Punjab State Board PSEB 6th Class English Book Solutions Chapter 3 The Giving Tree Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Class 6th English Solutions Chapter 3 The Giving Tree Question Answers
The Giving Tree Class 6 Questions and Answers
Activity 1.
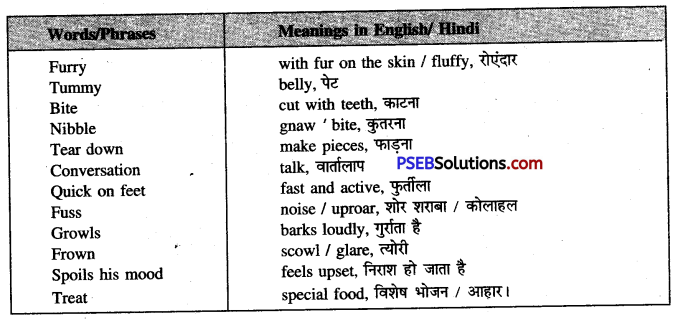
Look up the following words in a dictionary. You should seek the following information about the words and put them in your WORDS notebook.
1. Meaning of the word as used in the lesson (Adjective/Noun/Verb, etc.)
2. Pronunciation (The teacher may refer to the dictionary or the mobile phone for correct pronunciation.)
3. Spellings
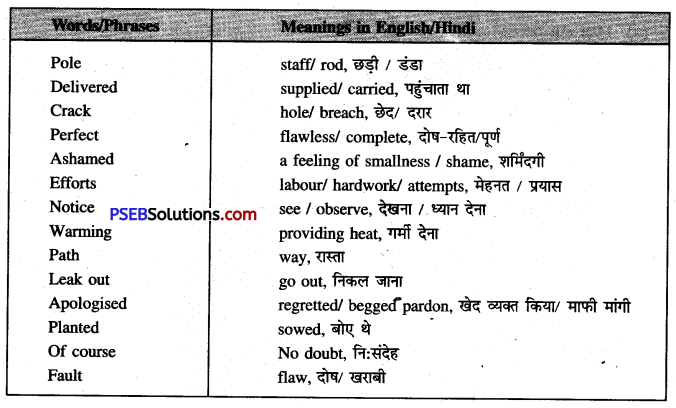
| Swing (verb) | trunk | branches |
| business | sail | resource |
Vocabulary Expansion
Activity 2.
Read the following phrases. Find out their meaning by reading the story again. Write two meaningful sentences using each phrase.
1. climb up
(a) He climbed up a tall tree.
(b) We climbed up a hill.
![]()
2. Cut off
(a) Our village was cut off from the city during rains.
(b) I cut off the spoiled part of the mango.
3. cut down
(a) He cut down the old neem tree.
(b) Many trees were cut down by the villagers
4. Stay away
(a) stay away from the bad people.
(b) I stay away from the crowd of people.
5. Take away
(a) Drinking took away his life.
(b) The thief took away my purse.
Learning to Read and Comprehend
Activity 3.
Read the story carefully and answer the following questions in “Yes”/“No’. For example :
Question : Did the boy love the tree when he was a child ?
Answer : Yes, he did.
Question 1.
Did the tree love the little boy ?
Answer:
Yes, she did.
Question 2.
Did the tree have money to give the boy ?
Answer:
No, she didn’t.
Question 3.
Did the boy want to go to a nearby village ?
Answer:
No, he didn’t.
Question 4.
Did the boy get married ?
Answer:
Yes, he did.
![]()
Question 5.
Did the tree allow the boy to sit down on the stump ?
Answer:
Yes, she did.
Activity 4.
Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
Who would come and play with the tree ?.
वृक्ष के साथ कौन आकर खेलता था ?
Answer:
A little boy would come and play with the tree.
Question 2.
Who was too big to climb and play ?
कौन इतना बड़ा था कि ऊपर चढ़ कर खेल नहीं सकता था ?
Answer:
The boy was too big to climb up the tree and play.
Question 3.
Why did the boy want a boat ?
लड़के को नाव क्यों चाहिए थी ?
Answer:
The boy wanted a boat to sail him away to another city.
Question 4.
Why did the boy want to go to another city ?
लड़का किसी दूसरे शहर क्यों जाना चाहता था ?
