Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class History Book Solutions Source Based Questions and Answers.
PSEB 12th Class History Source Based Questions
Physical Features of Punjab and their Influence on Its History:
Note: Read the following passages carefully and answer the questions that follow :
1. The holy land of Punjab, the territory of five rivers has, undoubtedly, contributed to a great extent in diversified fields, not only to India but to the world also. About love to five thousand years ago, the Indus Valley Civilisation or Harappa civilisation was born, in areas around Punjab which were one of the oldest civilisations of the world. The great characters of the Ramayana and the Mahabharata belonged to Punjab. The great Mahabharata war was also fought on this land and Lord Krishna delivered his spiritual message i.e. the Gita here.
This land has the honour of giving birth to great scholars like Kautilya, Charka and Panin the great Sanskrit scholar. Due to the economic position of Punjab, most of the foreign invaders invaded Punjab through the North-West frontier Chandragupta Maurya and Harsh Vardhana had started these campaigns in Punjab and were able to establish a vast empire.
1. Harappan civilisation was born at which place?
2. The characters of which epics were related to Punjab?
3. Lord Krishna gave the message ……………….. at which place?
4. The foreign invaders who attacked India came from which side of Punjab?
5. Panini was the scholar of which subject?
Answer:
1. Harappan civilisation was born in areas around Punjab.
2. The great characters of the Ramayana and the Mahabharata were related to Punjab.
3. Lord Krishna gave the message of Gita in the land of Punjab.
4. The foreign invaders who invaded India came from the North-West frontier of Punjab.
5. Panini was a great Sanskrit scholar.

2. Punjab has been known by various names during different periods of history. It was called ‘Sapta Sindhu’ in the Rigvedic period, on the basis of the seven rivers that flowed in this land. They were : Sindhu (Indus), Vitasta (Jhelum), Asikni (Chenab), Parushni (Ravi), Vipasha (Beas), Sutudri (Sutlej) and Saraswati. The rivers Sindhu and Saraswati were the outer boundaries of Punjab. It is called ‘Panchnada’ in the Epics and the Puranas. ‘Panchnada’ means the land of five rivers. The Greeks named it ‘Pentapotamia’ ‘Penta’ means five and ‘Potamia’ means river. So, the Greeks also called it the land of five rivers. The territory of Afghanistan and Baluchistan were annexed to Punjab during the Maurya period. Thus its north-western boundary stretched up to the Hindukush. As Tak’ tribe ruled this vast land for centuries, therefore Punjab was called Tak Desh’.
1. By what name Punjab was known during the Rigvedifc Age?
2. What is meant by Panchnada?
3. Who gave the name of Pentapotamia to Punjab?
4. Why was Punjab called ‘Tak Desh’?
5. Which of the following river flows from Punjab?
- Beas
- Ganga
- Yamuna
- None of the above.
Answer:
1. Punjab was known by the name of Sapta Sindhu during the Rigvedic Age.
2. Panchnada means the land of five rivers.
3. The name of Pentapotamia was given to Punjab by the Greeks.
4. Punjab was called Tak Desh because it was ruled by the Tak tribe for centuries.
5. Beas.
3. The Himalayas are situated to the north of Punjab. ‘Himalaya’ means ‘abode of snow5. Its tops remain covered with snow throughout the year. It stretches from Assam in the east to Afghanistan in the west. Its length is 2500 kilometres and the breadth ranges from 240 kilometres to 320 kilometres. On the basis of its height, the Himalayas can be divided into three parts. The first part, the Greater Himalayas, consists of those high peaks whose height is 20,000 ft. or above. Mount Everest, the world’s highest peak. Its height is about 29,028 feet or 8848 metres.
1. What is meant by the Himalayas?
2. What is the length and breadth of the Himalayas?
3. Which is the highest peak of the Himalayas?
4. Write any one advantage of the Himalayas.
5. The height of Mount Everest is a metre.
Answer:
1. the Himalayas means the abode of snow.
2. The length of the Himalayas is 2500 kilometres and the breadth ranges from 240 kilometres to 320 kilometres.
3. The highest peak of the Himalayas is Mount Everest.
4. It acted as a watchman both for the Punjab and India for centuries.
5. 8848.
4. The Plains constitute the largest and most important region of Punjab. It is rightly called Virtual Punjab. This part is located between the rivers of Indus and Jamuna. It is considered one of the best fertile plains in the world. Its average height from the sea level is less than 1000 feet. Five great rivers of Punjab (Sutlej, Beas, Ravi, Chenab, Jhelum) flow in this very part. The land of this area is very fertile, it receives ample rainfall and the means of transport are fairly developed. So, the population of this area is very dense.
1. Where are the Plains of Punjab located?
2. Which is considered the best fertile plains in the world?
3. Name the rivers of Punjab.
4. Why the population of Punjab is very dense?
5. The population of Punjab is very
Answer:
1. The Plains of Punjab is located between the rivers Indus and Jamuna.
2. The best fertile Plain in the world is Punjab Plains.
3. The five great rivers of Punjab are Sutlej, Beas, Ravi, Chenab and Jhelum.
4. It land is very fertile.
5. dense.
5. As a result of its geographical location, the Punjab has been the gateway of India for many centuries. There are a number of passes (Khyber, Koorram, Tochi, Bolan etc.) in the nerth-west of the Punjab which were easy to cross. So, the foreign invaders kept attacking by entering through these passes for centuries. The Aryans, Iranians, Greeks, Kushanas, Hunas, Turks, Mughals and Durranis invaded India crossing through these passes. First of all these invaders had to fight with the people of the Punjab. They could go further only after defeating the Punjab. So, the Punjab has been called the gateway of India.
1. Why is Punjab called as the gateway of India?
2. Which is the most important pass -located in the north-west of the Punjab?
3. Why the foreign invaders kept invading India through the passes?
4. Which foreign invaders invaded Punjab first of all?
5. Which foreign invaders were the first to invade Punjab?
- Iranians
- Aryans
- Greeks
- Kushanas.
Answer:
1. Punjab is called as the gateway of India because the foreign invaders invaded Punjab first of all.
2. Khyber is the most important pass located in the north-west of the Punjab.
3. Because it was easy to cross the passes.
4. The Aryans, Iranians, Greeks, Kushanas, Hunas, Turks, Mughals and Durranis were the first to invade Punjab.
5. Aryans.
Sources of the History of the Punjab:
Note : Read the following passages carefully and answer the questions that follow :
1. A good knowledge of the sources of the history of a country is in dispensable for a thorough understanding of its history. This knowledge is as much essential for the students of history as are surgical instruments for a doctor to undertake an operation. However, we had many difficulties regarding the sources of the history of Punjab. The Punjab remained the arena of battles in the 18th century. That is why, even the Sikhs could not have any time for writing their own history in this period of anarchy and confusion as they were fighting a battle of life and death for their very existence. Thus, most of the available sources of the history of the Punjab relate to the nineteenth century when Maharaja Ranjit Singh established an independent Sikh kingdom.
1. Why are the sources indispensable for the students of history?
2. Which problems do we confront while writing the history of Punjab? Mention any one.
3. In which century did Punjab became an arena of battles?
4. In which century did Maharaja Ranjit Singh establish an independent Sikh Kingdom?
5. The most of the available sources of the history of the Punjab relate to the ………….
Answer:
1. The sources are indispensable for the students of history to know the culture and civilisation of any country.
2. The available sources of the history concerning the period of the Gurus are very few.
3. The Punjab remained the arena of battles in the 18th century.
4. Maharaja Ranjit Singh established an independent Sikh Kingdom in Punjab in the 19th century.
5. 19th Century.

2. The Adi Granth Sahib Ji is the most sacred and authentic scripture of Sikhism. Guru Aijan Dev Ji compiled this great holy scripture in 1604 A.D. In it the hymns of the first five Sikh Gurus are compiled. Later on during the times of Guru Gobind Singh Ji the hymns of Guru Teg Bahadur Ji were also included in it and Adi Granth Sahib Ji was given the status of Guru Granth Sahib Ji. Although the Adi Granth Sahib Ji or Guru Granth Sahib Ji was not compiled for any Historical purpose, yet its thorough study gives us most valuable information regarding the political, religious, social and economic life of the people of those days.
1. When was Adi Granth Sahib Ji was compiled?
2. The Adi Granth Sahib Ji was compiled by ……………
3. Which Guru Sahib gave the status of Guru Granth Sahib to Adi Granth Sahib Ji?
4. The Banis of how many Guru Sahibs are given in Guru Granth Sahib Ji?
5. Write any one significances of Adi Granth Sahib Ji.
Answer:
1. Adi Granth Sahib Ji was compiled in 1604 A.D.
2. Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
3. Adi Granth Sahib Ji was given the status of Guru Granth Sahib Ji by Guru Gobind Singh Ji.
4. The Bams of six-Guru Sahibs are given in Guru Granth Sahib Ji.
5. It gives the message of universal brotherhood of mankind.
3. Dasam Granth Sahib Ji is another holy scripture of Sikhism. It is the compilation of the writings of Guru Gobind Singh Ji and his court poets. This holy scripture was compiled by Bhai Mani Singh Ji in 1721 A.D. The Dasam Granth was primarily compiled to awaken heroic sentiments among the Sikhs so that they were able to fight against political injustice and religious intolerance. It is a work of 18 compositions of which ‘Jaap Sahib’, ‘Akal Ustat’, ‘Chandi Di Var’, ‘Chaubis Avtar’, ‘Shabad Hazare’, ‘Shastra Nama’, ‘Bachitar Natak’ and ‘Zafamama’ are worth noting. ‘Bachitar Natak’ and ‘Zafamama’ are the most significant firom the historical point of view. ‘Bachitar Natak’ is the autobiography of Guru Gobind Singh Ji. ‘Zafamama’ (letter of victory) was written by Guru Gobind Singh Ji at Dina. It is a letter written by Guru Gobind Singh Ji to the Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb in Persian language.
1. By whom was Dasam Granth Sahib compiled?
2. When was Dasam Granth Sahib compiled?
- 1604 A.D.
- 1701 A.D.
- 1711 A.D.
- 1721 A.D.
3. What is Bachitar Natak?
4. What is the name of letter written by Guru Gobind Singh Ji to Aurangzeb?
5. What is written by Guru Gobind Singh Ji in Zafamama?
Answer:
1. Dasam Granth Sahib was compiled by Bhai Mani Singh Ji.
2. 1721 A.D.
3. Bachitar Natak is the name of autobiography of Gum Gobind Singh Ji.
4. The name of the letter written by Gum Gobind Singh Ji is Zafamama.
5. In it the account of the atrdCmes of Aurangzeb is given.
4. Bhai Gurdas Ji was the son of Bhai Datar Chand Bhalla, a brother of Guru Amar Das Ji. He was a contemporary of Guru Arjan Dev Ji and Guru Hargobind Ji. He composed 39 Vars. These Vars are considered the key to understand Guru Granth Sahib Ji. The Vars Nos. 1 and 11 are considered important from the historical point of view. The first Var contains a very detailed description of the life of Guru Nanak Dev Ji. Besides, we get a glimpse of Guru Angad Ji, Guru Amar Das Ji, Guru Ram Das Ji, Guru Arjan Dev Ji and Guru Hargobind Ji’s life from this Var. In the eleventh Var, we get information of the important Sikhs and places connected with the first six Gurus.
1. Who was Bhai Gurdas Ji?
2. How many vars are composed by Bhai Gurdas Ji?
3. The var contains very detailed description of the life of Guru Nanak Dev Ji.
4. Which is called the key of Guru Granth Sahib Ji?
5. What is the importance of Bhai Gurdas Ji?
Answer:
1. Bhai Gurdas, Ji was the son of Bhai Datar Chand Bhalla, a brother of Guru Amar Das Ji.
2. Bhai Gurdas Ji composed 39 vars.
3. First.
4. The vars of Bhai Gurdas Ji is called the key of Guru Granth Sahib Ji.
5. From these we get valuable imformation of the first six Gurus, important Sikhs and places.
5. The stories relating to the birth and life of Guru Nanak Dev Ji are called Janam Sakhis. Many such Janam Sakhis were written in the seventeenth and ‘ eighteenth centuries. They were written in the Punjabi language. They, were compiled for the faithful and not for students of history. Though they are a mixture of facts and fiction, yet they provide valuable information about the life of Guru Nanak Dev Ji.
1. What is meant by Janam Sakhis?
2. In which language Janam Sakhis were written?
3. Write the names of any two Janam Sakhis.
4. Write anyone demerit of Janam Sakhis.
5. Many Janam Sakhis were written in the ……………. and …………….
Answer:
1. By Janam Sakhis we meant the stories relating to the birth and life of Guru Nanak Dev Ji.
2. The Janam Sakhis were written in Punjabi language.
3. Puratan Janam Sakhi and Janam Sakhi of Bhai Mani Singh Ji.
4. The events narrated in them are not in chronological order.
5. 17th and 18th centuries.
6. Hukamnamas were those orders or proclamations that were issued by the Sikh Gurus or by the members of their families to the Sikhs from time to time. In majority of such Hukamnamas demands were made to supply grains for the Langar (common kitchen), to donate money for building religious places and to bring horses and arms for battles. These Hukamnamas were compiled by the famous historian Ganda Singh. 89 Hukamnamas are available upto this day. Of these, 34 Hukamnamas were issued by Guru Gobind Singh Ji and 23 Hukamnamas were issued by Guru Tegh Bahadur Ji. These Hukamnamas provide very valuable information about the political, religious, economic and literary history of the period of the great Gurus.
1. What is meant by Hukamnamas?
2. Why were Hukamnamas issued?
3. Which famous historian of Punjab compiled Hukamnamas?
4. Give any one significance of Hukamnamas.
5. How many Hukamnamas are available upto this day? 1
Answer:
1. Hukamnamas were those orders or proclamations that were issued by the Sikh Gurus or by the members of their families to the Sikhs from time to time.
2. Hukamnamas were issued to demand the supply of grains for the Langar, to donate money for construction of religious places and to bring horses and arms for battles.
3. Ganda Singh.
4. We get valuable information about Guru Sahibs.
5. 89.

