Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class English Book Solutions Chapter 1 Value of Money Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Class 8th English Solutions Chapter 1 Value of Money Question Answers
Value of Money Class 8 Questions and Answers
Activity 1.
Look up the following words in a dictionary. You should seek the following information about the words and put them in your WORDS notebook.
1. Meaning of the word as used in the lesson (adjective/noun/verb. etc.)
2. Pronunciation (The teacher may refer to the dictionary or a mobile phone for correct pronunciation.)
3. Spellings.
![]()
नोटः
1. विद्यार्थी Lesson के आरंभ मे दिए गएा Word – Meaning पढे
2. Pronunciation के लिए अपने अध्यापक से निर्देश लें।
3. दिए गए शब्दों की Spellings याद करें और इन्हें बार-बार सीखने का अभ्यास करें।
| processor | intrigue | review | feature | ultimate |
| limitations | consumerist | obsessed | storage | investing |
Activity 2.
Given below are a few words. Write them in the order as they appear in a dictionary.
1. Market
2. realized
3. decided
4. value
5. money
6. ultimate
7. moment
8. storage
9. arrange
10. machine
11. technology
12. consumerist
13. excited
14. faster
15. account
16. investing
17. pollution
18. disaster
19. persuade
20. prepare
Answer:
1. account
2. arrange
3. consumerist
4. decided
5. disaster
6. excited
7. faster
8. investing
9. machine
10. market
11. moment
12. money
13. persuade
14. pollution
15. prepare
16. realized
17. storage
18. technology
19. ultimate
20. value.
![]()
Activity 3.
Learning to Read and Comprehend
Answer the following questions.
a. What made the narrator unhappy ?
वक्ता किस बात से नाखुश थी ?
Answer:
The limitations of her computer against Bell computer made the narrator unhappy.
b. What was the narrator obessed with ?
वक्ता पर किस बात की सनक सवार थी ?
Answer:
The narrator was obessed with doing more work and earning more money.
c. What were the two features of Bell Computer that were being advertised on TV?
टी.वी. पर बेल कम्प्यूटर की किन विशेषताओं का विज्ञापन आ रहा था ?
Answer:
(i) It has the fastest processor.
(ii) It has very high storage.
d. What offer did the parents give to the narrator ?
वक्ता को माता-पिता ने क्या पेशकश दी ?
Answer:
The parents offered her to earn money by doing house jobs.
e. Which two things did the narrator do to complete the chores ?.
काम पूरे करने के लिए वक्ता ने क्या दो काम किए ?
Answer:
(i) She started getting up early. :
(ii) She started doing her work quickly.
f. What happened when the narrator went to the store to order the computer she wanted ?
जब अपनी पसंद के कम्प्यूटर का ऑर्डर देने के लिए वक्ता स्टोर पर गई तो क्या हुआ ?
Answer:
She found that a new model was coming out soon. It was even faster and had double the storage.
g. Why did she decide against buying the computer she was obessed with ?
वक्ता ने अपनी सनक का कम्प्यूटर न खरीदने का फ़ैसला क्यों किया ?
Answer:
She decided not to buy that computer because she had learned the value of money. Buying the computer she wanted meant the waste of money because of the fast changing technology.
![]()
h. Why did the Bell employee advise the narrator to wait for a few more days ?
बेल कम्पनी के कर्मचारियों ने वक्ता को कुछ और दिन इन्तज़ार करने की सलाह क्यों दी ?
Answer:
They advised the narrator to wait for a few days because a new model of the computer was coming out soon.
Activity 4.
Identify the speaker and the listener.
(a) “Oh, you don’t need to buy that one. We have another one coming out soon. It is even faster and has double the storage.”
Answer:
Speaker : employee at the Bell center.
Listener : the narrator.
(b) “Please dad ! Is there anything else you need help with ?”
Answer:
Speaker : the narrator
Listener : narrator’s father.
(c) “Give me more chores !”
Answer:
Speaker : the narrator
Listener : the narrator’s father.
Activity 5.
Think and discuss with your partner the given scenario.
“Oh you don’t need to buy that one. We have another one coming out soon. It is even faster and has double the storage.”
Do you think
(a) It was wise of the narrator to put her money in a savings account ? Why/why not?
Answer:
Yes, it was really wise of her because it enabled her to save her hard earned money.
(b) It would have been wiser of the narrator to work for two more months and buy the newer model of the computer ? Why/Why not?
Answer:
No, it was not wise. The models of machine go on changing with fast changing technology
![]()
(c) It is advisable for fourteen year old to overwork herself/himself as the narrator did ? Why/Why not?
Answer:
Doing overwork is bad as it tells upon ( बुरा प्रभाव डालता है) one’s health.
Learning Language
The Sentence
A sentence to a group of words which makes complete sense. Here are some examples :
पूरा अर्थ देने वाला शब्द-समूह वाक्य कहलाता है। यहां कुछ उदाहरण दिए हैं :
(a) Ram is going to school.
