Punjab State Board PSEB 10th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Ex 7.2 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Ex 7.2
Q.uestion 1.
Find the co-ordinates of the point which divides the join (- 1, 7) and (4, – 3) in the ratio 2 : 3.
Solution:
Let required point be P (x, y) which divides the join of given points A (- 1, 7)
and B (4, – 3) in the ratio of 2 : 3.
(-1, 7) (x, y) (4, – 3)
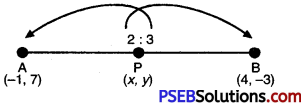
∴ x = \(\frac{2 \times 4+3 \times-1}{2+3}=\frac{8-3}{5}=\frac{5}{5}=1\)
and y = \(\frac{2 \times-3+3 \times 7}{2+3}=\frac{-6+21}{5}=\frac{15}{5}=3\)
Hence, required point be (1, 3).

Question 2.
Find the co-ordinates of the points of trisection of the line segment joining (4, – 1) and (2, – 3).
Solution:
Let P (x1, y1) and Q (x2, y2) be the required points which trisect the line segment joining A (4, – 1)and B (- 2, – 3) i.e., P(x1, y1) divides AB in ratio 1: 2 and Q divides AB in ratio 2 : 1.
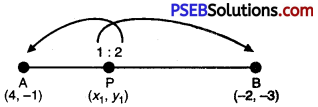
∴ x1 = \(\frac{1 \times-2+2 \times 4}{1+2}=\frac{-2+8}{3}=\frac{6}{3}=2\)
and y1 = \(\frac{1 \times-3+2 \times-1}{1+2}=\frac{-3-2}{3}=-\frac{5}{3}\)
∴ P(x1, y1) be (2, \(-\frac{5}{3}\))
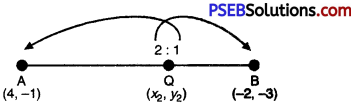
Now, x2 = \(\frac{2 \times-2+1 \times 4}{2+1}\)
= \(\frac{-4+4}{3}\) = 0
y2 = \(\frac{2 \times-3+1 \times-1}{2+1}=\frac{-6-1}{3}=-\frac{7}{3}\)
∴ Q(x2, y2) be (0, \(-\frac{7}{3}\))
Hence, required points be (2, \(-\frac{5}{3}\)) and (0, \(-\frac{7}{3}\)).

Question 3.
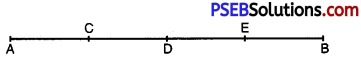
To conduct Sports Day activities, in your rectangular shaped school ground ABCD, lines have been drawn with chalk powder at a distance of 1 m each. 100 flower pots have been placed at a distance of 1m from each other along AD, as shown in fig. Niharika runs \(\frac{1}{4}\) th the distance AD on the 2nd line and posts a green flag.
Preet runs \(\frac{1}{5}\) th the distance AD on the eighth line and posts a red flag. What is the distance betweenboth the flags? If Rashmi has to post a blue flag exactly half way between the line (segment) joining the two flags, where should she post her flag?
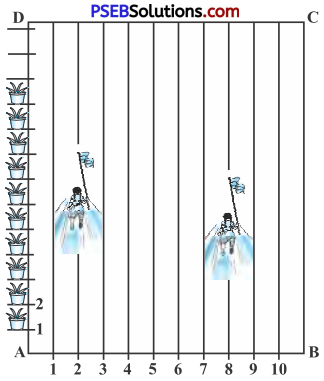
Solution:
In the given figure, we take A as origin. Taking x-axis along AB and y-axis along AD.
Position of green flag = distance covered by Niharika
= Niharika runs \(\frac{1}{4}\)th distance AD on the 2nd line
= \(\frac{1}{4}\) × 100 = 25 m
∴ Co-ordinates of the green flag are (2, 25)
Now, position of red flag = distance covered by Preet = Preet runs \(\frac{1}{5}\)th the distance AD on the 8th line
= \(\frac{1}{5}\) × 100 = 20 m.
Co-ordinates of red flag are (8, 20)
∴ distance between Green and Red flags = \(\sqrt{(8-2)^{2}+(20-25)^{2}}\)
= \(\sqrt{36+25}=\sqrt{61}\) m.
Position of blue flag = mid point of green flag and red flag
= \(\left(\frac{2+8}{2}, \frac{25+20}{2}\right)\)
= (5, 22.5).
Hence, blue flag is in the 5th line and at a distance of 22.5 m along AD.