Political, Social and Economic Conditions of the Punjab in the Beginning of the 16th Century:
Note : Read the following passages carefully and answer the questions that follow :
1. After the death of Bahlol Lodhi, his son Sikandar Lodhi succeeded to the throne of Delhi Sultanate. He ruled upto 1517 A.D. The Muslim historians speak very highly of Sikandar’s love of justice, wisdom and benevolence. However, his kindness and love of justice was confined, to the Muslims only. He hated the Hindus. He adopted a very harsh and cruel policy towards them. He demolished many famous Hindu temples and built mosques over them. He forbade the barbers to shave the beards and heads of the Hindus. He started converting them to Islam by force. He got a Brahman named Bodhan murdered because he had described Hinduism as good as Islam.
1. Who was Sikandar Lodhi?
2. When did Sikandar Lodhi sit on the throne?
- 1485 A.D.
- 1486 A.D.
- 1487 AJX
- 1489 A.D.
3. How was Sikandar Lodhi in the eyes of Muslim historians?
4. Which one step was taken by Sikandar Lodhi against the Hindus?
5. Why was a Brahman named Bodhan was murdered?
Answer:
1. Sikandar Lodhi was the Stdtan of Delhi. He ruled from 1489 A.D. to 1517 A.D.
2. 1489 A.D.
3. He was a justice-loving and benevolent Sultan.
4. He had demolished many Hindu temples.
5. He had described Hinduism as good as Islam.
2. In the beginning of the sixteenth century the condition of the subjects was also very deplorable. The rulers used to indulge in luxuries and merry-making. Extravagant parties had become a daily routine of the court. As a cousequence none had time to take care of the public. As a consequence of this, the government officials became corrupt. Bribery was common. Not to speak of the Sultan, even Qazis and Ulemas took bribe and delivered justice accordingly. All sorts of atrocities were let loose on the Hindus. They were being converted to Islam by force. Those who refused were put to death.
1. What was the condition of subjects in the beginning of the 16th century?
2. What was the character of the government officials in the beginning of the 16th century?
3.. How did Sultan, Qazis and Ulemas deliver justice in the beginning of the 16th century?
4. What was the policy adopted against the Hindus in the beginning of the 16th century?
5. In the 16th century the ruling class used to indulge in ……………. and …………….
Answer:
1. In the beginning of the 16th century the condition of subjects was very pitiable.
2. At that time the government officials had become very corrupt.
3. At that time Sultan, Qazis and Ulemas deliver justice by taking bribe.
4. At that time all sorts of atrocities were let loose on the Hindus.
5. Luxuries, merry-making.
3. The social condition of the Punjab in the beginning of the sixteenth century was also very deplorable. The society was divided into two major classes, namely the Hindus and the Muslims. The Muslims enjoyed many privileges,1 because they belonged to the ruling class. On the other hand, the Hindus, who formed the majority of population, were deprived of almost all the rights. They were called ‘Kafirs’ and ‘Zimmies’. Jaziya and the pilgrimage tax were forcibly charged from the Hindus. The Muslims subjected the Hindus to so much atrocity that a large number of them were compelled to embrace Islam. The condition of women in the society was not good. The moral character of the public had fallen to the lowest ebb.
1. Why was the social condition of Punjab in the beginning of the 16th century was called deplorable?
2. Who were deprieved of their rights in the beginning of the 16th century?
3. Who were called ‘Kafirs’?
4. What was Jaziya?
5. The Muslims belonged to the …………… class.
Answer:
1. The social condition of Punjab in the beginning of the 16th century
was called deplorable because the muslims let loose atrocities on the Hindus and the condition of women was pitiable.
2. Hindus were deprieved of their rights in the beginning of the 16th century.
3. All Non-Muslims were called Kafirs.
4. Jaziya was a tax imposed upon the Hindus.
5. ruling.

4. No remarkable progress was made in the field of education in the beginning of the sixteenth century. Ulemas and Maulvis taught the Muslims. They held classes in mosques, maktabs and madarasas. The government gave them grants. Primary education was given in the mosques and maktabs whereas higher education was provided in the madarasas. Madarasas were usually situated in cities. Lahore and Multan were the well-known centres of education for the Muslims in the Punjab.
1. Why no remarkable progress was made in the field of education in the beginning of the 16th century?
2. Whether the Maulvis taught the Muslims?
3. Where was elementary education given to the Muslims?
4. Which was the one famous centre of education of the Muslims in the beginning of the 16th century?
5. Madarasas were usually situated in ……………..
Answer:
1. Because it was not the responsibility of the government to provide education to the public.
2. Yes, the Maulvis used to provide education to the Muslims.
3. The elementary education to the Muslims was provided in the mosques and maktabs.
4. In the beginning of the 16th century the one famous centres of education was Lahore.
5. cities.
5. In the beginning of the 16th century, this sect had become very popular. The Sufi saints were known as Shaikhs or Pirs. They believed in the Allah. They did not repose faith in any other power except Allah. According to them, Allah is omnipotent and omni- present. One could realise Allah only through Pir or Guru. They did not believe in fake externalities. They started the tradition of Qawalis. They considered service of mankind as service to God. They did not believe in caste-system. They respected other faiths.
1. To which sect Sufism was related Shaikhs?
2. By which other name Sufi Shaikhs were known?
3. What is the ideology of Sufi Shaikhs called?
4. Write any one principle of Sufism.
5. According to Sufis one could realise Allah through.
- Pir
- Qawali
- Dargah
- All of the above.
Answer:
1. Sufism was a sect related with Islam.
2. Sufi Shaikhs are also known as Pirs.
3. The ideology of Sufi Shaikhs is called as Tasawnf.
4. They believed in one Allah.
5. Pir.
Guru Nanak Dev Ji’s Life and his Teachings:
Note: Read the following passages carefully and answer the Questions that follows:
1. Guru Nanak Dev Ji was the founder of Sikhism1. At the time of his birth in the fifteenth century A.D., there was chaos all around. People had become very -’’pprstitious. They were stumbling in the darkness of ignorance. Impiety, falsehood and corruption were rampant everywhere. People had forgotten the essence of religion and it had been reduced to mere rituals and vain show. The rulers and the officials had no longer any concern about public welfare and remained busy in merry-making. In such a deplorable state of affairs, Guru Nanak Dev Ji showed a path of truthfulness and knowledge to the humanity.
1. Who was the founder of Sikhism?
2. What was the condition of society at the time of the birth of Guru Nanak Dev Ji?
3. What was the attitude of rulers and the officials towards subjects at the time of birth of Guru Nanak Dev Ji?
4. Which path was shown to the humanity by Guru Nanak Dev Ji?
5. People had forgotten the of religion.
Answer:
1. Guru Nanak Dev Ji was the founder of Sikhism.
2. At that time people had become very superstitious.
3. At the time of birth of Guru Nanak Dev Ji the attitude of rulers and the officials towards subjects was atrocitious.
4. Guru Nanak Dev Ji showed the path of truthfulness and knowledge to the humanity.
5. essence.

2. After attaining enlightenment in 1499 A.D., Guru Nanak Dev Ji did not stay for a long time at Sultanpur Lodhi. So, he set out on long travels in India and in foreign countries. He spent about 21 years in these travels. These travels of Guru Nanak Dev Ji are known as Udasis because he wandered like an Udasi (unconcerned, unattached) during these years and renounced his home and family. We had to face some difficulties regarding the Udasis of Guru Nanak Dev Ji.
1. Where did Guru Nanak Dev Ji attain enlightenment?
2. What is meant by Udasis?
3. Which was the one difficulty being faced regarding the Udasis of Guru Nanak Dev Ji?
From where did Guru Nanak Dev Ji start his Udasis? , When did Guru Nanak Dev Ji attained enlightenment?
- 1469 AJD.
- 1479 A.D.
- 1489 A.D.
- 1499 A.D.
1. Guru Nanak Dev Ji attained enlightenment at Sultanpur Lodhi.
2. By Udasis we meant the travels of Guru Nanak Dev Ji.
3. We get no contemporary sources regarding Udasis.
4. Guru Nanak Dev Ji started his Udasis from Saidpur.
5. 1499 A.D.
3. When Guru Nanak Dev Ji reached Saidpur at the end of 1520 A. D., Babar attacked this town with a view to occupy it. The Mughal army put to death thousands of innocent people during this attack. Saidpur was looted heavily and the houses were set on fire. Women were dishonoured. Thousands of men, women and children were taken prisoners. Guru Nanak Dev Ji was also arrested along with them. But when Babar came to know that Guru Nanak Dev Ji was a great saint, he himself came for his Darshan. He was so much impressed by Guru Nanak Dev Ji’s personality that he set free not only Guru Nanak Dev Ji but many other prisoners also. Guru Nanak Dev Ji writes about the cruelties of Babar in Babar Vani.
1. When did Babar attack Saidpur?
2. What did the army do at Saidpur?
3. Was Babar imprisoned Guru Nanak Dev Ji at Saidpur?
4. What did Babar do when he came for the Darshan of Guru Nanak Dev Ji?
5. How did the army of Babar treat the women in Saidpur?
- It illtreated the women
- It respected the women.
- It imprisoned the women.
- None of the above.
Answer:
1. Babar attacked Saidpur in 1520 A.D.
2. The army of Babar sacked Saidpur on an extensive way.
3. Yes, Babar did imprison Guru Nanak JDev Ji at Saidpur.
4. When did Babar have the Darshan of Guru Nanak Dev Ji he was greatly impressed. So he ordered the release of Guru Nanak Dev Ji along with other prisoners.
5. It illtreated the women.
4. Guru Nanak Dev Ji founded a town named Kartarpur (the abode of God) at the banks of the Ravi river in 1521 A.D. and spent the last 18 years of his life at this place. He started the institutions of ‘Sangat’ and ‘Pangat’ during this period. ‘Sangat’ meant the congregation held daily to listen to the Bani (hymns) of Guru Ji. Everybody could join it without any consideration of caste or sex. The ‘Name’ of only one God was recited in it. Similarly ‘Pangat’ meant to sit in a queue and to partake langar (food). No discrimination of any kind regarding caste or religion, high or low was made in the ‘langar’. These two institutions proved very helpful in spreading the message of Guru Nanak Dev Ji. Besides, he composed 976 Sabads, which also proved extremely helpful for the spread and development of Sikhism.
1. What is meant by Kartarpur?
2. Which two institutions were founded by Guru Nanak Dev Ji at Kartarpur?
3. How many hymns were composed by Guru Nanak Dev Ji?
4. Write the names of any two main Banis of Guru Nanak Dev Ji.
5. When was Kartarpur founded by Guru Nanak Dev Ji?
- 1501 A.D.
- 1511 A.D.
- 1521 A.D.
- 1531 A.D.
Answer:
1. Guru Nanak Dev Ji founded Kartarpur in 1521 A.D.
2. Guru Nanak Dev Ji founded two institutions named Sangat and Pangat.
3. Guru Nanak Dev Ji composed 976 hymns.
4. The two main Banis composed by Guru Nanak Dev Ji are Japji Sahib and Asa di Var.
5. 1521 A.D.

Development of Sikhism Under Guru Angad Deli Ji, Guru Amar Das Ji and Guru Ram Das Ji:
Note : Read the following passages carefully and answer the questions that follow :
1. Before meeting Guru Nanak Dev Ji, Bhai Lehna Ji used to visit Jawalamukhi ‘ (in Kangra district) every year along with a group of devotees (Jatha) but his search for truth did not culminate in success. One day he heard in Khadur Sahib, the recitation of ‘Asa Di Var’ from Bhai Jodha Ji, who was a devotee of Guru Nanak Dev Ji. Bhai Lehna Ji was so much impressed by it that he decided to meet Guru Nanak Dev Ji. Thus, when he set out for the pilgrimage of Jawalamukhi with his group of devotees next year,he stopped on the way at Kartarpur to meet Guru Nanak Dev Ji. He was so much overwhelmed by the great personality and teachings of Guru Nanak Dev Ji that he became a follower of Guru Nanak Dev Ji. He spent his life in the service of Guru Nanak Dev Ji.
1. Bhai Lehna Ji was the devotee of which goddess before he met Guru Nanak Dev Ji?
2. At Khadur Sahib Bhai Lehna Ji heard the recitation of Asa Di Var from whom?
3. What did Bhai Lehna Ji decide after he heard the recitation of Asa Di Var?
4. Why did Bhai Lehna Ji became the follower of Guru Nanak Dev Ji?
5. At which place Bhai Lehna Ji met Guru Nanak Dev Ji?
- At Kartarpur
- At Jawalamukhi
- At Kiratpur
- At Amritsar.
Answer:
1. Bhai Lehna Ji was the devotee of Mata Durga before he met Guru Nanak Dev Ji.
2. At Khadur Sahib Bhai Lehna Ji heard the recitation of Asa Di Var from Bhai Jodha Ji.
3. After listening the recitation of Asa Di Var Bhai Lehna Ji decided’to meet Guru Nanak Dev Ji.
4. Bhai Lehna Ji was greatly impressed by the personality and teachings of Guru Nanak Dev Ji.
5. At Kartarpur.
2. It is true that Gurmukhi existed before Guru Angad Dev Ji, but anybody could be confused very easily by reading it. Therefore, Guru Angad Dev Ji improved and polished it. Now it became very easy even for common people to understand it. All the religious books of Sikhism were written in it. Its very name ‘Gurmukhi’ (an utterance of words frem the Guru’s mouth) reminded the Sikhs of their duties towards the Guru and constantly kept alive in their minds the consciousness that they were something distinct from the common mass of Hinduism. This script was also instrumental-in rapid spread of education, among the Sikhs. Besides, the introduction of this script gave a severe blow to the Supremacy of the Brahmans, who recognised Sanskrit as the only religious language.”
1. Gurrmukhi script was popularised by which Guru Sahib?
2. Which script wa prevalent before Gurnukhi script?
3. What is meant by Gurmukhi?
4. What is the importance of Gurmukhi script?
5. All the reIigius books of Sikhism were written in …………….
Answer:
1. Gurmukhi script was popularised by which Guru Sahib?
3. By Gurmukhi we meant the utterance of words from the Gurus mouth.
4. It led to the rapid spread of education among the Sikhs.
5. Gurmukhi.
3. The construction of a Baoli at Goindwal Sahib was started in 1552 A.D. and it was completed in 1559 A.D. Guru Ji had two objectives in its construction. First, he wanted to give the Sikhs a separate place of pilgrimage so that they could be separated from the Hindus. Secondly, he wanted to solve the water problem of the people of that place. Eighty four steps were built to reach the Baoli. After its construction was over. Guru Amar Das Ji declared, “Whoever would attentively and reverently repeat the Japji on every step after a bath in the baoli would escape from the wandering in the wombs of the 84 lakhs of living creatures.”
The construction of Baoli Sahib proved a very important step in the development of Sikhism.
1. Which Guru Sahib had constructed the Baoli at Goindwal Sahib?
2. When was the construction of the Baoli at Goindwal Sahib started?
- 1552 A.D.
- 1559 A.D.
- 1562 A.D.
- 1569 A.D.
3. How many years were spent in building Baoli at Goindwal Sahib?
4. How many stairs were built to reach at the bottom of the Baoli at Goindwal Sahib?
5. How did the Baoli at Goindwal Sahib prove an important step in the consolidation of Sikhism?
Answer:
1. The Baoli at Goindwal Sahib was constructed by Guru Amar Das Ji.
2. 1552 A.D.
3. Total of 7 years were spent in building Baoli at Goindwal Sahib.
4. A total of 84 stairs were built to reach at the bottom of Baoli.
5. It gave a. new boost to Sikhism.

