Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class Hindi Book Solutions Chapter 23 फलों की चौपाल Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Hindi Chapter 23 फलों की चौपाल
Hindi Guide for Class 8 PSEB फलों की चौपाल Textbook Questions and Answers
(क) भाषा – बोध
I. शब्दार्थ:
चौपाल = खुली मंडपाकार बैठक जहाँ गाँव के लोग बैठकर पंचायत आदि करते हों, छायादार बड़ा चबूतरा।
कफ़ सिरप = खांसी की दवा।
नेत्र ज्योति = आँखों की देखने की शक्ति।
इजाजत = आज्ञा
अवशेष = बचा हुआ।
विसर्जित = त्यागा हुआ, छोड़ा हुआ।
![]()
(ख) विचार – बोध
I. इन प्रश्नों के उत्तर एक या दो वाक्यों में लिखें :
प्रश्न (क)
अमरूद को कब खाना चाहिए ?
उत्तर:
अमरूद को अच्छी तरह धोकर दोपहर के समय खाना चाहिए।
प्रश्न (ख)
गाजर ने खाने से पहले अपने बारे में क्या हिदायत दी ?
उत्तर:
गाजर ने खाने से पहले अपने बारे में हिदायत दी कि मुझे खाने से पहले अच्छी तरह मल-मल कर धोना चाहिए और साफ करना चाहिए।
प्रश्न (ग)
उन दो सब्जियों के नाम लिखें जिन पर रोएं होते हैं ?
उत्तर:
गाजर और मूली पर रोएं होते हैं।
प्रश्न (घ)
अंगूर ने अपने क्या फायदे बताये ?
उत्तर:
अंगूर से खून बढ़ता है, खून साफ होता है, पाचन क्रिया ठीक होती है, नेत्र ज्योति बढ़ती है और कमजोर लोग स्वस्थ हो जाते हैं।
प्रश्न (ङ)
फलों को खाने से पहले धोना क्यों ज़रूरी है ?
उत्तर:
धूल-मिट्टी और हानिकारक बेक्टीरिया को दूर करने के लिए उन्हें धोना ज़रूरी है।
प्रश्न (च)
उन दो फलों के नाम लिखें जिन्हें खाने से पहले कुछ देर तक पानी में भिगोना चाहिए ?
उत्तर:
अंगूर और गाजर को खाने से पहले कुछ देर तक पानी में भिगोना चाहिए।
![]()
प्रश्न (छ)
सेब के छिलके क्यों नहीं उतारने चाहिए ?
उत्तर:
सेब के छिलके के ठीक नीचे विटामिन ‘सी’ और ‘ए’ होते हैं जो उसे उतारने से नष्ट हो जाते हैं इसलिए उसका छिलका नहीं उतारना चाहिए।
II. इन प्रश्नों के उत्तर चार या पाँच वाक्यों में लिखें :
प्रश्न (क)
फलों को खाने से पहले क्या-क्या सावधानी बरतनी चाहिए ?
उत्तर:
फलों को खाने से पहले साफ पानी से अच्छी तरह मल-मल कर धोना चाहिए। अंगूर, सेब, गाजर आदि को कुछ समय तक पानी में रखा जाना चाहिए। फलों का छिलका नहीं उतारना चाहिए। छिलकों के ठीक नीचे सेब जैसे फलों में विटामिन होते हैं जो छिलका उतर जाने से नष्ट हो जाते हैं।
प्रश्न (ख)
फलों को पकाने के लिए रसायनों का प्रयोग घातक है, क्यों ?