Answer:
The boy wanted to go to another city for business.
Question 5.
What did the tree say in the end ?
अंत में वृक्ष ने क्या कहा ?
Answer:
In the end the tree asked the boy to sit on her stump and rest.
Activity 5.
Fill in the blanks with the words given below. You can use each word twice, if necessary.
sailed, tree, stump, grew, happy, climb up, swing, house, tired, apples
1. Once there was a boy and a ……………….
2. The boy played with the ……………………
3. The tree asked the boy to …………………… and ………………….. from her branches.
4. The boy ………………….. older.
5. The tree asked the boy to sell-off …………………… to get money.
6. The boy cut off the branches to make a …….
7. The boy made a boat from the trunk of the tree and …………………. away.
8. The tree was not ……………
9. The boy came back to the tree. He said that he was
10. The boy sat on the ………………….. to rest.
Answer:
1. tree
2. tree
3. climb up, swing
4. grew
5. apples
6. house
7. sailed
8. happy
9. tired
10. stump.
![]()
Activity 6.
Give opposites of the given words in the given space.
Word — Opposite
1. happy — sad
2. give — take
3. sell — buy
4. come — go
5. quiet — noisy
6. climb up — climb down
Activity 7.
Add ‘ed to the following words and write a meaningful sentence.
Example: Stay: I stayed in Jammu for a week.

Answer:
1. want – He wanted to take rest.
2. climb – He climbed up a hill.
3. play – We played football,
4. sail – The ship sailed away to U.S.A.
5. rest – We rested under a tree.
Learning Language
Pronoun
A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun.
Noun (संज्ञा) के स्थान पर प्रयोग होने वाला शब्द Pronoun (सर्वनाम) कहलाता है|
The words ‘they’ ; ‘she’; ‘her’; ‘he’; ‘it are used in place of nouns.
We call them Pronouns. There are three main kinds of pronouns :
Pronouns मुख्य रूप से तीन प्रकार के होते हैं —
1. Personal Pronoun
2. Demonstrative pronoun
3. Interrogative pronoun
1. Personal Pronoun :
Pronouns which are used in place of proper nouns to avoid repetition are called personal pronouns. ये Pronouns वाक्य में Proper Noun की बारम्बारता से बचने के लिए प्रयोग में लाये जाते हैं।
For example :
My mother is very tired because my mother has been working the whole day.
My mother is very tired because she has been working for the whole day.
![]()
There are three kinds of personal pronouns.
1. Pronouns of the First Person
Singular — Plural
I, my, mine, me, myself — We, our, ours, us, ourselves
2. Pronouns of the Second Person
Singular — Plural
you, yours, yourselves, your — you, yours, yourself, your
3. Pronouns of the Third Person
Singular — Plural
he, she, it, him, her — them, their, theirs
Activity 8.
Fill in the blanks using personal pronouns.
Question 1.
……………. often reads until late at night.
(a) he
(b) Aman
(c) Meena
(d) they
Answer:
(a) he
Question 2.
…………….. is running up and down the stairs.
(a) the cat
(b) she
(c) my brother
(d) you
Answer:
(b) she

Question 3.
……………….. is from Mumbai.
(a) Rosy
(b) my friend
(c) he
(d) this statue
Answer:
(c) he
Question 4.
Have ……………….. got a dog, Meena ?
(a) anyone
(b) they
(c) someone
(d) it
Answer:
(b) they
Question 5.
We enjoy the roses so much. ………………. really make the garden beautiful.
(a) they
(b) its
(c) someone
(d) flowers
Answer:
(a) they
![]()
Question 6.
Aman isn’t an architect. ……………. . is an engineer
(a) he
(b) they
(c) it
(d) she
Answer:
(a) he
Question 7.
Are …………. friends or not ?
(a) he
(b) she
(c) we
(d) it
Answer:
(c) we
Question 8.
My doctor was born in London. …. ………….. teaches language lessons in his spare time.
(a) they
(b) it
(c) she
(d) he
Answer:
(d) he
Question 9.
All my teachers are from Europe. …………….. come from all over the continent.
(a) she
(b) we
(c) they
(d) them
Answer:
(c) they
Question 10.
Our friends are athletes. All of ………………. are either strong, fast, or both.