4. The establishment of Manji system was one of the most important works of Guru Amar Das Ji. During his Guruship, the number of the followers of Sikhism had increased considerably. Thus, it became impossible for Guru Amar Das Ji to reach every Sikh. So, he established twenty two Manjis to convey the message of Sikhism living in far off areas. The head of every Manji was called Manjidar. This post was given only to a very pious Sikh. The area of propaganda of the Manjidar was not limited to any specific area. He could visit any place for propaganda at his will.
1. By which Guru Sahib Manji system was established?
2. How many Manjis were established?
3. Who was the head of Manji?
4. What was the one main function of the Manjidar?
5. The area of ‘propaganda of the Manjidar was not limited to any specific ……………..
Answer:
1. Manji system was established by Guru Amar Das Ji.
2. A total of 22 Manjis were established.
3. Manjidar was the head of Manji.
4. He used to preach Sikhism.
5. area.
5. The most important contribution of Guru Ram Das Ji towards the Sikh Panth was the foundation of Ramdaspura. After assuming the Guruship, he himself settled here. In 1577 A.D. he founded Ramdaspura. He settled fifty two other traders, belonging to different trades, at this place in order to make it popular and attract people. It soon became a famous trade centre. Guru Ram Das Ji planned to construct two sarovars (tanks) Amritsar and Santokhsar at Ramdaspura. The digging of Amritsar sarovar was started first. Baba Buddha Ji was entrusted to look after this project. Later on the name of Ramdaspura came to be known as Amritsar.
1. Ramdaspura was established by which Guru Sahib?
2. Ramdaspura was later on came to known by which other name?
3. What was the name given to the market for the traders of Ramdaspura?
4. What was the importance of Ramdaspura?
5. When was Ramdaspura founded?
- 1571 A.D.
- 1573 A.D.
- 1575 A.D.
- 1577 A.D.
Answer:
1. Ramdaspura was established by Guru Ram Das Ji.
2. Ramdaspura later on came to be known as Amritsar.
3. ‘Guru Ka Bazaar’ was given the name for the traders of Ramdaspura.
4. It gave the Sikhs their most sacred religious place.
5. 1577 A.D.
Guru Arjan Dev Ji and his Martyrdom:
Note: Read the following passages carefully and answer the questions that follow :
1. The foremost achievement of Guru Arjan Dev Ji for the consolidation of Sikhism was the construction of Harmandir Sahib. Guru Ram Das Ji had started the digging of Amrit Sarover and it was completed by Guru Arjan Dev Ji. After this, he started the construction work of Harmandir Sahib (Temple of God) in Amrit Sarovar. Its foundation was laid on 13th January, 1588 A.D. by a very famous Sufi saint, named Mian Mir. According to Sikh tradition, the Sikhs suggested to Guru Arjan Dev Ji that the temple should be higher than the surrounding buildings. But Guru Sahib said, “He who is humble shall be exalted.” That is why the building of the temple was kept lower as compared to the other buildings. Another distinguishing feature of Harmandir Sahib was that it has four doorways, one on each side.
1. By which Guru Sahib Ha rmandir Sahib was constructed?
2. Who laid the foundation of Harmandir Sahib?
3. The foundation of Harmandir Sahib was laid in ………………
4. How many doors were kept for the entry in the Harmandir Sahib?
5. What wais the importance of Harmandir Sahib?
Answer:
1. Harmandir Sahib was constructed by Guru Aijan Dev Ji.
2. The foundation of Raima p dir Sahib was laid by Sufi Saint Mian Mir.
3. 1588 A.D.
4. Four doors were kept for the entry in the Harmandir Sahib.
5. It gave the Sikhs their most sacred religious place.
2. Development of Masand system was one of the greatest achievements of Guru Aijan Dev Ji. This system was founded by Guru Ram Das Ji. The word Masand has been derived from the Persian word ‘Masnad’ which means high place. As the representatives of Guru Ji used to sit on a higher place than others, so they were called as Ms sands. With the passage of time, the number of Sikhs had increased considerably. As a consequence, Guru Ji needed money for Langar and other development programmes. It was enjoined upon every Sikh to give Daswandh of his total income to Guru Sahib. For collecting this money from Sikhs, he appear red very responsible persons called Masands.
1. Which Guru Sahib had founded the Masand System?
2. Masand is the word of which language?
3. What is meant by Daswandh?
4. What was the importance of Masand system?
5. During whose Guru pontificate the development of Masand system took place?
- Guru Ram Dss Ji
- Guru Arjan Dev Ji
- Guru Hargobmd Ji
- Guru Gobind Singh Ji.
Answer:
1. The Masand system was founded by Guru Ram Das Ji.
2. Masand is the word of Persian language.
3. Daswandh means l/10th of the total income.
4. It spread the message of Sikhism far and wide.
5. Guru Aijan Dev Ji.

3. Jahangir was a fanatic Sunni Muslim. So, he could not bear to see any other religion more prosperous than Islam. He could not tolerate the growing popularity of Sikhs in Punjab. So, he was looking for a chance to hamper their development. He wanted to put a stop to all this. In his book Tuzak-i-Jahangiri, he has himself written, “In Goindwal on the banks of the river Beas lived a Hindu named Arjan in the garb of‘Pir’ or ‘Shaikh’.
By his ways and manners he captured the fancy of many of the simple hearted Hindus and even many ignorant Muslims. He had loudly sounded the drum of his being Pir and a holy person. They called him Guru and from all sides innocent and foolish people crowded to manifest their complete faith in him. For three or four generations they had kept their shop warm. Many times I thought of putting a stop to this vain affair or to bring him
to Islam.”
1. What was the name of autobiography of Jahangir?
2. Why was Jahangir against Guru Arjan Sahib?
3. To whom did Jahangir call the shop of liar?
4. When Guru Arjan Dev Ji was martyred?
5. Guru Arjab Dev Ji was martyred at …………………
Answer:
1. Tuzak-i-Jahangiri was the name of autobiography of Jahangir.
2. He was not ready to tolerate the spread of Sikhism day by day.
3. Jahangir’called the peachings of Guru Arjan Dev Ji as the shop of liar.
4. Guru Arjan Dev Ji was martyred on 30th May, 1606 A.D.
5. Lahore.
Guru Hargobind Ji and Transformation of Slkhism:
Note : Read the following passages carefully and answer the questions that follow :
1. At the time of assuming Guruship, Guru Hargobind Ji decided to wear the swords of Miri and Piri. The sword of Miri was a symbol of temporal power and the sword of Piri a symbol of religious leadership. It meant that henceforth, Guru Hargobind Ji would lead his followers in temporal matters in addition to the religious matters. Guru Hargobind ji enjoined on his Sikhs to recite the name of God on one hand, and to wear arms for self-defence on the other. In this way, Guru Hargohind Ji turned the Sikhs into saint soldiers. This policy of Miri and Piri as adopted by Guru Hargobind Ji exercised a deep impact on the Sikh History.
1. When did Guru Hargobind Ji sat on Gurgaddi?
2. Which title was assumed by Guru Hargobind Ji?
3. Miri sword was the symbol of which power?
4. Piri sword was the symbol of …………. power.
5. Which Guru Sahib had declared the Sikhs as Saint Soldier? 1
Answer:
1. Guru Hargobind Ji sat on Gurgaddi in 1606 A.D.
2. Guru Hargobind Ji assumed the title of Sacha Padshah.
3. The sword of Miri was the symbol of temporal power, religious.
4. Guru Hargobind Ji had declared the Sikhs as Saint Soldier.
2. The construction of Akal Takht proved very helpful in the evolution of the New Policy. In fact, it was a great task of Guru Hargobind Ji. The construction of Akal Takht was begun by Guru Hargobind Ji in front of Harmandir Sahib in 1606 A.D. This stupendous task was completed in 1609 A.D. Inside it was built a -12 feet high rostrum, which was like a throne. Guru Hargobind Ji used to guide the political and military affairs of the Sikhs by occupying the throne.
1. What is meant by Akal Takht?
2. In which city Akal Takht Sahib was built?
3. Why was Akal Takht Sahib built?
4. What functions were carried by Guru Hargobind Ji at Akal Takht Sahib? Write any one. ”
5. When was the construction of Akal Takht Sahib started?
- 1605 A.D.
- 1606 A.D.
- 1607 A.D.
- 1609 A.D.
Answer:
1. Akal Takht meant seat of the Almighty.
2. Akal Takht Sahib was built in Amritsar.
3. Akal Takht Sahib was built to guide the political and military affairs of the Sikhs.
4. Guru Hargobind Ji gave military training to the Sikhs.
5. 1606 A.D.
3. Soon after the battle of Amritsar, second battle was fought between the Mughals and the Sikhs at a place called Lahira (near Bathinda). The immediate cause of this battle was two horses named Dilbag and Gulbag. Two Masands named Bakht Mai and Tara Chand were bringing these horses from Kabul to present them to Guru Hargobind Sahib. On the way the Mughals dispossessed them of these horses and sent them to the royal stable.
Bhai Bidhi Chand Ji, a devotee of Guru Ji could not tolerate it. He went in disguise of a grass cutter and brought out both the horses from the royal stable and sent them to Guru Hargobind Ji. When Shah Jahan heard this news, he became very angry. He immediately sent a large army under the command of Lala Beg and Qamar Beg to crush the power of the Sikhs. A fierce battle was fought between the Mughals and the Sikhs at a place called Lahira. The Mughals had to suffer a heavy loss of life and both their commanders were killed.
1. When was the battle of Lahira took place between Guru Hargobind Ji and the Mughals?
2. Write the names of those two horses which led to the battle of Lahira.
3. Which Sikh devotee brought out both the horses from the royal stable?
4. Which two Mughal commanders were killed in the battle of Lahira?
5. The Mughals had to suffer a heavy loss of ……………
Answer:
1. The battle of Lahira took place between Guru Hargobind Ji and the Mughals in,1634 A.D.
2. Dilbagh and Gulbagh were those two horses which led to the battle of Lahira.
3. Bhai Bidhi Chand Ji was the name of Sikh devotee who brought out both the horses from the royal stable.
4. Lala Beg and Qamar Beg were the two commanders who were killed in the battle of Lahira.
5. life.

Guru Har Rai Ji and Guru Har Krishan Ji:
Note: Read the following passages carefully and answer the questions that follow :
1. Guru Har Rai Ji remained on Gurgaddi from 1645 to 1661 A.D. His pontificate is considered peaceful in Sikh History. In order to preach Sikhism, Guru Har Rai Ji travelled to different parts of the Punjab i.e. Jalandhar, Amritsar, Kartarpur, Gurdaspur, Ferozepur, Patiala, Ambala, Kamal and Hissar. Besides, he sent his preachers outside Punjab. During his journey to the Malwa region, Guru Sahib blessed Phul that he would become great and his descendants would rule. This prophecy of Guru Sahib turned out to be true. Dara Shikoh, the elder son of Shah Jahan was a devoted follower of Guru Har Rai Ji. In 1658 A.D. he was defeated by Aurangzeb. Thereafter, Dara Shikoh visited Guru Har Rai Ji to seek his blessings.
Guru Heir Rai Ji boosted his morale. After Aurangzeb firmly established himself on the throne he summoned Guru Har Rai Ji to Delhi. Guru Har Rai Ji sent his elder son Ram Rai to Delhi. In order to save himself from Aurangzeb’s wrath he wrongly interpreted a hymn of Adi Granth Sahib. Consequently, the Guru Ji declared Ram Rai unfit for Guruship and nominated his younger son Har Krishan Ji as the next successor of the Sikhs.
1. When Guru Har Rai Ji ascended the Gurgaddi?
2. Which places of Punjab were visited by Guru Har Rai Ji for preaching Sikhism? Name any two.
3. Name the devotee who was blessed by Guru Har Rai Ji.
4. Who was nominated the successor of Guru Har Rai Ji?
5. Who was the oldest son of Shah Jahan?
- Dara
- Shujha
- Aurangzeb
- Murad
Answer:
1. Guru Har Rai Ji ascended the Gurgaddi in 1645 A.D.
2. The four places of Punjab visited by Guru Har Rai Ji for preaching Sikhism were Jalandhar and Amritsar.
3. Guru Har Rai Ji blessed his devotee Phul that his descendants would rule.
4. Guru Har Rai Ji nominated Guru Har Krishan Ji as his successor.
5. Dara.
2. Guru Har Krishan Ji was the younger son of Guru Har Rai Ji. His pontificate began in 1661 A.D. Thus, he became the 8th Guru of the Sikhs. At the time of his assumption of Guruship he was only five years old. That is why Guru Har Krishan Ji is also known as the Child Guru (Bal Guru) in Sikh History. Ram Rai, the elder brother of Guru Har Krishan Ji stoutly opposed him. He considered himself to be the real claimant of Guruship. He tried his best to wrest Guruship from his brother but when he did not succeed, he sought help from Aurangzeb, who called Guru Har Krishan Ji to Delhi. Guru Har Krishan Ji went to Delhi in 1664 A.D. He stayed at the house of Mirza Raja Jai Singh. Cholera and small pox had broken out in Delhi in those days. Guru Har Krishan Ji devoted himself to the help of the sick, the poor and the orphAnswer: He himself became a victim of sma – pox and was taken ill. He breathed his last on March 30, 1664 A.D., but befo v that he uttered the words Baba Bakala’ which meant that his successor would found at Bakala.
1. Who was the eighth Guru of the Sikhs?
2. Guru Har Krishan Ji sat on Gurgaddi in ……………
3. Why is Guru Har Krishan Ji called as ‘Ral Guru’?
4. Who was Ram Rai?
5. Which service was rendered by Guru Har Krishan Ji in Delhi?
Answer:
1. Guru Har Krishan Ji was the eighth Guru of the Sikhs.
2. 1661 A.D.
3. Because he was only of .five years when he ascended the Gurgaddi.
4. Ram Rai was the elder brother of Guru Har Krishan Ji.
5. In those days cholera and small-pox had broken out in Delhi. Guru Har Krishan Ji served the Sikhs, the poor and the orphans with open heart.
Guru Tech Bahadur Ji and his Martyrdom:
Note : Read the following passages carefully and answer the questions that follow :
1. Guru Tegh Bahadur Ji was the ninth Sikh Guru. He held the Guruship from 1664 A.D. to 1675 A.D. Guru Tegh Bahadur Sahib undertook tours to various places in and outside Punjab, to spread Sikhism and to remove prevalent blind faiths and superstitions among the masses. At that time, Mughal emperor, Aurangzeb ruled over India. He was a staunch Sunni Muslim. He had spread terror in the whole country with a view to convert Hindus into Muslims. Kashmiri Pandits were the worst sufferers of his persecutions. For the protection of Hindu religion, Guru Tegh Bahadur Ji courted martyrdom on 11th November, 1675 A.D. at Delhi. This unique martyrdom of Guru Sahib had far reaching impacts.
It marked the beginning of a new era, not only in the history of Punjab, but also in the history of India. The martyrdom of Guru Tegh Bahadur Ji kindled such a spark, which soon assumed the shape of a big flame, which eventually reduced the powerful Mughal empire to ashes. Guru Tegh Bahadur Ji gave his martyrdom for the protection of the Hindu religion Therefore he is known in History as ‘Hind Di .Chadar’.
1. When dud Guru Tegh Bahadur Ji ascend the Gurgaddi?
2. What were the objectives of the travels of Guru Tegh Bahadur Ji?
3. Which Mughal emperor gave order to martyr Guru Tegh Bahadur Ji?
4. Where was Guru Tegh Bahadur Ji was Martyred?
- Lahore
- Delhi
- Amritsar
- None of the above.