उत्तर:
अनेक फलों को पकाने के लिए कुछ लालची फल विक्रेता और व्यापारी उन्हें विशेष रसायनों में डुबो कर रखते हैं या उन पर रसायनों का छिड़काव करते हैं। आम जैसे फल की पेटी में कैल्शियम कार्बाइड का टुकड़ा रखते हैं जो नमी की अवस्था में एसीटीलीन गैस उत्पन्न करता है जिससे फल तो पक जाते हैं पर फल के माध्यम से वह मनुष्य के शरीर को बहुत अधिक नुकसान पहुँचाते हैं। इससे शरीर को तरह-तरह की बीमारियाँ हो जाती हैं।
प्रश्न (ग)
पीले रंग के फलों के नाम लिखें जिनमें विटामिन ‘ए’ की मात्रा अधिक होती है।
उत्तर:
पीले रंग के अनेक फलों में विटामिन ‘ए’ काफ़ी मात्रा में होता है लेकिन सभी पीले रंग के फल विटामिन ‘ए’ के भंडार नहीं होते। गाजर में विटामिन ‘ए’ पर्याप्त मात्रा में होता है जो चाहे बाहर से लाल और भीतर से पीली होती है। अंगूर और सेब भी विटामिन ‘ए’ से भरपूर होते हैं। आम में विटामिन ‘ए’ काफी मात्रा में होता है।
![]()
प्रश्न (घ)
खट्टे/रस वाले फलों के नाम लिखें जिनमें विटामिन ‘सी’ की मात्रा अधिक होती है।
उत्तर:
खट्टे/रस वाले फलों को सिटरिक परिवार के सदस्य कहते हैं। इनमें विटामिन ‘सी’ की मात्रा अधिक होती है। ये रोगों से लड़ने की क्षमता शरीर को देते हैं। संतरा, नींबू, मालटा, कीन, ग्रेफ्रूट, चकोतरा आदि फल इसी परिवार से जुड़े हुए हैं।
प्रश्न (ङ)
कौन-से ऐसे फल हैं जो यदि काटकर थोड़ी देर पड़े रहें तो काले हो जाते हैं ? उनमें भोजन का कौन-सा खनिज लवण होता है ?
उत्तर:
अनेक फल ऐसे हैं जिनमें लोहा नामक तत्व की मात्रा अन्य फलों की अपेक्षा अधिक होती है। जब इन्हें काटा जाता है तो इनमें उपस्थित लोहा वायु में उपस्थित ऑक्सीजन से क्रिया करता है और उससे लोहा ऑक्साइड बन जाता है। इस कारण वे गहरे भूरे या काले रंग को प्रकट करने लगते हैं। सेब, नाशपाती, अमरूद, आम आदि इस वर्ग के फल हैं। इनको खाने से रक्त में लोहा बढ़ता है जो शरीर को शक्ति प्रदान करता है।
प्रश्न (च)
फलों और सब्जियों पर प्रचलित मुहावरे/लोकोक्ति इकट्ठी करें। जैसे आम के आम गुठलियों के दाम।
उत्तर:
फलों और सब्जियों पर आधारित और समाज में प्रचलित अनेक मुहावरे और लोकोक्तियाँ हैं जिनमें से कुछ निम्नलिखित हैं
(क) आम के आम गुठलियों के दाम
(ख) मिर्च का स्वभाव होना
(ग) एक अनार सौ बीमार
(घ) एक करेला दूसरा नीम चढ़ा
(ङ) थाली का बैंगन
(च) बन्दर क्या जाने अदरक का स्वाद
(छ) किस खेत की मूली
(ज) गूलर का फूल होना
(झ) नमक-मिर्च लगाना
(ञ) गाजर-मूली के भाव बिकना
![]()
(छ) उन फलों के नाम लिखें जिन्हें छिलका सहित/छिलका रहित खाया जाता है।
उत्तर:
छिलका सहित खाये जाने वाले फल
सेब
नाशपाती
अंगूर
जामुन
अमरूद
चैरी
खुमानी
आडू
आलू बुखारा
रसभरी
स्ट्राबरी
छिलका रहित खाये जाने वाले फल
खरबूजा
आम
तरबूज
अनानास
केला
श्रीफल/सीताफल/शरीफ़ा
संतरा
मौसमी
कीनू
लीची
अनार
(ग) व्यावहारिक व्याकरण
I. इन शब्दों में से मूल शब्द अलग करें
प्रतिनिधित्व = प्रतिनिधि
फायदेमंद = ……………….
लापरवाही = ……………….
स्पष्टीकरण = ……………….
महत्त्वपूर्ण = ……………….
गुणवान = ……………….
अधिकाँश = ……………….
विसर्जित = ……………….
उत्तर:
प्रतिनिधित्व = प्रतिनिधि
फायदेमंद = फायदा
लापरवाही = परवाह
स्पष्टीकरण = स्पष्ट
महत्त्वपूर्ण = महत्त्व
गुणवान = गण।
अधिकाँश = अधिक
विसर्जित = सर्जित
![]()
II. इन शब्दों के विपरीत शब्द लिखें
फायदा = ……………….
आवश्यक = ……………….
कमज़ोर = ……………….
रोगी = ……………….
ज़रूरी = ……………….
गुण = ……………….
महत्त्वपूर्ण = ……………….
विश्वास = ……………….
उपयोगी = ……………….
गुणवान = ……………….
विसर्जन = ……………….
