Punjab State Board PSEB 9th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 2 Polynomials Ex 2.5 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Ex 2.5
Question 1.
Use suitable identities to find the following products:
(i) (x + 4) (x + 10)
Answer:
(x + 4) (x + 10)
= (x)2 + (4 + 10)x + (4)(10)
= x2 + 14x + 40

(ii) (x + 8) (x – 10)
Answer:
(x + 8) (x – 10)
= (x)2 + (8 – 10)x + (8)(- 10)
= x2 – 2x – 80
(iii) (3x + 4) (3x – 5)
Answer:
(3x + 4) (3x – 5)
= (3x)2 + (4 – 5) (3x) +(4) (- 5)
= 9x2 – 3x – 20
(iv) \(\left(y^{2}+\frac{3}{2}\right)\left(y^{2}-\frac{3}{2}\right)\)
Answer:
\(\left(y^{2}+\frac{3}{2}\right)\left(y^{2}-\frac{3}{2}\right)\)
= (y2)2 – \(\left(\frac{3}{2}\right)^{2}\)
= y4 – \(\frac{9}{4}\)
(v)(3 – 2x) (3 + 2x)
Answer:
(3 – 2x) (3 + 2x)
= (3)2 – (2x)2
= 9 – 4x2

Question 2.
Evaluate the following products without multiplying directly:
(i) 103 × 107
Answer:
103 × 107
= (100 + 3) (100 + 7)
= (100)2 + (3 + 7) (100) + (3) (7)
= 10000 + 1000 + 21
= 11,021
(ii) 95 × 96
Answer:
95 × 96
= (90 + 5) (90 + 6)
= (90)2 + (5 + 6) (90) + (5) (6)
= 8100 + 990 + 30 = 9120
OR
95 × 96
= (100 – 5) (100 – 4)
= (100)2 + (- 5 – 4) (100) + (- 5) (- 4)
= 10000 – 900 + 20
= 10020 – 900 = 9120

(iii) 104 × 96
Answer:
104 × 96
= (100 + 4)(100-4)
= (100)2 – (4)2
= 10000 – 16 = 9984
Question 3.
Factorise the following using appropriate identities:
(i) 9x2 + 6xy + y2
Answer:
9x2 + 6xy + y2
= (3x)2 + 2(3x) (y) + (y)2
= (3x + y)2 = (3x + y) (3x + y)
(ii) 4y2 – 4y + 1
Answer:
4y2 – 4y + 1
= (2y)2 – 2(2y)(1) + (1)2
= (2y – 1)2 = (2y – 1) (2y – 1)
(iii) x2 – \(\frac{y^{2}}{100}\)
Answer:
x2 – = (x)2 – \(\left(\frac{y}{10}\right)^{2}\)
= \(\left(x+\frac{y}{10}\right)\) \(\left(x-\frac{y}{10}\right)\)

Question 4.
Expand each of the following using suitable identities:
(i) (x + 2y + 4z)2
Answer:
(x + 2y + 4z)2
= (x)2 + (2y)2 + (4z)2 + 2 (x) (2y) + 2(2y)(4z) + 2(4z)(x)
= x2 + 4y2 + 16z2 + 4xy + 16yz + 8zx
(ii) (2x – y + z)2
Answer:
(2x – y + z)2
= [2x + (- y) + z]2
= (2x)2 + (- y)2 + (z)2 + 2 (2x)(- y) + 2(- y)(z) + 2(z) (2x)
= 4x2 + y2 + z2 – 4xy – 2yz + 4zx
(iii) (- 2x + 3y + 2z)2
Answer:
(- 2x + 3y + 2z)2
= [(- 2x) + 3y + 2z]2
= (- 2x)2 + (3y)2 + (2z)2 + 2(- 2x)(3y) + 2(3y)(2z) + 2(2z)(- 2x)
= 4x2 + 9y2 + 4z2 – 12xy + 12yz – 8zx
(iv) (3a – 7b – c)2
Answer:
(3a – 7b – c)2
= [3a + (- 7b) + (- c)]2
= (3a)2 + (- 7b)2 + (- c)2 + 2 (3a) (- 7b) + 2(- 7b) (- c) + 2(- c) (3a)
= 9a2 + 49b2 + c2 – 42ab + 14bc – 6ca