(a) we
(b) they
(c) them
(d) you
Answer:
(c) them
2. Demonstrative Pronoun
A demonstrative pronoun is a pronoun that is used to point to something within a sentence. These pronouns can indicate items in space or time and they can be either singular or plural.
TE Pronoun aice À force on ha ca as forgeim H GIRT GIGI ITE Singular Haal Plural fti
नीचे दिए गए वाक्यों में italicized शब्द Demonstrative Pronouns हैं : This was my mother’s purse. That looks like the car I used to drive. These are nice shoes, but they look uncomfortable. Those look like riper than the apples on my tree.
![]()
Activity 9.
Fill in the blanks using demonstrative pronouns. Choose the best answer to complete each sentence.
Question 1.
……………… was such an interesting experience.
(a) that
(b) these
(c) those
(d) such
Answer:
(a) that
Question 2.
Are ……………. your shoes ?
(a) that
(b) them
(c) those
(d) this
Answer:
(c) those
Question 3.
You’ll have to get your own pen. ……… is mine.
(a) that
(b) those
(c) such
(d) this
Answer:
(d) this
Question 4.
There is no end to ……..
(a) such
(b) those
(c) this
(d) none
Answer:
(c) this
Question 5.
Because of their bad behaviour, ……….. ……… of the children were given allowances.
(a) none
(b) that
(c) those
(d) them
Answer:
(a) none
Question 6.
………………. of them had seen it before.
(a) those
(b) neither
(c) such
(d) this
Answer:
(b) neither
Question 7.
Is …………… yours ?
(a) this
(b) those
(c) these
(d) such
Answer:
(a) this
Question 8.
Everyone ate early. When we arrived ……………… was left.
(a) that
(b) such
(c) none
(d) neither
Answer:
(c) none
Question 9.
Please give me one of .
(a) that
(b) those
(c) this
(d) such
Answer:
(b) those
![]()
Question 10.
……………….. are nice looking.
(a) this
(b) that
(c) these
(d) such.
Answer:
(c) these
3. Interrogative (प्रशनवाचक) Pronoun
An interrogative pronoun is used to make asking questions easy. There are just five interrogative pronouns. ये Pronoun प्रश्न पूछने के लिए प्रयोग किए जाते हैं और प्रायः प्रश्नवाचक शब्द से आरंभ होते हैं।
The five interrogative pronouns are what, which, who, whom, and whose.
— What is used to ask questions about people or objects.
(लोगों तथा वस्तुओं के बारे में प्रश्न)
What do you want for dinner ?
What is your name ?
— Which is used to ask questions about people or objects.
Which seat would you like?
Which of these ice cream flavours is you favourite ?
— Who is used to ask questions about people.
(व्यकतियों के बारे में प्रशन)
Who is that man over there ?
Who is the strongest in the class ?
— Whom is used to ask questions about people.
With whom did you go to the class ?
— Whose is used to ask questions about people or objects, always related to possession.
Whose sweater is this?
I wonder whose dog is digging our lawn ?
Activity 10.
Fill in the blanks with an interrogative pronoun.
Question 1.
……………….. threw the football ?
(a) who
(b) what
(c) which
(d) whose
Answer:
(a) who
Question 2.
…… Would you prefer, coffee or tea ?
(a) who
(b) whom
(c) which
(d) whose
Answer:
(c) which
![]()
Question 3.
………………. time do we need to be at the station?
(a) which
(b) what
(c) whose
(d) whom
Answer:
(b) what
Question 4.
…………….. bike is that ?
(a) whom
(b) whose
(c) what
(d) who
Answer:
(b) whose
Question 5.
……………. is your brother’s name?
(a) who
(b) whom
(c) what
(d) whose
Answer:
(c) what
Question 6.
……………. did you tell ?
(a) whom
(b) what
(c) whose
(d) which
Answer:
(b) what
Question 7.
……………. of these books have you read ?
(a) what
(b) whom
(c) whose
(d) which
Answer:
(d) which
Question 8.
…………….. wants ice-cream ?
(a) what
(b) whom
(c) who
(d) whose
Answer:
(c) who
Learning to Write
Activity 11.
Did you like the story ? Talk to your partner and discuss two things you liked and one thing you did not like in the story. After discussion, add another paragraph to change the ending of the story.
