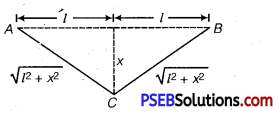
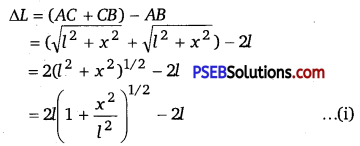
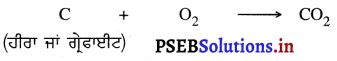Punjab State Board PSEB 10th Class Science Important Questions Chapter 8 ਜੀਵ ਪ੍ਰਜਣਨ ਕਿਵੇਂ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ? Important Questions and Answers.
PSEB 10th Class Science Important Questions Chapter 8 ਜੀਵ ਪ੍ਰਜਣਨ ਕਿਵੇਂ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ?
ਵੱਡੇ ਉੱਚਰਾਂ ਵਾਲੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ (Long Answer Type Questions)
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਪੌਦਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਇਕ ਪ੍ਰਜਣਨ ਦਾ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਵਰਣਨ ਕਰੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਪੌਦਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਾਇਕ ਪ੍ਰਜਣਨ ਮੁੱਖ ਰੂਪ ਵਿਚ ਦੋ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ-
(i) ਕੁਦਰਤੀ ਅਤੇ
(ii) ਬਨਾਵਟੀ ਕਾਇਕ ਪ੍ਰਜਣਨ ।
(i) ਕੁਦਰਤੀ ਕਾਇਕ ਪ੍ਰਜਣਨ-ਇਹ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਕਲਿਕਾ ਹਨ-
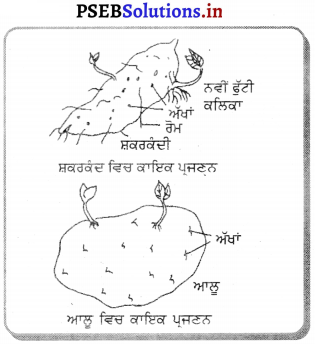

(ਉ) ਜੜ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੁਆਰਾ – ਕੁਝ ਪੌਦਿਆਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਜੜ੍ਹਾਂ, ਜਿਵੇਂ ਸ਼ਕਰਕੰਦੀ ਵਿਚ ਕਲਿਕਾਵਾਂ (ਅੱਖਾਂ) ਮੌਜੂਦ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ! ਸ਼ਕਰਕੰਦੀ ਨੂੰ ਜ਼ਮੀਨ ਵਿਚ ਗੱਡ ਦੇਣ ਤੇ ਕਲਿਕਾਵਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਕੋਪਲ ਫੁਟਦੇ ਹਨ ਜਿਸ ਤੋਂ ਨਵਾਂ ਪੌਦਾ ਬਣਦਾ ਹੈ ।
(ਅ) ਤਣਿਆਂ ਦੁਆਰਾ – ਕੁਝ ਤਣਿਆਂ ਤੇ ਵੀ ਅੱਖਾਂ ਜਾਂ ਕਲਿਕਾਵਾਂ ਮੌਜੂਦ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ , ਜਿਵੇਂ-ਆਲ, ਅਦਰਕ ਆਦਿ । ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਵੀ ਜ਼ਮੀਨ ਵਿਚ ਬੀਜ ਦੇਣ ਤੇ ਕਲਿਕਾਵਾਂ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਕੋਪਲਾਂ ਫੁੱਟ ਪੈਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
(ੲ) ਪੱਤਿਆਂ ਦੁਆਰਾ – ਬਾਇਓਫਿਲਮ, ਬਿਗੋਨੀਆ ਆਦਿ ਦੀਆਂ ਪੱਤੀਆਂ ਦੀ ਕਿਨਾਰੀ ਉੱਤੇ ਵਿਕਸਿਤ ਕਲੀਆਂ ਮਿੱਟੀ ਵਿਚ ਡਿੱਗ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ਅਤੇ ਨਵੇਂ ਪੌਦਿਆਂ ਵਜੋਂ ਵਿਕਸਿਤ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
(ii) ਬਨਾਵਟੀ ਕਾਇਕ ਪ੍ਰਜਣਨ – ਇਹ ਮੁੱਖ ਰੂਪ ਵਿਚ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ-

(ਉ) ਦਾਬ ਲਗਾਉਣਾ – ਕੁੱਝ ਪੌਦਿਆਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਟਹਿਣੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਝੁਕਾ ਕੇ ਭੂਮੀ ਦੇ ਅੰਦਰ ਮਿੱਟੀ ਵਿਚ ਦਬਾ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਕੁੱਝ ਦਿਨਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਮਿੱਟੀ ਵਿਚ ਦੱਬੀ ਟਹਿਣੀ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਕੋਪਲਾਂ ਫੁੱਟ ਆਉਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
ਉਦਾਹਰਨ-ਚਮੇਲੀ, ਅੰਗੁਰ ਆਦਿ ।
(ਅ) ਕਲਮ – ਗੁਲਾਬ, ਗੁੜਹਲ, ਚਮੇਲੀ ਆਦਿ ਦੀ ਅਜਿਹੀ ਸ਼ਾਖਾ ਕੱਟ ਲਈ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਭੁਮੀ ਵਿਚ ਗੱਡ ਦੇਣ ਤੇ ਇਸ ਤੋਂ ਅਪਸਥਾਨਿਕ ਜੜਾਂ ਨਿਕਲ ਆਉਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ਅਤੇ ਕਲਿਕਾਵਾਂ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਕੋਪਲਾਂ ਫੁੱਟ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
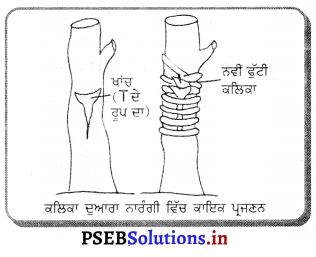
(ੲ) ਪਿਉਂਦ ਲਾਉਣਾ – ਇਸ ਵਿਚ ਇਕ ਰੁੱਖ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਾਖਾ ਨੂੰ ਕੱਟ ਕੇ ਉਸ ਵਿਚ ‘T’ ਦੇ ਆਕਾਰ ਦਾ ਖਾਂਚਾ ਬਣਾ ਲਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਨੂੰ ਸਟਾਕ (Stock) ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਹੁਣ ਉਸ ਜਾਤੀ ਦੇ ਦੂਸਰੇ ਰੁੱਖ ਦੀ ਟਹਿਣੀ ਨੂੰ ਕੱਟ ਕੇ ਸਟਾਕ ਦੇ ਖਾਂਚੇ ਦੇ ਅਨੁਰੂਪ ਖਾਂਚਾ ਬਣਾ ਲਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ, ਇਸਨੂੰ ਸਿਆਨ (Scion) ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਸਿਆਨ ਨੂੰ ਸਟਾਕ ਵਿਚ ਫਿਟ ਕਰ ਦਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਖਾਂਚ ਦੇ ਚਾਰੋਂ ਪਾਸੇ ਮਿੱਟੀ ਲਗਾ ਕੇ ਬੰਨ੍ਹ ਦਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਕੁਝ ਦਿਨਾਂ ਬਾਅਦ
ਦੋਨੋਂ ਜੁੜ ਕੇ ਪੌਦਾ ਬਣ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਉਦਾਹਰਨ-ਗੰਨਾ, ਅੰਬ, ਅਮਰੂਦ, ਲੀਚੀ ਆਦਿ ।
(ਸ) ਬਡੌਗ-ਇਸ ਵਿਚ ਇੱਕ ਰੁੱਖ ਦੀ ਇਕ ਟਹਿਣੀ ਦੀ ਛਾਲ ਵਿਚ ‘T’ ਦੀ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਖਾਂਚਾ ਬਣਾ ਲਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਕਿਸੇ ਦੁਸਰੇ ਚੁਣੇ ਹੋਏ ਪੌਦੇ ਦੀ ਕਲਿਕਾ ਨੂੰ ਲੈ ਕੇ ਸਟਾਕ ਦੇ ਖਾਂਚੇ ਵਿਚ । ਘਮਾ ਦਿੰਦੇ ਹਾਂ । ਇਸ ਨੂੰ ਚੰਗੀ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਬੰਨ੍ਹ ਕੇ ਇਸਦੇ ਉੱਪਰ ਮਿੱਟੀ ਲਪੇਟ ਦਿੰਦੇ ਹਾਂ । ਕੁਝ ਦਿਨਾਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਉਸ ਸਥਾਨ ਤੇ ਕੋਪਲਾਂ ਨਿਕਲ ਆਉਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
ਉਦਾਹਰਨ-ਨਿੰਬੂ, ਨਾਰੰਗੀ ਆਦਿ ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਅੰਕਿਤ ਚਿੱਤਰ ਦੀ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਨਾਲ ਫੁੱਲ ਦੇ ਭਾਗਾਂ ਦਾ ਵਰਣਨ ਕਰੋ ।
ਜਾਂ
ਫੁੱਲ ਦੀ ਲੰਬਾਤਮਕ ਕਾਟ ਦਾ ਅੰਕਿਤ ਚਿੱਤਰ ਬਣਾ ਕੇ ਫੁੱਲ ਦੇ ਵੱਖ-ਵੱਖ ਭਾਗਾਂ ਦਾ ਵਰਣਨ ਕਰੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
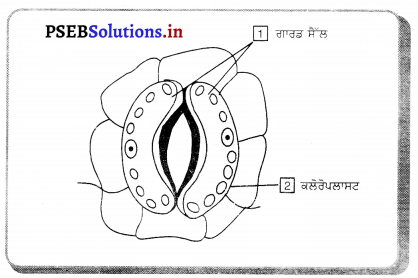
ਫੁੱਲ – ਫੁਲਦਾਰ ਪੌਦਿਆਂ (Angiosperms) ਵਿਚ ਫੁੱਲ ਲਿੰਗੀ ਜਣਨ ਵਿਚ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਫੁੱਲਾਂ ਦੀ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਨਾਲ ਬੀਜ ਬਣਦੇ ਹਨ । ਫੁੱਲ ਵਿਚ ਇਕ ਆਧਾਰੀ ਭਾਗ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਉੱਪਰ ਫੁੱਲ ਦੇ ਸਾਰੇ ਭਾਗ ਲੱਗੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਸ ਨੂੰ ਫੁਲ ਆਸਨ (Thalamus) ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਫੁੱਲ ਦੇ ਮੁੱਖ ਰੂਪ ਵਿਚ ਚਾਰ ਭਾਗ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
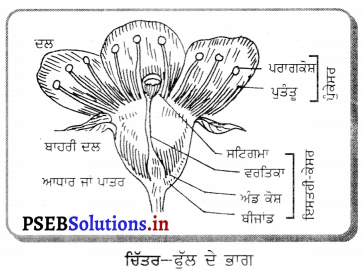
- ਬਾਹਰੀ ਦਲਪੁੰਜ ਜਾਂ ਹਰੀਆਂ ਪੱਤੀਆਂ – ਇਹ ਫੁੱਲ ਦਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਹਰੀ ਭਾਗ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਹਰੇ ਪੱਤਿਆਂ । ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿਚ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਬਾਹਰੀ ਦਲ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਕਲੀ ਦੀ ਅਵਸਥਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਫੁੱਲ ਦੀ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਦਲਪੁੰਜ ਜਾਂ ਰੰਗਦਾਰ ਪੱਤੀਆਂ – ਬਾਹਰੀ ਦਲਪੁੰਜ ਦੇ ਅੰਦਰਲੇ ਭਾਗ ਨੂੰ ਦਲਪੁੰਜ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਹਰ ਅੰਗ ਪੰਖੁੜੀ ਜਾਂ ਦਲ ਕਹਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸਦਾ ਰੰਗ ਵੱਖ-ਵੱਖ ਫੁੱਲਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੱਖ-ਵੱਖ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦਾ ਕਾਰਜ ਕੀਟਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਆਕਰਸ਼ਿਤ ਕਰਕੇ ਪਰਾਗਣ ਵਿਚ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਕਰਨਾ ਹੈ ।
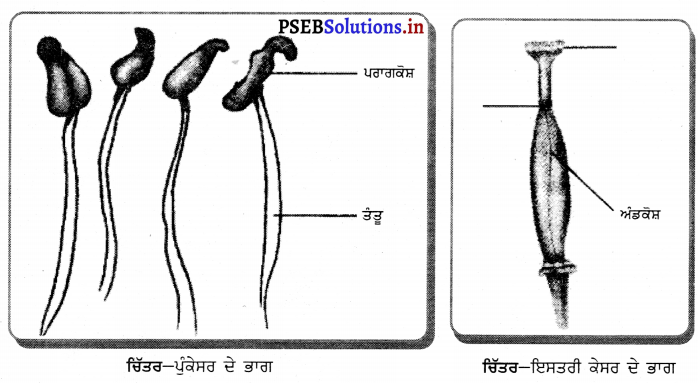
