Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class Chemistry Book Solutions Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds
PSEB 12th Class Chemistry Guide Coordination Compounds InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain the bonding in coordination compounds in terms of Werner’s postulates.
Answer:
(i) The primary valencies are satisfied by negative ions and equal-to the oxidation state of the metal.
(ii) The secondary valencies can be satisfied by neutral or negative ions. It is equal to the coordination number of the central metal atom and is fixed.
(iii) The ions bound to the central metal ion to secondary linkages have definite spatial arrangements and give geometry to the complex. While primary valency is non-directional.
Question 2.
FeSO4 solution mixed with (NH4)2SO4 solution in 1 : 1 molar ratio gives the test of Fe2+ ion but CuSO4 solution mixed with aqueous ammonia in 1 : 4 molar ratio does not give the test of Cu2+ ion. Explain why?
Answer:
FeSO4 solution mixed with (NH4)2SO4 solution in 1 : 1 molar ratio forms double salt, FeSO4∙(NH4)2SO4∙6H2O which ionises in the solution to give Fe2+ ions. Hence, it gives the test of Fe2+ ions.
CuSO4 solution mixed with aqueous ammonia in 1 : 4 molar ratio forms a complex, with the formula [Cu(NH3)4]SO4. The complex ion, [CU(NH3)]2+ does not ionise to give Cu2+ ions. Hence, it does not give the test of Cu2+ ion.
Question 3.
Explain with two examples each of the following: Coordination entity, ligand, coordination number, coordination polyhedron, homoleptic and heteroleptic.
Answer:
Coordination entity: A coordination entity constitutes usually a central metal atom or ion, to which a fixed number of other atoms or ions or groups are attached by coordinate bonds. A coordination entity may be neutral, positively or negatively charged. For examples : [Ni(CO)4], [CoCl3(NH3)3], [Co(NH3)6]3+.
Ligand : A ligand is an ion or a small molecule having at least one lone pair of electrons and capable of forming a coordinate bond with central atom or ion in the coordination entity. For example: Cl–, OH–, CN–, CO, NH3, H2O etc.
Coordination number : The coordination number of the central atom or ion is determined by the number of a bonds between the ligands and the central atom or ion. n bonds are not consider for the determination of coordination number. The a bonding electrons may be indicated by a pair of dots (:). For example, [Co(:NH3)6]3+ and [Fe(:CN)6]3-.
Coordination polyhedron : The spatial arrangement of the ligands which are directly attached to the central atom or ion called coordination polyhedron.
For example: [Co(NH3)6]3+ is octahedral, [Ni(CO)4] is tetrahedral and [PtCl4 ]2- is square planar.
Homoleptic and heteroleptic : Complexes in which a metal is bound to only one type of donor groups are known as homoleptic.
For example : [Co(NH3)6]3+, [PtCl6]2- .
Complexes in which a metal is bound to more than one kind of donor groups are known as heteroleptic. ‘
For example : [Co(NH3)4Cl2]+, [PdI2(ONO)2 (H2O)2],

Question 4.
What is meant by unidentate, didentate and ambidentate ligands? Give two examples for each.
Answer:
A molecule or an ion which has only one donor atom to form one coordinate bond with the central metal atoms is called unidentate ligand, e.g., Cl– and NH3.
A molecule or an ion which contains two donor atoms and hence forms two coordinate bonds with the central metal atoms is called a didentate ligand, e.g., NH2—CH2—CH2—NH2 and –OOC — COO–.
A molecule or an ion which contains two donor atoms but only one of them forms a coordinate bond at a time with the central metal atom is called ambidentate ligand, e.g., CN–or NC– and \(\) or : ONO–.
Question 5.
Specify the oxidation numbers of the metals in the following coordination entities:
(i) [Co(H2O)(CN)(en)2]2+
(ii) [CoBr2(en)2]+
(iii) [PtCl2]2-
(iv) K3Fe(CN)6]
(v) [Cr(NH3)2Cl3]
Answer:
(i) x + (-1) + (0) + (0) = + 2 so x = +3 (III)
(ii) x + 2(-1) + 0 = +1 so x = +3 (III)
(iii) x + 4(-1) = -2 so x = +2(11)
(iv) x + 6(-1) = -3 so x = +3 (III)
(v) x + 3(-1) + 0 = 0 so x = +3 (III)
Question 6.
Using IUPAC norms write the formulas for the following:
(i) Tetrahydroxozincate(II)
(ii) Potassium tetrachloridopalladate(II)
(iii) Diamminedichloridoplatinum(II)
(iv) Potassium tetracyanonickelate(II)
(v) Pentaamminenitrito-O-cobalt(III)
(vi) Hexaamminecobalt(III) sulphate
(vii) Potassium tri(oxalato)chromate(III)
(viii) Hexaammineplatinum(IV)
(ix) Tetrabromidocuprate(Il)
(x) Pentaamminenitrito-N-cobalt(lll)
Answer:
(i) [Zn(OH)4]2-
(ii) K2[PdCl4]
(iii) pt(NH3)2Cl2]
(iv) K2[Ni(CN)4]
(v) [Co(ONO) (NH3)5]2+
(vi) [CO(NH3)6]2 (SO4)3
(vii) K3[Cr(C2O4)3]
(viii) [Pt(NH3)6]4+
(ix) [Cu(Br)4]2-
(x) [Co (NO2) (NH3)5]2+