5. Why is Guru Tegh Bahadur Ji called ‘Hind Di Chadar’?
Answer:
1. Guru Tegh Bahadur Ji ascended the Gurgaddi in 1664 A.D.
2.
- To preach Sikhism.
- To remove superstitious prevalent among the people.
3. Mughal emperor Aurangzeb gave order to martyr Guru Tegh Bahadur Ji.
4. Delhi.
5. Because Guru Tegh Bahadur Ji gave his martyrdom for the protection of Hindu religion so he is called as ‘Hind Di Chadar’.
2. The Pandits living in Kashmir were firm believers in their religion and culture. The Hindus all over India revered them. Aurangzeb thought if these Kashmiri Pandits were converted to Islam the Hindus living in other parts of India would readily follow their example. With this object in view Aurangzeb appointed Sher Afghan as the Governor of Kashmir. Sher Afghan forced the Pandits to embrace Islam. He offered them the choice between Islam and death. They were tortured and brutally killed everyday in large numbers. When they found no way out to save their faith, a sixteen member deputation led by Pandit Kirpa Ram met Guru Tegh Bahadur Ji at Chakk Nanaki, (Sri Anandpur Sahib) on 25th May, 1675 A.D. They sought Guru Tegh Bahadur Ji’s help.
1. Who was Sher Afghan?
2. Why was Sher Afghan infamous?
3. Under whose leadership a deputation of Kashmiri Pandits came to Guru Tegh Bahadur Ji for help?
4. At which place the Pandits of Kashmir met Guru Tegh Bahadur Ji
- Lahore
- Amritsar
- Chakk Nanaki
- Jalandhar.
5. What is the modern name of Chakk Nanaki?
Answer:
1. Sher Afghan was the governor of Kashmir.
2. He had inflicted great atrocities on Kashmiri Pandits.
3. A deputation of Kashmiri Pandits under the leadership of Pandit Kjrpa Ram had met Guru Tegh Bahadur Ji at Chakk Nanaki for help.
4. Chakk Nanaki.
5. The modern name of Chakk Nanaki is Sri Anandpur Sahib.
Guru Gobind Singh Ji: The Foundation of Khalsa, his Battles and his Personality:
Note : Read the following passages carefully and answer the questions that follow :
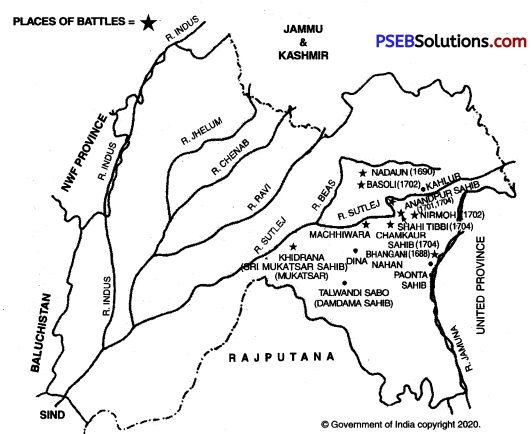
1. The Battle of Bhangani was the first battle fought between Guru Gobind Singh Ji and the Hill Chiefs. It took place on September 22, 1688 A.D. Many factors were responsible for this battle. Firstly, the Hill Chiefs were alarmed to see the military activities of Guru Gobind Singh Ji. Their freedom seemed to be jeopardised. Secondly, the Hill Chiefs deemed the reforms of Guru Gobind Singh Ji an interference in their religious matters. Thirdly, these Hill Chiefs used to harass the Sikh Sangat. Fourthly, the Mughal government was also instigating these Chiefs to take steps against Gum Ji.
The allied forces of Hill Chiefs under the command of Bhim Chand, the ruler of Kahlur and Fateh Shah, the ruler of Kashmir attacked Guru Gobind Singh Ji’s army at Bhangani on September 22, 1688 A.D. Pir Buddhu Shah of Sadhaura rendered valuable help to Guru Gobind Singh Ji in this battle. The Sikhs bravely resisted the allied forces and became victorious in this battle. This victory boosted the morale of the Sikhs and Guru Gobind Singh Ji’s fame reached far and wide. The Hill Chiefs deemed it wise to shun Guru Ji’s opposition and establish amicable relations with him.
1. Which was the first battle to be fought between Guru Gobind Singh Ji and the Hill Chiefs?
2. Write any one cause of the battle of Bhangani.
3. When was the battle of Bbangani fought?
- 1686 AD.
- 1687 A.D.
- 1688 AD.
- 1699 A.D.
4. In the battle of Bhangani who provided help to Guru Gobind Singh Ji?
5. What was the significance of the victory of Sikhs in the battle of Bhangani?
Answer:
1. The first battle to be fought between Guru Gobind Singh Ji and the Hill Chiefs is the battle of Bhangani.
2. The Hill Chiefs were alarmed on seeing the war preparations of the Sikhs.
3. 1688 A.D.
4. In the battle of Bhangani Guru Gobind Singh Ji was provided help by Pir Buddhu Shah.
5. As a result of the victory of the Sikhs in the battle of Bhagani the fame of Gum Gobind Singh Ji spread far and wide.

2. On the day of Baisakhi in 1699 A.D. Guru Gobind Singh Ji held a congregation at Kesgarh at Sri Anandpur Sahib. 80000 Sikhs attended the congregation. When all the people sat down, Guru Ji appeared on the stage. With his sword unsheathed—he spoke, “Is there any Sikh who would sacrifice his life for Dharma?” His words numbed the audience. When Guru Sahib repeated his call for the third time, Bhai Daya Ram Ji offered himself for sacrifice.
Guru Ji repeated this process for four more times. Bhai Dharara Das Ji, Bhai Mohkam Chand Ji, Bhai Sahib Chand Ji and Bhai Himmat Rai Ji were thus selected. Guru Gobind Singh Ji selected the ‘Panj Payaras’, the five beloveds. Guru Sahib gave the Nectar of Immortality (Khande Ka Pahul) to the five beloved ones and then begged to be baptised by them. Guru Sahib gave the name of Khalsa i.e. pure to the love beloved ones. He said Khalsa is in Guru and the Guru is in Khalsa therefore, Guru Gobind Singh Ji is also called ‘Aape Gur Chela’. In this way, Guru Gobind Singh Ji laid the foundation of the Khalsa.
1. What is meant by Khalsa?
2. Who was the first to offer his head to the Guru?
3. Which was the unanimous name given to those who offered their heads?
4. Who is called ‘Aape Gur Chela’?
5. Which of the following offered his head?
- Dharm Das
- Mohkam Chand
- Sahib Chand
- All of the above.
Answer:
1. Khalsa meant pure.
2. Bhai Daya Ram Ji was the first to offer his head.
3. Five beloved ones.
4. Guru Gobind Singh Ji is called ‘Aape Gur Chela’.
5. All of the above.
3. After the creation of the Khalsa in 1899 A.D., people .in a large number had started adopting Sikh religion. This increasing strength of Guru Sahib gave sleepless nights to the Hill Chiefs. Raja Bhim Chand of Kahlur, in whose dominion Sri Anandpur Sahib fell, told Guru Gobind Singh Ji to vacate Sri Anandpur Sahib. Guru Sahib flatly refused to oblige him. He held the view that Guru Tegh Bahadur Ji had purchased that land by. .making proper payment for it. So, Bhim Chand in collusion with some other Hill Chiefs attacked the fort of Sri Anandpur Sahib in 1701 A.D.
The siege continued for days together. Although the number of the Sikhs inside the fort was very small yet they strongly resisted the joint forces of the Hill Chiefs. When the Hill Chiefs lost hope of victory, they compromised with Guru Sahib. This compromise was only a pretense on the part of the Hill Chiefs.
1. When was the first battle of Sri Anandpur Sahib fought?
2. Who was Bhim Chand’?
3. Write anyone cause of the first battle of Sri Anandpur Sahib.
4. Bhim Chand in collusion with some other Hill Chiefs attacked the fort of Sri Anandpur Sahib in …………….
5. What was the result of the first battle of Sri Anandpur Sahib?
Answer:
1. The first battle of Sri Anandpur Sahib was fought in 1701 A.D.
2. Bhim Chand was the ruler of Kahlur.
3. The Hill chiefs were not prepared to see the war preparation of the Sikhs.
4. 1701 A.D.
5. The Hill Chiefs had entered into a treaty with Guru Gobind Singh Ji.
4. The battle of Khidrana was the last decisive battle fought between Guru Gobind Singh Ji and the Mughal forces. After facing many hardships in the forests of Machhiwara, Guru Sahib reached Khidrana. When the Mughal forces came to know of it, the Nawab of Sirhind Wazir Khan planned to attack Khidrana. On 29th December, 1705 A.D., Wazir Khan, under the command of a huge army attacked Guru Sahib at Khidrana. The Sikhs showed exemplary bravery in the battle. They inflicted a crushing defeat on the Mughal forces as a result of which they took to their heels.
In this way, Guru Sahib won a glorious victory in this last battle. In this battle, those 40 Sikhs also fell martyrs who had deserted Guru Sahib in the second battle of Sri Anandpur Sahib. Impressed by the sacrifice made by them, and on the request of their leader Maha Singh, who was struggling with life, Guru Sahib tore the Bedawa, which they had written at Sri Anandpur Sahib. He also gave them the boon of Mukti (salvation).
1. Which was the last battle to be fought between Guru Gobind Singh Ji and the Mughals?
2. Who was the Nawab of Sirhind?
3. Which Sikhs had got martyrdom in the battle of Khidrana?
4. When was the battle of Khidrana fought?
- 1699 A.D.
- 1701 A.D.
- 1703 A.D.
- 1705 A.D.
5. What is the modern name of Khidrana?
Answer:
1. The last battle to be fought between Guru Gobind Singh Ji and the Mughals was the battle of Khidrana.
2. The Nawab of Sirhind was Wazir Khan.
3. In the battle of Khidrana those 40 Sikhs were martyred who had given bed away to Guru Gobind Singh Ji in the second battle of Sri Anandpur Sahib.
4. 1705 A.D.
5. The modern name of Khidrana is Sri Muktsar Sahib.

5. Guru Gobind Singh Ji was a poet and laureate of exceptional order. His poetry is unexcelled for its freshness and vigour. It remains unsurpassed in any language in proclaiming the supreme holiness and majesty of God. The scenes of the battles are recaptured in a very vivid manner. For its intellectual sweep and rhythm, his poetry is so different from the literary creation of the period. In his compositions, Guru Gobind Singh Ji made use of languages like Arabic, Persian, Punjabi, Hindi, Sanskrit etc. Among his compositions Jaap Sahib, Bachitar Natak, Zafamama, Chandi Di Var and Akal Ustat are very prominent.
These compositions are so thrilling that they have the power to infuse a new life even among the dead. It gave the message of universal brotherhood of mankind. It also inspires to boldly face the prepetrators of cruelity.
1. Write the names of any four famous compositions of Guru Gobind Singh Ji.
2. What is Bachitar Natak?
3. Which letter was written by Guru Gobind Singh Ji to Aurangzeb?
4. What was explained in Zafamama?
- The atrocities of Aurangzeb
- The battle between Aurangzeb and Dara.
- The religious policy of Aurangzeb.
- All of the above.
5. Write any one feature of the literature of Guru Gobind Singh Ji.
Answer:
1. The names of four famous compositions of Guru Gobind Singh Ji were Jaap Sahib, Bachitar Natak, Zafamama and Chandi Di Var.
2. Bachitar Natak is the name of autobiography of Gum Gobind Singh Ji.
3. The name of letter written by Gum Gobind Singh Ji to Aurangzeb was Zafamama.
4. The atrocities of Aurangzeb.
5. It gave the message of universal brotherhood of mankind to humanity.
Banda Singh Bahadur:
Note : Read the following passages carefully and answer the questions the follow :
1. Banda Singh Bahadur, whose first name was Lachhman Dev was a resident of Rajauri village in district Poonch of Kashmir. His father was a poor peasant. His heart was moved when he hunted down a pregnant she-deer. As a result he turned a bairagi. He changed his name from Lachhman Dev to Madho Das. He obtained teaching in occultism (Tantric Knowledge) from a saint of Panchvati, named Aughar Nath. Staying there for some time, Madho Das came to Nanded. It was at Nanded that a meeting took place between him and Guru Gobind Singh Ji in 1708 A.D.
A discussion took place between Madho Das and Guru Gobind Ji. In this meeting Madho Das was so much impressed by the personality of Guru Gobind Singh Ji that he became his Banda (slave). Guru Gobind Singh Ji administered him Amrit and gave him a new name—Banda Singh Bahadur. In this way, Banda Bairagi became a Sikh.
1. What was the childhood name of Banda Singh Bahadur?
2. Which incident had a deep impact on the mind of Banda Singh Bahadur?
3. At which place the meeting between Guru Gobind Singh Ji and Banda Singh Bahadur were held?
4. When was a meeting held between Guru Gobind Singh Ji and Banda Singh Bahadur?
- 1705 A.D.
- 1706 A.D.
- 1707 A.D.
- 1708 A.D.
5. How did Banda Bairagi become a Sikh?
Answer:
1. The childhood name of Banda Singh Bahadur was Lachhman Dev.
2. By hunting she deer which was pregnant had a deep impact on the mind of Banda Singh Bahadur.
3. Guru Gobind Singh Ji and Banda Singh Bahadur had met at Nanded.
4. 1708 A.D.
5. Guru Gobind Singh Ji had baptised Madho Das. Thus Banda Bairagi had become a sikh.
2. Wazir Khan, the Faujdar of Sirhind had got the two younger sons, Zorawar Singh and Fateh Singh, of Guru Gobind Singh Ji killed by bricking them alive in the wall. So, Banda Singh Bahadur wanted to teach him such a lesson which should be remembered by the Muslims for a long time. On May 12, 1710 A.D., Banda Singh Bahadur attacked the army of Wazir Khan at Chapar Chiri.
The Sikhs massacred the Muslims to such an extent that they shuddered at the very thought of it. Wazir Khan was killed and hanged on a tree upside down. Massacre stalked the whole Sirhind on May 14, 1710 A.D. This glorious conquest further boosted the morale of the Sikhs.
1. Who was Wazir Khan?
2. Why did Banda Singh Bahadur attack Sirhind?
3. At which place Wazir Khan was killed by the Sikhs?
4. When was the battle of Chapar Chiri fought?
- 1706 A.D.
- 1708 A.D.
- 1709 A.D.
- 1710 A.D.
5. Who became victorious in the battle of Chapar Chiri?
Answer:
1. Wazir Khan was the Nawab of Sirhind.
2. Banda Singh Bahadur wanted to avenge the martyrdom of two younger sons of Guru Gobind Singh Ji who were bricked alive in a wall at Sirhind.
3. Wazir Khan was killed at Chapar Chiri by the Sikhs.
4. 1710 A.D.
5. The Sikhs became victorious in the battle of Chapar Chiri.

3. Abdus-Samad-Khan besieged Banda Singh Bahadur at Gurdas Nangal in April 1715 A.D. This siege continued for eight months. Gradually provisions ran out and condition of the Sikhs grew critical. At this juncture, Baba Binod Singh advised Banda Singh Bahadur to escape from the haveli but Banda Singh Bahadur refused to do so. So, Binod Singh escaped from the haveli with his companions. At last Banda Singh Bahadur had to give in on December 7, 1715 A.D.
1. Who was Abdus Samad Khan?
2. At Gurdas Nangal Banda Singh Bahadur had faced the Mughal forces from which Haveli?
3. For what time the battle of Gurdas Nangal lasted?
4. Which companion of Banda Singh Bahadur had left him during the battle of Gurdas Nangal?
5. When was Banda Singh Bahadur arrested?
- 1705 AJD.
- 1710 A.D.
- 1711 A.D.
- 1715 A.D.
Answer:
1. Abdus Samad Khan was the Subedar of Lahore.
2. At Gurdas Nangal Banda Singh Bahadur had faced the Mughal forces from the haveli of Duni Chand.
3. The battle of Gurdas Nangal lasted for 8 months.
4. During the battle of Gurdas Nangal Baba Binod Singh, a companion of Banda Singh Bahadur had left him.
5. 1715 A.D.
Abdus Samad Khan, Zakariya Khan and Mir Mannu: Their Relations with the Sikhs:
Note: Read the following passages carefully and answer the questions the follow:
1. After the issuance of the royal edict, Abdus Samad Khan had started torturing the sikhs in various ways. Hundreds of innocent Sikhs were daily arrested and brought to Lahore. They were tempted to embrace Islam in exchange for their life but the Guru’s Sikhs preferred death to this type of life. The executioners killed such Sikhs after subjecting them to untold tortures. In order to escape this bloody policy of Abdus Samad Khan, many Sikhs took shelter in the Lakhi jungles and in the Shivalik hills. There they had to face many hardships. They had to go without food for days together or feed on tree leaves and roots.
The Mughal officials started committing harshness on women and children, who were left behind. In this way during the early years of Abdus Samad Khan’s rule, this policy paid rich dividends. Feeling happy with him Farrukh Siyar honoured him with the title of “Sword of the State”.
1. Who was Abdus Samad Khan?
2. After the issuance of the royal edict …………… had started torturing the sikhs daily martyred?
3. Where were Sikhs daily martyred?
4. What steps were taken by the Sikhs to escape the tyranny of Abdus Samed Khan?
5. With which title Farrukh Siyar honoured Abdus Samed Khan?
Answer:
1. Abdus Samed Khan was the Subedar of Lahore.
2. Abdus Samad Khan.
3. The Sikhs were daily martyred at Lahore.
4. To escape the tyranny of Abdus Samad Khan the sikhs took shelter in Lakhi jungles and Shivalik Hills.
5. Farrukh Siyar had honoured Abdus Samad Khan with the title of ‘Sword of the State’.
2. Zakariya Khan was greatly disturbed due to the growing activities of the Sikhs. He raised the slogan of ‘Jihad’ to crush the Sikhs. As a result, thousands of Muslims gathered under his banner. The command of this army was entrusted to Inayatulla Khan. On the auspicious day of Id, they were given a Haidri flag and it was proclaimed that God would certainly bestow victory on those who fought under this flag. When the Sikhs learnt about it they once again went to their hideouts. One day about seven thousand Sikhs suddenly attacked these Ghazis and caused havoc in their ranks. Thousands of Ghazis were killed. Besides, the Sikhs plundered their possessions.
1. Who was Zakariya Khan?
2. What is meant by Jihad?
3. Who was given the command of Haidri flag?
4. Who was the Subedar of Punjab at the time of the incident of Haidri flag?
- Abdus Samad Khan
- Zakariya Khan
- Mir Mannu
- Ahmad Shah Abdali.
5. Where did the Sikhs took shelter?
Answer:
1. Zakariya Khan was the Subedar of Lahore.
2. Jihad meant religious war.
3. The command of Haidri flag was given to Inayatulla Khan.
4. Zakariya Khan.
5. The Sikhs took shelter in forests and hills.

