Punjab State Board PSEB 7th Class English Book Solutions Poem 2 The Hunter and the Deer Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Class 7th English Solutions Poem Chapter 2 The Hunter and the Deer Question Answers
The Hunter and the Deer Class 7 Questions and Answers
Activity 1.
1. Meaning of the word as used in the poem (adjective/noun/verb, etc.)
2. Pronunciation (The teacher may refer to the dictionary or the mobile phone for correct pronunciation.)
3. Spellings :
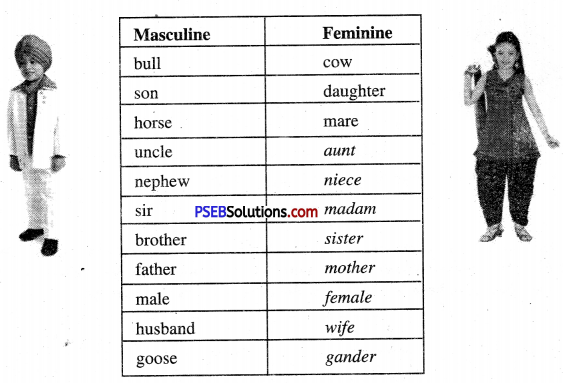
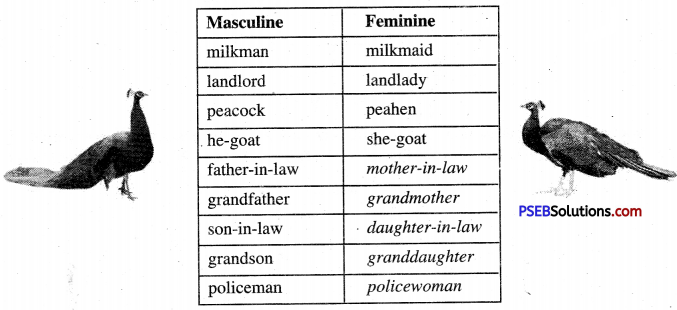
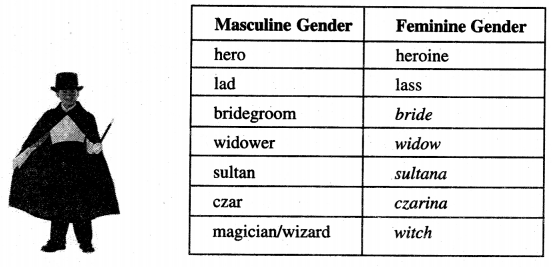
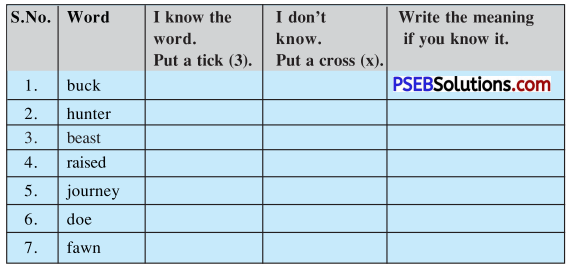
| Journey | plea | buck |
| doe | fawn | beast |
Vocabulary Expansion
Activity 2.
Pick up words from the poem that match the rhyme of the following words.