- ਪੁੰਕੇਸਰ – ਇਹ ਫੁੱਲ ਦਾ ਬਾਹਰੋਂ ਤੀਸਰਾ ਭਾਗ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਦੇ ਹਰ ਅੰਗ ਨੂੰ ਪੁੰਕੇਸਰ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਪੁੰਕੇਸਰ ਦੇ ਮੁੱਖ ਦੋ ਭਾਗ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ-ਪਰਾਗਕੋਸ਼ ਅਤੇ ਪਗਡੰਡੀ । ਪਰਾਗਕੋਸ਼ ਯੋਜੀ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪਰਾਗ ਕੋਸ਼ ਨਾਲ ਜੁੜਿਆ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਪਰਾਗ ਕੋਸ਼ ਦੇ ਅੰਦਰ ਪਰਾਗਕਣ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਬੀਜ ਬਣਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਸਤਰੀ ਕੇਸਰ – ਇਹ ਫੁੱਲ ਦਾ ਮਾਦਾ ਭਾਗ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਦੇ ਹਰ ਅੰਗ ਨੂੰ ਇਸਤਰੀ ਕੇਸਰ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਸਦੇ ਤਿੰਨ ਭਾਗ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ-(1) ਸਟਿਗਮਾ (2) ਸਟਾਇਲ (3) ਅੰਡਕੋਸ਼ । ਅੰਡਕੋਸ਼ ਦੇ ਅੰਦਰ ਬੀਜ ਅੰਡ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਪਰਾਗਣ ਤੋਂ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਕਰਕੇ ਪੌਦਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਬੀਜ ਬਣਾਉਣ ਤੱਕ ਸਾਰੀਆਂ ਅਵਸਥਾਵਾਂ ਦੱਸੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
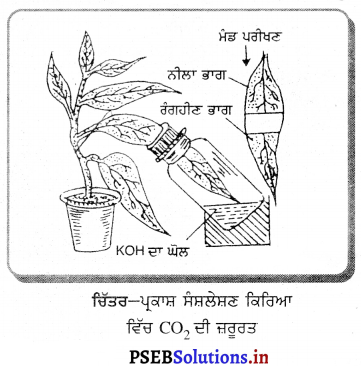
ਪਰਾਗਕੋਸ਼ (Pollensac) ਤੋਂ ਪਰਾਗਕਣਾਂ (Pollengrains) ਦਾ ਸਟਿਗਮਾ ਤਕ ਸਥਾਨਾਂਤਰਨ ਪਰਾਗਣ (Pollination) ਕਹਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਫੁੱਲ ਦੇ ਪੁੰਕੇਸਰ ਵਿਚ ਪਰਾਗਕੋਸ਼ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ, ਜੋ ਪਰਾਗਕਣ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਸਤਰੀ ਕੇਸਰ ਦੇ ਤਿੰਨ ਭਾਗ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ-ਅੰਡਕੋਸ਼ (Ovary), ਸਟਾਇਲ (Style) ਅਤੇ ਸਟਿਗਮਾ (Stigma) । ਪਰਾਗਣ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਪਰਾਗਕਣ ਤੋਂ ਇਕ ਨਲੀ ਨਿਕਲਦੀ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਪਰਾਗਨਲੀ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਗਨਲੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਦੋ ਨਰ ਯੁਗਮਕ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਇਕ ਨਰ ਯੁਜ ਪਰਾਗਨਲੀ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੋਇਆ ਬੀਜ ਅੰਡ ਤਕ ਪੁੱਜ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਬੀਜ ਅੰਡ ਨਾਲ ਮੇਲ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਨਾਲ ਯੁਗਮਜ਼ ਬਣਦਾ ਹੈ । ਦੂਸਰਾ ਨਰ ਯੁਗਮਕ ਦੋ ਧਰੁਵੀ ਕੇਂਦਰਕਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਮਿਲ ਕੇ ਪ੍ਰਾਥਮਿਕ ਐਂਡਸਪਰਮ (ਭਰੂਣਕੋਸ਼) ਕੇਂਦਰਕ ਬਣਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਤੋਂ ਅੰਤ ਵਿਚ ਐਂਡੋਸਪਰਮ ਬਣਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਉੱਚ ਵਰਗੀ (ਐਂਜੀਓਸਪਰਮੀ) ਪੌਦੇ ਦੋਹਰੀ ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਪ੍ਰਦਰਸ਼ਿਤ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਫੁੱਲ ਦੀਆਂ ਪੰਖੜੀਆਂ, ਪੁੰਕੇਸਰ, ਸਟਾਇਲ ਅਤੇ ਸਟਿਗਮਾ ਡਿਗ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ । ਬਾਹਰੀ ਦਲ ਸੁੱਕ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਅੰਡਕੋਸ਼ ਤੇ ਲੱਗਿਆ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਅੰਡਕੋਸ਼ ਤੇਜ਼ੀ ਨਾਲ ਵਾਧਾ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਮੌਜੂਦ ਸੈੱਲ ਵਿਭਾਜਿਤ ਹੋ ਕੇ ਵਾਧਾ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ਅਤੇ ਬੀਜ ਦਾ ਬਣਨਾ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਬੀਜ ਵਿਚ ਇਕ ਭਰੁਣ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਭਰੂਣ ਵਿਚ ਇੱਕ ਛੋਟੀ ਜੜ੍ਹ (ਮੂਲ ਜੜ੍ਹ), ਇੱਕ ਛੋਟਾ ਪ੍ਰੋਹ (ਕੁਰ) ਅਤੇ ਬੀਜ ਪੱਤਰ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਬੀਜ ਪੱਤਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਭੋਜਨ ਸੰਚਿਤ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
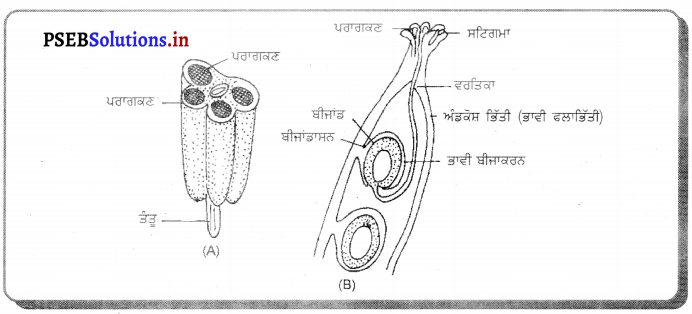
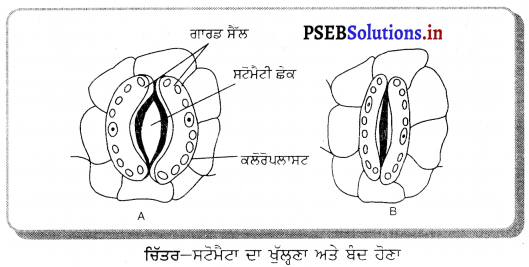
ਚਿੱਤਰ – (A) ਪਰਾਗਕੋਸ਼ ਦੀ ਰਚਨਾ (ਸਿਖਰ ਕੱਟਿਆ ਹੋਇਆ) (B) ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਦੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਇਸਤਰੀ ਕੇਸਰ ਦੀ ਲੰਮੇਦਾਅ ਕਾਟ | ਸਮੇਂ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਬੀਜ ਸਖ਼ਤ ਹੋ ਕੇ ਸੁੱਕ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਬੀਜ ਪ੍ਰਤਿਕੂਲ ਹਾਲਤਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਜੀਵਤ ਰਹਿ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ ! ਅੰਡਕੋਸ਼ ਦੀ ਦੀਵਾਰ ਵੀ ਸਖ਼ਤ ਹੋ ਸਕਦੀ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਇਕ ਫਲੀ ਬਣ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ । ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਸਾਰੇ ਅੰਡਕੋਸ਼ ਨੂੰ ਫਲ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਬਾਹਰੀ ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਅਤੇ ਅੰਦਰੂਨੀ ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਦਾ ਕੀ ਅਰਥ ਹੈ ? ਪਰ ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਅਤੇ ਸਵੈ-ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਵਿਚ ਕੀ ਅੰਤਰ ਹੈ ? ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਕਿਹੜਾ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਲਾਭਦਾਇਕ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਬਾਹਰੀ ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਅਤੇ ਅੰਦਰੂਨੀ ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ – ਜਦੋਂ ਨਰ ਅਤੇ ਮਾਦਾ ਆਪਣੇ-ਆਪਣੇ ਸ਼ੁਕਰਾਣੂ ਅਤੇ ਅੰਡੇ ਸਾਰੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਹਰ ਪਾਣੀ ਵਿਚ ਛੱਡ ਦਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ਅਤੇ ਸ਼ੁਕਰਾਣੂ ਅਤੇ ਅੰਡੇ ਦਾ ਸੰਯੋਗ ਸਰੀਕ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਹਰ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਤਾਂ ਇਸ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਨੂੰ ਬਾਹਰੀ ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਜਿਵੇਂ-ਡੱਡੂ ਅਤੇ ਮੱਛੀਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ । ਅੰਦੂਰਨੀ ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਵਿਚ ਨਰ ਆਪਣੇ ਸ਼ੁਕਰਾਣੁ ਮਾਦਾ ਦੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਛੱਡਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਸ਼ੁਕਰਾਣੁ ਮਾਦਾ ਦੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਡੇ ਨਾਲ ਸੰਯੋਗ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ, ਜਿਵੇਂ ਪੰਛੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਥਣਧਾਰੀਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ।
ਪਰ ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਅਤੇ ਸਵੈ-ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ-
ਪਰ ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ (Cross Fertilization) – ਇਹ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਜੀਵਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਥੇ ਨਰ ਅਤੇ ਮਾਦਾ ਵੱਖ-ਵੱਖ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਦੋ-ਲਿੰਗੀ ਜੰਤੂਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਇਹ ਹੋ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ ਜੇ ਜਣਨ ਅੰਗ ਵੱਖ-ਵੱਖ ਸਮੇਂ ਤੇ ਪਰਿਪੱਕ ਹੋਣ । ਇਸ ਨਾਲ ਜੀਵਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਿੰਨਤਾਵਾਂ ਆਉਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
ਸਵੈ-ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ (Self Fertilization) ਦੋ-ਲਿੰਗੀ ਜੀਵਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਜਿੱਥੇ ਨਰ ਅਤੇ ਮਾਦਾ ਜਣਨ ਅੰਗ ਇਕੋ ਸਮੇਂ ਤੇ ਹੀ ਪਰਿਪੱਕ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ, ਸਵੈ-ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਵਿਧੀ ਵਿਚ ਪਿਤਰੀ ਗੁਣ ਪੀੜ੍ਹੀ-ਦਰ-ਪੀੜ੍ਹੀ ਕਾਇਮ ਰਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਪਰਪਰਾਗਣ ਵਿਚ ਜੀਵਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਵਿਵਿਧਤਾਵਾਂ ਪੈਦਾ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ਜਿਸ ਨਾਲ ਜੀਵਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਸਮਰੱਥਾ ਵੱਧਦੀ ਹੈ । ਜੀਵਨ ਦੇ ਨਵੇਂ ਯੁਗਮ ਬਣਨ ਵਿਚ ਅਨੁਵੰਸ਼ਿਕ ਭਿੰਨਤਾਵਾਂ ਦਾ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 5.