उत्तर:
फायदा = घाटा
आवश्यक = अनावश्यक
कमज़ोर = शक्तिशाली
रोगी = निरोगी
ज़रूरी = गैर-ज़रूरी
गुण = अवगुण
महत्त्वपूर्ण = महत्त्वहीन
विश्वास = अविश्वास
उपयोगी = अनुपयोगी
गुणवान = गुणहीन
विसर्जन = सृजन।
III. उचित योजक शब्द लगाकर वाक्य पूरे करें
(i) …………… लोगों को ऐसे ही परेशान करोगे …………. तुम्हें भला कौन पूछेगा।
(ii) ………………. यह बात सच है कि बंटी को खाँसी मेरी वजह से ही हुई है ………………… इसमें मेरा रत्ती भर भी दोष नहीं।
(iii) दाँतों …………….. मसूड़ों के लिए भी मैं फायदेमंद हूँ।
(iv) इसको कई बार समझाया गया ……………….. यह अपनी आदत से बाज़ नहीं आ रही है।
(v) मेरे शरीर के रोओं में घातक जीवाणु होते हैं …………….. मुझे खाने से पहले खूब अच्छी तरह से धो लेना चाहिए।
(vi) आप ऐसा कोई उपाय बतायें ………………. लोग बीमार न पड़ें।
(vii) लोग हमें खाने का सही तरीका नहीं जानते ………………… हम लोग चाहते हुए भी पूरा फायदा नहीं पहुंचा पाते हैं।
उत्तर:
(i) अगर लोगों को ऐसे ही परेशान करोगे तो तुम्हें भला कौन पछेगा।
(ii) यद्यपि यह बात सच है कि बंटी को खाँसी मेरी वजह से ही हुई है तथापि इसमें मेरा रत्ती भर भी दोष नहीं।
(iii) दाँतों और मसूड़ों के लिए भी मैं फायदेमंद हूँ।
(iv) इसको कई बार समझाया गया लेकिन यह अपनी आदत से बाज़ नहीं आ रही है।
(v) मेरे शरीर के रोओं में घातक जीवाणु होते हैं अतः मुझे खाने से पहले खूब अच्छी तरह से धो लेना चाहिए।
(vi) आप ऐसा कोई उपाय बतायें ताकि लोग बीमार न पड़ें।
(vii) लोग हमें खाने का सही तरीका नहीं जानते इसलिए हम लोग चाहते हुए भी पूरा फायदा नहीं पहुंचा पाते हैं।
![]()
योग्यता विस्तार
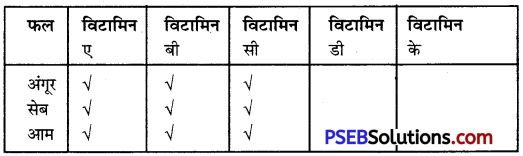
हमें स्वस्थ रहने के लिए संतुलित भोजन करना चाहिए। संतुलित भोजन वह है जिसमें सभी पोषक तत्व यथा-कार्बोहाइड्रेट्स, प्रोटीन, वसा, विटामिन, खनिज लवण, जल और रेशे उचित मात्रा में हों। नीचे एक ओर फलों के नाम दिये गये हैं, दूसरी ओर विटामिनों के नाम हैं। जिस फल में जो विटामिन अधिक मात्रा में पाया जाता है उसके नीचे सही शिान अंकित करें।
उत्तर:
अभिनय
इस एकाँकी का स्कूल के वार्षिक उत्सव पर अभिनय करवायें।
PSEB 8th Class Hindi Guide फलों की चौपाल Important Questions and Answers
बहुविकल्पीय प्रश्न निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर सही विकल्प चुनकर लिखें
प्रश्न 1.
फलों का राजा किस फल को कहते हैं ?
(क) सेब को
(ख) आम को
(ग) केले को
(घ) अंगूर को।
उत्तर:
आम को।
प्रश्न 2.
क्या खाने से लड़के को खाँसी हो गई थी ?
(क) अनार
(ख) अमरूद
(ग) अंगूर
(घ) आम।
उत्तर:
अमरूद।
प्रश्न 3.
अमरूद कब खाना चाहिए ?
(क) रात को
(ख) दोपहर को
(ग) संध्या के समय
(घ) प्रभातकाल में।
उत्तर:
दोपहर को।
![]()
प्रश्न 4.
गाजर के लम्बे बालों में कौन-से जीवाणु होते हैं ?
(क) अमीबा
(ख) एटामीबा
(ग) अक्टोबा
(घ) इकाबीमा।
उत्तर:
एटामीबा।
प्रश्न 5.
शरीर में खून बढ़ाने में सबसे अधिक योगदान किस फल का होता है ?
(क) केला
(ख) अमरूद
(ग) सेब
(घ) अंगूर।
उत्तर:
अंगूर।
प्रश्न 6.
