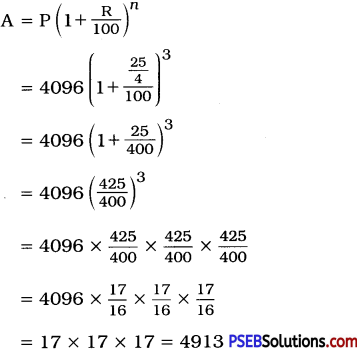
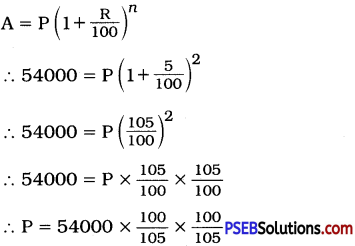
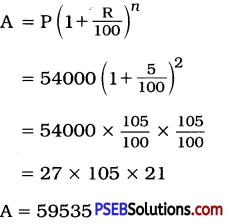
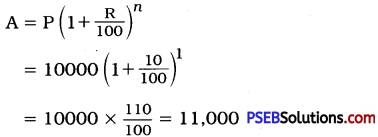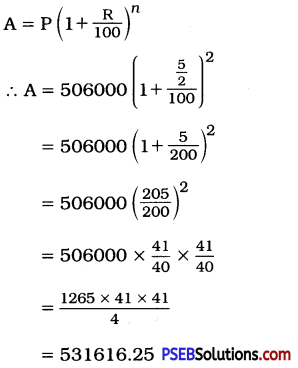Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class English Book Solutions English Precis Writing Exercise Questions and Answers, Notes.
PSEB 12th Class English Precis Writing
The word precis though much used in English is a French word. It means summary, a compendium, an abridgement, an abstract, a condensed statement, an epitome, etc. These words all mean the same thing at the bottom. When a student is asked to write a precis of a paragraph, or of a series of paragraphs, what he has to do is to pick out the important details and to omit all those which are unimportant.
All those facts or details which are related to the theme or subject-matter of the piece are important .while all others which merely illustrate, explain or elucidate these facts or details are unimportant.
The ability to write a precis is of great benefit to its possessor. In many walks of life, this ability is indispensable. As a member of the Lok Sabha eager to deliver a big speech in the house, as an advocate anxious to argue before a learned judge and as a businessman eager to know the facts and to avoid waste of valuable time, you require a precis of facts.
![]()
I. Five Rules for Guidance
1. The first step is to master the subject-matter of the passage of which a precis is to be made. For this, read the passage carefully so as to form some idea of its subject and contents. If one reading fails to give you the central point or the theme of the piece, read the extract a second time or even a third time in order to find the basic idea, or the chief purpose to elucidate which the writer began to write.
2. When you feel certain about the correct meaning of the piece, read it carefully once again. This time put down the key sentence which embodies the theme. Generally speaking, this sentence has to be constructed by the students. Mostly, it is not found in the original piece.
3. Now begin comparing each sentence of the original with the thematic sentence. Underline all these sentences or parts of the sentence having no bearing on it. Rewrite the piece after omitting the rejected parts but inserting dots instead. This is the skeleton or outline precis.
4. Now read the outline precis and try to substitute single words or phrases with fewer words, for expressions which can be contracted. Sometimes, it is possible to find a single word for a whole expression. This word should be inserted in place of that expression. Sometimes, it is possible to convert an adjective clause into a participle expression or an adjective phrase, or a noun clause into a noun phrase. This should also be done here.
5. Now you are ready to write the final draft. Remember that the final draft should be a connected account of the relevant details in your own words. A good precis is the expression within the prescribed limits of the salient facts of the original in the words of the writer of the precis.
Important Note. Revise your precis after you complete writing it out.
II. Characteristics of a Good Precis
1. A good precis is brief. Though brevity of expression is essential, such brevity should not be achieved at the cost of clarity of expression. The precis should not be so brief as to become ambiguous.
2. Lucidity of Expression. The language of the precis must be clear and unmistakable. Lucidity of expression is one mark of a good precis. Since the language of precis will be the writer’s for the most part, he must bear in mind that his words must mean nothing more or less than those of the author.
Note. Care must be taken to distinguish between the theme and the title. While the title indicates in a general way the contents of the piece, the theme is a complete statement of the fundamental idea to explain which the author began to write. It permeates the entire writing of the author. A theme is to a piece of writing as the soul is to the human body, making its influence felt in every part of the structure. Poems or essays may have the same title but their themes may vary. In fact, they do usually vary. Thus, Herrick and Wordsworth have both written a lyric entitled, “The Daffodils”, but their themes are different.
3. Uniformity. Uniformity is another very important quality of writing a precis. As a rule, the writer of a precis should not depart from the order of ideas of the original. He should keep his narrative in the same tense throughout. It is desirable to avoid the present tense or the direct quotation. Where the original contains concrete illustrations or specific examples, it is desirable to insert there the main purpose.
4. Subordination of the unimportant to . the important. Another thing essential in a good summary is what is called the correct perspective. The writer must be able to subordinate the unimportant to the important. He must get a correct view of the events he is reporting and must not give undue space to matter which is not so important. Eliminate the non-essential and incorporate the essential is a golden rule in precis making.
III. How to Write a Precis
The following hints should be borne in mind while making a precis of a given passage:
1. Read thoroughly the given passage to get at the central or general idea. Go on reading the passage till you understand it clearly.
2. Underline the main ideas in the passage according to the sequence of thought and note them down in a skeleton form.
3. Read only the underlined words this time and try to estimate their relative importance.
4. Re-arrange all these points in order of their importance.
5. Reconstruct in your own mind, the whole subject-matter of the passage in this new order.
6. Make in your own words a rough draft of these points as a continuous narrative, much smaller than the original and the words of your precis.
7. Check up the number of words of the original and the words of your precis.
8. Bring it near the requisite length by the addition or omission of the comparatively less important details. There should be nothing superfluous, redundant, perfunctory, irrelevant or non-essential in a precis. All repetition of ideas, all introductory remarks, illustrations, comparisons, examples, similes, metaphors, quotations and references should be avoided.
9. Conform to the prescribed length. If no instructions are given, the precis should be one-third of the original passage.
10. As far as possible a precis should be in your own words. Do not steal phrases and sentences from the original.
11. It should be brief, clear and concise. It must be a well-connected or organic whole. One idea should lead to the other and give an impression of unity and not of a series of unconnected sentences and ideas.
