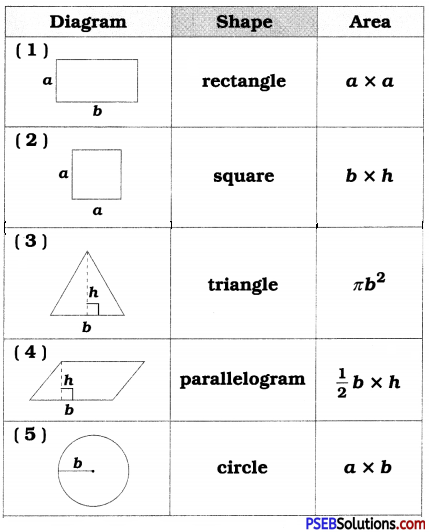
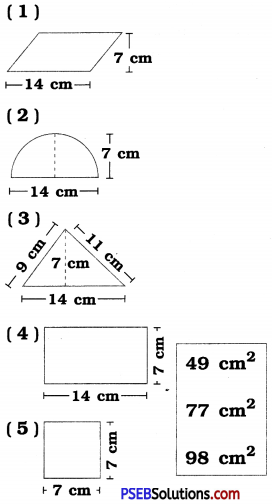
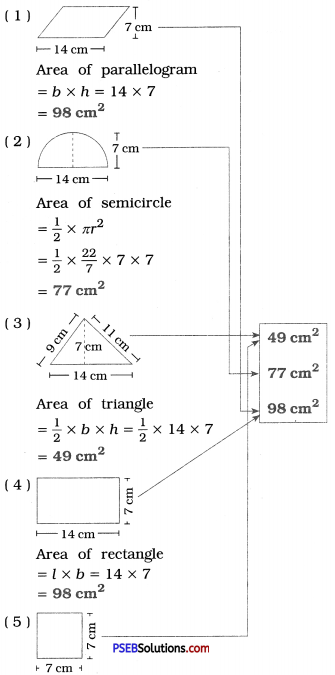
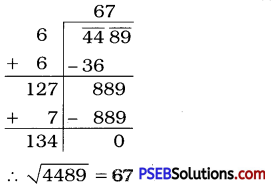
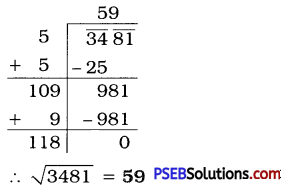
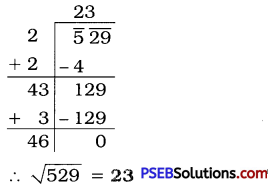
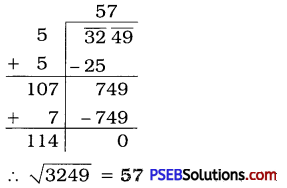
Punjab State Board PSEB 6th Class English Book Solutions English Grammar Noun Exercise Questions and Answers, Notes.
PSEB 6th Class English Grammar Noun
A noun is a name of a person, place or thing; as-
किसी व्यक्ति स्थान अथवा वस्तु के नाम को अंग्रेजी में noun कहते हैं।
India. Mohan, taxi, class, toy, boy, table, etc.
Look at these sentences:

- Geeta went to Patiala.
- The fox is looking at the grapes.
- The boys are playing football.
The underlined words in the above sentences are all nouns because they are the names of some person, place, animal or thing.

There are four kinds of noun:
- Common Noun
- Proper Noun
- Abstract Noun
- Collective Noun.
1. Common Nouns
A Common Noun is the name of every person, place or thing of the same class; as- pen, cow. bird, man, animal, bridge.
Look at these sentences:

- The boys are playing.
- These mangoes are pulpy.
- The birds build nests.
The underlined words in the given sentences are Common Nouns because they are common to every person, place or thing.
Exercises (Solved)
I. Underline the Common Nouns in the following sentences:

1. Keep the books on the table.
2. The shops are closed today.
3. The tiger lives in the forest.
4. The farmer bought a tractor.
5. This building has many offices.
6. There is a dairy near our house.
7. Ail birds do not build their nests.
8. A fish lives in water and not on land.