Answer:
The boy sat there thinking. He thought of trees who give something to man all through their lives. They gift their all happily and become a stump. They give the message : “Real happiness lies in giving’. But it is a pity that man cuts down trees unwisely. He has no regard for their usefulness and selflessness.
Learning to Use Language
Activity 12.
Write a letter to your friend inviting him for the birthday party.
Kailash Colony
…………. City
March 12, 20…
My dear Vinod
You will be glad to know that my birthday falls on March 20. I am planning to celebrate it at home. There will be a programme of dance and music. A dinner will also be served. All our friends are coming to the party. I hope you will also join us. I am sure you will enjoy yourself.
Yours sincerely
Prem
![]()
Learning to Listen
Activity 13.
The teacher will read the story to the students again. Listen to the story carefully. Write whether the statements are ‘True’ or ‘False’ in the given space.
1. The tree loved the little boy. — (True)
2. The tree liked the boy to swing from the branches of the tree. — (True)
3. The tree became sad whenever the boy came back. — (False)
4. The tree gave the boy a lot of money. — (False)
5. The tree asked the boy to cut off her branches and make a house. — (True)
6. The boy wanted a ship to go to another city. — (False)
7. The tree allowed the boy to cut down her trunk. — (True)
8. At last, the boy wanted a quiet place to sit and rest. — (True)
9. The tree refused the boy from sitting on her old stump. — (False)
10. The story shows that the boy is selfish. — (True)
Learning to Speak.
Activity 13 (Role Play)
The children will work in pairs.
Practise speaking the following sentences with your partner. One of you will become the tree and one will become the boy. After practice, all the pairs will speak in front of the class.
1. The tree: Come, boy, come. Climb up my trunk, swing from my branches, eat apples and be happy.
2. The boy: I am too big to climb and play. I want some money to buy things and have fun. Can you give me some money ?
3. The tree: I have no money but you can take my apples and sell them in the city. Then you will have some money and you will be happy.
4. The tree: Come, boy, come. Climb up my trunk, swing. from my branches, eat apples and be happy.
5. The boy: I am too busy to climb trees. I want to get married. I need a house. Can you give me a house ?
6. The trees : You may cut off my branches. Build a house and be happy.
Comprehension Of Passages
Read the given passages and answer the questions that follow each.
(1) Once there was a tree and she loved a little boy. Every day the boy would come, eat applies and play with her. He would swing from her branches and eat apples. The boy loved the tree very much. And the tree was very happy.
The time went by. The boy grew older. The tree was often alone. One day the boy came to the tree. The tree said, “Come, boy, come. Climb up my trunk, swing from my branches, eat apples and be happy.” “I am too big to climb and play,” said the boy. “I want some money to buy things and have fun. Can you give me some money ?” The tree said, “I have no money but you can take my apples and sell them in the city. Then you will have some money and you will be happy.” The boy did so and went away. The tree was happy.
(i) What made the tree very happy ?
वृक्ष को क्या बात बहुत अधिक खुशी देती थी ?
(ii) Why did the tree give the boy her apples ?
वृक्ष ने लड़के को अपने सेब क्यों दिए ?
(iii) Choose true or false statements.
(a) The boy grew younger.
(b) The boy wanted money to buy things for fun.
(iv) Complete the following sentences according to the meaning of the passage.
(a) The tree was often ————
(b) The tree loved ————
Or
Match the words with their meanings :
| (a) alone | go down |
| (b) climb | lonely |
| go up |
Answer:
(i) The boy’s love for her made the tree very happy.
(ii) She gave the boy her apples to sell and get money.
(iii)
(a) False
(b) True
(iv)
(a) The tree was often alone.
(b) The tree loved a little boy.
Or
(a) alone – lonely
(b) climb – go up
![]()
(2) The boy again stayed away for a long time. One day he came back. The tree was very happy and said, “Come, boy, come. Climb up my trunk, swing from my branches, eat apples and be happy.” The boy said, “I am too sad to play. I want to go to another city for business.
Can you give me a boat that will take me away to another city.” The tree said, “Cut down my trunk and make a boat. Then you can sail away and be happy. The boy did so and sailed away. The tree was very happy, but not really.
After a long time, the boy who was now an old man came back again. “I am sorry, boy. I have nothing to give you,” said the tree. I wish I could give you something. I am just an old stump.” “I don’t need anything now. I just want a quiet place to sit and rest.