Question 7.
Using IUPAC norms write the systematic names of the following:
(i) [CO(NH3)6]Cl3
(ii) [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NH2CH3)]Cl
(iii) [Ti(H2O)6]3+
(iv) [CO(NH3)4Cl(NO2)]CI
(v) [Mn(H2O)6]2+
(vi) [NiCl4]2-
(vii) [Ni(NH3)6]Cl2
(viii) [Co(en)3]3+
(ix) [Ni(CO)4]
Answer:
(i) Hexaamminecobalt(III) chloride
(ii) Diamminechlorido(methylamine) platinum(II) chloride
(iii) Hexaquatitanium(III) ion
(iv) Tetraamminechloridonitrito-N-Cobalt(III) chloride
(v) Hexaquamanganese(II) ion
(vi) Tetrachloridonickelate(II) ion
(vii) Hexamminenickel(II) chloride
(viii) Tris(ethane-1, 2-diamine) cobalt(III) ion
(ix) Tetracarbonylnickel(O)
Question 8.
List various types of isomerism possible for coordination compounds giving an example of each.
Answer:
Two principal types of isomerism are known among coordination compounds :
(A) Sterioisomerism,
(B) Structural isomerism.
Each of which can be further sub-divided as :
(A) Stereoisomerism
(i) Geometrical isomerism : It arises in heteroleptic complexes due to different possible geometric arrangements of the ligands.
Example: Pt[(NH3)2Cl2]
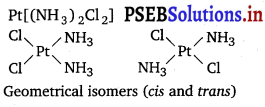
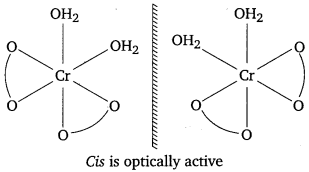
(ii) Optical isomerism : It is common in octahedral complexes involving didentate ligands.
Example : [Pt Cl2(en) 2]2+
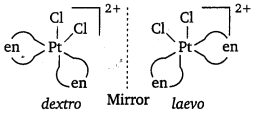
Optical isomers (d and l) of cis-[PtCl2(en)2]2+
(B) Structural isomerism
(i) Linkage isomerism.
Example: [Co(NH3)5 (NO2)]Cl2
(ii) Coordination isomerism.
Example: [Co(NH3)6] [Cr(CN)6]
(iii) Ionisation isomerism.
Example: [Co(NH3)5SO4]Br and [CO(NH3)5 Br]SO4
(iv) Solvate isomerism.
Example : [Cr(H2O)6] Cl3 (violet) its solvate isomer
[Cr(H2O)5Cl]Cl2. H2O (grey-green)
Question 9.
How many geometrical isomers are possible in the following coordination entities? ’
(i) [Cr(C2O4)3]3-
(ii) [Co(NH3)3Cl3]
Answer:
(i) [Cr(C2O4)3]3-,
No geometric isomer is possible as it is a bidentate ligand.
(ii) [CO(NH3)3Cl3] .
Two geometrical isomers are possible.

Question 10.
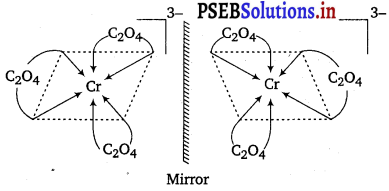
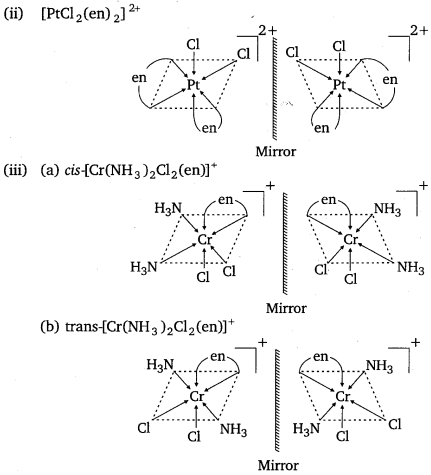
Draw the structures of optical isomers of:
(i) [Cr(C2O4)3]3-
(ii) [PtCl2(en)2]2+
(iii) [Cr(NH3)2 Cl2 (en)]+
Answer:
(i) [Cr(C2O4)3]3-
Question 11.
Draw all the isomers (geometrical and optical) of:
(i) [CoCl2 (en)2]+
(ii) [Co(NH3)Cl(en)2]2+
(iii) [Co(NH3)2Cl2(en)]+
Answer:
(i) [CoCl2 (en)2]+
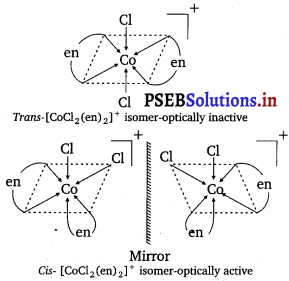
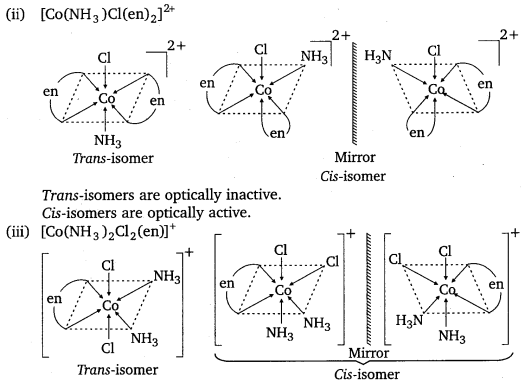
Question 12.
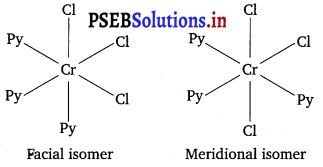
Write all the geometrical isomers of [Pt(NH3)(Br)(Cl)(py)] and how many of these will exhibit optical isomers?
Answer:
Three isomers are possible as follows :
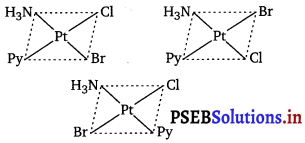
Isomers of this type do not show any optical isomerism. Optical isomerism rarely occurs in square planar or tetrahedral complexes and that too when they contain unsymmetrical chelating ligand.