ਅਲਿੰਗੀ ਜਣਨ ਦੀਆਂ ਵੱਖ-ਵੱਖ ਵਿਧੀਆਂ ਕਿਹੜੀਆਂ ਹਨ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਅਲਿੰਗੀ ਪ੍ਰਜਣਨ ਵਿਚ ਜੀਵ ਖ਼ੁਦ ਗੁਣਿਤ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਅਲਿੰਗੀ ਪ੍ਰਜਣਨ ਦੀਆਂ ਵੱਖ-ਵੱਖ ਵਿਧੀਆਂ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਹਨ-
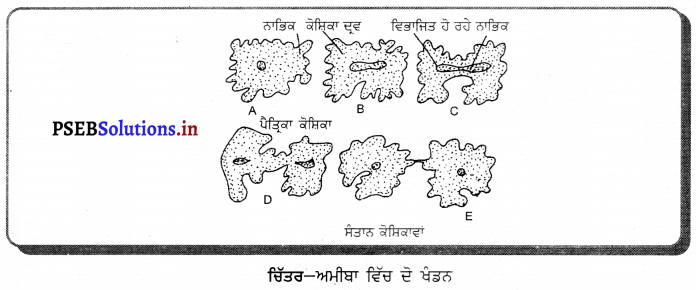
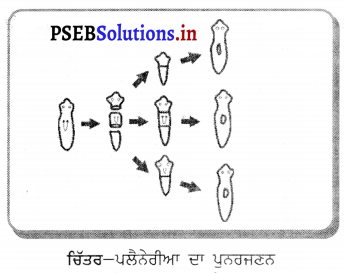
(1) ਦੋ ਖੰਡਨ (Binary fission) – ਦੋ ਖੰਡਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਜੀਵ ਦਾ ਸਰੀਰ ਲੰਬਾਈ ਦੇ ਰੁਖ ਤੋਂ ਦੋ ਬਰਾਬਰ ਭਾਗਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਵਿਭਾਜਿਤ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਹਰ ਭਾਗ ਜਣਕ ਦੇ ਸਮਾਨ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਜਣਨ ਦੀ ਇਹ ਵਿਧੀ ਪੋਟੋਜ਼ੋਆ (ਅਮੀਬਾ, ਪੈਰਾਮੀਸ਼ੀਅਮ ਆਦਿ) ਵਿਚ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਇਹ ਵਿਧੀ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਹੀ ਸੈੱਲ ਵਿਭਾਜਨ ਦੀ ਵਿਧੀ ਹੈ ਜਿਸਦੇ ਨਤੀਜੇ ਵਜੋਂ ਸੰਤਾਨ ਸੈੱਲਾਂ ਦਾ ਵੱਖਰੇਵਾਂ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਬਹੁਕੋਸ਼ੀ ਜੰਤੂਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਵੀ ਇਸ ਵਿਧੀ ਨੂੰ ਦੇਖਿਆ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ । ਜਿਵੇਂ-ਸੀ-ਐਨੀਮੋਨ ਵਿਚ ਲੰਬਵਤ ਖੰਡਨ ਅਤੇ ਪਲੇਨੇਰੀਆ ਵਿਚ ਅਨੁਪ੍ਰਥ ਖੰਡਨ ।
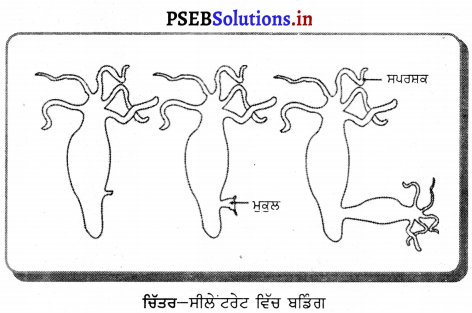
(2) ਡੰਗ (Budding) – ਬਡਿੰਗ ਜਾਂ ਮੁਕੁਲਨ ਇਕ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਦੀ ਅਲਿੰਗੀ ਜਣਨ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਵਿਚ ਨਵਾਂ ਜੀਵ ਜੋ ਤੁਲਨਾ ਵਿਚ ਛੋਟੇ ਪੁੰਜ ਦੇ ਸੈੱਲਾਂ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਨਿਕਲਦਾ ਹੈ, ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਵਿਚ ਜਨਕ ਜੀਵ ਵਿਚ ਬੱਡ (Bud) ਜਾਂ ਮੁਕੁਲ ਬਣਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਬੱਡ ਜਾਂ ਮੁਕੁਲ ਅਲੱਗ ਹੋਣ ਤੋਂ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਜਨਕ ਦਾ ਰੂਪ ਧਾਰਨ ਕਰ ਲੈਂਦਾ ਹੈ , ਜਿਵੇਂ-ਬਾਹਰੀ ਮੁਕੁਲਨ ਵਿਚ ਜਾਂ ਜਨਕ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਖ ਹੋਣ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਆਂਤਰਿਕ ਮੁਕੁਲਨ ਵਿਚ ।
ਬਾਹਰੀ ਮੁਕੁਲਨ ਸਪੰਜ, ਸੀਲੇਂਟਰੇਟਾ (ਜਿਵੇਂ ਹਾਈਡਰਾ), ਚਪਟੇ ਕ੍ਰਿਮੀ ਅਤੇ ਟਿਉਨੀਕੇਟ ਵਿਚ ਮਿਲਦਾ ਹੈ ਪਰ ਕੁੱਝ ਸੀਲੇਟਰੇਟ ਜਿਵੇਂ ਔਬੇਲੀਆਂ ਪੋਲੀਪ ਦੀ ਤੁਲਨਾ ਵਿਚ ਮੈਡੂਯੁਸੀ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
(3) ਖੰਡਨ (Fragmentation) – ਸਪਾਈਰੋਗਾਈਰਾ ਵਰਗੇ ਕੁੱਝ ਜੀਵ ਪੂਰਨ ਵਿਕਸਿਤ ਹੋਣ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਆਮ ਕਰਕੇ ਦੋ ਜਾਂ ਵੱਧ ਭਾਗਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਟੁੱਟ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਭਾਗ ਵਾਧਾ ਕਰਕੇ ਪੂਰਨ ਵਿਕਸਿਤ ਜੀਵ ਬਣ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ । ਖੰਡਨ ਚਪਟੇ ਫ਼ਿਮੀ, ਰਿਬਨ ਕ੍ਰਿਮੀ ਅਤੇ ਐਨੇਲੀਡਾ ਸੰਘ ਦੇ ਪਾਣੀਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਵੀ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
(4) ਬਹੁ-ਖੰਡਨ (Multiple fission) – ਕਦੇ-ਕਦੇ । ਪ੍ਰਤੀਕੂਲ ਹਾਲਾਤਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਸੈੱਲ ਦੇ ਚਾਰੇ ਪਾਸੇ ਇਕ ਸੁਰੱਖਿਆ ਪਰਤ ਜਾਂ ਭਿੱਤੀ ਬਣ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ । ਅਜਿਹੀ ਅਵਸਥਾ ਨੂੰ ਪੁਟੀ (cyst) ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਪੁਟੀ ਦੇ ਅੰਦਰ ਸੈੱਲ ਕਈ ਵਾਰ ਵਿਭਾਜਿਤ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਨਾਲ ਬਹੁਤ ਸਾਰੇ ਸੰਤਾਨ ਸੈੱਲ ਬਣ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ਅਜਿਹੀ ਪ੍ਰਕਿਰਿਆ ਨੂੰ ਬਹੁਖੰਡਨ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਪਟੀ (cyst) ਦੇ ਫਟਣ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਬਹੁਤ ਸਾਰੇ ਸੈੱਲ ਬਾਹਰ ਨਿਕਲ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।

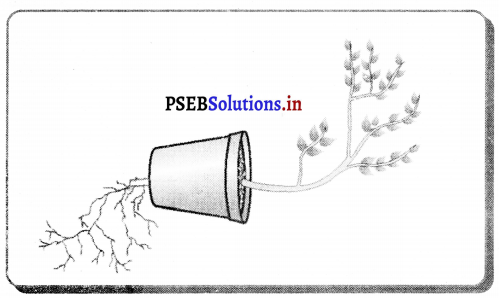
(5) ਕਾਇਕ ਪ੍ਰਜਣਨ (Vegetative reproduction) – ਜਦੋਂ ਪੌਦੇ ਦੇ ਕਿਸੇ ਬਨਸਪਤੀ ਅੰਗ ਜਿਵੇਂ-ਪੱਤਾ, ਤਣਾ ਅਤੇ ਜੜ੍ਹ ਤੋਂ ਨਵਾਂ ਪੌਦਾ ਉਗਾਇਆ ਜਾ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੋਵੇ ਤਾਂ ਇਸ ਪ੍ਰਕਿਰਿਆ ਨੂੰ ਇਕ ਪ੍ਰਜਣਨ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 6.