Hints:
1. books, table
2. shops
3. tiger, forest
4. farmer, tractor building, offices
6. dairy, house
7. birds, nests
8. fish.
II. Add five Common Nouns in each set:
1. birds : parrot, sparrow, peacock, crow, niehtineale. pigeon.
2, colours : red, white, black, green, yellow, orange
3. games : hockey, football, volleyball, cricket, basketball, baseball.
4. animals : dog, camel, cow, sheep, buffalo, goat.
5. vegetables : potato, tomato, cabbage, radish, brinial, pumpkin.
6. fruits : mango, grape, apple, banana, papaya, pear.
7. In a school : library, science room, assembly hall office, staff-room, class room
8. In a house : kitchen, bathroom, dining room, store, bed-room, guest room.
2. Proper Nouns
A Proper Noun is the name of some particular (विशेष) person.
Delhi, Kolkata, Beas, Kama!
Look at these sentences:

- Moti loves to play.
- My brother lives in Amritsar.
- J.C. Bose was a great scientist.
- The Shan-e-Puniab has left just now.
The underlined w’ords in the above sentences are proper nouns because they are the names of particular persons, places or things.
Note that-
A Proper Noun always begins with a capital letter.
Proper Nouns include (शामिल हैं) the names of people, countries, cities, villages, rivers, ships, streets, buildings, mountains, seas, months of the year, days of the week, festivals, etc.
Exercises (Solved)
I. Underline the Proper Nouns in the following sentences
1. We named the cat Silky.
2. Kabir was a great saint.
3. We visited the. Taj in Agra.
4. Delhi is the capital of India.
5. I have never been to Mumbai.
6. Misha and Monu went to Delhi.
7. Do you know Sunny and Chinkv ?
8. We visited the Golden Temple on Sunday.

Hints:
1. Silky
2. Kabir
3. Taj. Agra
4. Delhi. India
5. Mumbai
6. Misha, Manu, Delhi
7. Sunny, Chinky
8. Golden Temple.
II. Rewrite each Proper Noun correctly in these sentences:

1. Have you visited the taj mahal ?
Have you visited the Taj Mahal ?
2. lam going to ropar on Monday.
3. The amritsar mail goes to kolkata.
4. muslims go to mosques on fridays,
5. black beauty is the story of a horse.
6. Where were the last Olympics held ?
7. bill clinton was the president of ameriea.
Hints:
2. Ropar, Monday
3. Amritsar Mail, Kolkata
4. Muslims, Mosques, Fridays
5. Black Beauty
6. Olympics
7. Bill Clinton, America.
3. Abstract Nouns
An Abstract Noun is the name of a quality, feeling or state (गुण भाव या स्थिति); as-
goodness, hardness, wisdom, love, hatred, theft, boyhood, slavery, freedom.
Look at these sentences:

- Fire gives us heat.
- He had pain in his body.
- He acted upon my advice.
- Do you know the depth of this well ?
The underlined words in the given sentences are abstract nouns because they refer to some quality, feeling or state.
The following words are all Abstract Nouns:
theft
peace
poverty
kindness
hope
misery
honesty
darkness
truth
greed
courage
weakness
sleep
sorrow
sickness
childhood
death
hunger
patience
treatment

Exercises (Solved)
I. Underline the Abstract Nouns in the following sentences:

1. Please control your anger.
2. Honesty is the best policy.
3. There was silence all around.
4. We get knowledge from books.
5. There was darkness in the room.
6. What is the height of this building?
7. You should have kindness for the poor.
8. Wars always bring death and destruction.
Hints:
1. anger
2. Honesty, best policy
3. silence
4. knowledge
5. darkness
6. Height
7. kindness
8. death, destruction.
II. Form Abstract Nouns from the given words:
laugh – laughter
hate – hatred
true – truth
treat – treatment
child – childhood
soft – softness
cruel – cruelty
bright – brightness
brave – bravery
strong – strength
punctual – punctuality
dangerous – danger
III. Use any five Abstract Nouns in sentences of your own:

- She likes the softness of her skin.
- Always speak the truth.
- He was rewarded for his bravery.
- Punctuality is a great virtue.
- Her life was in danger.
4. Collective Nouns
A Collective Noun is the name of a group of persons, animals or things of the same kind; as-
flock, cattle, class, army, family, committee.
Look at these sentences:

