहक पर आक्रोश व्यक्त करने लगते हैं। कई लोग तो समाचार-पत्र के अभाव में अपनी नित्य क्रियाओं से भी मुक्त नहीं हो पाते। वास्तव में जिस दिन समाचार-पत्र नहीं आता वह दिन अत्यंत फीका-फीका, उत्साह रहित लगता है।
68. वर्षा ऋतु की पहली बरसात
गरमी का महीना था। सूर्य आग बरसा रहा था। धरती तप रही थी। पशु-पक्षी तक गरमी के कारण परेशान थे। मज़दूर, किसान. रेहडी-खोमचे वाले और रिक्शा चालक तो इस तपती गरमी को झेलने के लिए विवश होते हैं। पंखों, कूलरों और एयर कंडीशनरों में बैठे लोगों को इस गरमी की तपन का अनुमान नहीं हो सकता। जुलाई महीना शुरू हुआ इस महीने में ही वर्षा ऋतु की पहली वर्षा होती है। सबकी दृष्टि आकाश की ओर उठती है। किसान लोग तो ईश्वर से प्रार्थना के लिए अपने हाथ ऊपर उठा देते हैं। अचानक एक दिन आकाश में बादल छा गए। बादलों की गड़गड़ाहट सुनकर मोर पिऊ-पिऊ मधुर आवाज़ में बोलने लगे। हवा में भी थोड़ी ठंडक आ गई। धीरे-धीरे हल्कीहल्की बूंदा-बाँदी शुरू हो गई। मैं अपने साथियों के साथ गाँव की गलियों में निकल पड़ा।
साथ ही हम नारे लगाते जा रहे थे, ‘बरसो राम धड़ाके से, बुढ़िया मर गई फाके से’। किसान भी खुश थे। उनका कहना था-‘बरसे सावन तो पाँच के हों बावन’ नववधुएँ भी कह उठी ‘बरसात वर के साथ’ और विरहिणी स्त्रियाँ भी कह उठीं कि ‘छुट्टी लेके आजा बालमा, मेरा लाखों का सावन जाए।’ वर्षा तेज़ हो गई थी। खुले में वर्षा में भीगने, नहाने का मजा ही कुछ और है। वर्षा भी उस दिन कड़ाके से बरसी। मैं उन क्षणों को कभी भूल नहीं सकता। मैं उसे छू सकता था, देख सकता था और पी सकता था। मुझे अनुभव हुआ कि कवि लोग क्योंकर ऐसे दृश्यों से प्रेरणा पाकर अमर काव्य का सृजन करते हैं।
69. बस अड्डे का दृश्य
हमारे शहर का बस अड्डा राज्य के अन्य उन बस अड्डों में से एक है जिसका प्रबंध हर दृष्टि से बेकार है। इस बस अड्डे के निर्माण से पहले बसें अलग-अलग स्थानों से अलग-अलग अड्डों से चला करती थीं। सरकार ने यात्रियों की असुविधा को ध्यान में रखते हुए सभी बस अड्डे एक स्थान पर कर दिए। आरंभ में तो ऐसा लगा कि सरकार का यह कदम बडा सराहनीय है किंतु ज्यों-ज्यों समय बीतता गया जनता की परेशानियाँ बढ़ने लगीं। बस अड्डे पर अनेक दुकानें बनाई गई हैं जिनमें खान-पान, फल-सब्जियों, पुस्तकों आदि की अनेक दुकानें हैं । खानपान की दुकान से उठने वाला धुआँ सारे यात्रियों की परेशानी का कारण बनता है। दुकानों की साफ़-सफ़ाई की तरफ़ कोई ध्यान नहीं देता। वहाँ माल बहुत महँगा मिलता है और गंदा भी। बस अड्डे में कई रेहडी वालों को भी फल बेचने की आज्ञा दी गई है।
ये लोग पोलीथीन के काले लिफ़ाफ़े रखते हैं जिनमें वे सड़े-गले फल पहले से ही तोल कर रखते हैं और लिफ़ाफ़ा इस चालाकी से बदलते हैं कि यात्री को पता नहीं चलता। घर पहुँचकर ही पता चलता है कि उन्होंने जो फल चुने थे वे बदल दिए गए हैं। बस अड्डे की शौचालय की साफ़-सफ़ाई न होने के बराबर है। यात्रियों को टिकट देने के लिए लाइन नहीं लगवाई जाती। लोग भाग-दौड़ कर बस में सवार होते हैं। औरतों, बच्चों और वृद्ध लोगों का बस में सवार होना ही कठिन होता है। अनेक बार देखा गया है कि जितने लोग बस के अंदर होते हैं उतने ही बस के ऊपर चढ़े होते हैं। अनेक बस अड्डों का हाल तो उनसे भी गया-बीता है। जगहजगह गंदा पानी, कीचड़, मक्खियाँ, मच्छर और न जाने किस-किस गंदगी की भरमार है। सभी बस अड्डे जेबकतरों के अड्डे बने हुए हैं। हर यात्री को अपने-अपने घर पहुँचने की जल्दी होती है इसलिए कोई भी बस अड्डे की इस बुरी हालत की ओर ध्यान नहीं देता।
70. शक्ति अधिकार की जननी है