12. It must be complete and self-contained. It must be a faithful picture of the ideas contained in the original passage.
13. There should be no personal comments, additions or connections of facts. Do not * give your own views, whether you agree or disagree with the writer.
14. The precis must be, as a rule, written throughout in the Indirect speech ; Third person and Past Tense, unless the passage expresses a universal truth. So change the Direct manner of speech into Indirect manner of speech. Change the first person into the third person.
15. Don’t begin your precis with such words as the writer says or the author remarks.
16. You must give a suitable title or heading to your precis. Remember Two Marks are assigned to the Title in the Board Examination.
17. The opening sentence of a precis should be very expressive. It must clearly show what is to follow.
18. A precis should be thoroughly revised. It must be in simple English. There should be no ambiguities and obscurities. As far as possible a precis should not contain the vocabulary of the original. High flown or bombastic style should not be made use of. Mistakes of spelling, punctuation, grammar, etc. should be corrected.
The Title of a Precis
The questions in. the Board Examination assign separate marks to finding the title of the piece of which a precis is to be made. Care must be taken in choosing the title.
The title must be brief, comprehensive and relevant. As far as possible avoid inserting a proverb or a whole sentence as the title. It is always advisable to find out a phrase or an expression forming part of the thematic sentence, which will serve as the title. Bear in mind the important fact that a title suggests, in a general way, the nature of the contents of a piece.
Model Exercises (Solved)
Exercise 1
Self-control is at the root of all virtues. Let a man give the rein to his impulses and passions and from that moment he yields up his moral freedom. He is carried along the current of life and becomes a slave of his strongest desire for the time being. To be morally free-to be more than an animal-man must be able to resist the instinctive impulse, and this can be done only by the exercise of self-control. Thus it is this power which constitutes the real distinction between physical and moral life, and forms the primary basis of individual character. In the Bible, praise is given, not to the strong man who “taketh a city” but to the stronger man who “ruleth his own spirit”. This stronger man is he who, by discipline, exercises a control over his thoughts, his speech and his acts. Nine-tenths of the vicious desires that degrade society, and when indulged, swell into the crimes that disgrace it, would sink into insignificance before the advance of valiant self-discipline, self-respect and self-control. By the watchful exercise of those virtues, purity of heart and mind becomes habitual and the character is built up in chastity, virtue and temperance. (201 Words)
Hints:
Primary – chief or main. Vicious – evil. Valiant – bold. Chastity – purity. Temperance – moderation.
PRECIS:
Self-control is the source of all virtues. If a person does not have self-control, he becomes a slave of evil desires and degrades himself. To be morally free, a person has to exercise self-control. This quality is the real basis of character. A person having self¬control is more respected than those who rule over a city. Self-control develops into self-discipline and strong character. Self-control is most important.
Words of the Original Passage = 201
Words of the Precis = 67
Heading : Self-control
![]()
Exercise 2
The test of a great book is whether we want to read it only once or more than once. Any really great book we want to read the second time even more than we wanted to read it the first time, and every additional time that we read it, we find new meanings and new beauties in it. A book that a person of education and good taste does not care to read more than once is very probably not worth much. But we cannot consider the judgement of a single individual infallible.
The opinion that makes a book great must be the opinion of many. For even the greatest critics are apt to have certain dullness, certain inappreciation. Carlyle, for example, could not endure Browning. Browning could not endure some of the greatest English poets. A man must be many-sided to utter a trustworthy estimate of many books. We may doubt the judgement of the single critic at a time. But there is no doubt possible in regard to the judgement of generations. (175 Words)
Hints:
Additional – more. Infallible – one who is not liable to m ike mistake. Apt – likely. Inappreciation no praise. Endure – tolerate.
PRECIS:
A great book is that which a person wants to read more than once, because a great book reveals new beauties in its every reading. But the judgement of an individual can’t be relied upon since the greatest critic can lose his proper sense of appreciation. Only the judgement of generations is the real test of a great book.
Words of the Original Passage = 175
Words of the Precis = 59
Heading : Test of a Great Book
Exercise 3
Of the duty of the artist in the coming years much has been said, indeed, rather too much. He is always being preached at and being told that he ought to preach. Naturally, he will be interested in his surroundings and wants to comment on them ; he will express the feelings of the people and reflect their attitude and he will, if generously minded, desire to champion the oppressed and reform abuses. But to say that his fundamental duty is to these things is a mistake. His fundamental duty is to do his job.
He must first and foremost, write properly, paint properly, express himself as an individual. When he has done that, his message, if he has one, is sure to show through. I am all against him starting off with a message ; if he does that, he is not an artist, he is a pamphleteer. His message, however, deeply he feels it, must come out incidentally when he is actually writing or painting or whatever it is. His fundamental feeling ought to be: “Let me make something, not let me preach.” His primary duty is not to society, but to himself. (195 Words)
Hints:
Generously – liberally. Champion – support. Oppressed – downtrodden; weak and suffering people. Fundamental – primary or main. Pamphleteer – one who writes for propaganda. Incidentally – by the way.
PRECIS:
People believe that the duty of the artist of the future is to give moral lessons, preach his ideas and reform social evils. But this is the duty of a pamphleteer and not of an artist. His primary duty is not to society but to himself. He should work thoroughly well. He should not start with a message. His message should come out only indirectly.
Words of the Original Passage = 195
Words of the Precis = 65
Heading : Duty of the Artist
Exercise 4
If today I have a quarrel with another man, I do not get beaten merely because I am physically weaker and he can knock me down. I go to law, and the law will decide as fairly as it can between the two of us. Thus in disputes between man and man right has taken the place of might. Moreover, the law protects me from robbery and violence. Nobody may come and break into my house, steal my goods, or run off with my children. Of course, there are burglars, but they are very rare and the law punishes them whenever it catches them.
It is difficult for us to realize how much this safety means. Without safety those higher activities of mankind which make up civilization could not go on. The inventor could not invent, the scientist find out or the artist make beautiful things. Hence order and safety, although they are not themselves civilization, are things without which civilization would be impossible. They are as necessary to our civilization as the air we breathe is to us ; and we have grown so used to them that we do not notice them any more than we notice the air. (200 Words)
Hints:
Might – brute force. Burglars – thieves.