(b) Do not spit on the floor.
(c) What is your name?
(d) May God bless you !
(e) What a fine morning!
The examples above are complete sentences because each of these makes complete sense.
Forms of Sentences.
Sentences can be classified (वर्गीकरण) into five important types according to the functions they perform.
They are :
- Assertive Sentence
- Interrogative Sentence
- Imperative Sentence
- Exclamatory Sentence
- Optative Sentence
Assertive Sentence : An Assertive sentence is the one that makes a statement or assertion. It may be affirmative (positive) or negative. An Assertive sentence ends with a period (full stop).
कथन वाला वाक्य Assertive Sentence कहलाता है| यह Positive या Negative कोई भी हो सकता है।
Examples :
- We love our country. (Affirmative)
- She speaks the truth. (Affirmative)
- I do not like this picture. (Negative)
- Rakesh does not smoke. (Negative)
An Assertive sentence is sometimes also called a Declarative sentence or a statement.
Interrogative Sentence : An Interrogative sentence is the one which asks a question.
(प्नरन पूछने वाला वाक्य)
Examples :
- Where is my book ?
- Why do you scold the child ?
- Did he learn his lesson ?
Imperative Sentence : An Imperative sentence is the one which expresses a command, a request, an advice or an entreaty.
Examples :
(a) Shut the front door. — (command)
(b) Find my leather jacket. — (command)
(c) Clean your room. — (command)
(d) Wait for me. — (entreaty)
(e) Get out! — (command)
(f) Make sure you pack warm clothes. — (advice)
(g) Please be quiet. — (request/entreaty)
(h) Be nice to your friends. — (advice)
(i) Sit down. — (command)
(j) Please help. — (request)
(k) Help the poor. — (advice)
(l) Do pay us a visit some time. — (entreaty)
![]()
Exclamatory Sentence: An Exclamatory sentence makes a statement that conveys some sudden strong emotion or excitement. मन के अकस्मात् भाव व्यक्त करने वाला वाक्य
Examples :
(a) Hey! I have got the film tickets.
(b) What a fine hit!
(c) How beautiful the flower is !
(d) Happy birthday, Amit !
(e) Thank you, Shashi !
(f) I hate you !
(g) Ice cream and sundaes are my favourite !
Optative Sentence : An Optative sentence expresses a prayer, keen wish, curse etc. This kind of sentence generally starts with ‘may’ or ‘wish’. Sometimes, ‘may remains hidden. (प्रार्थना, मनोकामना, श्राप, आदि भाव व्यक्त करने वाला वाक्य)
Examples :
(a) May you live long !
(b) Long live the king !
(c) May you live long enough to see your grandchildren prosper!
(d) May God bless us all!
(e) May you all succeed !
(f) May God give you good health !
(g) Wish you a very successful married life !
(h) Wish you a happy journey together!
(i) May you win the race !
Activity 6.
Read the sentences given below and state which type of sentences they are in the given space.

Answer:
(a) He plays fooball —- (Affirmative)
(b) She does not live here. —- (Assertive)
(e) Please help me. —- (Imperative)
(ci) May you grow wiser! —- (Optative)
(e) Do you play? —- (Interrogative)
(J) How brave he is! —- (Exclamatory)
(ç) Always speak the truth. —- (Imperative)
(h) Who does not love his country? —- (Interrogative)
(1) How ugly the camel is! —- (Exclamatory)
(i) Does he come here daily? —- (Interrogative)
(k) Leave his place. —- (Imperative)
(1) May you live long! —- (Optative)
(m) Has he come here ? —- (Interrogative)
(n) May you succeed! —- (Optative)
(o) The earth moves round the sun. —- (Assertive)
(p) I wish you were rich! —- (Optative)
(q) Where is your pen ? —- (Interrogative)
(r) I wish I were a King! —- (Optative)
(s) What a pity ! You missed your chance. —- (Exclamatory)
![]()
Assertive and Interrogative Sentences
Study the give ahead sentences carefully and note how Declarative sentences have been changed into Interrogative sentences.