शक्ति का लोहा कौन नहीं मानता है? इसी के कारण मनुष्य अपने अधिकार प्राप्त करता है। प्राय: यह दो प्रकार की मानी जाती है-शारीरिक और मानसिक। दोनों का संयोग हो जाने से बड़ी-से-बड़ी शक्ति को घुटने टेकने पर विवश किया जा सकता है। अधिकारों को प्राप्त करने के लिए संघर्ष की आवश्यकता होती है। इतिहास इस बात का गवाह है कि अधिकार सरलता, विनम्रता और गिड़गिड़ाने से प्राप्त नहीं होते। भगवान् कृष्ण ने पांडवों को अधिकार दिलाने की कितनी कोशिश की पर कौरव उन्हें पाँच गाँव तक देने के लिए सहमत नहीं हुए थे। तब पांडवों को अपने अधिकारों को प्राप्त करने के लिए युद्ध का रास्ता अपनाना पड़ा। भारत को अपनी आज़ादी तब तक नहीं मिली थी जब तक उसने शक्ति का प्रयोग नहीं किया। देशवासियों ने सत्य और अहिंसा के बल पर अंग्रेज़ सरकार से टक्कर ली थी।
तभी उन्हें सफलता प्राप्त हुई थी और देश को आजादी प्राप्त हो गयी। कहावत है कि लातों के भूत बातों से नहीं मानते। व्यक्ति हो अथवा राष्ट्र उसे शक्ति का प्रयोग करना ही पड़ता है। तभी अधिकारों की प्राप्ति होती है। शक्ति से ही अहिंसा का पालन किया जा सकता है, सत्य का अनुसरण किया जा सकता है, अत्याचार और अनाचार को रोका जा सकता है। इसी से अपने अधिकारों को प्राप्त किया जा सकता है। वास्तव में ही शक्ति अधिकार की जननी है।
71. भाषण नहीं राशन चाहिए
हर सरकार का यह पहला काम है कि वह आम आदमी की सुविधा का पूरा ध्यान रखे। सरकार की कथनी तथा करनी में अंतर नहीं होना चाहिए। केवल भाषणों से किसी का पेट नहीं भरता। यदि बातों से पेट भर जाता तो संसार का कोई भी व्यक्ति भूख-प्यास से परेशान न होता। भूखे पेट से तो भजन भी नहीं होता। भारत एक प्रजातंत्र देश है। यहाँ के शासन की बागडोर प्रजा के हाथ में है, यह केवल कहने की बात है। इस देश में जो भी नेता कुरसी पर बैठता है, वह देश के उद्धार की बड़ी-बड़ी बातें करता है पर रचनात्मक रूप से कुछ भी नहीं होता। जब मंच पर आकर नेता भाषण देते हैं तो जनता उनके द्वारा दिखाए गए सब्जबाग से खुशी का अनुभव करती है। उसे लगता है कि नेता जिस कार्यक्रम की घोषणा कर रहे हैं, उससे निश्चित रूप से गरीबी सदा के लिए दूर हो जाएगी, लेकिन होता सब कुछ विपरीत है।
अमीरों की अमीरी बढ़ती जाती है और आम जनता की गरीबी बढ़ती जाती है। यह व्यवस्था का दोष है। इन नेताओं पर हाथी के दाँत खाने के और दिखाने के और वाली कहावत चरितार्थ होती है। जनता को भाषण की नहीं राशन की आवश्यकता है। सरकार की ओर से ऐसी व्यवस्था होनी चाहिए कि जनता को ज़रूरत की वस्तुएँ प्राप्त करने में कठिनाई का अनुभव न हो। उसे रोटी, कपड़ा, मकान की समस्या का सामना न करना पड़े। सरकार को अपनी कथनी के अनुरूप व्यवहार भी करना चाहिए। उसे यह बात गाँठ बाँध लेनी चाहिए कि जनता को भाषण नहीं राशन चाहिए। भाषणों की झूठी खुराक से जनता को बहुत लंबे समय तक मूर्ख नहीं बनाया जा सकता।
72. हमारे पड़ोसी
अच्छे पड़ोसी तो रिश्तेदारों से अधिक महत्त्वपूर्ण होते हैं। वे हमारे सुख-दुख के भागीदार होते हैं। जीवन के हर सुख-दुख में पड़ोसी पहले आते हैं और दूर रहने वाले सगे-संबंधी तो सदा ही देर से पहुँचते हैं। आज के स्वार्थी युग में ऐसे पड़ोसी मिलना बहुत कठिन है। जो सदा कंधे-से-कंधा मिलाकर सुख-दुख में एक साथ चलें। हमारे पड़ोस में एक अवकाश प्राप्त अध्यापक रहते हैं। वे सारे मुहल्ले के बच्चों को मुफ्त पढ़ाते हैं। एक दूसरे सज्जन हैं जो सभी पड़ोसियों के छोटे-छोटे काम बड़ी प्रसन्नता से करते हैं। हमारे पड़ोस में एक प्रौढ़ महिला भी रहती है जिन्हें सारे मुहल्ले वाले मौसी कहकर पुकारते हैं। यह मौसी मुहल्ले भर के लड़के-लड़कियों की खोज-खबर रखती है। यहाँ तक कि किसकी लड़की अधिक फ़ैशन करती है, किसका लड़का अवारागर्द है।