- Our army won the battle.
- I have lost my bunch of keys.
- The cattle are grazing in the field.
The underlined words in the above sentences are collective nouns because they refer to a collection of persons or things of the same kind.
The word army is a collection of soldiers.
The word cattle is a collection of farm animals.
The word bunch is a collection of things tied together.
Learn the following Collective Nouns:
1. a shoal of fish
2. a hive of bees
3. a pride of lions
4. a herd of cattle
5. a flight of stairs
6. a bunch of keys
7. a flock of sheep
8. a crew of sailors
9. a heap of stones
10. a string of pearls
11. a suite of rooms
12. a basket of fruits
13. a gang of thieves
14. a library of books
15. a bundle of sticks
16. a bench of judges
17. a crowd of people
18. a brood of chickens
19. a band of musicians
20. a wardrobe of clothes
21. a regiment of soldiers
22. a fleet of ships or cars
23. a litter of pups / piglets
24. a pack of cards / wolves
Exercises (Solved)
I. Match the Collective Nouns with the given phrases:
| 1. A collection of pups |
Pack |
| 2. A collection of ships |
flock |
| 3. A collection of sheep |
fleet |
| 4. A collection of books |
suite |
| 5. A collection of rooms |
litter |
| 6. A collection of wolves |
herd |
| 7. A collection of flowers |
library |
| 8. A collection of elephants |
bouquet |
Hints:
1. litter
2. fleet
3. flock
4. library
5. suite
6. pack
7. bouquet
8. herd.
II. Fill in the blanks with suitable Collective Nouns:
1. A filght of stairs.
2. A ………… of fish.
3. A ………… of lions.
4. A ………… of cows.
5. A ………… of cards.
6. A ………… of fruits.
7. A ………… of pearls.
8. A ………… of judges.
9. A ………… of grapes.
10. A ………… of clothes.
11. A ………… of thieves.
12. A ………… of soldiers.

Hints:
2. shoal
3. pride
4. herd
5. pack
6. basket
7. string
8. bench
9. bunch
10. wardrobe
11. gang
12. regiment.
Miscellaneous Exercises (Solved)
I. What is a Noun ?
II. Name the different kinds of Noun.
Give two examples of each.
III. The italicized words in the following sentences are Nouns. Classify these Nouns (Common / Proper /Abstract / Collective):

1. He won much praise.
2. Nitin lives in Mumbai.
3. I saw a flock of sheep.
4. Silver is a white metal.
5. You cannot cheat God.
6. My sweater is made of wool.
7. I bought some new furniture.
8. The old woman was very happy now.
Hints:
1. praise – abstract
2. Mumbai – roper
3. sheep – common
4. silver – common, metal- common
5. God – proper
6. sweater – common, wool – common
7. furniture – collective
8. woman – common.
IV. Choose suitable Nouns to fill in the blanks:
duty, profit, courage, marriage, need, weight, freedom, childhood

1. Be careful about your weight.
2. We want to live in …………..
3. Her ………….. took place last month.
4. It is our………….. to obey our parents.
5. Seema lost her parents in her …………..
6. We helped him when he was in …………..
7. The soldier was rewarded for his …………..
8. Jatin made good ………….. from his business.
Hints:
2. freedom
3. marriage
4. duty
5. childhood
6. need
7. courage
8. profit.

V. Pick out the Nouns in the following sentences and say whether they are Common, Proper, Collective or Abstract:

1. I love music.
2. Meera studies in sixth class.
3. Ludhiana is an industrial city.
4. He bought a doll for his sister.
5. These tables are made of wood.
6. A drowning man catches at a straw.
7. His father left for London yesterday.
8. Mathematics is my favourite subject.
Hints:
1. music – abstract.
2. Meera – proper; class – collective.
3. Ludhiana – proper, city – common.
4. doll – common, sister – common.
5. tables – common, wood – common.
6. man – common, straw – common.
7. father – common, London – proper.
8. Mathematics – collective, subject – common.
VI. Choose a suitable Abstract Noun to match each phrase:
pride, silence, poverty, courage, strength, greatness, innocence, intelligence