PRECIS:
Order and safety are the greatest blessings of modern civilization. Law today protects the weak from being beaten by the strong. Right has taken the place of might. Law protects the peaceful citizens. Law and order have made it possible for man to develop civilization. Though law, order and safety are not themselves civilization, yet it would be impossible without them. They are as essential as the air.
Words of the Original Passage = 200
Words of the Precis = 67
Heading : Importance of Law and Order
Exercise 5
English is a language of international commerce it is the language of diplomacy, and it contains many a rich literary treasure, it gives us an introduction to western thought and culture. For a few of us, therefore, knowledge of English is necessary. They can carry on the departments of national commerce and international thought and science. That would be the legitimate use of English whereas today English has usurped the dearest place in our hearts and dethroned our mother-tongues.
It is wrong and unnatural due to our unequal relations with Englishmen. The highest development of the Indian mind must be possible without a knowledge of English. It is doing violence to the manhood and specially the womanhood of India to encourage our boys and girls to think that an entry into the best society is impossible without a knowledge of English. It is too humiliating a thought to be bearable. To get rid of the infatuation for English is one of the essentials of Swaraj. (178 Words)
Hints:
Diplomacy – political relations of one country with another. Legitimate – legal; genuine; right; proper. Usurped – seized; snatched; possessed. Humiliating – insulting; degrading. Infatuation – foolish love; too much fondness.
PRECIS:
A knowledge of English is necessary. It is a language of national and international trade and diplomacy. It opens the doors of literature, western thought, culture and science. But it should not be given undue importance. India can make progress without English. It is really shameful and foolish to consider a knowledge of English as the highest sign of culture.
Words of the Original Passage = 178
Words of the Precis = 59
Heading : The Place of English
Exercise 6
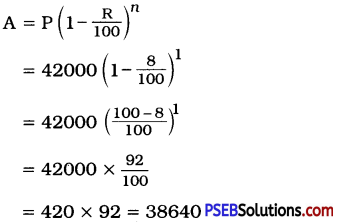
Self-reliance is the pilgrim’s best staff, the workers best tool. It is the master key that unlocks all the difficulties of life. ‘Help yourself and heaven will help you’ is a maxim which receives daily confirmation. He who begins with crutches will generally end with crutches. Help from within always strengthens but help from without invariably enfeebles the recipient. It is not in the sheltered garden, but in the rugged Alpine cliff, where the storms beat most violently, that the toughest plants are reared. It is not by the use of corks, bladders and life-buoys that you can best learn to swim but plunging courageously into the waves and buffeting them. To wait until some charitable man passes by, – to stand with arms folded sighing for a helping hand, – is not the part of any manly mind.
The habit of depending upon others should be vigorously resisted, since it tends to weaken the intellectual faculties and paralyse the judgement. The struggle against adverse circumstances has, on the contrary, a bracing and strengthening effect like that of the pure mountain air on the enfeebled frame. This is a lesson which, nowadays, is not taught in colleges. To us it seems the vice of modern systems of education that they lay down too many ‘royal roads’ to knowledge. Those impediments which formerly compelled the student to think and labour for himself are now most carefully removed and he glides so smoothly along the well-beaten highway that he pauses not to heed the flowers on either side. (255 Words)
Hints:
Self-reliance – self-dependence. Unbcks – removes. Maxim – saying or proverb. Confirmation – to establish an act firmly. Crutches – staff for a lame person -here it means dependence. Invariably – constantly. Enfeebles – weakens. Rugged Alpine cliff – atmosphere full of (roughly Alpine rocks) difficulties. Violently – terribly. Toughest – strongest, hardest. Reared – grown. Life-buoys – floating cases used for swimming. Buffeting – fighting. Arms folded – idly; doing nothing. Vigorously – strongly. Resisted – opposed. Paralyse – to lose power of moving and feeling. Adverse – unfavourable. Bracing – healthy. Enfeebled frame – weak body. Impediments – obstacles. Well-beaten highway – common path.
PRECIS:
Depending on one’s own effort is a source of success to all. It solves man’s problems. The evil habit of depending on others weakens man’s mental powers. It must be fought against. Man must fight against unfavourable circumstances. It will not have a depressing but a healthy effect on man’s life. But it is really sad that the habit of self-reliance is not taught in the colleges today. The modern system of education does not encourage se1freliance among the students who only depend upon help books.
Words of the Original Passage = 255
Words of the Precis = 85
Heading: Sdf-reliance
![]()
Exercise 7
The spirit of the age is in favour of equality, though practice denies it almost everywhere. We have got rid of slavery in the narrow sense of the word, that a man can be the property of another. But a new slavery, in some ways worse than the old, has taken its place all over the world. In the name of individual freedom, political and economic systems exploit human beings and treat them as commodities. And again, though an individual cannot be the property of another, a country and a nation can still be the property of another nation, and thus group slavery is tolerated. Racialism also is a distinguishing feature, of our time, and we have not only master nations but also master races. (127 Words)
Hints:
Exploit – take undue advantage of; suck the blood of; cruel to. Commodities – lifeless things. Racialism – belief in superior and inferior races of mankind.
PRECIS:
There ¡s equality in theory, but not in practice. Old slavery has been replaced by a new slavery in the form of exploitation of human beings by treating them as commodities. Colonialism and racialism are some manifestations of the new slavery.
Words of the Original Passage = 127
Words of the Precis = 43
Heading : Modern Slavery or Slavery in a New Form
Exercise 8
Speech is a great blessing, but it can also be a great curse, for, while it helps us to make our intentions and desires known to our fellows, it can also, if we use it carelessly, make our attitude completely misunderstood. A slip of the tongue, the use of an unusual or an ambiguous word, and so on, may create an enemy where we had hoped to win a friend. Again, different classes of people use different vocabularies, and the ordinary speech of an
educated man may strike an uneducated listener as showing pride; unwittingly we may use a word which bears a different meaning for our listener from what it does to men. of our own class. Thus, speech is not a gift to use lightly without thought, but one which demands careful handling. Only a fool will express himself alike to all kinds and conditions of men. (114 Words)
Hints:
Attitude – outlook. Unusual – uncommon. Ambiguous – not clear. Handling – treatment.
PRECIS :
Speech is a valuable gift, but if used carelessly, may cause misunderstanding. The careless use of words may create an enemy. Since different classes use different words, we must use speech carefully to avoid being misunderstood.
