Punjab State Board PSEB 10th Class Physical Education Book Solutions Chapter 1 ਕਸਰਤ ਦੇ ਸਾਹ ਕਿਰਿਆ, ਲਹੂ ਚੱਕਰ, ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਮਲ-ਨਿਕਾਸ ਉੱਤੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ Textbook Exercise Questions, and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 10 Physical Education Chapter 1 ਕਸਰਤ ਦੇ ਸਾਹ ਕਿਰਿਆ, ਲਹੂ ਚੱਕਰ, ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਮਲ-ਨਿਕਾਸ ਉੱਤੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ
Physical Education Guide for Class 10 PSEB ਕਸਰਤ ਦੇ ਸਾਹ ਕਿਰਿਆ, ਲਹੂ ਚੱਕਰ, ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਮਲ-ਨਿਕਾਸ ਉੱਤੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵTextbook Questions and Answers
ਬਹੁਤ ਛੋਟੇ ਉੱਤਰਾਂ ਵਾਲੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ (Very Short Answer Type Questions)
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਜਾਂ ਪੱਠੇ ਕੀ ਹਨ ? (Describe Muscles.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਮਾਸ ਸੁਤਰ ਸੈੱਲਾਂ ਦਾ ਸੁਮੇਲ ਹਨ । ਹਰੇਕ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀ ਹੱਡੀ ਨਾਲ ਜੁੜੀ ਹੋਣ ਕਰਕੇ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਸੁੰਗੜਨ ਤੇ ਭਿੰਨ-ਭਿੰਨ ਅੰਗ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਕਿਸਮਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਂ ਲਿਖੋ । (Name the types of Muscles.)
ਉੱਤਰ –
- ਸਵੈ-ਇੱਛਤ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ (Voluntary Muscles)
- ਅਣਇੱਛਤ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ (Involuntary Muscles)
- ਦਿਲ ਦੀਆਂ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ (Cardiac Muscles) ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਮਲ-ਤਿਆਗ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਕੀ ਹੈ ? (What is Excretory System ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਮਲ-ਤਿਆਗ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਉਸ ਪ੍ਰਬੰਧ ਨੂੰ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ਜਿਸ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਫਾਲਤੂ ਅਤੇ ਹਾਨੀਕਾਰਕ ਪਦਾਰਥਾਂ ਦਾ ਨਿਕਾਸ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਮਲ-ਤਿਆਗ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਦੇ ਮੁੱਖ ਅੰਗਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਂ ਲਿਖੋ । (Name the organs of Excretory System.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
- ਫੇਫੜੇ
- ਗੁਰਦੇ
- ਚਮੜੀ
- ਅੰਤੜੀਆਂ ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 5.
ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਕੋਈ ਦੋ ਕੰਮ ਲਿਖੋ । (Give two functions of Muscles.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
- ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਰੂਪ ਪ੍ਰਦਾਨ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਮੱਦਦ ਨਾਲ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਚਲਦਾ-ਫਿਰਦਾ, ਕੁੱਦਦਾ-ਟੱਪਦਾ ਅਤੇ ਸਾਹ ਆਦਿ ਲੈਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 6.
ਸਵੈ-ਇੱਛਤ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ (Voluntary Muscles) ਕੀ ਹਨ ? (What is Voluntary Muscles ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਸਵੈ-ਇੱਛਤ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਉਹ ਹਨ ਜੋ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦੀ ਇੱਛਾ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
ਪਸ਼ਨ 7.
ਅਣ-ਇੱਛਤ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ (Involuntary Muscles) ਕੀ ਹਨ ? (What is Involuntary Muscles ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਇਹ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦੇ ਵਸ ਵਿਚ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ । ਇਹ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦੀ ਇੱਛਾ ਦੇ ਬਿਨਾਂ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 8.
ਦਿਲ ਦੀਆਂ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਵੀ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ? (What is Cordiac Muscles ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਇਹ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਅਣ-ਇੱਛਤ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਵਰਗੀਆਂ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਪਰ ਇਹ ਲਗਾਤਾਰ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਨ ਨਾਲ ਵੀ ਥੱਕਦੀਆਂ ਨਹੀਂ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 9.
ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਕਿੰਨੇ ਗੁਰਦੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ? (How many kidneys are there in our body ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਦੋ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 10.
ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਫੇਫੜਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਦੱਸੋ । (How many lungs a person possesses ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਦੋ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 11. ਨਬਜ਼ ਕੀ ਹੈ ? (What is Pulse ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
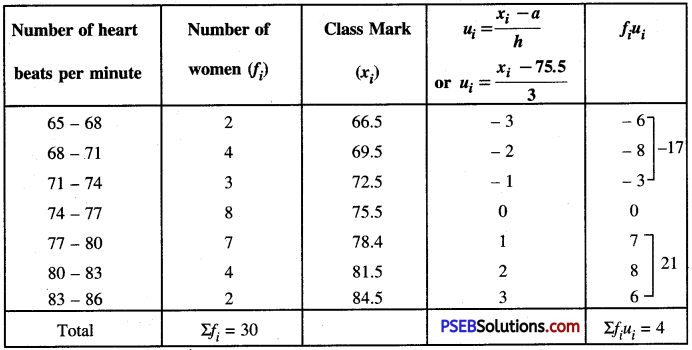
ਨਬਜ਼ ਦਰ ਦਾ ਭਾਵ ਦਿਲ ਦੀ ਧੜਕਣ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਦਰ 72 ਤੋਂ 80 ਇਕ ਮਿੰਟ ਵਿਚ ਹੋ ਸਕਦੀ ਹੈ । ਦਿਲ ਦੀ ਧੜਕਣ ਵੀ ਨਬਜ਼ ਦੀ ਦਰ ਦੇ ਬਰਾਬਰ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 12.
ਲਹੂ ਦਾ ਕੰਮ ਲਿਖੋ । (Write the function of the blood.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਲਹੂ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਆਕਸੀਜਨ ਸਪਲਾਈ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਅਰਥ ਪਦਾਰਥਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਮਲ-ਤਿਆਗ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਨਾਲ ਬਾਹਰ ਕੱਢਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 13.
ਨੱਕ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਸਾਹ ਲੈਣ ਦੇ ਕੀ ਲਾਭ ਹਨ ? (What are the uses of nose breathing ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਨੱਕ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਸਾਹ ਲੈਣ ਨਾਲ ਹਵਾ ਸ਼ੁੱਧ ਅਤੇ ਗਰਮ ਹੋ ਕੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 14.
ਸਾਹ ਲੈਂਦੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਅਸੀਂ ਕਿਹੜੀ ਗੈਸ ਅੰਦਰ ਲੈ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਾਂ ? (Which gas do we take while breathing ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਆਕਸੀਜਨ ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 15.
ਸਰੀਰਕ ਥਕਾਵਟ ਤੋਂ ਕੀ ਭਾਵ ਹੈ ? (What do you mean by physical fatigue ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਇਸ ਵਿਚ ਸਰੀਰ ਥੱਕ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਨ ਨੂੰ ਮਨ ਨਹੀਂ ਕਰਦਾ । ਮਾਨਸਿਕ ਥਕਾਵਟ ਮਨ ਦੀ ਥਕਾਵਟ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 16.
ਮਾਨਸਿਕ ਥਕਾਵਟ ਦੇ ਮੁੱਖ ਕਾਰਣ ਕੀ ਹਨ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
- ਭੋਜਨ ਵਿਚ ਪੌਸ਼ਟਿਕ ਪਦਾਰਥਾਂ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ
- ਠੀਕ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੀਂਦ ਨਾ ਲੈਣਾ ।
- ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦੀ ਸਮਰੱਥਾ ਤੋਂ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾ ਕੰਮ ਦਾ ਬੋਝ
- ਰੋਗ
- ਇਕਾਗਰਤਾ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ।
ਛੋਟੇ ਉੱਤਰਾਂ ਵਾਲੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ (Short Answer Type Questions)
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਸਾਹ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਕਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ? (What is Respiration ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਸਾਹ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਦੋ ਕਿਰਿਆਵਾਂ ਦਾ ਮੇਲ ਹੈ : ਸਾਹ ਅੰਦਰ ਲੈ ਜਾਣ ਦੀ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਜਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਉੱਛਵਾਸ ਕਿਰਿਆ (Inspiration) ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ਅਤੇ ਸਾਹ ਬਾਹਰ ਕੱਢਣ ਦੀ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਜਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਨਿਰਸੁਆਹ ਕਿਰਿਆ (Expiration) ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ | ਸਾਹ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਦਾ ਮਨੁੱਖੀ ਜੀਵਨ ਲਈ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ ਮਹੱਤਵ ਹੈ । ਆਮ ਅਰੋਗੀ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਮਿੰਟ 20 ਤੋਂ 22 ਵਾਰ ਸਾਹ ਲੈਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਲਹੂ ਕਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ? (What is Blood ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਲਹੁ ਇਕ ਕਿਸਮ ਦਾ ਤਰਲ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਸ਼ਿਰਾਵਾਂ (Veins) ਅਤੇ ਧਮਨੀਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਦਿਨ-ਰਾਤ ਚੱਲਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਗਾੜੇ ਰੰਗ ਦਾ ਨਮਕੀਨ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਵਿਚ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਜਾਂ 5 ਭਾਗ ਦੇ ਬਰਾਬਰ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਲਹੂ ਦੇ ਭਾਗਾਂ ਬਾਰੇ ਤੁਸੀਂ ਕੀ ਜਾਣਦੇ ਹੋ ? (What do you know about the composition of Blood ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਲਹੂ ਵਿਚ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ
- ਪਲਾਜ਼ਮਾ (Plasma),
- ਲਾਲ ਲਹੂ ਕਣ (Red Corpuscles),
- ਚਿੱਟੇ ਲਹੂ | ਕਣ (White Corpuscles),
- ਪਲੇਟਲੇਟਸ (Platelets) ।
ਪਲਾਜ਼ਮਾ ਪੀਲੇ ਰੰਗ ਦਾ ਨਮਕੀਨ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਵਿਚ ਲਾਲ ਅਤੇ ਚਿੱਟੇ ਲਹੂ ਕਣ ਤੈਰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਲਾਲ ਲਹੂ ਕਣ ਗੋਲ ਅਤੇ ਦੋਨੋਂ ਪਾਸੇ ਚਿੰਬੜੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਉਮਰ 15 ਦਿਨ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਚਿੱਟੇ ਲਹੂ ਕਣ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੀ ਰੋਗਾਂ ਦੇ ਹਮਲਿਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਰੰਗਹੀਨ ਅਤੇ ਬੇਡੌਲ ਆਕਾਰ ਕਣਾਂ ਦੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਪਲੇਟਲੇਟਸ ਦਾ ਆਕਾਰ \(\frac{1}{2}\) ਜਾਂ \(\frac{1}{3}\) ਨੂੰ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਲਹੂ ਨੂੰ ਵਗਣ ਤੋਂ ਰੋਕਦੇ ਹਨ ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਹੂ ਦਾ ਦਬਾਅ ਕੀ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ? (What is Blood Pressure ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਸ਼ਿਰਾਵਾਂ, ਧਮਨੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਰੱਤ ਵਾਲਾਂ ਦੀ ਮਦਦ ਨਾਲ ਖੂਨ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਭਿੰਨ-ਭਿੰਨ ਅੰਗਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਦੌਰਾ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਸ਼ਿਰਾਵਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਸ਼ੁੱਧ ਅਤੇ ਧਮਨੀਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਅਧ ਲਹੂ ਕਣ ਚੱਕਰ ਲਗਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਸ ਦੌਰੇ ਵਿਚ ਖੂਨ ਨਾਲੀਆਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਕੰਧਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਟਕਰਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ, ਜਿਸ ਨਾਲ ਦਬਾਅ ਵਧਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਦਬਾਅ ਘੱਟ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਤਾਂ ਲਹੁ ਅੱਗੇ ਵਧਦਾ ਹੈ । ਖੂਨ ਦੀ ਇਸ ਵਧਣ ਅਤੇ ਘੱਟ ਹੋਣ ਦੀ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਨੂੰ ਲਹੂ ਦਾ ਦਬਾਅ (Blood Pressure) ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਸ ਦਬਾਅ ਨੂੰ ਮਾਪਨ ਲਈ ਸਫੀਰਾਨੋ ਮੈਨੋਮੀਟਰ (sphygne manometer) ਯੰਤਰ ਦੀ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਕੀਤੀ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 5.
ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਕੰਮ ਦੱਸੋ । (Describe the functions of Muscles.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਨਾਲ ਜੁੜੀਆਂ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦੇ ਮੁੱਖ ਕੰਮ ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਹਨ
- ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਰੂਪ ਪ੍ਰਦਾਨ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਗਤੀ ਵਿਚ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਪ੍ਰਦਾਨ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਮਦਦ ਨਾਲ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਤੁਰਦਾ-ਫਿਰਦਾ, ਟੱਪਦਾ ਅਤੇ ਸਾਹ ਆਦਿ ਲੈਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਛਾਤੀ ਦੇ ਪੱਠਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਫੈਲਣ ਵਿਚ ਮਦਦ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹਨਾਂ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਸਰੀਰ ਸਮੁੱਚਾ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਰੱਖਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਜੋੜਾਂ ਦਾ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਕਰਨ ਵਿਚ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 6.
ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਕਿੰਨੀ ਕਿਸਮ ਦੀਆਂ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ? (Mention the types of Muscles.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਤਿੰਨ ਕਿਸਮ ਦੀਆਂ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ (There are three types of the muscles )
1. ਸਵੈ-ਇੱਛਤ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ (Voluntary Muscles)-ਸਵੈ-ਇੱਛਤ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਉਹ ਹਨ ਜੋ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦੀ ਇੱਛਾ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਚੱਲਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਉਹਨਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਜਿਵੇਂ ਸੂਚਨਾ ਮਿਲਦੀ ਹੈ ਉਸੇ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਹੀ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਗਤੀ ਪ੍ਰਦਾਨ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਸੰਭਾਲ ਕੇ ਰੱਖਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ਅਤੇ ਇਸ ਵਿਚ ਗਰਮੀ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਲੱਤਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਬਾਹਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਪਾਈਆਂ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
2. ਅਣ-ਇੱਛਤ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ (Involuntary Muscles)-ਇਹ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦੇ ਵਸ ਵਿਚ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ । ਇਹ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦੀ ਇੱਛਾ ਦੇ ਬਿਨਾਂ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਰਹਿੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦੇ ਸੁੱਤਿਆਂ ਵੀ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਰਹਿੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਦਿਲ, ਜਿਗਰ ਅਤੇ ਅੰਤੜੀਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਪਾਈਆਂ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
3. ਦਿਲ ਦੀਆਂ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ (Cardiac Musclesਇਹ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਅਣ-ਇੱਛਤ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਵਰਗੀਆਂ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ, ਪਰ ਇਹ ਲਗਾਤਾਰ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਨ ਨਾਲ ਵੀ ਥੱਕਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 7.
ਚਮੜੀ ਦੇ ਬਾਰੇ ਵਿਚ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਜਾਣਕਾਰੀ ਦਿਓ । (Describe briefly about Skin.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਚਮੜੀ ਇਕ ਕਿਸਮ ਦਾ ਪਰਦਾ ਹੈ ਜੋ ਅੰਦਰੂਨੀ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਅੰਗਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਢੱਕ ਕੇ ਰੱਖਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਦੋ ਕਿਸਮ ਦੀ ਹੈ-ਬਾਹਰੀ ਜਾਂ ਉੱਪਰਲੀ(Epidermis) ਅਤੇ ਹੇਠਲੀ ਜਾਂ ਅੰਦਰੂਨੀ (Endodermis) । ਉੱਪਰਲੀ ਚਮੜੀ ਵਿਚ ਛੋਟੇ-ਛੋਟੇ ਮੁਸਾਮ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਪਸੀਨਾ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਬਾਹਰ ਨਿਕਲਦਾ ਹੈ । ਅੰਦਰੂਨੀ ਜਾਂ ਹੇਠਲੀ ਚਮੜੀ ਵਿਚ ਚਰਬੀ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ਜੋ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਗਰਮੀ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਨ ਵਿਚ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਪ੍ਰਦਾਨ ਕਰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 8.
ਗੁਰਦਿਆਂ ਦੇ ਕੰਮ ਦੱਸੋ । (Describe the functions of the Kidneys.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਗੁਰਦੇ ਢਿੱਡ ਦੇ ਪਿੱਛੇ ਵਲ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਸੰਖਿਆ ਵਿਚ ਦੋ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦਾ ਆਕਾਰ ਸੇਮ ਦੇ ਬੀਜ ਵਰਗਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਕੰਮ-
- ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪੇਸ਼ਾਬ ਵਿਚ ਯੂਰੀਆ, ਯੂਰਿਕ ਐਸਿਡ, ਖਣਿਜ ਲੂਣ, ਪੇਸ਼ਾਬ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿਚ ਸਰੀਰ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਹਰ ਆਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹ ਖੂਨ ਵਿਚ ਪਾਣੀ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਨੂੰ ਸਮਾਨ ਰੱਖਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਸ ਦੇ ਫਲਸਰੂਪ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਐਸਿਡ ਅਤੇ ਖਾਰ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਵਿਚ ਸਮਾਨਤਾ ਰਹਿੰਦੀ ਹੈ |
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 9.
ਫੇਫੜਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਕੀ ਹੈ ? ਇਸ ਬਾਰੇ ਲਿਖੋ । [ਅਭਿਆਸ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ-2] (What is Vital Capacity ? Write briefly.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਫੇਫੜਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ (Capacity of Lungs or Vital Capacity)-ਉਹ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਜਿਸ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਡੂੰਘੇ ਸਾਹ ਲੈਣ ਨਾਲ ਹਵਾ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਅੰਦਰ ਲਿਜਾਈ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਫੇਰ ਜ਼ੋਰ ਨਾਲ ਬਾਹਰ ਕੱਢੀ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ, ਉਸ ਨੂੰ ਫੇਫੜਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ (Vital Capacity) ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਸਾਧਾਰਨ ਤੌਰ ‘ਤੇ ਅਸੀਂ ਲਗਪਗ 500 ਸੀ.ਸੀ. ਹਵਾ ਲੈ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਲਗਪਗ 1500 ਸੀ. ਸੀ. ਹੋਰ ਹਵਾ ਕੱਢ ਸਕਦੇ ਹਾਂ । ਇੰਨਾ ਕਰਨ ਤੇ ਵੀ ਸਾਡੇ ਫੇਫੜੇ ਹਵਾ ਤੋਂ ਰਹਿਤ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੇ । ਤਦ ਵੀ ਲਗਪਗ 500 ਸੀ. ਸੀ. ਹਵਾ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਰਹਿ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ । ਫੇਫੜਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਇਸ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਜਾਂ ਸਮਰੱਥਾ ਨੂੰ ਮਾਪਣ ਲਈ ਸਪਾਇਰੋ ਮੀਟਰ ਯੰਤਰ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਯੋਗ ਕੀਤਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 10.
ਥਕਾਵਟ ਕੀ ਹੈ ? (What is Fatigue ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਥਕਾਵਟ (Fatigue)-ਮਾਸਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਨ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਥਕਾਵਟ ਅਖਵਾਉਂਦੀ ਹੈ ਜਦੋਂ ਸਾਡੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੀਆਂ ਮਾਸਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਲਗਾਤਾਰ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ਤਾਂ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਲੈਕਟਿਨ ਐਸਿਡ ਇਕੱਠਾ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਥੱਕ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਥਕਾਵਟ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾ ਦੇਰ ਖੇਡਣ, ਤੁਰਨ ਜਾਂ ਜ਼ੋਰ ਵਾਲੇ ਕੰਮ ਕਾਰਨ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਨੀਂਦ, ਆਰਾਮ, ਮਾਲਸ਼ ਤੇ ਮਨੋਰੰਜਨ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਨਾਲ ਦੂਰ ਕੀਤੀ ਜਾ ਸਕਦੀ ਹੈ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 11.
ਥਕਾਵਟ ਕਿੰਨੇ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਦੀ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ? (What are the kinds of Fatigue ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਥਕਾਵਟ ਦੋ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ –
- ਸਰੀਰਕੇ
- ਮਾਨਸਿਕ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 12.
ਲਹੂ ਗੇੜ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਦੇ ਅੰਗਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਂ ਲਿਖੋ । (Name the organs of blood circulation.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
- ਦਿਲ
- ਆਰਟਰੀਮ ਸ਼ਿਰਾਵਾਂ
- ਧਮਨੀਆਂ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 13.