1. A quiet room [silence]
2. A clever boy
3. A great king
4. A strong girl
5. A proud child
6. A poor beggar
7. A brave policeman
8. An innocent woman
Hints:
1. silence
2. intelligence
3. greatness
4. strength
5. pride
6. poverty
7. courage
8. innocence.
The Noun – Number
Singular and Plural Nouns
A noun that refers to one thing is said to be Singular; as-
ball, chair, book, town, cow etc.
A noun that refers to more than one thing is said to be Plural; as-
books, balls, chairs, towns, animals, etc.
Now look at these sentences:

- Rita has three dolls.
- Reema has a bag of books.
- All the babies were crying.
- Joy got a big ball on his birthday.
The underlined nouns in the above sentences are either singular or plural. They tell whether they refer to one or more than one thing.
Forming Plurals of Nouns
1. As a general rule, the plural of a noun is formed by adding -s to a singular noun.
Singular – Plural
cat – cats
cap – caps
ball – balls
flag – flags
doll – dolls
bird – birds
hare – hares
goat – goats
horse – horses
rat – rats
toy – toys
son – sons
owl – owls
lion – lions
page – pages
table – tables
sister – sisters
orange – oranges
2. Nouns ending in -s, -x, -ch, or -sh form their plurals by adding -es.
Singular – Plural
bunch – bunches
brush – brushes
dish – dishes
church – churches
match – matches
fox – foxes
bush – bushes
dress – dresses
gas – gases
class – classes
loss – losses
box – boxes
glass – glasses
tax – taxes
3. Nouns ending in -y (with a consonant before them) form their plural by changing -y to -ies.
Singular – Plural
city – cities
story – stories
fairy – fairies
lady – ladies
pony – ponies
sky – skies
dairy dairies
baby – babies
family – families
puppy – puppies
butterfly – butterflies
country – countries
4. Nouns ending in -y (with a vowel before them), form their plural by taking an -s only.
Singular – Plural
key – keys
valley – valleys
ray – rays
storey – storeys
day – days
holiday – holidays
boy – boys
journey – journeys
play – plays
monkey – monkeys
5. Nouns ending in -f or -fe form their plural by changing -f or -fe to -ves.
Singular – Plural
calf – calves
loaf – loaves
wolf – wolves
shelf – shelves
life – lives
half – halves
knife – knives
thief – thieves
6. Some nouns ending in -/ or -fe form their plural by taking -s only.
Singular – Plural
roof – roofs
safe – safes
proof – proofs
hoof – hoofs
chief – chiefs
dwarf – dwarfs
7. Nouns ending in -o (with a consonant before them), form their plural by taking -es.
Singular – Plural
echo – echoes
negro – negroes
hero – heroes
mango – mangoes
potato – potatoes
volcano – volcanoes
buffalo – buffaloes
mosquito – mosquitoes
Exceptions : The words photo and piano take -s only to form their plural.
8. Nouns ending in -o (with a vowel before them), form their plural by taking -s only.
Singular – Plural
radio – radios
cuckoo – cuckoos
bamboo – bamboos
9. Some nouns have irregular plurals.
Singular – Plural Singular – Plural
man – men
foot – feet
tooth – teeth
goose – geese
ox – oxen
louse – lice
mouse – mice
child – children
10. A compound noun generally forms its plural by adding -s to the principal word.
| daughters-in-law |
lookers-on |
step-daughters |
| mothers-in-law |
step-sons |
maid-servants |
| fathers-in-law |
sons-in-law |
passers-by |
11. The following Compound Nouns take a double plural.
man-servant – men-servants
woman-teacher – women-teachers
woman-servant – women-servants
Exercises (Solved)
I. Give the plural form of:
fly – flies
box – boxes
hero – heroes
roof – roofs
shoe – shoes
shelf – shelves
dwarf – dwarfs
potato – potatoes
pencil – pencils
mouse – mice
life – lives
fish – fishes
foot – feet
child – children
piano – pianos
II. Give the singular form of:
foxes – fox
teeth – tooth
halves – half
armies – army
watches – watch
gases – gas
ladies – lady
mosquitoes – mosquito
oxen – ox
copies – copy
knives – knife
negroes – negro
chimneys – chimney
shoes – shoe
wolves – wolf