Words of the Original Passage = 114
Words of the Precis = 38
Heading : Use of Speech
Exercise 9
Of all the amusements which can possibly be imagined for a hard-working man, after his toil, there is nothing like reading an entertaining book. It calls for no bodily exercise of which he has had enough. It relieves his home of its dullness. It transports him to a livelier and more interesting scene, and while he enjoys himself there, he may forget the evils of the present moment. Nay, it accompanies him to his day’s next work, and if the book he has been reading be anything above the very idlest and lightest, gives him something to think of, besides the drudgery of his everyday occupation. If I were to pray for a taste which should stand me in good stead under every variety of circumstances and to be a source of happiness and cheerfulness through life, it would be a taste for reading. Give a man this taste, and the means of gratifying it, and you can hardly fail to make a % man happy unless indeed, you put into his hands a most perverse selection of books. (180 Words)
Hints:
Amusements – entertainment. Toil – hard work. Bodily – physically. Transports— carries. Drudgery – routine. Gratifying – satisfying. Perverse – improper.
PRECIS:
Reading a good book is the best source of entertainment after the day’s hard work. It requires no physical exertion. It removes the dullness of home and makes the reader forget the evils of the present. It often provides interesting subjects to think about. Taste for reading is the greatest and most unfailing source of happiness under all circumstances.
Words of the Original Passage = 180
Words of the Precis = 60
Heading : Pleasures of Reading
Exercise 10
People moan about poverty as a great evil, and it seems to be an accepted belief that if people had plenty of money, they would be happy and useful and get more out of life. As a rule, there is more genuine satisfaction in life in the humble cottages of the poor than in the lordly mansions of the rich. I always pity the sons and daughters of the rich who are attended by servants and have governesses at a little age. It is because I know how street, happy and pure the home of honest poverty is, how free from perplexing care and from social envies and jealousies the members of the family are that I sympathise with the rich man’s boy and congratulate the poor man’s son. It is for these reasons that from the ranks of the poor so many strong, eminent, self-reliant men have always sprung. If you will read the list of the immortals who were not born to die, you will find that most of them had the advantage of being cradled, nursed and reared in the hard school of poverty. (180 Words)
Hints:
Moan – complain. Genuine – true. Mansions – palaces. Perplexing – confusing. Self-reliant – self-dependant. Eminent – famous. Immortals – deathless.
PRECIS:
Mostly people regard poverty as an evil. They consider money necessary for a happy and useful life. But generally, a poor man is more satisfied with life than a rich person is. Rich persons who have servants deserve sympathy. The greatest men who have won undying fame in the world have been nursed in the lap of poverty.
Words of the Original Passage = 180
Words of the Precis = 59
Heading : Poverty as a Blessing
Exercise 11
One of the defects of our civilization is that it does not know what to do with its knowledge. Science, as we have seen, has given us powers fit for the gods, yet we use them like small children. For example, we do not know how to manage our machines. Machines were made to be man’s servants, yet he has grown so dependent on them that they are in a fair way to become his masters. Men spend most of their lives looking after and waiting upon machines. And the machines are very stern masters.
They must be fed with coal, and given petrol to drink, and oil to wash with, and they must be kept at the right temperature. And if they do not get their meals when they expect them, they grow sulky and refuse to work, burst with rage and blow up, and spread ruin and destruction all around them. So we have to wait upon them very attentively and do all that we can to keep them in good temper. Already we find it difficult either to work or play without the machines and a time may come when they will rule us altogether, just as we rule the animals. (207 Words)
Hints:
Waiting upon – serving. Stern – severe, harsh or cruel. Sulky – angry or ill- tempered. Rage – anger. Good temper – good mood.
PRECIS:
Civilization has, undoubtedly, blessed us with immense knowledge. But we don’t know what to do with it. Science has given us immense power but we fail to make proper use of it. Machines intended to be our servants have turned out to be our masters. But we have become utterly helpless without them. If we do not look after them properly, they may go wrong or collapse, causing destruction.
Words of the Original Passage = 207
Words of the Precis = 69
Heading : Man and Machines
Exercise 12
Speaking in public is as difficult as singing or acting, and it ought to have quite as careful rehearsals, even more careful, because one of the aims of the public speaker is to appear entirely spontaneous. The great speakers of Greece and Rome used to prepare an important speech as carefully as an opera star nowadays studies a new role. After writing it out a dozen times, they would deliver it before a few trusted friends, critics and tutors, repeating it again and again until they knew every syllable and gesture, and yet the whole thing appeared not a highly elaborated product of art, but a genuine outpouring of real and overwhelming emotion. That is why we still study the speeches of men like Cicero a single page of them contains the result of more concentrated thought, active experience, intricate psychological knowledge, and training in language than modern speakers can command in whole lifetime. (175 Words)
Hints:
Spontaneous – natural; effortless. Gesture – movement. Elaborated – highly finished. Concentrated – deep. Intricate – difficult.
PRECIS:
Public speaking is as difficult as singing and acting. It needs careful rehearsals. A public speaker has to appear natural. Classical speakers used to master their speeches in private. Yet they appeared to be natural, full of emotions. They contained more deep thought and training in language than modern speakers can command.
Words of the Original Passage = 175
Words of the Precis = 55
Heading : Public Speaking
Exercise 13
People once thought that the great barrier to human progress was illiteracy, the widespread inability to read. When once everybody could read the written or printed word, all, it was thought, would be well. Though people would still differ in attainment, owing to the differences in mental ability, the great majority would, at any rate, be able to read and understand the newspapers, and keep themselves properly informed of what was going on around them. Events have by no means justified this optimism.
The majority are able, it is true, to read written or printed characters. But reading, it has been discovered, has a variety of meanings. To some people it means little more than the ability to pronounce aloud the printed word ; to others it means an ability to gain merely a general impression of what they read. Even students daily engaged in the study of books often develop a superficial ability to read rapidly and with apparent understanding, what they subsequently prove to have understood very imperfectly. (170 Words)
Hints:
Barrier – obstacle; hindrance. Mental ability – intelligence. Characters – letters. Variety – number. Pronounce – speak. Superficial – shallow. Apparent – seeming. Subsequently – as a result of that. Imperfectly – wrongly.