ਨਬਜ਼ ਕੀ ਹੈ ? (What is pulse ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
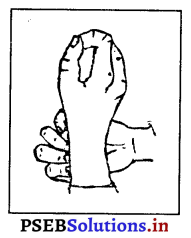
ਲਹੂ ਦੀ ਤੇਜ਼ ਗਤੀ ਕਾਰਨ ਲਹੂ ਦੀਆਂ ਧਮਨੀਆਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਦੀਵਾਰਾਂ ਵੱਧਦੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਘੱਟਦੀਆਂ ਰਹਿੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਇਸ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਨੂੰ ਨਬਜ਼ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਜੋ ਆਮ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਵਿਚ 76 ਤੋਂ 80 ਵਾਰੀ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਮਿੰਟ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਨਬਜ਼ ਨੂੰ ਇਕ ਹੱਥ ਨਾਲ ਦੂਸਰੀ ਬਾਜੂ ਤੋਂ ਉਂਗਲਾਂ ਦਾ ਦਬਾਅ ਪਾ ਕੇ ਦੇਖਿਆ ਜਾ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਖਿਡਾਰੀਆਂ ਦੀ ਨਬਜ਼ ਇਕ ਮਿੰਟ ਵਿਚ 60 ਤੋਂ ਘੱਟ ਵੀ ਹੋ ਸਕਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਵੱਡੇ ਉੱਤਰਾਂ ਵਾਲੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ (Long Answer Type Questions)
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
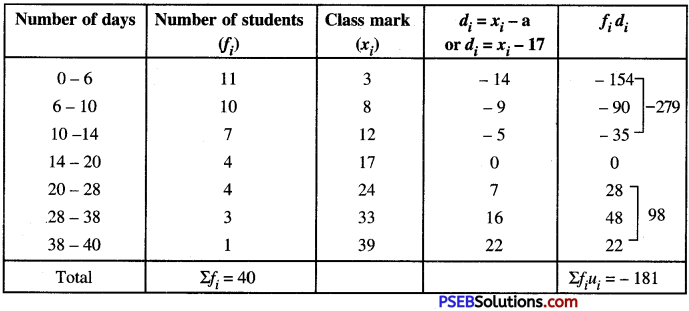
ਲਹੂ ਦੇ ਵੱਖ-ਵੱਖ ਅੰਸ਼ਾਂ ਦਾ ਵਰਣਨ ਕਰੋ । ਲਹੂ ਦੇ ਮੁੱਖ ਕੰਮ ਕੀ ਹਨ ? (What is composition of Blood ? Discuss its functions.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਲਹੂ ਅਤੇ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਅੰਸ਼ (Blood and its Parts)-ਰਕਤ ਜਾਂ ਲਹੂ ਇਕ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਦਾ ਤਰਲ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਦਾ ਨਿਰਮਾਣ ਖਾਣ ਅਤੇ ਪੀਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਪਦਾਰਥਾਂ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਲਹੂ ਸਾਡੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਇਕ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਨ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਆਦਮੀ ਦੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਭਾਰ ਦਾ ਬਾਵਾਂ \(\left(\frac{1}{12}\right)\) ਨੇ ਹਿੱਸਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਆਮ ਤੌਰ ‘ਤੇ ਇਕ ਨੌਜਵਾਨ ਦੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਖੂਨ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ 12-13 ਪਿੰਟ (Pint) ਤਕ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਕਈ | ਹਾਲਤਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਇਹ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਘੱਟ ਜਾਂ ਵੱਧ ਵੀ ਹੋ ਸਕਦੀ ਹੈ । ਤਰਲ (liquid) ਪਦਾਰਥ ਨਿਕਲਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਤਰਲ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਦਾ ਨਾਂ ਹੀ ‘ਲਹੁ’ ਹੈ । ਦੇਖਣ ਨੂੰ ਤਾਂ ਇਹ ਲਾਲ ਰੰਗ ਦਾ ਮਾਲੂਮ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ, ਪਰ ਅਸਲ ਵਿਚ ਅਜਿਹਾ ਨਹੀਂ । ਜੇ ਅਸੀਂ ਇਸ ਤਰਲ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਅਰਥਾਤ ਲਹੂ ਨੂੰ ਖੁਰਦਬੀਨ (Microscope) ਵਿਚ ਦੇਖੀਏ ਤਾਂ ਸਾਨੂੰ ਪਤਾ ਲੱਗੇਗਾ ਕਿ ਲਹੂ ਵਿਚ ਬਹੁਤ ਛੋਟੇ-ਛੋਟੇ ਕਣ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਕਣਾਂ ਦਾ ਰੰਗ ਚਿੱਟਾ ਤੇ ਲਾਲ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਇਹਨਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਲਾਲ ਲਹੂ ਕਣ (Red Corpuscles) ਅਤੇ ਚਿੱਟੇ ਲਹੂ ਕਣ (White Corpuscles) ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਇਕ ਕਿਸਮ ਦੇ ਹਲਕੇ ਪੀਲੇ ਤਰਲ (Yellow Liquid) ਵਿਚ ਤੈਰਦੇ ਹਨ, ਜਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਪਲਾਜ਼ਮਾ (Plasma) ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਲਹੂ ਵਿਚ ਮੁੱਖ ਤੌਰ ‘ਤੇ ਜੋ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਹਨ ਉਹਨਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਹੇਠ ਦਿੱਤੇ ਗਏ ਚਾਰਟ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਪ੍ਰਗਟ ਕੀਤਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ-
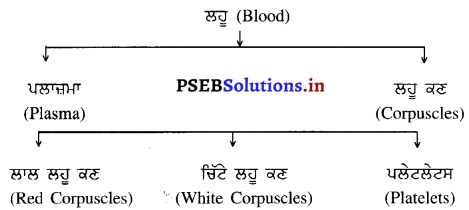
(i) ਪਲਾਜ਼ਮਾ (Plasma) – ਇਹ ਲਹੂ ਦੇ ਹਲਕੇ ਪੀਲੇ ਰੰਗ ਦਾ ਪਾਰਦਰਸ਼ਕ (Transparent) ਪਦਾਰਥ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਵਿਚ ਲਾਲ ਅਤੇ ਚਿੱਟੇ ਲਹੂ ਦੇ ਕਣ ਤੈਰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਸ ਵਿਚ 90% ਪਾਣੀ ਤੇ 10% ਠੋਸ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਘੁਲੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਠੋਸ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ, ਖਣਿਜ ਲੂਣ ਤੇ ਚਰਬੀ (Fat) ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ | ਪਲਾਜ਼ਮਾ
(Plasma) ਲਹੂ ਦੇ ਦਬਾਅ (Pressure) ਨੂੰ ਠੀਕ ਰੱਖਦਾ ਹੈ ਤੇ ਲਾਲ ਅਤੇ ਚਿੱਟੇ ਲਹੂ ਕਣਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਲਿਜਾਣ ਵਿਚ ਮਦਦ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਦੀ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਲਹੁ ਨੂੰ ਵਹਿਣ ਤੋਂ ਰੋਕਣ ਵਿਚ ਮਦਦ ਦਿੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
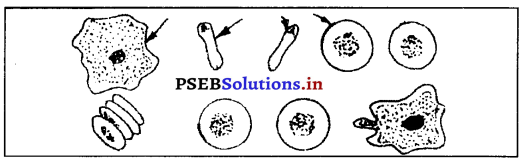
(ii) ਲਾਲ ਲਹੂ ਕਣ (Red Corpuscles) – ਆਦਮੀ ਦੇ ਲਾਲ ਲਹੂ ਕਣ ਗੋਲ ਤੇ ਦੋਹਾਂ ਪਾਸਿਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਚਿਪਕੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਆਦਮੀ ਦੇ ਇਕ ਘਣ ਮਿਲੀ ਮੀਟਰ ਲਹੂ ਵਿਚ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਲਗਪਗ 50,00,000 ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਇੰਨੇ ਛੋਟੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ਕਿ ਜੇਕਰ ਕੰਢੇ ਨਾਲ ਮਿਲਾ ਕੇ ਰੱਖੇ ਜਾਣ ਤਾਂ 2.5 ਵਰਗ ਸੈਂਟੀਮੀਟਰ ਥਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਲਗਪਗ 1 ਕਰੋੜ ਆ ਜਾਣਗੇ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਬਾਹਰਲੀ ਪਰਤ ਇਕ ਲਚਕੀਲੇ ਠੋਸ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿਚ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਦੇ ਅੰਦਰ ਪੀਲੇ ਰੰਗ ਦਾ ਲੋਹੇ ਦਾ ਇਕ ਰੰਗ (Pigment) ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਹਿਮੋਗਲੋਬਿਨ (Haemoglobin). ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ਜੋ ਕਿ ਲੋਹੇ ਅਤੇ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਵਸਤਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਮਿਲ ਕੇ ਬਣਦਾ ਹੈ । ਹਿਮੋਗਲੋਬਿਨ ਆਕਸੀਜਨ ਨੂੰ ਚੂਸ ਲੈਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਕਾਰਨ ਇਸ ਦਾ ਰੰਗ ਚਮਕਦਾਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਆਕਸੀ-ਹਿਮੋਗਲੋਬਿਨ (Oxy Haemoglobin) ਵਿਚ ਬਦਲ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਖੂਨ ਫੇਫੜਿਆਂ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਆਕਸੀਜਨ ਚੂਸ ਕੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਹਰ ਹਿੱਸੇ ਤਕ ਪਹੁੰਚਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਲੜਕੀਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਲਾਲ ਲਹੂ ਕਣ ਲੜਕਿਆਂ ਨਾਲੋਂ ਘੱਟ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾ ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਤੇ ਉਚਾਈ (Heights) ਉੱਤੇ ਲਾਲ ਕਣਾਂ ਦੀ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਵੱਧ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ।
![]()
(iii) ਚਿੱਟੇ ਲਹੂ ਕਣ (White Corpuscles) – ਸਰੀਰ ਦੀ ਤੁਲਨਾ ਇਕ ਰਾਜ ਨਾਲ ਕੀਤੀ ਜਾ ਸਕਦੀ ਹੈ । ਜਿਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਰਾਜ ਦੀ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਲਈ ਫ਼ੌਜ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਬੰਧ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ, ਉਸੇ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਸਰੀਰ ਰੂਪੀ ਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਲਈ ਲਹੂ ਕਣ ਰੂਪੀ ਫ਼ੌਜ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਬੰਧ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਚਿੱਟੇ ਲਹੂ ਕਣਾਂ ਦੀ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਲਾਲ ਲਹੂ ਕਣਾਂ ਨਾਲੋਂ ਘੱਟ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ | ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਲਗਪਗ 600 ਲਾਲ ਲਹੂ ਕਣਾਂ ਮਗਰੋਂ ਕੇਵਲ ਇਕ ਚਿੱਟਾ ਲਹੂ ਕਣ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਕ ਘਣ ਕਿਲੋ ਲਹੂ ਵਿਚ ਚਿੱਟੇ ਲਹੂ ਕਣਾਂ ਦੀ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਲਗਪਗ 8000 ਤੋਂ 10000 ਦੇ ਲਗਪਗ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਰੰਗਹੀਣ ਤੇ ਬੇਡੌਲ (irregular) ਆਕਾਰ ਦੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਮਦਦ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਰੋਗਾਂ ਦਾ ਟਾਕਰਾ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦਾ ਕੰਮ ਰੋਗਾਂ ਦੇ ਜੀਵਾਣੂਆਂ (germs) ਨੂੰ ਘੇਰ ਕੇ ਉਹਨਾਂ ਦਾ ਖ਼ਾਤਮਾ ਕਰਨਾ ਹੈ | ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਸੱਟ ਆਦਿ ਲੱਗਣ ਕਾਰਨ ਇਹੀ ਜ਼ਖ਼ਮਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਭਰਨ ਵਿਚ ਸਹਾਇਕ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
(iv) ਪਲੇਟਲੇਟਸ (Platelets) -ਆਦਮੀ ਦੇ ਹੁ ਵਿਚ ਲਾਲ ਤੇ ਚਿੱਟੇ ਕਣਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਬਿਨਾਂ ਇਕ ਤੀਜੀ ਕਿਸਮ ਦੇ ਲਹੂ ਕਣ ਵੀ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪਲੇਟਲੇਟਸ (Platelets) ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਲਾਲ ਅਤੇ ਚਿੱਟੇ ਲਹੂ ਕਣਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਬਿਲਕੁਲ ਵੱਖਰੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਲਾਲ ਲਹੂ ਕਣਾਂ \(\frac{1}{2}\) ਜਾਂ \(\frac{1}{3}\) ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਲਹੂ ਦੇ ਇਕ ਘਣ ਮਿਲੀਮੀਟਰ ਵਿਚ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਸੰਖਿਆ ਲਗਪਗ 3 ਲੱਖ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਚਿੱਟੇ ਤੇ ਬੇਡੌਲ (irregular) ਆਕਾਰ ਦੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦਾ ਮੁੱਖ ਕੰਮ ਲਹੂ ਨੂੰ ਵਹਿਣ ਤੋਂ ਰੋਕਣਾ ਹੈ ।