III. Rewrite each sentence using the plural form of Nouns:

1. The monkey was in a cage.
The monkeys were in cages.
2. The knife is on the shelf.
3. He put his foot on the bench.
4. The hero in the film acted well.
5. The policeman chased the thief.
6. The woman told the child a story.
7. Sam plucked a leaf from the tree.
8. The maid washed the glass and the dish.
Answer:
2. The knives are on the shelves.
3. He put his feet on the benches.
4. The heroes in the films acted well.
5. The policemen chased the thieves.
6. The women told the children stories.
7. Sam plucked leaves from the trees.
8. The maids washed the glasses and the dishes.
IV. Rewrite each sentence using the singular form of Nouns

1. The oxen are pulling the carts The ox is pulling the cart.
2. Neha heard the cries of wolves.
3. The women rode on the ponies.
4. The loaves are kept in the boxes.
5. The mice were afraid of the geese.
6. The children were bitten by mosquitoes.
7. These stories are about witches and fairies.
8. The men told the ladies stories of Indian heroes.
Answer:
2. Neha heard the cry of a wolf.
3. The woman rode on a pony.
4. The loaf is kept in the box.
5. The mouse was afraid of the goose.
6. The child was bitten by a mosquito.
7. This story is about a witch and a fairy.
8. The man told the lady a story of an Indian hero.
Remember that-
1. Some Nouns have the same form in the plural and the singular; as-
कुछ Nouns एकवचन तथा बहवचन में एक जैसे होते हैं: जैसे-
deer, sheep, fish, dozen, score, hundred, thousand.
The following Nouns have a plural form but always take the singular verb; as-
निम्नलिखित Nouns बहुवचन में होते हैं, परन्तु उनके साथ हमेशा एकवचन क्रिया (verb) लगती है; जैसे-
news, civics, politics, physics, mathematics, means, gallows.

- This news is true.
- Physics is a difficult subject.
3. The following Nouns are always used in the plural form and take the plural verb; as-
निम्नलिखित Nouns का प्रयोग हमेशा बहुवचन में किया जाता है और उनके साथ बहुवचन क्रिया लगती है; जैसे-
thanks, scissors, trousers, pants, alms, wages, spectacles, socks.

- My thanks are to you all.
- The scissors were blunt.
4. The following Nouns are used only in the singular form and take the singular verb; as-
नीचे लिखे Nouns केवल एकवचन में प्रयोग किये जाते हैं और उनके साथ एकवचन क्रिया लगती है; जैसे-
furniture, scenery, luggage, machinery, advice, bread, hair, business, mischief.

- This furniture is not for sale.
- Where is my luggage ?
5. The word ‘hair’ is used in the plural when a definite number of hairs are to be mentioned.
जब बालों का निश्चित संख्या में उल्लेख किया जाए, तो hair शब्द का प्रयोग बहुवचन (hairs) में किया जाता है।
1. There were two hairs in my tea.
2. My aunt has four white hairs on her head.
Miscellaneous Exercises (Solved)
I. Give the plural of the following nouns:
1. ox
2. leaf
3. knife
4. chief
5. tooth
6. fox
7. wife
8. child
9. story.
10. mouse.
Answer:
1. oxen
2. leaves
3. knives
4. chiefs
5. teeth
6. foxes
7. wives
8. children
9. stories
10. mice.
II. Rewrite each sentence with a plural subject:

1. A cow eats grass.
2. The child is playing
3. The army was fighting.
4. A crow is sitting in the tree.
5. The ox is grazing in the field.
6. This road is closed for repairs.
Answer:
1. Cows eat grass.
2. The children are playing.
3. The armies were fighting.
4. Crows are sitting in the tree.
5. The oxen are grazing in the field.
6. These roads are closed for repairs.
III. Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the given words:
1. She has white …………..
2. I have lost my …………..
3. This ………….. is not true.
4. The ………….. were crying.
5. The house has two …………..
6. Your ………….. were not new.
Hints:
1. teeth
2. shoes
3. news
4. babies
5. storeys
6. trousers
IV. Correct the following sentences:

1. Her hairs are black.
2. Your scissor is blunt.
3. Where is my trouser ?
4. Please accept my thank.
5. These furnitures are for sale.
6. We saw many wolfs in the zoo.
Answer:
1. Her hair is black
2. Your scissors are blunt.
3. Where are my trousers ?
4. Please accept my thanks.
5. This furniture is for sale.
6. We saw many wolves in the zoo.
The Noun – Gender
Gender means being a male (नर) or a female (मादा).
On the basis of gender, we can classify nouns into four kinds:

- Masculine Gender
- Feminine Gender
- Common Gender
- Neuter Gender
1. A noun that refers to a male is said to be of the Masculine (पुरुषवाचक) Gender; as-
horse, boy, man, lion, king, dog.
2. A noun that refers to a female is said to be of the Feminine (स्तरीवाचक) Gender; as-
mare, girl, woman, lioness, queen, bitch.
3. A noun that refers to both a male and a female, is said to be of the Common (सामान्य) Gender; as-
child, baby, parent, cousin, friend, student, thief.
4. A noun that refers to neither a male nor a female, is said to be of the Neuter (नपुंसक) Gender; as-
book, pen, toy, house, table, knife, etc.
Genders
1. Masculine (male)
2. Feminine (female)
3. Common (either sex)
4. Neuter (neither sex)

Change of Gender
We can change the gender of a Noun in different ways; as-
1. By using a different word:
Masculine – Feminine
monk – nun
fox – vixen
father – mother
uncle – aunt
boy – girl
son – daughter
man – woman
nephew – niece
bull – cow
cock – hen
king – queen
brother – sister
husband – wife
sir – madam
gentleman – lady
dog – bitch
horse – mare
bachelor – maid
2. By adding ‘-ess’, ‘-ss’ to the masculine and making some change in it:
Masculine – Feminine
god – goddess
prince – princess
lion – lioness
master – mistress
tiger – tigress
emperor – empress
3. By changing a part of the word:
Masculine – Feminine
bride – bridegroom
granduncle – grandaunt
peacock – peahen
he-goat – she-goat
landlord – landlady
headmaster – headmistress
milkman – milkwoman
father-in-law – mother-in-law
grandfather – grandmother
brother-in-law – sister-in-law
Exercises (Solved)
I. Put each word in the column it belongs to:
van
duke
horse
milkmaid
bull
child
flower
governess
box
book
parent
gentleman
nun
baby
servant
hairdresser
aunt
table
duchess
shopkeeper
road
monk
daughter
policeman
duchess
Answer:
Table
II. Change the Gender of the following:
sir – madam
lion lioness
bull – cow
cock – hen
mare – horse
uncle – aunt
tigress – tiger
peacock – peahen
gentleman – lady
grandfather – grandmother

Miscellaneous Exercises (Solved)
I. Give the opposite Gender of the following:
1. sir
2. aunt
3. mare
4. king
5. lady
6. cock
7. horse
8. tiger
9. wife
10. male
11. lioness
12. mother
Answer:
1. madam
2. uncle
3. horse
4. queen
5. gentleman
6. hen
7. mare
8. tigress
9. husband
10. female
11. lion
12. father.
II. Rewrite each sentence, changing the Gender of Nouns and Pronouns:
1. A cruel man killed the fox.
2. Mr. Sharma is a businessman.
3. The Emperor welcomed the Duke.
4. The dog is barking at the servant.
5. Madam, my aunt wants to see you.
6. His nephew went to Shimla with his son.
7. The headmaster punished the naughty boys.
8. The bride touched the feet of her mother-in-law.
Answer:
1. A cruel woman killed the vixen.
2. Mrs. Sharma is a businesswoman.
3. The Empress welcomed the Duchess.
4. The bitch is barking at the maid.
5. Sir, my uncle wants to see you.
6. Her niece went to Shimla with her daughter.
7. The headmistress punished the naughty girls.
8. The bridegroom touched the feet of his father-in-law.

III. Fill in the blanks with the Feminine gender of the words in italics:
1. We pray to gods and …………….
2. The hotel has a waiter and a …………….
3. The actor married an ……………. in Mumbai.
4. The lion and the ……………. are in their den.
5. The witch changed the prince into a …………….
6. The tiger and the ……………. look after their cubs.
7. The emperor and the ……………. of Japan live in Tokyo.
8. The guests were received by the host and the …………….
Hints:
1. goddesses
2. waitress
3. actress
4. lioness
5. wizard, princess
6. tigress
7. empress
8. hostess.
![]()
![]()