3. The compromise with the Mughals gave the Sikhs a golden opportunity to organise their power. Nawab Kapoor Singh sent a message to the Sikhs that they should return to their homes from their hideouts in jungles and hills. Thus, the two decade old struggle between the Mughals and Sikhs came to an end. The Sikhs heaved a sigh of relief. In order to strengthen the power of the Sikhs Nawab Kapoor Singh organised them in two groups in 1734 A.D.
These groups were known as Buddha Dal and Taruna Dal. The Sikhs above the age of 40 were recruited in the Buddha Dal and below the age of 40 in the Taruna Dal. The Taruna Dal was further divided into five groups. Each group comprised 1300 to 2000 Sikhs and had its own leader and banner. The Buddha Dal looked after the religious places and the Taruna Dal fought with the enemies.
1. When was a pact signed between the Mughals and the Sikhs?
2. Who was the Subedar of Punjab when a pact was signed between the Mughals and the Sikhs?
- Ahmad Shah Abdali
- Mir Mannu
- Zakariya Khan
- None of these.
3. Who was Nawab Kapoor Singh?
4. When was Buddha Dal and Taruna Dal formed?
5. Who were recruited in the Buddha Dal and Taruna Dal?
Answer:
1. A pact was signed between the Mughals and the Sikhs in 1733A.D.
2. Zakariya Khan.
3. Nawab Kapoor Singh was a prominent sikh leader of the 18th centuiy.
4. Buddha Dal and Taruna Dal were formed in 1734 A.D.
5. The Sikhs above the age of 40 were recruited in the Buddha Dal and below the age of 40 in the Taruna Dal.
4. The martyrdom of Bhai Mani Singh Ji occupies a significant place in the Sikh History. Because of his matchless service to the Sikh Panth, he was greatly respected by the Sikhs. He had been the Head Priest of Harmandir Sahib since 1721 A.D. The Sikhs were greatly perturbed when the soldiers of Zakariya Khan occupied Harmandir Sahib and established army posts to prevent the entry of the Sikhs. In 1738 A-D. Bhai Mani Singh Ji requested Zakariya Khan to allow the Sikhs to enter the Harmandir Sahib on the Diwali festival, he would offer him Rs. 5000.
Zakariya Khan readily accepted the offer. In fact, he hatched a plan. According to this plan he wanted to attack suddenly and completely decimate the Sikhs who were supposed to gather at Amritsar on Diwali.
1. Who was Bhai Mani Singh Ji?
2. To whom Bhai Mani Singh Ji requested to give the Sikhs permission to celebrate Diwali at Amritsar?
3. Bhai Mani Singh Ji offered what amount to Zakariya Khan in case of allowing the Sikhs to enter Amritsar.
- Rs. 2000
- Rs. 3000
- Rs. 4000
- Rs. 5000.
4. When was Bhai Mani Singh Ji martyred?
5. What was the result of the martyrdom of Bhai Mani Singh Ji?
Answer:
1. Bhai Mani Singh Ji was the Head Priest of Harmandir Sahib from 1721 A.D.
2. He requested Zakariya Khan, the Subedar of Lahore.
3. Rs. 5000.
4. Bhai Mani Singh Ji was martyred in 1738 A.D.
5. It boosted the morale of the Sikhs.
5. With a view to decimate the Sikhs, Yahiya Khan and Lakhpat Rai raised a huge army. This army, unexpectedly, besieged 15,000 Sikhs at Kahnuwan. The Sikhs escaped from there and took shelter in the hills of Basoli. The Mughal soldiers gave them a hot chase. Here the Sikhs were trapped in a difficult situation. On one side there were high hills, while on the other the river Ravi was in full spate. The Mughal soldiers were chasing them from behind while in front they were faced by the Hill Chiefs and those people, who were their bitter enemies.
The Sikhs were short of food-stuffs. Owing to the shortage of fodder, the horses too were suffering from starvation. In this attack, 7000 Sikhs were martyred and 3000 arrested. These Sikhs were martyred at Lahore. It was the first occasion in Sikh history, when the Sikhs suffered such a heavy loss of life. That is why this event is known as first Ghallughara or small holocaust in history.
1. When did first holocaust take place?
2. Who was the Subedar of Lahore at the time of first holocaust?
3. How many Sikhs were martyred in the first holocaust?
4. Sikhs were arrested during the first holocaust.
5. The first holocaust was known by which other name?
Answer:
1. The first holocaust took place in May 1746 A.D.
2. At the time of the first holocaust Yahiya Khan was the Subedar of Lahore.
3. In the first holocaust 7000 Sikhs were martyred.
4. 3000
5. The first holocaust was known as chotta Ghallughara.
Rise of the Dal Khalsa and its Mode of Fighting:
Note: Read the following passages carefully and answer the questions that follow :
1. When the persecution of the Sikhs by Zakariya Khan failed to crush the power of the Sikhs, he compromised with the Sikhs in 1733 A.D. So the Sikhs got a golden opportunity to organise their power. In 1734 A.D. Nawab Kapoor Singh, by merging all small Jathas organised them into two chief Dais. These Dais were named Buddha Dal and Taruna Dal. In the Buddha Dal, Sikhs above 40 years of age were recruited. The function of this Dal was to look after the religious places and to propagate Sikh religion. The chief function of the Taruna Dal was to defend the community and to fight with the enemies.
The Taruna Dal was further divided into five Jathas and each Jatha was placed under an experienced Sikh Jathedar. Each Jatha comprised 1300 to 2000 young men. Each Jatha had its flag and drum. Although, Nawab Kapoor Singh was entrusted with the leadership of Buddha Dal, he acted as a common link between the two Dais. After having been united into two Dais the Sikhs were able to intensify their activities against the government.
1. Who was Zakariya Khan?
2. When was Buddha Dal and Taruna Dal formed?
3. Who formed Buddha Dal and Taruma Dal?
- Banda Singh Bahadur
- Nawab Kapoor Singh
- Guru Gobind Singh Ji
- None of these.
4. Who were included in the Taruna Dal?
5. Who led the Buddha Dal?
Answer:
1. Zakariya Khan was the Subedar of Lahore.
2. Buddha Dal and Taruna Dal was formed in 1734 A.D.
3. Nawab Kapoor Singh. 5:
4. In Taruna Dal the Sikhs below the age of 40 were included.
5. Buddha Dal was led by Nawab Kapoor Singh.

2. On 29th March, 1748 A.D. on the day of Baisakhi the Sikhs gathered at Amritsar. Nawab Kapoor Singh suggested that in view of the hard time ahead, there was a great need for unity and strength of the Panth, Keeping this objective in view, the Dal Khalsa was organised on this day. 65 Sikh Jathas were merged into 12 Jathas. Each Jatha had its own separate leader and flag. Sardar Jassa Singh Ahluwalia was appointed the Supreme Commander of the Dal Khalsa. Every Sikh, who had faith in the principles of Guru Gobind Singh Ji was considered to be the member of the Dal Khalsa.
It was imperative for every Sikh to join the Dal Khalsa to face the enemy. It was expected of every Sikh who joined the Dal Khalsa to be expert in both horse-riding and use of weapons. Every member of the Dal Khalsa was at full liberty to join any Jatha. At the time of war, one of the 12 Sardars was selected the Chief of the Dal Khalsa and the other Sardars complied
with his orders.
1. By whom was Dal Khalsa established?
2. When was Dal Khalsa established?
- 1733 A.D.
- 1734 A.D.
- 1738 A.D.
- 1748 A.D.
3. Who was S. Jassa Singh Ahluwalia?
4. Who could be recruited in the Dal Khalsa?
5. Write any one feature of the Dal Khalsa.
Answer:
1. Dal Khalsa was established by Nawab Kapoor Singh.
2. 1748 A.D.
3. S. Jassa Singh Ahluwalia was the Supreme Commander of the Dal Khalsa.
4. In Dal Khalsa every Sikh who had faith in the principles of Guru Gobind Singh Ji could join it.
5. Cavalry was the most important organ of the army of the Dal Khalsa.
Social and Economic Conditions of the Punjab under the Mughals:
Note : Read the following passages carefully and answer the questions the follow :
1. In the Mughal period, it wasnot the responsibility of the government to impart education to the people. The Hindus received their early education in the temples, while the Muslims received*! in the mosques. The pupils were also given education about their religions, ’JThe Hindus took more interest in education than the Muslims. No fee was charged from the students. After the completion of studies, the pupils would give some offerings to the teachers. There were centres of higher education at places like Lahore, Multan, Sialkot, Jalandhar, Sultanpur, Batala, Ambala, Sirhind in Punjab. The government would give them financial aid. Dining this period no attention was paid to women’s education. Only a few women of upper class families got education. Private arrangement for their education was made at homes.
1. Why was education not developed during the Mughal times?
2. During the Mughal period the Hindus and the Muslims get their early education from where?
3. Write any one feature of the prevelent education during the Mughal times.
4. During the Mughal times what was the status of women education.
5. During the Mughal times the pupils would give some to the teachers after the completion of their studies.
Answer:
1. Because it was not the responsibility of the government to provide education during the Mughal times.
2. During the Mughal times the Hindus ’got their early education in temples and the Muslims got their early education in mosques.
3. At that times no fee was charged from the students.
4. No attention was paid to the women education during the Mughal times.
5. offerings.
2. The chief occupation of the people of Punjab during the Mughal period was agriculture. 80% population of the Punjab was engaged in this occupation. The reason behind this was that the land of Punjab was very fertile and there was no shortage of means of irrigation. The Mughal emperors were well aware of the fact that the prosperity of the empire depended on the economic condition of the. farmers. So, they paid special attention to encourage agriculture. In 1581 A.D., ‘Zabti system’ was enforced in Punjab. Under this system the cultivable land in the Punjab was measured.
On the basis of its fertility, it was classified as Polz, Parauti, Chachar and Banjar. The government would determine its land revenue on the basis of the fertility of the soil, convenience of irrigation and average output of the previous decade. The maximum revenue of the government was one-third. The government collected its land revenue in kind or cash according to the convenience of the farmers.
1. What was the chief occuption of the people of Punjab during the Mughal period?
2. During the Mughal times what % of people depended upon agriculture?
3. What is meant by Zabti system?
4. Write any two features of agriculture during the Mughal period.
5. How did the government collected its revenue from the farmers during the Mughal times?
Answer:
1. The chief occupation of the people of Punjab during the Mughal period was agriculture.
2. 80%.
3. Zabti system meant the measurement of the cultivated land.
4. The government would determine its land revenue on the basis of fertility of the soil, irrigational facilities and average output of the previous decade.
5. The government collected its land revenue either in kind or in cash taking int6 the convenience of the farmers.

3. Sikhism was founded during the Mughal period,, This religion was founded by Guru Nanak Dev Ji in the 15th century. Guru Nanak Dev Ji condemned the prevailing social evils of the times. He preached the worship of one God and delivered the message of universal brotherhood of*mankind. He founded Sangat and Pangat institutions. The doors of his religion were open for people of all castes and creeds. He showed the right path of knowledge to the people who were groping in the darkness. His nine successors carried forward his message!
The policy of religious tolerance of Mughal emperor Akbar provided a golden opportunity for the Sikh religion to prosper. Tension between the Mughals and the Sikhs started with accession of Mughal emperor Jahangir. The Sikhs were incited due to the martyrdom of Guru Aijan Dev Ji in 1606 A.D. and of Guru Tegh Bahadur Ji in 1675 A.D. To confront the cruelties of the Mughals, Guru Gobind Singh Ji founded Khalsa Panth in 1699 A.D. The foundation of Khalsa started a new era in the history of Punjab.
1. During which period Sikhism was born?
2. Who was the founder of Sikhism?
3. What do you mean by ‘Sangat’ and ‘Pangat’?
4. When was Guru Tegh Bahadur Ji was martyred?
- 1605 A.D.
- 1606 A.D.
- 1665 A.D.
- 1675 A.D.
5. When was Khalsa Panth founded?
Answer:
1. Sikhism was founded during the Mughal period.
2. Guru Nanak Dev Ji was the founder of Sikhism.
3.
- Sangat means that congregation which listens to the hymns of the Guru.
- Pangat means a group of people sitting in a queue to partake langar.
4. 1675 A.D.
5. Khalsa Panth was founded in 1699 A.D. by Guru Gobind Singh Ji.
Invasions of Ahmad Shah Abdali and Disintegration of Mughal rule in the Punjab:
Note: Read the following passages carefully and answer the questions the follow :
1. Ahmad Shah Abdali ruled from 1747 A.D. to 1772 A.D. He invaded Punjab eight times, during his rule from 1747 to 1767 A.D. In 1752 A.D. after defeating the Mughal Governor, Mir Mannu, he annexed Punjab to Afghanistan. Ahmad Shah Abdali and the Governors appointed by him committed innumerable atrocities on the Sikhs. In the big holocaust of 1762 A.D., Abdali brutally martyred a large number of Sikhs. Despite all this, the Sikhs stood firm like a rock.
Through guerilla warfare they never allowed any sigh of relief to Abdali. In 1765 A.D. the Sikhs took possession of Lahore and declared their independence. Despite his best efforts Abdali had failed to crush the power of the Sikhs.
1. Who was Ahmad Shah Abdali?
2. When did Ahmad Shah Abdali became the king of Afghanistan.
- 1747 A.D.
- 1748 A.D.
- 1752 A.D.
- 1767 A.D.
3. How many times Ahmad Shah Abdali invaded Punjab?
4. When did Wadda Ghallughara take place?
5. Why did Ahmad Shah Abdali fail to crush the Sikhs? Write any one cause.
Answer:
1. Ahmad Shah Abdali was the rdler of Afghanistan.
2. 1747 A.D.
3. Ahmad Shah Abdali invaded Pui\jab for the eight times.
4. Wadda Ghallughara take place in 1762 A.D.
5. The determination of the Sikhs was very strong.
2. Ahmad Shah Abdali reached Delhi in January 1757 A.D. None resisted Abdali in Delhi. In Delhi, he looted enormously. Afterwards, he looted Mathura and Brindaban. Then he marched towards Agra but owing to the outbreak of cholera in the army, he decided to go back to Kabul. On reaching Punjab, he made his son Timur Shah, the Governor of Punjab. He ordered Timur Shah to teach the Sikhs a lesson for their activities. In order to crush the power of the Sikhs, he sent an army to Amritsar under the command of Jahan Khan. A fierce battle was fought near Amritsar between the Afghans and the Sikhs. In this battle, the Sikh leader Baba Deep Singh Ji displayed unparalleled heroism.
As tradition goes, he continued to fight the enemy even after his head was severed. He breathed his last after reaching Harmandir Sahib on November 11, 1757 A.D. The martyrdom of Baba Deep Singh Ji infused a new spirit among the Sikhs. The Sikhs started looting the adjoining areas of Lahore. It frightened the Afghans, so much that the gates of Lahore city were closed an hour before nightfall.
1. In 1757 A.D. Ahmad Shah Abdali looted the which cities of India?
2. Why Ahmad Shah Abdali returned from Agra?
3. Who was Timur Shah?
4. When and where did Baba Deep Singh Ji got martydom?
5. The martyrdom of Baba Deep Singh Ji infused a new mong the Sikhs.
Answer:
1. In 1757 A.D. Ahmad Shah Abdali looted the Indian cities of Delhi, Mathura, Brindaban and Punjab.
2. Ahmad Shah Abdali had returned from Agra because cholera had spread in that city.
3. Timur Shah was the son of Ahmad Shah Abdali,
4. Baba Deep Singh Ji got martyrdom in 1757 A.D. at Amritsar.
5. spirit.
3. On 14 January, 1761 A.D. the Marathas attacked the army of Abdali. This was a fearful battle. At the beginning of the battle the Marathas seemed to have the odds in their favour. But when Vishwas Rao was killed by a bullet the whole situation was easily reversed. Sadashiv Rao Bhau got down from his elephant to express sorrow. When the Maratha soldiers saw his palanquin empty on the elephant they thought he had also been killed.
As a result panic spread amongst the Maratha soldiers. Abdali’s soldiers grabbed this golden opportunity and followed them and caused them heavy losses. In this battle nearly all important Maratha leaders and 28,000 Maratha soldiers were killed. Thousands of Maratha soldiers were wounded and thousands were taken prisoners.
1. When was the third battle of Panipat fought?
2. Between whom the third hattle of Panipat was fought?
- Sikhs and Marathas
- Marathas and Abdali
- Sikhs and Abdali
- None of these.
3. Who was Vishwas Rao?
4. Who was Sadashiv Rao Bhau?
5. Write any one result of the third battle of Panipat.
Answer:
1. The third battle of Panipat was fought on 14th January, 1761 A.D.
2. Marathas and Abdali.
3. Vishwas Rao was the son of Peshwa Balaji Baji Rao.
4. Sadashiv Rao Bhau was the commander in chief of the Marathas during the third battle of Panipat.
5. It resulted in the heavy loss of the Marathas in men and money.