PRECIS:
Once illiteracy was considered an obstacle to human progress. It was supposed that more literacy would increase human progress. But it has not proved so. Today, majority of people can read and write but their knowledge is limited. Reading has varied meanings. Some people read things quickly without full understanding. Others consider it as mere loud reading.
Words of the Original Passage =170
Words of the Precis = 57
Heading : Reading and Human Progress
![]()
Exercises For Practice
Make a precis of the following passages and give a suitable title:
(1) Youth is not a time of life, it is a state of mind; it is not a matter of rosy cheeks, red lips and supple knees; it is a matter of the will, a quality of the imagination, vigour, of deep springs of life. Youth means the predominance1 of courage over timidity2, of adventure over the love of ease. This often exists in a man of sixty more than in a boy of twenty. Nobody grows old merely by the number of years. We grow old by deserting3 our ideals. Years may wrinkle the skin but to give up enthusiasm wrinkles the soul. Worry, doubt, self-distrust, fear and despair4 these bow the heart5 and turn the spirit back to dust6. You are as young as your faith, as old as your doubt. (131 Words)
Word-notes:
1. excess. 2. lack of courage. 3. giving up. 4. lack of hope. 5. dishearten. 6. make you dead in spirit.
(2) We have political independence. But it is not to be regarded as giving us complete freedom. There are ever so many other things which require to be fulfilled, if this first step is to be regarded as a preparation for the liberation1 of this great land. If we wish to follow up political revolution by a social and economic one, our universities must send out batches2 of scientists, technicians, engineers, agriculturists etc. These are essential for changing the face of our country, the economic character of our society. But we should not believe that science and technology alone are enough. There are other countries, much advanced countries in the world, which have achieved marvellous3 progress in scientific and technological side, but yet they are torn by strife4 and they are unable to bring about peace, safety and security of their own people. It only shows that other qualities are also necessary besides those developed by science and technology. (157 Words)
Word-notes:
1. freedom. 2. groups. 3. wonderful. 4 unrest.
(3) Work and play are the complements1 of each other; in fact each is incomplete without the other. “All work and no play makes jack a dull boy”, is true to the core; but the contrary “If all working days had been playing holidays, to play would have been as difficult as to work” holds equally good2. Hence a suitable admixture3, a due proportion of both is what should be aimed at in a school, for there is no denying the fact that play is no less important a part in the accomplishment of a child’s education than work. On the other hand, children acquire greater zest for work if approach to it is made in playway, for play is the outlet4 – nature’s provision for the over-flow of children’s superfluous5 energy. Apart from its value as a great relaxation6 and diversional7 agency8, for it relieves children of the stress and strain9 of their work, play is a great conservator10 of mental, moral and physical energy. It is also a great antidote11 of vice. These are the important results of the achievements on which a school should set its heard12.
Wind-notes:
1. completing parts. 2. is true. 3. mixing together. 4. channel for taking out. 5. extra. 6. providing rest. 7. change from work. 8. means. 9. exertion and pressure. 10. preserver. 11. check against 12. aspire for.
(4) A proper consideration of the value of time will inspire habits of punctuality. Punctuality is the politeness of kings, the duty of the gentlemen and the necessity of the men of business. Nothing begets confidence in a man sooner than the practice of this virtue1, and nothing shakes confidence sooner than the want2 of it. He who holds to his appointment and does not keep you waiting for him shows that he has regard for your time as well as his own. Thus punctuality is one of the ways in which we show our personal respect for those whom we are called upon3 to meet in the business of life. It is also conscientiousness4 in a measure, for an appointment is a contract expressed5 or implied6 and he who does not keep it is guilty of breaking faith as well as dishonesdy using other people’s time. We naturally come to the conclusion that the person who is careless about business is not a person to be trusted with the transaction of matters of importance. When Washington’s Secretary excused himself for lateness of his attendance and laid the blame on his watch, his master quietly said, “Then you must get another watch or I another Secretary.”
Word-notes:
1. quality. 2. lack. 3. required. 4. moral sense. 5. clearly stated. 6 suggested.
(5) Fortune has often been blamed for her blindness, but fortune is not so blind as men are. Those who look into practical life will find that fortune is usually on the side of the industrious, as the winds and the waves are on the side of the best navigator. In the pursuit of even the highest branches of human enquiry the common qualities are found the most useful such as common sense, attention, application and perseverance. Genius may not be necessary, though even genius of the highest sort does not disdain the use of these ordinary qualities. Some have even defined genius to be only common sense intensified. A distinguished teacher and president of a college spoke of it as the power of making efforts. John Foster held it to be power of lighting one’s own fire. Buffon said of genius, “It is patience.”
Word-notes:
Industrious – hard-working. Navigators – trained sailors who are given the assignment of steering the direction of the ship. Application – hard work. Perseverance – steadfastness in doing something. Genius – extraordinary capacity. Disdain – hatred. Intensified – made more deep or intense.
(6) That science has become one of the most powerful factors in modern life is generally an accepted and indeed obvious fact. The proper role of the scientist himself is, however, a point on which there is no general agreement. On the one hand are those die-hards1 who, ignoring the changed circumstances of the outside world, contend that outside the laboratory the personal influence of the scientist should be no more than that of any other citizen. On the other hand, are extremists who advocate a state verging on2 a technocracy3 in which scientists would have special privileges and a large measure of control. Those who tend towards the latter view are much more vociferous41 than their more conservative and much more numerous colleagues, with the unfortunate result that there is a widespread impression that scientists generally share these views and wish to claim a far larger share in the control of world affairs than they possess at present. It is, therefore, timely to attempt an assessment5 of the proper status6 of the scientist in modern society.
Word-notes:
1. obstinate people. 2. nearly. 3. rule of the technicians. 4. vocal. 5. estimate. 6. position.
(7) In India, at any rate, we must aim at equality. That does not and cannot mean that everybody is physically or intellectually or spiritually equal or can be made so. But it does mean equal opportunities for all and no political, economic or social barrier1 in the way of any individual or group. It means a faith in humanity and a belief that there is no race or group that cannot advance and make good in its own way, given the chance to do so. It means a realization of the fact that the backwardness or degradation2 of any group is not due to inherent failings3 in it, but principally due to lack of opportunities and long suppression by other groups. It should mean an understanding of the modern world wherein real progress and advance, whether national or international, have become very much a joint affair and backward groups pull back others. Therefore, not only must equal opportunities be given to all but special opportunities for educational, economic and cultural growth must be given to backward groups so as to enable them to catch up to those who are ahead of them. Any such attempt to open the doors of opportunity to all in India will release enormous energy and ability and transform4 the country with amazing5 speed.