(v)(- 2x + 5y – 3z)2
Answer:
(- 2x + 5y – 3z)2
= [(-2x) + 5y + (-3z)]2
= (- 2x)2 + (5y)2 + (- 3z)2 + 2 (- 2x) (5y) + 2 (5y) (- 3z) + 2 (- 3z) (- 2x)
= 4x2 + 25y2 + 9z2 – 20xy – 30yz + 12zx
(vi) [\(\frac{1}{4}\)a – \(\frac{1}{2}\)b + 1]2
Answer:
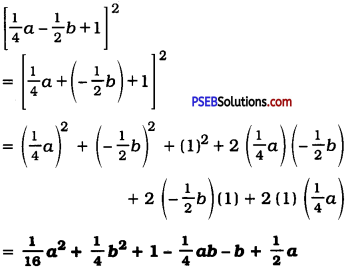
Question 5.
Factorise:
(i) 4x2 + 9y2 + 16z2 + 12xy – 24yz – 16xz
Answer:
4x2 + 9y2 + 16z2 + 12xy – 24yz – 16xz ;
= (2x)2 + (3y)2 + (- 4z)2 + 2 (2x) (3y) + 2(3y) (- 4z) + 2(- 4z) (2x)
= [2x + 3y + (- 4z)]2
= (2x + 3y – 4z)2
= (2x + 3y – 4z) (2x + 3y – 4z)

(ii) 2x2 + y2 + 8z2 – 2√2 xy + 4√2 yz – 8xz
Answer:
2x2 + y2 + 8z2 – 2√2 xy + 4√2 yz – 8 xz
= (- √2x)2 + (y)2 + (2√2 z)2 + 2 (- √2x) (y) + 2(y) (2√2 z) + 2(2√2 z) (- √2 x)
= [(- √2 x) + y + 2√2 z]2
= (- √2x + y + 2√2 z)2
= (- √2x + y + 2√2 z) (- √2 x + y + 2√2 z)
Question 6.
Write the following cubes in expanded form:
(i) (2x + 1)3
Answer:
(2x + 1)3
= (2x)3 + (1)3 + 3(2x) (1)(2x + 1)
= 8x3 + 1 + 6x(2x + 1)
= 8x3+ 1 + 12x2 + 6x
OR
(2x + 1)3
= (2x)3 + 3(2x)2(1) + 3(2x) (1)2 + (1)3
= 8x3 + 12x2 + 6x + 1
(ii) (2a – 3b)3
Answer:
(2a – 3b)3
= (2a)3 – (3b)3 – 3 (2a) (3b) (2a – 3b)
= 8a3 – 27b3 – 18ab(2a – 3b)
= 8a3 – 27b3 – 36a2b + 54ab2

(iii) \(\left[\frac{3}{2} x+1\right]^{3}\)
Answer:
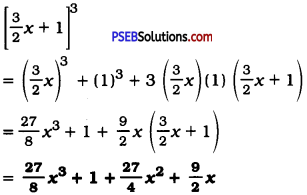
(iv) \(\left[x-\frac{2}{3} y\right]^{3}\)
Answer:
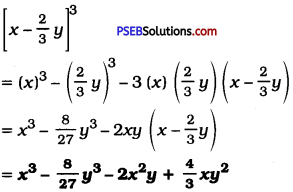
Question 7.
Evaluate the following using suitable identities:
(i) (99)3
Answer:
(99)3 = (100 – 1)3
= (100)3 – (1)3 – 3 (100) (1) (100 – 1)
= 1000000 – 1 – 300(99)
= 1000000 – 1 – 29700
= 9,70,299
(ii) (102)3
Answer:
(102)3 = (100 + 2)3
= (100)3 + (2)3 + 3(100) (2) (100 + 2)
= 1000000 + 8 + 600(102)
= 1000000 + 8 + 61200
= 10,61,208

(iii) (998)3
Answer:
(998)3 = (1000 – 2)3
= (1000)3 – (2)3 – 3(1000) (2) (1000 – 2)
= 1000000000 – 8 – 6000(1000 – 2)
= 1000000000 – 8 – 6000000 + 12000
= 994000000 + 12000 – 8
= 994012000 – 8
= 99,40,11,992
Question 8.
Factorise each of the following:
(i) 8a3 + b3 + 12a2b + 6ab2
Answer:
8a3 + b3 + 12a2b + 6ab2
= (2a)3 + (b)3 + 3 (4a2) (b) + 3 (2a) (b2)
= (2a)3 + (b)3 + 3 (2a)2 (b) + 3 (2a) (b2)
= (2a + b)3
= (2a + b) (2a + b) (2a + b)
(ii) 8a3 – b3 – 12a2b + 6ab2
Answer:
8a3 – b3 – 12a2b + 6ab2
= (2a)3 + (- b)3 + 3 (4a2) (- b) + 3 (2a) (b2)
= (2a)3 + (- b)3 + 3 (2a)3 (- b) + 3 (2a) (- b)2
= (2a – b)3
= (2a – b) (2a – b) (2a – b)