Question 13.
Aqueous copper sulphate solution (blue in colour) gives :
(i) a green precipitate with aqueous potassium fluoride, and
(ii) a bright green solution with aqueous potassium chloride. Explain these experimental results.
Answer:
Aqueous copper sulphate exists as [Cu(H2O)4]SO4. It is a labile complex. The blue colour of the solution is due to [Cu(H2O)4]2+ ions,
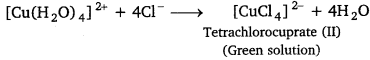
(i) When KF is added, the weak H2O ligands are replaced by F– ligands forming [CuF4]2- ions, which is a green precipitate.
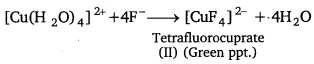
(ii) When KCl is added, Cl– ligands replace the weak H2O ligands forming [CuCl4]2- ion, which has bright green colour.
Question 14.
What is the coordination entity formed when excess of aqueous KCN is added to an aqueous solution of copper sulphate? Why is it that no precipitate of copper sulphide is obtained when H2S (g) is passed through this solution?
Answer:
K2[Cu(CN)4] is formed when excess of aqueous KCN is added to an aqueous solution of CuSO4.
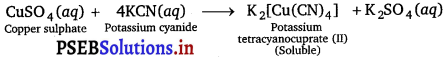
As CN–ions are strong ligands the complex is very stable. It is not replaced by S2- ions when H2S gas is passed through the solution and thus no precipitate of CuS is obtained.

Question 15.
Discuss the nature of bonding in the following coordination entities on the basis of valence bond theory:
(i) [Fe(CN)6]4-
(ii) [FeFe6]3-
(iii) [Co(C2O4)3]3-
(iv) [CoF6]3-
Answer:
(i) [Fe(CN)6]4-
In the above coordination complex, iron exists in the +2 oxidation state.
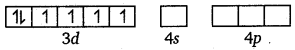
Fe = [Ar] 3d6 4s2
Outer configuration of Fe2+ = 3d6 4s0
Orbitals of Fe2+ ion:
As CN– is a strong field ligand, it causes the pairing of the unpaired 3d electrons.
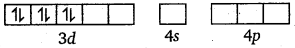
Since, there are six ligands around the central metal ion, the most feasible hybridisation is d2sp3. d2sp3 hybridised orbitals of Fe2+ are :
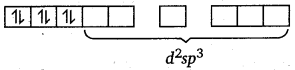
6 electron pairs from CN ions occupy the six hybrid d2sp3 orbitals.
Then,
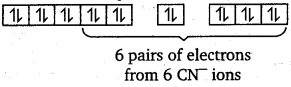
Hence, the geometry of the complex is octahedral and the complex is diamagnetic (as there are no unpaired electrons).
(ii) [FeF6]3-
In this complex, the oxidation state of Fe is + 3.
Fe3+ = 3d5 4s0
Orbitals of Fe3+ ion:

There are 6F– ions. Thus, it will undergo d2sp3 or sp3d2 hybridisation. As F– is a weak field ligand, it does not cause the pairing of the electrons in the 3d orbital. Hence, the most feasible hybridisation is sp3d2. sp3d2 hybridised orbitals of Fe are:
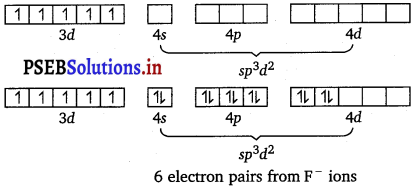
Hence, the geometry of the complex is found to be octahedral.
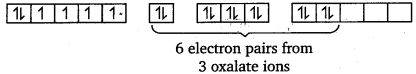
(iii) [Co(C2O4)3]3-
Cobalt exists in the + 3 oxidation state in the given complex.
Outer configuration of Co = 3d7 4s2
Co3+ = 3d64s0
Orbitals of Co3+ ion:
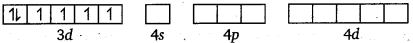
Oxalate is a weak field ligand. Therefore, it cannot cause the pairing of the 3d electrons. As there are 6 ligands, hybridisation has to be either sp3d2 or d2sp3 hybridisation. sp3d2 hybridisation of Co3+.
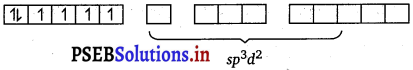
The 6 electron pairs from the 3 oxalate ions (oxalate anion is a bidentate ligand) occupy these sp3d2 orbitals.
Hence, the geometry of the complex is found to be octahedral.
(iv) [CoF2]3-
Cobalt exists in the + 3 oxidation state.
Orbitals of Co3+ ion:
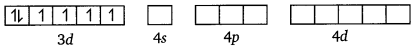
Again, fluoride ion is a weak field ligand. It cannot cause the pairing of the 3d electrons. As a result, the Co3+ ion will undergo sp3d2 hybridisation.
sp3d2 hybridised orbitals of Co3+ ion are :
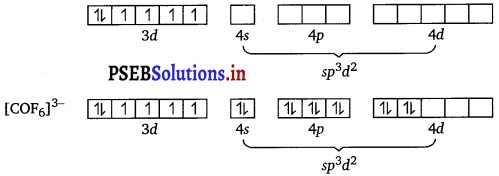
Hence, the geometry of complex is octahedral, 6 electron pants.
Question 16.
Draw figure to show the splitting of d-orbitals in an octahedral crystal field.
Answer:
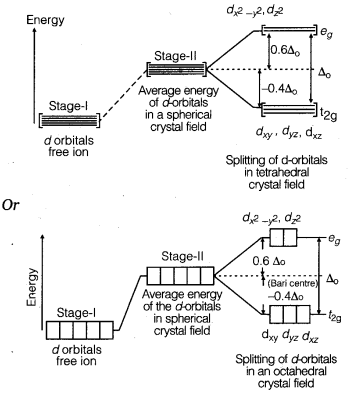

Question 17.
What is spectrochemical series? Explain the difference between a weak field ligand and a strong field ligand.
Answer:
The arrangement of ligands in order of their increasing field strengths, i.e., increasing crystal field splitting energy (CFSE) values is called spectrochemical series.
The ligands with a small value of CFSE (△0) are called weak field ligands whereas those with a large value of CFSE are called strong field ligands.
Question 18.
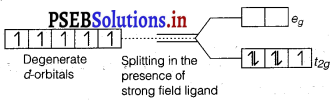
What is crystal field splitting energy? How does the magnitude of △0 decide the actual configuration of d-orbitals in a coordi-nation entity?
Answer:
When ligands approach a transition metal ion, the d-orbitals split into two sets, one with lower energy and the other with higher energy. The difference of energy between the two sets of orbitals is called crystal field splitting energy (△0) in case of octahedral field.
If △0 < P, (pairing energy), the 4th electron enters one of the eg orbitals giving the configuration \(t_{2 g}^{3} e_{g}^{1}\), thereby forming high spin complexes.
Such ligands for which A 0 < P are called weak field ligands.
If △0 > P, the 4th electron pairs up in one of the t2g orbitals giving the configuration \(t_{2 g}^{4} e_{g}^{0}\), thus forming low spin complexes. Such ligands for which △0 > P are called strong field ligands.
Question 19.
[Cr(NH3)6]3+ is paramagnetic while [Ni(CN)4]2- is diamagnetic. Explain why?
Answer:
Cr is in the +3 oxidation state i.e., d3 configuration. Also, NH3 is a weak field ligand that does not cause the pairing of the electrons in the orbital.

Therefore, it undergoes d2sp3 hybridisation and the electrons in the 3d orbitals remain unpaired. Hence, it is paramagnetic in nature.
In [Ni(CN)4]2-, Ni exists in the + 2 oxidation state i. e., d8 configuration.
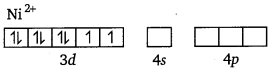
CN– is a strong field ligand. It causes the pairing of the 3d electrons. Then, Ni2+ undergoes dsp2 hybridisation.
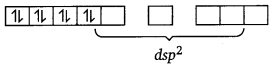
As there are no unpaired electrons, it is diamagnetic.

Question 20.
A solution of [Ni(H2O)6]2+ is green but a solution of [Ni(CN)4]2- is colourless. Explain.
Answer:
In [Ni(H2O)6]2+, \(\mathrm{H}_{2} \ddot{\mathrm{O}}\) is a weak field ligand. Therefore, there are unpaired electrons in Ni2+. In this complex, the d electrons from the lower energy level can be excited to the higher energy level i. e., the possibility of d-d transition is present. Hence, [Ni(H2O)6]2+ is coloured.
In [Ni(CN)4]2+, the electrons are all paired as CN– is a strong field ligand. Therefore, d-d transition is not possible in [Ni(CN)4]2-. Hence, it is colourless.
Question 21.
[Fe(CN)6]4- and [Fe(H2O)6]2+ are of different colours in dilute solutions. Why?
Answer:
In both the complex compounds, Fe is in +2 oxidation state with configuration 3d6, i.e., it has four unpaired electrons. In the presence of weak H2O ligands, the unpaired electrons do not pair up. But in the presence of strong ligand CN– they get paired up. Then no unpaired electron is left. Due to this, difference in the number of unpaired electrons, both complex ions have different colours.
Question 22.
Discuss the nature of bonding in metal carbonyls.
Answer:
The metal carbon in metal carbonyls possesses both CT and π character. The ligand to metal is CT bond and metal to ligand is π bond. The effect of CT bond strengthens the rcbond and vice-versa. This is called synergic effect. This unique synergic provides stability to metal carbonyls.