Word-notes:
1. obstacle. 2. disgrace. 3. inborn defects. 4. change. 5. surprising.
(8) The value, of university for educational purposes lies not principally1 in its examination, not even wholly in its teaching, however admirable that teaching may be. It lies and must lie in the collision of minds2 between student and student. We learn at all times of life, but perhaps most when we are young, as much from our contemporaries3 as from anybody else and when we are young we learn from our contemporaries what no professor, however eminent, can teach us. Therefore, it is that while I admire the lives admirable, beyond any power of mine to express my admiration, the lives of those solitary students who under great difficulties come upto Edinburgh from some other University, and without intercourse with their fellows doggedly and perseveringly4 pursue their studies – very often under most serious pressure of home difficulties – their course however admirable is not the course which can give to them those great advantages which are possessed by those whose lot is more happily cast than theirs. I, therefore, associate myself entirely with what Lord Rosebery said about Athletics. I do not think that the athletic movement has been overdone. I believe, on the contrary, that the intercourse between studies which it has given birth, and the good fellowship which it has secured, are of infinite educational value.
Word-notes:
1. mainly. 2. meeting of minds. 3. living in the same age. 4. persistently.
(9) The highest expression in the life of a nation must be intellectual eminence and its power of enriching the world by advancing the frontiers1 of knowledge. When a nation has lost this power, when it merely receives and has nothing to give, then its healthy life is over and sinks into a degenerate2 existence which is purely parasitic3. The status of great university cannot be secured by any artificial means, nor can any character assure it. Its world status is only to be won by the intrinsic4 value of great contribution made by its scholars. To be organic and vital, our national university must stand primarily5 for self¬expression and winning for India her true place among the federation of nations.
Word-notes:
1. boundaries. 2. declined. 3. depending upon others. 4. real. 5. mainly.
From Board Papers
Passage 1
The background of Indian dance is infinitely rich and as varied as the land itself, yet with the same underlying unity which binds the people of the country together. The dances of India, whether folk or classical, are an eloquent expression of an ancient civilisation, whose timeless wisdom continues to evoke the passionate search of man for conscious identity with God. Folk and tribal dances of India are of innumerable types. But they all express its people’s natural gaiety, sense of abandon and rhythm. The origin of classical dances is from the Hindu temples. It was in the temples that they were first conceived and nourished; it was also in the temples that they attained their full stature. While it is true that dances were also performed in courts, on festive occasions etc. yet the impulse that gave them birth was religious.
Precis:
The Indian dance is rich and varied. Folk or classical dances are a fine expression of an old civilisation. Through dance man tries for identity with God. The origin of classical dances is the Hindu temple. They attained full growth here. Dances performed on happy occasions were religious. (48 words)
Heading : Indian Dance
Passage 2
One of the most alarming trends of the present century has been the rising population, specially in the under-developed countries. Advancement in medicine has decreased the infant mortality rate and increased the life span. This rise in population is increasing the pressure on land, steadily reducing its capacity to supply not just food, but fuel wood for cooking and foliage for cattle. The search for agricultural land and fuel wood leads in its own ways to destruction of forests which further leads to soil erosion, a fall in water level and finally conversion of fertile land into desert.
Besides, it has led to congestion in cities, rise in crime, inflation, etc. It is expected that world population will reach eleven billion by the year 2050, and could result in a crisis causing vast poverty and misery specially in the Third World. If we do not come to grip with this problem, then in the decades to come we will really have an acute problem of feeding the people, providing them shelter and security.
Precis:
Population is increasing rapidly in the under-developed countries because of decline in infant mortality and increase in life span. Pressure on land has led to destruction of forests, soil erosion, fall in water level and desertification. This has led to crowding in cities, crime and inflation. World population will soon touch eleven billion. Increasing population should be contained to reduce poverty.
Heading : Increasing Population and Poverty.
![]()
Passage 3
Girls as well as boys spend much of their precious time on fashion. Boys are seen dressed in expensive suits of the latest cut. They are skilled judges in the matter of the dress and eye one another’s clothes with keen interest. Each tries to excel others in the beauty and design in his clothes. Critical remarks are freely made regarding classmates, whose clothes do not fit them properly. Envious glances are cast upon a student, whose clothes are striking in design and perfect in tailoring. Everyone aims at wearing his clothes to the best advantage and at producing a favourable impression upon his classmates. Students who are expensively dressed claim special privileges in the school or college because they think that their costly clothes are an additional qualification. Students do not pay attention to class lectures. The teachers are helpless in this matter, which results in an increase in the number of flops.
Precis:
Boys and girls spend time and money on wearing fashionable clothes. Badly dressed boys and girls are often criticised. Fashionably dressed boys and girls are envied. All students try to create good impression on other classmates by wearing fashionable clothes. Expensively dressed students claim special privileges and consider fashionable clothes an additional qualification. Dressy boys and girls often fail in examinations.
Heading : Fashions and Flops
Passage 4
People generally cherish a false notion about beauty and handsomeness. Almost everybody wishes to look handsome or beautiful. Red cheeks, rosy lips, bright eyes, curly hair and an attractive figure are the dreams of young people. Almost every young man and woman pines to look like his or her favourite film star. Nobody cares to bear in mind that the physical beauty is subject to decay and death. On the other hand, spiritual beauty is eternal in nature. Spiritual beauty means the sound and solid qualities of character.
Handsome is he whose actions are just and virtuous. Handsome deeds, noble thoughts and strength of character know no decay. Man dies physically, but his virtue survives. Socrates, Aristotle, George Washington, Abraham Lincoln, Mahatma Gandhi and Lai Bahadur Shastri had no attraction in their physical appearances, but the handsomeness in their conduct, character and deeds will always continue to attract and inspire. Handsome indeed is the man, whose deeds are handsome. (158 Words)
Precis:
All young men and women desire to look attractive like their favourite film stars. But physical beauty is short-lived while spiritual beauty means solid qualities of character. Handsome is he whose actions are just and virtuous. The noble deeds done by great men live after them. Great men are remembered for their noble deeds and not for their handsome or ugly appearances.