I am very tired,” said the boy. “Well, an old stump is good for sitting and resting. Come, boy, sit down and rest.” The boy sat on the stump to rest. And the tree was very happy.
(i) Why was the boy sad ?
लड़का क्यों उदास था ?
(ii) What was the only thing that the boy wanted in the end ?
अंत में लड़का कौन-सी एक मात्र चीज़ चाहता था ?
(iii) Choose true or false statements and write them in your answer book :
(a) The boy had grown old.
(b) He was too sad to play.
(iv) Complete the following sentences according to the meaning of the passage.
(a) Cut down my trunk and ……………..
(b) An old stump is good for ……………
Or
Match the words with their meanings :
| (a) business | calm |
| (b) quiet | trade |
| sad |
Answer:
(i) The boy was sad because he wanted to go to another city for business, but he had no boat.
(ii) In the end, he just wanted a quiet place to sit and rest.
(iii)
(a) True
(b) True
(iv)
(a) Cut down my trunk and make a boat.
(b) An old stump is good for sitting and resting.
Or
(a) business – trade
(b) quiet – calm
![]()
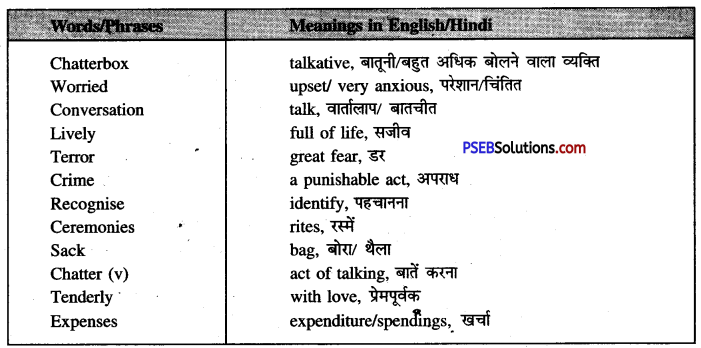
Use Of Words/Phrases In Sentences
1. Swing (Verb)(move to and fro on a swing) –
The girls are swinging in the park.
लड़कियां पार्क में झूला झूल रही हैं।
2. Branches (off-shoots) –
A big tree has many branches.
बड़े वृक्ष की कई शाखाएं होती हैं।
3. Business (trade) –
He has gone out for a business.
वह व्यापार के लिए बाहर गया हुआ है।
4. Climb (go up) –
I can’t climb this wall,
मैं इस दीवार पर नहीं चढ़ सकता।
5. Stump (remaining part of a chopped tree) –
The stump of tree was very hard.
वृक्ष का ढूंठ बहुत ही कठोर था।
6. Another (one more). –
Please give me another pen.
कृपया मुझे एक और पेन दीजिए।
7. Build (make, construct) –
We are building a new house.
हम एक नया मकान बना रहे हैं। .
8. Carry away (take away) –
Carry away your books from here.
अपनी पुस्तकें यहां से ले जाओ।
Word Meanings

The Giving Tree Summary in Hindi
Once there was ……………. tree was happy.