| Assertive (Declarative) | Interrogative (Question) |
| 1. The cow is eating grass. | Is the cow eating grass ? |
| 2. I am writing a book. | Am I writing a book ? |
| 3. The Germans were merching into Belgium. | Were the Germans marching into Belgium ? |
| 4. Meena was writing a letter. | Was Meena writing a letter ? |
| 5. They were being questioned. | Were they being questioned ? |
| 6. The train started at ten. | Did the train start at ten ? |
| 7. I got an e-mail from my son in New York. | Did I get an e-mail from my son in New York ? |
| 8. She sings well. | Does she sing well ? |
| 9. They have studied very hard. | Have they studied very hard ? |
| 10. They play a match. | Do they play a match ? |
| 11. I shall leave for Mumbai tomorrow. | Shall I leave for Mumbai tomorrow ? |
| 12. You should speak the truth. | Should you speak the truth ? |
| 13. He can run a mile in four minutes. | Can he run a mile in four minutes ? |
| 14. We shall discuss the matter with the Principal. | Shall we discuss the matter with the Principal ? |
| 15. He should pay the fee in time. | Should he pay the fee in time ? |
| 16. The mother looks after her child. | Does the mother look after her child ? |
| 17. Idle boys shirk work. | Do idle boys shirk work ? |
| 18. We go to the fair with our friends. | Do we go to the fair with our friends ? |
| 19. A goat grazes in the field. | Does a goat graze in field ? |
| 20. We do not quarrel with our class fellows. | Do we not quarrel with our class fellows ? |
Activity 7.
Change the following Affirmative (Declarative) sentences into Interrogative sentences.
1. He is clever. — Is he clever ?
2. He was simple. — Was he simple ?
3. Ram was feeling tired. — Was Ram feeling tired ?
4. Sita was angry. — Was Sita angry?
5. They were good friends. — Were they good friends?
6. He painted the door blue. — Did he paint the door blue ?
7. He has three pencils. — Has he three pencils ?
8. We had a good time there. — Had we a good time there?
9. I have to do it. — Have I to do it?
10. Sohan had finished his work. — Had Sohan finished his work ?
11. I shall go there tomorrow — Shall I go there tomorrow ?
12. He will play a match. — Will he play a match ?
13. I can do it. — A Can I do it?
14. He may help you. — May he help you ?
15. The sun does not shine at night. — Does the sun not shine at night?
![]()
Activity 8.
Convert the following Interrogative sentences into Assertive (Declarative) sentences.
1. Are you on leave today? — You are on leave today.
2. Was the train late ? — The train was late.
3. Were the boys not lazy? — The boys were not lazy.
4. Am I strong? — I am strong
5. Is your sister ill ? — You sister is ill.
6. Has it been raining since morning ? — It has been raining since morning.
7. Have you fulfilled your promise ? — You have fulfilled your promise.
8. Has he taken the test ? — She has taken the test.
9. Had you seen this picture ? — You had seen the picture.
10. Did he come by train yesterday? — He came by train yesterday.
11. Can you travel fifty miles a day? — You can travel fifty miles a day.
12. Should I stick to my promise ? — I should stick to my promise.
13. Does the watchman keep watch over — The watchman keeps watch over the house? the house.
14. Do you pray to God everyday? — You pray to God everyday.
Positive and Negative Sentences
Study the following sentences and note how Positive sentences have been changed into Negative sentences :
| Positive | Negative |
| 1. I am a student. | I am not a student. |
| 2. It is a garland. | It is not a garland. |
| 3. We are tourists. | We are not tourists. |
| 4. The mango was sweet. | The mango was not sweet. |
| 5. The knives were sharp. | The knives were not sharp. |
| 6. You can win the game. | You cannot (can’t) win the game. |
| 7. We must help him. | We must not help him. |
| 8. She may resign from her post. | She may not resign from her post. |
| 9. You should follow this path. | You should not follow this path. |
| 10. I may be dropped out of the team. | I may not be dropped out of the team. |
| 11. I have learnt my lesson. | I have not learnt my lesson. |
| 12. They had reached there. | They had not reached there. |
| 13. He has written a book. | He has not written a book. |
| 14. We had a dog. | We did not (didn’t) have a dog. |
| 15. I have a book. | I do not (don’t) have a book. |
Activity 9.
Change the following Positive sentences into their Negative form.
1. This dress is very costly. — This dress is not very costly.
2. His neighbour was quite well yesterday. — His neighbour was not quite well yesterday.
3. Your friends were good to me. — Your friends were not good to me.
4. Shyam has a lotus in his hand. — Shyam does not have lotus in his hand.
5. I have a horse. — I have no horse.
6. I have seen this picture. — I have not seen this picture.
7. You have corrected me. — You have not corrected me.
8. The cattle graze in the pasture. — The cattle don’t graze in the pasture.
9. I get up early in the morning. — I don’t get up early in the morning.
10. We saw a snake in the grass.— We saw no snake in the grass.
![]()
Note : You can also use the shortened forms as ‘weren’t’ in place of ‘were not’, ‘isn’t’ in place of‘is not’, ‘wasn’t’ in place of‘was not’, ‘don’t’ in place of‘do not’, ‘didn’t’ in place of‘did not’, ‘doesn’t’ in place of‘does not’, ‘can’t’ in place of‘cannot’, etc. These shortened forms are generally used in conversation i.e. Spoken English.
Activity 10.
Convert the following Negative sentences into their Positive form.