Question 23.
Give the oxidation state, d-orbital occupation and coordination number of the central metal ion in the following complexes:
(i) K3[CO(C2O4)3]
(ii) cis-[Cr(en)2Cl2]Cl
(iii) (NH4)2[CoF4]
(iv) [Mn(H2O)6]S04
Solution:
(i) K3[CO(C2O4)3]
The central metal ion is Co.
The oxidation state can be given as :
(+1) × 3 + × + (- 2) × 3 = 0
x – 6 = -3 ⇒ x = + 3
The d orbital occupation for Co3+ is \(t_{2 g}^{6} e g^{0}\).
(as \(\mathrm{C}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{4}^{2-}\) is strong field ligand)
Coordination number of Co = 3 × denticity of C2O4
= 3 × 2 (as \(\mathrm{C}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{4}^{2-}\) is a bidentate ligand) = 6
(ii) cis-[Cr(en)2Cl2]Cl
The central metal ion is Cr.
The oxidation state can be given as:
x + 2(0) + 2(-1) + (-1) = 0
x – 2 – 1 = 0
x = + 3
The d orbital occupation for Cr3+ is \(t_{2 g}^{3}\).
Coordination number of Cr
= 2 × denticity of en + 2
= 2 × 2 + 2 = 6
(iii) (NH4)2[CoF4]
The central metal ion is Co.
The oxidation state can be given as:
(+1) × 2 + × + (-1) × 4 = 0
x – 4 = -2
x = + 2
The d orbital occupation for Co2+ is d7 or \(t_{2 g}^{5} e_{g}^{2}\). (as F– is a weak ligand)
Coordination number of Co = 4
(iv) [Mn(H2O)6]S04
The central metal ion is Mn.
The oxidation state can be given as:
x + (0) × 6 + (- 2) = 0
x = + 2
The d orbital occupation for Mn is d5 or [latext_{2 g}^{3} e_{g}^{2}][/latex].
Coordination number of Mn = 6
Question 24.
Write down the IUPAC name for each of the following complexes and indicate the oxidation state, electronic configuration and coordination number. Also give stereochemistry and magnetic moment of the complex:
(i) K[Cr(H2O)2(C2O4)2] 3H2O
(ii) [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2
(iii) CrCl3(py)3
(iv) Cs[FeCl4]
(v) K4[Mn(CN)6]
Answer:
(i) K[Cr(H2O)2 (C2O4)2 ] ∙ 3H2O
IUPAC name : Potassium diaquadioxalatochromate (III) hydrate.
Oxidation state of chromium
+1 + x + (0) × 2 + (- 2) × 2 + 3(0) = 0
+ 1 + x – 4 = 0
x = + 3
Electronic configuration of Cr+3= 3d3 = (\(t_{2 g}^{3} e_{g}^{0}\))
Coordination number = 6
Shape : Octahedral
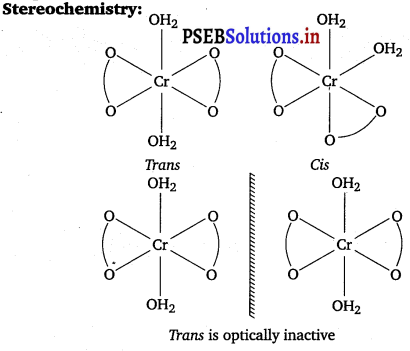
Magnetic moment (μ) = \(\sqrt{n(n+2)}\)
= \(\sqrt{3(3+2)}\)
= \(\sqrt{15}\) = 3.87 BM
(ii) [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2
IUPAC name : Pentaammine chlorido cobalt(III) chloride
Oxidation state of Co
x + (0)5 + (-1) + (-1) × 2 = 0
x – 3 =0
x = + 3
Coordination number = 6
Shape: Octahedral.
Electronic configuration of Co3+ = 3d6 = \(t_{2 g}^{6} e_{g}^{0}\)
The complex does not exhibit geometrical as well as optical isomerism.
Magnetic Moment (μ) = \(\sqrt{n(n+2)}\)BM = \(\sqrt{0(0+2)}\) BM = 0 BM
(iii) CrCl3(py)3
IUPAC name : Trichlorido tripyridine chromium (III) Oxidation state of Cr
x + (-1) × 3 + (0)3 = 0
x = + 3
Electronic configuration of Cr = 3d3 = (\(t_{2 g}^{3} e_{g}^{0}\))
Coordination number = 6
Shape : Octahedral
Stereochemistry
Both isomers are optically active. Therefore, a total of 4 isomers exist.
Magnetic moment (μ) = \(\sqrt{n(n+2)}\) = \(\sqrt{3(3+2)}\)
= \(\sqrt{15}\) = 3.87 BM
(iv) Cs[FeCl4]
IUPAC name : Caesium tetrachlorido ferrate (III)
Oxidation state of Fe
+ 1 + x + (-1) × 4= 0
x – 3 = 0
x = + 3
Electronic configuration of Fe = 3d5(\(t_{2 g}^{3} e_{g}^{2}\))
Coordination number = 4
Shape : Tetrahedral
The complex does not exhibit geometrical or optical isomerism, (stereo isomerism).
Magnetic moment (μ) = \(\sqrt{n(n+2)}\)
= \(\sqrt{5(5+2)}\)
= \(\sqrt{35}\) = 5.92 BM
(v) K4[Mn(CN)6]
IUPAC name : Potassium hexacyanomanganate(II)
Oxidation state of Mn
(+1) × 4 + x + (-1) × 6 = 0
x – 2 = 0
x = + 2
Electronic configuration of Mn = 3d5 (\(t_{2 g}^{5} e_{g}^{0}\))
Coordination number = 6
Shape : Octahedral.
The complex does not exhibit stereo isomerism.
Magnetic moment (μ) = \(\sqrt{n(n+2)}\)
= \(\sqrt{1(1+2)}\)
= \(\sqrt{3}\)
= 1.732 BM