Heading : Handsomeness lies in Handsome Deeds
Passage 5
The soldier who holds the sword stands for the defence of the country. The writer who holds the pen signifies the powerful ideas. The conquests of the soldier are glamorous, but they are short-lived. His victories are over body and land only. The writer conquers not only body, but heart and soul also. The sword may kill a man, but cannot convert his heart. It is true to say that ideas rule the mind and mind rules the world. The victories of the mind are everlasting.
The names of great Commanders and Generals are soon forgotten, but Shakespeare, Wordsworth and Kali Dass will continue to conquer the mind and heart of man till eternity. Even the victories of the sword are immortalized by the pen. Who would know about Lord Rama in the absence of Valmiki’s pen ? The sword is powerful only during a war, but the pen wields its power in peace as well as in war. Thus the superiority of the pen to the sword cannot be contested. (170 Words)
Precis:
The soldier defends the country. The writer gives ideas to the world. The glamorous conquests of the soldier are short-lived. A writer’s words have a lasting appeal. Conquerors are soon forgotten but the words of great writers live for ever. The pen immortalises the victories of great soldiers. Valmiki has immortalised Lord Rama. The pen is powerful during peace and war.
Heading : The Pen is Mightier than the Sword
Passage 6
Although TV programmes have become the most popular source of recreation, reading books is the highest type of pleasure that a man can get before and after his everyday work. In fact, it is a source of everlasting joy. Books are our unfailing friends. Their reading is one of the best ways of passing our leisure time. We do not have to depend upon others for company. Books give us a great relief from boredom. They are the best companions even during journeys.
They express life in an interesting way. They transport us, in our imagination, thousands of kilometres away. We live not only in the present, but in the past and future also. In addition to being our best friends, books are our guides and philosophers. A lover of books lives in the company of great writers and poets of all the ages. He gets delight in prosperity and relief in times of misery. Thus he enriches his experience of life. (162 Words)
Precis:
Reading books gives greater pleasure than recreation by television. Books are man’s unfailing friends. They provide him everlasting joy. Books enable us to spend our time in the best possible way. They are our friends and philosophers in the present, past and future. A lover of books enjoys the company of masterminds. Books delight us in prosperity and relieve us in times of misery.
Heading : Pleasures of Reading Books
Passage 7
Beauty is a wonderful creation of God. It tempts man more quickly than even wealth. But for beauty, this world would have been a dull place. Human beauty and natural beauty are equally attractive. Unfortunately beauty is subject to decay and death. Whatever is beautiful today will perish tomorrow. Time reaps the rich harvest of beauty. None can escape its grip and sickle. Nothing in this world enjoys permanent beauty. A beautiful flower blooms only for a day or two.
A beautiful woman can’t retain her beauty for long. Beauty departs with the period of youth. However, it is only physical beauty which is short-lived. This beauty is skin-deep. But there is beauty of character also. It lends man, immortality. Therefore, man should not run after physical beauty. He should create in him the beauty of thought and action. Only this beauty has a permanent value.
Precis:
Beauty is a remarkable creation of God. It is more tempting than wealth. A world without beauty would be dull and uninteresting. Both human and natural beauty are ravaged by time. Beauty of character has a lasting value. Man should create in him beauty of thought and character.
Heading : The Value of Beauty of Character
![]()
Passage 8
Courage is a virtue. There can be no other virtue without courage. In other words, courage is the basis of all virtues. There are two types of courage-physical courage and moral courage. Physical courage can be taught, but moral courage has to be developed. Physical courage enables us to face physical attacks on our body. Moral courage prepares us to face the challenges of life boldly. Nobody can be great if he does not have courage. Only a man of courage can give resistance to evil. He calls a spade a spade and is not afraid of results. No difficulties can stand in the way of a man if he grapples with them courageously. The virtue of courage should be cultivated in children. Parents and teachers should teach them courage. They should not strike fear in their hearts about small matters. Those who have courage give it to others in times of crisis.
Precis:
Courage is the basis of all virtues. Courage is physical and moral. Physical 1 courage can be taught but moral courage needs to be developed. Physical attacks can be faced with physical courage. Moral courage enables us to face challenges boldly. Courage > makes one great. Courage should be cultivated in children.
Heading : Importance of Courage
Passage 9
Education is an important activity in society. It gives an opportunity to man to understand the world around him and his place in it. In ancient times man was completely at the mercy of nature which was a complete mystery to him. The dark forces of nature were beyond the comprehension of man and to console himself he had to depend upon the existence of supernatural powers and this led to the growth of religion and superstition. The invention of tools, domestication of animals and growth of agriculture led to organisation of society and alongwith this, developed social sciences.
Thus, in education we combine the study of natural laws with the laws governing the development of society. Knowledge and understanding come to us through the study of natural sciences like chemistry, physics and biology etc., and the social sciences like history, political science, etc. The acquisition, interlinking and transmission of this knowledge and understanding is the primary function of education. (160 words)
Precis:
Education enables man to understand the world. Previously man was at the mercy of nature. He depended upon the supernatural forces to understand nature. This made the way for religion and superstition. Then came the organisation of society and education. Education brings us knowledge and understanding when we study natural and social sciences. (59 words)
Heading : Education and Knowledge
Passage 10
Where machines have benefited mankind in so many ways, they have also proved to be harmful. The machine age made many people unemployed. Now there is no need for so many hands to do a task. Only one person is required to manipulate the machine. Thus it has led to unemployment. Machines have also led to degradation of our environment. The poisonous fumes and gases emitted by vehicles and industrial units have polluted the air we breathe and pose a threat to the health of the people.
In the light of all these grave dangers, it is imperative that man tries to make judicious use of machines. After all man had applied his mind to invent new things not to make his life miserable, but to make it more comfortable and better. Machines should serve mankind. Man should ensure that he does not allow them to destroy his environment and health and put the life of all living things in grave danger beyond a point of no return.
Precis:
Machines have proved both useful and harmful to man. Many people have become unemployed because of machines. Machines have damaged the environment. Air is polluted and man’s health is endangered. Man should make wise use of machines. Man invented machines to make his life comfortable. Machines should serve man for better health and environment.