किस फल के छिलके नीचे विटामिन ए और सी होते हैं ?
(क) अनार
(ख) अमरूद
(ग) सेब
(घ) केला।
उत्तर:
सेब।
प्रश्न 7.
छिलका सहित खाने वाला फल कौन-सा है ?
(क) अनार
(ख) केला
(ग) आम
(घ) अंगूर।
उत्तर:
अंगूर।
![]()
प्रश्न 8.
छिलका रहित खाया जाने वाला फल है ?
(क) सेब
(ख) अंगूर
(ग) केला
(घ) अमरूद।
उत्तर:
केला।
फलों की चौपाल Summary
फलों की चौपाल पाठ का सार
तरह-तरह के फलों की एक सभा बुलाई गई। छोटे लड़के-लड़कियों ने फलों के मुखौटे लगाकर फलों का अभिनय किया। फलों के राजा आम ने अन्य फलों से पूछताछ की। वह जानना चाहते थे कि लोग उन्हें खाने के बाद बीमार क्यों पड़ जाते थे। केले ने सभा को आरम्भ किया और अमरूद पर आरोप लगाया कि उसे खाने से एक लड़के को खांसी हो गई। शारीरिक परेशानी के साथ-साथ उसे इलाज के लिए पैसे भी खर्च करने पड़े। अमरूद ने अपना बचाव करते हुए कहा कि सर्दी के दिन शाम के समय उस लड़के ने उसे बिना धोये हुए खाना शुरू कर दिया था। यदि उसे दोपहर के समय खाया जाता तो वह हानिकारक नहीं होता। वह पाचन क्रिया को बढ़ाता है, पेट साफ रखता है, दाँतोंमसूड़ों के लिए अच्छा है, कब्ज़ और बवासीर में उपयोगी है और दिमाग की गर्मी को कम करता है। वह पागलपन दूर करने में भी सहायक होता है। बस, उसका इस्तेमाल ठीक ढंग से किया जाना चाहिए।
संतरे ने गाजर पर आरोप लगाया कि उसके कारण लोगों में दस्त और पेट की गड़बड़ी होने की शिकायतें आ रही थीं। गाजर ने अपने उत्तर में कहा कि लोग उसे धोए बिना खा लेते हैं। उस पर लम्बे-लम्बे बालों में एंटामीबा नामक जीवाणु होते हैं जो पेट में जाकर पाचन क्रिया को प्रभावित करते हैं। उसमें विटामिन ‘ए’, ‘बी’, ‘डी’ और ‘के’ काफ़ी मात्रा में होते हैं जिससे शरीर का विकास होता है। उसे अच्छी तरह धोने के बाद ही खाया जाना चाहिए। गाजर के बैठते ही मूली ने अपने बारे में स्वयं कहा कि उसे खाने से पहले धोया जाना चाहिए।
केले ने अंगूर पर आरोप लगाया कि उसे खाने से अनेक लोग बीमार पड़ जाते हैं। इसका कारण क्या था ? अंगूर ने बताया कि उसमें विटामिन ए, बी, सी, प्रोटीन, वसा, कैल्शियम, फॉस्फोरस, लोहा आदि होते हैं जिनसे शरीर में खून बढ़ता है, खून साफ होता है, पाचन क्रिया ठीक होती है और नेत्र ज्योति ठीक होती है। वह कमज़ोर और रोगियो के लिए बहुत उपयोगी होता है। लोगों की बीमारी का कारण वह नहीं है बल्कि लोग स्वयं हैं। वे रेडियों और ठेले वालों से उसे खरीदते हैं। उस पर पड़ी धूल-मिट्टी, मक्खियों की गन्दगी आदि की परवाह किए बिना उसे खा जाते हैं जिस कारण वे बीमार पड़ जाते हैं। उसे पकाने के लिए रासायनिक पदार्थों का उपयोग भी नहीं किया जाना चाहिए। उसे खाने से पहले अच्छी तरह धोया जाना चाहिए। अंगूर के बैठते ही सेब स्वयं खड़ा हो गया। उसने बताया कि उसे खाने के लिए लोग उसका छिलका उतार देते हैं। छिलके के ठीक नीचे विटामिन ए और सी होते हैं। इसलिए अच्छी तरह धोकर छिलके सहित खाना चाहिए। सबकी बात सुनकर आम ने निष्कर्ष निकाला कि लोगों को फल सावधानी से खाने चाहिएं। उन्हें अच्छी तरह धोकर बिना छिलका उतारे ही खाना चाहिए।