1. Sohan is not an idle boy. — Sohan is an idle boy
2. I do not have an umbrella with me. — I have an umbrella with me.
3. He may not play well today. — He may play well today.
4. She cannot tell a lie. — She can tell a lie.
5. I must not take this medicine. — I must take this medicine
6. He does not take this risk. — He takes this risk.
7. Do not strike the match. — Strike the match.
8. Do not let him go. — Let him go.
9. Do not keep my book. — Keep my book
10. They did not catch the evening train. — They caught the evening train.
Exclamatory and Assertive Sentences
Study the following sentences carefully and note how Exclamatory sentences have been changed into Assertive sentences :
| Exclamatory | Assertive |
| 1. What a lovely scene ! | It is a very lovely scene. |
| 2. Long live our leader ! | We wish that our leader may live long. |
| 3. Alas ! I shall never be able to see him again. | It is very sad that I shall never be able to see him again. |
| 4. Hurrah ! We have won the match. | We are very happy that we have won the match. |
| 5. What a pity ! You have been wasting opportunities. | It is very sad that you have been wasting opportunities. |
| 6. Alas ! The soldier died fighting. | It is sad that the soldier died fighting. |
| 7. How hot it is today ! | It is very hot today. |
| 8. Death to the traitors ! | The traitors must be punished with death. |
| 9. How glad I am that you have come ! | I am very glad that you have come. |
| 10. What a disgrace for the family ! | It is a big disgrace for the family. |
Activity 11:
Change the following Exclamatory sentences into Assertive sentences
1. Bravo! You have done well. — It is brave of you to do the well.
2. Alas! The soldiers died at Galwan — It is sad that the soldiers died at Galwan Valley.
3. How beautiful the scenery is ! — The scenery is very beautiful.
4. How foolish I had been ! — I have been very foolish.
5. What a disaster the earthquake is ! — The earthquake is a big disaster.
6. How stiff the paper is ! — The paper is very stiff.
7. May God reward this act of yours ! — We wish that God may reward this act of yours.
8. What a terrible storm it is! — It is a very terrible storm.
9. Wonderful! I have never seen anything like this earlier — It is really wonderful to see such a thing.
10. May God pardon this sinner — We very much wish that God may pardon this sinner.
![]()
Activity 12:
Change the following Assertive sentences into Exclamatory sentences.
Answer:
1. He is truly noble. — 1. How noble he is !
2. This is indeed a great pleasure. — 2. What a pleasure !
3. It is very kind of you to help him — 3. What a kindness to help him like that. like it!
4. I wish I were young again. — 4. Oh! I were young again.
5. It is a very wonderful opportunity. — 5. What a wonderful opportunity!
6. It is a bitterly cold morning. — 6. What a cold morning!
7. It was an extremely delightful — 7. How delightful the party was ! party.
8. She danced very beautifully. — 8. How beautifully she danced !
9. I wish I had never met you. — 9. Would that I had never met you.
10. It is stupid of me to forget your name. — 10. How stupid ! I have forgotten your name.
Activity 13:
Listen to your teacher-talking about birds. Your teacher will read the text twice. Complete the following table and answer the question that follows while listening to the passage the second time.
First Listening
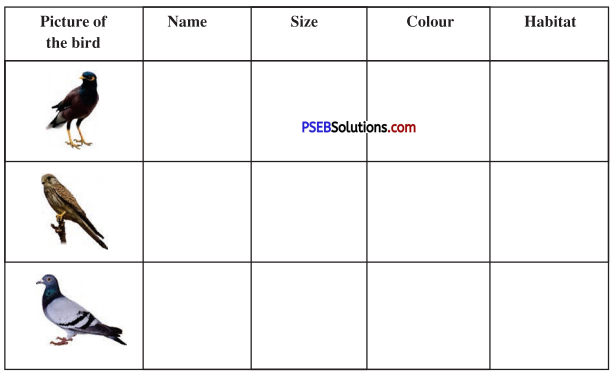
Answer:
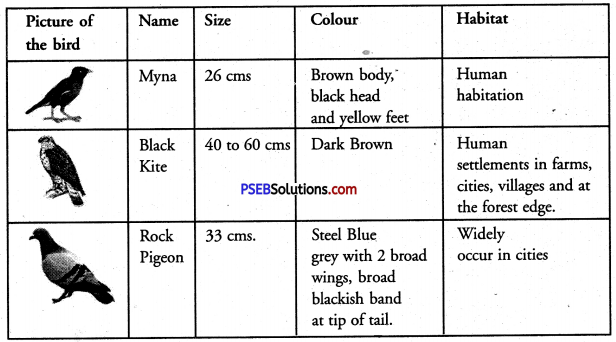
Second Listening Question :
Why are birds referred to as the friends of farmers’?
Answer:
They are friends of farmers because they eat the unuseful insects from the fields. If they don’t eat them they will spoil their crops.