Question 4.
Find the ratio in which (he segment joining the points (- 3, 10) and (6, – 8) is divided by (- 1, 6).
Solution:
Let point P (- 1, 6) divides the line segment joining the points A (- 3, 10) and B (6, – 8) the ratio K : 1.
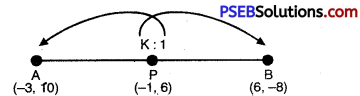
∴ -1 = \(\frac{6 \times \mathrm{K}-3 \times 1}{\mathrm{~K}+1}\)
or – K – 1 = 6K – 3
or – K – 6K = – 3 + 1
or – 7K = – 2
K : 1 = \(\frac{2}{7}\) : 1 = 2 : 7
Hence, required ratio is 2 : 7.
Question 5.
Find the ratio in which the line segment joining A (1, – 5) and B (- 4, 5) is divided by the x-axis. Also find the co
ordinates of the point of division.
Solution:
Let required point on x-axis is P (x, 0) which divides the line segment joining the points A (1, – 5) and B (- 4, 5) in the
ratio K : 1.
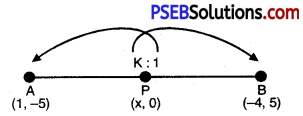
Consider, y co-ordinates of P ¡s:
0 = \(\frac{5 \times \mathrm{K}+(-5) \times 1}{\mathrm{~K}+1}\)
or 0 = \(\frac{5 \mathrm{~K}-5}{\mathrm{~K}+1}\)
or 5K – 5 = 0
or 5K = 5
or K = \(\frac{5}{5}\) = 1
∴ Required ratio is K : 1 = 1 : 1.
Now, x co-ordinate of P is:
x = \(\frac{-4 \times K+1 \times 1}{K+1}\)
Putting the value of K = 1, we get:
x = \(\frac{-4 \times 1+1 \times 1}{1+1}=\frac{-4+1}{2}\)
x = \(-\frac{3}{2}\)
Hence, required point be (\(-\frac{3}{2}\), 0).

Question 6.
If (1, 2); (4, y); (x, 6) and (3, 5)are the vertices of a parallelogram taken in order, find x and y.
Solution:
Let points of parallelogram ABCD are A (1, 2) (4, y) ; C (x, 6) and D (3, 5)
But diagonals of a || gm bisect each other.
Case I. When E is the mid point of A (1, 2) and C (x, 6)
∴ Co-ordinates of E are:
E = \(\left(\frac{x+1}{2}, \frac{6+2}{2}\right)\)
E = (\(\frac{x+1}{2}\), 4) …………..(1)
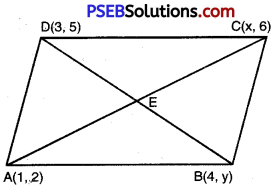
Case II. When E is the mid point B (4, y) and D (3, 5)
∴ Co-ordinates of E are:
E = \(\left(\frac{3+4}{2}, \frac{5+y}{2}\right)\)
E = \(\left(\frac{7}{2}, \frac{5+y}{2}\right)\) …………….(2)
But values of E in (1) and (2) are same, so comparing the coordinates, we get
\(\frac{x+1}{2}=\frac{7}{2}\)
or x + 1 = 7
or x = 6.
and 4 = \(\frac{5+y}{2}\)
or 8 = 5 + y
or y = 3
Hence, values of x and y are 6 and 3.