4. Ahmad Shah Abdali captured Lahore without any resistance. Then, he proceeded towards Jandiala. On reaching here, he received the information that the Sikhs had gone from there and gathered at a village Kup near Malerkotla. So, he hurriedly rushed towards Malerkotla. He ordered Zain Khan, the Governor of Sirhind, to reach there with his forces. These joint forces suddenly attacked the Sikhs at village Kup on 5th February, 1762 A.D. At that time the Sikhs were taking their families to some safe place. Their arms and rations were lying at village Garma, which was at a distance of 6 kilometres from there.
The Sikhs while forming a safety circle around their women and children started resisting Abdali’s soldiers. The Sikhs suffered heavy losses in the battle for want of arms. In this battle 25,000 to 30,000 Sikhs were massacred. This loss was too much for the Sikhs. That is why this incident is known as Wadda Ghallughara (Great Holocaust) in the Sikh history.
1. When and where did Wadda Ghallughara take place?
2. Who was responsible for Wadda Ghallughara?
3. Who was the Subedar of Sirhind at the time of Wadda Ghallughara?
4. What were the causes of heavy loss of the Sikhs during Wadda Ghallughara?
5. The Sikhs suffered in the battle.
Answer:
1. Wadda Ghallughara took place on 5th February, 1762 A.D. at Kup.
2. Ahmad Shah Abdali was responsible for Wadda Ghallughara.
3. Zain Khan was the Subedar of Sirhind at the time of Wadda Ghallughara.
4. The Sikhs had very few weapons with them.
5. Heavy losses.
Origin and Growth of the Sikh Misls and their nature of Organization:
Note: Read the following passages carefully and answer the questions the follow :
1. Nawab Kapoor Singh was the founder of the Faizalpuria Misl. First of all, he occupied a village named Faizalpur near Amritsar. The name of this village was changed into Singhpur. Therefore, Faizalpuria Misl is also known as Singhpuria Misl. Kapoor Singh was very brave and fearless. It was Bhai Mani Singh, who baptised him. Soon, he became a famous Sikh leader. In 1733 A.D., he received the title of Nawab and an estate which could fetch Rs. 1 lakh as annual income from the Mughal Governor of Punjab, Zakariya Khan. With a view to organise the Sikh power in .1734 A.D.
Nawab Kapoor Singh formed two ‘Jathas’ namely the Buddha Dal and the Taruna Dal. He led both the Dais very ably and intelligently. By founding the Dal Khalsa in 1748 A.D., he rendered a yeoman’s service to the Sikh Panth. In fact, the contribution of Nawab Kapoor Singh to the growth and organisation of the Sikh Panth is remarkable. He passed away in the year 1753 A.D.
1. Who was the founder of the Faizalpuria Misl?
2. By what other name Faizalpuria Mi$l was known?
3. In which year and from when S. Kapoor Singh received the title of Nawab?
4. Write any one achievement of Nawab Kapoor Singh.
5. Dal Khalsa was established in ………………
Answer:
1. The founder of the Faizalpuria Misl was Nawab Kapoor Singh.
2. Faizalpuria Misl was also known as Singhpuria Misl.
3. S. Kapoor Singh was given the title of Nawab in 1733 A.D. by Mughal Subedar Zakriya Khan.
4. He had organised the Buddha Dal and the Taruna Dal in 1734 A.D.
5. 1748 A.D.
2. The founder of the Ahluwalia Misl was Jassa Singh Ahluwalia. He was the inhabitant of Ahlu village near Lahore. So, this Misl came to be known as the Ahluwalia Misl. Jassa Singh was still very young when his father passed away. 3o, Jassa Singh’s maternal uncle, Bhag Singh brought him up. Nawab Kapoor Singh was greatly impressed by the personality of Jassa Singh. He kept Jassa Singh with him and brought him up as his own son.
Because of his qualities Jassa Singh soon became a famous leaded of the Sikhs. In 1739 A.D. under the leadership of Jassa Singh, the Sikhs attacked Nadir Shah’s army and robbed it of its wealth. In the small holocaust of 1746 A.D. Jassa Singh showed many feats of bravery. As a result, his name and fame spread, far and wide. When the Dal Khalsa was organised in 1748 A.D., Jassa Singh Ahluwalia was made its Commander-in-Chief. By leading the Dal Khalsa ably, he rendered a great service to the Sikh Panth.
Under the leadership of Jassa Singh Ahluwalia, the Sikhs conquered Lahore in 1761 A.D. It was the most significant conquest of the Sikhs. For this reason, the Khalsa Panth honoured S. Jassa Singh Ahluwalia by conferring on him the title of Sultan-ul-Quam. In 1762 A.D., at the time of Great Holocaust, Jassa Singh fought very bravely against the forces of Ahmad Shah Abdali. In 1764 A.D. Jassa Singh conquered Sirhind and put its ruler, Zain Khan to death. In 1778 A.D. Jassa Singh captured Kapurthala and made it the capital of the Ahluwalia Misl.
1. Who was Jassa Singh Ahluwalia?
2. Why was Ahluwalia Misl so called?
3. What was the name of the capital of Jassa Singh Ahluwalia?
4. Write any one achievement of Jassa Singh Ahluwalia.
5. When was Kapurthala occupied by Jassa Singh Ahluwalia?
- 1761 A.D.
- 1768 A.D.
- 1778 A.D.
- 1782 A.D.
Answer:
1. Jassa Singh Ahluwalia was the founder of Ahluwalia Misl.
2. Ahluwalia Misl was so called because Jassa Singh Ahluwalia belonged to village Ahlu.
3. Kapurthala was the capital of Jassa Singh Ahluwalia.
4. He had ably led the Dal Khalsa.
5. 1778 A.D.
3. Jassa Singh was the most famous leader of the Ramgarhia Misl. Under his leadership, this Misl reached the pinnacle of glory. Jassa Singh at first served under the Faujdar of Jalandhar Doab, Adina Beg. In October 1748 A.D. the forces of Mir Mannu and Adina Beg besieged 500 Sikhs in a surprise attack in the Ram Rauni fort. Jassa Singh’s blood boiled on seeing his brethren in trouble. He left Adina Beg’s job and came to the rescue of the Sikhs. The result of his co-operation was that the lives of 300 Sikhs could be saved. Pleased over it, the Sikhs handed over the Ram Rauni fort to Jassa Singh. Jassa Singh named the fort Ramgarh. From this the Misl came to be known as Ramgarhia Misl.
Taking advantage of the disturbed condition after the death of Mir Mannu in 1753 A.D., Jassa Singh captured Kalanur, Batala, Hargobindpur, Qadian, Urmur Tanda, Dipalpur, Kartarpur and Haripur. Thus, he largely expanded Ramgarhia Misl. He declared Sri Hargobindpur the capital of the Ramgarhia Misl. Jassa Singh did not have cordial relations with the Ahluwalia and tfie Sukarchakia Misls.
1. Who was Jassa Singh Ramgarhia?
2. What was the name given to Ram Rauni fort by Jassa Singh Ramgarhia?
3. What was the name of the capital of Jassa Singh Ramgarhia?
4. Write any one achievement of Jassa Singh Ramgarhia.
5. Mir Mannu died in ……………..
Answer:
1. Jassa Singh Ramgarhia was the most famous leader of the Ramgarhia Misl.
2. Jassa Singh Ramgarhia gave the name of Ramgarh to the Ram Rauni fort.
3. Sri Hargobindpur was the name of the capital of Jassa Singh Ramgarhia.
4. He saved the Sikhs during the seige of the Mughals of the Ram Rauni fort.
5. 1753 A.D.

4. Ala Singh was the founder of the Patiala House. He was very brave right from the beginning. In 1731 A.D. he gave a crushing defeat to the joint forces of the Faujdars of Jalandhar Doab and Malerkotla. Ala Singh made Bamala the centre of his activities. He founded villages like Longowal, Chhajli, Dirrba and Shoron. During Ahmad Shah Abdali’s first invasion in 1748 A.D., Ala Singh helped the Mughals against him. In view of his services, the Mughal emperor, Mohammad Shah Rangila, presented him a ‘Khillat’ (Robe of Honour). It added to the name and fame of Ala Singh. Soon, Ala Singh defeated the Bhatti brothers who were his bitter enemies and, took possession of their areas of Budhlada, Tohana, Bhattner and Jaimalpur.
In 1761 A.D., Ala Singh helped the Marathas against Ahmad Shah Abdali. Soon, in 1762 A.D. during his 6th invasion Ahmad Shah Abdali attacked Bamala and arrested Ala Singh. Ala Singh saved his life by giving Abdali a huge amount of money. In 1764 A.D. Ala Singh with other leaders of the Dal Khalsa attacked Sirhind. In 1765 A.D., Ahmad Shah Abdali appointed Ala Singh the Governor of Sirhind. The other members of the Dal Khalsa were annoyed with him over this compromise and told him to snap his ties with Ahmad Shah Abdali. But soon after, Ala Singh passed away.
1. Who was Ala Singh?
2. What was the name of the capital of Ala Singh?
3. When was Ala Singh arrested by Ahmad Shah Abdali?
4. Ahmad Shah Abdali had appointed Ala Singh the Subedar of which place?
When was Ala Singh made the Subedar of Sirhind?
- 1748 A.D.
- 1761 A.D.
- 1762 A.D.
- 1764 A.D.
Answer:
1. Ala Singh was the founder of Phulkian Misl in Patiala.
2. Bamala was the capital df, Ala Singh.
3. Ahmad Shah AbdaU had arrested Ala Singh in 1762 A.D.
4. Ahmad Shah Abdali had appointed Ala Singh as the Subedar of Sirhind.
5. 1764 A.D.
Maharaja Ranjit Singh’s Career and Conquests:
Note : Read the following passages carefully and answer the questions the follow :
1. Maharaja Ranjit Singh was born in 1780 A.D. in the family of the Sukarchakia Misl Chief, Mahan Singh. Although Maharaja Ranjit Singh was illiterate yet he had acquired deftness in swordsmanship and horse-riding. He had begun to display feats of bravery right from his childhood. In 1797 A.D. when Ranjit Singh took over the reins of the Sukarchakia Misl, the political situation in the Punjab, was in a state of constant turmoil. It was passing through a dark age. By virtue of his ability and bravery Maharaja Ranjit Singh converted his small state into a vast and powerful empire. Ip this way, Maharaja Ranjit Singh translated the dream of Sikh empire into a reality.
1. Maharaja Ranjit Singh was born in ……………..
2. Maharaja Ranjit Singh belonged to which Misl?
3. What was the political condition of the Punjab in the 18th century?
4. Which werie the two important conquests of Maharaja Ranjit Singh?
5. When did Maharcqa Ranjit Singh die?
Answer:
1. 1780 A.D.
2. Maharaja Ranjit Singh belonged to the Sukarchakia Misl.
3. The political condition of the Punjab in the 18th century was in a dwindling condition.
4. The two important conquests of Maharaja Ranjit Singh were Lahore, and Peshawar.
5. Maharaja Ranjit Singh had died in 1839 A.D.
2. When Ranjit Singh was only 12 years old, his father Mahan Singh died in 1792 A.D. Since Ranjit Singh was only a minor, the task of state administration passed into the hands of his mother, Raj Kaur. Raj Kaur did not have any administrative skills, so she handed over the charge to her favourite, Diwan Lakhpat Rai. In 1796 A.D. when Ranjit Singh was married to Mehtab Kaur, his mother-in-law, Sada Kaur too began to take interest in matters of administration. In this way from 1792 A.D. to 1797 A.D. the administration of Sukarchakia Misl remained in the hands of three persons i.e. Raj Kaur, Diwan Lakhpat Rai and Sada Kaur. So, this period is called the period of the Triune Regency.
1. Who was the father of Maharaja Ranjit Singh?
2. Who was Raj Kaur?
3. With whom was Maharaja Ranjit Singh first married?
4. Mehtab Kaur was related with which Misl?
- Sukarchakia Misl
- Kanahia Misl
- Bhangi Misl
- Ramgarhia Misl.
5. Who was Sada Kaur?
Answer:
1. Mahan Singh was the father of Maharaja Ranjit Singh.
2. Raj Kaur was the name of the mother of Maharaja Ranjit Singh.
3. Maharaja Ranjit Singh was married to Mehtab Kaur for the first time.
4. Kanahia Misl.
5. Sada Kaur was the mother-in-law of Maharaja Ranjit Singh.
3. Before the growth of Ranjit Singh’s power, the Bhangi Misl in the North¬West of the Sutlej river was very powerful. The two most important towns of the Punjab, Lahore and Amyitsar, were under this Misl. Besides these, the areas of Gujarat and Sialkot were also under it. In 1797 A.D., Lahore was jointly being ruled by Chet Singh, Sahib Singh and Mohar Singh, Amritsar by Gulab Singh, Sialkot by Jiwan Singh and Gujarat by Sahib Singh. All these Bhangi rulers were great addicts of ‘bhang (hemp). They spent most of their time in merry¬making. Besides, they had started quarrelling with each other for power. Consequently, the Bhangi Misl had lost much of its previous glory and power. It was heading fast towards its end.
1. Why was Bhangi Misl so called?
2. The Bhangi Misl ruled over which cities?
3. In …………… Lahore was jointly ruled by three Bhangi rulers.
4. What was the nature of the rule of Bhangi rulers?
5. Which Bhangi rulers had started quarrelling with each other?
Answer:
1. The Bhangi Misl was so called because its rulers were addicts of bhang (hemp).
2. The Bhangi Misl ruled over the cities of Lahore, Amritsar, Sialkot and Gujarat.
3. 1797 A.D.
4. The Bhangi rulers used to spent most of their time in merry-making.
5. The ruler of Gujarat Sahib Singh had started fighting with other Bhangi rulers.
4. The founder of the Sukarchakia Misl Charat Singh was the grandfather of Ranjit Singh. He had under him Gujranwala, Eminabad and Sialkot. After the death of Charat Singh in 1774 A.D. he was succeeded by his son, Mahan Singh. He had all the qualities of a great Sardar. He expanded his Misl by conquering the areas of Rasul Nagar and Alipur. After the death of Mahan Singh in 1792 A.D., his son Ranjit Singh became his successor.
Since Ranjit Singh was barely 12 years old at that time, the task of running the administration of the Misl fell into the hands of his mother Raj Kaur, Diwan Lakhpat Rai and mother-in-law, Sada Kaur. When Ranjit Singh grew to be young enough in 1797 A.D. he took over the charge of Sukarchakia Misl independently. He proved to be an able, brave and far-sighted ruler.
1. Who was the founder of Sukarchakia Misl?
2. Which two territories were conquered by Mahan Singh?
3. What was the period of Triune Regency?
4. Ranjit Singh took the independent charge of Sukarchakia Misl in ……………
5. What type of ruler was Maharaja Ranjit Singh?
Answer:
1. The founder of Sukarchakia Misl was Charat Singh.
2. Mahan Singh had conquered Rasul Nagar and Alipur.
3. The period of Triune Regency was from 1792 to 1797 A.D.
4. 1797 A.D.
5. Ranjit Singh proved to be an able, brave and far-sighted ruler.