मौसी को सारे मुहल्ले की ही नहीं, सारे शहर की खबर रहती है। हम मौसी को चलता-फिरता अखबार कहते हैं। वह कई बार झूठी चुगली करके कुछ पड़ोसियों को आपस में लड़वाने की कोशिश भी कर चुकी है। परंतु सब उसकी चाल को समझते हैं। हमारे सारे पड़ोसी बहुत अच्छे हैं। एक-दूसरे का ध्यान रखते हैं और समय पड़ने पर उचित सहायता भी करते हैं।
73. सपने में चाँद पर यात्रा
आज के समाचार-पत्र में पढ़ा कि भारत भी चंद्रमा पर अपना यान भेज रहा है। सारा दिन यही समाचार मेरे अंतर में घूमता रहा। सोया तो स्वप्न में लगा कि मैं चंद्रयान से चंद्रमा पर जाने वाला भारत का प्रथम नागरिक हूँ। जब मैं चंद्रमा के तल पर उतरा तो चारों ओर उज्ज्वल प्रकाश फैला हुआ था। वहाँ की धरती चाँदी से ढकी हुई-सी लग रही थी। तभी एकदम सफ़ेद वस्त्र पहने हुए परियों जैसी सुंदरियों ने मुझे पकड़ लिया और चंद्रलोक के महाराज के पास ले गईं। वहाँ भी सभी सफ़ेद उज्ज्वल वस्त्र पहने हुए थे। उनसे वार्तालाप में मैंने स्वयं को जब भारत का नागरिक बताया तो उन्होंने मेरा सफ़ेद रसगुल्लों जैसी मिठाई से स्वागत किया। वहाँ सभी कुछ अत्यंत निर्मल और पवित्र था। मैंने मिठाई खानी शुरू ही की थी कि मेरी मम्मी ने मेरी बाँह पकड़कर मुझे उठा दिया और डाँट पड़ी कि चादर क्यों खा रहा है ? मैं हैरान था कि यह क्या हो गया? कहाँ तो मैं चंद्रलोक का आनंद ले रहा था और यहाँ चादर खाने पर डाँट पड़ रही है। मेरा स्वप्न भंग हो गया था और मैं भाग कर बाहर की ओर चला गया।

74. मेट्रो रेल : महानगरीय जीवन का सुखद सपना
मेट्रो रेल वास्तव में ही महानगरीय जीवन का एक सुखद सपना है। भाग-दौड़ की जिंदगी में भीड़-भाड़ से भरी सड़कों पर लगते हुए गतिरोधों से मुक्त दिला रही है मेट्रो रेल। जहाँ किसी निश्चित स्थान पर पहुँचने में घंटों लग जाते थे वहीं मेट्रो रेल मिनटों में पहुँचा देती है। यह यातायात का तीव्रतम एवं सस्ता साधन है। यह एक सुव्यवस्थित क्रम से चलती है। इससे यात्रा सुखद एवं आरामदेह हो गई है। बसों की धक्का-मुक्की, भीड़-भाड़ से मुक्ति मिल गई है। समय पर अपने काम पर पहुँचा जा सकता है। एक निश्चित समय पर इसका आवागमन होता है इसलिए समय की बचत भी होती है। व्यर्थ में इंतज़ार नहीं करना पड़ता है। महानगर के जीवन में यातायात क्रांति लाने में मेट्रो रेल का महत्त्वपूर्ण योगदान है।
एक ही अनुच्छेद में किसी विषय से संबंधित विचारों को व्यक्त करना ‘अनुच्छेद लेखन’ कहलाता है। इसे लिखने के लिए कुशलता प्राप्त करना निरन्तर अभ्यास पर निर्भर करता है। अनुच्छेद को लिखने के लिए निम्नलिखित बातों की ओर ध्यान देना आवश्यक होता है-
- अनुच्छेद लिखने के लिए दिए गए विषय को भली-भांति समझ लेना चाहिए। शीर्षक में दिए गए भावों को अच्छी तरह से समझ लेना चाहिए।
- अनुच्छेद की भाषा शुद्ध, स्पष्ट और क्रमबद्ध, सुव्यवस्थित और उचित शब्दों से युक्त होनी चाहिए।
- अनुच्छेद पूरी तरह से विषय पर ही आधारित होना चाहिए। उसमें व्यर्थ का विस्तार कदापि नहीं होना चाहिए।
- अनुच्छेद की शैली ऐसी होनी चाहिए कि कम-से-कम शब्दों में अधिक-से-अधिक बात कह दी जाए। अप्रासंगिक और इधर-उधर की बातों को अनुच्छेद में स्थान नहीं दिया जाना चाहिए।
- अनुच्छेद के सभी वाक्य विषय से ही संबंधित होने चाहिए।
- अनुच्छेद किसी निबन्ध की तरह विस्तृत नहीं होना चाहिए।
- वाक्य संरचना सरल, सरस, सार्थक और सुगठित होनी चाहिए।
- भाव और भाषा में स्पष्टता, मौलिकता और सरलता विद्यमान रहनी चाहिए।
- भाषा निश्चित रूप से विषय के अनुरुप और स्तरीय होनी चाहिए। विचार-प्रधान विषयों में विचारात्मकता और. तार्किकता होनी चाहिए। भावात्मकता में अनुभूतियों की अधिकता होनी चाहिए।