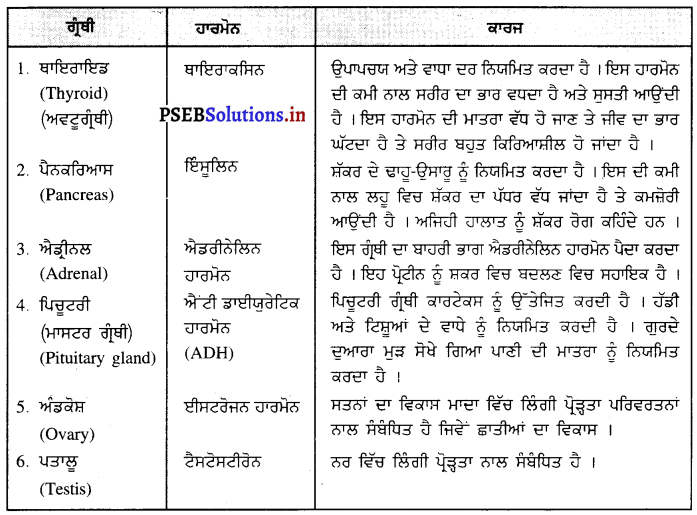
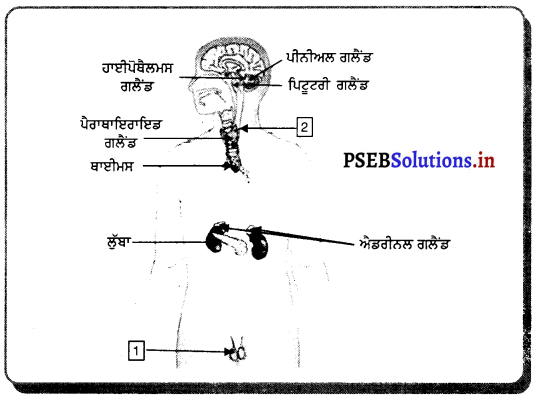
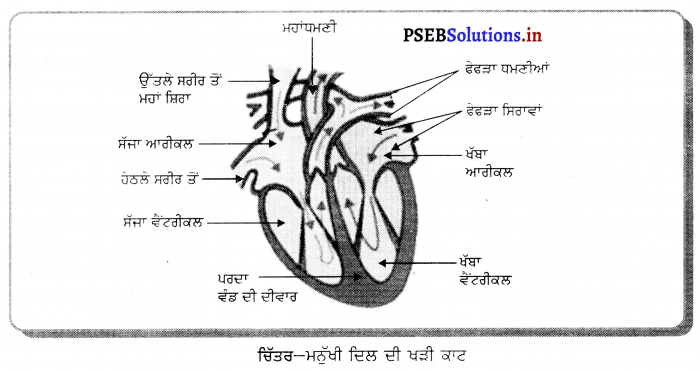
ਮਨੁੱਖ ਦੀ ਨਰ ਜਣਨ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਦਾ ਚਿੱਤਰ ਵਰਣਨ ਕਰੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਨਰ ਮਨੁੱਖ ਵਿਚ ਜੰਘਨਾਸਥੀ ਖੇਤਰ ਵਿਚ ਇਕ ਮਾਂਸਲ ਸੰਰਚਨਾ ਪੀਨਸ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਸਦੇ ਅੰਦਰ ਮੂਤਰਵਾਹਿਣੀ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ | ਪੀਨਸ ਦੇ ਹੇਠਾਂ ਉਸਦੀ ਜੜ੍ਹ ਵਿਚ ਇਕ ਮਾਂਸਲ ਥੈਲੀ ਜਾਂ ਪਤਾਲੂ ਥੈਲੀ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ
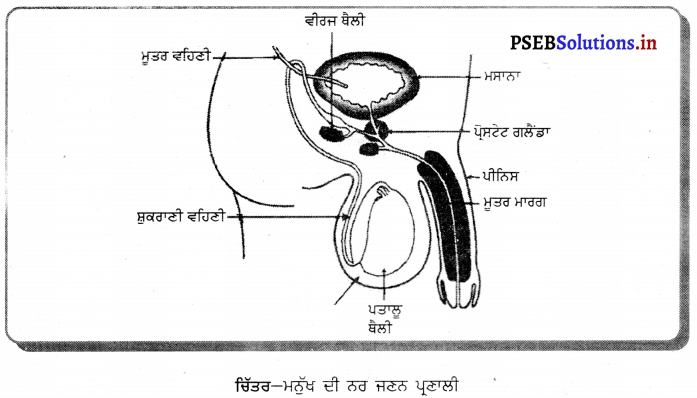
ਵਿਚ ਅੰਡਾਕਾਰ ਸੰਰਚਨਾਵਾਂ ਪਤਾਲੂ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਪਤਾਲੂ ਨਰ ਯੁਗਮਕ ਸ਼ੁਕਰਾਣੂ ਦਾ ਨਿਰਮਾਣ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਪਤਾਲੂ ਵਿਚ ਇਕ ਖ਼ਾਸ ਸੰਰਚਨਾ ਸ਼ੁਕਰਾਣੂ ਵਹਿਣੀ ਪਾਇਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਵਿਚ ਸ਼ੁਕਰਾਣੂ ਦੇ ਪੋਸ਼ਣ ਦੇ ਲਈ ਚਿਪਚਿਪਾ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਪੈਦਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਚਿਪਚਿਪੇ ਪਦਾਰਥ (ਵੀਰਜ) ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਸ਼ੁਕਰਾਣੂ ਇੱਕ ਸੰਕਰੀ ਨਲੀ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਮੂਤਰ ਵਾਹਿਣੀ ਵਿਚ ਪੁੱਜਦੇ ਹਨ । ਜਿੱਥੋਂ ਪੀਨਸ ਦੀ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਨਾਲ ਮਾਦਾ ਦੀ ਯੋਨੀ ਵਿਚ ਛੱਡ ਦਿੱਤੇ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ । ਪੀਨਸ ਮੁਤਰ ਸ਼ੁਕਰਾਣੂ ਯੁਕਤ ਵੀਰਜ ਦੋਨਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਹੀ ਬਾਹਰ ਕੱਢਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 7.
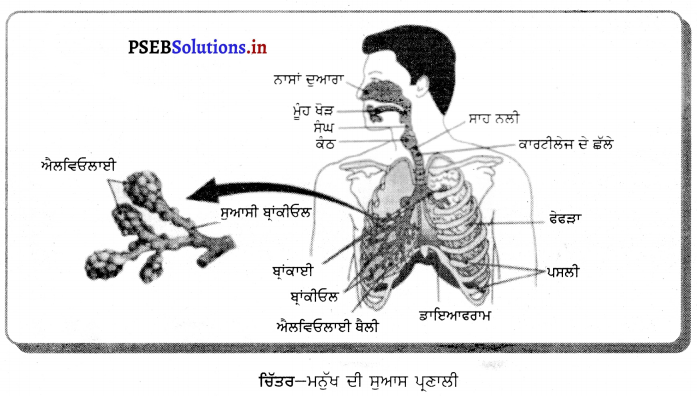
ਮਨੁੱਖ ਦੀ ਮਾਦਾ ਜਣਨ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਦਾ ਵਰਣਨ ਕਰੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
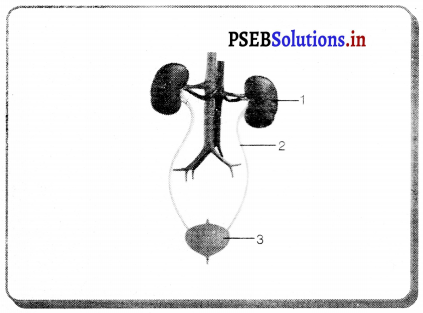
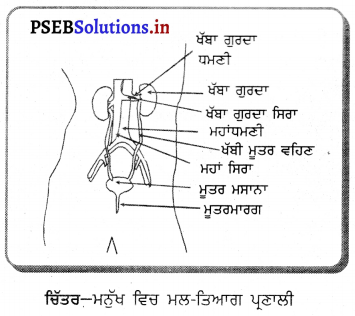
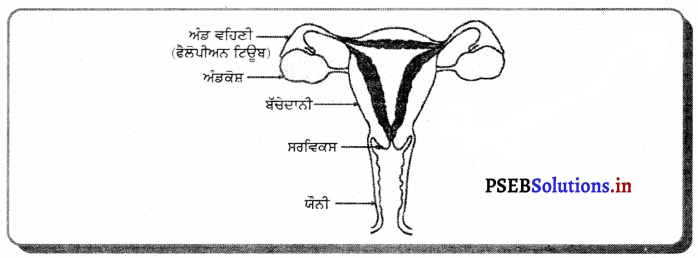
ਮਨੁੱਖ ਦੀ ਮਾਦਾ ਜਣਨ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਦੇ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਭਾਗ ਹਨ-
(1) ਅੰਡਕੋਸ਼ (Ovary) – ਮਨੁੱਖੀ ਮਾਦਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਦੋ ਅੰਡਕੋਸ਼ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ਜੋ ਬਹੁਤ ਛੋਟੇ ਆਕਾਰ ਦੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਅੰਡਕੋਸ਼ ਵਿਚ ਅੰਡੇ ਬਣਦੇ ਹਨ । ਅੰਡਕੋਸ਼ ਦੇ ਅੰਦਰ ਦੀ ਸਤਹਿ ਤੇ ਐਪੀਥੀਲੀਅਮ ਸੈੱਲਾਂ ਦੀ ਪਤਲੀ ਪਰਤ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਜਣਨ ਐਪੀਥੀਲੀਅਮ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਸ ਦੇ ਸੈੱਲ ਵਿਭਾਜਿਤ ਹੋ ਕੇ ਫੋਲੀਕਲ ਅਤੇ ਅੰਡਾ ਬਣਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ । ਅੰਡਕੋਸ਼ ਦੀ ਗੁਹਾ ਵਿਚ ਸੰਯੋਜੀ ਟਿਸ਼ੂ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਸਟਰੋਮਾ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਹਰ ਫੋਕਲ ਵਿਚ ਇੱਕ ਜਣਨ ਸੈੱਲ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਸਦੇ ਚਾਰੇ ਪਾਸੇ ਸਟਰੋਮਾ ਦੇ ਸੈੱਲ ਰਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਅਰਧ ਸੁਤਰੀ ਵਿਭਾਜਨ ਦੇ ਨਤੀਜੇ ਵਜੋਂ ਜਣਨ ਸੈੱਲ ਅੰਡੇ ਦਾ ਨਿਰਮਾਣ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਐਸਟਰੋਜਨ ਅਤੇ ਪ੍ਰੋਜੈਸਟਰੋਨ ਨਾਮਕ ਦੋ ਹਾਰਮੋਨ ਅੰਡਕੋਸ਼ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਸਾਵਿਤ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ਜੋ ਮਾਦਾ ਵਿਚ ਪ੍ਰਜਣਨ ਸੰਬੰਧੀ ਵਿਭਿੰਨ ਕਿਰਿਆਵਾਂ ਦਾ ਨਿਯੰਤਰਨ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
(2) ਅੰਡ ਵਹਿਣੀ (Fallopian Tube) – ਇਹ ਰਚਨਾ ਨਲਿਕਾ ਜਾਂ ਟਿਊਬ ਵਰਗੀ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਸਦਾ ਇਕ ਸਿਰਾ ਗਰਭਕੋਸ਼ ਨਾਲ ਜੁੜਿਆ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਦੂਸਰਾ ਸਿਰਾ ਅੰਡਕੋਸ਼ ਦੇ ਨੇੜੇ ਖੁੱਲ੍ਹਾ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸਦੇ ਸਿਰੇ ਤੇ ਝਾਲਦਾਰ
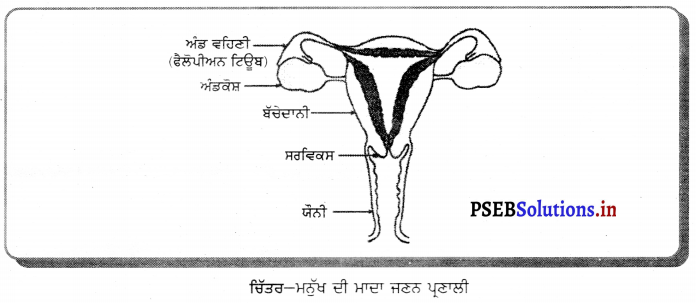
ਰਚਨਾ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਫੌਰੀ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਅੰਡਕੋਸ਼ ਤੋਂ ਜਦੋਂ ਅੰਡਾ ਨਿਕਲਦਾ ਹੈ ਤਾਂ ਫਿਬਰੀ ਦੀ ਸੰਕੁਚਨ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਅੰਡ ਵਹਿਣੀ ਵਿਚ ਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਥੋਂ ਗਰਭਕੋਸ਼ ਵੱਲ ਵੱਧਦਾ ਹੈ । ਅੰਡ ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਅੰਡ ਵਹਿਣੀ ਵਿਚ ਹੀ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਜੇ ਅੰਡੇ ਦਾ ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਤਾਂ ਇਹ ਗਰਭਕੋਸ਼ ਤੋਂ ਹੋ ਕੇ ਯੋਨੀ ਵਿਚ ਅਤੇ ਮਾਹਵਾਰੀ ਯੌਨੀ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਬਾਹਰ ਨਿਕਲ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
(3) ਗਰਭਕੋਸ਼ ਜਾਂ ਬੱਚੇਦਾਨੀ (Uterus) – ਇਹ ਇਕ ਮਾਂਸਲ ਰਚਨਾ ਹੈ । ਫੈਲੋਪੀਅਨ ਨਲਿਕਾਵਾਂ ਇਸਦੇ ਦੋਨੋਂ ਪਾਸੇ ਉੱਪਰਲੇ ਭਾਗਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਖੁੱਲ੍ਹਦੀ ਹੈ । ਗਰਭਕੋਸ਼ ਦਾ ਹੇਠਲਾ ਸਿਰਾ ਘੱਟ ਚੌੜਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਯੋਨੀ ਵਿਚ ਖੁੱਲਦਾ ਹੈ । ਗਰਭਕੋਸ਼ ਦੇ ਅੰਦਰ ਦੀ ਦੀਵਾਰ ਐਂਡਰੋਮੀਟਰੀਅਮ ਦੀ ਬਣੀ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਗਰਭਕੋਸ਼ ਦਾ ਮੁੱਖ ਕਾਰਜ ਨਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ਿਤ ਅੰਡੇ ਨੂੰ ਵਾਧਾ ਕਾਲ ਵਿਚ ਜਦੋਂ ਤੱਕ ਕਿ ਗਰਭ ਵਿਕਸਿਤ ਹੋ ਕੇ ਸ਼ਿਸ਼ੂ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿਚ ਜਨਮ ਨਾ ਲੈ ਲਵੇ, ਸਹਾਰਾ ਅਤੇ ਭੋਜਨ ਪ੍ਰਦਾਨ ਕਰਨਾ ਹੈ ।
(4) ਯੌਨੀ (Vagina) – ਇਹ ਮਾਂਸਲ ਨਲਿਕਾ ਵਰਗੀ ਰਚਨਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸਦਾ ਪਿਛਲਾ ਭਾਗ ਗਰਭਕੋਸ਼ ਦੀ ਸ੍ਰੀਵਾ ਵਿਚ ਖੁੱਲ੍ਹਦਾ ਹੈ । ਮਾਦਾ ਵਿਚ ਮੂਤਰ ਨਿਸ਼ਕਾਸਨ ਲਈ ਵੱਖ ਛੇਦ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਜੋ ਯੌਨੀ ਵਿਚ ਖੁਲਦਾ ਹੈ ।
(5) ਭਗ (Vulva) – ਯੋਨੀ ਬਾਹਰ ਵੱਲ ਇੱਕ ਸੁਰਾਖ ਵਿਚ ਖੁਲ੍ਹਦੀ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਭਗ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 8.
(ਉ) ਪਰਾਗਣ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਨਾਲੋਂ ਕਿਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਭਿੰਨ ਹੈ ?
(ਅ) ਫੁੱਲ ਦੇ ਨਰ ਅਤੇ ਮਾਦਾ ਜਣਨ ਅੰਗਾਂ ਦਾ ਅੰਕਿਤ ਚਿੱਤਰ ਬਣਾਓ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(ੳ) ਪਰਾਗਣ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਅਤੇ ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਵਿਚ ਅੰਤਰ –
