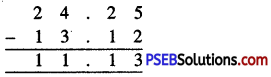
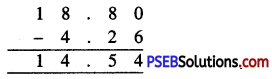
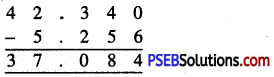
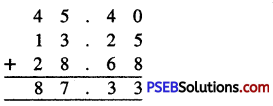
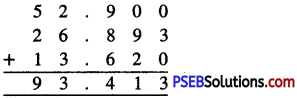
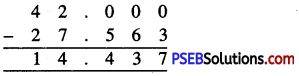
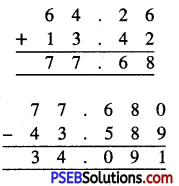
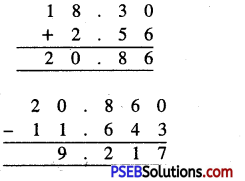
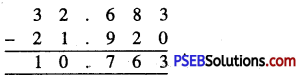
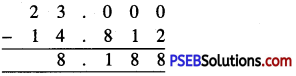
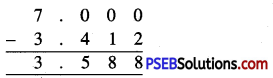
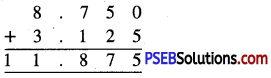
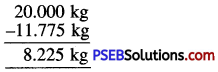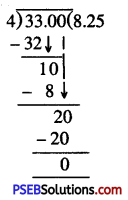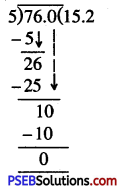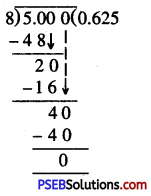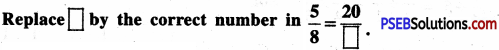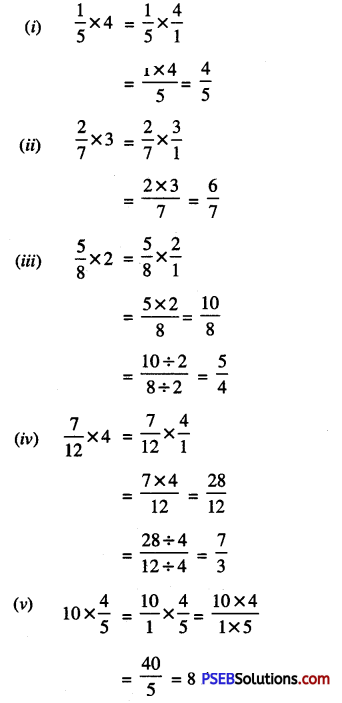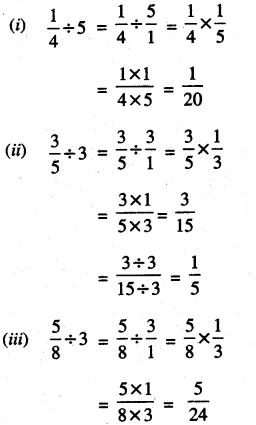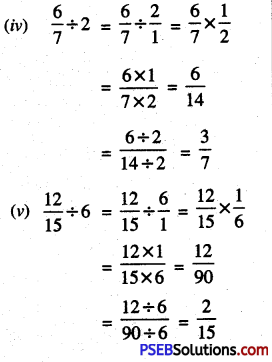Punjab State Board PSEB 6th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 6 Decimals Ex 6.2 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 6 Decimals Ex 6.2
1. Convert the following decimal numbers into fractions and reduce it to lowest form.
Question (i)
1.4
Solution:
1.4 = \(\frac{14}{10}=\frac{14 \div 2}{10 \div 2}\)
(H.C.F. of 14 and 10 is 2)
= \(\frac {7}{5}\)