Question 25.
What is meant by stability of a coordination compound in solution? State the factors which govern the stability of complexes.
Answer:
The stability of a coordination compound in solution refers to the degree of association between the two species involved in the state of equilibrium. The stability of the coordination compound is measured in term of magnitude of stability or formation of equilibrium constant.
M + 4L → ML4
K = \(\frac{\left[\mathrm{ML}_{4}\right]}{[\mathrm{M}][\mathrm{L}]^{4}}\)
Larger the stability constant, the higher is the proportion of ML4 that exists in solution.
Factors on which stability of the complex depends are as follows :
- Charge on the central metal ion : Greater the charge on the central metal ion, greater is the stability of the complex.
- Nature of the metal ion : Groups 3 to 6 and inner transition element form stable complexes when donor atoms of the ligands are N, O and F. The element after group 6 of the transition metals which have d-orbitals (e.g., Rh, Pd, Ag, Au, Hg, etc.) form stable complexes when the donor atoms of the ligands are heavier members of N, O and F family.
- Basic nature of the ligand : Greater the basic strength of the ligand, greater is the stability of the complex.
- Chelate effect: Presence of chelate rings in the complex increases its stability. It is called chelate effect. It is maximum for the 5- and 6- membered rings.
- Effect of multidentate cyclic ligands : If the ligands happen to be multidentate and cyclic without any steric effect, the stability of the complex is further increased.
Question 26.
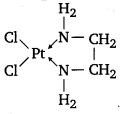
What is meant by chelate effect? Give an example.
Answer:
When a didentate or a polydentate ligand contains donor atoms positioned in such a way that when they coordinate with the central metal ion, a five or a six-membered ring is formed, the effect is called chelate effect. Example, [PtCl2(en)].

Question 27.
Discuss briefly giving an example in each case the role of coordination compounds in:
(i) biological systems
(ii) medicinal chemistry
(iii) analytical chemistry
(iv) extraction/metallurgy of metals
Answer:
(i) Role of coordination compounds in biological systems :
- Haemoglobin, the oxygen carrier in blood, is a complex of Fe2+ with porphyrin.
- The pigment chlorophyll in plants, responsible for photosynthesis, is a complex of Mg2+ with porphyrin.
- Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamine) the antipemicious anaemia factor, is a complex of cobalt.
(ii) Role of coordination compounds in medicinal chemistry :
- The platinum complex cis-[Pt(NH3)2Cl2] (cis-platin) is used in the treatment of cancer.
- EDTA complex of calcium is used in the treatment of lead poisoning. Ca-EDTA is a weak complex; when it is administered, calcium in the complex is replaced by the lead present in the body and is eliminated in the urine.
- The excess of copper and iron present in animal system are removed by the chelating ligands D-penicillamine and desferroxime B via the formation of complexes.
(iii) Role of coordination compounds in analytical chemistry :
Complex formation is frequently encountered in qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis.
(a) Qualitative analysis
I. Detection of Cu2+ is based on the formation of a blue tetraammine copper (II) ion.
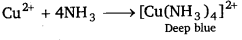
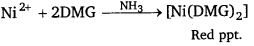
II. Ni2+ is detected by the formation of a red complex with dimethyl glyoxime (DMG).
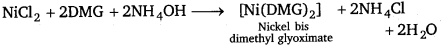
III. The separation of Ag+ and Hg2+ in group I is based on the fact that while AgCl dissolves in NH3, forming a soluble complex, Hg2Cl2 forms an insoluble black substance.

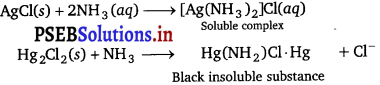
(b) Quantitative analysis : Gravimetric estimation of Ni2+ is carried out by precipitating Ni2+ as red nickel dimethyl glyoxime complex in the presence of ammonia.
EDTA is used in the complexometric determination of several metal ions such as Ca2+, Zn2+, Fe2+, Co2+, Ni2+ etc.
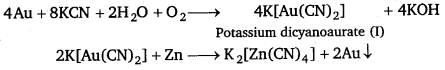
(iv) Role of coordination compounds in extraction/metallurgy of metals : Extraction of various metals from their ore involves complex formation. For example, silver and gold are extracted from their ore by forming cyanide complex.
Purification of some metals can be achieved through complex formation. For example in Mond process, impure nickel is converted into [Ni(CO)4] which is decomposed to yield pure nickel.
Question 28.
How many ions are produced from the complex Co(NH3)6 Cl2 in solution?
(i) 6
(ii) 4
(iii) 3
(iv) 2
Answer:
The correct option is (iii)
Coordination number of cobalt = 6. It ionises in the solution as
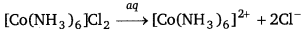
Hence, 3 ion are produced.

