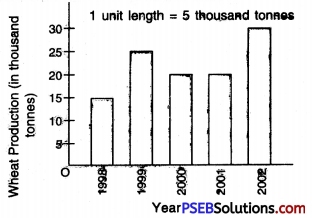
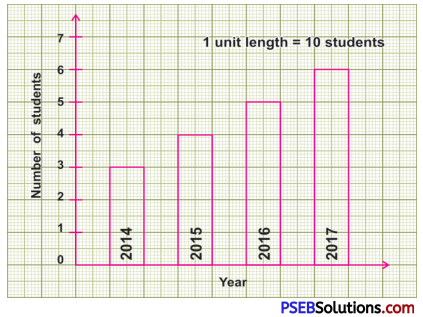
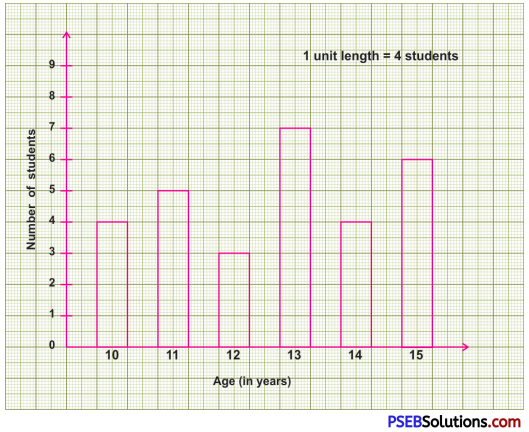
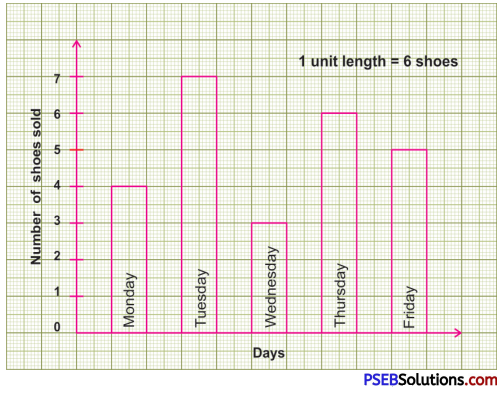
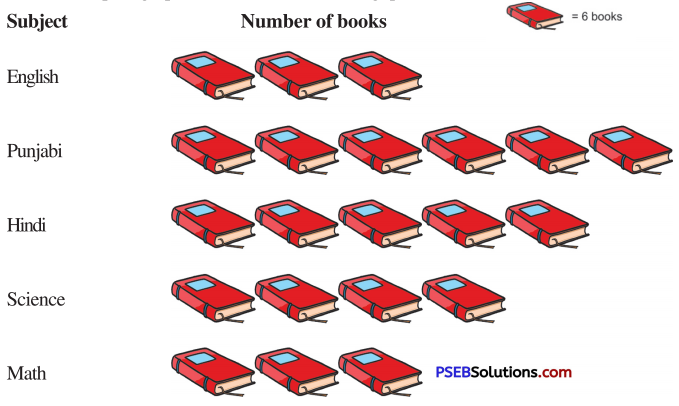
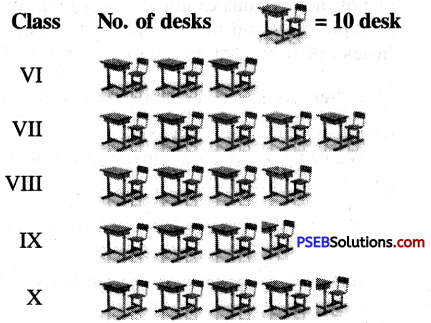
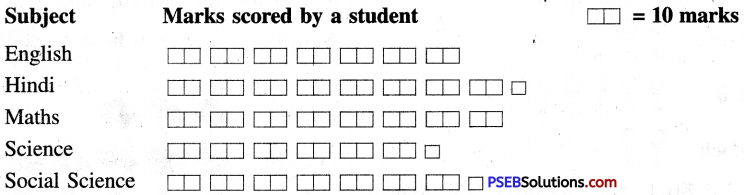
Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class English Book Solutions English Letter/Application Writing Exercise Questions and Answers, Notes.