![]()
Learning to Speak (Pairwork)
Activity 14.
Work with your partner. You will play the roles of a shop owner and a customer. Both of you will ask and answer the questions asked during the conversation. The beginning of the conversation is given. You will start with the given conversation and then continue.
Shop owner : How may I help you ?
Customer : I need to buy some biscuits and ice cream.
Shop owner : Which biscuits do you want ?
Customer : I want good cream biscuits. Which ones do you have ?
Shop owner : I have Little Magic biscuits.
Customer : Little Magic ? Never heard of them!
Shop owner : Oh, they are chocolate biscuits with vanilla and strawberry cream.
Customer : That sounds interesting! I think I will buy some.
Shop owner : …………………………..
Customer : …………………………..
Shop owner : …………………………..
Customer : …………………………..
Shop owner : …………………………..
Customer : …………………………..
Shop owner : …………………………..
Customer : …………………………..
Shop owner : …………………………..
Shop owner : …………………………..
Customer : …………………………..
Shop owner : …………………………..
Answer:
Shop owner : How may I help you ?
Customer : I need to buy some biscuits and ice cream.
Shop owner : Which biscuits do you want ?
Customer : I want good cream biscuits. Which ones do you have ?
Shop owner : I have Little Magic biscuits.
Customer : Little Magic ? Never heard of them!
Shop owner : Oh, they are chocolate biscuits with vanilla and strawberry cream.
Customer : That sounds interesting! I think I will buy some.
Shop owner : How much do you want to buy?
Customer : Two or three packets.
Shop owner : Don’t worry. They are not very costly.
Customer : What is the price of one packet after all ?
Shop owner : We sell it ten rupees per packet !
Customer : Is there any scheme?
Shop owner : Why not, if you buy five packets, one is free.
Customer : Then pack me the five packets.
Shop owner : Buy more. The rates are going up next week.
Customer : What about the free scheme?
Shop owner : It will continue for about two months.
Customer : Please pack me ten packets soon. The weather is going bad.
Shop owner : Hurry up, boys ! The customer must not get wet.
Learning to Write
Learning to write is an art. Whenever we plan to write, we find it difficult to start. Let us try and make it a little less difficult. Think of a story or an advertisement or any other form of writing. You will need to understand four things about it. They are :
- Setting — It answers the questions ‘where’ and ‘when’ (the place and time) the C story or the action taken place.
- Characters — It answers the question ‘who’ (the people) is involved in the action.
- Problem — It answers the question ‘what the issue is or the problem that needs to be solved.
- Solution — It answers the question ‘how the problem is solved.
Activity 15:
Think of a story that you have read in this book. Identify the setting, characters, problem and the solution.
| Name of the Story | The Value of Money |
| Setting | An Urban Area |
| Characters | Narrator, Bell center employees |
| Problem | Buying the Latest Computer, Changing Models with the fast changing technology. |
| Solution | Go on with your current computer. Save Money. Honour its value. |
Activity 16
Write about a real incident that happened with you in the form of a story keeping the components of the story in your mind. First make your notes and then write the incident in the space given.
| Setting | City Market, A Book Shop |
| Characters | I, my friend, my uncle. |
| Problem | Buying new school books. Pocket picked. |
| Solution | Got money from my uncle and bought books. |
| Incident/story | Yesterday I went to the city market to buy new school books. My friend was with me. But to our surprise, someone had picked my pocket. Suddenly I saw my uncle passing by the Book shop. I told him my problem. We bought two new books after he gave me the money, I needed. |
![]()
Activity 17
Narrate a situation when your parents offered you money in exchange for doing something in the box given below.
Answer:
Money for Mobile
I wanted to buy a new mobile. But my parents refused to buy it to me. I was sad. But in the evening, I got an offer to work in the home garden for money. I did digging job and watered the plants for a month. I got twenty thousand rupees for this. How happy I was ! I bought a mobile worth five thousand only and saved the rest of money.
Learning to Use the Language
The ground water in Punjab is declining. We need to do something to stop this. You would certainly have seen awareness campaigns on TV advising the citizens to save water. Hos
Activity 18.
Prepare a list of Do’s and Don’ts that will help us to save water. You can start thinking of your everyday routine when you use water. You will put up this list at a prominent place in your home where everybody can see it and make efforts to save water. You must write complete sentences.