Question 29.
Amongst the following ions, which one has the highest magnetic moment value?
(i)[Cr(H2O)6]3+
(ii)[Fe(H2O)6]2+
(iii) [Zn(H2O)6]2+
Answer:
The oxidation state are: Cr (III), Fe (II) and Zn (II).
Electronic configuration of Cr3+ = 3d3, unpaired electrons = 3
Electronic configuration of Fe2+ = 3d6, unpaired electrons = 4
Electronic configuration of Z2+ = 3d10, unpaired electrons = 0
As μ = \(\sqrt{n(n+2)}\), therefore, (ii) has the highest magnetic moment.
Question 30.
The oxidation number of cobalt in K[Co(CO)4] is
(i) +1
(ii) +3
(iii) -1
(iv) -3
Solution:
Oxidation number of Co : K[Co(CO)4]
x+ (4 × 0) = -1; x = -1
Thus, correct answer is (iii).
Question 31.
Amongst the following, the most stable complex is
(i) [Fe(H2O)6]3+
(ii) [Fe(NH3)6]3+
(iii) [Fe(C2O4)3]3-
(iv) [FeCl6]3-
Answer:
In all these complexes, Fe is in +3 oxidation state. However, the complex (iii) is a chelate because three \(\mathrm{C}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{4}^{2-}\) ions acts as the chelating ligands. Thus, the most stable complex is [Fe(C2O4)3]3-. Thus, correct answer is (iii).

Question 32.
What will be the correct order for the wavelengths of absorption in the visible region of the following:
[Ni(NO2)6]4-, [Ni(NH3)6]2+, [Ni(H2O)6]2+
Answer:
As metal ion is fixed, the increasing CFSE values of the ligands from the spectrochemical series are in the order :
H2O < NH3 < \(\mathrm{NO}_{2}^{-}\)
Hence, the energies absorbed for excitation will be in the order :
[Ni(H2O)6]2+ < [Ni(NH3)6]2+ < [Ni(NO2)6]4-
As E = \(\frac{h c}{\lambda}\), therefore, the wavelengths absorbed will be in the opposite order,
[Ni(NO2)6]4- < [Ni(NH3)6]2+ < [Ni(H2O)6]2+
Chemistry Guide for Class 12 PSEB Coordination Compounds Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write the formulas for the following coordination compounds :
(i) Tetraamminediaquacobalt (III) chloride
(ii) Potassiumtetracyanidonickelate(II)
(iii) Tris(ethane-l,2-diammine)chromium(III) chloride
(iv) Amminebromidochloridonitrito-N-platinate(II)
(v) Dichloridobis(ethane-l,2-diammine) platinum (IV) nitrate
(vi) Iron(III)hexacyanidoferrate(II).
Answer:
(i) [Co(NH3)4(H2O)2]Cl3
(ii) K2[Ni(CN)4
(iii) (Cr(en)3]Cl3
(iv) [Pt(NH3)BrCl(NO2)]–
(v) [PtCl2(en)2] (NO3)2
(vi) Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3

Question 2.
Write the IUPAC names of the following coordination compounds:
(i) [CO(NH3)6]Cl3
(ii) [CO(NH3)5Cl]Cl2
(iii) K3[Fe(CN)6]
(iv) K3[Fe(C2O4)3]
(v) K2[PdCl4]
(vi) [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NH2CH3)]Cl
Answer:
(i) Hexaamminecobalt(III)chloride
(ii) Pentaamminechloridocobalt(III)chloride
(iii) Potassiumhexacyanoferrate(III)
(iv) Potassiumtrioxalatoferrate (III)
(v) Potassiumtetrachloridopalladate (II)
(vi) Diamminechloridomethylamine platinum(II) chloride.
Question 3.
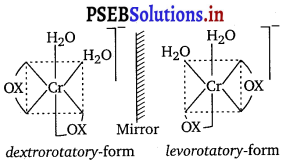
Indicate the types of isomerism exhibited by the following complexes and draw the structures of these isomers :
(i) K[Cr(H2O)2](C2O4)2]
(ii) [Co(en)3]Cl3
(iii) [CO(NH3)5(NO2)](NO3)2
(iv) [Pt(NH3)(H2O)Cl2]
Answer:
(i) (a) Both geometrical isomer (cis and traits):
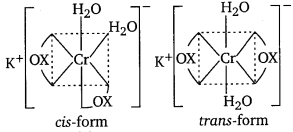
(b) Cis-isomer of this compound can exist as pair of optical is :
(ii) Complex will exist as optical isomers:
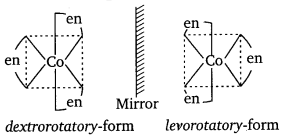
The compound will show ionisation as well as linkage isomerism.
(iii) Ionisation isomer :
[Co(NH3)5(NO2)](NO3)2,
[Co(NH3)5 (NO)3] (NO2) (NO3)
Linkage isomers :
[Co(NH3)5 (NO2)](NO3)2;
[CO(NH3)5 (ONO)](NO3)2
(iv) Geometrical isomerism (cis and trans) :
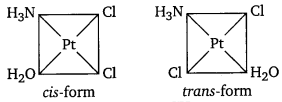