(iii) 27 – 125a3 – 135a + 225a2
Answer:
27 – 125a3 – 135a + 225a2
= (3)3 + (- 5a)3 + 3(9) (- 5a) + 3 (3) (25a2)
= (3)3 + (- 5a)3 + 3(3)2 (- 5a) + 3 (3) (- 5a)2
=(3 – 5a)3.
= (3 – 5a)(3 – 5a) (3 – 5a)
(iv) 64a3 – 27b3 – 144a2b + 108ab2
Answer:
64a3 – 27b3 – 144a2b + 108ab2
= (4a)3 + (- 3b)3 + 3(16a2)(-3b) + 3(4a) (9b2)
= (4a)3 + (- 3b)3 + 3(4a)2(- 3b) + 3(4a)(- 3b)2
= (4a – 3b)3
= (4a – 3b) (4a – 3b) (4a – 3b)
(v) 27p3 – \(\frac{1}{216}\) – \(\frac{9}{2}\)p2 + \(\frac{1}{4}\)p
Answer:
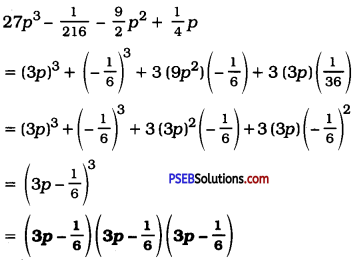

Question 9.
Verify:
(i) x3 + y3 = (x + y) (x2 – xy + y2)
Answer:
R.H.S. = (x + y) (x2 – xy + y2)
= x(x2 – xy + y2) + y(x2 – xy + y2)
= x3 – x2y + xy2 + x2y – xy2 + y3
= x3 + y3
= L.H.S.
(ii) x3 – y3 = (x – y) (x2 + xy + y2)
Answer:
R.H.S. = (x – y) (x2 + xy + y2)
= x(x2 + xy + y2) – y(x2 + xy + y2)
= x3 + x2y + xy2 – x2y – xy2 – y3
= x3 – y3
= L.H.S.

Question 10.
Factorise each of the following:
[Hint: See Question 9]
(i) 27y3 + 125z3
Answer:
27y3 + 125z3
We know, a3 + b3 = (a + b) (a2 – ab + b2)
Replacing a by 3y and b by 5z, we get
(3y)3 + (5z)3 = (3y + 5z) [(3y)2 – (3y)(5z) + (5z)2]
∴ 27y3 + 125z3 = (3y + 5z) (9y2 – 15yz + 25z2)
OR
We know, a3 + b3 = (a + b)3 – 3ab(a + b)
Replacing a by 3y and b by 5z, we get
(3y)3 + (5z)3 = (3y + 5z)3 – 3 (3y) (5z) (3y + 5z)
∴ 27y3 + 125z3 = (3y + 5z) [(3y + 5z)3 – 45yz]
= (3y + 5z)(9y3 + 30yz + 25z2 – 45yz)
= (3y + 5z) (9y2 – 15yz + 25z2)
(ii) 64m3 – 343n3
Answer:
We know, a3 – b3 = (a – b) (a2 + ab + b2)
Replacing a by 4m and b by 7n, we get
(4m)3 – (7n)3 = (4m – 7n) [(4m)3 + (4m) (7n) + (7n)2]
∴ 64m3 – 343n3 = (4m – 7n) (16m2 + 28mn + 49n2)
OR
We know. a3 – b3 = (a – b)3 + 3ab(a – b)
Replacing a by 4m and b by 7n, we get
(4m)3 – (7n)3 = (4m – 7n)3 + 3 (4m) (7n)(4m – 7n)
= (4m – 7n) [(4m 7n)2 + 84mn]
= (4m – 7n) (16m2 – 56mn + 49n2 + 84mn)
= (4m – 7n) (16m2 + 28mn + 49n2)

Question 11.
Factorise: 27x3 + y3 + z3 – 9xyz
Answer:
We know, a3 + b3 + c3 – 3abc = (a + b + c) (a2 + b2 + c2 – ab – bc – ca)
Replacing a by 3x, b by y and c by z, we get
(3x)3 + (y)3 + (z)3 – 3 (3x) (y) (z) = (3x + y + z) [(3x)2 + (y)2 + (z)2– (3x) (y) – (y) (z) — (z) (3x)]
∴ 27x3 + y3 + z3 – 9xyz = (3x + y + z) (9x2 + y2 + z2– 3xy – yz – 3zx)
Question 12.
Verify that x3 + y3 + z3 – 3xyz = \(\frac{1}{2}\)(x + y + z) [(x – y)2 + (y – z)2 + (z – x)2)
Answer:
R.H.S. = \(\frac{1}{2}\)(x + y + z) [(x – y)2 + (y – z)2 + (z – x)2]
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) (x + y + z) (x2 – 2xy + y2 + y2 – 2yz + z2 + z2 – 2zx + x2)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) (x + y + z) (2x2 + 2y2 + 2z2 – 2xy – 2yz – 2zx)
= (x + y + z) (x2 + y2 + z2 – xy – yz – zx)
= x(x2 + y2 + z2 – xy – yz – zx) + y(x2 + y2 + z2 – xy – yz – zx) + z(x2 + y2 + z2 – xy – yz – zx)
= x3 + xy2 + xz2 – x2y – xyz – zx2 + x2y + y3 + yz2 – xy2 – y2z – xyz + x2z + y2z + z3 – xyz – yz2 – z2x
= x3 + y3 + z3 – 3xyz
= L.H.S.
Question 13.
If x + y + z = 0, show that x3 + y3 + z3 = 3xyz.
Answer:
We know the Idendity
x3 + y3 + z3 – 3xyz = (x + y + z) (x2+ y3 + z2 – xy – yz – zx)
If x + y + z = 0. we get
x3 + y3 + z3 – 3xyz = (0) (x2 + y2 + z2 – xy – yz – zx)
∴ x3 + y3 + z3 – 3xyz = 0
∴ x3 + y3 + z3 = 3xyz

Question 14.
Without actually calculating the cubes, find the value of each of the following:
(i) (- 12)3 + (7)3 + (5)3
Answer:
Taking a = -12, b = 7 and c = 5, we get
a + b + c = (- 12) + 7 + 50.
Now, If a + b + c = 0, then a3 + b3 + c3 = 3abc.
∴ (- 12)3 + (7)3 + (5)3 = 3(- 12) (7) (5)
= (- 36) (35)
= – 1260
(ii) (28)3 + (- 15)3 + (- 13)3
Answer:
Talking a = 28, b = – 15 and c = – 13, we get
a + b + c = 28 + (- 15) + (- 13) = 0.
Now, If a + b + c = 0, then a3 + b3 + c3 = 3abc.
∴ (28)3 + (- 15)3 + (- 13)3 = 3 (28) (- 15) (- 13)
= (84)(195)
= 16,380
Question 15.
Give possible expressions for the length and breadth of each of the following rectangles, in which their areas are given:
(i) Area: 25a2 – 35a + 12
Answer:
We know, area of a rectangle = length × breadth
Hence, two factors of area can give possible expressions for length and breadth. So here, we will try to obtain two factors of the expression of area.
25a2 – 35a + 12 = 25a2 – 20a – 15a + 12
= 5a(5a – 4) – 3(5a – 4)
=(5a – 4) (5a – 3)
Thus, the length and breadth of the rectangle are (5a – 3) and (5a – 4) respectively.
Note : Traditionally, length > breadth in a rectangle.

(ii) Area: 35y2 + 13y – 12
Answer:
We know, area of a rectangle = length × breadth
Hence, two factors of area can give possible expressions for length and breadth. So here, we will try to obtain two factors of the expression of area.
35y2 + 13y – 12 = 35y2 + 28y – 15y – 12
= 7y(5y + 4) – 3(5y + 4)
= (5y + 4) (7y – 3)
Thus, the length and breadth of the rectangle are (7y – 3) and (5y + 4) respectively.
Question 16.
What are the possible expressions for the dimensions of the cuboids whose volumes are given below?
Answer:
(i) Volume: 3x2 – 12x
Answer:
We know, volume of a cuboid = length × breadth × height
Hence, three factors of volume can give possible expressions for length, breadth and height.
So here, we will try to obtain three factors of the expression of volume.
3x2 – 12x = 3x(x – 4)
= 3 × x × (x – 4)
Thus, one possible answer for the dimensions of the cuboid is 3. x and (x – 4).
Note: Other possible answers can be given as 1. 3x and (x – 4) or 1, x and (3x – 12).

(ii) Volume: 12ky2 + 8ky = 20k
Answer:
We know, volume of a cuboid = length × breadth × height
Hence, three factors of volume can give possible expressions for length, breadth and height.
So here, we will try to obtain three factors of the expression of volume.
12ky2 + 8ky – 20k = 4k (3y2 + 2y – 5)
= 4k (3y2 – 3y + 5y – 5)
= 4k [3y (y – 1) + 5(y – 1)1]
= 4k (y – 1) (3y + 5)
Thus, one possible answer for the dimensions of the cuboid is 4k, (y – 1) and (3y + 5).
![]()
![]()
![]()