ਲਹੂ ਦੇ ਕੰਮ (Functions of Blood)-ਖੂਨ ਦੇ ਕੰਮ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ –
- ਲਹੂ ਸਾਡੇ ਭੋਜਨ ਦੇ ਪਚੇ ਹੋਏ ਹਿੱਸੇ ਨੂੰ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਭਿੰਨ-ਭਿੰਨ ਅੰਗਾਂ ਤਕ ਪਹੁੰਚਾਉਣ ਦਾ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਹੁ ਹੀ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਜ਼ਹਿਰੀਲੇ ਤੇ ਵਿਅਰਥ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਨੂੰ ਬਾਹਰ ਕੱਢਣ ਵਿਚ ਮਦਦ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਪਦਾਰਥਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਆਪਣੇ ਅੰਦਰ ਘੋਲ ਕੇ ਗੁਰਦੇ ਵਿਚ ਲੈ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ, ਜਿੱਥੇ ਉਹ ਪੇਸ਼ਾਬ (Urine) ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿਚ ਬਾਹਰ ਨਿਕਲਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਲਹੂ ਵਿਚ ਮੌਜੂਦ ਲਾਲ ਲਹੂ ਕਣ (Red Corpuscles) ਫੇਫੜਿਆਂ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਆਕਸੀਜਨ ਚੂਸ ਕੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਭਿੰਨ-ਭਿੰਨ ਭਾਗਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਲਿਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਲਾਲ ਲਹੂ ਕਣ ਹੀ ਆਕਸੀਜਨ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਤੋਂ ਮਗਰੋਂ ਬਣੀ ਕਾਰਬਨ-ਡਾਈਆਕਸਾਈਡ (Carbon Dioxide) ਨੂੰ ਫੇਫੜਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਲਿਆ ਕੇ ਬਾਹਰ ਕੱਢਣ ਦਾ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਲਹੂ ਦੇ ਚਿੱਟੇ ਲਹੂ ਕਣ (White Corpuscles) ਸਰੀਰ ਦੀ ਜਰਮਾਂ ਜਾਂ ਕੀਟਾਣੂਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਲਹੂ ਪਲੇਟਲੇਟਸ ਸੱਟ ਲੱਗਣ ਵੇਲੇ ਲਹੁ ਨੂੰ ਸਰੀਰ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਹਰ ਵਹਿ ਜਾਣ ਤੋਂ ਰੋਕਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਲਹੁ ਹਾਰਮੋਨਜ਼ (Hormones) ਨੂੰ ਇਕ ਥਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਦੂਜੀ ਥਾਂ ਲਿਜਾਣ ਦਾ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਲਹੁ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਭਿੰਨ-ਭਿੰਨ ਅੰਗ ਆਪਸ ਵਿਚ ਮਿਲੇ ਰਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ਅਤੇ ਸੁੱਕ ਕੇ ਨਸ਼ਟ ਹੋਣ ਤੋਂ ਬਚੇ ਰਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਹੂ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਹੀ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਭਿੰਨ-ਭਿੰਨ ਅੰਗਾਂ ਦਾ ਤਾਪਮਾਨ ਇੱਕੋ ਜਿਹਾ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਸੰਖੇਪ ਵਿਚ ਅਸੀਂ ਇਹ ਆਖਾਂਗੇ ਕਿ ਖ਼ੂਨ ਜੀਵਨ ਪ੍ਰਦਾਨ ਕਰਨ ਵਾਲਾ ਹੈ । ਜੇਕਰ ਕਿਸੇ ਅੰਗ ਵਿਚ ਖੂਨ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਵਾਹ ਨਾ ਹੋਵੇ ਤਾਂ ਉਹ ਅੰਗ ਪੀਲਾ ਪੈ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਕਮਜ਼ੋਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਵਧੇਰੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਤਕ ਇਸ ਕੂਮ ਦੇ ਬੰਦ ਰਹਿਣ ਨਾਲ ਉਹ ਅੰਗ ਮਰ ਵੀ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਸਾਹ-ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਦੇ ਅੰਗਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਂ ਲਿਖੋ । ਸਾਹ-ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਉੱਤੇ ਕਸਰਤਾਂ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ ਲਿਖੋ । (Mention the main organs of Respiration. Discuss the effects of Exercises on Respiratory System.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਸਾਹ ਲੈਣ ਅਤੇ ਛੱਡਣ ਦੀ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਨੂੰ ਸਾਹ-ਕਿਰਿਆ (Respiration) ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਸ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਮਨੁੱਖ ਹਵਾ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਆਕਸੀਜਨ ਫੇਫੜਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਲੈ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਹਵਾ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਪੈਦਾ ਹੋਈ ਕਾਰਬਨ-ਡਾਈਆਕਸਾਈਡ ਬਾਹਰ ਕੱਢ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਸਾਹ-ਕਿਰਿਆ ਵਿਚ ਕਈ ਅੰਗ ਜਿਵੇਂ ਨੱਕ, ਸਾਹ ਨਲੀ ਅਤੇ ਫੇਫੜੇ ਆਦਿ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਸਾਹ-ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਦੇ ਭਿੰਨ-ਭਿੰਨ ਅੰਗ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਹਨ
- ਨੱਕ (Nose)
- ਗਨਿਕਾ ਜਾਂ ਸੰਘ (Pharynx)
- ਸੁਰ-ਯੰਤਰ ਜਾਂ ਕੰਠ (Larynx)
- ਸੁਆਸ ਨਲੀ ਜਾਂ ਟੱਟੂਆ (Wind-Pipe or Trachea)
- ਸੁਆਸ ਨਲੀਆਂ (Bronchial Tubes).
- ਫੇਫੜੇ (Lungs) ।
1. ਨੱਕ (Nose-ਇਸ ਦੀ ਥਾਂ ਦੋਨਾਂ ਅੱਖਾਂ ਦੇ ਵਿਚਕਾਰ ਹੈ | ਸਾਹ ਲੈਣ ਦੀ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਨੱਕ ਤੋਂ ਆਰੰਭ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਨੱਕ ਵਿਚ ਦੋ ਛੇਕ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਨਾਸਾਂ (Nostrils) ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ | ਨਾਸਾਂ ਦੇ ਅੰਦਰਲੇ ਹਿੱਸੇ ਵਿਚ ਛੋਟੇ-ਛੋਟੇ ਵਾਲ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਹਵਾ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ੁੱਧ ਕਰਕੇ ਅੰਦਰ ਜਾਣ ਦਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਦੀਵਾਰ ਇਕ ਝਿੱਲੀ ਦੀ ਬਣੀ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਨਾਲ ਖ਼ਾਸ ਵ ਬਣਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਤ੍ਰ ਹਵਾ ਦੇ ਕੀਟਾਣੂਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਨਸ਼ਟ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਹਵਾ ਨੂੰ ਠੰਢਾ ਰੱਖਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਦੇ ਪਿਛਲੇ ਹਿੱਸੇ ਵਿਚ ਸੁੰਘਣ ਦੀਆਂ ਗਿਆਨ-ਇੰਦਰੀਆਂ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਹਿੱਸਾ ਦੋ ਛੇਕਾਂ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਕੰਨ ਵਿਚ ਖੁੱਲ੍ਹਦਾ ਹੈ । ਨਾਸਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਲੱਗੇ ਹੋਏ ਵਾਲਾਂ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਜਦੋਂ ਹਵਾ ਨਿਕਲਦੀ ਹੈ, ਉਸ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਠੋਸ ਕਣ ਉੱਥੇ ਹੀ ਰਹਿ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ । ਦੂਸਰੇ ਨੱਕ ਦੀ ਖਿੱਲੀ ਦੇ ਸੰਪਰਕ ਵਿਚ ਆ ਕੇ ਹਵਾ ਗਰਮ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਨਾਲ ਫੇਫੜਿਆਂ ਆਦਿ ਵਿਚ ਠੰਢ ਲੱਗਣ ਦਾ ਡਰ ਨਹੀਂ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ । ਇਸ ਦੇ ਉਲਟ ਮੂੰਹ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਸਾਹ ਲੈਣ ਨਾਲ ਨਾ ਤਾਂ ਹਵਾ ਛਣ ਕੇ ਹੀ ਅੰਦਰ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ਤੇ ਨਾ ਹੀ ਗਰਮ ਹੋ ਕੇ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਇਹ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਸਾਹ ਨੱਕ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਲਿਆ ਜਾਵੇ, ਮੂੰਹ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਨਹੀਂ ।
2. ਸ਼ਨਿਕਾ (Pharynx) ਜਾਂ ਸੰਘ-ਇਹ ਅੰਗ (Organ) ਗਲੇ ਦੀਆਂ ਗਿਲਟੀਆਂ (Tonsils) ਦੇ ਪਿੱਛੇ ਸਥਿਤ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਦਾ ਆਕਾਰ ਕੀਪ (Funnel) ਵਰਗਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਛੋਟੀਆਂ-ਛੋਟੀਆਂ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਨਾਲ ਮਿਲ ਕੇ ਬਣੀ ਹੋਈ ਇਕ ਲੱਛੇਦਾਰ ਨਲੀ ਹੈ ਜੋ ਨੱਕ ਦੇ ਉੱਪਰਲੇ ਹਿੱਸੇ ਤੋਂ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਹੋ ਕੇ ਜੀਭ ਦੀ ਜੜ੍ਹ ਤਕ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਕੰਠ-ਸੰਘ ਜਾਂ ਨਿਕਾ ਉਹ ਸਥਾਨ ਹੈ ਜਿੱਥੇ ਹਵਾ ਅਤੇ ਭੋਜਨ ਦੀਆਂ ਨਾਲੀਆਂ ਮਿਲਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਭੋਜਨ ਦੀ ਨਾਲੀ ਹਵਾ ਦੀ ਨਾਲੀ ਤੋਂ ਪਿੱਛੋਂ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਹਵਾ ਦੀ ਨਾਲੀ ਤੇ ਇਕ ਢੱਕਣ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਕੰਠ ਵਿਧਾਨ (Epiglottis) ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਢੱਕਣ ਭੋਜਨ ਨੂੰ ਨਿਕਲਦੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਹਵਾ ਨਾਲੀ ਨੂੰ ਬੰਦ ਕਰ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ, ਜਿਸ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਇਹ ਭੋਜਨ ਨੂੰ ਹਵਾ ਨਾਲੀ ਵਿਚ ਜਾਣ ਤੋਂ ਰੋਕਦਾ ਹੈ ।
3. ਸੁਰ-ਯੰਤਰ ਜਾਂ ਕੰਠ (Larynx)-ਇਹ ਹਵਾ ਨਲੀ ਦਾ ਉੱਪਰਲਾ ਮੋਟਾ ਅਤੇ ਚੌੜਾ ਬਕਸੇ ਜਿਹਾ ਹਿੱਸਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸੇ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਆਵਾਜ਼ ਪੈਦਾ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਇਸ ਨੂੰ ਸੁਰ ਵਾਲਾ ਡੱਬਾ (Sound Box) ਵੀ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇੱਥੋਂ ਹੋ ਕੇ ਹਵਾ ਸਾਹ-ਨਲੀ ਜਾਂ ਟੱਟੂਆ (Trachea) ਵਿਚ ਪਹੁੰਚਦੀ ਹੈ । ਸੁਰ-ਯੰਤਰ ਦੇ ਮੂੰਹ ‘ਤੇ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ (Cartilages) ਦਾ ਇਕ ਢੱਕਣ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ, ਜਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਉਪ-ਜੀਵ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਢੱਕਣ ਅਕਸਰ ਸਿੱਧਾ ਖੜਾ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਤਾਂ ਜੋ ਹਵਾ ਆਸਾਨੀ ਨਾਲ ਦਾਖ਼ਲ ਹੋ ਸਕੇ |
4. ਸੁਆਸ ਨਲੀ ਜਾਂ ਟੱਟੂਆ (Wind-Pipe or Trachea)-ਸੁਆਸ ਨਲੀ 4″ ਲੰਬੀ ਅਤੇ \(\frac{3 “}{4}\) ਵਿਆਸ ਦੀ ਇਕ ਨਾਲੀ ਹੈ ।