Question 4.
Give evidence that [Co(NH3)5Cl]SO4 and [Co(NH3)5SO4]Cl are ionisation isomers.
Answer:
When they are dissolved in water, they give different ions in the solution which can be tested by adding AgNO3 solution and BaCl2 solution. If Cl– dons are the counter ions, a white precipitate will be obtained with AgNO3 solution. If \(\mathrm{SO}_{4}^{2-}\) ions are the counter ions, a white precipitate will be obtained with BaCl2 solution.
Question 5.
Explain on the basis of valence bond theory that [Ni(CN)4]2- ion with square planar structure is diamagnetic and the [Ni(Cl)24]2- ion with tetrahedral geometry is paramagnetic.
Answer:
Nickel in [Ni(CN)4]2- is in the +2 oxidation state. The formation of [[Ni(CN)4]2- may be explained through hybridisation as follows :
Ni atom in the ground state
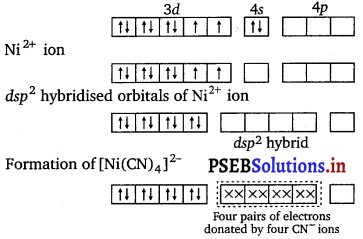
Since no unpaired electrons is present, the square planar complex is diamagnetic. In [Ni(CN)4]2-, Cl– is a weak field ligand. It is, therefore, unable to pair up the unpaired electrons of the 3d orbital. Hence, the hybridisation involved is sp3 and the shape is tetrahedral. Since all the electrons are unpaired, it is paramagnetic
Question 6.
[Ni(CN)4]2- is paramagnetic while [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic though both are tetrahedral. Why?
Answer:
In [Ni(CO)4] Ni is in zero oxidation state whereas in [NiCl4]2-, it is in
+ 2 oxidation state. In the presence of strong ligand, CO ligand, the unpaired d electrons of Ni pair up but Cl– being a weak ligand is unable to pair up the unpaired electrons.

Question 7.
[Fe(H2O)6]3+ is strongly paramagnetic whereas [Fe(CN)6]3- is weakly paramagnetic. Explain.
Answer:
In presence of CN– (a strong ligand), the 3d5 electrons pair up leaving only one unpaired electron. The hybridisation is d2sp3 forming an inner orbital complex. In the presence of H2O (a weak ligand), 3d electrons do not pair up. The hybridisation is sp3d2 forming an outer orbital complex containing five unpaired electrons. Hence, it is strongly paramagnetic.
Question 8.
Explain [Co(NH3)6]3+ is an inner orbital complex whereas [Ni(NH3)6]2+ is an outer orbital complex.
Answer:
In [CO(NH3)6]3+, CO is in +3 oxidation state and has d6 electrons. In the presence of NH3, the 3d electrons pair up leaving two d-orbitals empty to be involved in d2sp3 hybridisation forming inner orbital complex. In [Ni(NH3)6]2+, Ni is in +2 oxidation state and has d8 configuration. The hybridisation involved is sp3d2, forming the outer orbital complex.
Question 9.
Predict the number of unpaired electrons in the square planar [Pt(CN)4]2- ion.
Answer:
78Pt lies in group 10 with the configuration 5d96s1. Thus Pt2+ has the configuration :
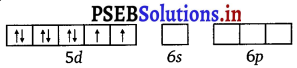
For square planar shape, the hybridisation is dsp2. Hence, the unpaired electrons in 5d orbital pair up to make one d orbital empty for dsp2 hybridisation.
Thus there is no unpaired electron.

Question 10.
The hexaquomanganese(II) ion contains five impaired electrons, while the hexacyano ion contains only one unpaired electron. Explain using crystal field theory.
Answer:
Mn in the + 2 oxidation state has the configuration 3d5. In the presence of H2O a weak ligand, the distribution of these five electrons is \(t_{2 g}^{3} e_{g}^{2}\)
i.e., all the electrons remain unpaired
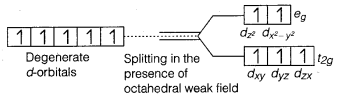
However, in the presence of CN– the distribution of these electrons is \(\), i.e., two t2g orbitals contain paired electrons while the third t2g orbital contains one unpaired electron.
Question 11.
Calculate the overall complex dissociation equilibrium constant for the \(\mathrm{Cu}\left(\mathrm{NH}_{3}\right)_{4}^{2+}\) ion, given that β4 for this complex is 2. 1 × 1013.
Solution:
The overall complex dissociation equilibrium constant is the reciprocal of the overall stability constant, β4.
∴ \(\frac{1}{\beta_{4}}\) = \(\frac{1}{2.1 \times 10^{13}}\)
∴ = 4.7 × 10-14
![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()