| ਪਰਾਗਣ ਕਿਰਿਆ (Pollination) | ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਕਿਰਿਆ (Fertilization) |
| (1) ਉਹ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਜਿਸ ਵਿਚ ਪਰਾਗਕਣ ਇਸਤਰੀ-ਕੇਸਰ ਦੇ ਸਟਿਗਮਾ ਤੱਕ ਪੁੱਜਦੇ ਹਨ, ਪਰਾਗਣ ਕਹਾਉਂਦੀ ਹੈ । | (1) ਉਹ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਜਿਸ ਵਿਚ ਨਰ ਯੁਗਮਕ ਅਤੇ ਮਾਦਾ ਯੁਗਮਕ ਮਿਲ ਕੇ ਯੁਗਮਜ ਬਣਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ, ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਕਹਾਉਂਦੀ ਹੈ । |
| (2) ਇਹ ਜਣਨ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਦਾ ਪਹਿਲਾ ਚਰਨ ਹੈ । | (2) ਇਹ ਜਣਨ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਦਾ ਦੂਸਰਾ ਚਰਨ ਹੈ । |
| (3) ਪਰਾਗਣ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਦੋ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਦੀ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ-ਸਵੈ-ਪਰਾਗਣ ਅਤੇ ਪਰ-ਪਰਾਗਣ । | (3) ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਵੀ ਦੋ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਦੀ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ-ਬਾਹਰੀ ਅਤੇ ਅੰਦਰੂਨੀ ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਕਿਰਿਆ । |
| (4) ਪਰਾਗਕਣਾਂ ਦੇ ਸਥਾਨਾਂਤਰਨ ਦੇ ਲਈ ਵਾਹਕਾਂ ਦੀ ਲੋੜ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । | (4) ਇਸ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਵਿਚ ਵਾਹਕਾਂ ਦੀ ਕੋਈ ਲੋੜ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦੀ । |
| (5) ਅਨੇਕ ਪਰਾਗਕਣਾਂ ਦਾ ਨੁਕਸਾਨ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । | (5) ਇਸ ਵਿਚ ਪਰਾਗਕਣਾਂ ਦਾ ਨੁਕਸਾਨ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦਾ । |
| (6) ਇਸ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਵਿਚ ਖ਼ਾਸ ਲੱਛਣਾਂ ਦੀ ਲੋੜ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । | (6) ਇਸ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਵਿਚ ਖ਼ਾਸ ਲੱਛਣਾਂ ਦੀ ਲੋੜ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦੀ । |
(ਅ) ਫੁੱਲ ਦਾ ਜਣਨ ਅੰਗ – ਪੁੰਕੇਸਰ ।
ਫੁੱਲ ਦਾ ਮਾਦਾ ਜਣਨ ਅੰਗ – ਇਸਤਰੀ-ਕੇਸਰ ।
ਛੋਟੇ ਉੱਤਰਾਂ ਵਾਲੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ (Short Answer Type Questions)
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਕਾਇਕ ਪ੍ਰਜਣਨ ਦੇ ਲਾਭ ਦੱਸੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਕਾਇਕ ਪ੍ਰਜਣਨ ਦੇ ਲਾਭ-
- ਸਾਰੇ ਨਵੇਂ ਪੌਦੇ ਮਾਤਰੀ ਪੌਦੇ ਦੇ ਸਮਾਨ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਸ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਇੱਕ ਵਧੀਆ ਗੁਣਾਂ ਵਾਲੇ ਪੌਦਿਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਕਲਮ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਉਸਦੇ ਵਰਗੇ ਹੀ ਕਈ ਪੌਦੇ ਤਿਆਰ ਕੀਤੇ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਫਲਾਂ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪੈਦਾ ਸਾਰੇ ਬੀਜ ਇੱਕੋ ਜਿਹੇ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਪਰ ਕਾਇਕ ਪ੍ਰਜਣਨ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪੈਦਾ ਪੌਦਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਪੂਰਨ ਸਮਾਨਤਾ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਕਾਇਕ ਪ੍ਰਜਣਨ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਨਵੇਂ ਪੌਦੇ ਥੋੜ੍ਹੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਵਿਚ ਹੀ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਉਹ ਪੌਦੇ ਜੋ ਬੀਜ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਸਰਲਤਾ ਨਾਲ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਨਹੀਂ ਕੀਤੇ ਜਾ ਸਕਦੇ, ਕਾਇਕ ਪ੍ਰਜਣਨ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਕੀਤੇ ਜਾ ਸਕਦੇ ਹਨ । ਕੇਲਾ, ਅੰਗੂਰ, ਸੰਤਰੇ ਆਦਿ ਦੀ ਖੇਤੀ ਇਸੇ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਕੀਤੀ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਪੁਨਰਜਣਨ ਕਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਪੁਨਰਜਣਨ – ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਕੱਟੇ ਹੋਏ ਕਿਸੇ ਭਾਗ ਵਿਚ ਪੂਰਨ ਜੀਵ ਬਣਾ ਲੈਣਾ ਜਾਂ ਫਿਰ ਤੋਂ ਵਿਕਸਿਤ ਕਰ ਲੈਣ ਦੀ ਸਮਰੱਥਾ ਨੂੰ ਪੁਨਰਜਣਨ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ | ਸਟਾਰ ਫਿਸ਼ ਕੱਟੀ ਹੋਈ ਬਾਜੂ ਨੂੰ ਫਿਰ ਤੋਂ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਕਰ ਲੈਂਦੀ ਹੈ । ਸਪਾਈਰੋਗਾਈਰਾ, ਹਾਈਡਰਾ, ਪਲੈਨੇਰੀਆ ਆਦਿ ਇਸ ਵਿਧੀ ਨਾਲ ਜਣਨ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਟਿਸ਼ੂ ਕਲਚਰ (Tissue Culture) ਕਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਟਿਸ਼ੂ ਕਲਚਰ (Tissue Culture) – ਇਸ ਵਿਧੀ ਵਿਚ ਪੌਦੇ ਦੇ ਟਿਸ਼ੂ ਜਾਂ ਵੱਧਦੇ ਸਿਰੇ ਦੀ ਨੋਕ ਤੋਂ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਸੈੱਲਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਵੱਖ ਕਰਕੇ ਨਵੇਂ ਪੌਦੇ ਉਗਾਏ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇੱਕ ਬੀਕਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਪੋਸ਼ਕ ਤੱਤਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਯੁਕਤ ਮਾਧਿਅਮ ਲੈ ਕੇ ਉਸ ਵਿਚ ਅਨੁਕੂਲ ਹਾਲਤਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਟਿਸ਼ੂ ਦੇ ਟੁੱਕੜੇ ਨੂੰ ਰੱਖ ਦਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਸ ਬੀਕਰ ਦੇ ਅੰਦਰ ਉਸ ਟਿਸ਼ੂ ਦਾ ਵਾਧਾ ਇੱਕ ਅਸੰਗਤ ਪਿੰਡ ਦੀ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ, ਜਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਕੈਲਸ (Callus) ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਕੈਲਸ ਦਾ ਥੋੜ੍ਹਾ ਜਿਹਾ ਭਾਗ ਇਕ ਹੋਰ ਮਾਧਿਅਮ ਵਿਚ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਵਿਚ ਬਹੁਤ ਹੀ ਛੋਟੇ ਪੌਦਿਆਂ ਦਾ ਵਿਭੇਦਨ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਬਹੁਤ ਹੀ ਛੋਟੇ ਪੌਦਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਗਮਲੇ ਜਾਂ ਮਿੱਟੀ ਵਿਚ ਰੋਪਿਤ ਕਰ ਦਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਸ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਇੱਕ ਨਵਾਂ ਪੌਦਾ ਬਣ ਕੇ ਤਿਆਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਰਾਈਜ਼ੋਪਸ ਵਿੱਚ ਬੀਜਾਣੁਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਨਵੇਂ ਜੀਵ ਕਿਸ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਪੈਦਾ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ? ਸਪੱਸ਼ਟ ਕਰੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਕਈ ਸਰਲ ਬਹੁਕੋਸ਼ੀ ਜੀਵਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਿਸ਼ਿਸ਼ਟ ਜਣਨ ਸੰਰਚਨਾਵਾਂ ਪਾਈਆਂ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਨਮੀ ਯੁਕਤ ਬੈਡ ਤੇ ਧਾਗੇ ਦੇ ਸਮਾਨ ਕੁਝ ਸੰਰਚਨਾਵਾਂ ਵਿਕਸਿਤ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਰਾਈਜ਼ੋਪਸ ਦੇ ਹਾਈਵੇ (Hyphae) ਹਨ । ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਹਾਈਵੇ ਦੇ ਸਿਰੇ ਤੇ ਗੋਲ ਸੂਖ਼ਮ ਗੁੱਛੇ ਬਣਦੇ ਹਨ ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਸਪੋਰੇਜੀਆ (Sporangia) ਆਖਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਗੁੱਛੇ ਬੀਜਾਣੂਧਾਨੀ ਹਨ ਜਿਸ ਵਿਚ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ ਸੈੱਲ ਜਾਂ ਬੀਜਾਣੂ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਬੀਜਾਣੂ ਵਾਧਾ ਕਰਕੇ ਰਾਈਜ਼ੋਪਸ ਦੇ ਨਵੇਂ ਜੀਵ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਬੀਜਾਣੂ ਦੇ ਚਾਰੇ ਪਾਸੇ ਇੱਕ ਮੋਟੀ ਕਿੱਤੀ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ਜੋ ਪ੍ਰਤੀਕੂਲ ਹਾਲਾਤਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਉਸਦੀ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਕਰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਨਮ ਸਤਹਿ ਦੇ ਸੰਪਰਕ ਵਿਚ ਆਉਣ ਤੇ ਇਹ ਵਾਧਾ ਕਰਨ ਲਗਦੇ ਹਨ ।
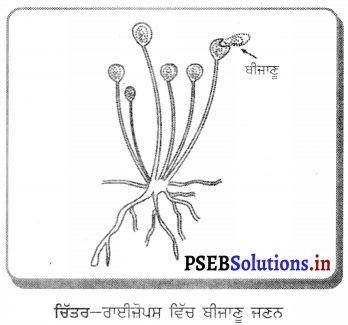
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 5.
ਮਾਹਵਾਰੀ ਦੇ ਬੰਦ ਹੋਣ ਦਾ ਕੀ ਕਾਰਨ ਹੈ ? ਚਿੱਤਰ-ਰਾਈਜ਼ੋਪਸ ਵਿੱਚ ਬੀਜਾਣੂ ਜਣਨ
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਗਰਭਕੋਸ਼ ਵਿਚ ਭਰੂਣ ਦੀ ਮੌਜੂਦਗੀ ਵਿਚ ਪਲੇਸੈਂਟਾ ਬਣਦਾ ਹੈ । ਪਲੇਸੈਂਟਾ ਐਸਟਰੋਜਨ ਅਤੇ ਪ੍ਰੋਜੇਸਟਰੋਜਨ ਹਾਰਮੋਨ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ਜੋ ਮਾਹਵਾਰੀ ਨੂੰ ਬੰਦ ਕਰ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 6.
ਗਰਭ ਧਾਰਨ ਕਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਿਤ ਅੰਡਾ ਬਾਰ-ਬਾਰ ਮਾਈਟੋਟਿਕ ਵਿਭਾਜਨ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਨਾਲ ਸੈੱਲਾਂ ਦਾ ਇੱਕ ਪੁੰਜ ਜਿਹਾ ਬਣਦਾ ਹੈ ਜੋ ਅੰਡਵਾਹਨੀ ਤੋਂ ਗਰਭਕੋਸ਼ ਤੱਕ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਥੇ ਇਹ ਗਰਭਕੋਸ਼ ਦੀਆਂ ਗਰਭ ਦੀਵਾਰਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਧਸ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਨੂੰ ਗਰਭ ਧਾਰਨ ਕਰਨਾ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 7.
ਮੈਨੋਪਾਜ਼ (Menopause) ਤੋਂ ਕੀ ਭਾਵ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਮੈਨੋਪਾਜ਼ – ਮਾਦਾ ਵਿਚ ਕੁਦਰਤੀ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਾਹਵਾਰੀ ਦੀ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਬੰਦ ਹੋਣ ਨੂੰ ਮੈਨੋਪਾਜ਼ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਮਨੁੱਖੀ ਮਾਦਾ ਵਿਚ ਇਹ 45-50 ਸਾਲ ਦੀ ਅਵਸਥਾ ਵਿਚ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਮੈਨੋਪਾਜ਼ ਦੇ ਬੰਦ ਹੋਣ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਇਸਤਰੀ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਜਨਮ ਨਹੀਂ ਦੇ ਸਕਦੀ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 8.
ਇੱਕ ਲਿੰਗੀ ਅਤੇ ਦੋ ਲਿੰਗੀ ਦੀ ਪਰਿਭਾਸ਼ਾ ਇੱਕ-ਇੱਕ ਉਦਾਹਰਨ ਦਿੰਦੇ ਹੋਏ ਲਿਖੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਇੱਕ ਲਿੰਗੀ – ਉਹ ਜੀਵ ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਨਰ ਅਤੇ ਮਾਦਾ ਸਪੱਸ਼ਟ ਰੂਪ ਨਾਲ ਵੱਖ-ਵੱਖ ਹੋਣ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਇੱਕ ਲਿੰਗੀ ਜੀਵ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਉਦਾਹਰਨ – ਮਨੁੱਖ ।
ਦੋ-ਲਿੰਗੀ – ਜਿਹੜੇ ਜੀਵਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਨਰ ਅਤੇ ਮਾਦਾ ਲਿੰਗ ਇਕੋ ਵੇਲੇ ਮੌਜੂਦ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ, ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਦੋ-ਲਿੰਗੀ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਉਦਾਹਰਨ – ਗੰਡੋਇਆ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 9.
ਪੁਰਸ਼ ਅਤੇ ਇਸਤਰੀ ਦੇ ਸੈਕੰਡਰੀ ਲਿੰਗੀ ਲੱਛਣਾਂ ਦਾ ਵਰਣਨ ਕਰੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(ਉ) ਨਰ ਦੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਦਿਖਾਈ ਦੇਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਪਰਿਵਰਤਨ-
- ਆਵਾਜ਼ ਵਿਚ ਭਾਰੀਪਣ ਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਦਾੜੀ ਅਤੇ ਮੁੱਛਾਂ ਉੱਗ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਜਣਨ ਅੰਗਾਂ ਤੇ ਵਾਲ ਉੱਗ ਆਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਪੀਨਸ ਦਾ ਆਕਾਰ ਵੱਧ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਦਿਨ ਜਾਂ ਰਾਤ ਦੇ ਸੁਪਨਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਉਸਦਾ ਅਕੜਾਅ ਵੱਧ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਮੋਡੇ ਚੌੜੇ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ | ਮਾਸਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਵਿਕਸਿਤ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਉਲਟ ਲਿੰਗ ਵੱਲ ਆਕਰਸ਼ਨ ਵੱਧ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
(ਅ) ਮਾਦਾ ਦੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਦਿਖਾਈ ਦੇਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਪਰਿਵਰਤਨ-
- ਜਣਨ ਅੰਗਾਂ ਤੇ ਵਾਲ ਉੱਗ ਆਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਛਾਤੀਆਂ ਵੱਡੀਆਂ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਮਹਾਮਾਰੀ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਕੁਲਿਆਂ ਦੇ ਆਸ-ਪਾਸ ਚਰਬੀ ਇਕੱਠੀ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਉਲਟ ਲਿੰਗ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਖਿੱਚ ਵੱਧ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਜਣਨ ਅੰਗਾਂ ਦਾ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 10.
ਅੰਡੇ ਅਤੇ ਸ਼ੁਕਰਾਣੂ ਵਿਚ ਕੀ ਅੰਤਰ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
| ਅੰਡੇ (Ovum) | ਸ਼ੁਕਰਾਣੂ (Sperm) |
| (1) ਇਹ ਮਾਦਾ ਜਣਨ ਸੈੱਲ ਹੈ । | (1) ਇਹ ਨਰ ਜਣਨ ਸੈੱਲ ਹੈ । |
| (2) ਇਹ ਸ਼ੁਕਰਾਣੂ ਦੀ ਤੁਲਨਾ ਵਿਚ ਆਕਾਰ ਵਿਚ ਵੱਡਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । | (2) ਇਹ ਅੰਡੇ ਦੀ ਤੁਲਨਾ ਵਿਚ ਆਕਾਰ ਵਿਚ ਛੋਟਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । |
| (3) ਇਸਦੀ ਪੂਛ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦੀ । | (3) ਇਸਦੀ ਪੁਛ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । |
(4) ਇਹ ਤੈਰ ਨਹੀਂ ਸਕਦੇ । |
(4) ਇਹ ਪੂਛ ਦੀ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਨਾਲ ਤੈਰ ਸਕਦੇ ਹਨ । |
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 11.
