Punjab State Board PSEB 9th Class Social Science Book Solutions Economics Chapter 1 एक गांव की कहानी Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Economics Chapter 1 एक गांव की कहानी
SST Guide for Class 9 PSEB एक गांव की कहानी Textbook Questions and Answers
(क) वस्तुनिष्ठ प्रश्न
रिक्त स्थान भरें:
- मानव की आवश्यकताएं
- …………. जोखिम उठाता है।
- ………… उत्पादन का प्राकृतिक साधन है।
- एक वर्ष में एक भूखण्ड पर एक से अधिक फसलें पैदा करने को ………. कहते हैं।
- जो श्रमिक एक राज्य से दूसरे राज्य में श्रम करने के लिए जाते हैं उन्हें ………….. श्रमिक कहते हैं।
- पंजाब को देश के ……………. के रूप में जाना जाता है।
उत्तर-
- असीमित
- उद्यमी
- भूमि
- बहुविविध फसल प्रणाली
- प्रवासी श्रमिक
- अन्न के कटोरे।
बहुविकल्पी प्रश्न :
प्रश्न 1.
उत्पादन का कौन-सा कारक अचल है ?
(क) भूमि
(ख) श्रम
(ग) पूंजी
(घ) उद्यमी।
उत्तर-
(क) भूमि
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
वह आर्थिक क्रिया जो वस्तुओं व सेवाओं के मूल्य अथवा उपयोगिता की वृद्धि के साथ जुड़ी हुई है, कहलाती है
(क) उत्पादन
(ख) उपभोक्ता
(ग) वितरण
(घ) उपयोगिता।
उत्तर-
(क) उत्पादन
प्रश्न 3.
कृषि में विशेषकर गेहूँ व धान के उत्पादन में असाधारण वृद्धि को क्या कहते हैं ?
(क) हरित क्रांति
(ख) गेहूं क्रांति
(ग) धान क्रांति
(घ) श्वेत क्रांति।
उत्तर-
(क) हरित क्रांति
प्रश्न 4.
इग्लैंड की मुद्रा कौन-सी है ?
(क) रुपए
(ख) डॉलर
(ग) यान
(घ) पौंड।
उत्तर-
(घ) पौंड।
सही/गलत :
- भूमि की पूर्ति सीमित है।
- मनुष्य की सीमित आवश्यकताएं असीमित साधनों के साथ पूरी होती हैं।
- श्रम की पूर्ति को बढ़ाया एवं घटाया नहीं जा सकता।
- उद्यमी जोखिम उठाता है।
- मशीन व पशुओं द्वारा करवाया कार्य श्रम है।
- बाज़ार में वस्तुओं के मूल्य बढ़ जाने से उनकी मांग बढ़ जाती है।
उत्तर-
- सही
- ग़लत
- ग़लत
- सही
- ग़लत
- ग़लत।
(क) अति लघु उत्तरों वाले प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
अर्थशास्त्र से क्या अभिप्राय है ?
उत्तर-
अर्थशास्त्र मनुष्यों के व्यवहार का अध्ययन है जो यह बताता है कि किस प्रकार एक मनुष्य अपनी असीमित आवश्यकताओं को सीमित साधनों से पूरा कर सकता है।
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
भारत के गांवों की मुख्य उत्पादन क्रिया कौन-सी है ?
उत्तर-
खेती, भारत के गांवों की मुख्य उत्पादन है।
प्रश्न 3.
गांवों में सिंचाई के दो प्रमुख साधन कौन-से हैं।
उत्तर-
- टयूबवैल
- नहरें।
प्रश्न 4.
अर्थशास्त्र में श्रम से क्या अभिप्राय है ? .
उत्तर-
अर्थशास्त्र में श्रम का कार्य उन सभी मानवीय प्रयासों से हैं, जो धन कमाने के उद्देश्य से किए जाते हैं। ये प्रयास शारीरिक या बौद्धिक दोनों हो सकते हैं।
प्रश्न 5.
माँ द्वारा अपने बच्चे को पढ़ाने की क्रिया श्रम है अथवा नहीं ?
उत्तर-
इस कार्य को श्रम नहीं माना जाएगा क्योंकि यह कार्य धन प्राप्ति के उद्देश्य से नहीं किया गया है।
प्रश्न 6.
श्रमिकों को परिश्रमिक किस रूप में मिलता हैं ?
उत्तर-
श्रमिक अपनी मजदूरी नकद या किस्म के रूप में प्राप्त कर सकता है।
प्रश्न 7.
गांव के लोगों द्वारा की जाने वाली कोई दो गैर कृषि क्रियाएं बताएं।
उत्तर-
गैर कृषि क्रियाएं निम्न हैं1. डेयरी 2. मुर्गीपालन।
प्रश्न 8.
बड़े व लघु किसान कृषि के लिए वांछित पूंजी कहां से प्राप्त करते हैं ?
उत्तर-
बड़े किसान कृषि क्रियाओं के लिए पूंजी अपनी कृषि क्रियाओं से होने वाली बचतों से प्राप्त करते हैं जबकि छोटे किसान बड़े किसानों से ऊंची ब्याज दर पर रकम लेते हैं।
प्रश्न 9.
भूमि की कोई एक विशेषता लिखें।
उत्तर-
भूमि प्रकृति का निःशुल्क उपहार है।
प्रश्न 10.
मज़दूर एक राज्य से दूसरे राज्यों में प्रवास क्यों करते हैं ?
उत्तर-
श्रमिक अपनी आजीविका कमाने के लिए एक राज्य से दूसरे राज्य को प्रवास करते हैं।
प्रश्न 11.
किसान पराली को क्यों जलाते हैं ?
उत्तर-
धान के अवशिष्ट भाव पराली का कोई निवेष प्रबंध न होने के कारण किसान उस पराली को आग लगाते हैं।
(स्व) लघु उत्तरों वाले प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
हम अर्थशास्त्र का अध्यायन क्यों करते हैं ?
उत्तर-
हम अर्थशास्त्र का अध्ययन इसलिए करते हैं क्योंकि यह एक विज्ञान है जो हमें यह बताता है कि किस प्रकार हम अपने सीमित साधनों का प्रयोग करके अपनी असीमित आवश्यकताओं को पूरा कर सकते हैं। अर्थशास्त्र का अध्ययन करके ही हम अपनी आय को इस प्रकार व्यय कर सकते हैं जिससे हमें अधिकतम सन्तुष्टि प्राप्त हो।
प्रश्न 2.
आर्थिक क्रिया क्या है ? एक उदाहरण दें।
उत्तर-
आर्थिक क्रिया वह क्रिया है जो एक व्यक्ति द्वारा अपनी असीमित आवश्यकताओं को पूरा करने के लिए सीमित साधनों को कम करके की जाती है। इस क्रियाओं को किए जाने का मुख्य उद्देश्य धन प्रकट करना होता है।
उदाहरण-एक शिक्षक द्वारा विद्यालय में पढ़ाना।
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
सिंचाई के लिए टयूबवैल का निरन्तर प्रयोग भूमि के नीचे के जलस्तर को कैसे प्रभावित करता है ?
उत्तर-
सिंचाई के लिए टयूबवैल द्वारा पानी के निरंतर प्रयोग किए जाने से भूमिगत जल का स्तर कम होता जा रहा है। पंजाब में भूमिगत जल स्तर का कम होना एक गंभीर समस्या है। पंजाब में हर वर्ष अधिक से अधिक जल का प्रयोग करने हेतु भूमि के नीचे से नीचे स्तर से भी जल निकाला जा रहा है। इस तरह 20 वर्ष के बाद भूमिगत के पूरी तरह कम हो जाने का माप उत्पन्न होने लगा है।
प्रश्न 4.
भूमि के एक ही भाग पर उत्पादन वृद्धि के कोई दो भिन्न ढंग बताएं।
उत्तर-
एक ही भूमि के टुकड़ें पर एक वर्ष में एक से अधिक फसलें एक साथ उगाने से उत्पादन बढ़ाया जा सकता है। इसे बहुविविध फसल प्रणाली कहते हैं। भूमि के एक ही टुकड़े पर उत्पादन बढ़ाने की यह एक सामान्य प्रक्रिया है। यह विद्युत टयूवबैल तथा किसानों को विद्युत की लगातार पूर्ति से संभव हो सका है।
दूसरी ओर, एक ही भूमि के टुकड़े पर उत्पादन बढ़ाने का अन्य तरीका आधुनिक विधियों का प्रयोग करना है जैसे उच्च पैदावार वाले बीज, रासायनिक खाद की पर्याप्त मात्रा कीटनाशक आदि।
प्रश्न 5.
बहुफसली विधि से क्या अभिप्राय है ? वर्णन करें।
उत्तर-
एक वर्ष में भूमि के एक टुकड़े पर एक साथ एक से अधिक फसलें उगाने की क्रिया को बहुविविध फसल प्रणाली कहते हैं। यह भूमि के एक ही टुकड़े पर उत्पादन बढ़ाने का साधारण तरीका है। यह विद्युत टयूवबैल तथा किसानों को निरंतर विद्युत की पूर्ति से संभव हो सका है। छोटी-छोटी नहरों से भी किसानों को कृषि के लिए जल उपलब्ध होता रहता है। जिसने वर्ष भर किसानों को कृषि करने के लिए प्रेरित किया है।
प्रश्न 6.
हरित क्रांति से क्या अभिप्राय है ? यह कैसे संभव हुई है ?
उत्तर-
भारत में योजनाओं की अवधि में अपनाए गए कृषि सुधारों के फलस्वरूप 1967-68 में अनाज के उत्पादन में 1966-67 की तुलना में 25 प्रतिशत की वृद्धि हुई। किसी एक वर्ष में अनाज के उत्पादन में इतनी अधिक वृद्धि किसी क्रांति से कम नहीं थी। इसलिए इसे हरित क्रांति का नाम दिया गया। हरित क्रांति से अभिप्राय कृषि उत्पादन में होने वाली भारी वृद्धि से है जो कृषि की नई नीति को अपनाने के कारण हुई।
प्रश्न 7.
भूमि पर आधुनिक कृषि पद्धति व ट्यूबवैल सिंचाई के कौन-से हानिकारक प्रभाव पड़े हैं ?
उत्तर-
भूमि एक प्राकृतिक संसाधन हैं, आधुनिक कृषि विधियां इसकी उपजाऊ शक्ति को कम कर रही हैं। आधुनिक कृषि विधियों के प्रयोग द्वारा प्रारंभिक स्तर में तो कृषि उत्पादन बढ़ता रहता है परंतु बाद में यह धीरे-धीरे घटता जाता है।
भूमिगत जल का स्तर भी टयूवबैल का अधिक प्रयोग करने से घटता जा रहा है। प्रत्येक वर्ष पंजाब के किसान भूमि को और अधिक नीचे तक खोदते रहते हैं। इन स्थितियों के द्वारा 20 वर्ष के बाद भूमिगत जल के पूरी तरह कम हो जाने का संकट उत्पन्न हो गया है।
प्रश्न 8.
गांव के किसानों में भूमि किस प्रकार वितरित हुई है ?
उत्तर-
इस गांव में दुर्भाग्यवश सभी लोग कृषि योग्य भूमि की पर्याप्त मात्रा न होने के कारण कृषि कार्यों में संलग्न नहीं हैं। लगभग 20 परिवार ऐसे हैं जो अपनी भूमि के स्वामी हैं और 100 परिवार ऐसे हैं जिनके पास कृषि योग्य थोड़ी सी भूमि उपलब्ध है। जबकि 50 परिवार ऐसे भी हैं जिनके पास अपनी कृषि योग्य भूमि नहीं है। यह लोग अन्य लोगों की भूमि पर काम करके अपनी आजीविका कमाते हैं।
प्रश्न 9.
गांव में कृषि के लिए श्रम के कोई दो स्त्रोत बताएं।
उत्तर-
किसानों कृषि कार्यों के लिए श्रम का स्वयं प्रबंध करते हैं। इसके अलावा, कुछ निर्धन परिवार अपनी आजीविका कमाने के लिए बड़े कृषकों की भूमि पर श्रम का कार्य करते हैं। ज़मींदारों की भूमि पर नाम करने के लिए कुछ प्रवासी श्रमिक अन्य राज्यों जैसे बिहार और उत्तर प्रदेश से भी गांव में आए हैं। इन्हें प्रवासी श्रमिक कहते हैं।
प्रश्न 10.
बड़े व मध्यम वर्गीय किसान कृषि के लिए आवश्यक पूंजी का प्रबंध कैसे करते हैं ?
उत्तर-
मझौले और बड़े किसानों के पास अधिक भूमि होती है अर्थात् उनकी जोतों का आकार काफ़ी बड़ा होता है जिससे वे उत्पादन अधिक करते हैं।
उत्पादन अधिक होने से वे इसे बाज़ार में बेच कर काफी पूंजी प्राप्त कर लेते हैं जिसका प्रयोग वे उत्पादन को आधुनिक विधियों को अपनाने में करते हैं।
![]()
प्रश्न 11.
आर्थिक तथा अनार्थिक क्रिया में अंतर लिखें।
उत्तर-
| आर्थिक क्रियाएं | अनार्थिक क्रियाएं |
| 1. आर्थिक क्रियाएं अर्थव्यवस्था में वस्तुओं व सेवाओं का प्रवाह करती हैं। | 1. अनार्थिक क्रियाओं से वस्तुओं व सेवाओं का कोई प्रवाह अर्थव्यवस्था में नहीं होता। |
| 2. जब आर्थिक क्रियाओं में वृद्धि होती है तो इसका अर्थ है कि अर्थव्यवस्था प्रगति | 2. अनार्थिक क्रियाओं में होने वाली कोई भी वृद्धि अर्थव्यवस्था की प्रगति का निर्धारक नहीं है। में है। |
| 3. आर्थिक क्रियाओं से वास्तविक व राष्ट्रीय आय व आय में वृद्धि होती है। | 3. अनार्थिक क्रियाओं में से कोई राष्ट्रीय व्यक्तिगत आय में वृद्धि नहीं होती है। |
प्रश्न 12.
श्रम की मुख विशेषताएं कौन-सी हैं ?
उत्तर-
श्रम की मुख्य विशेषताएं निम्न हैं-
- श्रम उत्पादन का एकमात्र सक्रिय साधन है।
- श्रम को पूर्ति घटाई व बढ़ाई जा सकती है।
- भारत में श्रम प्रचुर मात्रा में उपलब्ध है।
- धन कमाने के उद्देश्य से किए गए सभी मानवीय प्रयास श्रम है।
- श्रम को खरीदा व बेचा जा सकता है।
- श्रम गतिशील है।
प्रश्न 13.
लघु किसान कृषि के लिए वांछित पूंजी का प्रबंध कैसे करते हैं ?
उत्तर-
छोटे किसानों की पूंजी की आवश्यकता बड़े किसानों से भिन्न होती है क्योंकि छोटे किसानों के पास भूमि कम होने के कारण उत्पादन उनके भरण-पोषण के लिए भी कम बैठता है। उन्हें अधिकतम प्राप्त न होने के कारण बचतें नहीं होती। इसलिए खेती के लिए उन्हें पूंजी बड़े किसानों या साहूकारों से उधार लेकर पूरी करनी पड़ती है, जिस पर उन्हें काफी ब्याज चुकाना पड़ता है।
प्रश्न 14.
बड़े किसान अतिरिक्त कृषि उत्पादों को क्या करते हैं ?
उत्तर-
बड़े किसान अपने कृषि उत्पाद को नज़दीक के बाजार में बेचते हैं और बहुत अधिक धन कमा लेते हैं। इस कमाई हुई अतिरिक्त पूंजी का प्रयोग वे छोटे किसानों को ऊंची ब्याज दर पर ऋण देने के लिए करते हैं। इसके अलावा वो इस आधिक्य का प्रयोग अगले कृषि मौसम में उपज उगाने के लिए भी करते हैं और अपनी जमाओं को बढ़ाते हैं।
प्रश्न 15.
भारत के गांवों में कौन-सी गैर-कृषि क्रियाएं की जाती हैं ?
उत्तर-
ग्रामीण क्षेत्र में जो गैर-कृषि कार्य हो रहे हैं वे निम्नलिखित हैं-
- पशुपालन द्वारा दुग्ध क्रियाएं।
- छोटे-छोटे उद्योग हैं जिसमें आटा चक्कियां, बुनकर उद्योग टोकरियां बनाना, फर्नीचर बनाना, लोहे के औज़ार बनाना आदि शामिल हैं।
- दुकानदारी।
- यातायात के साधनों का संचालन आदि।
प्रश्न 16.
भारत के ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में कौन-कौन सी गैर-कृषि क्रियाएं (गतिविधियां) चलाई जा रही है ?
उत्तर-
गैर-कृषि क्रियाओं को कम मात्रा में भूमि की आवश्यकता होती है । वर्तमान में, गांवों में गैर-कृषि क्षेत्र अधिक विस्तृत नहीं हैं। गांवों में प्रत्येक 100 श्रमिकों में से केवल 24 श्रमिक ही गैर-कृषि क्रियाओं में संलग्न हैं। लोग गैर-कृषि क्रियाएं या तो अपनी बचतों से या ऋण लेकर शुरू कर सकते हैं। गांवों को आधुनिक सुविधाएं प्रदान करवा कर जैसे सड़क, बिजली, संचार, यातायात आदि से शहर के साथ जोड़ा जा सकता है तथा गैर-कृषि क्रियाओं को शुरू किया जा सकता है।
प्रश्न 17.
फसलों के अवशिष्ट को खेतों में जलाने से भूमि की गुणवत्ता में पतन क्यों आता है ?
उत्तर-
फसलों के अवशिष्ट को खेतों में जलाने से ज़मीन की उपरी सतह का तापमान बढ़ जाता है, जिस कारण ज़मीन में मिलने वाले सूक्ष्म जीव, बैक्टीरिया, मित्रकीट, फफूंद, पक्षी मौत का शिकार हो जाते हैं। इसके साथ-साथ ज़मीन के लाभदायक तत्त्व और यौगिक भी तापमान में बढ़ौतरी के कारण नष्ट हो जाते हैं, परिणामस्वरूप भूमि की गुणवत्ता में पतन हो जाता है।
अन्य अभ्यास के प्रश्न
गतिविधि-1
अपने निकटतम खेत में जाकर कुछ किसानों से चर्चा कीजिए तथा मालूम करने की कोशिश कीजिए।
प्रश्न 1.
किसान कृषि में परम्परावादी अथवा आधुनिक में किस विधि का प्रयोग कर रहे हैं : व क्यों।
उत्तर-
मेरे पड़ोस के खेतों में जिन किसानों की छोटी जोतें थीं वे खेती की पुरानी विधि का प्रयोग कर रहे हैं तथा जिन किसानों की जोतें बड़ी थीं वे नयी विधि का प्रयोग कर रहे थे। इन विधियों को प्रयोग करने का मुख्य कारण यही था कि जिन किसानों की जोतें छोटे आकार की हैं वे आधुनिक विधियों को प्रयोग करने में कम आय होने के कारण असमर्थ हैं। दूसरी ओर बड़े किसानों की आय अधिक होने के कारण वे आधुनिक विधि का प्रयोग करने में समर्थ हैं।
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
उसके द्वारा सिंचाई के कौन-से स्त्रोत का प्रयोग हो रहा हैं ?
उत्तर-
मेरे गांव में अधिकतर किसान सिंचाई के लिए वर्षा पर निर्भर हैं परंतु कुछ बड़े किसान ट्यूवबैल, पंपसैट से भी सिंचाई करते हैं।
प्रश्न 3.
किसानों द्वारा बोई जाने वाली फसलों के प्रकार तथा इन फसलों को बीजने तथा काटने का समय क्या है ?
उत्तर-
मेरे गांव के किसान खरीफ़ तथा रवी दोनों प्रकार की फसलें उगाते हैं। खरीफ मौसम में मक्की, सूरजमुखी तथा चावल उगाते हैं तथा सर्दी से पहले इनकी कटाई हो जाती है। सर्दी में रवी फसल जैसे गेहूं, जौ, चना, सरसों उगाते हैं तथा अप्रैल मास में इनकी कटाई करते हैं।
प्रश्न 4.
किसानों द्वारा प्रयुक्त खादों व कीटनाशक दवाइयों के नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर-
खादों के नाम-
- यूरिया (Urea)
- वर्मीकंपोस्ट (Vermicompost)
- जिप्सम (Gypsum)
कीटनाशक-
- Emanection Benzoate
- RDX BIO Pesticide
- Bitentrin 2.5% Ec
- Star one.
गतिविधि-2
प्रश्न 1.
अपने गांव या निकटवर्ती गांव के खेतों में जाकर पता करें कि किसान खेतों में पराली जला रहे हैं या नहीं ? यदि वे ऐसा कर रहे हैं तो उन्हें ऐसा करने से होने वाले दुष्प्रभावों के बारे में समझाइए।
उत्तर-
गांव के खेतों में जाने से मालूम हुआ कि किसान अगली फसल की बुआई करने की जल्दी के कारण विशेष रूप से धान की कटाई के बाद व गेहूं की बुआई से पहले अवशेषों को ठिकाने लगाने की व्यवस्था के अभाव में जल्दी हल के लिए वे खेतों में ही खूटी (Stubble) को जला रहे थे। मैंने उन्हें ऐसा करने से होने वाले बुरे परिणामों से अवगत करवाया उन्हें बताया कि इससे पर्यावरण प्रदूषित होता है जो कि वातावरण असंतुलन फैलाता है। इससे भूमि की ऊपरी सतह का तापमान बढ़ जाता है जिसने विभिन्न प्रकार के जीवाणु, कवक, मित्र कीट आदि मर जाते हैं तथा भूमि के आवश्यक तत्वों का नाश होता है।
आइए चर्चा करें:
प्रश्न 1.
लघु स्तर के किसानों को बड़े स्तर के किसानों के खेतों में श्रमिकों की तरह कार्य क्यों करना पड़ता है ?
उत्तर-
उन्हें अपनी आजीविका कमाने के लिए श्रमिक के रूप में काम करना पड़ता है क्योंकि उन्होंने बड़े किसानों से निर्धनता के कारण ऋण लिए होते हैं जिसकी अदायगी के लिए उन्हें अपने खेतों को भी देना पड़ जाता है।
प्रश्न 2.
क्या कृषि श्रमिकों को पूरे वर्ष के लिए रोजगार उपलब्ध हो जाता है ?
उत्तर-
नहीं, खेतिहर मजदूरों को पूरे वर्ष भर रोज़गार नहीं मिलता। उन्हें दैनिक मज़दूरी आधार पर अथवा किसी विशेष खेती पर होने वाले क्रियाकलाप के दौरान जैसे कटाई या बुआई के समय ही काम मिलता है। वे मौसमी रोज़गार प्राप्त करते हैं।
प्रश्न 3.
कृषि श्रमिक को अपना पारिश्रमिक किस रूप में मिलता है।
उत्तर-
वे नकदी अथवा प्रकार में भी जैसे अनाज (चावल या गेहूँ) के रूप में भी मज़दूरी प्राप्त करते हैं।
प्रश्न 4.
प्रवासी श्रमिक किन्हें कहा जाता हैं ?
उत्तर-
जब बड़े किसानों के खेतों में अन्य राज्यों से लोग आकर मजदूरी पर काम करते हैं तो उन्हें प्रवासी मजदूर कहते हैं।
प्रश्न 5.
श्रमिक प्रवास क्यों करते हैं ? अपने अध्यापक महोदय के साथ चर्चा करें।
उत्तर-
श्रमिक इसलिए प्रवास करते हैं क्योंकि उनके स्थान पर आजीविका कमाने के लिए काम उपलब्ध नहीं होता है। हमने अपने गांव में देखा है कि अन्य राज्यों से लोग अपने वहां काम के अभाव से यहां गांव में आते हैं। इन्हें प्रवासी मज़दूर के नाम से जाना जाता है।
![]()
PSEB 9th Class Social Science Guide एक गांव की कहानी Important Questions and Answers
रिक्त स्थान भरें:
- वे सभी वस्तुएं जो मनुष्य की आवश्यकताओं को संतुष्ट करती हैं, ……. कहलाती हैं।
- किसी वस्तु की प्रति इकाई को ………… लागत कहते हैं।
- पूर्ण प्रतियोगिता में औसत आय तथा सीमांत आय ……… होती है।
- उत्पादन के मुख्य …………. साधन हैं।
- ……….. में समरूप वस्तु के बहुत सारे क्रेता और विक्रेता होते हैं।
- आर्थिक लगान केवल …………. की सेवाओं के लिए प्राप्त होता है।
- दुर्लभता का अर्थ किसी वस्तु अथवा सेवा की पूर्ति का उसकी मांग से ……. होता है।
- …………. वह इकाई है जो लाभ प्राप्त करने की दृष्टि से बिक्री के लिए उत्पादन करती है।
- …………. वह स्थिति है जिसमें एक बाज़ार में केवल एक ही उत्पादक होता है।
- किसी वस्तु की आवश्यकताओं को संतुष्ट करने की शक्ति है।
उत्तर-
- पदार्थ
- औसत
- समान
- चार
- पूर्ण प्रतियोगिता
- भूमि
- कम
- फर्म :
- एकाधिकार
- उपयोगिता।।
बहुविकल्पीय प्रश्न :
प्रश्न 1.
इनमें से कौन मुद्रा का एक कार्य है ?
(क) विनिमय का माध्यम
(ख) मूल्य का मापदंड
(ग) धन का संग्रह
(घ) उपरोक्त सभी।
उत्तर-
(घ) उपरोक्त सभी।
प्रश्न 2.
इनमें से कौन पदार्थ का प्रकार नहीं हैं ?
(क) भौतिक
(ख) संतुलित
(ग) नाशवान
(घ) टिकाऊ।
उत्तर-
(ख) संतुलित
प्रश्न 3.
इनमें से कौन उद्यमी का पारितोषिक है ?
(क) लाभ
(ख) लगान
(ग) मजदूरी
(घ) ब्याज।
उत्तर-
(क) लाभ
प्रश्न 4.
ब्याज किसकी सेवाओं के बदले में दिया जाता है?
(क) भूमि
(ख) श्रम
(ग) पूंजी
(घ) उद्यमी।
उत्तर-
(ग) पूंजी
प्रश्न 5.
किसी वस्तु की बिक्री करने पर एक फ़र्म को जो राशि प्राप्त होती है उसे कहते हैं ?
(क) आगम
(ख) उपयोगिता
(ग) मांग
(घ) इनमें से कोई नहीं।
उत्तर-
(क) आगम
![]()
प्रश्न 6.
दुर्लभता का अर्थ किसी वस्तु की पूर्ति का उसकी मांग से होना है-
(क) कम
(ख) अधिक
(ग) समान
(घ) इनमें कोई नहीं।
(ख) उत्पादन की मात्रा
उत्तर-
(क) कम
प्रश्न 7.
औसत आय निकालने का सूत्र क्या है ?
![]()
(ग) कुल आय × उत्पादन की मात्रा
(घ) इनमें कोई नहीं।
उत्तर-
![]()
प्रश्न 8.
इनमें से कौन पूर्ण प्रतियोगिता की विशेषता है ?
(क) समरूप वस्तु
(ख) समान कीमत
(ग) पूर्ण ज्ञान
(घ) उपरोक्त सभी।
उत्तर-
(घ) उपरोक्त सभी।
प्रश्न 9.
एक विक्रेता व अधिक क्रेता किस बाज़ार का लक्ष्य है ?
(क) एकाधिकार
(ख) पूर्ण प्रतियोगिता
(ग) अल्पाधिकार
(घ) एकाधिकार प्रतियोगिता।
उत्तर-
(क) एकाधिकार
प्रश्न 10.
इनमें से कौन बाज़ार का एक प्रकार है ?
(क) अल्पाधिकार
(ख) पूर्ण प्रतियोगिता
(ग) एकाधिकार
(घ) उपरोक्त सभी।
उत्तर-
(घ) उपरोक्त सभी।
सही/गलत :
- U.S.A. की करंसी डॉलर है।
- अध्यापक द्वारा घर में अपने बच्चे को पढ़ाना एक आर्थिक क्रिया है।
- भूमि की पूर्ति असीमित है।
- एक एकड़ 8 कनाल के बराबर होता है।
- हमारे देश में कुल खेती योग्य क्षेत्र का केवल 40 प्रतिक्षत क्षेत्र ही सिंचाई योग्य है।
- पंजाब पांच नदियों की भमि है।
- भूमिगत जल का स्तर पंजाब में बढ़ रहा है।
- भारत में लगभग 70% स्त्रोतों का आकार 2 हैक्टेयर से भी कम है।
- श्रम को हम बेच अथवा खरीद नहीं सकते हैं।
- पूंजी में घिसावट होती है।
उत्तर-
- सही
- गलत
- ग़लत
- सही
- सही
- सही
- ग़लत
- सही
- ग़लत
- सही।
अति लघु उत्तरों वाले प्रश्न।।
प्रश्न 1.
उपयोगिता की परिभाषा दें।
उत्तर-
उपयोगिता किसी वस्तु की वह शक्ति अथवा गुण है जिसके द्वारा हमारी आवश्यकताओं की संतुष्टि होती है।
प्रश्न 2.
सीमांत उपयोगिता की परिभाषा दें।
उत्तर-
किसी वस्तु की एक अतिरिक्त इकाई का उपयोग करने से कुल उपयोगिता में जो वृद्धि होती है, उस सीमांत उपयोगिता कहते हैं।
प्रश्न 3.
पदार्थ की परिभाषा दें।
उत्तर-
मार्शल के शब्दों में, “वे सभी वस्तुएं जो मनुष्य की आवश्यकताओं को संतुष्ट करती हैं, अर्थशास्त्र में पदार्थ कहलाती हैं।”
प्रश्न 4.
मध्यवर्ती और अंतिम वस्तुओं से क्या अभिप्राय है ?
उत्तर-
मध्यवर्ती वस्तुएं वे वस्तुएं हैं जिनका प्रयोग अन्य वस्तुओं के उत्पादन के लिए किया जाता है, जिनकी पुनः बिक्री की जाती है। अंतिम वस्तुएं वे वस्तुएं हैं जो उपभोग या निवेश के उद्देश्य से बाज़ार में बिक्री के लिए उपलब्ध
![]()
प्रश्न 5.
पूंजीगत वस्तुओं की परिभाषा दें।
उत्तर-
वे पदार्थ जिनके द्वारा किसी दूसरी वस्तु का उत्पादन होता है, जैसे कच्चा माल, मशीन इत्यादि, पूंजीगत वस्तुएं कहलाती हैं।
प्रश्न 6.
वस्तुओं और सेवाओं में क्या अंतर है ?
उत्तर-
वस्तुओं को देखा, छुआ तथा एक स्थान से दूसरे स्थान पर ले जाया जा सकता है। सेवाओं को देखा, छुआ और हस्तांतरित नहीं किया जा सकता है।
प्रश्न 7.
धन की परिभाषा दें।
उत्तर-
अर्थशास्त्र में वे सभी वस्तुएं जो विनिमय साध्य हैं, जिनमें उपयोगिता है तथा जो सीमित मात्रा में हैं. धन कहलाती हैं।
प्रश्न 8.
दुर्लभता से क्या अभिप्राय है ?
उत्तर-
दुर्लभता का अर्थ किसी वस्तु अथवा सेवा की पूर्ति का उसकी मांग से कम होता है।
प्रश्न 9.
क्या बी०ए० की डिग्री और व्यवसाय की साख धन है ?
उत्तर-
- बी०ए० की डिग्री धन नहीं है क्योंकि यह उपयोगी और दुर्लभ तो है पर हस्तांतरणीय नहीं होती।
- व्यवसाय की साख धन है क्योंकि इसमें धन के तीन गुण-उपयोगिता, दुर्लभता तथा विनिमय साध्यता हैं।
प्रश्न 10.
मुद्रा की परिभाषा दें।
उत्तर-
मुद्रा कोई भी वस्तुं हो सकती है जिसको सामान्य रूप से, वस्तुओं के हस्तांतरण में विनिमय के माध्यम के रूप में स्वीकार किया जाता है।
प्रश्न 11.
मांग से क्या अभिप्राय है ?
उत्तर-
मांग किसी वस्तु की वह मात्रा है जिसे एक उपभोक्ता समय की एक निश्चित अवधि में, एक निश्चित कीमत पर खरीदने के लिए इच्छुक तथा योग्य है।
प्रश्न 12.
पूर्ति की परिभाषा दें।
उत्तर-
किसी वस्तु की पूर्ति से अभिप्राय वस्तु की उस मात्रा से है जिसको एक विक्रेता एक निश्चित कीमत पर निश्चित समय-अवधि में बेचने के लिए तैयार होता है।
प्रश्न 13.
मौद्रिक लागत की परिभाषा दें।
उत्तर-
किसी वस्तु का उत्पादन और बिक्री करने के लिए मुद्रा के रूप में जो धन खर्च किया जाता है, उसे उस वस्तु की मौद्रिक लागत कहते हैं।
प्रश्न 14.
सीमांत लागत की परिभाषा दें।
उत्तर-
किसी वस्तु की एक अतिरिक्त इकाई का उत्पादन करने पर कुल लागत में जो वृद्धि होती है, उसे सीमांत लागत कहते हैं।
प्रश्न 15.
औसत लागत से क्या अभिप्राय है ?
उत्तर-
किसी वस्तु की प्रति इकाई को औसत लागत कहते हैं। कुल लागत को उत्पादन की मात्रा में भाग देने पर औसत लागत निकल आती है।
प्रश्न 16.
आय की परिभाषा दें।
उत्तर-
किसी वस्तु की बिक्री करने पर एक फ़र्म को जो राशि प्राप्त होती है, उसे फर्म की आय या आगम कहा जाता है।
![]()
प्रश्न 17.
सीमांत आय की परिभाषा दें।
उत्तर-
एक फ़र्म द्वारा अपने उत्पादन की एक अतिरिक्त इकाई बेचने से कुल आगम में जो वृद्धि होती है, उसे सीमांत आगम कहते हैं।
प्रश्न 18.
कीमत की परिभाषा दें।
उत्तर-
किसी वस्तु अथवा सेवा की एक निश्चित गुणवत्ता की एक इकाई प्राप्त करने के लिए दी जाने वाली मुद्रा की राशि को कीमत कहते हैं।
प्रश्न 19.
पूर्ण प्रतियोगिता में सीमांत आय और औसत आय में क्या संबंध होता है ?
उत्तर-
पूर्ण प्रतियोगिता में चूंकि कीमत (औसत आय) एक समान रहती है, इसलिए औसत आय तथा सीमांत आय दोनों बराबर होती हैं।
प्रश्न 20.
एकाधिकार की स्थिति में सीमांत आगम और औसत आगम में क्या संबंध होता है ?
उत्तर-
एकाधिकार की स्थिति में अधिक उत्पादन बेचने के लिए कीमत (औसत आगम) कम करनी पड़ती है। इसलिए अगर औसत आगम और सीमांत आगम दोनों नीचे की ओर गिर रही होती हैं।
प्रश्न 21.
पूर्ण प्रतियोगिता की परिभाषा दें।
उत्तर-
पूर्ण प्रतियोगिता वह स्थिति है जिसमें किसी समरूप वस्तु के बहुत सारे क्रेता और विक्रेता होते हैं और वस्तु की कीमत उद्योग द्वारा निर्धारित होती है।
प्रश्न 22.
एकाधिकार की परिभाषा दें।
उत्तर-
एकाधिकार बाजार की वह स्थिति है जिसमें किसी वस्तु या सेवा का केवल एक ही उत्पादक होता है, पर वस्तु का कोई निकटतम प्रतिस्थानापन्न नहीं होता।
प्रश्न 23.
बाज़ार की परिभाषा दें।
उत्तर-
अर्थशास्त्र में बाज़ार का अर्थ किसी विशेष स्थान से नहीं है बल्कि ऐसे क्षेत्र से है जहां क्रेता और विक्रेता में एक-दूसरे से इस प्रकार स्वतंत्र संपर्क हो कि एक ही प्रकार की वस्तु की कीमत की प्रवृत्ति आसानी से एक होने की पाई जाए।
प्रश्न 24.
उत्पादन के साधनों से क्या अभिप्राय है ?
उत्तर-
उत्पादन की प्रक्रिया में शामिल होने वाली सेवाओं के स्रोतों को उत्पादन साधन कहा जाता है।
प्रश्न 25.
भूमि की परिभाषा दें।
उत्तर-
भूमि से अभिप्राय केवल ज़मीन की ऊपरी सतह से नहीं है, बल्कि उन सभी पदार्थों और शक्तियों से है जिन्हें प्रकृति, भूमि, पानी, हवा, प्रकाश और गर्मी के रूप में मनुष्य, की सहायता के लिए मुफ़्त प्रदान करती है।
प्रश्न 26.
पूंजी की परिभाषा दें।
उत्तर-
मार्शल के शब्दों में, “प्रकृति के मुफ़्त उपहारों को छोड़कर सब प्रकार की संपत्ति जिससे आय प्राप्त होती है, पूंजी कहलाती है।”
प्रश्न 27.
श्रम से क्या अभिप्राय है ?
उत्तर-
मनुष्य के वे सभी शारीरिक तथा मानसिक कार्य जो धन प्राप्ति के लिए किए जाते हैं, श्रम कहलाते हैं।
प्रश्न 28.
उद्यमी से क्या अभिप्राय है ?
उत्तर-
उद्यमी उत्पादन का वह साधन है जो भूमि, श्रम, पूंजी तथा संगठन को इकट्ठा करता है, आर्थिक निर्णय करता है और जोखिम उठाता है।
प्रश्न 29.
लगान की परंपरागत परिभाषा दें।
उत्तर-
परंपरावादी अर्थशास्त्रियों के अनुसार, “आर्थिक लगान वह लगान है जो सिर्फ़ भूमि की सेवाओं के लिए प्राप्त होता है।”
![]()
प्रश्न 30.
लगान की आधुनिक परिभाषा दें।
उत्तर-
आधुनिक अर्थशास्त्रियों के अनुसार, “उत्पादन के प्रत्येक साधन से आर्थिक लगान उत्पन्न होता है जबकि उसकी पूर्ति सीमित हो। किसी साधन की वास्तविक आय और हस्तांतरण आय के अंतर को लगान कहा जाता है।”
प्रश्न 31.
मज़दूरी की परिभाषा दें।
उत्तर-
मजदूरी से अभिप्राय उस भुगतान से है जो सभी प्रकार के मानसिक तथा शारीरिक परिश्रम के लिए दिया जाता है।
प्रश्न 32.
वास्तविक मजदूरी से क्या अभिप्राय है ?
उत्तर-
वास्तविक मज़दूरी से अभिप्राय वस्तुओं तथा सेवाओं की उस मात्रा से है जो एक श्रमिक अपनी मजदूरी के बदले में प्राप्त कर सकता है।
प्रश्न 33.
नकद मज़दूरी से क्या अभिप्राय है ?
उत्तर-
नकद मजदूरी मुद्रा की वह मात्रा है जो प्रति घंटा, प्रतिदिन, प्रति सप्ताह, प्रति मास के हिसाब से प्राप्त होती
प्रश्न 34.
ब्याज की परिभाषा दें।
उत्तर-
ब्याज वह कीमत है जो मुद्रा को एक निश्चित समय के लिए प्रयोग करने के लिए ऋणी द्वारा ऋणदाता को दी जाती है।
प्रश्न 35.
कुल ब्याज तथा शुद्ध ब्याज में क्या अंतर है ?
उत्तर-
कुल ब्याज से अभिप्राय उस सारे धन से है जो ऋणी ऋणदाता को देता है जबकि शुद्ध ब्याज कुल ब्याज का वह अंग है जो केवल पूंजी के उपयोग के लिए दिया जाता है।
प्रश्न 36.
लाभ से क्या अभिप्राय है ?
उत्तर-
एक उद्यमी अपने व्यवसाय की कुल आय में से कुल लागत को घटाकर जो धनात्मक (-) शेष प्राप्त करता है, उसे लाभ कहते हैं।
प्रश्न 37.
कुल लाभ तथा शुद्ध लाभ में क्या अंतर है ?
उत्तर-
शुद्ध लाभ का अभिप्राय है कुल लाभ तथा आंतरिक लागतों का अंतर जबकि कुल लाभ का अभिप्राय है कुल आय तथा कुल बाहरी लागतों का अंतर।
प्रश्न 38.
कुल लाभ की परिभाषा दें।
उत्तर-
कुल लाभ वह अधिशेष है जो उत्पादन कार्य में उत्पादन के सभी साधनों को उनके परिश्रम का पुरस्कार चुकाने के बाद उद्यमी को प्राप्त होता है।
प्रश्न 39.
शुद्ध लाभ से क्या अभिप्राय है ?
उत्तर-
शुद्ध लाभ का अनुमान लगाने के लिए कुल लाभ में से आंतरिक.लागतों, घिसावट और बीमा आदि का खर्च . घटा दिया जाता है।
![]()
छोटे उत्तरों वाले प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
उपयोगिता की परिभाषा दें। उसकी विशेषताएं बताएं।
उत्तर-
उपयोगिता की परिभाषा-उपयोगिता किसी वस्तु की वह शक्ति है जिसके द्वारा मनुष्य की आवश्यकताओं की संतुष्टि होती है। उपयोगिता की विशेषताएं
- उपयोगिता एक भावगत तथ्य है-उपयोगिता को हम केवल अनुभव कर सकते हैं, उसे स्पर्श अथवा देखा नहीं जा सकता।
- उपयोगिता सापेक्षिक है-यह समय, स्थान तथा व्यक्ति के साथ बदल जाती है।
- उपयोगिता का लाभदायक होना आवश्यक नहीं है-यह ज़रूरी नहीं कि जिस वस्तु की उपयोगिता है, वह लाभदायक भी हो।
- उपयोगिता का नैतिकता के साथ संबंध नहीं है-यह ज़रूरी नहीं कि जो वस्तु उपयोगी है, वह नैतिक दृष्टि से भी ठीक हो।
प्रश्न 2.
कुल उपयोगिता, सीमांत उपयोगिता और औसत उपयोगिता की धारणाओं को उदाहरण सहित समझाइये।
उत्तर-
- कुल उपयोगिता-किसी वस्तु की विभिन्न मात्राओं के उपभोग से प्राप्त उपयोगिता की इकाइयों के जोड़ को कुल उपयोगिता कहा जाता है।
- सीमांत उपयोगिता-किसी वस्तु की एक अतिरिक्त इकाई का उपभोग करने से कुल उपयोगिता में जो परिवर्तन आता है, उसे सीमांत उपयोगिता कहते हैं। माना पहला रसगुल्ला खाने से एक व्यक्ति को 15 इंकाई उपयोगिता प्राप्त होती है। दूसरा रसगुल्ला खाने के फलस्वरूप दोनों रसगुल्लों से मिलने वाली कुल उपयोगिता 25 इकाई हो जाती है। अत: 25 – 15 = 10 इकाई सीमांत उपयोगिता है। इस प्रकार प्रारंभिक उपयोगिता 15 इकाई होगी।
- औसत उपयोगिता-किसी वस्तु की कुल इकाइयों की कुल उपयोगिता को इकाइयों की मात्रा से विभाजित करने से हमारे पास औसत उपयोगिता आ जाती है। 3 वस्तुओं से 15 उपयोगिता मिलती है तो एक वस्तु की औसत उपयोगिता \(\frac{15}{3}\) = 5 है।
प्रश्न 3.
पदार्थ की परिभाषा दें और उसका वर्गीकरण करें।
उत्तर-
पदार्थ की परिभाषा-मार्शल के शब्दों में, “वे सब पदार्थ जो मनुष्य की आवश्यकताओं को संतुष्ट करते हैं, अर्थशास्त्र में पदार्थ कहलाते हैं।”
पदार्थ का वर्गीकरण-
- भौतिक पदार्थ-जिन्हें देखा जा सकता है।
- अभौतिक पदार्थ या सेवाएं-जिन्हें देखा नहीं जा सकता।
- आर्थिक पदार्थ-ये वे पदार्थ हैं जो मूल्य द्वारा प्राप्त किए जाते हैं।
- निःशुल्क पदार्थ-वे पदार्थ हैं जो बिना किसी मूल्य के मिल जाते हैं।
- उपभोक्ता पदार्थ उपभोक्ता की आवश्यकता को प्रत्यक्ष रूप से संतुष्ट करते हैं।
- उत्पादक पदार्थ-अन्य वस्तुओं का उत्पादन करने में सहायक होते हैं।
- नाशवान् पदार्थ-जिनका केवल एक बार ही प्रयोग किया जा सकता है।
- टिकाऊ पदार्थ-वे पदार्थ जो काफ़ी समय तक काम में लाए जा सकते हैं।
- मध्यवर्ती पदार्थ-मध्यवर्ती पदार्थ वे पदार्थ हैं जिनका प्रयोग अन्य वस्तुओं और सेवाओं के उत्पादन के लिए किया जाता है।
- अंतिम पदार्थ-अंतिम पदार्थ वे पदार्थ हैं जो उपभोग या निवेश के उद्देश्य से बाज़ार में बिक्री के लिए उपलब्ध
- सार्वजनिक पदार्थ-जिन पदार्थों पर सरकार का स्वामित्व होता है।
- निजी पदार्थ-वे पदार्थ जिन पर किसी व्यक्ति का निजी अधिकार होता है।
- प्राकृतिक पदार्थ-जो प्रकृति ने लोगों को उपहार के रूप में प्रदान किए हैं।
- मानव द्वारा निर्मित पदार्थ-जिनका उत्पादन मानव द्वारा किया जाता है।
प्रश्न 4.
मुद्रा की परिभाषा दें। मुद्रा के मुख्य कार्य कौन-से हैं ?
उत्तर-
मुद्रा का अर्थ-मुद्रा कोई भी वस्तु हो सकती है जिसको सामान्य रूप से, वस्तुओं के हस्तांतरण में विनिमय के माध्यम के रूप में स्वीकार किया जाता है।
मुद्रा के कार्य-
- विनिमय का माध्यम-सभी वस्तुएं मुद्रा के द्वारा खरीदी और बेची जाती हैं।
- मूल्य का मापदंड-सभी वस्तुओं का मूल्य मुद्रा में ही व्यक्त किया जाता है।
- भावी भुगतान का मान-सभी प्रकार के ऋण मुद्रा के रूप में ही लिए और दिए जाते हैं।
- धन का संग्रह- मुद्रा के रूप में धन का संग्रह करना सरल हो जाता है।
- विनिमय शक्ति का हस्तांतरण-मुद्रा के रूप में धन को एक स्थान से दूसरे स्थान पर आसानी से भेजा जा सकता है।
प्रश्न 5.
मांग से क्या अभिप्राय है ? एक तालिका और रेखाचित्र की सहायता से मांग की धारणा को स्पष्ट करें।
उत्तर-
मांग का अर्थ-“मांग किसी वस्तु की वह मात्रा है जिसको एक उपभोक्ता समय की एक निश्चित अवधि में, एक निश्चित कीमत पर खरीदने के लिए इच्छुक और योग्य है।”
मांग तालिका–मांग की धारणा को निम्नलिखित तालिका द्वारा स्पष्ट किया जा सकता है-
| कीमत (₹) | मांग की मात्रा (कि० ग्रा०) |
| 1 | 40 |
| 2 | 30 |
| 3 | 20 |
| 4 | 10 |
तालिका से स्पष्ट है कि जैसे-जैसे वस्तु की कीमत बढ़ती जाती है, उसकी मांग कम होती जाती है।
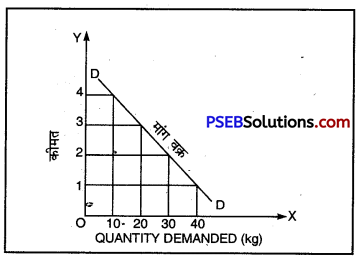
मांग वक्र-मांग वक्र वह वक्र है जो मांग और कीमत का संबंध प्रकट करता है। मांग वक्र की सहायता से भी मांग को स्पष्ट किया जा सकता है। जब कीमत ₹ 1 है तो मांग 40 इकाइयां है, जब कीमत ₹4 है तो मांग 10 इकाइयां है। इस प्रकार मांग वक्र का ढलान ऊपर से बाईं ओर तथा नीचे दाईं
ओर होता है जो यह दर्शाता है कि कीमत अधिक होने पर मांग कम होती है और कीमत कम होने पर मांग अधिक होती है।
![]()
प्रश्न 6.
पूर्ति की परिभाषा दें। एक तालिका और रेखाचित्र द्वारा पूर्ति की धारणा को स्पष्ट करें।
उत्तर-
पूर्ति की परिभाषा-किसी वस्तु की पूर्ति से अभिप्राय वस्तु की उस मात्रा से है जिसको एक विक्रेता एक निश्चित समय में किसी कीमत पर बेचने के लिए तैयार होता है।
पूर्ति तालिका-पूर्ति तालिका एक ऐसी तालिका है जिसके द्वारा वस्तु की पूर्ति की मात्रा का उसकी कीमत से संबंध दिखाया जा सकता है।
पूर्ति तालिका-पूर्ति की धारणा को निम्नलिखित तालिका द्वारा स्पष्ट किया जा सकता है
| कीमत (₹) | मांग की मात्रा (कि० ग्रा०) |
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 10 |
| 3 | 20 |
| 4 | 30 |
तालिका से स्पष्ट होता है कि जैसे-जैसे वस्तु की कीमत बढ़ रही है, उसकी पूर्ति की मात्रा भी बढ़ रही है। इस प्रकार पूर्ति तालिका कीमत और बेची जाने वाली मात्रा के संबंध को दिखाती है।
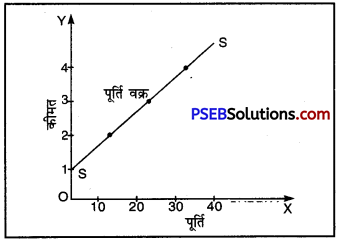
पूर्ति वक्र-पूर्ति वक्र वह वक्र है जो किसी वस्तु की कीमत तथा पूर्ति का संबंध प्रकट करता है। रेखाचित्र में पूर्ति वक्र है जो बाएं से दाएं ऊपर को जा रहा है। SS पूर्ति वक्र के धनात्मक ढलान से ज्ञात होता है कि कीमत के बढ़ने पर पूर्ति बढ़ती है और कीमत के कम होने पर पूर्ति कम होती है।
प्रश्न 7.
लागत की परिभाषा दें। कुल लागत, सीमांत लागत और औसत लागत की धारणाओं की व्याख्या करें।
उत्तर-
लागत की परिभाषा-किसी वस्तु की एक निश्चित मात्रा का उत्पादन करने के लिए उत्पादन के साधनों को जो कुल मौद्रिक भुगतान करना पड़ता है, उसे मौद्रिक उत्पादन लागत कहते हैं।
कुल लागत-किसी वस्तु की एक निश्चित मात्रा का उत्पादन पाने के लिए जो धन खर्च करना पड़ता है, उसे कुल लागत कहते हैं।
औसत लागत-किसी वस्तु की प्रति इकाई लागत को औसत लागत कहते हैं। कुल लागत को उत्पादन की मात्रा से भाग देने पर औसत लागत का पता लगता है।
कुल लागत
![]()
सीमांत लागत-सीमांत लागत कुल लागत में वह परिवर्तन है जो एक वस्तु की एक और इकाई पैदा करने पर खर्च आती है।
प्रश्न 8.
आय की परिभाषा दें। कुल आय, सीमांत आय और औसत आय से क्या अभिप्राय है ?
उत्तर-
आय की परिभाषा-किसी वस्तु की बिक्री करने पर एक फ़र्म को जो कुल राशि प्राप्त होती है, उसे फ़र्म की आगम (आय) कहा जाता है।
कुल आय-एक फ़र्म द्वारा अपने उत्पादन की एक निश्चित मात्रा बेच कर जो धन प्राप्त होता है, उसे कुल आय कहते हैं।
सीमांत आय–एक फ़र्म द्वारा अपने उत्पादन की एक इकाई अधिक बेचने से कुल आगम में जो वृद्धि होती है, उसको सीमांत आय कहा जाता है।
औसत आय-किसी वस्तु की बिक्री से प्राप्त होने वाली प्रति इकाई आगम औसत आय कहलाती है।
![]()
प्रश्न 9.
फ़र्म की परिभाषा दें। एक उत्पादक के रूप में फ़र्म के कार्यों का वर्णन करें।
उत्तर-
फ़र्म की परिभाषा-फ़र्म उत्पादन की वह इकाई है जो लाभ प्राप्त करने की दृष्टि से बिक्री के लिए उत्पादन करती है।
एक उत्पादक के रूप में फ़र्म के कार्य-उत्पादक के रूप में फ़र्म वस्तुओं और सेवाओं का उत्पादन करती है और उनकी बिक्री करती है। एक फ़र्म अपना उत्पादन न्यूनतम लागत पर करने का प्रयत्न करती है और वह उसको बेचकर अधिकतम लाभ प्राप्त करना चाहती है। एक उत्पादक के रूप में फ़र्म वास्तव में उद्यमी का ही एक रूप होती है।
प्रश्न 10.
बाजार की परिभाषा दें। बाजार की मख्य विशेषताएं कौन-सी हैं ?
उत्तर-
बाज़ार की परिभाषा-कूरनो के शब्दों में, “अर्थशास्त्री बाज़ार का अर्थ किसी विशेष स्थान से नहीं लेते जहां वस्तुएं खरीदी या बेची जाती हैं बल्कि उस सारे क्षेत्र से लेते हैं जहां क्रेता और विक्रेता में एक-दूसरे से इस प्रकार स्वतंत्र संपर्क हो कि एक ही प्रकार की वस्तु की कीमत की प्रवृत्ति आसानी और शीघ्रता से एक होने की पाई जाए।”
बाज़ार की मुख्य विशेषताएं-
- क्षेत्र-अर्थशास्त्र में ‘बाज़ार’ शब्द से आशय किसी स्थान विशेष से नहीं है बल्कि बाज़ार का बोध उस संपूर्ण क्षेत्र से होता है, जिसमें बेचने वाले और खरीदने वाले फैले होते हैं।
- एक वस्तु-अर्थशास्त्र में ‘बाजार’ एक ही वस्तु का माना जाता है; जैसे घी का बाज़ार, फल का बाज़ार इत्यादि।
- क्रेता-विक्रेता-क्रेता एवं विक्रेता दोनों ही बाजार के महत्त्वपूर्ण एवं अभिन्न अंग हैं।
- स्वतंत्र प्रतियोगिता-बाज़ार में क्रेताओं एवं विक्रेताओं में स्वतंत्र रूप से प्रतियोगिता होनी चाहिए।
- एक कीमत-जब बाज़ार में क्रेताओं एवं विक्रेताओं में स्वतंत्र प्रतियोगिता होगी तो इसका परिणाम यह होगा कि वस्तु की कीमत एक समय में एक ही होगी।
प्रश्न 11.
संतुलन की धारणा से क्या अभिप्राय है ?
उत्तर-
संतुलन का अर्थ-“संतुलन वह अवस्था है, जिसमें विरोधी दिशा में परिवर्तन लाने वाली शक्तियां पूर्ण रूप से एक-दूसरे के बराबर होती हैं अर्थात् परिवर्तन की कोई प्रवृत्ति नहीं पाई जाती।”
उदाहरण के लिए, जब एक फ़र्म को अधिकतम लाभ प्राप्त होते हैं, उसमें परिवर्तन की प्रवृत्ति नहीं पाई जाती। फ़र्म की इस स्थिति को संतुलन की स्थिति कहा जाएगा।
![]()
प्रश्न 12.
पूर्ण प्रतियोगिता की परिभाषा दें। इसकी विशेषताएं कौन-सी हैं ?
उत्तर-
पूर्ण प्रतियोगिता की परिभाषा-पूर्ण प्रतियोगिता बाज़ार की वह स्थिति है जिसमें बहुत सारी फ़र्मे होती हैं और वे सभी एक समरूप वस्तु की बिक्री करती हैं। इस अवस्था में फ़र्म कीमत स्वीकार करने वाली होती है न कि निर्धारित करने वाली।
पूर्ण प्रतियोगिता की विशेषताएं-पूर्ण प्रतियोगिता की मुख्य विशेषताएं निम्नलिखित हैं-
- क्रेताओं और विक्रेताओं की अधिक संख्या
- समरूप वस्तुएं
- पूर्ण ज्ञान
- फ़र्मों का स्वतंत्र प्रवेश व निकास
- समान कीमत
- साधनों में पूर्ण गतिशीलता।
प्रश्न 13.
एकाधिकार की परिभाषा दें। इसकी विशेषताएं कौन-सी हैं ?
उत्तर-
एकाधिकार की परिभाषा-एकाधिकार वह स्थिति है जिसमें बाजार में एक वस्तु का केवल एक ही उत्पादक होता है।
एकाधिकार की विशेषताएं-एकाधिकार बाजार की मुख्य विशेषताएं इस प्रकार हैं
- एक विक्रेता तथा अधिक क्रेता-एकाधिकार बाज़ार में वस्तु का केवल एक ही विक्रेता होता है। वस्तु के क्रेता बहुत अधिक संख्या में होते हैं।
- नई फ़र्मे बाज़ार में नहीं आ सकतीं-एकाधिकारी बाज़ार में कोई नई फ़र्म प्रवेश नहीं कर सकती।
- निकटतम स्थानापन्न नहीं होता-एकाधिकार बाज़ार में उत्पादित वस्तुओं का कोई निकटतम स्थानापन्न नहीं होता।
- कीमत पर नियंत्रण-एकाधिकारी का वस्तु की कीमत पर नियंत्रण होता है।
प्रश्न 14.
आर्थिक क्रियाएं क्या हैं ? उनके मुख्य प्रकार कौन-से हैं ?
उत्तर-
आर्थिक क्रियाओं का अर्थ-आर्थिक क्रियाएं वे क्रियाएं हैं जिनका संबंध धन के उपभोग, उत्पादन, विनिमय तथा वितरण से होता है। इन क्रियाओं का मुख्य उद्देश्य धन की प्राप्ति होता है।
आर्थिक क्रियाओं के प्रकार-
- उपभोग-उपभोग वह आर्थिक क्रिया है जिसका संबंध आवश्यकताओं की प्रत्यक्ष संतुष्टि के लिए वस्तुओं और सेवाओं की उपयोगिता के उपभोग से होता है।
- उत्पादन-उत्पादन वह आर्थिक क्रिया है जिसका संबंध वस्तुओं और सेवाओं की उपयोगिता या कीमत में वृद्धि करने से है।
- विनिमय-विनिमय वह क्रिया है जिसका संबंध किसी वस्तु के क्रय-विक्रय से है।
- वितरण-वितरण का संबंध उत्पादन के साधनों की कीमत अर्थात् भूमि की कीमत (लगान), श्रम की कीमत (मज़दूरी), पूंजी की कीमत (ब्याज) और उद्यमी को प्राप्त होने वाली कीमत (लाभ) के निर्धारण से है।
प्रश्न 15.
आर्थिक और अनार्थिक क्रियाओं में अंतर बताओ।
उत्तर-
यदि कोई क्रिया धन प्राप्त करने के लिए की जाती है तो इस क्रिया को आर्थिक क्रिया कहा जाता है। इसके विपरीत यदि वह ही क्रिया मनोरंजन, धर्म, प्यार, दया, देश-प्रेम, समाज-सेवा, कर्त्तव्य आदि उद्देश्यों के लिए की जाती है तो उसको अनार्थिक क्रिया कहा जायेगा। इस अंतर को एक उदाहरण के द्वारा स्पष्ट किया जा सकता है। माना अर्थशास्त्र के अध्यापक 500 रुपए प्रति माह फीस लेकर आपको एक घंटा घर पर ही अर्थशास्त्र पढ़ाते हैं तो उनकी यह क्रिया आर्थिक क्रिया कहलाती है। इसके विपरीत यदि वह आपको एक निर्धन विद्यार्थी होने के नाते बिना कोई फीस लिए मुफ्त में अर्थशास्त्र पढाते हैं, तो उनकी यह क्रिया अनार्थिक क्रिया कहलाती है।
प्रश्न 16.
भूमि की परिभाषा दें। इसकी मुख्य विशेषताएं कौन-सी हैं ?
उत्तर-
भूमि की परिभाषा-अर्थशास्त्र में भूमि के अंतर्गत भूमि की ऊपरी सतह ही नहीं बल्कि पृथ्वी के तल पर, उसके नीचे और उसके ऊपर, प्रकृति द्वारा निःशुल्क प्रदान की जाने वाली सब वस्तुएं सम्मिलित हो जाती हैं, जो धनोत्पादन में मनुष्य की सहायता करती हैं।
भूमि की मुख्य विशेषताएं-
- भूमि परिमाण में सीमित है।
- भूमि उत्पादन का प्राथमिक साधन है।
- भूमि स्थिर है।
- भूमि उपजाऊपन की दृष्टि से भिन्नता रखती है।
- भूमि अक्षय है।
- भूमि का मूल्य स्थिति पर निर्भर करता है।
- भूमि प्रकृति की नि:शुल्क देन है।
- भूमि उत्पादन का निष्क्रिय साधन है।
प्रश्न 17.
श्रम से क्या अभिप्राय है ? इसकी मुख्य विशेषताएं बताएं।
उत्तर-
श्रम का अर्थ-साधारण भाषा में श्रम का आशय उस प्रयत्न या चेष्टा से है जो किसी कार्य के संपादन हेतु किया जाता है लेकिन श्रम का यह व्यापक अर्थ अर्थशास्त्र में नहीं लिया जाता। अर्थशास्त्र में किसी प्रतिफल के लिए किया गया मानवीय प्रयत्न, मानसिक या शारीरिक श्रम कहलाता है।
श्रम की मुख्य विशेषताएं-
- श्रम एक मानवीय साधन है।
- श्रम एक सक्रिय साधन है।
- श्रम को श्रमिक से अलग नहीं किया जा सकता है।
- श्रम नाशवान होता है।
- श्रमिक अपने श्रम को बेचता है अपने आपको नहीं बेचता है।
- श्रमिक उत्पादन का साधन और साध्य दोनों है।
- श्रमिक की कार्यकुशलता में विभिन्नता पाई जाती है।
- श्रम में गतिशीलता होती है।
प्रश्न 18.
पूंजी की परिभाषा दें। इसकी मुख्य विशेषताएं कौन-सी हैं ?
उत्तर-
पूंजी की परिभाषा–मार्शल के शब्दों में, “प्रकृति प्रदत्त उपहारों के अतिरिक्त पूंजी में सभी प्रकार की संपत्ति शामिल होती है जिससे आय प्राप्त होती है।”
पूंजी की विशेषताएं-
- पूंजी उत्पादन का निष्क्रिय साधन है।
- पूंजी में उत्पादकता होती है।
- पूंजी अत्यधिक गतिशील होती है।
- पूंजी श्रम द्वारा उत्पादित होती है।
- पूंजी में ह्रास होता है।
- पूंजी बचत किए गए धन का एक रूप है।
![]()
प्रश्न 19.
उद्यमी से क्या अभिप्राय है ? उद्यमी के कार्यों का वर्णन करें।
उत्तर-
प्रत्येक व्यवसाय में चाहे वह छोटा हो अथवा बड़ा, कुछ-न-कुछ जोखिम अथवा लाभ-हानि की अनिश्चितता अवश्य बनी रहती है। इस जोखिम को सहन करने वाले व्यक्ति को ‘साहसी’ या ‘उद्यमी’ कहा जाता है।
उद्यमी के कार्य-
- व्यवसाय का चुनाव करता है।
- उत्पादन का पैमाना निर्धारित करता है।
- साधनों का अनुकूलतम संयोग प्राप्त करता है।
- उत्पादन के स्थान का निर्धारण करता है।
- वस्तु का चयन करता है।
- वितरण संबंधी कार्य करता है।
- जोखिम उठाने का दायित्व उद्यमी पर होता है।
प्रश्न 20.
लगान की धारणा से क्या अभिप्राय है?
उत्तर-
साधारण बोलचाल की भाषा में लगान या किराया शब्द का प्रयोग उस भुगतान के लिए किया जाता है जो किसी वस्तु जैसे मकान, दुकान, फर्नीचर, क्राकरी आदि की सेवाओं का उपयोग करने के लिए अथवा उत्पादन के साधनों के रूप में प्रयोग करने के लिए नियमित रूप से एक निश्चित अवधि के लिए दिया जाता है। परंतु अर्थशास्त्र में लगान शब्द का प्रयोग विभिन्न अर्थों में किया जाता है। प्रो० कारवर के अनुसार, “भूमि के प्रयोग के लिए दी गई कीमत लगान है।” परंतु आधुनिक अर्थशास्त्रियों के अनुसार अर्थशास्त्र में लगान शब्द का प्रयोग उत्पादन के उन साधनों को दिए जाने वाले भुगतान के लिए ही किया जाता है जिनकी पूर्ति बेलोचदार होती है। आधुनिक अर्थशास्त्रियों के अनुसार किसी साधन की वास्तविक आय तथा हस्तान्तरण आय के अंतर को लगान कहते हैं।
प्रश्न 21.
मज़दूरी की परिभाषा दें। नकद और वास्तविक मजदूरी से क्या अभिप्राय है ?
उत्तर-
मजदूरी की परिभाषा-मजदूरी से अभिप्राय उस भुगतान से है जो सभी प्रकार की मानसिक तथा शारीरिक क्रियाओं के लिए दिया जाता है।
नकद मजदूरी-जो मजदूरी रुपयों के रूप में दी जाती है, उसे नकद मज़दूरी कहते हैं। यह दैनिक, साप्ताहिक, पाक्षिक या मासिक हो सकती है।
वास्तविक मजदूरी-श्रमिक को मुद्रा के अतिरिक्त जो वस्तुएं या सुविधायें प्राप्त होती हैं, उसे असल या वास्तविक मज़दूरी कहते हैं; जैसे—मुफ़्त मकान, पानी, बिजली, चिकित्सा सुविधा, शिक्षा आदि।
प्रश्न 22.
ब्याज की परिभाषा दें। शुद्ध और कुल ब्याज से क्या अभिप्राय है ?
उत्तर-
ब्याज की परिभाषा-ब्याज वह कीमत है जो मुद्रा को एक निश्चित समय के लिए प्रयोग करने के लिए ऋणी द्वारा ऋणदाता को दी जाती है।
कुल ब्याज-एक ऋणी द्वारा वास्तव में ऋणदाता को ब्याज के रूप में जो कुल भुगतान किया जाता है, उसको कुल ब्याज कहते हैं।
शुद्ध ब्याज-शुद्ध ब्याज वह धनराशि है जो केवल मुद्रा के प्रयोग के बदले में चुकाई जाती है। चैपमैन के शब्दों में, “शुद्ध ब्याज पूंजी के ऋण के लिए भुगतान है, जबकि कोई जोखिम न हो, कोई असुविधा न हो, (बचत की असुविधा को छोड़कर) और उधार देने वाले के लिए कोई कार्य न हो।”
प्रश्न 23.
लाभ की धारणा से क्या अभिप्राय है ? कुल और शुद्ध लाभ से क्या अभिप्राय है ?