- वाक्य संरचना में सुघड़ता और लयात्मकता को स्थान दिया जाना चाहिए।
पाठ्य पुस्तक में दिए गए विषयों पर आधारित अनुच्छेद
1. मेरी दिनचर्या
प्रतिदिन किए जाने वाले कार्य को दिनचर्या कहते हैं। मैं प्रतिदिन सुबह पाँच बजे उठता हूँ। शरीर को स्वस्थ रखने के लिए सबसे अच्छा साधन व्यायाम है। व्यायामों में सबसे सरल और लाभदायक व्यायाम प्रातः भ्रमण ही है इसलिए मैं प्रतिदिन भ्रमण के लिए जाता हूँ। प्रातःकाल भ्रमण के अनेक लाभ हैं। इससे हमारा स्वास्थ्य उत्तम होता है। इसके बाद कुछ योगासन करता हूँ। मैंने अपनी दिनचर्या बड़े क्रमबद्ध तरीके से बनाई हुई। योगासन के बाद स्नान आदि से निवृत्त होकर नाश्ता करता हूँ। फिर अपना बस्ता तैयार करके स्कूल के लिए साइकिल पर निकल जाता हूँ। दोपहर दो बजे तक विद्यालय पढ़ाई करने के बाद घर आकर भोजन करता हूँ। शाम को दोस्तों के साथ खेलने के लिए पार्क में जाता हँ। वहाँ हम सभी दोस्त मिलकर खेलते हैं। इसके बाद घर आकर अपना पढ़ाई का काम करता हूँ। फिर कुछ देर टी० वी० भी देखता हूँ। इतने में माँ रात का भोजन लगा देती है। रात का भोजन करने के बाद मैं बिस्तर में जाकर सो जाता हूँ।
2. मेरी पहली हवाई यात्रा
मानव जीवन में प्रायः ऐसी रोमांचक घटनाएं घटित होती हैं जो मानव को सदैव याद रह जाती हैं। ऐसे कुछ क्षण, ऐसी कुछ यादें ऐसी कुछ यात्राएँ जिन्हें मनुष्य सदा याद कर रोमांचित हो उठता है। बैंगलौर की हवाई यात्रा मेरे जीवन की एक ऐसी ही रोमांचकारी यात्रा थी। जो सदैव मुझे याद रहेगी। मुझे अच्छी तरह याद है कि वह जनवरी का महीना था। हमारी अर्द्धवार्षिक परीक्षा हो चुकी थी। हम घर पर छुट्टियों का आनंद उठा रहे थे कि एक दिन पिता जी दफ्तर से घर आए और कहा कि हम सब दो दिन बाद बैंगलौर घूमने जा रहे हैं। उन्होंने इसके लिए पूरे परिवार की जैट एयर से उड़ान की टिकट बुक करवा ली थीं। ये सुनते ही मेरी खुशी का तो कोई ठिकाना न था। निश्चित दिन हम सभी टैक्सी से एयरपोर्ट पहुँच गए। काऊंटर पर हमने अपना सामान जमा करवाया। कंप्यूटर से सारे सामान की जाँच हुई।
उसके बाद हमें यात्री पास मिले। हमारी भी चैकिंग हुई। इसके बाद हम विमान के अंदर गए। वहाँ विमान परिचारिकाओं ने हमें हमारी निश्चित सीट पर बैठाया। उड़ान से पूर्व हमें बताया गया कि हमारी उड़ान कहाँ और कितनी देर की है। हमें सीट बेल्ट बाँधने को कहा गया। मेरी सीट खिड़की के साथ थी। मैं आकाश से धरती के लगातार बदलते रूपों को देख रहा था। यह एक ऐसा निर्वचनीय आनंद था जिसकी अनुभूति तो हो सकती है पर वर्णन नहीं। यह मेरे जीवन की एक रोमांचक यात्रा थी जिसे मैं कभी नहीं भुला सकता।
3. मेरे जीवन का लक्ष्य
संसार में प्रत्येक मनुष्य के जीवन का कोई-न-कोई लक्ष्य अवश्य होता है। एक मनुष्य एवं सामाजिक प्राणी होने के नाते मैंने भी अपने जीवन का लक्ष्य निर्धारित किया है। मैं बड़ा होकर एक आदर्श अध्यापक बनना चाहता हूँ और अध्यापक के रूप में अपने कर्तव्यों को निभाता हुआ अपने राष्ट्र की सेवा करना चाहता हूँ। मैं आदर्श शिक्षक बनकर अपने राष्ट्र की भावी पीढ़ी के बौद्धिक स्तर को उच्च स्तर पर पहुँचाना चाहता हूँ ताकि मेरे देश की युवा पीढ़ी कुशल, विवेकशील, कर्मनिष्ठ बन सके और मेरा देश फिर से शिक्षा का सिरमौर बन सके। फिर से हम विश्व-गुरु की उपाधि को ग्रहण कर सकें। विद्यार्थी होने के कारण मैं भली-भांति जानता हूँ कि किसी अध्यापक का विद्यार्थियों पर कैसा प्रभाव पड़ता है। कोई अच्छा अध्यापक उनको उच्छी दिशा दे सकता है। मैं भी ऐसा करके देश के युवा वर्ग को नई दिशा देना चाहता हूँ।
4. हम घर में सहयोग कैसे करें?