Activity 3.
Read the words in the following table and do as directed.
Answer:
![]()
Activity 4
Read the poem and select the appropriate option to fill in the given blanks.
Question 1.
The hunter went on a journey to find some …………………..
(a) deer meat
(b) dog meat
(c) horse meat
Answer:
(a) deer meat
Question 2.
The hunter found …………………
(a) a dog
(b) a buck
(c) a bear
Answer:
(b) a buck
Question 3.
The other word for a male deer is ………..
(a) doe
(b) fawn
(c) buck
Answer:
(c) buck
Question 4.
The poet thought that the buck was begging for ………
(a) the fawn’s life
(b) his own life
(c) the doe’s life
Answer:
(b) his own life
![]()
Question 5.
A female deer is called a ………
(a) doe
(b) fawn
(c) buck
Answer:
(a) doe
Question 6.
A young deer is called a …………
(a) doe
(b) fawn
(c) buck
Answer:
(b) fawn
Question 7.
The hunter remembered what he came for and raised his ……….
(a) hand
(b) gun
(c) head
Answer:
(b) gun
Question 8.
A …….. came out of nowhere.
(a) doe
(b) fawn
(c) buck
Answer:
(b) fawn
Question 9.
The hunter felt that he could not the buck.
(a) kill
(b) raise
(c) look at
Answer:
(a) kill
Question 10.
The hunter gathered__for feeding the deer.
(a) fruits
(b) leaves
(c) nuts.
Answer:
(c) nuts.
Activity 5.
Write answers to the following questions.
Question 1.
What did the hunter want to eat ?
शिकारी क्या खाना चाहता था ?
Answer:
The hunter wanted to eat some deer meat.
Question 2.
What did the hunter see ?
शिकारी ने क्या देखा ?
Answer:
The hunter saw a buck.
![]()
Question 3.
Why did the hunter not kill the buck ?
शिकारी ने हिरण को क्यों नहीं मारा ?
Answer:
The hunter did not kill the buck because he saw a plea of mercy in his eyes. He begged for his life.
Question 4.
What did the hunter do ?
शिकारी ने क्या किया ?
Answer:
The hunter gathered some nuts and fed the buck.
Question 5.
How did the buck feel after eating nuts ?
नट्स खा कर हिरण ने कैसा महसूस किया ?
Answer:
After eating nuts, the buck felt himself out of fear.
Activity 6.
Explain the following statements in your own words.
1. And if he killed the buck he’d feel like a beast.
2. And something grew in him.
3. And he felt the deer’s lack of fear.
Answer:
1. Killing is a beastly act.
2. A feeling of mercy arose in him.
3. He felt that the deer had lost his fear.
Learning Language
Determiners
Let us look at the following sentences :
1. The rabbit found its hole.
2. I ate the vanilla cake in the evening.
3. The metal cans are recyclable.

The italicized words above are determiners.
Determiners are words like ‘the’, ‘an’, ‘this’ or ‘some that always come before a noun or before any other adjectives used for the noun.
![]()
There are four different types of determiners in English :
(1) Articles
(2) Demonstratives
(3) Quantifiers and
(4) Possessives.
1. Articles बहुत ही महत्त्वपूर्ण Determiners हैं। ये तीन हैं-a, an, तथा the. इनका प्रयोग Singular nouns gent Adjectives on the IT Articles are among the most common of the determiners. There are three singular articles: ‘a’, ‘an’, and ‘the’. Articles specify (or determine) which noun the speaker is referring to. ‘A’ and ‘an’ are indefinite articles. They are used when you are talking about a general version of the noun.
For example:
1. A cat is a cute animal.
2. An eagle can see the ground from the sky.
‘A’ is used before words that begin with the sound of a consonant such as ‘p’, ‘l’, ‘d’, ‘s’, and ‘an’ is used before words beginning with the sound of a vowel such
as ‘a’, ‘e’, ‘i’, o’, ‘u’.
Examples : Consonant sound
1. a cat
2. a pan.
3. a European :
4. a cow
5. a hen

Examples : Vowel sound
1. an apple
2. an honest man
3. an umbrella
4. an hour
5. an egg

“The’ is a definite article. It is used before a specific noun, as-
1. He went to the best restaurant in the city.
2. The kitten is meowing too loudly.
Here the speaker is talking about a particular (विशेष) kitten and a particular restaurant.
![]()
Activity 7.
In the following sentences, choose one of the three options and put a tick on the right one.
1. I have a/an/the/good idea.
2. That is a/an/the/interesting toy!
3. I have kept the bag in alan/the/cupboard.
4. Do the Sharmas have a/an/the/blue car ?
5. The water in a/an/the/river is dirty.
6. He had a/an/the/piece of chocolate.
7. I like to eat a/an/the/egg everyday.
8. She has a/an/the/good habit of brushing her teeth twice a day.

9. Raghav likes to walk in a/an/the/rain.
10. Radha plays a/an/the game of chess everyday.
Answer:
1. a
2. an
3. the
4. a
5. the
6. a
7. an
8. the
9. the
10. the.
2. Demonstrative adjectives : are also used as determiners in English. They are – “this”, “that, “these’ and ‘those’. Demonstratives are used in a situation in which the speaker can point to an item.

For example:
1. Do you want this piece of cake ?
2. I don’t want to watch that movie.
3. These black grapes are sour.
4. He wanted to hire those boys for the job.
“This’ and ‘these’ point to the items close to us; “that and those’ refer to items far away. Note also “this’ and ‘that are singular while these’ and ‘those’ are plural.
![]()
Activity 8.
Let us help Richard describe his office.

Write ‘this’ or ‘these for things that are near him, and that’ or ‘those’ for things that are not near him. One has been done for you.
1. This laptop is new.
2. ………….. wooden cabinet is for his papers.
3. ………….. books are about business.
4. ………….. computer is also new.
5. ………….. dustbin is very good
6. ……….. curtains are very old.
7. ………… plant is beautiful.
8. …………… wooden horses are nice.
9. …………. cage does not have a real bird.
10. ……….. drawers need repair.
Answer:
2. This
3. These
4. This
5. That
6. These
7. That
8. These
9. This
10. These.
3. Quantifiers: Quantifiers are determiners that indicate how much or how little of the noun is being talked about. They include words such as ‘all’, “a few’, and many’.
For example :
1. She read all the books.
2. She liked all the sweets equally.
3. A few children like beans, so the school canteen stopped serving beans to them.
4. Many kittens are taught to hunt by their mothers.
![]()
Activity 9.
In the following sentences choose one of the options and put a tick on the right one.

1. There are only ……………… bananas left in the box.
(a) a few
(b) a little
2. We need ……………. butter for this cake.
(a) a few
(b) a little
3. There are only ……….. days left to give the reports.
(a) a few
(b) a little
4. I bought …………. apples from this shop.
(a) a few
(b) a little
5. …………….. people live in your city ?
(a) How much
(b) How many
6. …………… water is there in the sea ?
(a) How much .
(b) How many
7. We need …………… bananas.
(a) some
(b) any
8. You can’t buy …………….. oranges in this shop.
(a) some
(b) any
9. There is a bus ……………… 2 hours.
(a) each
(b) every
10. We enjoyed …………….. minute of our holidays.
(a) each
(b) every
Answer:
1. (a) a few
2. (b) a little
3. (a) a few
4. (a) a few
5. (b) How many
6. (a) How much
7. (a) some
8. (b) any
9. (b) every
10. (a) each.
4. Possessive Adjectives: When talking about a noun that belongs to someone or something, we use possessive adjectives to show ownership. Possessive adjectives include ‘my’, ‘your’, ‘his’, ‘her’, ‘its’, ‘our’ and their’. For example :
1. Where is your mother ?
2. The dog growled and showed its teeth.
3. My best friend loves cats.
4. Which one is his car ?
5. Speaking the truth is her best quality.
6. In the autumn season, trees shed their leaves.
7. It’s our house.
The possessive adjective (determiner) comes before the noun.
Activity 10
Complete the following letter written by Ashok to Deepak. Fill in the correct possessive adjectives.
Hello Deepak
…….1. ….. name is Ashok. This is ……. 2……….. friend Satish. He is thirteen years old …….. 3. ……. sister is nine. They have got a pet. ……. 4. ……. pet is a dog. …… 5. ……. name is Caesar. Satish and I go to the same school. There are 600 boys and girls in ……. 6. ……. school. Satish’s class teacher’s name is Mrs. Sharma. She has got a pet, too. ……. 7. ……. pet is a cat. Our class teacher is Mr. Gupta. I like ……. 8……… lessons. He has three dogs. The dogs love to play in …….. 9. ……. garden. Now I have a question for you. What is ……. 10. ……. pet ?
Yours
Ashok

Answer:
1. My
2. my
3. His
4. Their
5. His/Its
6. our
7. Her
8. his
9. his/their
10. your.
![]()
Learning to Listen
Activity 11.
Your teacher will speak five words. You will listen to him/her carefully and write the words in the space provided. Thereafter, you will write three rhyming words for each in the space given under each word. An example is given :
| Example Word Light |
| fight |
| kite |
| white |

नोट – कृपया अपने अध्यापक से अन्य शब्द लेकर rhyming words लिखने का अभ्यास करें। हमने यहां अपनी ओर से ये शब्द दिए हैं।
| S.No. | Word 1 hit |
Word 2 book |
Word 3 sing |
Word 4 peep |
Word 5 behind |
| 1. | hit | shook | ring | deep | find |
| 2. | sit | took | bring | sleep | kind |
| 3. | fit | hook | king | keep | bind |
Learning to Speak (Pairwork)
Kindness to other people and animals is very important for human beings. We must be kind to others. In our life, many people have been kind to us. Do you remember any kind act done to you by your neighbour, friend, mother, uncle or a stranger ?
Activity 12.
Tell your partner about how someone was kind to you/how you were kind to someone (a human being/an animal).
Some useful words/phrases
1. my neighbour/friend
2. kindness
3. sympathy
4. virtue
5. made me smile
6. generosity
7. greatest gift
8. won my heart
9. I can’t forget
Answer:
Yesterday it was very cold. I saw an old and weak beggar by the roadside. He was poorly clothed and was shivering badly. But I was in full winter dress, i.e., all woollen. I had a blanket too. I took it off and put it on the beggar. His body stopped shaking soon. Had I not given him the blanket, he would have surely died. He blessed and blessed me. It made me smile. I felt great within me. Really the acts of kindness fetch true happiness. Sympathy is divine.
![]()
Learning to Write
Application
Study the following format of writing an application for fee concession.
| Addressed to The Principal [Name of the school] [Address] [Date] Subject Subject : Application for Fee Concession Salutation Sir/Madam Body of Application I beg to say that I am a student of class 7 in this school. I am a good student. I always stand 1st in the class. My parents are poor. They are unable to pay full fees. Therefore, I request you to kindly grant me a concession in my fee. I shall be very thankful to you. Closing Thanking you Yours obediently [Your Name] [Class and section] [Roll No.] |
Activity 13
Write an application to your Principal requesting him/her to grant you sick leave for three days.
The Headmaster
SD High School
Sangrur
Sir
I beg to say that I am a student of VIIth class. I am ill. My whole body is aching. So I cannot come to school. Kindly grant me leave for three days.
I shall be thankful to you for this kind act.
Yours obediently
XYZ
February 19, 20……
Learning to Use Language
Read the following example of a four line poem.
| My Home My home is a brick house Where it’s warm and safe to be ; I wish all the world’s children Could be lucky, like me. — Trevor Harvey |

Activity 14.
Use some of the following words/phrases or any other you like to write your own four line poem.
I, see, blue, violet, red, rainbow, colours, flowers, evening, breeze, trees, swaying, dance
Look ! A colourful garland in the sky,
A beautiful rainbow, necklace of a bride.
After the rain all fresh and gay,
Among dancing flowers, she wears it with pride.
![]()
Stanzas For Comprehension
Read the following stanzas carefully and answer the questions that follow each :
(1) The Hunter and the Deer
The Hunter went on a journey
To find some deer meat
He saw a buck and looked into his eyes
He saw a plea, the buck begging for his life
A doe and a fawn came from behind
Needing the buck in their lives.
1. What did the hunter see in the buck’s eye ?
शिकारी ने हिरण की आंखों में क्या देखा ?
2. Who needed the buck in their lives?
जीवन में हिरण की ज़रूरत किसे थी ?
3. Name the poem and the poet ?
कविता और कवि का नाम बताएं।
Answer:
1. The hunter saw an appeal of mercy for life in the buck’s eyes.
2. His family members, the doe and the fawn, needed the buck in their lives.
3. The name of the poem is ‘The hunter and the Deer’. Its poet is anonymous
(2) The hunter knew what he came for and raised his gun
But out of nowhere, he saw the buck’s son
It was cute, to say the least
And if he killed the buck he’d feel like a beast
The hunter looked at the deer again
And something grew in him.
1. How did the buck’s son look ?
हिरण का पुत्र कैसा लगता था ?
2. What feeling arrested the hunter ?
शिकारी के मन में क्या भावना आई ?
3. What is the central idea of the poem ?
कविता का केंद्रीय भाव क्या है ?
Answer:
1. The buck’s son looked very cute.
2. He felt that if he killed the buck, he would be no better than an animal.
3. Mercy and pity for animals is the central idea of the poem. Having pity on the weak and innocent is a great virtue. The art of kindness gives real happiness.
(3) He gathered some nuts and fed the deer
And he felt the deer’s lack of fear
He smiled a great big smile
He stayed with the deer for a while
And he went home feeling great
1. How did he feed the deer ?
उसने हिरण को भोजन कैसे कराया ?
2. Why did he smile a big smile ?
वह खुल कर क्यों मुस्कराया ?
3. Write the rhyming words in the Stanza. Two or three pairs.
पद्य में से लय वाले शब्द लिखें। दो या तीन जोड़े।
Answer:
1. He collected some nuts and fed the deer.
2. He smiled a big smile to see the buck without fear.
3. deer – fear; smile – while.
![]()
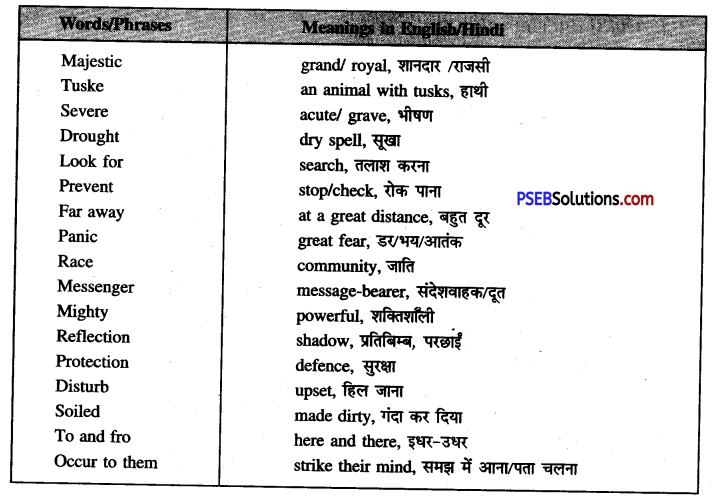
Word Meanings

The Hunter and the Deer Summary in Hindi
यह कविता पशुओं के प्रति दया और प्रेम का व्यवहार करने का पाठ पढ़ाती है। एक शिकारी हिरण का मांस प्राप्त करने के लिए वन में शिकार करने गया। उसने एक हिरण को देखा और उसे मारना चाहा। परंतु उसने उसकी आँखों में अपनी याचना के भाव देखे जो जिंदगी की भीख मांग रहे थे। इतने में एक हिरणी और उसका बच्चा भी आ गए। वे चाहते थे कि शिकारी हिरण को उनकी खातिर छोड़ दे। शिकारी तो शिकार के लिए आया था।
इसलिए उसने अपनी बंदूक उठाई। तभी हिरण का बच्चा (पुत्र) आगे आ गया जो बहुत ही प्यारा था। उसे देखकर शिकारी के विचार बदल गए। उसने सोचा कि किसी की जान लेना तो जानवरों का काम है। अत: उसने कुछ नट्स इकट्ठे करके हिरण को खिलाए। हिरण खुश हो गया और उसका डर जाता रहा। परंतु दयावान शिकारी उससे भी अधिक प्रसन्न था क्योंकि उसने नेकी का एक महान् कार्य किया था।
Class 7 PSEB Solutions Poetry