ਲਿੰਗੀ ਅਤੇ ਅਲਿੰਗੀ ਜਣਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਕੋਈ ਤਿੰਨ ਅੰਤਰ ਲਿਖੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਲਿੰਗੀ ਅਤੇ ਅਲਿੰਗੀ ਜਣਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਅੰਤਰ-
| ਲਿੰਗੀ ਜਣਨ (Sexual Reproduction) | ਅਲਿੰਗੀ ਜਣਨ (Asexual Reproduction) |
| (1) ਇਸ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਵਿਚ ਨਰ ਅਤੇ ਮਾਦਾ ਦੋਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਲੋੜ ਪੈਂਦੀ ਹੈ । | (1) ਇਸ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਵਿਚ ਨਰ ਅਤੇ ਮਾਦਾ ਦੋਵਾਂ ਦੀ ਲੋੜ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦੀ । |
| (2) ਇਸ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਦਾ ਜਣਨ ਉੱਚ ਸ਼੍ਰੇਣੀ ਦੇ ਜੀਵਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । | (2) ਇਹ ਨਿਮਨ ਸ਼੍ਰੇਣੀ ਦੇ ਜੀਵਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । |
| (3) ਲਿੰਗੀ ਜਣਨ ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਜੀਵ ਬਣਨਾ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ । | (3) ਅਲਿੰਗੀ ਜੀਵ ਵਿਚ ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦੀ । |
| (4) ਇਸ ਜਣਨ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪੈਂਦਾ ਸੰਤਾਨ ਵਿਚ ਨਵੇਂ ਗੁਣ ਵਿਕਸਿਤ ਹੋ ਸਕਦੇ ਹਨ । | (4) ਇਸ ਜਣਨ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪੈਦਾ ਸੰਤਾਨ ਵਿਚ ਨਵੇਂ ਗੁਣ ਨਹੀਂ ਆ ਸਕਦੇ । |
| (5) ਇਸ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਵਿਚ ਬੀਜਾਣੂ ਪੈਦਾ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦੇ । | (5) ਇਸ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਵਿਚ ਇਕ ਸੈੱਲੀ ਬੀਜਾਣੁ (ਜਿਵੇਂ ਫਫੁਦੀ ਵਿਚ) ਪੈਦਾ ਹੋ ਸਕਦੇ ਹਨ । |
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 12.
ਨਰ ਮਨੁੱਖ ਵਿੱਚ ਪਤਾਲੂ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਬਾਹਰ ਕਿਉਂ ਸਥਿਤ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਨਰ ਮਨੁੱਖ ਵਿਚ ਪਤਾਲੂ ਦੀ ਸਥਿਤੀ ਪਤਾਲੂ-ਕੋਸ਼ ਵਿਚ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ਜੋ ਉਦਰ ਗੁਹਿਕਾ ਦੇ ਬਾਹਰ ਹੇਠਾਂ ਵੱਲ ਸਥਿਤ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਸ਼ੁਕਰਾਣੂਆਂ ਦੇ ਜਣਨ ਦੇ ਲਈ ਨਿਮਨ ਤਾਪ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤੀ ਦੇ ਲਈ ਅਜਿਹਾ ਸੰਭਵ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਤਾਂਕਿ ਸ਼ੁਕਰਾਣੂ ਦੇਰ ਤੱਕ ਕਿਰਿਆਸ਼ੀਲ ਰਹਿ ਸਕਣ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 13.
ਏਡਸ (AIDS) ਤੇ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਟਿੱਪਣੀ ਲਿਖੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਏਡਸ (AIDS) – ਏਡਸ (ਐਕਵਾਇਰਡ ਇਮੂਊਨੋ ਡੇਫੀਸ਼ਿਐਂਸੀ ਸਿੰਡਰੋਮ) ਨਾਮਕ ਰੋਗ ਇਕ ਅਜਿਹੇ ਵਿਸ਼ਾਣੂ (Virus) ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ਜੋ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਤੀਰੱਖਿਅਣ ਸੰਸਥਾਨ ਨੂੰ ਅਕਿਰਿਆਸ਼ੀਲ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਸਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਕੋਈ ਵੀ ਰੋਗ ਸਰਲਤਾ ਨਾਲ ਲੱਗ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸਦੇ ਵਾਇਰਸ ਦਾ ਨਾਮ HIV ਹੈ । ਏਡਸ ਦੇ ਰੋਗੀ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਕਮਜ਼ੋਰ ਸਰੀਰ ਤੇ ਹੋਏ ਹੋਰ ਹਮਲਿਆਂ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਮਰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਰੋਗ ਸੰਕਰਮਿਤ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਯੌਨ ਸੰਬੰਧ ਸਥਾਪਿਤ ਕਰਨ ਨਾਲ ਫੈਲਦਾ ਹੈ ਪਰ ਕਦੇ-ਕਦੇ ਇਸਦੇ ਵਿਸ਼ਾਣੂ ਸਿੱਧੇ ਹੀ ਲਹੂ ਵਿੱਚ ਪੁੱਜ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ । ਅਜਿਹਾ ਉਦੋਂ ਹੀ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਦੋਂ ਲਹੂ ਚੜ੍ਹਾਉਣ ਸਮੇਂ ਚੜਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ਹੂ ਸੰਕਰਮਿਤ ਹੋਵੇ ਜਾਂ ਟੀਕਾ ਲਗਾਉਣ ਦੇ ਲਈ ਸੰਕਰਮਿਤ ਸੂਈ ਦੀ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ ਹੋਵੇ । ਇਹ ਅਨੁਵੰਸ਼ਿਕ ਵੀ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਰੋਗ ਨਾਲ ਸੰਕਰਮਿਤ ਮਾਤਾਵਾਂ ਦੇ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਵੀ ਇਹ ਰੋਗ ਮਾਤਾ ਦੇ ਲਹੁ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪੁੱਜ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸਦੇ ਉਪਚਾਰ ਦਾ ਕੋਈ ਵੀ ਟੀਕਾ ਜਾਂ ਦਵਾਈ ਅਜੇ ਤੱਕ ਉਪਲੱਬਧ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੋਈ । ਇਸ ਰੋਗ ਦਾ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਅਸਰ ਅਫ਼ਰੀਕਾ ਅਤੇ ਪੱਛਮੀ ਦੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਹੈ । ਅਗਿਆਨਤਾ, ਗ਼ਰੀਬੀ ਅਤੇ ਅਨਪੜ੍ਹਤਾ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਸਾਡਾ ਦੇਸ਼ ਇਸ ਰੋਗ ਦੇ ਚੁੰਗਲ ਵਿਚ ਬਹੁਤ ਤੇਜ਼ੀ ਨਾਲ ਆ ਰਿਹਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 14.
ਮਨੁੱਖੀ ਮਾਦਾ ਜਣਨ ਅੰਗਾਂ ਦਾ ਅੰਕਿਤ ਚਿੱਤਰ ਬਣਾਓ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਮਾਦਾ ਜਣਨ ਅੰਗ ਦਾ ਅੰਕਿਤ ਚਿੱਤਰ
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 15.
ਕਿਸ਼ੋਰ ਅਵਸਥਾ ਦੌਰਾਨ ਲੜਕੀਆਂ (ਕੁੜੀਆਂ) ਵਿੱਚ ਕਿਹੜੇ ਪਰਿਵਰਤਨ ਆਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
(ਉ) ਨਰ ਦੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਦਿਖਾਈ ਦੇਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਪਰਿਵਰਤਨ-
- ਆਵਾਜ਼ ਵਿਚ ਭਾਰੀਪਣ ਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਦਾੜੀ ਅਤੇ ਮੁੱਛਾਂ ਉੱਗ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਜਣਨ ਅੰਗਾਂ ਤੇ ਵਾਲ ਉੱਗ ਆਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਪੀਨਸ ਦਾ ਆਕਾਰ ਵੱਧ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਦਿਨ ਜਾਂ ਰਾਤ ਦੇ ਸੁਪਨਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਉਸਦਾ ਅਕੜਾਅ ਵੱਧ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਮੋਡੇ ਚੌੜੇ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ | ਮਾਸਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਵਿਕਸਿਤ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਉਲਟ ਲਿੰਗ ਵੱਲ ਆਕਰਸ਼ਨ ਵੱਧ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
(ਅ) ਮਾਦਾ ਦੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਦਿਖਾਈ ਦੇਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਪਰਿਵਰਤਨ-
- ਜਣਨ ਅੰਗਾਂ ਤੇ ਵਾਲ ਉੱਗ ਆਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਛਾਤੀਆਂ ਵੱਡੀਆਂ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਮਹਾਮਾਰੀ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਕੁਲਿਆਂ ਦੇ ਆਸ-ਪਾਸ ਚਰਬੀ ਇਕੱਠੀ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਉਲਟ ਲਿੰਗ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਖਿੱਚ ਵੱਧ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਜਣਨ ਅੰਗਾਂ ਦਾ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਬਹੁਤ ਛੋਟੇ ਉੱਤਰਾਂ ਵਾਲੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ (Very Short Answer Type Questions)
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
DNA ਦਾ ਪੂਰਾ ਨਾਂ ਲਿਖੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਡਿਆਕਸੀਰਾਈਬੋ ਨਿਉਕਲੀ ਐਸਿਡ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਕਿਹੜੇ ਜੀਵਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਇਕੋ ਵੇਲੇ ਕਈ ਸੰਤਾਨ ਸੈੱਲਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਿਭਾਜਨ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਮਲੇਰੀਆ ਪਰਜੀਵੀ, ਪਲਾਜ਼ਮੋਡੀਅਮ ਵਰਗੇ ਇੱਕ ਕੋਸ਼ੀ ਜੀਵਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਕੈਲਸ ਕਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਟਿਸ਼ੂ ਸੰਵਰਧਨ ਵਿਚ ਜਦੋਂ ਸੈੱਲ ਵਿਭਾਜਿਤ ਹੋ ਕੇ ਅਨੇਕ ਸੈੱਲਾਂ ਦਾ ਛੋਟਾ ਸਮੂਹ ਬਣਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ ਤਾਂ ਉਸ ਨੂੰ ਕੈਲਸ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਫੁੱਲ ਦੇ ਜਣਨ ਭਾਗ ਕਿਹੜੇ ਹਨ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਪੁੰਕੇਸਰ ਅਤੇ ਇਸਤਰੀ-ਕੇਸਰ ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 5.
ਇਕ ਲਿੰਗੀ ਫੁੱਲਾਂ ਦੇ ਦੋ ਉਦਾਹਰਨ ਲਿਖੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
- ਪਪੀਤਾ,
- ਤਰਬੂਜ਼ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 6.
ਦੋ ਲਿੰਗੀ ਫੁੱਲਾਂ ਦੇ ਦੋ ਉਦਾਹਰਨ ਦਿਓ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
- ਗੁਹਲ,
- ਸਰੋਂ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 7.
ਕਲਮ ਅਤੇ ਦਾਬ ਲਗਾ ਕੇ ਨਵੇਂ ਪੌਦੇ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਨ ਦੇ ਦੋ ਮੁੱਖ ਲਾਭ ਕਿਹੜੇ ਹਨ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
- ਸਾਰੇ ਨਵੇਂ ਪੌਦੇ ਮੁਲ ਪੌਦੇ ਜਾਂ ਮਾਤਰੀ ਪੌਦੇ ਦੇ ਬਰਾਬਰ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਨਵੇਂ ਪੌਦੇ ਥੋੜੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਤਿਆਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 8.
ਪਰਾਗਣ ਦੀ ਪਰਿਭਾਸ਼ਾ ਲਿਖੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਪਰਾਗਣ – ਪੌਦਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਤੋਂ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਪਰਾਗਕਣਾਂ ਦੇ ਇਸਤਰੀ-ਕੇਸਰ ਦੇ ਸਟਿਗਮਾ ਤੱਕ ਪੁੱਜਣ ਦੀ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਨੂੰ ਪਰਾਗਣ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 9.