मानव एक सामाजिक प्राणी है इसलिए उसे अपने जीवन-यापन हेतु समाज में दूसरों से किसी-न-किसी कार्य के लिए सहयोग लेना और देना पड़ता है। मानवीय जीवन में सहयोग का बहुत महत्त्व है। हमें इसका प्रारंभ अपने घर से ही करना चाहिए। हमें अपने घर में प्रत्येक सदस्य के साथ सहयोगपूर्ण भावना से मिलजुल कर कार्य करना चाहिए जैसे माता-पिता अपना सब कुछ समर्पित करके घर को चलाते हैं। पिता जी सुबह से शाम तक कठिन परिश्रम करते हैं और माता जी सुबह से लेकर रात तक साफ-सफाई, भोजन बनाना, बर्तन धोना आदि घर के अनेक कार्यों को निपटाने में लगी रहती हैं।
इसलिए हमें भी घर के किसी-न-किसी कार्य में माता-पिता का सहयोग ज़रूर करना चाहिए। हम अनेक छोटे-बड़े कार्यों में माता-पिता का सहयोग कर सकते हैं ; जैसे-दुकान से फल-सब्जियां तथा रसोई का सामान लाना, लांड्री से कपड़े लाना, खाना परोसना आदि। हम अपने छोटे भाई-बहनों को उनके पढ़ाने में उनकी मदद कर सकते हैं। अपने बगीचे की साफ-सफाई तथा घर की सफाई में सहयोग दे सकते हैं। पौधों में खाद-पानी दे सकते हैं तथा उनकी नियमित देख-रेख कर सहयोग दे सकते हैं। इस प्रकार घर में सहयोग की भावना का विकास होगा जिससे पारस्परिक सद्भाव एवं प्रेम की भावना बढ़ेगी और घर खुशहाल बन जाएगा।

5. गाँव का खेल मेला
मेले भारतीय संस्कृति की अनुपम पहचान हैं। ग्रामीण संस्कृति में इनका विशेष महत्त्व है। हमारे गाँव में प्रति वर्ष
खेल मेले का आयोजन किया जाता है। इस वर्ष भी हमारे गांव में मई मास में खेल मेले का धूमधाम से आयोजन किया गया। इस अवसर पर पूरे गाँव को दुल्हन की तरह सजाया गया था। गांव की प्रत्येक गली में बड़ी-बड़ी लाइटें तथा ध्वनि यंत्र लगाए गए। खेल मैदान में दर्शकों के लिए बैठने की विशेष सुविधा की गई थी। मैदान में चारों तरफ लाइटों का भी विशेष प्रबंध था। इस मेले का उद्घाटन राज्य खेल मंत्री के कर कमलों से हुआ।
खेल प्रारंभ होने से पूर्व खेल मंत्री ने सभी टीमों से मुलाकात की तथा उन्हें संबोधित करते हुए कहा कि खिलाड़ियों को खेल-भावना से खेलना चाहिए। प्रथम दिवस कबड्डी, खो-खो तथा साइकिल दौड़ का आयोजन किया गया तथा दूसरे दिन सौदो सौ तथा पाँच सौ मीटर दौड़ आयोजित की गई। क्रिकेट मैच ने सब दर्शकों का मन मोह लिया। खेल मेले के समापन अवसर पर मुख्य अतिथि शिक्षा अधिकारी ने प्रत्येक वर्ग में प्रथम, द्वितीय और तृतीय स्थान पर रहे सभी खिलाड़ियों को मेडल प्रदान किए। वास्तव में हमारे गाँव का खेल मेला अत्यंत रोचक, मनोरंजकपूर्ण रहा। यह हमारे लिए अविस्मरणीय रहेगा।
6. परीक्षा में अच्छे अंक पाना ही सफलता का मापदंड नहीं
परीक्षा में विद्यार्थियों के धैर्य और वर्षभर किए गए परिश्रम की परख होती है। यह सत्य है कि परीक्षा में सभी विद्यार्थियों की अच्छे अंक पाने की कामना होती है और अच्छे अंक प्राप्त करने से उनका सभी जगह सम्मान होता है। इससे विद्यार्थी का आत्म-सम्मान और आत्मविश्वास बढ़ता है। उसकी स्वर्णिम भविष्य की राहें आसान हो जाती हैं। किंतु परीक्षा में अच्छे अंक पाना ही सफलता का मापदंड नहीं हैं क्योंकि सफलता केवल अच्छे अंकों से ही प्राप्त नहीं होती बल्कि सफलता के इसके अतिरिक्त कई पहलू और भी हैं। सफलता के लिए आत्मविश्वास, साहस, विवेक, इच्छाशक्ति, सकारात्मक सोच होनी चाहिए। कम अंक पाने वाले लोग भी इन बिंदुओं के आधार पर सफलता की ऊँचाइयों को छू सकते हैं।
इसके लिए आदमी को अपनी क्षमता की पहचान अवश्य होनी चाहिए। दुनिया में ऐसे बहुत उदाहरण हैं जिन्हें कम अंक पाने के बावजूद भी श्रेष्ठ स्तर की सफलता को प्राप्त किया है। दुनिया के श्रेष्ठ वैज्ञानिक आइंस्टाइन स्कूली स्तर पर औसत विद्यार्थी रहे लेकिन आगे चलकर उन्होंने अनूठे आविष्कार किए। इसी तरह मुंशी प्रेमचन्द ने दसवीं की परीक्षा मुश्किल से द्वितीय श्रेणी में पास की और कई बार फेल होने के बाद बी०ए० की परीक्षा पास की थी। इसके बावजूद भी मुंशी प्रेमचंद दुनिया के अमर उपन्यासकार के रूप में जाने जाते हैं। इसी प्रकार अनेक क्रिकेटर, खिलाड़ी, संगीतकार, नेता, अभिनेता, गायक आदि हुए हैं जो अपने अकादमिक रूप में नहीं बल्कि अच्छे प्रदर्शन के लिए प्रसिद्ध हैं। सचमुच परीक्षा में केवल अच्छे अंक पाना ही जीवन में सफलता की प्राप्ति का मापदंड नहीं है।
7. ज्ञान वृद्धि का साधन-भ्रमण
संसार में ज्ञान-वृद्धि और ज्ञानार्जन के अनेक साधन हैं। पाठ्य-पुस्तकें, पत्र-पत्रिकाएं आदि पढ़कर तथा अनेक स्थलों की यात्राएं करके भी ज्ञान प्राप्त किया जा सकता है। रेडियो, टेलीविज़न सुन-देखकर भी देश-विदेश की अनेक जानकारियां प्राप्त की जा सकती हैं। किन्तु भ्रमण ज्ञान वृद्धि का अनुपम साधन है। यह ज्ञानवृद्धि के साथ-साथ आनंद . और मौज-मस्ती का अनूठा साधन है। ऐतिहासिक एवं धार्मिक स्थलों के भ्रमण से ज्ञानवृद्धि ही नहीं, मन की शांति, आत्मिक प्रसन्नता और सौंदर्यानुभूति भी प्राप्त होती है। इसी तरह नदियों, पर्वतों, झरनों, वनों, तालाबों आदि के भ्रमण से प्राकृतिक सौंदर्य का ज्ञान एवं आनंद ग्रहण किया जा सकता है। भ्रमण से मनुष्य को चहुँमुखी ज्ञान की प्राप्ति होती है। उसके आत्मविश्वास को बढ़ावा मिलता है वस्तुतः भ्रमण ज्ञान वृद्धि का साधन है।
8. प्रकृति का वरदान : पेड़-पौधे
प्रकृति ने संसार को अनेक अनूठे उपहार भेंट किए हैं। पेड़-पौधे प्रकृति का अनूठा वरदान है। पेड़-पौधे संपूर्ण जीवजगत के जीवन का मूलाधार हैं। ये पर्यावरण को साफ, स्वच्छ एवं सुंदर बनाते हैं। ये कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड को ग्रहण करते हैं और ऑक्सीजन दूसरों को देते हैं। इस ऑक्सीजन से सम्पूर्ण प्राणी जगत सांस लेता है। पेड़-पौधे स्वयं सूर्य की तपन को सहन कर दूसरों को छाया प्रदान करते हैं। वे अपने फल स्वयं कभी नहीं खाते बल्कि उन्हें भी हमें ही दे देते हैं। वे इतने विन्रम होते हैं कि फल आने पर स्वयं ही नीचे की तरफ झुक जाते हैं। पेड़-पौधे वातावरण को शुद्ध बनाते हैं। धरा की उपजाऊ शक्ति को बढ़ाते हैं। भूमि को पानी के कटाव से रोकते हैं। पेड़-पौधों से हमें लकड़ियाँ, औषधियाँ, छाल आदि अनेक अमूल्य उपहार प्राप्त होते हैं। संभवतः पेड़-पौधे प्रकृति का अनूठा वरदान हैं। हमें भी पेड़-पौधों का संरक्षण करना चाहिए। अधिक-से-अधिक पेड़-पौधे लगाने चाहिए।
9. अपने नए घर में प्रवेश
मैंने बचपन में एक सपना देखा था कि हमारा नया घर होगा जिसमें हम सपरिवार खुशी से रहेंगे। मेरा यह सपना गत सप्ताह पूर्ण हुआ। पिछले सप्ताह ही हमारा नया घर बनकर तैयार हुआ जिसमें घर के अनुरूप नए पर्दै, फर्नीचर आदि लगवाया गया। सोमवार को हमारा गृह-प्रवेश था जिसमें हमने अपने सभी मित्रों, रिश्तेदारों और पड़ोसियों को सादर आमंत्रित किया था। इस अवसर पर सुबह सात बजे ही पंडित जी ने पूजा विधान का कार्यक्रम आरंभ कर दिया। इसके बाद हवन-यज्ञ किया गया जिसमें परिवार के सभी लोग सम्मिलित हुए। पंडित जी ने नारियल फोड़कर परिवार से गृहप्रवेश करवाया। पूजा-विधान के पश्चात् दोपहर के भोजन का प्रबंध किया गया था। हमारे सभी मित्रों, रिश्तेदारों और पड़ोसियों ने आनंदपूर्वक भोजन किया और जाते समय सभी ने गृह-प्रवेश पर लाखों बधाइयां दी। हमने सपरिवार सभी मेहमानों का धन्यवाद किया। वास्तव में नए गृह-प्रवेश के अवसर पर हम सब बहुत उत्साहित थे।
10. कैरियर चनाव में स्वमूल्यांकन
कैरियर चुनाव मानव-जीवन का महत्त्वपूर्ण हिस्सा है क्योंकि कैरियर चुनाव की सार्थकता ही मानव-जीवन की सफलता की सीढ़ी है। यह वर्तमान युवा वर्ग की सबसे बड़ी चुनौती है। यह बात सच है कि कैरियर के चुनाव में माता पिता, मित्र, रिश्तेदार आदि अनेक लोगों की राय होती हैं किंतु कैरियर चुनाव में स्वमूल्यांकन सर्वोत्तम है। युवा वर्ग को अपने विद्यार्थी जीवन के प्रारंभ से ही इसकी जानकारी होनी चाहिए। उसे प्रारंभ से स्वमूल्यांकन कर लेना चाहिए। अपनी पसंद, क्षमता, पुरुषार्थ, विवेक, बुद्धि कौशल और आत्म-विश्वास को ध्यान में रखकर अपने कैरियर का चुनाव करना अति महत्त्वपूर्ण है। यदि विद्यार्थी अपनी क्षमता, पुरुषार्थ, विवेक बुद्धि-कौशल और आत्मविश्वास को ध्यान में रखकर अपने कैरियर का चुनाव करता है तो वह अवश्य ही सफल होता है। उसे अपने कैरियर के चुनाव में किसी बात की कोई कठिनाई नहीं आती। वह अपनी रुचि के अनुकूल अपना कैरियर बनाने में सफल हो सकता है। अत: कैरियर चुनाव में दूसरों की राय की अपेक्षा स्वमूल्यांकन अत्यावश्यक है।
11. विद्यार्थी और अनुशासन
विद्यार्थी और अनुशासन एक-दूसरे के पूरक हैं। यूं कहें कि अनुशासन ही विद्यार्थी जीवन की नींव है। विद्यार्थी जीवन में अनुशासन का बहुत महत्त्व है। अनुशासित विद्यार्थी ही सफलता की ऊंचाई को छूने में सफल होता है जो विद्यार्थी अपने जीवन में अनुशासन को नहीं अपनाता वह कभी भी सफल नहीं होता बल्कि अपने जीवन को ही बर्बाद कर लेता है। बिना अनुशासन के विद्यार्थी जीवन कटी-पतंग के समान होता है जिसका कोई लक्ष्य नहीं होता। जो विद्यार्थी अपने विद्यालय के प्रांगण में रहकर प्रतिक्षण अनुशासन का पालन करता है। अपने शिक्षकों का आदर करता है और इतना ही नहीं जीवन में हर पल नियमों-अनुशासन में बंधकर चलता है ; वह कदापि निष्फल नहीं हो सकता। सफलता उसके कदम अवश्य ही चूमती है। इसलिए विद्यार्थी को कभी भी अनुशासन भंग नहीं करना चाहिए बल्कि सदैव अनुशासन का पालन करना चाहिए। एक अनुशासित विद्यार्थी ही राष्ट्र का आदर्श नागरिक बनता है और देश के चहुंमुखी विकास में अपना योगदान देता है।
12. कोचिंग संस्थानों का बढ़ता जंजाल
वर्तमान युग कंपीटीशन का युग है। आज हर क्षेत्र में प्रतियोगिता है। आज के विद्यार्थी को पग-पग पर अनेक प्रतियोगी परीक्षाओं से गुजरना पड़ता है। मेडिकल, सेना, कानून, प्रशासनिक सेवाओं, इंजीनियरिंग आदि कोरों में प्रवेश लेने के लिए अलग-अलग परीक्षाएं देनी पड़ती हैं। इतना ही नहीं अनेक प्रकार की नौकरियां पाने के लिए भी आजकल प्रतियोगी परीक्षाएं आयोजित की जाती हैं जिनके पास करने के उपरांत ही प्रतियोगी को आगे बढ़ने का मौका मिलता है। आज के युग में प्रतियोगिता निरन्तर बढ़ती जा रही है। एक-एक सीट पर दाखिला लेने और नौकरी पाने के लिए हजारों-लाखों प्रतियोगी पंक्तिबद्ध होकर प्रतीक्षा में रहते हैं जिसके चलते आज कोचिंग संस्थानों की भरमार हो रही है।
चूंकि हर कोई अपने को सिद्ध करने के लिए कोचिंग संस्थानों की ओर भागता है। परिणामस्वरूप छोटे से लेकर बड़े शहरों तक कोचिंग संस्थानों ने अपना जाल बिछा दिया है। दिल्ली, मुंबई, बंगलौर जैसे शहरों में तो जगह-जगह बड़ेबड़े संस्थान खुले हुए हैं जिनमें लाखों लोग पढ़ रहे हैं। ये संस्थान लाखों की फीस ऐंठकर अपना उल्लू सीधा कर रहे हैं क्योंकि कोचिंग से बढ़कर स्वाध्ययन ज़रूरी है। स्वध्ययन से ही प्रतियोगी के अंदर आत्मविश्वास की भावना उत्पन्न होती है और आत्मविश्वास ही सफलता होती है। इसलिए हमें स्वाध्ययन को ही आधार बनाना चाहिए।

13. मैंने लोहड़ी का त्योहार कैसे मनाया?
लोहड़ी भारतीय संस्कृति का पवित्र और महत्त्वपूर्ण त्योहार माना जाता है। यह प्रतिवर्ष 13 जनवरी को संपूर्ण भारत वर्ष में बड़े हर्षोल्लास एवं मौज-मस्ती के साथ मनाया जाता है। इस वर्ष मैंने लोहड़ी का त्योहार अपने मामा जी के घर अमृतसर में मनाया। मैं एक दिन पहले ही अपने मामा जी के घर पहुंच गया था। लोहड़ी वाले दिन सुबह से ही ढोल-नगाड़े बजने प्रारंभ हो गए थे। सब गले मिलकर एक-दूसरे को पावन पर्व की बधाइयाँ दे रहे थे। मैंने भी अपने भाई के साथ मिलकर पूरे मोहल्ले वालों को बधाइयां दी। सब लोग एक-दूसरे के घर मिठाइयां, रेवड़ी, मूंगफली बांट रहे थे।
उस दिन शाम को मोहल्ले के बीच में सबने अपने-अपने घर से लकड़ियाँ लाकर बड़ा ढेर लगा दिया। सभी उसके चारों तरफ इकट्ठे हो गए। पूरी श्रद्धा एवं आनंद के साथ लकड़ियों में अग्नि प्रज्वलित की गई। तत्पश्चात् सबने लोहड़ी की पूजा अर्चना की। सब उसकी परिक्रमा कर रहे थे और गीत गा रहे थे। पूजा के बाद सबको रेवड़ी, मूंगफली आदि का प्रसाद बांटा गया। इसके बाद ढोल-नगाड़े बजने लगे तो सभी लोग झूम उठे। लड़कियां गिद्दा पाने लगी तो लड़के भांगड़ा करने लगे। सचमुच यह लोहड़ी का त्योहार मैंने खूब आनंदपूर्वक मनाया। यह मेरे लिए अविस्मरणीय रहेगा।
14. जनसंचार के माध्यम
वर्तमान युग विज्ञान, प्रौद्योगिकी एवं भूमंडलीकरण का युग है। आज के युग में जनसंचार के क्षेत्र में क्रांति-सी आ गई है। आज पहले की अपेक्षा जनसंचार के आधुनिक एवं अनेक साधन हैं जिनसे हम दूसरों तक अपनी बात को आसानी से पहँचा सकते हैं। अब तो जनसंचार के लिए मोबाइल फोन हर व्यक्ति की जेब में सदा विद्यमान रहता है जिससे आप देश-विदेश कहीं भी बात कर सकते हो, संदेश प्राप्त कर सकते हो या उन्हें कहीं भी भेज सकते हो। इंटरनेट की सुविधा ने तो पूरे संसार को एक गाँव में बदल कर रख दिया है। पत्र-पत्रिकाएं, रेडियो, टेलीविज़न, मोबाइल, टेलीफोन, इंटरनेट, ई-मेल, फैक्स आदि जनसंचार के विभिन्न माध्यम हैं। जनसंचार के इन माध्यमों को हम अनेक वर्गों में बांट सकते हैं। मौखिक और लिखित। दृश्य और श्रव्य तथा दृश्य एवं श्रव्य दोनों। इन सभी माध्यमों का देश के शिक्षा, व्यापार, व्यवसाय, मनोरंजन आदि क्षेत्रों में अनूठा योगदान है।
15. भ्रूण हत्या : एक जघन्य अपराध
आज हमारे देश में दहेज प्रथा, बाल विवाह, जनसंख्या वृद्धि, कन्या भ्रूण हत्या आदि अनेक समस्याएं हैं जिनमें कन्या भ्रूण हत्या एक भयंकर समस्या है। यह एक ऐसा जघन्य अपराध है जो देश की महानता और गौरव-गरिमा को धूमिल कर रहा है। वैज्ञानिक उन्नति ने इस अपराध को बढ़ावा देने का कार्य किया है। मेडिकल क्षेत्र में नवीन खोज़ से जो बड़ीबड़ी और अति आधुनिक अल्ट्रासाऊंड मशीनें आई हैं जिनका उपयोग जनकल्याण कार्यों के लिए किया जाना था। आज कुछ स्वार्थी लोग अपनी स्वार्थपूर्ति हेतु उनका गलत कार्यों के लिए उपयोग कर रहे हैं।
वे माता-पिता को जन्म से पूर्व ही अल्ट्रासांऊड के माध्यम से यह बता देते हैं कि गर्भ में पल रहा भ्रूण बेटा है अथवा बेटी। हालांकि ऐसा करना हमारे देश में कानूनी अपराध है किन्तु फिर भी कुछ लोग अपने लालच के कारण ऐसा कर रहे हैं जिससे मातापिता एक बेटे की चाह में उस कन्या को जन्म से पहले ही गर्भ में मरवा देते हैं। इसका दुष्परिणाम यह है कि देश में लड़कियों की संख्या दिन-प्रतिदिन कम होती जा रही है। कन्या भ्रूण हत्या को रोकने के लिए सरकार को कड़े कानून बनाने चाहिए। इसके लिए ज़िम्मेदार व्यक्ति को कड़ी सजा देनी चाहिए।
16. मेरी दिनचर्या
प्रतिदिन किए जाने वाले कार्य को दिनचर्या कहते हैं। मैं प्रतिदिन सुबह पाँच बजे उठता हूँ। शरीर को स्वस्थ रखने के लिए सबसे अच्छा साधन व्यायाम है। व्यायामों में सबसे सरल और लाभदायक व्यायाम प्रातः भ्रमण ही है इसलिए मैं प्रतिदिन भ्रमण के लिए जाता हूँ। प्रातःकाल भ्रमण के अनेक लाभ हैं। इससे हमारा स्वास्थ्य उत्तम होता है। इसके बाद कुछ योगासन करता हूँ। मैंने अपनी दिनचर्या बड़े क्रमबद्ध तरीके से बनाई हुई है। योगासन के बाद स्नान आदि से निवृत्त होकर नाश्ता करता हूँ। फिर अपना बस्ता तैयार करके स्कूल के लिए साइकिल पर निकल जाता हूँ। दोपहर दो बजे तक विद्यालय पढ़ाई करने के बाद घर आकर भोजन करता हूँ। शाम को दोस्तों के साथ खेलने के लिए पार्क में जाता हूँ। वहाँ हम सभी दोस्त मिलकर खेलते हैं। इसके बाद घर आकर अपना पढ़ाई का काम करता हूँ। फिर कुछ देर टी०वी० भी देखता हूँ। इतने में माँ रात का भोजन लगा देती है। रात का भोजन करने के बाद मैं बिस्तर में जाकर सो जाता हूँ।
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()