Answer:
| S.No. | Dos | Don’ts |
| 1. | Save water at all costs. | Don’t waste water in any way. |
| 2. | Use less water while bathing. | Don’t wash your car with a pipe. |
| 3. | Use dirty water for flush. | Don’t let the tap run while brushing teeth. |
| 4. | Use a bucket to wash your car. | Don’t fill your cooler tank to the brim. |
| 5. | Stop the leakage of water through taps. | Don’t do over-watering of your plants. |
| 6. | Put a plastic bottle in your toilet tank ’ | Don’t use a tub for a bath. |
| 7. | Turn off water while brushing your teeth. | Don’t (Never) keep drinking water uncovered. |
| 8. | Turn off water while shaving. | Don’t fill the bucket full for bathing. |
Comprehension of Passages
Read the following passage and answer the questions given below each :
(1) It was summer break and I had been watching a lot of T.V. There was this one advertisement that would pop up on screen all the time. It was for the latest Bell Computer. It had ‘the fastest processor’ and ‘unbelievably high storage’among many other new features. Every time I saw it, I was intrigued. I would go online and watch people reviewing the computer just to find out more about its features. I would read articles about its features in tech magazines. It appeared to be an ultimate computer while the limitations of my own computer made me unhappy. But my parents refused to buy me the computer when I asked them about it.
1. What was the advertisement for ?
विज्ञापन किस बात के लिए था ?
2. What did the narrator want to buy and why?
वक्ता क्या खरीदना चाहती थी और क्यों ?
3. Choose true and false statements and write them in your answer-book :
(a) The narrator had been watching a lot of T.V. during summer break.
(b) The narrator’s a parents bought her the latest Bell Computer.
![]()
4. Complete the following sentences according to the meaning of the passage :
(a) It appeared to be an …..
(b) The narrator’s computer made her unhappy because of …………..
Or
Match the words with their meaning :
| (i) find out | emerge |
| (ii) pop up | go out |
| know |
Answer:
1. The advertisement was for the latest Bell Computer.
2. The narrator wanted to buy to latest Bell Computer because it had many new features over her computer.
3. (a) True, (b) False.
4.
(a) It appeared to be an ultimate computer.
(b) The narrator’s computer made her unhappy because of its limitations.
Or :
(i) find out — know
(ii) pop up – emerge
(2) Looking back now, I probably did not even need all those extra features. I could do everything. I wanted to do on my own computer without running into any issues but the consumerist in me seemed to think otherwise.
After a while, my parents noticed how obsessed I was with this new computer so they decided to give me a chance to earn it. They told me if I started doing house chores they would give me money for it and I could save up until I had enough to buy the computer on my own. It seemed like a good idea and I jumped at the opportunity. The very next day, I started waking up early to make extra time to be able to do more chores.
![]()
1. Why did the narrator need money?
वक्ता को पैसे की ज़रूरत क्यों थी ?
2. How could the narrator earn it ?
वक्ता पैसे कैसे कमा सकती थी ?
3. Choose true and false statements and write them in your answer-book :
(a) The narrator was very happy with her computer.
(b) The narrator jumped at the opportunity of earning money.
4. Complete the following sentences according to the meaning of the passage :
(a) I probably did not need all ……………..
(b) The consumerist in the narrator seemed …
Or
Write the meanings of the following words in english : (Any two)
features, opportunity, chores
Answer:
1. The narrator needed money to buy a new computer.
2. The narrator could earn it buy doing house chores.
3. (a) False, (b) True.
4. (a) I probably did not need all those extra features.
(b) The consumerist in the narrator seemed to think otherwise.
Or
features — qualities, opportunity-chance, Chores — jobs.
(3) As I got quicker, I started having more free time and didn’t really know what to do with it. “Please dad! Is there anything else you need help with ? I’m willing to do anything; just lay it on me. Give me more chores !” I remember pleading with dad.
I was obsessed. Any free time I had, I wanted to fill it with more work and more money. Since the summer break was almost over and I knew I would have less time once I started going to school again. So, I wanted to work as much as possible during the break.
It took me a few months but I eventually saved up enough to buy myself the Bell Computer. It was a week before my birthday and I went to the Bell Center to place an order. I knew it would take at least a week for the store to get it in case it was out of stock.
1. How did the narrator want to use her free time?
वक्ता अपना खाली समय कैसे बिताना चाहती थी ?
2. When did she go to the Bell center and why?
वह बेल सेंटर पर कब गई और क्यों ?
3. Choose true and false statements and write them in your answer-book :
(a) The summer break was almost over.
(b) The narrator did not want to go to school again.
4. Complete the following sentences according to the meaning of the passage :
(a) I wanted to work as much as possible …..
(b) As I got quicker, I started having …..
Or
Match the words with them meaning :
| (i) lay | ultimately |
| (ii) eventually | leave |
| possibly |
Answer:
1. She wanted to use her free time by doing more and more work.
2. She went to the Bell center a week before her birthday to place an order for the new computer.
3. (a) True, (b) False.
4. (a) I wanted to work as much as possible during the break.
(b) As I got quicker, I started having more free time.
Or
(i) lay — leave
(ii) eventually — ultimately
![]()
Use of Words and phrases in sentences.