5. The valley of Kashmir has been famous for its beauty, delicious fruits and prosperous trade since-ancient times. That is why, Maharaja Ranjit Singh wanted to conquer this province. In this regard, he sent two- expeditions to Kashmir in 1813 and 1814 A.D., but both these expeditions failed to achieve the desired objective. Maharaja Ranjit Singh got a new impetus with the conquest of Multan in 1818 A.D. Therefore, in 1819 A.D., he sent a huge force under the command of Misar Diwan Chand, the victor of Multan, to Kashmir. He succeeded in defeating the Afghan Governor of Kashmir, Jabbar Khan.
The conquest of Kashmir added . to the prestige of Maharaja Ranjit Singh. Misar Diwan Chand was honoured with the title of‘Fateh-o-Nusrat Nasib’ (one who is destined to win). The conquest of Kashmir gave a stunning blow to the Afghan power. It boosted the morale of the Sikh forces. Moreover, it proved beneficial to the Maharaja from the commercial point of view.
1. Why did Maharaja Ranjit Singh wanted to conquer Kashmir?
2. When was Rohtas pact signed?
3. Who was the governor of Kashmir at the time first compaign of Maharaja Ranjit Singh?
4. When did Maharaja Ranjit Singh conquer Kashmir?
5. Who was the Governor of Kashmir at the time of its conquest by Maharqja Ranjit Singh?
- Fateh Khan
- Jabbar Khan
- Nusrat Khan
- Diwan Mohkam Chand.
Answer:
1. Maharaja Ranjit Singh wanted to conquer Kashmir because of its splendid beauty and prosperous trade.
2. Rohtas pact was signed in 1813 A.D.
3. Ata Mohammed Khan was the governor of Kashmir at the time of first campaign of Maharaja Ranjit Singh to Kashmir.
4. Maharaja Ranjit Singh had conquered Kashmir in 1819 A.D.
5. Jabbar Khan.
Anglo-Sikh Relations: 1800-1839:
Note: Read the following passages carefully and answer the questions that follow :
1. Maharaja Ranjit Singh wanted to bring all the Sikh states under him. So, he invaded the Malwas region twice in 1806 A.D. and 1807 A.D. He conquered many regions. The conversation between Ranjit Singh and Charles Metcalfe in 1808 A.D. failed. Ranjit Singh attacked Malwa for the third time in 1808 A.D. He had occupied some territories of Malwa and collected Nazrana from the rulers. Now the English started military preparations to make Ranjit Singh accept their conditions. As a results, a treaty was sighed between Ranjit Singh and the English. It was known as the Treaty of Amritsar.
1. When did Maharaja Ranjit Singh attack Malwa for the first time?
- 1805 A.D.
- 1806 AJD.
- 1807 AJD.
- 1808 AU.
2. Why did Maharaja Ranjit Singh attack Malwa?
3. What is meant by Nazrana?
4. Why did the Sardars of Malwa want the help of Britishers?
5. When was the treaty of Amritsar signed between Maharaja Ranjit Singh and the Britishers?
Answer:
1. 1806 A.D.
2. The main objective of these attacks was that Maharaja Ranjit Singh wanted to annex these states into his empire.
3. Nazrana meant the gifts to be given to the Maharaja.
4. The Sardars of Malwa wanted the help of Britishers because they feared that Maharaja Ranjit Singh would annex their states.
5. The treaty of Amritsar was signed between Maharaja Ranjit Singh and the Britishers on 25th April 1809 A.D.
2. The area of Sind was geographically and commercially very significant. So both, Maharaja Ranjit Singh and the British were keen in controlling it. In 1831 A.D. the British sent Alexander Bums to gather information about Sind. In order that Maharaja Ranjit Singh might not develop any doubt, he was invited to Ropar to hold a meeting with Governor-General William Bentinck. This meeting was held on 26th October, 1831 A.D. The Britishers very cleverly kept him absorbed in talks. On the other hand, the English sent Col. Pottinger to sign a treaty with the Amirs of Sind. He succeeded in signing a commercial treaty with Sind in 1832 A.D.
1. Why did Maharaja Ranjit Singh wanted to conquer Sind?
2. Who was Alexander Bums?
3. When did a meeting was held between Maharaja Ranjit Singh and Lord William Bentinck?
4. Where was a meeting held between Maharaja Ranjit Singh and Lord William Bentinck.
- At Ropar
- At Amritsar
- At Lahore
- At Delhi.
5. Who succeeded in entering into a commercial treaty between the British and Sind?
Answer:
1. Maharaja Ranjit Singh wanted to conquer Sind becuase it was geographically and commercially very significant.
2. Alexander bums was a British official who was sent to Sind to gather information about Sind.
3. A meeting was held between Maharaja Ranjit Singh and Lord William Bentinck on 26th October, 1831 A.D.
4. At Ropar.
5. Col. Pottinger succeeded in signing a commercial treaty between the Britishers and Sind.

3. The Britishers wanted to bring Ferozepur under their control. This city was hardly at a distance of 40 miles from Lahore. The English could have a better view of Ranjit Singh’s activities from this place. Besides, the possession of Ferozepur was essential to surround the Punjab. Although the Britishers had been looking towards Ferozepur greedily for a long time,’ they had been postponing its acquisition lest Ranjit Singh should feel annoyed with them.
That is why, the Britishers had been conceding his control over Ferozepur till 1835 A.D. But, by now the situation had changed. -The Britishers did not need Ranjit Singh’s friendship any more. Therefore, they forcibly took possession of Ferozepur in 1835 A.D. In 1838 A.D., the Britishers set up a big military cantonment here. Although Ranjit Singh expressed his resentment over the seizure of Ferozepur and setting up of a military cantonment there by the British, yet they did not bother about it.
1. Why did the Britishers wanted to bring Ferozepur under these control?
2. The possession of ………………. was essential to surround the Punjab.
3. When was Ferozepur occupied by the Britishers?
4. When a military cantonment was established by the Britishers in Ferozepur?
5. What had Maharcga Ranjit Singh yielded on the question of Ferozepur?
Answer:
1. The Britishers wanted to bring Ferozepur under their control because they could have a better view of Ranjit Singh’s activities from this place.
2. Ferozepur.
3. The Britishers had occupied Ferozepur in 1838 A.D.
4. The Britishers had established a military cantonment in 1838 A.D.
5. Yes, the Maharaja Ranjit Singh had yielded to the British on the question of Ferozepur.
Ranjit Singh’s Relations with Afghanistan and his N.W.F. Policy:
Note : Read the following passages carefully and answer the questions that follow :
1. In 1800 A.D., a war of succession for the royal throne had started in Kabul. Shah Zaman was dethroned and Shah Mehmud became the new king of Afghanistan. He ruled only for three years (1800-03 A.D.). In 1803 A.D., Shah Shuja forcibly took possession of the throne from Shah Mehmud. He ruled till 1809 A.D. He proved to be an unworthy king. It led to chaos-in Afghanistan. On finding this golden opportunity, the Afghan Governors of Attock, Kashmir, Multan and Deraj at declared their independence. Maharaja Ranjit Singh also took advantage of the weakness of the Kabul government and took possession of the Afghan areas like Kasur, Jhang, Khushal and Sahiwal. In 1809 A.D. Shah Shuja was dethroned and Shah Mehmud again became the new king of Afghanistan. Since Fateh Khan had rendered every possible help to Shah Mehmud in getting the royal throne, so he appointed him his Prime Minister.
1. In a war of succession for the royal throne had started in Kabul.
2. When did Shah Mehmud become the ruler of Afghanistan for the first time?
3. What type of ruler was Shah Shuja?
4. Who was Fateh Khan?
5. When was Shah Shuja was dethroned?
Answer:
1. 1800 A.D.
2. Shah Mehmud became the ruler of Afghanistan for the first time in 1800 A.D.
3. Shah Shuja was an incompetent ruler.
4. Fateh Khan was the Wazir (Prime Minister) of Shah Mehmud.
5. Shah Shuja was dethroned in 1809 A.D.
2. Maharaja Ranjit Singh decided to teach Fateh Khan a lesson for his deceit. He at once sent Faqir Aziz-ud-Din to take possession of Attock. The ruler of Attock, Jahandad Khan, handed over the area of Attock to the Maharaja in exchange for an estate of Rs. 1 lakh. When Fateh Khan came to know of it, he lost his temper. He handed over the Kashmir administration to his brother, Azim Khan and himself proceeded with a huge army to drive out the Sikhs from Attock. On July 13, 1813 A.D. a fierce battle was fought at a place called Hazro or Haidru, in which Maharaja Raujit Singh inflicted a crushing defeat on Fateh Khan. It was the first battle fought between the Sikhs and the AfghAnswer: This victory gave a severe blow to the power of the Afghans and enhanced the prestige of the Sikhs.
1. Who was Fateh Khan?
2. Who was the ruler of Attock during the times of Maharaja Ranjit Singh?
3. Which was the first battle fought between the Sikhs and the Afghanis?
4. When was the battle of Hazro fought?
- 1811 AJD.
- 1812 A.D.
- 1813 A.D.
- 1814 A.D.
5. Who become victorious in the battle of Hazro.
Answer:
1. Fateh Khan was the wazir of Shah Mehmud, the ruler of Afghanist.
2. Jahandad Khan was the ruler of Attock during the times of Maharaja Ranjit Singh.
3. The battle of Hazro was the first battle to be fought between the Sikhs and the Afghans.
4. 1813 A.D.
5. The Sikhs became victorious in the battle of Hazro.

3. During the period 1827 A.D. to 1831 A.D., Syed Ahmad a religious leader of the Muslims had created disturbance against the Sikhs in Attock and Peshawar. He belonged to Bareilly. He declared, “God has sent me to conquer Punjab and India, and to drive out the Sikhs from the Afghan territories.” Taken in by his utterances, many Afghan Sardars became his disciples. In no time, he was able to organise a big army. It was a challenge to Maharaja Ranjit Singh’s power. The Sikh forces defeated him first at Saidu and then at Peshawar, but fortunately he escaped both the times. Despite these defeats, he continued his struggle against the Sikhs. At last in 1831 A.D., he died at Balakot while fighting against Prince Sher Singh. In this way a big nuisance for the Sikhs was over.
1. Who was Syed Ahmad?
2. Syed Ahmad was the inhabitant of which place?
3. At which two places the sikh forces had defeated Syed Ahmad?
4. Syed Ahmad was killed where and fighting with whom?
5. When was Syed Ahmad killed?
- 1813 A.D.
- 1821 A.D.
- 1824 A.D.
- 1831 A.D.
Answer:
1. Syed Ahmad was a religious leader of the Muslims.
2. Syed Ahmad was the resident of Bareilly.
3. The Sikh forces had defeated Syed Ahmad at Saidu and Peshawar.
4. Syed Ahmad was killed at Balakot while fighting with prince Sher Singh.
5. 1831 A.D.
4. Dost Mohammad Khan wanted to avenge his humiliation suffered at the hands of the Sikhs. On-the other hand, the Sikhs also wanted to consolidate their position in Peshawar. In order to counter the Afghan invasions, Hari Singh Nalwa got a strong fort constructed at Jamraud. In order to check this operation of Hari Singh N.alwa, Dost Mohammad Khan sent a huge army of 20,000 soldiers under the command of his son Mohammad Akbar and Shamsudin.
This army attacked the fort of Jamraud on 28th April, 1837 A.D. Hari Singh Nalwa was then lying seriously ill at Peshawar. When he heared the news of Afghan attack, he with his 10,000 soldiers attacked the Afghans at Jamraftd with a view to teach them a lesson. Although Hari Singh Nalwa was killed in this battle, the Sikhs caused such a havoc among the Afghans that they never turned their face towards Peshawar thereafter.
1. Who was Dost Mohammad Khan?
2. Who built the Jamraud fort?
3. The fort of Jamraud was attacked on …………..
4. Which general of Maharsya Ranjit Singh was martyred in the battle of Jamraud and when?
5. Who became victorious in the battle of Jamraud?
Answer:
1. Dost Mohammad Khan was the ruler of Peshawar.
2. The fort of Jamraud was built by S. Hari Singh Nalwa.
3. 28th April, 1837 A.D.
4. S. Hari Singh Nalwa was martyred in the battle of Jamraud on 30th April, 1837 A.D.
5. In the battle of Jamraud the Sikhs became victorious.
Civil and Military Administration of Ranjit Singh:
Note : Read the following passages carefully and answer the qu estions that follow :
1. Every word uttered by Maharaja Ranjit Singh was deemed law. In order to get cooperation in running the administration, the Maharaja had appointi jd many ministers, of which prominents were the Prime Minister, Foreign Minister , Diwan, Chief Commander and Deorhiwala. It rested on Maharaja’s will to acct 3pt their advice or not. He had also established 12 departments of daftars for the 5 smooth functioning of administration.
1. During the times of Maharaja Ranjit Singh who was tl ie head of the Central Administration?
2. Who was the Prime-Minister of Maharaja Ranjit Singh?
3. Who was the Foreign Minister of Maharaja Ranjit Singh?
- Raja Dhian Singh
- Hari Singh Nalwa
- Faqtiir Aziz-ud-Din
- Diwan Mohkam Chand.
4. How many Daftars were established for the admi nistrative efficiency during the times of Maharaja Ranjit Singh?
5. What is the function of Daftar-i-Taujihat?
Answer:
1. Maharaja himself was the head of Central Administrf ition during the times of Maharaja Ranjit Singh.
2. Raja Dhian Singh was the Prime Minister of Maharaja Ranjit Singh.
3. Faqir Aziz-ud-Din.
4. During the times of Maharaja Ranjit Singh 12 Daftars were established for the administrative efficiency.
5. Daftar-i-Taujihat maintained the account of royal family.