Heading : Machines in Service of Man
Number of words in the Original Passage = 169
Number of words in the Precis = 56
Passage 11
The exploration of space has been one of the most exciting developments. Most spacecrafts which have been launched in the space in the last fifty years, since the time space age began, have transmitted vast amount of knowledge back to earth. It now does not seem so distant a reality or a difficult dream to realise that one day we shall be able to establish human colonies on other planets with our present techniques and resources. It is only the development and application of computers which has brought man closer to realising his dreams. Besides, satellites which are launched in space ate of immense use in communication. They have made it possible to obtain television linkage between distant countries and pleasing greatly television viewers all over the world by taking their favourite programmes or events of world significance right into their living rooms. Photographs from satellites have helped in the field of agriculture, geology and meterology. Weather satellites help to give advance warning of any such developments which may be dangerous to human life.
Precis:
Exploration of space is a very exciting development. Spacecrafts have given us very useful knowledge. Hopefully one day human colonies would be established on other planets. Computers have made this possible. Satellites in space are very useful in communication. They have made link between distant countries possible. Photographs from satellites have helped in several fields like agriculture, affecting human life.
Heading : Exploration of Space
Number of words in the Original Passage = 174
Number of words in the Precis = 58
Passage 12
One of the chief aims of education is to build the moral character of individuals and to teach them to live in society in a spirit of cooperation and brotherhood. Sports are a great help towards this goal of moral development. Every game is played according to certain rules which are recognised by all. Any departure from these rules means foul play. The decision of the referee is final. So games help to develop in players the habit of fair play, sportsmanship, honesty, teamspirit, punctuality, obedience and leadership. These qualities go a long way in making individuals self-disciplined. These habits learnt on the playground then extend to the wider sphere of life. Fair play is a noble quality when practised in political and social dealings. Spirit of sportsmanship teaches one to play game for the sake of playing and accepting defeat with a smile. It is not important whether you win or lose, what is important is how you play it.
Precis:
The main aim of education is to build moral character and enable individuals to live in a spirit of brotherhood. Sports help us in moral development. Games help players in having the spirit of fair play. Qualities learnt on the playground extend to the wider sphere of life. True sportsmen play without caring for victory or defeat.
Number of words in the Original Passage = 161
Number of words in the Precis = 54
Heading : Sports and Moral Development
Passage 13
Anger may sometimes be right and holy. Bad temper is always wrong. It is generally foolish too. A bad tempered person is always selfish. Let a selfish person have his own way and he will be very nice to you. But cross him in the smallest thing and he flies into a rage. Bad temper is due to lack of self-control. Even the best men feel vexed and cross sometimes but they control their feelings. They do not lose their temper. Bad-tempered people are the slaves of their feelings. They cannot control them. A bad-tempered man is an unhappy man. How can you be happy when every little thing makes you angry ? Bad temper grows into a habit if not checked. The cure for bad temper is to think less of oneself and more of others. Learn to control yourself. When angry, count twelve before you speak.
Precis:
A bad-tempered man is often wrong, foolish and selfish. He will be nice to others if he has his own way. He becomes angry when opposed. Best men often control their feelings and temper. A bad-tempered man is often unhappy. One gets rid of bad temper by thinking more of others.
Heading : Getting Rid of Bad Temper
Number of words in the Original Passage = 146
Number of words in the Precis = 49
![]()
Exercise 14
Obedience is the habit of doing what we are told to do. It is not easy to learn obedience but it is necessary. Children must obey their parents. Pupils must obey their teachers. Servants must obey their masters. Soldiers must obey their officers. Subjects must obey the government and all men must obey God. Why should children obey their parents ? The reason is that they are ignorant and need training. Similarly a servant must obey the master because he is paid to do what his master wants. Soldiers must obey their officers because an army is of no use without discipline. Subjects must obey their government because there would be no law and order if they did not. Obedience to God is the first law. If any man tells us to do wrong we must disobey, so that we may obey God. God’s law must come first.
Precis:
Obedience means doing what is necessary. Children, pupils, servants, soldiers, subjects and all men must obey parents, teachers, masters, officers and God respectively. Children need to be trained by parents. There would be total chaos without obedience and discipline at every stage of life. All must obey Gods law and disobey a wrong one.
Heading : Obedience and God’s Law
Number of words in the Original Passage = 148
Number of words in the Precis = 54
Exercise 15
The system of education in India today is devoid of any goal or ideal. It does not satisfy the aspirations of the students. The result is that there is frustration which in turn breeds indiscipline. There is so much of stress on examinations in these days that the student sets the passing of the examination as his only goal but after he passes the examination and goes to the wide world outside, he finds himself unequipped to meet the demands of new age. The best system of education is one which draws both on the present and the past. What we want today is a harmonious blending of the best from our heritage and the finest from modern science.
Precis:
The present system of education is without any goal. It does not meet the aspirations of the students. It is examination-ridden. It fails to prepare students for the demands of the wide world. The best education should combine the best from heritage and the finest from modern science.
Heading : The Best Education
Passage 16
No man can suddenly become great or famous. Long years of hard work and struggle are wanted from him to attain some heights. No man can reach the summit of a mountain without a long and laborious climb. No man can become great or achieve fame without much toil, labour and sacrifice. We are dazzled by the great heights of fame and glory reached by a man but often we forget the long years of toil and suffering spent by him in his pursuit. A student has to work patiently and industriously for years before he can be a great scholar. An actor passes through arduous series of monotonous practices before making any achievement. Often defeats, humiliations and insults lie behind the success of a great reformer, leader or preacher.
Precis:
Long years of hard labour enable one to win fame and glory in one’s field. Outstanding success of others impresses us. Students become scholars through hard labour and industry. A successful reformer or leader has to overcome several obstacles and frustrations.
Heading : No Pains, No Gains
Passage 17
Many men and women are so money-minded that they do not undertake any serious work that does not pay. They believe that it is foolish to exert themselves for such study and brain work as cannot be converted into cash. Hard work only for money, and then plenty of play and pleasure : this seems to be their rule of life. They value intellect only as the key to material prosperity and regard personal mental development as foolish fad. This miserable materialistic psychology is very deep-rooted in all classes of society. Rich and poor, all suffer from it. An old working woman complained to me of her son’s habit of occasionally buying some cheap books, and said, “He wastes his money on books. What good are they to him ? He is a carpenter, not a schoolmaster.”
Precis:
Most men and women are money-minded. They do serious work only for cash payment. Hard work for money is the motto of their lives. They regard intellect as the key to material prosperity. They dislike mental development. Money-minded people think that a carpenter has nothing to do with books.
Heading : Materialism and Intellect