एक बार एक मादा वृक्ष था और वह एक छोटे से बच्चे को प्यार/दुलार करता था। बच्चा प्रतिदिन आता था, सेब खाता था और उसके साथ खेलता था। वह उसकी टहनियों पर झूलता था और सेब खाता था। बच्चा वृक्ष को बहुत प्यार करता था। इसलिए वृक्ष खुश था।
समय बीतता गया। बच्चा बड़ा हो गया। वृक्ष प्रायः अकेला रहता था। एक दिन बच्चा वृक्ष के पास आया। वृक्ष ने कहा, “आओ, बच्चे, आओ। मेरे तने पर चढ़ जाओ, मेरी टहनियों पर झूलो, सेब खाओ और खुश रहो।” बच्चे ने कहा, “मैं इतना बड़ा हो गया हूँ कि मैं चढ और खेल नहीं सकता।
![]()
मुझे मनोरंजन के लिए कुछ चीजें खरीदने के लिए कुछ पैसे चाहिएं। क्या तुम मुझे कुछ पैसे दे सकते हो ?” वृक्ष ने कहा, “मेरे पास पैसे नहीं है परन्तु तुम मेरे सेब ले सकते हो और उन्हें ले जाकर शहर में बेच सकते हो तब तुम्हारे पास कुछ पैसा आ जायेगा और तुम खुश रहोगे।”
बच्चे ने वैसा ही किया और चला गया। वृक्ष खुश था। बच्चा लम्बे समय तक वापिस नहीं आया। वृक्ष उदास था। एक दिन बच्चा वापिस आया। वृक्ष ने खुशी से कहा, “आओ, बच्चे, आओ। मेरे तने पर चढ़ जाओ, मेरी टहनियों पर झूलो, सेब खाओ और खुश रहो।” बच्चे ने कहा, “मैं इतना व्यस्त हूँ कि मैं वृक्षों पर नहीं चढ़ सकता।
मैं शादी करना चाहता हूँ। मुझे एक घर चाहिए। क्या तुम मुझे एक घर दे सकते हो ?” वृक्ष ने कहा, “तुम मेरी शाखाओं को काट . सकते हो। घर बना लो और खुश रहो। “बच्चे ने उसकी शाखाओं को काटा और ले जाकर अपना घर बना लिया। वृक्ष खुश था।
The boy again ……… was very happy.
बच्चा फिर से एक लम्बे समय तक दूर रहा। एक दिन वह वापिस आया। वृक्ष बहुत खुश हुआ और कहा, “आओ, बच्चे, आओ। मेरे तने पर चढ़ जाओ, मेरी टहनियों पर झूलो, सेब खाओ और खुश रहो।” बच्चे ने कहा, “मैं इतना उदास हूँ कि मैं खेल नहीं सकता। मैं व्यापार के लिए दूसरे शहर जाना चाहता हूँ।
क्या तुम मुझे एक नाव दे सकते हो जो मुझे दूसरे शहर ले जाये ?” वृक्ष ने कहा, “मेरा तना काट लो और नाव बना लो। तब तुम नाव चला कर दूर जा सकते हो और खुश रह सकते हो।” बच्चे ने वही किया और नाव पर चला गया। वृक्ष खुश हो गया परन्तु वास्तव में वह खुश नहीं था।
बहुत समय बाद वह बच्चा जो अब बूढ़ा आदमी बन चुका था वापिस लौट आया। वृक्ष ने कहा, “बच्चे, मुझे खेद है, मेरे पास तुम्हें देने के लिए कुछ नहीं है। काश! मैं तुम्हें कुछ दे पाता। मैं केवल एक पुराना ढूंठ हूँ।” बालक (बूढ़ा आदमी) ने कहा, “मुझे अब कुछ नहीं चाहिए।
मैं तो केवल बैठने और आराम करने के लिए एक शांत जगह चाहता हूँ। मैं बहुत थक चुका हूँ।” “अच्छा, एक पुराना लूंठ बैठने और आराम करने के लिए अच्छी जगह है। आओ, बच्चे बैठ जाओ और आराम करो।” बालक आराम करने के लिए ढूंठ पर बैठ गया। इससे वृक्ष बहुत ही खुश हो गया।
Retranslation Of Isolated Sentences
1. She loved a little boy.
वह एक छोटे से बालक से प्रेम करती थी।
2. The boy grew older.
लड़का बड़ा हो गया।
3. The tree was often alone.
वृक्ष प्राय: अकेला रहता था।
4. I am too big to climb and play.
मैं इतना बड़ा हो गया हूं कि चढ़ (ऊपर) और खेल नहीं सकता।
5. The tree was happy.
वृक्ष खुश था।
6. The boy did not come back for a long time.
लड़का लम्बे समय तक वापिस नहीं आया।
![]()
7. I want to get married.
मैं शादी करना चाहता हूँ।
8. You may cut off my branches.
तुम मेरी शाखाएं काट सकते हो।
9. I want to go to another city for business.
मैं व्यापार के लिए किसी दूसरे शहर जाना चाहता
10. Cut down my trunk and make a boat.
मेरा तना काट कर नाव बना लो।
11. I wish I could give you something.
काश! मैं तुम्हें कुछ दें पाती/पाता।
12. I just want a quiet place to sit and rest.
मुझे केवल बैठने और आराम करने के लिए एक शांत जगह चाहिए।
English Class 6 Solutions PSEB Prose