ਨਿਸ਼ੇਚਨ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਯੁਗਮਨਜ਼ ਵਿੱਚ ਕੀ ਬਣਦਾ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਭਰੁਣ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 10.
ਨਰ ਅਤੇ ਮਾਦਾ ਯੁਗਮਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਕੀ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਨਰ ਯੁਰਮਕ-ਸ਼ੁਕਰਾਣੁ ।
ਮਾਦਾ ਯੁਗਮਕ-ਅੰਡਾਣੁ ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 11.
ਫੀਟਸ ਕਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਗਰਭ ਧਾਰਨ ਦੇ ਦੋ ਜਾਂ ਤਿੰਨ ਮਹੀਨੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਵਿਕਸਿਤ ਹੋ ਰਹੇ ਬੱਚੇ ਨੂੰ ਫੀਟਸ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 12.
ਵੀਰਜ ਕੀ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਵੀਰਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ੁਕਰਾਣੂ ਅਤੇ ਕੁੱਝ ਗ੍ਰੰਥੀਆਂ ਦਾ ਸਾਵ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 13.
ਪਲੇਸੈਂਟਾ ਕਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਗਰਭਵਤੀ ਮਾਂ ਦੇ ਗਰਭਕੋਸ਼ ਦੀ ਦੀਵਾਰ ਅਤੇ ਭਰੂਣ ਦੀ ਤਿੱਲੀ ਦੇ ਸੰਯੋਜਨ ਦੀ ਇਕ ਨਾਲ ਦੀ ਰਚਨਾ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਔਲ ਦਾ ਗਰਭ ਨਾਲ ਜਾਂ ਪਲੇਸੈਂਟਾ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਪਲੇਸੈਂਟਾ ਵਿਚ ਕਾਫ਼ੀ ਲਹੂ ਸੈੱਲ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ, ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਮਾਤਾ ਦਾ ਲਹੁ ਭਰੁਣ ਜਾਂ ਗਰਭ ਦੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਆਉਂਦਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 14.
ਪੁਨਰਜਣਨ ਤੋਂ ਪੈਦਾ ਪਾਣੀ ਦਾ ਇਕ ਉਦਾਹਰਨ ਲਿਖੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਸਟਾਰਫਿਸ਼ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 15.
ਜਵਾਨੀ ਦੀ ਉਮਰ ਕੀ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਮੁੰਡਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ 13-14 ਸਾਲ, ਲੜਕੀਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ 10-12 ਸਾਲ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 16.
ਮਨੁੱਖ ਦੀ ਮਾਦਾ ਵਿਚ ਗਰਭਕਾਲ ਕਿੰਨਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਲਗਭਗ 9 ਮਹੀਨੇ ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 17.
IUCD ਕੀ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
IUCD (ਇੰਟਰਾਯੂਟੀਰੀਨ ਕੰਟਰਾਸੈਪਟਿਵ ਡਿਵਾਈਸ) ਨਾਰੀ ਗਰਭਕੋਸ਼ ਵਿੱਚ ਲਗਾਈ ਜਾਣ ਵਾਲੀ ਇੱਕ ਯੁਕਤੀ ਹੈ ਜੋ ਗਰਭ ਨਿਰੋਧਕ ਦਾ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 18.
STD ਕੀ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
STD (Sexually Transmitted Disease) ਯੌਨ ਸੰਕਰਮਿਤ ਰੋਗ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 19.
ਦੋ ਯੌਨ ਰੋਗਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਂ ਲਿਖੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
- ਗੋਨੋਰੀਆ,
- ਸਿਫਲਿਸ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 20.
ਹੇਠਾਂ ਦਿੱਤੇ ਚਿੱਤਰ ਕਿਸ ਜੀਵ ਦੇ ਹਨ ਅਤੇ ਇਹ ਕਿਹੜੀ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਨੂੰ ਦਰਸਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ ?
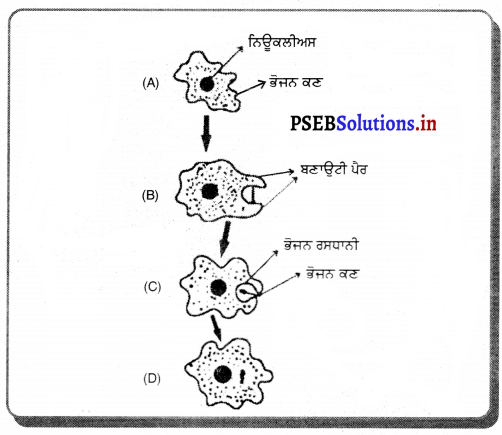
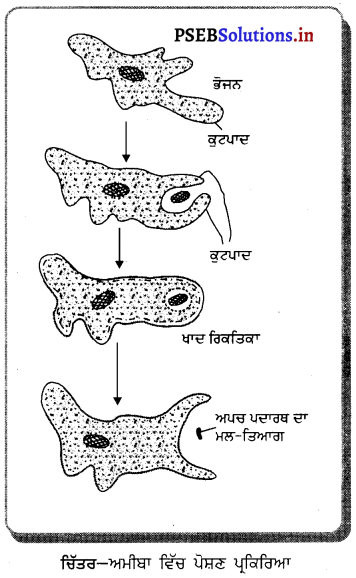
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਜੀਵ ਦਾ ਨਾਂ : ਅਮੀਬਾ
ਕਿਰਿਆ : ਪੋਸ਼ਣ ਕਿਰਿਆ ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 21.
ਹੇਠ ਦਿੱਤੇ ਚਿੱਤਰ ਵਿਚ ਅਮੀਬਾ ਦੀ ਕਿਹੜੀ ਜੀਵਨ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਦਰਸਾਈ ਗਈ ਹੈ ?

ਉੱਤਰ-
ਜਣਨ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਦੀਆਂ ਦੋ-ਖੰਡਨ ਵਿਧੀ ।
ਵਸਤੂਨਿਸ਼ਠ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ (Objective Type Questions)
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਅਲਿੰਗੀ ਜਣਨ ਬਡਿੰਗ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਜਿਸ ਵਿੱਚ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਉਹ ਹੈ :
(a) ਅਮੀਬਾ
(b) ਯੀਸਟ
(c) ਪਲਾਜਮੋਡੀਅਮ
(d) ਲੇਸ਼ਮਾਨੀਆ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(b) ਯੀਸਟ (Yeast) ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਕਿਹੜਾ ਮਨੁੱਖ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਾਦਾ ਜਣਨ ਪ੍ਰਣਾਲੀ ਦਾ ਭਾਗ ਨਹੀਂ :
(a) ਅੰਡਕੋਸ਼
(b) ਗਰਭਭੋਸ਼
(c) ਸ਼ੁਕਰਾਣੂ ਵਾਹਿਣੀ
(d) ਫੈਲੋਪੀਅਨ ਟਿਊਬ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(c) ਸ਼ੁਕਰਾਣੂ ਵਾਹਿਣੀ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਯੀਸਟ ਵਿੱਚ ਅਲਿੰਗੀ ਜਣਨ ਆਮ ਤੌਰ ‘ਤੇ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ-
(a) ਬਡਿੰਗ ਦੁਆਰਾ
(b) ਵਿਖੰਡਨ ਦੁਆਰਾ
(c) ਬੀਜਾਣੂ ਦੁਆਰਾ
(d) ਰੋਪਣ ਦੁਆਰਾ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(a) ਬਡਿੰਗ ਦੁਆਰਾ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਵਿਖੰਡਨ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਅਲਿੰਗੀ ਜਣਨ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ-
(a) ਅਮੀਬਾ ਵਿੱਚ
(b) ਯੀਸਟ ਵਿੱਚ
(c) ਸਪਾਇਰੋਗਾਇਰਾ ਵਿੱਚ
(d) ਫਰਨ ਵਿੱਚ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(c) ਸਪਾਇਰੋਗਾਇਰਾ ਵਿੱਚ ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 5.
ਹਾਈਡਰਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਅਨੁਕੂਲ ਪਰਿਸਥਿਤੀਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਅਲਿੰਗੀ ਜਣਨ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ-
(a) ਵਿਖੰਡਨ ਦੁਆਰਾ
(b) ਬਡਿੰਗ ਦੁਆਰਾ
(c) ਬੀਜਾਣੂਆਂ ਦੁਆਰਾ
(d) ਦੋ-ਖੰਡਨ ਦੁਆਰਾ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(b) ਬਡਿੰਗ ਦੁਆਰਾ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 6.
ਇਕ ਪ੍ਰਜਣਨ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ-
(a) ਦੂਬ ਘਾਹ ਵਿੱਚ
(b) ਆਲੂ ਵਿੱਚ
(c) ਬਰਾਇਓਫਿਲਮ ਵਿੱਚ
(d) ਉਪਰੋਕਤ ਸਾਰਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(d) ਉਪਰੋਕਤ ਸਾਰਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 7.
ਇਸਤਰੀਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਾਹਵਾਰੀ ਚੱਕਰ ਪੂਰਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ-
(a) 14 ਦਿਨਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ
(b) 21 ਦਿਨਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ
(c) 28 ਦਿਨਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ
(d) 30 ਦਿਨਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(b) 21 ਦਿਨਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 8.
ਕਿਹੜਾ ਹਾਰਮੋਨ ਲੜਕੀਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਜੋਬਨ ਅਵਸਥਾ ਦੇ ਲੱਛਣਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਕੰਟਰੋਲ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ?
(a) ਐਸਟਰੋਜਨ
(b) ਟੇਸਟੋਸਟੀਰੋਨ
(c) ਥਾਇਰਾਕਸਿਨ
(d) ਇੰਸੂਲਿਨ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(a) ਐਸਟਰੋਜਨ ।
ਖ਼ਾਲੀ ਥਾਂਵਾਂ ਭਰਨਾ
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ-ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੀਆਂ ਖ਼ਾਲੀ ਥਾਂਵਾਂ ਭਰੋ :
(i) ਨਰ ਅਤੇ ਮਾਦਾ ਜਣਨ ਸੈੱਲਾਂ ਦੇ ਮੇਲ ਨਾਲ ਬਣੀ ਰਚਨਾ ਨੂੰ ……………. ਆਖਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਯੁਗਮਨਜ
![]()
(ii) ਜਨਣ ਅੰਗਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਹੋਣ ਵਾਲੀ ਸੈੱਲ ਵੰਡ ਨਾਲ …………….. ਸੈੱਲ ਬਣਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਜਣਨ
(iii) ਮਨੁੱਖ ਦਾ ਜੀਵਨ ……………… ਸੈੱਲ ਤੋਂ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਇਕ
(iv) ਜਦੋਂ ਵਾਧਾ ਇਕ ਨਿਸਚਿਤ ਅਨੁਪਾਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਤਾਂ ਇਸਨੂੰ ……………… ਆਖਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਪਰਿਵਰਧਨ
(v) ਅਮੀਬਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਅਲਿੰਗੀ ਜਣਨ ……………… ਵਿਧੀ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਦੋਖੰਡਨ ।