Punjab State Board PSEB 7th Class Hindi Book Solutions Chapter 5 हिमालय Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 7 Hindi Chapter 5 हिमालय
Hindi Guide for Class 7 PSEB हिमालय Textbook Questions and Answers
(क) भाषा-बोध
1. शब्दार्थ:
सरलार्थों के साथ दे दिए गए हैं।
अविचल = जो विचलित न हो, दूढ, स्थिर
प्रण = प्रतिज्ञा, वचन
पथ = रास्ता, मार्ग
संकट = मुसीबत
अचल = अडिग, स्थिर
जग = संसार
2. हिमालय शब्द हिम+आलय शब्दों से मिलकर बना है इसी प्रकार अन्य शब्द बनाएं:
हिम+आलय = हिमालय
पुस्तक+आलय = ………………
चिकित्सा+आलय = ………………
भोजन+आलय = ………………..
देव+आलय = ………………..
उत्तर:
बना हुआ शब्द
हिम+आलय = हिमालय
पुस्तक+आलय = पुस्तकालय
चिकित्सा+आलय = चिकित्सालय
भोजन+आलय = भोजनालय
देव+आलय = देवालय
3. अचल शब्द ‘चल’ शब्द से पूर्व ‘अ’ जुड़ने से बना है इसी प्रकार ‘अ’ लगाकर नए विपरीत शब्द बनाएँ:
अ+चल = अचल
अ+सफलता = …………………
अ+शुद्ध = ……………….
अज्ञिान = ……………….
उत्तर:
शब्द विपरीत शब्द
अ+चल = अचल
अ+सफलता = असफलता
अ+शुद्ध = अशुद्ध
अ+ज्ञान = अज्ञान

4. इन शब्दों के पर्यायवा ची शब्द लिखें:
पानी = सलिल, नीर
नभ = …………….
प्रण = ……………
पथ = ……………
पथ = ……………
जग = …………….
मुसीबत = ………………
उत्तर:
शब्द पर्यायवाची शब्द
पानी = सलिल, नीर, जल
नभ = आकाश, गगन, व्योम
प्रण = प्रतिज्ञा, वचन, कसम
पथ = मार्ग, रास्ता, राह
जग = संसार, दुनिया, विश्व
मुसीबत = कठिनाई, कष्ट, पीड़ा
5. प्रयोगात्मक व्याकरण
हिम +आलय = हिमालय
अ+आ = आ
उपुर्यक्त उदाहरण में ‘हिम’ ‘के’ ‘म’ ‘में’ ‘अ’ तथा आलय के शुरू में ‘आ’ स्वर है। इस प्रकार ‘अ+आ’ के मेल से एक नई ध्वनि ‘आ’ बनने से शब्द बना = हिमालय। वर्णों के ऐसे मेल को संधि कहते हैं।
संधि विच्छेद
संधि संधि विच्छेद
योगाभ्यास योग+अभ्यास
अतः विच्छेद का अर्थ है अलग करना। संधि के नियमों द्वारा मिले हुए वर्णों को पुनः पूर्व अवस्था में ले जाने को संधि विच्छेद कहते हैं।
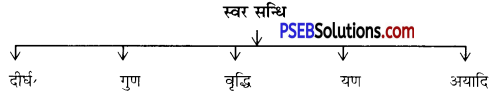
संधि के भेद
(1) विद्या+आलय = विद्यालय
आ+आ = आ
उपर्युक्त उदाहरण में विद्या’ में अंत में ‘आ’ स्वर है तथा पर अर्थात् बाद के शब्द आलय के शुरू में ‘आ’ स्वर है। इन दोनों स्वरों में (आ+आ) के मेल से ‘आ’ होने पर शब्द बना-विद्यालय।
अतः स्वर के बाद स्वर के मेल से जो परिवर्तन आता है, उसे स्वर संधि कहते हैं।
(2) संधि विच्छेद = संधि विशेष
जगत्+नाथ = जगन्नाथ त् को न्
जगत्+ईश = जगदीश त् को द्
पहले उदाहरण में व्यंजन ‘त’ के बाद ‘न’ होने से ‘त’ को ‘न’ हो गया तथा दूसरे उदाहरण में ‘त्’ के बाद स्वर में ‘ई’ होने से ‘त’ को ‘द’ हो गया (और बाद में द् + ई – दी) है। अतः व्यंजन वर्ण के बाद किसी स्वर या व्यंजन के आ जाने पर उसमें जो परिवर्तन आता है, उन्हें व्यंजन संधि कहते हैं।
(3) संधि विच्छेद = संधि विशेष
नमः+ते = नमस्ते विसर्ग के बाद ‘त’ होने से विसर्ग को ‘स्’ हो गया।
नि:+आधार = निराधार विसर्ग से पूर्व ‘इ’ स्वर होने से विसर्ग को ‘र’ हो गया तथा बाद वाला स्वर (आ) र् में मिलकर ‘रा’ बन गया।
अतः विसर्ग के बाद स्वर या व्यंजन होने पर जो विकार सहित मेल होता है, उसे विसर्ग संधि कहते हैं।
संधि विच्छेद = संधि विशेष
(क) देव + आलय = देवालय अ+आ = आ
सती + ईश = सतीश ई+ई = ई
गुरु + उपदेश = गुरुपदेश उ+उ = ऊ
अतः जब ह्रस्व या दीर्घ ‘अ’, ‘इ’ और ‘उ’ के बाद ह्रस्व या दीर्घ ‘अ’, ‘इ’, ‘उ’ आएँ तो दोनों के मेल से क्रमशः इनका दीर्घ रूप ‘आ’, ‘ई’, ‘इ’ और ‘ऊ’ हो जाता है। इसे दीर्घ संधि कहते हैं।
इसी प्रकार नीचे लिखे पदों की संधि करें:
अति+इव = …………….
दया-आनन्द = …………….
परि+ईक्षा = …………….
विद्या+अर्थी = …………….
नारी+ इच्छा = …………….
सिंधु-ऊर्मि = …………….
वधू+उत्सव = …………….
उत्तर:
अति+इव = अतीव
दया+आनन्द = दयानन्द
परि+ईक्षा = परीक्षा
विद्या+अर्थी = विद्यार्थी
नारी+इच्छा = नारीच्छा
सिंधु+ऊर्मि = सिंधूर्मि
वधू+उत्सव = वधूत्सव

(ख) विचार-बोध
1. निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर एक या दो वाक्यों में लिखें :
(क) हिमालय पर्वत भारत की किस दिशा में स्थित है ?
उत्तर:
हिमालय पर्वत भारत की उत्तर दिशा में स्थित है।
(ख) सभी संकटों के समय हमारा व्यवहार कैसा होना चाहिए ?
उत्तर:
सभी संकटों के समय हमें स्थिर रहना चाहिए।
(ग) हम सब कुछ कैसे पा सकते हैं ?
उत्तर:
अपने प्रण पर अटल रहने से हम सब कुछ पा सकते हैं।
(घ) संसार में सफलता कैसे लोगों को मिलती है ?
उत्तर:
संसार में सफलता उन लोगों को मिलती है, जो लाख मुसीबतों के आने पर भी अपने पथ पर कायम रहते हैं।
2. इन काव्य पंक्तियों की सप्रसंग व्याख्या करें
प्रश्न 1.
तुम भी ऊँचे उठ सकते हो,
छू सकते हो नभ के तारे
उत्तर:
उत्तर के लिए सप्रसंग सरलार्थ देखिए।
प्रश्न 2.
हिमालय से हम कौन-कौन से गुण सीख सकते हैं ?
उत्तर:
हिमालय से हम आँधी-तूफान में भी अडिग भाव से डटे रहना, अपने प्रण का पालन करना, मुसीबतों से भी नहीं घबराना तथा संकटों का सामना करना सीख सकते हैं।
प्रश्न 3.
हिमालय पर्वत से हमारे देश को कौन-कौन से लाभ हैं ?
उत्तर:
हिमालय हमारे देश की उत्तरी सीमा का रक्षक है। यह ठंडी हवाओं को भारत में आने से रोकता है। इससे अनेक जड़ी-बूटियाँ और बहुमूल्य पदार्थ प्राप्त होते हैं।
(ग) कुछ करो
(1) अपने भूगोल वाले अध्यापक की सहायता से भारत में स्थित अन्य पर्वतों तथा उनकी स्थिति के बारे में पता करें।
(2) भारत में हिमालय पर्वत की सबसे ऊँची चोटी का नाम पता करें।
(3) हिमालय पर्वत से निकलने वाली नदियों के नाम पता करें और अपने अध्यापक/ अध्यापिका की सहायता से करें।
उत्तर:
अपने अध्यापक/अध्यापिका की सहायता से करें।
PSEB 7th Class Hindi Guide हिमालय Important Questions and Answers
1. निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर उचित विकल्प चुनकर लिखिए
प्रश्न 1.
‘हिमालय’ कविता में कवि ने किसके समान अडिग रहने का संदेश दिया है ?
(क) हिमालय
(ख) राहुल
(घ) विवेक
(घ) भगवान
उत्तर:
(क) हिमालय
प्रश्न 2.
हिमालय खड़ा होकर हमें क्या बता रहा है ?
(क) खूब पढ़ो
(ख) आँधी-पानी से नहीं डरना
(घ) नाचो
(घ) कोई नहीं
उत्तर:
(ख) आँधी-पानी से नहीं डरना
प्रश्न 3.
‘हिमालय’ कविता में अचल शब्द का क्या अर्थ है |
(क) अडिग
(ख) डिंग
(ग) आना
(घ) जाना
उत्तर:
(क) अडिग
प्रश्न 4.
अपने प्रण पर अडिग रहने से मनुष्य क्या पा लेता है ?
(क) कलम
(ख) रुपया
(ग) सब कुछ
(घ) इनमें से कोई नहीं
उत्तर:
(ग) सब कुछ
प्रश्न 5.
जो मरने से नहीं डरते उन्हें क्या मिलता है ?
(क) सफलता
(ख) असफलता
(ग) पुरस्कार
(घ) वेतन
उत्तर:
(क) सफलता
2. निम्नलिखित रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति उचित विकल्पों से कीजिए
प्रश्न 1.
हिमालय सदा …………… रहता है।
(क) डटकर
(ख) बैठा
(ग) खड़ा
(घ) रोता
उत्तर:
(क) डटकर
प्रश्न 2.
जो व्यक्ति अपने ……….. पर मजबूती से खड़ा रहता है, उसे सफलता मिलती है।
(क) घर
(ख) पथ
(घ) छत
(घ) विद्यालय
उत्तर:
(ख) पथ

प्रश्न 3.
संकटों के समय हमारा व्यवहार ………………. रहना चाहिए।
(क) स्थिर
(ख) कठोर
(ग) डाँवाडोल
(घ) नरम
उत्तर:
(क) स्थिर
प्रश्न 4.
भारत के उत्तर में ………… पर्वत स्थित है।
(क) विध्यांचल
(ख) हिमालय
(ग) अरावली
(घ) शिवालिक
उत्तर:
(ख) हिमालय
प्रश्न 5.
गंगा नदी …………. से निकलती है।
(क) विध्यांचल
(ख) शिवालिक
(ग) हिमालय
(घ) कोई नहीं
उत्तर:
(ग) हिमालय
3. दिए गए शब्द का सही अर्थ से मिलान कीजिए:
प्रश्न 1.
प्रतिज्ञा:
प्राण
प्रण
प्रात:काल
उत्तर:
प्रण
प्रश्न 2.
सलिल:
सरल
कठिन
जल
उत्तर:
जल
प्रश्न 3.
देवालय:
मंदिर
गिरजाघर
मस्जिद
उत्तर:
मंदिर
प्रश्न 4.
अडिग:
अकड़ना
दृढ़
उत्तर:
दृढ़
सप्रसंग सरलार्थ
1. खड़ा हिमालय बता रहा है,
डरो न आंधी पानी से,
खड़े रहो तुम अविचल होकर,
सब संकट तूफानों में।
शब्दार्थ:
अविचल = स्थिर, अडिग, दृढ़। संकट = मुसीबत।
प्रसंग:
यह पद्यांश हिमालय’ कविता से लिया गया है। इसमें कवि ने मनुष्य को सदा मज़बूती से सब मुसीबतों का सामना करने की प्रेरणा दी है।
सरलार्थ:
कवि कहता है कि खड़ा हुआ हिमालय यह बता रहा है कि आंधी-पानी से मत डरो। तुम सब मुसीबतों और तूफानों में भी घबराओ मत तथा उनका मज़बूती से सामना करो।
भावार्थ:
कवि का कहना है कि हमें जीवन की राह में आने वाली सब मुसीबतों का सामना इस प्रकार डट कर करना चाहिए जैसे हिमालय सदा डट कर खड़ा रहता है।
2. डिगो न अपने प्रण से, तो तुम,
सब कुछ पा सकते हो प्यारे।
तुम भी ऊँचे उठ सकते हो,
छू सकते हो नभ के तारे।
शब्दार्थ:
डिगना = हिलना, किसी बात पर स्थिर न रहना। प्रण = प्रतिज्ञा, वचन। नभ = आकाश।
प्रसंग:
यह पद्यांश ‘हिमालय’ कविता से लिया गया है। इसमें कवि ने मुसीबतों में भी न घबराने तथा स्थिर रहने की प्रेरणा दी है।
सरलार्थ:
कवि कहता है कि तुम कभी भी अपने वचनों से मत फिरो, क्योंकि ऐसा करने से तुम सब कुछ प्राप्त कर सकते हो। तुम ऊँचे उठ कर आकाश के तारे भी छू सकते हो।
भावार्थ:
कवि का कथन है कि अपने प्रण पर अडिग रहने से मनुष्य सब कुछ पा कर ऊँचा उठ सकता है तथा आकाश की ऊँचाइयों को भी छू सकता है।
3 अचल रहा तो अपने पथ पर,
लाख मुसीबत आने में,
मिली सफलता जग में उसको,
जीने में मर जाने को
शब्दार्थ:
अचल = अडिग, स्थिर। पथ = शस्ता, मार्ग, उद्देश्य, लक्ष्य। जग = संसार, दुनिया।
प्रसंग:
यह पद्यांश ‘हिमालय’ कविता से लिया गया है। इसमें कवि ने जीवन में आने वाली कठिनाइयों का डट कर सामना करने की प्रेरणा दी है।
सरलार्थ:
कवि कहता है कि जो व्यक्ति लाख मुसीबतों के आने पर भी नहीं घबराता और अपने पथ पर मज़बूती से स्थिर रहता है, उसे ही संसार में सफलता मिलती है जो जीते हुए भी मरने के लिए सदा तैयार रहता है।
भाव:
संसार में सफलता सदा उन्हें मिलती है जो मरने से नहीं डरते तथा हर मुसीबत में अडिग रहते हैं।
हिमालय Summary
हिमालय कविता का सार
‘हिमालय’ कविता में कवि हिमालय के समान अडिग बनने का संदेश देता है। कवि कहता है कि हिमालय खड़े होकर हमें यह बता रहा है कि कभी भी आँधी-पानी से नहीं डरना चाहिए और सभी मुसीबतों और तूफानों में भी हमें मजबूती से खड़े रहना चाहिए। यदि हम अपने वचनों पर डटे रहें तो सब कुछ पा सकते हैं और ऊँचे उठकर आकाश के तारों को भी छू सकते हैं। जो व्यक्ति लाखों मुसीबतों के आने पर भी अपने पथ पर स्थिर रहता है, उसी को संसार में सफलता मिलती है।
![]()