1. Review – Let us review, the problem.
2. Features – This computer has many good features.
3. Pop up – The differences of the two brothers popped up.
4. Limitations – Every machine has its own limitations.
5. Find out – I want to find out of the truth behind the quarrel.
6. Out of stock – Sugar is out of stock these days.
7. Plead – He pleaded for mercy.
8. Opportunity – Avail of every opportunity.
9. Sore – My eyes are sore.
Word Meaning:
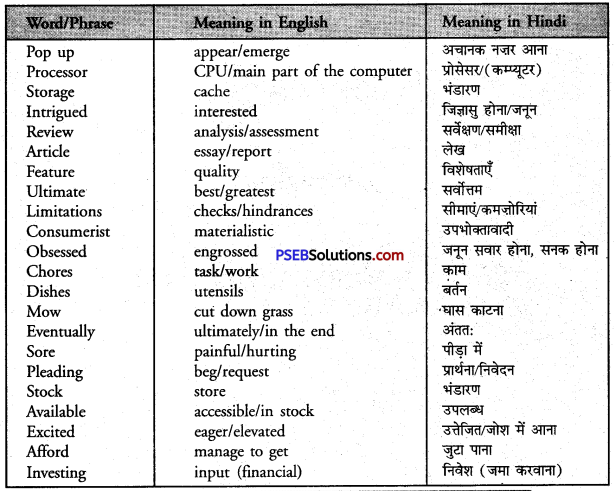
Value of Money Summary in Hindi
It was 14 when ……….. to think otherwise.
मैं चौदह (14) वर्ष की थी, जब मुझे धन के महत्त्व का पता चला । यद्यपि मेरे पास एक कम्प्यूटर था और उसमें कोई खराबी भी नहीं थी, फिर भी मैं अपने लिए एक नया कम्प्यूटर लेना चाहती थी। गर्मी की छुट्टियां थीं और मैं बहुत ज्यादा टी.वी. देख रही थी। वहां स्क्रीन पर हर समय अचानक एक विज्ञापन दिखाई देता था। यह बेल के नए कम्प्यूटर का था। इसमें बहुत सी अन्य नई विशेषताओं के साथ-साथ ‘तीव्रतम प्रोसेसर’ और ‘अविश्वसनीय उच्च भंडारण’ क्षमता भी थी । जब भी मैं इसे देखती मुझ पर इसे पाने का जनून सवार हो जाता था। कम्प्यूटर की और अधिक विशेषताओं को जानने के लिए मैं ऑनलाइन जाती और लोगों के सर्वेक्षणों (विचारों) को देखती। मैं तकनीकी (Tech) से जुड़ी पत्रिकाओं में उसकी विशेषताओं के लेखों को पढ़ती।
वह सर्वोत्तम कम्प्यूटर लगता था जबकि मेरे अपने कम्प्यूटर की सीमाएं/कमजोरियां मुझे दुःखी कर देती थीं। परन्तु जब मैंने अपने माता-पिता से कम्प्यूटर खरीदने के लिए कहा तो उन्होंने मना कर दिया। अब मैं जब भी पीछे मुड़ कर देखती हूँ तो मुझे लगता है कि शायद मुझे अतिरिक्त विशेषताओं की कोई आवश्यकता ही नहीं थी। मैं अपने कम्प्यूटर पर बिना किसी रुकावट के हर वह काम कर सकती थी जो मैं करना चाहती थी परन्तु मेरे अन्दर छिपे उपभोक्तावादी के विचार इसके विपरीत थे।
After a while …………………………… during the break.
कुछ समय के बाद मेरे माता-पिता ने ध्यान दिया कि मुझ पर नए कम्प्यूटर का कितना जनून सवार है। इसलिए उन्होंने निश्चय किया कि वे मुझे पैसा कमाने का एक अवसर देंगे। उन्होंने मुझसे कहा कि यदि मैं घर के काम करने आरम्भ कर दूं तो वे मुझे उसके लिए पैसा देंगे और मैं तब तक पैसा इकट्ठा करूं जब तक कि मैं अपने कम्प्यूटर न खरीद सकूँ। मुझे यह विचार अच्छा लगा और मैं यह मौका पाकर उछल पड़ी। अगले ही दिन से मैंने जल्दी उठना आरम्भ कर दिया ताकि मैं ज्यादा काम करने के लिए अधिक समय निकाल पाऊँ।
मैं दिन में तीन बार बर्तन साफ करती; कूड़ा बाहर निकालती; सप्ताह के अंत में लॉन (Lawn) की घास काटती; सारा घर साफ करती और जब कभी भी आवश्कता होती कार को धोती। मैं प्रतिदिन बिना थके लगातार तब तक काम करती जब तक कि मेरा सारा शरीर दुखने नहीं लगता और अगले दिन उठकर फिर से वही करती। अंततः मैं इसकी आदी हो गयी और यह सब मुझे आसान लगने लगा। मेरी क्षमता और अधिक बढ़ गई और मैं हर काम पहले से अधिक जल्दी करने लगी।
जैसे ही मुझमें तेजी आई। मेरे पास और अधिक समय बचने लगा और मुझे समझ नहीं आता था कि मैं उस समय का क्या करूं। मुझे याद आ रहा है मैं अपने डैड से प्रार्थनी करती हूँ कि “आप पिता जी (डैड) कृपया बताएं, क्या आपको किसी और काम में मेरी मदद की आवश्यकता है ? मैं कुछ भी करने को तैयार हूं, बस काम मुझ पर छोड़ दें। मुझे और अधिक काम दें।”
![]()
मुझे जनून था। मेरे पास जितना भी खाली समय होता मैं उसे और अधिक काम करके व्यतीत करना चाहती ताकि और अधिक पैसा कमा सकूँ क्योंकि ग्रीष्म अवकाश लगभग समाप्त होने वाला था और मुझे मालूम था कि जैसे ही मैं स्कूल जाना आरम्भ कर दूंगी तो मेरे पास समय कम रह जाएगा। इसलिए मैं छुट्टियों में ही अधिक-से-अधिक काम कर लेना चाहती थी।
It took me a …………….. the value of money.