Question (ii)
2.25
Solution:
2.25 = \(\frac{225}{100}=\frac{225 \div 25}{100 \div 25}\)
(H.C.F. of 225 and 100 is 25)
= \(\frac {9}{4}\)
Question (iii)
18.6
Solution:
18.6 = \(\frac{186}{10}=\frac{186 \div 2}{10 \div 2}\)
(H.C.F. of 186 and 10 is 2)
= \(\frac {93}{5}\)
Question (iv)
4.04
Solution:
4.04 = \(\frac{404}{100}=\frac{404 \div 4}{100 \div 4}\)
(H.C.F. of 404 and 100 is 4)
= \(\frac {101}{25}\)
Question (v)
21.6
Solution:
21.6 = \(\frac{216}{10}=\frac{216 \div 2}{10 \div 2}\)
(H.C.F. of 216 and 10 is 2)
= \(\frac {108}{5}\)
2. Convert the following fractions into decimal numbers:
Question (i)
\(\frac {7}{100}\)
Solution:
\(\frac {7}{100}\) = 0.07
(Here denominator is 100)

Question (ii)
\(\frac {12}{10}\)
Solution:
\(\frac {12}{10}\) = 1.2
(Here denominator is 10)
Question (iii)
\(\frac {215}{100}\)
Solution:
\(\frac {215}{100}\) = 2.15
(Here denominator is 100)
Question (iv)
\(\frac {18}{1000}\)
Solution:
\(\frac {18}{1000}\) = 0.018
(Here denominator is 1000)
Question (v)
\(\frac {245}{10}\)
Solution:
\(\frac {245}{10}\) = 24.5
(Here denominator is 10)
3. Convert the following fractions into decimal numbers by equivalent fraction method:
Question (i)
\(\frac {5}{2}\)
Solution:
Here denominator is 2.
Convert into equivalent fraction with denominator 10 by multiplying it by 5.
∴ \(\frac{5}{2}=\frac{5 \times 5}{2 \times 5}=\frac{25}{10}\) = 2.5

Question (ii)
\(\frac {3}{4}\)
Solution:
Here denominator is 4.
Convert into equivalent fraction with denominator 100 by multiplying it by 25.
∴ \(\frac{3}{4}=\frac{3 \times 25}{4 \times 25}=\frac{75}{100}\) = 0.75
Question (iii)
\(\frac {28}{5}\)
Solution:
Here denominator is 5.
Convert into equivalent fraction with denominator 10 by multiplying it by 2.
∴ \(\frac{28}{5}=\frac{28 \times 2}{5 \times 2}=\frac{56}{10}\) = 5.6
Question (iv)
\(\frac {135}{20}\)
Solution:
Here denominator is 20.
Convert into equivalent fraction with denominator 100 by multiplying it by 5.
∴ \(\frac{135}{20}=\frac{135 \times 5}{20 \times 5}=\frac{675}{100}\)
= 6.75
Question (v)
\(\frac {17}{4}\)
Here denominator is 4.
Convert into equivalent fraction with denominator 100 by multiplying it by 25.
∴ \(\frac{17}{4}=\frac{17 \times 25}{4 \times 25}=\frac{425}{100}\)
= 4.25

4. Convert the following fractions into decimals by long division method:
Question (i)
\(\frac {17}{2}\)
Solution:
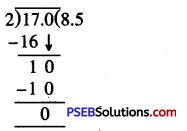
= 8.5
Question (ii)
\(\frac {33}{4}\)
Solution:
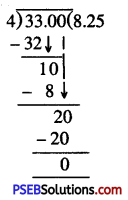
= 8.25
Question (iii)
\(\frac {76}{5}\)
Solution:
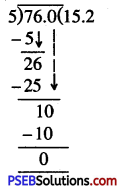
= 15.2

Question (iv)
\(\frac {24}{25}\)
Solution:

= 0.96
Question (v)
\(\frac {5}{8}\)
Solution:
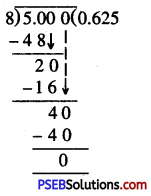
= 0.625
5. Represent the following decimals on number line:
Question (i)
(i) 0.7
(ii) 1.6
(iii) 3.7
(iv) 6.3
(v) 5.4
Solution:
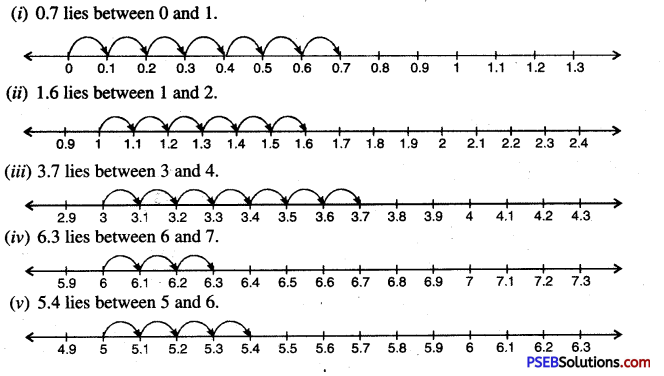

6. Write three decimal numbers between:
Question (i)
1.2 and 1.6
Solution:
Three decimal numbers between 1.2 and 1.6 are:
1.3, 1.4, 1.5
Question (ii)
2.8 and 3.2
Solution:
Three decimal numbers between 2.8 and 3.2 are:
2.9, 3, 3.1
Question (iii)
5 and 5.5.
Solution:
Three decimal numbers between 5 and 5.5 are:
5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4.
7. Which number is greater:
Question (i)
0.4 or 0.7
Solution:

Since, 7 > 4
So, 0.7 > 0.4

Question (ii)
2.6 or 2.5
Solution:
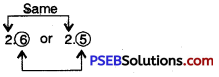
Since, 6 > 5
So, 2.6 > 2.5
Question (iii)
1.23 or 1.32
Solution:

Since, 3 > 2
So, 1.32 > 1.23
Question (iv)
12.3 or 12.4
Solution:
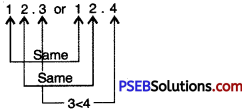
Since, 4 > 3
So, 12.4 > 12.3
Question (v)
18.35 or 18.3
Solution:
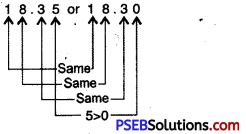
Since, 5 > 0
So, 18.35 > 18.30

Question (vi)
12 or 1.2
Solution:

Since, 12 > 1
So, 12 > 1.2
Question (vii)
5.06 or 5.061
Solution:
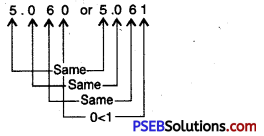
Since, 1 > 0
So, 5.061 > 5.060
Question (viii)
2.34 or 23.3
Solution:
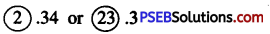
Since, 23 > 2
So, 23.3 > 2.34

Question (ix)
13.08 or 13.078
Solution:
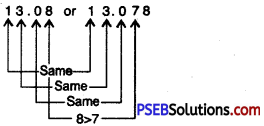
Since, 8 > 7
So, 13.08 > 13.078
Question (x)
2.3 or 2.03.
Solution:
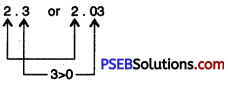
Since, 3 > 0
So, 2.3 > 2.03
8. Arrange the decimal numbers in ascending order:
Question (i)
2.5, 2, 1.8, 1.9
Solution:
Ascending order is :
1.8, 1.9, 2, 2.5

Question (ii)
3.4, 4.3, 3.1, 1.3
Solution:
Ascending order is :
1.3, 3.1, 3.4, 4.3
Question (iii)
1.24, 1.2, 1.42, 1.8.
Solution:
Ascending order is :
1.2, 1.24, 1.42, 1.8.
9. Arrange the decimal numbers in descending order:
Question (i)
4.1, 4.01, 4.12, 4.2
Solution:
Descending order is :
4.2, 4.12, 4.1, 4.01
Question (ii)
1.3, 1.03, 1.003, 13
Solution:
Descending order is :
13, 1.3, 1.03, 1.003

Question (iii)
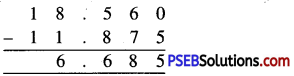
8.02, 8.2, 8.1, 8.002.
Solution:
Descending order is :
8.2, 8.1, 8.02, 8.002.

![]()
![]()
![]()