2. With a view to run the administration efficiently, Mahamja Ranjit Singh had divided his kingdom into four Provinces. The main duty of Nazim was to maintain peace and order in the Suba. For this purpose, he was aillowed to maintain a small force. In addition, he supervised the work of other officials of the Suba. He got the orders of Maharaja implemented in the Suba. He decided the civil and criminal cases. He heard the appeals against the decisions, of the Kardars.
He helped the various Suba officials in the collection of land revenue. He also supervised the work of district Kardars. Thus, the Nazim exercised vast powers in his own Suba. But, he had to seek the prior approval of the Maharaja, before taking any crucial decision about his Suba. The Maharaja could change the Nazim, whenever he wanted.
1. The kingdom of Maharaja Ranjit Singh was divided into how many Subas?
2. Write the names of any two Subas of Maharaja Ranjit Singh.
3. Who was the head of the Suba during the times of Maharaja Ranjit Singh?
4. Write any one function of the Nazim?
5. The Maharaja could…………… the Nazim whenever he wanted.
Answer:
1. Maharaja Ranjit Singh had divided his Kingdom into four Subas.
2. The names of the two Subas of Maharaja Ranjit Singh were Suba-i- Lahore and Suba-i-Kashmir.
3. The Nazim was the head of the suba during Maharaja Ranjit Singh’s times.
4. To implement the orders of Maharaja Ranjit Singh under his province.
5. Change.
3. The smallest unit of administration was the village. It was then called Mauza The administration of the village was in the hands of the Panchayat. The Panchayat looked after the people of the village and settled their petty disputes. The people showed great regard for the Panchayat and they mostly accepted its decisions. The Patwari maintained the record of the village land. The Chaudhary would help the government in collecting land revenue. Muqaddam (Lambardar) was head of the village. He worked as a link between the government and the people. The Chowkidar was the watchman of the village. The Maharaja did not interfere in the working of the village.
1. Which was the smallest unit of administration of Maharaja Ranjit Singh?
2. What was village called during the times of Maharaja Ranjit Singh?
3. In whose hands the administration of the village was during the times of Maharaja Ranjit Singh.
4. Who was Muqaddam during the times of Maharaja Ranjit Singh?
5. Who kept the record of village land during the times of Maharaja Ranjit Singh?
- Muqaddam
- Chaudhary
- Patwari
- None of these.
Answer:
1. The smallest unit of administration during the times of Maharaja Ranjit Singh was village.
2. During the times of Maharaja Ranjit Singh the village was called Mauza.
3. During the times of Maharaja Ranjit Singh the village administration was in the hands of the Panchayat.
4. Muqaddam was head of the village.
5. Patwari.

4. During the period of Maharaja Ranjit Singh, the administration of Lahore city was run differently from other cities. The whole city was divided into Mohallas. A Mohalla was under a Mohalladar. The Mohalladar maintained peace and order in his mohalla and looked after the arrangement of cleanliness. The chief official of Lahore city was ‘Kotwal’. Mostly he used to be a Muslim. The chief functions of a Kotwal were to give practical shape to the Maharaja’s orders, to maintain peace in the city, to supervise the work of Mohalladars, to make arrangements for cleanliness in the city, to keep details of the foreign visitors, to supervise trade and industry and to examine weights and measures etc. He used to take necessary action against the guilty persons.
1. Who was the chief official of Lahore city during the times of Maharaja Ranjit Singh?
2. Who was appointed on the post of Kotwal during the times of Maharaja Ranjit Singh?
3. What was the one main function of Kotwal?
4. Who was the head of Mohalla during the times of Maharaja Ranjit Singh?
5. During the times of Maharaja Ranjit Singh the administration of ………………… city was run differently from other cities.
Answer:
1. Dining the times of Maharaja Ranjit Singh the chief official of Lahore city was Kotwal.
2. During the times of Maharaja Ranjit Singh Imam Bakhsh was appointed on the post of Kotwal.
3. To maintain peace in the city.
4. Mohalladar was the head of Mohalla dining the times of Maharaja Ranjit Singh.
5. Lahore.
5. Fauj-i-Khas was the most important and the powerful organ of Maharaja Ranjit Singh’s army. It was trained under the command of General Ventura. It consisted of four battalions of infantry, two regiments of cavalry, and a troop of artillery. The artillery of Fauj-i-Khas was under the command of General Illahi Bakhsh. It was trained and disciplined strictly on European pattern. In it, very selected soldiers were recruited. Their weapons and horses were, also, of the superior type. That is why this army was called Fauj-i-Khas. It had a separate flag and emblem. It used French words of command. It grew to be the best organised section of the regular army. Even the European officers were amazed to see its performance.
1. Which was the most important and powerful organ of Maharaja Ranjit Singh’s army?
2. Who was General Ventura?
3. Under whose command was the artillery of Fauj-i-Khas?
4. Write any one feature of Fauj-i-Khas.
5. Fauj-i-Khas used ……………. words of command.
Answer:
1. Fauj-i-KhaS was the most important and powerful organ of Mahara Ranjit Singh’s army.
2. Fauj-i-KhaS was trained under the command of General Ventura
3. The artillery of Fauj-i-Khas was under the command of General Illahi Bakhsh.
4. It was trained and disciplined strictly on European pattern.
5. French.
Character and Personality of Maharaja Ranjit Singh:
Note: Read the following passages carefully and answer the questions that follow :
1. Maharaja Ranjit Singh had an unshakable faith in Sikhism. Before starting his routine work, he used to listen to the recitation of Gurbani of Guru Granth Sahib Ji and the Kirtan. He never took any big decision or launched upon any undertaking without seeking guidance from Guru Granth Sahib. After each victory, the’Maharaja paid a thanks giving visit to the Darbar Sahib, Amritsar, and made costly offerings. He spent considerable sums of money on the maintenance of Gurdwaras. He called his government as Sarkar-i-Khalsa and liked to be addressed as Singh Sahib instead of Maharaja.
He considered himself to be the Kukar at the door of the Guru and the Panth. He took pride in proclaiming himself to be the mere drum (Ranjit Nagara) of Guru Gobind Singh. He issued coins in the name of Guru Nanak Dev Ji and Guru Gobind Singh Ji. The words ‘Nanak Sahai’ and ‘Gobind Sahai’. were inscribed on them. The royal seal of Maharaja Ranjit Singh was engraved with the words Akal Sahai.
1. Maharaja Ranjit Singh had unshakable faith in Sikhism. Give any one example.
2. What is meant by ‘Kukar’?
3. Maharaja Ranjit Singh called his government by which name?
4. Which words were inscribed on the royal seal of Maharaja Raqjit Singh?
5. The words ………….. and …………. were inscribed on coins.
Answer:
1. Before starting his routine work, he used to listen to the recitation of Gurbani of Guru Nanak Sahib Ji and Kirtan.
2. Kukar meant slave or servant.
3. Maharaja Ranjit Singh called his government as Sarkar-i-Khalsa.
4. ‘Akal Sahai’ were the words inscribed on the royal seals of Maharaja Ranjit Singh.
5. Nanak Sahai, Goind Sahai.

2. Although Ranjit Singh was a staunch Sikh, yet he was liberal towards other religions. He kept religious discrimination and communalism at an arm’s length. He knew very well that for the establishment of a strong and enduring empire, the co-operation of people of different religions was essential. By his policy of tolerance, he succeeded in winning over the hearts of the people of different religions. In his empire jobs were given on the basis of merit.
In his court, the Sikhs, Hindus, Muslims, Dogras and Europeans were appointed to the high posts without any discrimination of caste, creed or nationality. For instance, his Foreign Minister Faqir Aziz-ud-Din was a Muslim, his Prime Minister, Dhian Singh was a Dogra, his Diwan Bhiwani Das and his Commander Misar Diwan Chand were Hindus and his General Ventura and Allard were Europeans.
1. Maharaja Ranjit Singh was a tolerant ruler. How?
2. Who was Dhian Singh Dogra?
3. Who was the Foreign Minister of Maharaja Ranjit Singh?
4. Who was Diwan Bhiwani Das?
5 was the Commander-in-Chief of Maharqja Ranjit Singh.
Answer:
1.
- In his empire jobs were given on the basis of merit.
- He respected all the religions.
2. Dhian Singh Dogra was the Prime Minister of Maharaja Ranjit Singh.
3. Faqir Aziz-ud-Din was the Foreign Minister of Maharaja Ranjit Singh.
4. Diwan Bhiwani Das was the Finance Minister of Maharaja Ranjit Singh.
5. Misar Diwan Chand.
First Anglo-Sikh War: Causes and Results:
Note : Read the following passages carefully and answer the questions that follow :
1. In 1842 A.D., Lord Ellenborough was appointed the new Governor-General of India in place of Lord Auckland. Lord Ellenborough wanted to erase the disgrace of the defeat which the British had to taste in the First Anglo-Afghan War. empire, it further embittered the Anglo-Sikh relations.
1. Who was Lord Ellenborough?
2. When was Lord Ellenborough appointed the new Governor General of India?
- 1812 A.D.
- 1822 A.D.
- 1832 A.D.
- 1842 A.D.
3. Why did the British want to conquer Sind?
4. When was Sind conquered by the Britishers?
5. What was the consequence of the conquest of Sind by the Britishers?
Answer:
1. Lord Ellenborough was the Governor General of India.
2. 1842 A.D.
3. Because Sind was important from the geographical point of view.
4. The Sind was conquered by the Britishers in 1842 A.D.
5. It resulted in great tension between the Britishers and the Sikhs.
2. The second great’battle between the Sikhs and the British was fought at Ferozeshah or Pheru Shahar on 21st December, 1845 A.D. This place is located at a distance of 10 miles from Mudki. The British were fully prepared for this battle. They had called their forces from Ferozepur, Ambala and Ludhiana to Ferozeshah for attack. The strength of the British soldiers in this battle was 17,000. The British army was commanded by famous and experienced generals like Lord Hugh Gough, John Littler and Lord Hardinge. Qn the other hand, the strength of the Sikh soldiers was about 25,000 to 30,000. The Sikh soldiers were led by Lai Singh and Teja Singh. The Britishers were fully confident of the treachery of the Sikh generals and that they would score* an easy win in the battle. But the Sikhs gave such a baffling rebuff to the British that once it looked that their empire in India had shaken.
1. When was the battle of Ferozeshah fought?
2. Who was Lord Hugh Gough?
3. Who led the Sikh forces in battle of Ferozeshah?
4. The strength of the British soliders in the battle of Ferozeshah was ………….
5. Who was defeated in the battle of Ferozeshah and why?
Answer:
1. The battle of Ferozeshah was fought on 21st December, 1845 A.D.
2. Lord Hugh Gough was the commander in chief of the Britishers.
3. In the battle of Ferozeshah the Sikh forces were led by Lai Singh and Teja Singh.
4. 17000.
5. In the battle of Ferozeshah the Sikhs were defeated.

3. The battle of Sobraon was the last and the most decisive battle of the First Anglo-Sikh War. This battle was fought on 10th February, 1846 A.D. Before this battle 30,000 Sikh soldiers had reached Sobraon. In order to give a stiff resistance . to the British, they had started digging up their trenches. Lai Singh and Teja Singh who were commanding the Sikh army were sending every detail of the ’ preparations to the British. In order to face the Sikh army, the British had also made a good preparation. The strength of the British army in this battle was 15,000. Lord Hugh Gough and Lord Hardinge were commanding the British army. On 10th February, 1846 A.D., the Britishers attacked the Sikh army. As a result of the counter attack by the Sikh army, the British xarmy had to retreat. At this time, as pre-planned, at first Lai Singh and then Teja Singh fled away from the battlefield. While going away, Teja Singh sank the boats loaded with powder and ammunition, and also destroyed the Pontoon bridge.
1. Which was the last battle to be fought during the First Anglo-Sikh War?
2. When was the battle of Sobraon fought? 1
3. In the battle of Sobraon the British forces were led by…………..and …………..
4. Who was defeated in the battle of Sobraon? 1
5. Which Sikh leader had shown exemplary bravery in the battle of Sobrabn?
Answer:
1. The last battle to be fought during the First Anglo-Sikh War was the battle of Sobraon.
2. The battle of Sobraon was fought on.10th February, 1846 A.D.
3. Lord Hugh Gough, Lord Hardinge.
4. In the battle of Sobraon the Sikhs were defeated.
5. In the battle of Sobraon S. Sham Singh Attariwala showed an exemplary bravery.
Second Anglo-Sikh War: Causes, Results and Annexation of the Punjab:
Note : Read the following passages carefully and answer the questions that follow :
1. The revolt of Diwan Moolraj of Multan was one of the most -potent causes, which led to the Second Anglo-Sikh War. Multan was a province of the Lahore Raj. After the death of Sawan Mai, the Nazim (governor) of Multan in 1844 A.D., his son Moolraj was appointed the new Nazim. In 1847 A.D. the British Resident increased the annual revenue payable to the Lahore Darbar by Multan from Rs. 13,47,000 to Rs. 1,97,15,00. On the other hand, the British removed the excise duty on some essential goods and one-third part of Multan was taken from him. Owing to these reasons, Diwan Moolraj was not in position to pay the increased revenue. On being forced by the British Resident, Moolraj tendered his resignation in December, 1847.
In March 1848 A.D. the new Resident, Fredrick Currie, decided to nominate Sardar Kahan Singh as the new Nazim of Multan. In order to take over the charge of Multan, two British officers, Vans Agnew and Anderson were sent alongwith Kahan Singh. Moolraj warmly welcomed them. On 19th April, Moolraj handed over the keys of the fort to Kahan Singh. But the next day on 20th April, some soldiers of Moolraj murdered both the officers and imprisoned Kahan Singh. Fredrick Currie held Moolraj responsible for the revolt of Multan.
1. When was Diwan Moolrqj was appointed as the new Nazim of Multanh?
2. For which one reason Diwan Moolraj had given his resignation?
3. In 1848 A.D. which new Nazim of Multan was appointed by Fredrick Currie?
4. The responsiblity of the murder of which two British officers were put on Diwan Moolrqj by the Britishers?
5. Fredrick Currie held …………….. responsible for the revolt of Multan.
Answer:
1. Diwan Moolraj was appointed as the new Nazim of Multan in 1844 A.D.
The British resident had increased the annual revenue payable to the Lahore Darbar by Multan.
3. Sardar Kahan Singh.
4. Vans Agnew and Anderson.
5. Diwan Moolraj.

2. The battle of Chillianwala was one of the significant battles of the Second Anglo-Sikh War. This battle was fought on 13th January, 1849 A.D. Lord Gough was of the view that he did not have a strong force to face Sher Singh. So, he was waiting for more reinforcement, but when Lord Hugh Gough came to know that Chattar Singh with his soldiers was coming to the help of Sher Singh, he attacked the soldiers of Sher Singh on 13th January. It was one of the hardest and fiercest battles. The Sikhs fought with great determination and daring. They wrought havoc in the British army. The British lost 695 soldiers, including 132 officers in the battle and 1651 soldiers were wounded. Four British guns were also captured by the Sikhs.
1. Which was the most significant battle of the Second Anglo- Sikh War?
2. When was the battle of Chillianwala fought?
3. Who was Sher Singh?
4. Who was defeated in the battle of Chilianwala?
5. In the battle of ChiUianwala how many British officers were killed?
Answer:
1. The battle of Chillianwala was the most significant battle of the Second Anglo-Sikh War.
2. The battle of Chillianwala was fought on 13th January, 1849 A.D.
3. Sher Singh was the son of S. Chattar Singh, the Nazim of Hazara.
4. In the battle of Chillianwala, the Britishers were defeated.
5. 132.
3. The battle of Gujarat proved to be the most important and decisive battle of the Second Anglo-Sikh War. In this battle, Chattar Singh, Sher Singh and Bhai Maharaj Singh made a united front against the British. In addition, the king of Afghanistan, Dost Mohammad also sent 3,000 cavaliers under the command of his son, Akbar Khari to help the Sikhs. In this battle, the Sikhs had a total army of 40,000 soldiers. On the other hand, the English army was still led by Lord Hugh Gough because Sir Charles Napier had not yet reached India. The British army comprised 68,000 soldiers.
In this battle, guns were extensively used by both the sides, because of which this battle is also .famous in history as the Battle of Guns. This battle started at 7.30 a.m. on 21st February, 1849 A.D. The ammunition of the Sikhs was soon exhausted. When the Britishers came to know about it, they made a fierce attack on the Siklis. The Sikh soldiers unsheathed their swords, but they could not resist the guns for long. The Sikhs suffered heavy losses in this battle.
1. battle of the second Anglo-sikh War.
2. When was the battle of Gujarat fought?
3. Who led the British forces during the battle of Gujarat?
4. Why is the battle of Gujarat as the Battle of Guns?
5. Who became victorious in the battle of Gujarat?
Ans.
1. decisive.
2. The battle of Gujarat was fought on 21st february, 1849 A.D.
3. In the battle of Gujarat the British forces were led by Lord Hugh Gough.
4. The battle of Gujarat was known as the battle of guns because guns were extensively used by both the sides in this battle.
5. The Britishers became victorious in this battle.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()