मुझे कुछ महीने लग गए। परन्तु अंतत: मैंने इतना पैसा जोड़ लिया कि मैं अपने लिए बेल कम्प्यूटर खरीद सकू। अपने जन्म-दिन से एक सप्ताह पहले मैं आर्डर देने के लिए बेल सेंटर (केंद्र) पर गयी। मैं जानती थी उनके स्टोर में उपलब्ध नहीं होगा तो, इसे मंगवाने के लिए स्टोर वालों को कम-से-कम एक सप्ताह का समय चाहिए होगा।
मैं अंदर गई और सीधा सामने वाले डेस्क के पीछे बैठे कर्मचारी के पास यह जानने के लिए पहुंची कि क्या कम्प्यूटर उपलब्ध है। । उसने कहा, “ओह, आपको वह खरीदने की आवश्यकता नहीं है। हमारे पास शीघ्र ही एक और आ रहा है। वह इससे भी अधिक तेज़ और दोहरी क्षमता वाला है।” इससे पहले कि वह मुझे उसका मूल्य बताता मैं क्षण भर के लिए थोड़ी उत्तेजित हो उठी। मुझे आभास हुआ कि इसे पाने के लिए मुझे दो महीने तक और घर के काम करने होंगे।
तब मुझे अहसास हुआ कि तकनीक कितनी तेजी से बदलती है। मशीन चाहे कितनी भी अच्छी हो जब तक आप उसे चलाने में पूरी तरह अभ्यस्त होते हैं, बाजार में हमेशा उससे तेज़ और बेहतर मॉडल आ जाता है। मैंने उसी क्षण कम्प्यूटर न खरीदने का फैसला किया क्योंकि मैं कड़ी मेहनत से कमाए अपने पैसे को किसी ऐसी चीज़ पर खर्च नहीं करना चाहती थी जिसका मूल्य जल्दी ही कम हो सकता है। अन्ततः मैंने वह सारा पैसा बचत खाते में जमा (निवेश) करवा दिया। इस प्रकार मैंने धन के महत्त्व को सीखा।
Retranslation From English to Hindi
1. It was summer break. —- गर्मी की छुट्टियां थीं।
2. I had been watching a lot of T.V. —- मैं बहुत ज्यादा टी.वी. देख रही थी।
3. It appeared to be an ultimate computer. —- वह सर्वोत्तम कम्प्यूटर लगता था।
4. I could save up until I had enough to buy the computer on my own. —- मैं तब तक पैसा इकट्ठा करूं। जब तक कि मैं अपना कम्प्यूटर न खरीद सकू।
5. I would do the dishes three times a day. —- मैं दिन में तीन बार बर्तन साफ करती।
6. My whole body was sore. —- मेरा सारा शरीर दुखने लगा।
7. Eventually, I got used of it.—- अंतत: मैं इसकी आदी हो गई।
8. I also got more efficient at it. —- मेरी दक्षता और अधिक बढ़ गई।
9. I was doing everything a lot quicker. —- मैं हर काम पहले से अधिक जल्दी करने लगी।
10. I was obsessed. —- मुझे जनून था।
11. I walked in and went straight to the employee sitting behind the front desk. —- मैं अंदर गई और सीधा सामने वाले डेस्क के पीछे बैठे कर्मचारी के पास पहुंची।
12. You don’t need to buy that one.—- आपको वह खरीदने की आवश्यकता नहीं है।
13. It is even faster and has double the storage. —- वह और अधिक तेज़ तथा दोहरी क्षमता वाला है।
14. This is how I learned the value of money. —- इस प्रकार मैंने धन के महत्त्व को सीखा। .
English Guide for Class 8 PSEB Prose