Question 7.
Find the coordinates of a point A, where AB is the diameter of a circle whose centre is (2, – 3) and B is (1, 4).
Solution:
Let, coordinates of A be (x, y). But, centre is the’ niij ioint of the vertices of the diameter.
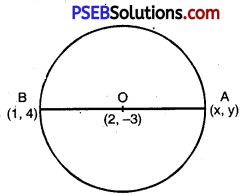
∴ O is the mid point of A(x, y) and B(1, 4)
∴ \(\left(\frac{x+1}{2}, \frac{y+4}{2}\right)\) = (2, -3)
On comparing, we get
\(\frac{x+1}{2}\)
or x + 1 = 4
or x = 3
and \(\frac{y+4}{2}\) = – 3
or y + 4 = – 6
or y = – 10
Hence, required point A be (3, – 10).

Question 8.
If A and B are (- 2, – 2) and (2, – 4) respectively, find the coordinates of P such that AP = AB and P lies ¡n the line segment AB.
Solution:
Let required point P be (x, y)
Also AP = \(\frac{3}{7}\) AB …(Given)
But, PB = AB – AP
= AB – \(\frac{3}{7}\) AB = \(\frac{7-3}{7}\) AB
PB = \(\frac{4}{7}\) AB
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{AP}}{\mathrm{PB}}=\frac{\frac{3}{7} \mathrm{AB}}{\frac{4}{7} \mathrm{AB}}=\frac{3}{4}\).
∴ P divides given points A and B in ratio 3 : 4.
Now,
x = \(\frac{3 \times 2+4 \times-2}{3+4}\)
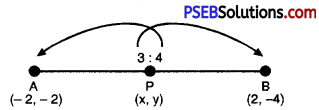
or x = \(\frac{6-8}{7}=-\frac{2}{7}\)
and y = \(\frac{3 \times-4+4 \times-2}{3+4}\)
= \(\frac{-12-8}{7}=-\frac{20}{7}\)
Hence, coordinates of P be (\(-\frac{2}{7}\), \(-\frac{20}{7}\)).
Question 9.
Find the coordinates of the points which divides the line segment joining A (- 2, 2) and B (2, 8) into four equal parts.
Solution:
Let required points are C, D and E which divide the line segment joming the points A (- 2, 2) and B (2, 8) into four equal parts. Then D is mid point of A and B ; C is the mid point of A and D ; E is the mid point of D and B such that
AC = CD = DE = EB
Now, mid point of A and B (i.e., Coordinates of D)
= \(\left(\frac{-2+2}{2}, \frac{2+8}{2}\right)\) = (0, 5)
Mid point of A and D (i.e., Coordinates of C)
= \(\left(\frac{-2+0}{2}, \frac{2+5}{2}\right)=\left(-1, \frac{7}{2}\right)\)
Mid point of D and B (i.e., Coordinates of E)
= \(\left(\frac{2+0}{2}, \frac{8+5}{2}\right)=\left(1, \frac{13}{2}\right)\)
Hence, requned points be (0, 5), (-1, \(\frac{7}{2}\)), (1, \(\frac{13}{2}\)).

Question 10.
Find the area of a rhombus if the vertices are (3, 0); (4, 5); (- 1, 4) and(- 2, – 1) taken in order.
[Hint: Areas of a rhombus = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (Product of its diagonals)]
Solution:
Let coordinates of rhombus ABCD are A (3, 0); B(4, 5); C(-1, 4) and D(- 2, – 1).
Diagonal, AC = \(\sqrt{(-1-3)^{2}+(4-0)^{2}}\)
= \(\sqrt{16+16}=\sqrt{32}=\sqrt{16 \times 2}\) = 4√2
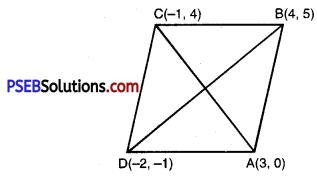
and diagonal BD
BD = \(\sqrt{(-2-4)^{2}+(-1-5)^{2}}\)
= \(\sqrt{36+36}=\sqrt{72}=\sqrt{36 \times 2}\) = 6√2.
∴ Area of rhombus ABCD = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × AC × BD
ABCD = [\(\frac{1}{2}\) × 4√2 × 6√2] sq. units
(\(\frac{1}{2}\) × 24 × 2) sq. units
= 24 sq. units
Hence, area of rhombus is 24 sq. units.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()