ਇਹ ਸ਼ਰ-ਯੰਤਰ ਦੇ ਥੱਲੇ ਤੋਂ ਆਰੰਭ ਹੋ ਕੇ ਛਾਤੀ ਦੇ ਅੰਦਰ ਹੇਠਾਂ ਵੱਲ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਉਪ-ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਅਧੂਰੇ ਛੱਲਿਆਂ ਨਾਲ ਮਿਲ ਕੇ ਬਣਦੀ ਹੈ, ਜੋ ਪਿੱਛੇ ਵੱਲੋਂ ਜੁੜੇ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦੇ, ਕਿਉਂਕਿ ਟੱਟੂਏ ਦੇ ਪਿੱਛੇ ਦਾ ਹਿੱਸਾ ਚਪਟਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਛੱਲਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਗਿਣਤੀ 16 ਤੋਂ 20 ਤਕ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਦੀ ਅੰਦਰਲੀ ਤਹਿ ਤੱਕ ਦੀ ਤਿੱਲੀ ਦੇ ਵਾਂਗ ਹੀ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਵਿਚ ਵੀ ਹਵਾ ਛਾਨਣ ਲਈ ਛੋਟੇ-ਛੋਟੇ ਵਾਲ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਹੇਠਲੇ ਸਿਰੇ ਤੇ ਇਹ ਨਲੀ ਦੋ ਹਿੱਸਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਵੰਡੀ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਜਿਸ ਦਾ ਇਕ ਹਿੱਸਾ ਸੱਜੇ ਪਾਸੇ ਦੇ ਫੇਫੜੇ ਵਿਚ ਚਲਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਦੂਸਰਾ ਖੱਬੇ ਪਾਸੇ ਦੇ ਫੇਫੜੇ ਵਿਚ । ਇਸ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਹਰੇਕ ਹਿੱਸੇ ਨੂੰ ਹਵਾ ਦੀ ਨਾਲੀ (Bronchi) ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ | ਅੱਗੇ ਚੱਲ ਕੇ ਇਹ ਨਾਲੀ ਵਾਲ ਸੂਖ਼ਮ ਹਿੱਸਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਵੰਡੀ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ।
5. ਹਵਾ ਨਾਲੀਆਂ (Bronchial Tubes-ਹਰੇਕ ਹਵਾ ਨਾਲ ਫੇਫੜੇ ਵਿਚ ਦਾਖ਼ਲ ਹੋਣ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਦੋ ਨਾਲੀਆਂ ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਹਵਾ ਨਾਲੀਆਂ (Bronchial Tubes) ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ, ਵਿਚ ਵੰਡੀ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ । ਫਿਰ ਇਹ ਕਈ ਹਿੱਸਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਵੰਡੀ ਜਾ ਕੇ ਛੋਟੀਆਂ-ਛੋਟੀਆਂ ਸੂਖ਼ਮ ਨਾਲੀਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਵੰਡੀ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ਜੋ ਅੰਤ ਵਿਚ ਛੋਟੀਆਂ-ਛੋਟੀਆਂ ਹਵਾ ਗੁਥਲੀਆਂ (Air Sacs) ਵਿਚ ਖੁੱਲ੍ਹਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਗੈਸਾਂ ਦੀ ਅਦਲਾ-ਬਦਲੀ (Exchange of Gases) ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
6. ਫੇਫੜੇ (Lungs-ਫੇਫੜੇ ਸਾਹ ਦੀ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਦੇ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਨ ਅੰਗ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਸਪੰਜ ਵਾਂਗ ਲਚਕੀਲੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦਾ ਰੰਗ ਕੁੱਝ ਨੀਲਾਹਟ ਵਾਲਾ ਭੂਰਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਛਾਤੀ ਵਿਚ ਦਿਲ ਵੱਲ ਸਥਿਤ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਫੇਫੜੇ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਵਿਚ ਦੋ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ-ਸੱਜਾ ਫੇਫੜਾ ਅਤੇ ਖੱਬਾ ਫੇਫੜਾ । ਸੱਜਾ ਫੇਫੜਾ ਖੱਬੇ ਨਾਲੋਂ ਕੁੱਝ ਵੱਡਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਭਾਰਾ ਵੀ । ਇਹ ਚਾਰ ਹਿੱਸਿਆਂ (Lobes) ਵਿਚ ਵੰਡਿਆ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਖੱਬਾ ਫੇਫੜਾ ਸਿਰਫ਼ ਦੋ ਭਾਗਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਵੰਡਿਆ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਹਰੇਕ ਫੇਫੜਾ ਇਕ ਦੋਹਰੀ ਖੁੱਲੀ ਦੇ ਥੈਲੇ ਵਿਚ ਸੁਰੱਖਿਅਤ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਥੈਲੇ ਨੂੰ ਪਲਰਾ (Pleura) ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਵਿਚਕਾਰ ਇਕ ਤਰਲ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਜੋ ਫੇਫੜਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਸੱਟ, ਰਗੜ ਅਤੇ ਧੱਕੇ ਆਦਿ ਤੋਂ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
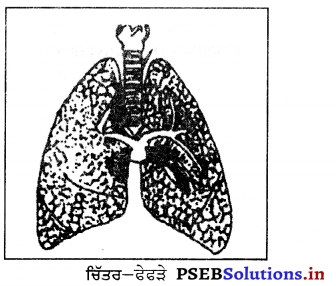
ਫੇਫੜਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਪਹੁੰਚ ਕੇ ਛੋਟੀਆਂ-ਛੋਟੀਆਂ ਰੱਤ ਰਵਾਲਾਂ ਅੰਤ ਵਿਚ ਫੁੱਲੇ ਹੋਏ ਹਵਾ ਦੇ ਥੈਲਿਆਂ ਦਾ ਰੂਪ ਧਾਰਨ ਕਰ ਲੈਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਥੈਲੇ ਫੇਫੜਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਅੰਗੂਰਾਂ ਦੇ ਗੁੱਛੇ ਵਾਂਗ ਦਿਖਾਈ ਦਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਹਵਾ ਦੇ ਥੈਲਿਆਂ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਫੇਫੜਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਬਣਤਰ ਸਪੰਜ ਜਿਹੀ ਹੋ ਗਈ ਹੈ । ਫੇਫੜਿਆਂ ਦੇ ਵਧਣ-ਫੁੱਲਣ ਲਈ ਸ਼ੁੱਧ ਖੂਨ ਦੀਆਂ ਅਨੇਕਾਂ ਨਾਲੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਨਾੜੀਆਂ ਆਦਿ ਵੀ ਫੇਫੜਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਫੈਲੀਆਂ ਹੋਈਆਂ ਹਨ । ਫੇਫੜੇ ਅਸ਼ੁੱਧ ਖੂਨ ਨੂੰ ਸਾਫ਼ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ | ਫੇਫੜਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਸਪੈਰੋਮੀਟਰ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਮਾਪੀ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ । ਫੇਫੜਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਸਮਰੱਥਾ, ਇਹਨਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਹਵਾ ਭਰਨ ਦੀ ਤਾਕਤ ਨੂੰ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਸਾਹ-ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਤੇ ਕਸਰਤ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ (Effect of Exercise on Respiration) –
ਕਸਰਤ ਸਾਹ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ‘ਤੇ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ ਪਾਉਂਦੀ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਦਾ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਵਰਣਨ ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਹੈ –
- ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਹਿਲ-ਜੁਲ ਪੈਦਾ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਨਾਲ ਜ਼ਹਿਰੀਲੇ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਪਸੀਨਾ, ਮਲ-ਤਿਆਗ ਅਤੇ ਪੇਸ਼ਾਬ ਦੇ ਰਸਤੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਬਾਹਰ ਨਿਕਲ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਸ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਰੋਗਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਮੁਕਤ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਨਾਲ ਫੇਫੜਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਹਵਾ ਭਰਨ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਵਿਚ ਵਾਧਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਦੇ ਫਲਸਰੂਪ ਫੇਫੜਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਲਚਕ ਆਉਂਦੀ ਅਤੇ ਇਹ ਕਈ ਰੋਗਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਬਚੇ ਰਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਖੂਨ ਵੱਧ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਵਿਚ ਸਾਫ਼ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਦੇ ਫਲਸਰੂਪ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਭਿੰਨ-ਭਿੰਨ ਸੈੱਲਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਸੁਆਸ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਖੂਨ ਵੱਧ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਵਿਚ ਪੁੱਜਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਫਜੂਲ ਪਦਾਰਥਾਂ ਦਾ ਨਿਕਾਸ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਨ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਵੱਧ ਪੈਦਾ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਸਭ ਸੈੱਲਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਵੱਧ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਵਿਚ ਆਕਸੀਜਨ ਮਿਲਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਦੇ ਫਲਸਰੂਪ ਸਰੀਰ ਤੰਦਰੁਸਤ ਅਤੇ ਸ਼ਕਤੀਸ਼ਾਲੀ ਬਣਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਸ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਜ਼ੋਰ ਦਾ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਨ ਨਾਲ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦੀ ਜੀਵਨ ਧਾਰਾ ਵਧ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਸ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਵੱਧ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਧ ਕੀਤਾ ਜਾ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਸ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਗੈਸਾਂ ਦੀ ਅਦਲਾ-ਬਦਲੀ ਤੇਜ਼ੀ ਨਾਲ ਤੇ ਠੀਕ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਸ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੀ ਮੁਕਾਬਲਾ ਕਰਨ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਵਧ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਨਾਲ ਕਾਰਬਨ-ਡਾਈਆਕਸਾਈਡ ਦੇ ਬਾਹਰ ਨਿਕਲਣ ਅਤੇ ਆਕਸੀਜਨ ਦੇ ਅੰਦਰ ਪ੍ਰਵੇਸ਼ ਕਰਨ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਵਿਚ ਵਾਧਾ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
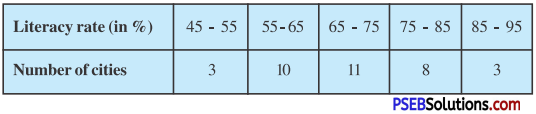
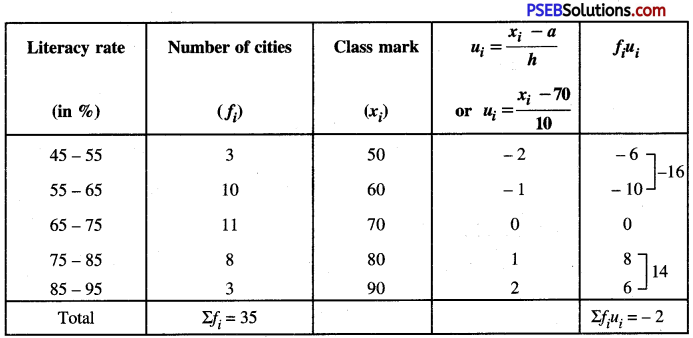
ਲਹੂ-ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਉੱਤੇ ਕਸਰਤ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ ਲਿਖੋ । [ਅਭਿਆਸ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ-3] (Write down the effects of exercises on Circulatory System.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਲਹੁ ਇਕ ਕਿਸਮ ਦਾ ਤਰਲ ਪਦਾਰਥ (Liquid) ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਦਾ ਨਿਰਮਾਣ ਉਸ ਭੋਜਨ ਅਤੇ ਪੀਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਤੋਂ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਅਸੀਂ ਆਪਣੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਪਹੁੰਚਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ | ਮਨੁੱਖੀ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਖੂਨ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਕੁੱਲ ਭਾਰ ਦਾ \(\frac{1}{12}\) ਜਾਂ \(\frac{1}{14}\) ਚ ਭਾਗ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਲਹੂ ਵਿਚ ਅਣਗਿਣਤ ਛੋਟੇ-ਛੋਟੇ ਲਾਲ ਅਤੇ ਚਿੱਟੇ ਕਣ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ਜੋ ਪਲਾਜ਼ਮਾ ਨਾਮੀ ਹਲਕੇ ਪੀਲੇ ਰੰਗ ਦੇ ਦ੍ਰਵ ਵਿਚ ਤੈਰਦੇ ਰਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਲਹੂ ਸਾਡੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਭਿੰਨ-ਭਿੰਨ ਅੰਗਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਦਿਨ-ਰਾਤ ਦੌਰਾ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਲਹੂ ਦੀ ਗਤੀ ਨੂੰ ਲਹੂ ਪਰਿਵਹਨ (Blood Circulation) ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਲਹੂ ਪਰਿਵਹਨ ਵਿਚ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਜੋ ਅੰਗ ਭਾਗ ਲੈਂਦੇ ਹਨ, ਉਹਨਾਂ ਦੇ ਸਮੂਹ ਨੂੰ ਲਹੂ-ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ (Circulatory System) ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਲਹੂ-ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਉੱਤੇ ਕਸਰਤ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ (Effects of Exercise on Circulatory System)-
ਲਹੂ-ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ‘ਤੇ ਕਸਰਤ ਦੇ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ ਪੈਂਦੇ ਹਨ
- ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਦੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਦਿਲ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਜ਼ਰੂਰਤ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਲਹੂ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਦੇ ਫਲਸਰੂਪ ਛੋਟੀਆਂ ਲਹੂ ਦੀਆਂ ਨਾਲੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਤੰਤੂਆਂ ਦੇ ਤਣਾਓ ਵਿਚ ਵਾਧਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਵਾਲਿਆਂ ਦੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਸ਼ੁੱਧ ਅਤੇ ਅਸ਼ੁੱਧ ਲਹੂ ਦੀ ਅਦਲਾ-ਬਦਲੀ ਛੇਤੀ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਦੇ ਫਲਸਰੂਪ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਪੌਸ਼ਟਿਕ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਅਤੇ ਆਕਸੀਜਨ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਮਿਲਦੀ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਕਾਰਬਨ-ਡਾਈਆਕਸਾਈਡ ਆਦਿ ਫਜ਼ੂਲ ਅਤੇ ਹਾਨੀਕਾਰਕ ਪਦਾਰਥਾਂ ਦਾ ਪਸੀਨੇ ਤੇ ਪੇਸ਼ਾਬ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿਚ ਨਿਕਾਸ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਰਿਸ਼ਟ-ਪੁਸ਼ਟ ਅਤੇ ਨਿਰੋਗ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਵਾਲੇ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦਾ ਲਹੁ ਦਬਾਅ ਵੱਧ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦਾ । ਉਸ ਦੀਆਂ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਸੁੰਗੜਦੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਫੈਲਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਨਤੀਜੇ ਦੇ ਤੌਰ ‘ਤੇ ਲਹੁ ਜਲਦੀ ਸਾਫ਼ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਦੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਸਰੀਰ ਦਾ ਹਰੇਕ ਅੰਗ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਕਾਰਨ ਉਹਨਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਆਕਸੀਜਨ ਦੀ ਵੱਧ ਜ਼ਰੂਰਤ ਪੈਂਦੀ ਹੈ | ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਵਾਲੇ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦੇ ਲਹੂ ਦੀ ਗਤੀ ਸਾਧਾਰਨ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਤੋਂ ਦੋ ਗੁਣਾ ਵੱਧ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਸ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਦਿਲ ਦੀ ਕਾਰਜ-ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਵਧ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ਜੋ ਲੋੜ ਦੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਹੋਣ ਦੀ ਸਮਰੱਥਾ ਰੱਖਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਸ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਲਹੂ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਵਾਹ ਵਧ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਸ ਨਾਲ ਹਾਜ਼ਮਾ ਠੀਕ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਕਸਰਤ ਨਾਲ ਅਸੀਂ ਚੰਗਾ ਲਹੂ ਤਿਆਰ ਕਰ ਸਕਦੇ ਹਾਂ ਜੋ ਸਾਡੇ ਜੀਵਨ ਦਾ ਆਧਾਰ ਹੈ ।
- ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਨਾਲ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ | ਇਸ ਦੇ ਫਲਸਰੂਪ ਆਰਾਮ ਦੀ ਹਾਲਤ ਵਿਚ ਦਿਲ ਦੀ ਧੜਕਣ ਠੀਕ ਚੱਲਦੀ ਹੈ ਪਰ ਖੂਨ ਦੀ ਗਤੀ ਤੇਜ਼ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਵਾਲੇ ਮਨੁੱਖ ਨੂੰ ਆਕਸੀਜਨ ਦੀ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਦੀ ਜ਼ਰੂਰਤ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਆਕਸੀਜਨ ਦੀ ਖਪਤ ਵਿਚ ਵਾਧਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਲਹੂ ਵਿਚ ਇਸ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਵਧਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਵਧੀ ਹੋਈ ਆਕਸੀਜਨ ਕਾਰਨ ਲੈਕਟਿਕ ਐਸਿਡ ਵਿਚ ਵਾਧਾ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦਾ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਖਿਡਾਰੀ ਅਤੇ ਐਥਲੀਟ ਬਿਨਾਂ ਥਕਾਵਟ ਮਹਿਸੂਸ ਕੀਤੇ ਕਾਫ਼ੀ ਸਮੇਂ ਤਕ ਖੇਡਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਭਾਗ ਲੈ ਸਕਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਦੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਲਹੂ ਨਾਲੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਮੂੰਹ ਖੁੱਲ੍ਹਦੇ ਅਤੇ ਬੰਦ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਰਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਭਾਰੀ ਕਸਰਤ ਅਤੇ ਦੌੜਦੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਆਕਸੀਜਨ ਵੱਧ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਵਿਚ ਅੰਦਰ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਰਹਿੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਭਾਰੀ ਕਸਰਤ ਅਤੇ ਦੌੜਦੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਆਕਸੀਜਨ 3500 ਘਣ ਮਿਲੀਲਿਟਰ ਤਕ ਅੰਦਰ ਚਲੀ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ਜਦੋਂ ਕਿ ਸਾਧਾਰਨ ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਵਾਲਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਆਕਸੀਜਨ ਦੀ ਇਹ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਕੇਵਲ 5000 ਤੋਂ 8000 ਘਣ ਮਿਲੀਲਿਟਰ ਤਕ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਵਾਲੇ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦੀਆਂ ਸ਼ਿਰਾਵਾਂ (Veins) ਤੇ ਧਮਨੀਆਂ (Arteries) ਨੂੰ ਵੱਧ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਨਾ ਪੈਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਫਲਸਰੂਪ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਕੰਧਾਂ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਵਾਲੇ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦੀ ਦਿਲ ਲਹੂ ਸਟਰੋਕ (Stroke Volume) ਆਮ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਧ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਕੀ ਹਨ ? ਇਹ ਕਿੰਨੀ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ? ਇਹਨਾਂ ਉੱਤੇ ਕਸਰਤਾਂ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ ਲਿਖੋ । [ਅਭਿਆਸ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ-4] (What are Muscles ? Give its types. Write down the effects of exercises on Muscular System.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ (Muscles)ਮਨੁੱਖੀ ਸਰੀਰ ਦਾ ਸਰਵ-ਉੱਤਮ ਗੁਣ ਇਸ ਦੀ ਗਤੀ ਜਾਂ ਚਲਣਾ-ਫਿਰਨਾ ਹੈ । ਮਨੁੱਖ ਦੇ ਘੁੰਮਣਫਿਰਨ ਵਿਚ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਧੁਰੀ ਦੀ ਭੂਮਿਕਾ ਨਿਭਾਉਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਮਾਸਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਜੁੜੀਆਂ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਭਿੰਨਭਿੰਨ ਕਿਸਮ ਦੀਆਂ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਮਾਸਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਮਾਸ ਸੁਤਰ ਸੈੱਲਾਂ ਦਾ ਸੁਮੇਲ ਹੈ ॥ ਹਰੇਕ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀ ਹੱਡੀ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਜੁੜੀ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀ ਦੇ ਸੁੰਗੜਨ ਨਾਲ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਵੀ ਖਿਚਾਅ ਉਤਪੰਨ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਭਿੰਨ-ਭਿੰਨ ਅੰਗ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਵਿਚ 75% ਪਾਣੀ, 18% ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਅਤੇ ਬਾਕੀ ਚਰਬੀ ਅਤੇ ਲਣ ਆਦਿ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ | ਖੂਨ ਅਤੇ ਸੁਖਮਣਾ ਨਾੜੀਆਂ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਸੂਚਨਾ ਪਹੁੰਚਾਉਣ ਦਾ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ |
ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਕਿਸਮਾਂ (Types of Muscles)-ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੀਆਂ ਦੋ ਕਿਸਮਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ
- ਸਵੈਇੱਛਿਤ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ (Voluntary Muscles)
- ਅਣਇੱਛਿਤ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ (Involuntary Muscles) ।
1. ਸਵੈਇੱਛਿਤ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ (Voluntary Muscles) – ਸਵੈਇੱਛਿਤ ਮਾਸਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਉਹ ਹਨ ਜੋ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦੀ ਇੱਛਾ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
ਇਹ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਪਿੰਜਰ ਦੇ ਉੱਪਰ ਲੱਗੀਆਂ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਲੱਤਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਬਾਹਾਂ ਵਿਚ

ਮਿਲਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਸੂਚਨਾ ਦੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਰਹਿੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਗਤੀ ਪ੍ਰਦਾਨ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ, ਸਰੀਰਕ ਢਾਂਚੇ ਨੂੰ ਸੰਭਾਲ ਕੇ ਰੱਖਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ਅਤੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਗਰਮੀ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
2. ਅਣਇੱਛਿਤ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ (Involuntary Muscles)-ਅਣਇੱਛਿਤ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਉਹ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਹਨ ਜੋ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦੇ ਵੱਸ ਵਿਚ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ਅਤੇ ਉਸ ਦੀ ਇੱਛਾ ਦੇ ਬਿਨਾਂ ਹੀ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਦਿਲ, ਜਿਗਰ ਅਤੇ ਅੰਤੜੀਆਂ ਆਦਿ ਵਿਚ ਪਾਈਆਂ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦੇ ਸੌਂਦੇ ਹੋਏ ਵੀ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਰਹਿੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਲਹੂ ਚੱਕਰ ਅਤੇ ਪਾਚਨ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਵਿਚ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਪਹੁੰਚਾਉਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦੇ ਲੱਛਣ ਸੁੰਗੜਨਾ, ਫੈਲਣਾ ਅਤੇ ਲਚਕ ਆਦਿ ਹੈ ।

ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਉੱਤੇ ਕਸਰਤ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ (Effects of Exercise on Muscles)-
ਕਸਰਤ ਦੇ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ‘ਤੇ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ ਪੈਂਦੇ ਹਨ –
- ਕਸਰਤ ਕੋਰਨ ਵਾਲੇ ਵਿਅਕਤੀਆਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਵੱਧ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਆਕਸੀਜਨ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪੌਸ਼ਟਿਕ ਖ਼ੁਰਾਕ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਮਾਤ੍ਰਾ ਵਿਚ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਨਾਲ ਇਹ ਵੱਧ ਪੁਸ਼ਟ ਅਤੇ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਬਣ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ |
- ਹਰ ਰੋਜ਼ ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਨਾਲ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਦਾ ਤਾਲਮੇਲ ਵੱਧਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਕਸਰਤ ਕਾਰਨ ਵੱਧ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਆਉਂਦੀ ਹੈ । ਫਲਸਰੂਪ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਲੰਮੀ ਮਿਆਦ ਤਕ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਕੇ ਵੀ ਥਕਾਵਟ ਮਹਿਸੂਸ ਨਹੀਂ ਕਰਦਾ ।
- ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਨਾਲ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਵੱਧ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਨਾ ਪੈਂਦਾ ਹੈ | ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਵਾਲੇ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦੇ ਅੰਦਰ ਆਕਸੀਜਨ ਦੀ ਖਪਤ ਵੀ ਵੱਧ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਤੇਜ਼ੀ ਨਾਲ ਖੂਨ ਪਹੁੰਚਦਾ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਹਿਲ-ਜੁਲ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਰਹਿੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਨਾਲ ਕਈ ਫਾਲਤੂ ਪਦਾਰਥਾਂ ਦਾ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਨਿਕਾਸ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਦਾ ਤਾਪਮਾਨ ਅਕਸਰ ਸਮਾਨ ਹੀ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ |
- ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਨਾਲ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਗਲਾਈਕੋਜਿਨ, ਫਾਸਫੋਰਾਟਿਨ ਅਤੇ ਪੋਟਾਸ਼ੀਅਮ ਆਦਿ ਰਸਾਇਣਿਕ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਰਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਰਸਾਇਣਿਕ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਖੂਨ ਦੀ ਗਤੀ ਵਿਚ ਵਾਧਾ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੀਆਂ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਲਚਕ ਅਤੇ ਫੁਰਤੀ ਆਉਂਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਨਾਲ ਸਾਡਾ ਸਰੀਰ ਨਿਰੋਲ ਅਤੇ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਨਾਲ ਛਾਤੀ ਦੀਆਂ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਪੱਠਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਫੈਲਣ ਦੀ ਸਮਰੱਥਾ ਵੱਧ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਸ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਪੱਠਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਦੇ ਯੋਗ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਜਾ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਸ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਸਾਡੀਆਂ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਸਖ਼ਤ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ਅਤੇ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਤਕ ਕੰਮ ਕਰ ਸਕਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਵਿਸਰਾਮ ਅਵਸਥਾ ਵਿਚ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦਾ ਇਕ ਲਹੂ ਚੱਕਰ ਪੂਰਾ ਹੋਣ ਲਈ 21 ਸੈਕਿੰਡ ਲੱਗਦੇ ਹਨ ਪਰ ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਨਾਲ ਇਹ 8-15 ਜਾਂ 10 ਸੈਕਿੰਡ ਵਿਚ ਪੂਰਾ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 5.
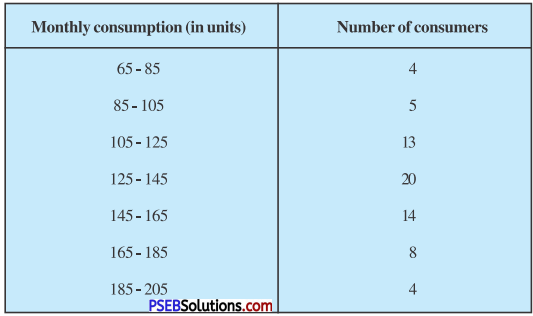
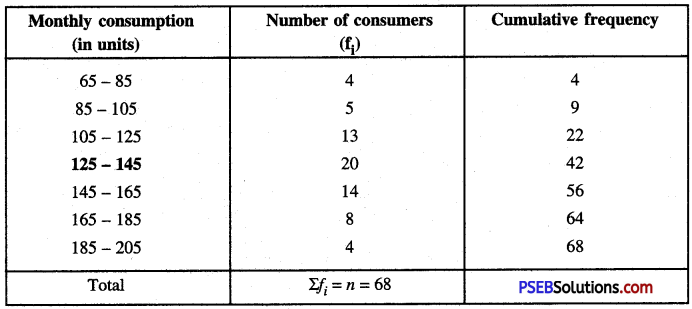
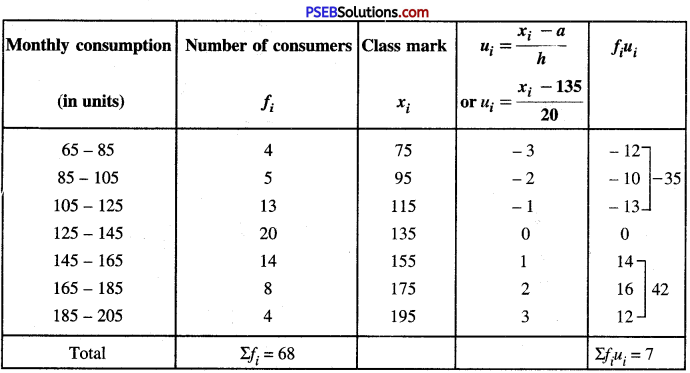
ਮਲ-ਤਿਆਗ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਦੇ ਅੰਗਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਮੁੱਖ ਰੱਖਦੇ ਹੋਏ ਕਸਰਤ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ ਬਿਆਨ ਕਰੋ । [ਅਭਿਆਸ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ-5] (Discuss the main organs of Excretory System. Give the effects of exercises on Excretory System.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਮਲ-ਤਿਆਗ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ (Excretory System) ਉਸ ਪ੍ਰਬੰਧ ਨੂੰ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ਜਿਸ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਫਾਲਤੂ ਅਤੇ ਹਾਨੀਕਾਰਕ ਪਦਾਰਥਾਂ ਦਾ ਨਿਕਾਸ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਜੇ ਇਹ ਫਜ਼ੂਲ ਅਤੇ ਹਾਨੀਕਾਰਕ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਹੀ ਜਮਾਂ ਰਹਿਣ ਤਾਂ ਸਰੀਰ ਅਨੇਕਾਂ ਰੋਗਾਂ ਦਾ ਸ਼ਿਕਾਰ ਹੋ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਬਾਹਰ ਆਉਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਪਦਾਰਥਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਯੂਰੀਆ, ਕਾਰਬਨ-ਡਾਈਆਕਸਾਈਡ, ਪਸੀਨਾ ਅਤੇ ਪਾਣੀ ਪ੍ਰਮੁੱਖ ਹਨ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਪਦਾਰਥਾਂ ਦਾ ਨਿਕਾਸ ਫੇਫੜਿਆਂ, ਗੁਰਦਿਆਂ, ਚਮੜੀ (Skin) ਅਤੇ ਅੰਤੜੀਆਂ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਕਸਰਤ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ (Effects of Exercise) -ਕਸਰਤ ਮਲ-ਤਿਆਗ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਨੂੰ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਢੰਗ ਨਾਲ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵਿਤ ਕਰਦੀ ਹੈ
- ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਹਿਲ-ਜੁਲ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਖੂਨ ਦੀ ਗਤੀ ਤੇਜ਼ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ | ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਗੈਸਾਂ ਦੀ ਅਦਲਾ-ਬਦਲੀ (Exchange of gases) ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਪੌਸ਼ਟਿਕ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਹਜ਼ਮ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ਅਤੇ ਫਾਲਤੂ ਪਦਾਰਥਾਂ ਦਾ ਨਿਕਾਸ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ, ਜਿਸ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਦਾ ਤਾਪਮਾਨ ਸਥਿਰ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਕਸਰਤ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੀਆਂ ਵੱਖ-ਵੱਖ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਨਾ ਪੈਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਟੁੱਟ-ਫੁੱਟ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਰਹਿੰਦੀ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਨਾਲ ਚਮੜੀ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਗੰਦਗੀ ਦਾ ਨਿਕਾਸ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਸਰੀਰ ਚਮੜੀ ਦੇ ਰੋਗਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਮੁਕਤ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਗੈਰ-ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਪਦਾਰਥਾਂ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿਚ ਜ਼ਹਿਰੀਲੀਆਂ ਵਸਤੂਆਂ ਦਾ ਸਰੀਰ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਹਰ ਨਿਕਾਸ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਜ਼ਹਿਰੀਲੇ ਕੀਟਾਣੂ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਇਕੱਠੇ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਅਤੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਜ਼ਹਿਰੀਲੇ ਕੀਟਾਣੂਆਂ ਦੇ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਸੰਘਰਸ਼ ਕਰਨ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਵਧਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਕਸਰਤ ਕਰਨ ਨਾਲ ਗੁਰਦੇ ਫਾਲਤੂ ਪਦਾਰਥਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਛਾਣ ਕੇ ਪੇਸ਼ਾਬ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿਚ ਬਾਹਰ ਕੱਢਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਇਹ ਇਕ ਛਾਣਨੀ ਦਾ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 6.
ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖਿਆਂ ‘ਤੇ ਨੋਟ ਲਿਖੋ –
(ਉ) ਚਮੜੀ ਦੇ ਕੰਮ
(ਅ) ਗੁਰਦੇ .
(ੲ) ਦਿਲ
(ਸ) ਸ਼ਿਰਾਵਾਂ ਤੇ ਧਮਨੀਆਂ (ਅਭਿਆਸ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 6) (Write a note on the following )
(a) Functions of Skin
(b) Kidney
(c) Heart
(d) Arteries and Veines.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
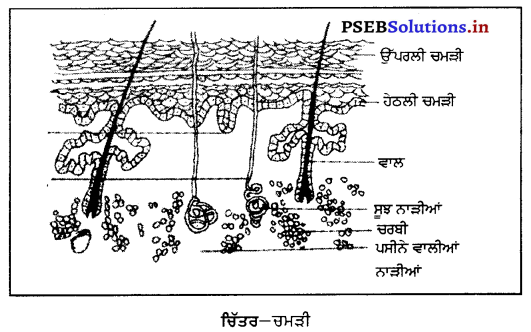
(ਉ) ਚਮੜੀ ਦੇ ਕੰਮ (Functions of Skin)-ਚਮੜੀ ਇਕ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਦਾ ਪਰਦਾ ਹੈ ਜੋ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਅੰਦਰੂਨੀ ਭਾਗਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਮਾਸਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਢੱਕ ਕੇ ਰੱਖਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਚਮੜੀ ਦੋ ਕਿਸਮ ਦੀ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ-ਉੱਪਰਲੀ ਜਾਂ ਬਾਹਰੀ (Epidermis) ਅਤੇ ਹੇਠਲੀ ਅੰਦਰੂਨੀ (Endodermis) । ਉੱਪਰਲੀ ਚਮੜੀ ਸਖ਼ਤ ਅਤੇ ਨਰਮ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ। ਇਸ ਵਿਚ ਛੋਟੇ-ਛੋਟੇ ਮੁਸਾਮ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਪਸੀਨਾ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਬਾਹਰ ਨਿਕਲਦਾ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਹੇਠਲੀ ਜਾਂ ਅੰਦਰੂਨੀ ਚਮੜੀ ਬੰਧਕ ਟਿਸ਼ੂਆਂ (Connective tissues) ਦੀ ਬਣੀ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਵਿਚ ਚਰਬੀ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ਜੋ ਗਰਮੀ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਨ ਵਿਚ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਪ੍ਰਦਾਨ ਕਰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਵਿਚ ਦੋ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਪਸੀਨਾ ਅਤੇ ਚਿਕਨਾਹਟ ਦੀਆਂ ਗੰਥੀਆਂ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ਜੋ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਤਾਪਮਾਨ ਨੂੰ ਇਕ ਸਮਾਨ ਰੱਖਣ ਵਿਚ ਮਦਦ ਦਿੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
(ਅ) ਗੁਰਦੇ (Kidneys) – ਗੁਰਦੇ ਸੰਖਿਆ ਵਿਚ ਦੋ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਢਿੱਡ ਵੱਲ ਸਥਿਤ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦਾ ਆਕਾਰ ਸੇਮ ਦੇ ਬੀਜ ਵਰਗਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਇਹ ਪੇਸ਼ਾਬ ਦਾ ਸਰੀਰ ਤੋਂ ਨਿਕਾਸ ਕਰਨ ਵਿਚ ਮਦਦ ਦਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਖੂਨ ਅਤੇ ਪਾਣੀ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਇਕ ਸਮਾਨ ਰੱਖਦੇ ਹਨ ।
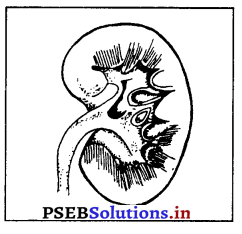
ਗੁਰਦਿਆਂ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਯੂਰੀਆ, ਯੂਰਿਕ ਐਸਿਡ, ਖਣਿਜ ਲੂਣ ਪੇਸ਼ਾਬ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿਚ ਨਿਕਲਦੇ ਰਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
(ੲ) ਦਿਲ (Heart) ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਦਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵਾਲਾ ਭਾਗ ਕੋਮਲ ਅਤੇ ਲਹੂ ਚੱਕਰ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਮੁੱਖ ਅੰਗ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਛਾਤੀ ਦੇ ਖੱਬੇ ਪਾਸੇ ਸਥਿਤ ਤਿੰਨ ਤਖਤੇ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਦਾ ਆਕਾਰ ਬੰਦ ਮੁੱਠੀ ਵਰਗਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਲੰਬਾਈ ਵਲੋਂ ਦੋ ਤਖ਼ਤੇ ਦੋ ਭਾਗਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਵੰਡਿਆ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਖੱਬਾ ਹੇਠਲਾ ਹਰੇਕ ਭਾਗ ਅੱਗੇ ਦੋ ਭਾਗਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਭਾਰਾ ਸੱਜਾ ਹੇਠਲਾ ਵੰਡਿਆ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
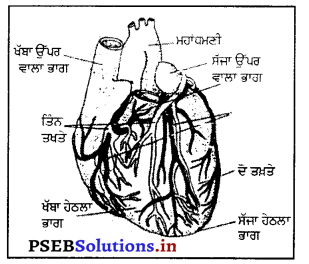
ਉੱਪਰਲਾ ਭਾਗ ਅਤੇ ਹੇਠਲਾ ਭਾਗ ਉੱਪਰਲੇ ਭਾਗ ਨੂੰ ਉੱਪਰਲਾ ਖਾਨਾ (Auricle) ਅਤੇ ਹੇਠਲੇ ਨੂੰ ਹੇਠਲਾ ਖਾਨਾ (Ventricle) ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਸ਼ੁੱਧ ਖੂਨ ਭਿੰਨ-ਭਿੰਨ ਅੰਗਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਸ਼ਿਰਾਵਾਂ ਦੇ ਮਾਧਿਅਮ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਦਿਲ ਦੇ ਸੱਜੇ ਉੱਪਰਲੇ ਖਾਨੇ (Auricle) ਵਿਚ ਪੁੱਜਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਉੱਪਰੋਂ ਤਿੰਨਪਦੀ ਦੁਆਰ (Triscuspid Valve) ਦੁਆਰਾ ਹੇਠਲੇ ਖਾਨੇ (Ventricle) ਵਿਚ ਪੁੱਜਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇੱਥੋਂ ਉੱਪਰ ਵਾਪਸ ਨਹੀਂ ਜਾ ਸਕਦਾ । ਸੱਜੇ ਹੇਠਲੇ ਖਾਨੇ ਤੋਂ ਖੂਨ ਫੇਫੜਿਆਂ ਵਾਲੀ ਧਮਨੀ (Pulmonary Artery) ਤੋਂ ਫੇਫੜਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਸ਼ੁੱਧ ਹੋਣ ਦੇ ਲਈ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਵਾਪਸੀ ਵਿਚ ਆਕਸੀਜਨ ਨਾਲ ਮਿਸ਼ਰਤ ਸ਼ੁੱਧ ਖੂਨ ਦਿਲ ਦੇ ਖੱਬੇ ਉੱਪਰਲੇ ਖ਼ਾਨੇ ਵਿਚ ਪੁੱਜ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਹੇਠਲੇ ਖ਼ਾਨੇ ਵਿਚ ਦੁਪਦੀ (Bricuspid) ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪੁੱਜਦਾ ਹੈ । | ਹੇਠਲੇ ਖਾਨੇ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਮਹਾਂਧਮਨੀ (Aorta) ਦੇ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਭਿੰਨ-ਭਿੰਨ ਅੰਗਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਪੁੱਜਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਲਹੂ ਚੱਕਰ ਦਾ ਇਕ ਚੱਕਰ ਲਗਾਤਾਰ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦਾ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
(ਸ) ਸ਼ਿਰਾਵਾਂ ਤੇ ਧਮਨੀਆਂ (Veins and Arteries) -ਜੋ ਨਾਲੀਆਂ ਖੂਨ ਨੂੰ ਫੇਫੜਿਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਹੋਰਾਂ ਭਾਗਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਫੇਫੜਿਆਂ ਵੱਲ ਲੈ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਭਾਗ ਹਨ, ਉਹਨਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ਿਰਾਵਾਂ (Veins) ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਕੰਧਾਂ ਦੀ ਬਨਾਵਟ ਤਾਂ ਧਮਨੀਆਂ ਵਰਗੀ ਹੀ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ, ਪਰ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਲਚੀਲੇ ਟਿਸ਼ੂਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਮਾਸਦਾਰ ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਦੀ ਤਹਿ ਬਹੁਤ ਬਰੀਕ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਪਲਮੋਨਰੀ ਸ਼ਿਰਾ ਨੂੰ ਛੱਡ ਕੇ ਬਾਕੀ ਸਭ ਸ਼ਿਰਾਵਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਅਸ਼ੁੱਧ ਖੂਨ ਨੂੰ ਹੀ ਦਿਲ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਲਿਆਉਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਧਮਨੀਆਂ -ਇਹ ਸ਼ੁੱਧ ਖੂਨ ਨੂੰ ਦਿਲ ਤੋਂ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਭਿੰਨ-ਭਿੰਨ ਭਾਗਾਂ ਤੱਕ ਪਹੁੰਚਾਉਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਲਚਕਦਾਰ ਅਤੇ ਮੋਟੀ ਕੰਧ ਦੀਆਂ ਬਣੀਆਂ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਸਾਫ਼ ਖ਼ੂਨ ਵਗਦਾ ਹੈ, ਪਰ ਫੇਫੜੇ ਵਿਚ ਖੂਨ
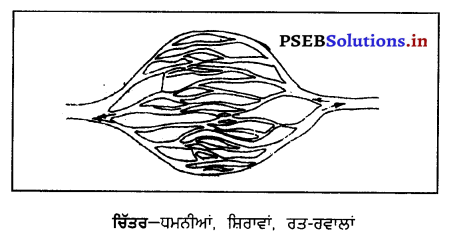
ਲੈ ਜਾਣ ਵਾਲੀ ਧਮਨੀ ਵਿਚ ਗੰਦਾ ਖੂਨ ਵਗਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਖੂਨ ਨੂੰ ਲੈ ਜਾਣ ਵਾਲੀ ਧਮਨੀ ਨੂੰ ਪਲਮੋਨਰੀ ਧਮਨੀ (Pulmonary Artery) ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ |
ਧਮਨੀਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਪ੍ਰਮੁੱਖ ਧਮਨੀ ਨੂੰ ਮੂਲ ਧਮਨੀ ਜਾਂ ਮਹਾਂਧਮਨੀ (Aorta) ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ |