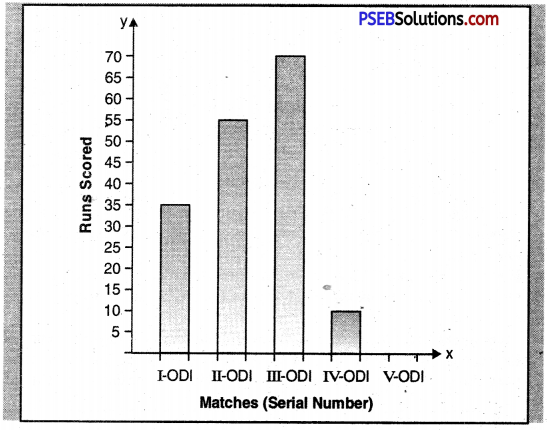
Punjab State Board PSEB 6th Class English Book Solutions English Reading Comprehension Unseen Passages Exercise Questions and Answers, Notes.
PSEB 6th Class English Reading Comprehension Unseen Passages
Read the given passages and answer the questions the follow each:
1. It is said that health is wealth. Healthy mind stays in a he%y body. Human body is like a machine. Over-eating and eating junk food harms our body. Ivular exercise keeps us fit and healthy. We must eat at regular intervals. It is our duty to ke, Gur body in good condition. Walking for a few kilometres daily is also a good exercise. If ycr body is in perfect health, you enjoy life. So we all must do regular exercise and stay fit.
Choose the correct option:
(i) Health is ……………
(a) money
(b) wealth
(c) gold
(d) nothing
Answer:
(b) wealth.

(ii) Human body is like a …………….
(a) scooter
(b) machine
(c) engine
(d) furniture.
Answer:
(b) machine.
(iii) When should we eat ?
(a) every time
(b) at regular in;rvals
(c) after long hours
(d) not eat in thtmorning.
Answer:
(b) at regular intervals.
(iv) What is our duty ?
(a) to eat junk food
(b) to eat all the tine
(c) to keep our body fit
(d) to get up late in the morning.
Answer:
(c) To keep our body fit.
(v) If your body is in perfect health
(a) you enjoy life
(b) you do not enjoy mything
(c) everything sounds dull
(d) you feel tired all tie time.
Answer:
(a) you enjoy life.
2. Golu did not like to read that much. One day, Golu’s mother bought him a nev book and Golu loved it. His favourite character in the book was a dog named Sheru. Golu read the whole book in one day. He read three pages before school, five pages after school and two pages before he went to bed. Golu loves reading now.
Choose the correct option:
(i) Golu did not like to:
(a) playgames
(b) watch t.v.
(c) read much
(d) talk to his mother.
Answer:
(c) read much.
(ii) Who bought a new book for Golu ?
(a) his father
(b) his mother
(c) his sister
(d) Sheru.
Answer:
(b) his mother.
(iii) Sheru was the name of:
(a) a dog
(b) Golu’s friend
(c) Golu’s neighbour
(d) none of these.
Answer:
(a) a dog.
(iv) Golu read three page’s of the book:
(a) after he went to bed
(b) before he went to bed
(c) before school
(d) after school.
Answer:
(c) before school
(v) Golu liked:
(a) the book
(b) the dog
(c) neither of these two
(d) both the book and the dog.
Answer:
(d) both the book and the dog.
3. Deenu was so involved r a his dream that he forgot he was carrying a tin on his head. He started running and slipped. The t: in fell down and the oil spilled on the ground. He felt very upset. He came back to the grocer w ith a sad heart and narrated the incident. The grocer scolded him and said. ‘ ‘You have caused m e a loss of rupees five hundred.”
Choose the correct option:
(i) Deenu was invo lved in:
(a) his story
(b) his dream
(c) a grocer
(d) shopping.
Answer:
(b) his dream.
(ii) In the tin, there was:
(a) milk
(b) ghee
(c) sugar
(d) oil.
Answer:
(d) oil

(iii) Why did the grocer scold Deenu ?
(a) because he stole his money.
(b) because of hi$ loss
(c) because he told a lie
(d) none of the above.
Answer:
(b) because of his loss.
(iv) Deem went to the grocer:
(a) happily
(b) cheerfully
(c) With a sad heart
(d) dreaming.
Answer:
(c) with a sad heart.
(v) Deenu felt very upset because:
(a) he fell down
(b) the oil spilled on the ground
(c) the oil made his clothes dirty
(d) he got hurt.
Answer:
(b) the oil spilled on the ground.
4. Shravan is the month of rains. After a long spell of summer, the weather becomes cool and pleasant. There is greenery all around. New plants start growing. All men, women and children begin to feel happy and cheerful. The festival of Teej in this month expresses their feelings of joy. People put on new and colourful clothes on this day. Girls sing folk songs and enjoy swinging.
Choose the correct option:
(i) Shravan is the month of:
(a) fairs
(b) festival after festival
(c) hot summer days
(d) rains
Ans.
(d) rains.
(ii) The weather becomes cool and pleasant in the month of:
(a) Barisakh
(b) Ashad
(c) Shravan
(d) Kartik.
Answer:
(c) Shravan.
(iii) What brings greenery all around ?
(a) rains
(b) summer heat
(c) cold winter
(d) all these.
Answer:
(a) rains.
(iv) The girls sing:
(a) fake songs
(b) folk songs
(c) new songs
(d) film songs
Answer:
(b) folk songs.
(v) When do girls enjoy swinging ?
(a) on Diwali
(b) on Lohri
(c) on Holi
(d) on Teej.
Answer:
(d) On Teej.
5. It was the 15th August last Monday. This day is celebrated as a national festival in India. It was on this day in the year 1947 that we won our Independence from the British rule after a long struggle. This year we celebrated this festival in our school with a great zeal. We had been working hard for a week to beautify our school. We prepared colourful banners and placards with patriotic slogans written on them.
Choose the correct option:
(i) We won our freedom from the British rule in:
(a) 1950
(b) 1952
(c) 1947
(d) 1974.
Answer:
(c) 1947.
(ii) We celebrate 15th August as a:
(a) social festival
(b) religious festival
(c) national festival
(d) none of these.
Answer:
(c) national festival
(iii) How did we win our freedom ?
(a) after a short period of struggle.
(b) after a long period of struggle
(c) without any struggle
(d) after a bloody struggle.
Answer:
(b) after a long period of struggle.
(iv) This year we celebrated the Independence Day
(a) with a great zeal
(b) without any preparation
(c) in a simple manner
(d) with the help of students
Answer:
(a) with a great zeal.

(v) Patriotic slogans were written on ………………….
(a) die walls
(b) walls and banners
(c) playcards
(d) both banners and placards
Answer:
(d) both banners and placards.
6. After the Headmaster’s speech, a cultural programme was organised. The children sang patriotic songs. Some recited poems related to the freedom movement. Some students spoke about the great patriots of India such as Jhansi ki Rani. Tantya Tope, Sardar Bhagat Singh, Neta Ji Subhash Chander Bose, Mahatma Gandhi and the other great sons and daughters of our motherland.
Choose the correct option:
(i) There was a cultural programme:
(a) before the Headmaster’s speech
(b) after the Headmaster’s speech.
(c) after the poems were recited
(d) after the speech of the students.
Answer:
(b) after the Headmaster’s speech.
(ii) What did the cultural programme include ?
(a) patriotic songs
(b) poems related to freedom movement
(c) speeches about the great patriots of India
(d) all the above.
Answer:
(d) all the above.
(iii) Mahatma Gandhi was:
(a) a common man
(b) an ordinary person
(c) a great scholar
(d) a great patriot.
Answer:
(d) a great patriot.
(iv) A great daughter of India mentioned in the passage is:
(a) Jhansi ki Rani
(b) Rani of motherland
(c) Tantya Tope
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(a) Jhansi ki Rani.
(v) What was the first item of the day?
(a) recitation of poems
(b) patriotic songs
(c) the Headmaster’s speech
(d) a cultural programme.
Answer:
(c) The Headmaster’s speech.
7. Vineet, a student of class VIII was also in the same bus. He swung into action. The exit door near the engine was all on fire. He broke open the emergency door and started pushing the children out through this door. The driver and the conductor saw Vineet, struggling alone. They rushed to help him. By the time the last student was rescued the entire bus had turned into a ball of fire. It was Vineet’s timely action that averted a big tragedy. He saved twenty seven lives. However, he himself suffered some bums during this heroic deed.
Choose the correct option:
(i) Vineet was the student of:
(a) Class VI
(b) Class VII
(c) Class Vin
(d) none of these.
Answer:
(c) Class VIII.
(ii) Which door was on fire ?
(a) entrance door
(b) front door
(c) exit door
(d) emergency dpor.
Answer:
(c) exit door.
(iii) The children were taken out through the ……………….
(a) main door
(b) exit door
(c) frontdoor
(d) emergency door.
Answer:
(d) emergency door.

(iv) Who helped Vineet ?
(a) The driver and the teacher
(b) The conductor and the children
(c) Both the driver and the conductor
(d) The teachers and the children.
Answer:
(c) Both the driver and the conductor.
(v) What happened to Vineet during the heroic deed ?
(a) He suffered some bums.
(b) His face was badly wounded.
(c) All his clothes were burnt.
(d) He came out safe and sound.
Answer:
(a) He suffered some bums.
8. One day the librarian said to him. “Do you really read the books or just return them without reading ?” Narendra said, “Of course, Sir, I thoroughly read all the books borrowed from the library. You can ask me any question from these books.” The librarian took out a book and asked him the questions. Narendra answered all the questions correctly. The librarian was amazed at his sharp memory.
Choose the correct option:
(i) Narendra answered correctly:
(a) two questions
(b) three questions
(c) all the questions
(d) no question.
Answer:
(c) all the questions.
(ii) Who borrowed books from the library ?
(a) librarian
(b) Narendra
(c) Surendra
(d) Narendra’s friends.
Answer:
(b) Narendra.
(iii) The librarian thought that Narendra:
(a) returned the books after reading them.
(b) returned the books after spoiling them.
(c) returned the books without reading them.
(d) all these.
Answer:
(c) returned the books without reading them.

![]()


![]()


![]()