उत्तर-
लाभ का अर्थ-साहसी को जोखिम के बदले में जो कुछ मिलता है, वह लाभ कहलाता है अर्थात् राष्ट्रीय आय का वह भाग जो किसी साहसी को अपने साहस के कारण प्राप्त होता है, उसे लाभ कहते हैं। कुल आय में से यदि कुल खर्च निकाल दिया जाए तो जो शेष बचे, उसे लाभ कहते हैं।
कुल लाभ-कुल आगम में से यदि हम उत्पादन की स्पष्ट लागतें घटा दें तो जो अतिरेक बचता है, उसे कुल लाभ कहा जाता है।
कुल लाभ = कुल आगम – स्पष्ट लागत
शुद्ध लाभ-यदि कुल आगम में से स्पष्ट और अस्पष्ट दोनों लागतें घटा दें तो जो अतिरेक बचता है, उसे शुद्ध लाभ कहा जाता है।
शुद्ध लाभ = कुल आगम – (स्पष्ट लागत + अस्पष्ट लागत)
दीर्घ उत्तरों वाले प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
बाज़ार किसे कहते हैं ? बाज़ार के वर्गीकरण के मुख्य आधारों का वर्णन कीजिए।
उत्तर-
बाज़ार का अर्थ-बाज़ार वह सम्पूर्ण क्षेत्र होता है जहां क्रेता और विक्रेता सम्पर्क में आते हैं।
बाज़ार के वर्गीकरण का आधार-बाज़ार का विस्तृत रूप से निम्नलिखित भागों में वर्गीकरण किया जाता है। जैसे-
- पूर्ण प्रतियोगी
- एकाधिकार
- एकाधिकारी प्रतियोगिता।
इस वर्गीकरण के मुख्य आधार निम्नलिखित हैं-
- क्रेताओं और विक्रेताओं की संख्या-यदि बाज़ार में क्रेताओं और विक्रेताओं की संख्या बहुत है तो वह पूर्ण प्रतियोगी अथवा एकाधिकारी प्रतियोगिता का बाज़ार होता है। यदि बाज़ार में वस्तु का केवल एक विक्रेता हो और क्रेताओं की संख्या अधिक हो तो वह एकाधिकारी बाज़ार होगा। यदि बाज़ार में वस्तु के थोड़े विक्रेता हों तो वह अल्पाधिकारी बाज़ार होगा।
- वस्तु की प्रकृति-यदि बाज़ार में बेची जाने वाली वस्तु एकसमान है तो वह पूर्ण प्रतियोगी बाज़ार की स्थिति होगी और इसके विपरीत वस्तु की विभिन्नता एकाधिकारी प्रतियोगिता का आधार माना जाता है।
- कीमत नियन्त्रण की डिग्री-बाज़ार में बेची जाने वाली वस्तु की कीमत पर यदि फ़र्म का पूर्ण नियन्त्रण हो तो वह एकाधिकारी होगा। आंशिक नियन्त्रण हो तो एकाधिकारी प्रतियोगिता होगी। शून्य नियन्त्रण पर पूर्ण प्रतियोगिता होती है।
- बाज़ार का ज्ञान-यदि क्रेताओं तथा विक्रेताओं को बाज़ार की स्थितियों का पूर्ण ज्ञान हो तो पूर्ण प्रतियोगिता होगी। इसके विपरीत अपूर्ण ज्ञान एकाधिकार तथा एकाधिकारी प्रतियोगिता की विशेषता है।
- साधनों की गतिशीलता- पूर्ण प्रतियोगिता की स्थिति में उत्पादन साधनों की गतिशीलता पूर्ण होती है परन्तु बाज़ार के अन्य प्रकारों में साधनों की गतिशीलता सामान्य नहीं होती।
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
मुद्रा के प्रमुख कार्य क्या-क्या हैं ?
उत्तर-
मुद्रा के निम्नलिखित कार्य हैं
- विनिमय का माध्यम-मुद्रा का एक महत्त्वपूर्ण कार्य विनिमय का माध्यम है। इसका अभिप्राय यह है कि मुद्रा के रूप में एक व्यक्ति अपनी वस्तुओं को बेचता है तथा दूसरी वस्तुओं को खरीदता है। मुद्रा क्रय तथा विक्रय दोनों में ही एक मध्यस्थ का कार्य करती है। मुद्रा को विनिमय के माध्यम के रूप में लोग सामान्य रूप से स्वीकार करते हैं। इसलिए मुद्रा के द्वारा लोग अपनी इच्छा से विभिन्न वस्तुएं खरीद सकते हैं।
- मूल्य की इकाई-मुद्रा का दूसरा कार्य वस्तुओं तथा सेवाओं के मूल्य को मापना है। मुद्रा लेखे की इकाई के रूप में मूल्य का माप करती है। लेखे की इकाई से अभिप्राय यह है कि प्रत्येक वस्तु तथा सेवा का मूल्य मुद्रा के रूप में मापा जाता है।
- स्थगित भुगतानों का मान-जिन लेन-देनों का भुगतान तत्काल न करके भविष्य के लिए स्थगित कर दिया जाता है, उन्हें स्थगित भुगतान कहा जाता है। मुद्रा के फलस्वरूप स्थगित भुगतान सरल हो जाता है।
- मूल्य का संचय-मुद्रा मूल्य के संचय के रूप में कार्य करती है। मुद्रा के मूल्य संचय का अर्थ है धन का संचय। इससे अभिप्राय यह है कि मुद्रा को वस्तुओं तथा सेवाओं के लिए खर्च करने का तुरन्त कोई विचार नहीं है। प्रत्येक व्यक्ति अपनी आय का कुछ भाग भविष्य के लिए बचाता है। इसे ही मूल्य का संचय कहा जाता है।
- मूल्य का हस्तान्तरण-मुद्रा के कारण मूल्य का हस्तांतरण सुविधाजनक बन गया है। आज इस युग में लोगों की आवश्यकताएं बढ़ गई हैं। इन आवश्यकताओं की पूर्ति के लिए दूर-दूर से वस्तुएं खरीदी जाती हैं। मुद्रा में तरलता तथा सामान्य स्वीकृति का गुण होने के कारण इसका एक स्थान से दूसरे स्थान पर हस्तान्तरण आसान हो जाता है।
- साख निर्माण का आधार-आज लगभग सभी देशों में चेक, ड्राफ्ट, विनिमय-पत्र इत्यादि साख-पत्रों का प्रयोग किया जाता है। इन साख-पत्रों का आधार मुद्रा ही है। लोग अपनी आय में से कुछ राशि बैंकों में जमा करवाते हैं। इस जमा राशि के आधार पर ही बैंक साख का निर्माण करते हैं।
एक गांव की कहानी PSEB 9th Class Economics Notes
- अर्थशास्त्र – अर्थशास्त्र मनुष्य के उन कार्यों का अध्ययन है जो हमें यह बताता है कि किस प्रकार दुर्लभ साधनों का प्रयोग करके अधिकतम संतुष्टि प्राप्त की जा सकती है।।
- वस्तुएं – वस्तुएं वे दृश्य मदें हैं जो मनुष्य की आवश्यकताएं पूरी करती हैं जैसे किताब, कुर्सी, मोबाइल आदि।
- सेवाएं – सेवाएं अदृश्य मदें हैं परंतु मनुष्य की आवश्यकताएं संतुष्ट करती हैं जैसे अध्यापन।
- उपयोगिता – आवश्यकताओं को संतुष्ट करने की शक्ति उपयोगिता है।
- कीमत – वस्तुओं और सेवाओं का वह मूल्य जो मुद्रा में व्यक्त किया जाता है।
- धन – वे सभी वस्तुएं तथा सेवाएं जो हम उपभोग करने के लिए कीमत देकर खरीदते हैं।
- मुद्रा – मुद्रा वह पदार्थ है जो सरकार द्वारा जारी किया जाता है तथा जिसे विनिमय के माध्यम के रूप में स्वीकार किया जाता है।
- मांग – अन्य बातें समान रहने पर, मांग किसी वस्तु की वह मात्रा है जिसे एक उपभोक्ता निश्चित कीमत तथा निश्चित समय पर खरीदने के लिए तैयार होता है।
- पूर्ति – पूर्ति किसी पदार्थ की वह मात्रा है जिसे एक उत्पादक निश्चित कीमत तथा निश्चित समय पर बेचने के लिए तैयार होता है।
- बाज़ार – बाज़ार एक स्थान है जहां क्रेता व विक्रेता एक साथ पाए जाते हैं।
- लागत – लागत मुद्रा के रूप में व्यय की गई वह मात्रा है जो वस्तु को बनाने से लेकर विक्री तक के बीच लगाई जाती है।
- आगम – आगम मुद्रा की वह मात्रा है जो किसी वस्तु की विक्री से प्राप्त होता है।
- आर्थिक क्रियाएं – आर्थिक क्रियाएं वे क्रियाएं हैं जो धन कमाने के उद्देश्य से की जाती हैं।
- गैर आर्थिक क्रियाएं – वे क्रियाएं जो धन कमाने के उद्देश्य से नहीं की जाती हैं।।
- उत्पादन – उपयोगिता का सृजन उत्पादन है।
- उत्पादन के साधन – भूमि, पूंजी, श्रम, उद्यमी उत्पादन के साधन हैं।
- भूमि – भूमि प्रकृति का निःशुल्क उपहार है जिसकी पूर्ति स्थिर है।
- श्रम – धन कमाने के उद्देश्य से किए गए सभी मानवीय प्रयास श्रम है।
- बहुविविध कृषि – भूमि के एक टुकड़े पर एक वर्ष में एक साथ एक से अधिक फसलें एक साथ उगाना बहु विविध कृषि कहलाती हैं।
- पूंजी – पूंजी का अर्थ उन सभी मानव निर्मित पदार्थों से है जो आगे उत्पादन करने के उद्देश्य से बनाए जाते हैं।
- उद्यमी – वह मानवीय तत्व जो उत्पादन संबंधी निर्णय तथा जोखिम उठाता है।