PSEB 8th Class English Letter/Application Writing
पत्र लिखना एक कला है। एक अच्छा पत्र लिख कर आप शत्रु का दिल भी जीत सकते हैं। पत्र मुख्यतः तीन प्रकार के होते हैं-व्यक्तिगत, व्यावसायिक अथवा अधिकारियों को लिखे गए पत्र।
व्यक्तिगत पत्र (Personal Letters)-व्यक्तिगत पत्र वे पत्र होते हैं जो हम अपने मित्रों या सगे-सम्बन्धियों को लिखते हैं। ऐसे पत्र प्रायः समाचारों से भरे होते हैं। इन पत्रों में हम अपने घर, परिवार, स्कूल या किसी अनुभव का वर्णन करते हैं। ये पत्र एक विशेष विधि द्वारा लिखे जाते हैं। इन्हें ऐसे लिखा जाता है जैसे कि आप किसी व्यक्ति से बातचीत कर रहे हों। पते के अतिरिक्त इन पत्रों के छ: भाग होते हैं।
- लिखने वाले का पता (The address of the sender)
- तिथि (Date)
- सम्बोधन या अभिवादन (The salutation or greeting)
- विषय-वस्तु (The body of letter)
- विधिवत् अन्त (The subscription or complimentary close)
- हस्ताक्षर (Signature)

प्रत्येक भाग को लिखने की अपनी अलग विधि होती है। आओ हम एक-एक करके इनका अध्ययन करें-
1. The Address of the Sender. पहले पत्र भेजने वाले का पता पृष्ठ पर सबसे ऊपर दायें कोने में लिखा जाता था। प्रत्येक लाइन में अन्त में Comma और आखिरी लाइन के अन्त में Full Stop लगाया जाता था।
परन्तु अब पता लिखते समय विराम चिन्ह लगाने की विधि में अन्तर आ गया है। अब पंक्तियों के अन्त में Commas और Full Stop का प्रयोग नहीं होता। इसके अतिरिक्त अब Sender’s Address दाहिने कोने की बजाये बाएं कोने में लिखा जाता है।
15 Model Town
Rajpura
2. Date. तिथि लिखने वाले के पते के बिल्कुल नीचे लिखी जाती है। तिथि लिखने की कई विधियां हैं, जैसे-
15 Model Town
Rajpura
March 12, 20……
या
12th March 20…..
या
12 March 20……
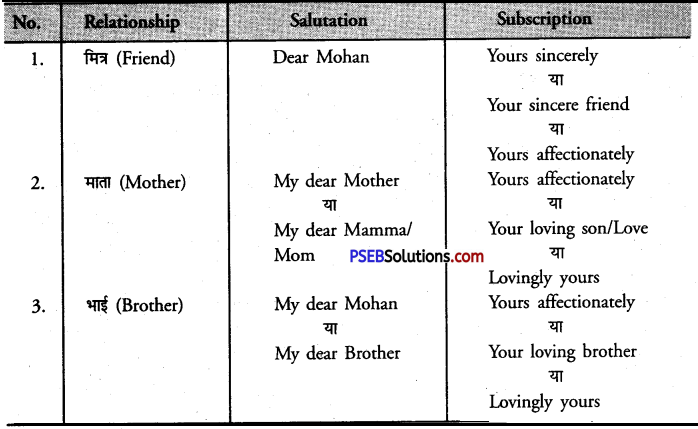
3. The Salutation or Greeting. (i) मित्र को पत्र लिखते समय उसे उसके नाम से सम्बोधित कीजिए; जैसे-Dear Mohan, जहां तक हो सके मित्र को उसी नाम (संक्षिप्त) से संबोधित कीजिए जिस नाम से आप बातचीत करते समय उसे सम्बोधित करते हैं; जैसे,
Dear Monu
Dear Sonu
(ii) माता-पिता, भाइयों, बहनों अथवा घनिष्ठ सगे सम्बन्धियों को आप यूं सम्बोधित कर सकते हैं-
My dear Father or Daddy/Dad
My dear Mother or Mamma/Mom
My dear Brother My dear Gopal
My dear Kamla
नोट-यदि आप Address में विराम चिन्ह नहीं लगाते तो आप सम्बोधन में भी इनका प्रयोग न करें।
4. The Body of the Letter-यह पत्र का सबसे महत्त्वपूर्ण भाग है। एक अच्छा पत्र वह माना जाता है जो सरल हो और जिसमें पाठक की रुचि बनी रहे। पत्र की प्रत्येक पंक्ति अर्थपूर्ण एवं रोचक हो। पत्र ऐसे लिखना चाहिए मानो आपका सम्बन्धी आपके सामने बैठा हो और आप से बातें कर रहा हो। पत्र का यह भाग लिखते समय विराम चिन्हों और Grammar के अन्य सभी नियमों का पूरा पालन करें।
5. The Subscription or Complimentary Close-(i) मित्र को लिखे गए पत्र का अन्त इस प्रकार करें
Yours sincerely
या
Your sincere friend
(ii) सगे-सम्बन्धियों को लिखे गये पत्रों का अन्त इस प्रकार करें-
Yours affectionately
(iii) निम्नलिखित phrases के साथ भी व्यक्तिगत पत्रों का अन्त किया जा सकता है- . Ever sincerely yours
या
Your loving son/Love
या
Lovingly yours
नोट-यदि आपने सम्बोधन के समय comma नहीं लगाया तो आप पत्र का अन्त करने वाले phrase के साथ भी comma न लगायें।
6. Signature-व्यक्तिगत पत्र में आप को अपने पूरे हस्ताक्षर नहीं करने चाहिएं। आपको या तो नाम का पहला हिस्सा लिखना चाहिए या फिर वह नाम लिखें जिस नाम से आप अपने सगे-सम्बन्धियों या मित्रों द्वारा पुकारे जाते हैं। जैसे-
Sohan
या
Sonu आप Sohan Lal Gupta अर्थात् पूरा नाम न लिखें।
Salutation and Subscription at a Glance
Official Letters या Business Letters.
(i) ऐसे पत्रों में कोई विशेष अन्तर तो नहीं होता। अन्तर केवल इतना है कि इन पत्रों के प्राय: छ: की बजाए सात भाग होते हैं।
(ii) ऐसे पत्रों में पत्र लिखने वाले का पता और तिथि व्यक्तिगत पत्रों की तरह ही लिखे जाते हैं।’
(iii) ऐसे पत्रों में उस फर्म (Firm) या व्यक्ति का पूरा पता भी पत्र में लिखा जाता है जिसे पत्र लिखा जा रहा हो, जैसे-
Messrs Malhotra Book Depot
(Producers of Quality Books)
Railway Road
Jalandhar City
(iv) ऐसे पत्रों में सम्बोधन की विधि इस प्रकार होती है
Dear Sir
या
Dear Sirs
या
Madam
या
Sir
नोट-यदि व्यक्ति आप से परिचित है तो आप उसे यूं भी सम्बोधित कर सकते हैं-
Dear Mr. Sharma
(v) ऐसे पत्रों की विषय-वस्तु संक्षिप्त, स्पष्ट और विनम्र-भाषी होनी चाहिए।
(vi) ऐसे पत्रों का अन्त यूं करना चाहिए
Yours truly
या
Yours faithfully

(vii) आप माननीय व्यक्तियों अथवा उच्च पद पर आसीन व्यक्तियों को पत्र लिखते हुए Yours respectfully या Yours obediently का प्रयोग भी कर सकते हैं। नाम से सम्बोधित पत्रों का अन्त Yours sincerely से ही करना चाहिए।
(viii) ऐसे पत्रों में हस्ताक्षर पूरे होने चाहिएं और हस्ताक्षर के पश्चात् लिखने वाले का नाम या पद लिखा जाना चाहिए, जैसे-
Yours faithfully
Mohan Lal Sharma
Manager
Important Applications and Letters
1. Application for Marriage Leave
Write an application to the Headmistress of your school for marriage leave.
The Headmistress
Khalsa Public School
Nawanshahr
Madam
I beg to say that the marriage of my elder brother/sister takes place next week. I am to help my parents in making marriage arrangements. So I cannot come to school. Kindly grant me leave for five days. I shall be very thankful to you for this.
Yours obediently
Jaspinder Kaur
Roll No. 25
23. VIII A
March 15, 20 ………….
Word-Meanings-Marriage = विवाह, Takes place = होगी, Arrangements = व्यवस्थाएं, Much = अधिक.
2. Leave for Urgent Work
Write an application to the Principal of your school for leave for a day.
The Principal
A.B. Sen. Sec. School
Patiala Sir
I beg to say that I have an urgent piece of work at home. So I cannot come to school. Kindly grant me leave for today. I shall be thankful to you for this.
Yours obediently
Raman
Roll No. 25
VIII C
February 5, 20 ……
Word-Meanings-Urgent piece of work = आवश्यक कार्य, Grant = प्रदान करो
3. Application for a Testimonial
Imagine you are Kavita, a student of Govt. Sen. Sec School, Ludhiana. Write an application to the Principal of your school requesting him to send a testimonial as you are applying for the post of a clerk.
11 Happy House
Model Town
Jalandhar
The Principal
Govt. Sen. Sec. School
Ludhiana
Sir
I beg to say that I am an old student of your school. I have to apply for the post of a clerk in a bank. I need a testimonial from you for that. I am writing down the following details for reference.
I passed my Sen. Sec. Examination in 2001 with 600 marks. I stood first in the district. I was a member of the school hockey team. I took part in the debates also and won many trophies and cups for the school. I was in the good books of my teachers.
Kindly send me the testimonial as soon as possible and oblige.
Yours obediently
Kavita
March 14, 20……
Word-Meanings-Testimonial = अचरण पत्र, In the good books of = नजरों में अच्छा, Oblige = कृतार्थ करें।
4. Application for Change of Section
Write an application to the Principal of your school requesting him to change your section.
The Principal
Govt. Sen. Sec. School
Sirhind
Sir
I am a student of VIII B of your school. I live in Main Bazaar. All my friends are in VIII A Section of the school. So I feel very lonely in VIII B.
Besides, I have to do my home task alone at home. Whenever I am unable to attend the school, I cannot do my homework. There is none to tell me about the homework given by the class teacher. The boys of my street can help me in other ways also. I hope you will appreciate my problem and change my section.
Thanking you
Yours obediently
Kirpal Singh
Roll No. 46
VIII B
March 15, 20……
Word-Meanings- Feel = अनुभव करना, Ways = ढंग, Lonely = अकेला, Appreciate = समझना।
5. For Admission to the Next Class
Write an application to the Headmaster of your school requesting him for admission to the next class.
The Headmaster
Govt. High School
Phagwara
Sir
I beg to say that I am a student of 7th class of your school. I fell ill in March. Still I appeared in the annual examination. I failed but my class-fellows went to the next class.
I am a good student. I got first division in the half-yearly examination. Kindly give me a test on any day and admit me to the 8th class. I assure you that I shall get first division in Middle Standard Examination.
Thanking you
Yours obediently
Mohan Lal
VIII C
March 5, 20…….
Word-Meanings- Annual = वार्षिक, Division = श्रेणी.

6. Application for Late Fee
Write an application to the Headmaster of your school requesting him to permit you to pay your fee for the month late by ten days.
The Headmaster
Govt. High School
Hoshiarpur
Sir
I beg to say that I am a student of VIII A of your school. Tomorrow is fee day and I am unable to pay it. My father has gone to Delhi. He will come back in ten days. Kindly allow me to pay my fee late by ten days.
Thanking you
Yours obediently
Sohan Lal
VIII A
March 9, 20……..
Word-Meanings- Unable = असमर्थ, Allow = अनुमति देना
7. Permission to take part in Games
Write an application to the Headmaster of your school requesting him to permit you to take part in the evening games.
The Headmaster
A.B.C. High School
Moga
Sir
I am a student of VIII D of your school. Our school is preparing for the Distt. Sports Meet. There are regular games in the school in the evening. I am also fond of games. I am a good player of football. Last year I was a member of the school football team. But this year my name is not in the players’ list because I could not perform well in the final trial. I request you to give me another chance and permit me to take part in the evening games. I assure you that I will try my best to improve my performance.
Thanking you
Yours obediently
Vijay Kumar
Roll No. 25
VIII D
Dated : March 9, 20…………
Word Meanings-Take part = भाग लेना, Permit = अनुमति देना, Assure = विश्वास दिलाना।
8. Permission to go on a Historical Tour
Write an application to your Principal requesting him/her to permit you to go on a historical tour.
The Principal
Govt. Sen. Sec. School
Ladowal
Madam
We, the students of class VIII, beg to seek your permission for a historical tour. The school will close for the summer vacation next week. We want to see the Taj Mahal. We also want to go to Fatehpur Sikri. On our way back, we want to visit Delhi. The trip will be very useful for us. It will give us first hand knowledge of History. The trip will cost two hundred rupees per head. Our teacher of History has agreed to take us to these places. We are 30 girls in all. I hope you will arrange this trip.
Thanking you
Yours obediently
Manjit Kaur
VIII A
April 30, 20……
Word-Meanings- Summer = गर्मी, Trip = भ्रमण, Useful = उपयोगी, Knowledge = ज्ञान
11. On Recovery From Illness
Write a letter to your friend congratulating him on his recovery from long illness.
135 New Road
Nawanshahr
March 18, 20…..
Dear Mohan
I am glad to know that you have recovered from long illness. I congratulate you on your recovery. You worked very hard. So you fell ill. Now please take care of your health.
Take long walks in the morning. Drink milk and eat fruit. All this will make you healthy soon.
With best wishes.
Yours sincerely
Hardeep
Word-Meanings-Glad = प्रसन्न, Recovered = ठीक हो गये हो, Take care of = ध्यान रखो, Congratulate = बधाई देना
12. Invitation on Brother’s Marriage
Write a letter to your friend inviting him to your brother’s marriage.
Govt. High School
Amritsar
March 4, 20………
My dear Kamlesh
You will be glad to know that the marriage of my elder brother comes off on March 9, 20……. The marriage party will leave Amritsar for Delhi the same day. We invite you to join us in our joys.
You know that Delhi is a historical city. There are many buildings worth-seeing. You will see the Red Fort, the Qutab Minar and Jantar Mantar. Rina and Tina have also been invited. They will reach here on Sunday. We will have good time together.
I hope you will reach in time.
Yours sincerely
Mitlesh
Address:
Kumari Kamlesh
45 Mall Road
Shimla
Word-Meanings-Comes off = पड़ती है, Marriage party = बारात, Worth-seeing = दर्शनीय
13. Inviting a Friend to the Birthday Party
Suppose you are Harish. You live at 38 Manavta Park, Hoshiarpur. Invite your friend to come to your birthday party.
38 Manavta Park
Hoshiarpur
February 22, 20……
My dear Surinder
You will be glad to know that my birthday falls on next Monday. There will be a tea party in the evening. I have invited all my friends to the party. I cannot forget you on this day. Please reach here on Sunday evening. We will have a good time together.
Thanking you
Yours sincerely
Harish
Word-Meanings-Falls on = पड़ता है, Invited = आमन्त्रित किया है, Forget = भूलना।
14. To Uncle for a Birthday Gift
Suppose you are Poonam. You live at 232, Phase IX, Mohali. Your uncle has sent you a wrist-watch on your birthday. Write a letter of thanks to your uncle.
232 Phase
IX Mohali
March 8, 20……
My dear Uncle
It is very kind of you to remember me on my birthday. You have sent me a beautiful wrist-watch as a gift. It shows your love for me. I received many gifts that day but I liked your gift the most. Everybody praised it.
The watch will help me a lot. It will make my life regular. I shall never be late for school now. I thank you for this lovely gift. I assure you thar I shall keep this watch with great care.
With regards
Yours lovingly
Poonam
Address :
Shri Manohar Singh
Joginder Nagar
Rohtak
Word-Meanings-Gift = उपहार, The most = सबसे बढ़कर, Praised = प्रशंसा की, A lot = बहुत ज्यादा, Regular = नियमित, Care = ध्यान.

15. To Younger Brother to Take Interest in Studies
Write a letter to your younger brother/sister scolding him/her for neglecting studies.
18 Mohan Nagar
Batala
February 18, 20…….
My dear Suman
I received your progress report yesterday. You have failed in all the subjects. You are not working hard. You are neglecting your studies. It is very bad. Final examinations are drawing near. Be careful. Do not waste your time. Work hard. Finish your syllabus in time.
I hope you will act upon my advice.
Yours affectionately
Mohan
Word-Meanings Subjects = विषय, Neglecting = उपेक्षा कार रहे, Waste = नष्ट करना, Avoid = दूर रहना, Act upon = अमल करना।
16. Invitation for Summer Vacation
Write a letter to your friend asking him to spend a part of his summer vacation with you.
1407 Green Avenue
Amritsar
February 18, 20 ……
My dear Gopal
Your school has closed for the summer vacation. You are free now. I invite you to come to Amritsar. Amritsar is a holy city. Here are many places worth-seeing. You will see Sri Harmandar Sahib, the Durgayana Mandir, the Jallianwala Bagh and other important places.
We shall also study together. I hope you will reach here soon.
Yours sincerely
Ramesh
Word-Meanings-Invite = बुलाना, Holy = पठित्र, Worth-seeing = देखने योग्य।
17. To a Friend on his Failure
Write a letter to your friend who has failed in the examination, asking him not to lose heart but try again.
15 New Colony
Kotkapura
March 18, 20 ……
Dear Raman
Your result is out today. It is very sad that you have failed. It is your own fault. You never worked hard. You moved in a bad company. The result is before you.
Please act upon my advice. Don’t lose heart. Give up bad company and work hard. You will pass next time.
Yours sincerely
Kamal
Address:
Mr. Raman
370 Nai Basti
Ambala
Word-Meaning-Moved = घूमते रहे, Act upon = अमल करना, Lose heart = धैर्य छोड़ना।
18. Condolence Letter.
Suppose you are Satish. You live at 6 Soni Street, Khanna. Your friend has lost his mother. Write a letter of condolence to him.
6 Soni Street
Khanna
Feb. 20, 20 ……
My dear X
I got your letter yesterday. I was shocked to read it. The sudden death of your mother is. a great loss. I share your sorrow.
I met your mother last month. She looked healthy. Her death is untimely. It is the will of God. We must bow before His will. Please have courage.
Yours sincerely
Satish
Address:
Mr. X
15-New Chowk
ABC
Word Meanings-Shocked = आघात पहुंचा, Sudden = आकस्मिक, Great loss = बहुत बड़ी क्षति, Share = बांटना, Sorrow – दुःख, Untimely death = अकाल मृत्यु, Will = इच्छा।
19. To Avoid Bad Company
Write a letter to your younger brother, advising him to avoid bad company. Examination Hall
………City
March 15, 20…….
My dear Mukesh
I received a letter from your headmaster. I gather that you move in a bad company. Ramesh and Dinesh are your friends these days. Both of them smoke. They go to pictures everyday. You, too, have started smoking in their company. You have become a film-fan. Your headmaster is worried about you.
Dear brother, we have high hopes on you. You are the light of our home. The examinations are drawing near. Please give up your bad company.
I hope you will act upon my advice.
With love
Yours affectionately
Kamleshwar
Address:
Mr. Mukesh Verma
Boys’ Hostel
A.B.C. Sen. Sec. School
…….. City
Word-Meaning-Film-fan = फिल्म देखने के शौकीन, Draw near = निकट आना, Act upon = अमल करना।
20. To Father about Your Success in the Examination
You have passed the Middle Standard Examination. Write a letter to your father telling him about your good result.
36 Raj Nagar
Khanna
July 3, 20 ……
My dear Father
Our result was out yesterday. You will be glad to know that I have stood second in the state. I have secured 85% marks. My teacher and headmaster came to our house in the morning. They blessed and patted me. They congratulated the mother. All missed you badly on the occasion. When are you coming home?
Your loving son
Amit
Word-Meanings-Secure = प्राप्त करना, Missed = याद आई, Occasion = अवसर।
21. Letter about Hostel Life
You are Anil, a student of class VIII. You are residing in hostel. Write a letter to your mother about your hostel life.
Boys’ Hostel
A.B.C. Sen. Sec. School
Chandigarh
My dear Mother
Our new session has started. I have got a good room in the school hostel. My hostel life is well disciplined. There are fixed hours for study, meals and games. We get up in time and go to bed in time. Our hostel warden is kind as well as strict to us. He does not allow us to go out of the hostel after the main gate is closed.
Dear Mother, I miss you very badly. I wish I got wings to fly home.
With regards
Yours lovingly
Anil
Word-Meanings- Session = सत्र, Disciplined = अनुशासित, Fixed = निरिचत, Strict = सख्त

22. To Father About Your Papers
You are appearing in the Middle Standard Examination. Write a letter to your father telling him about your progress in the examination.
8 The Mall
Jalandhar Cantt
March 18, 20…….
My dear Father
I am taking my Middle Standard Examination these days. The English paper was very easy. I hope to get 80 marks in it. The paper in Mathematics was a little tough. But I did all the sums.
Punjabi and Social Studies are easy subjects. I hope to do well in them. I am sure that I shall get good marks. I may win a scholarship.
With regards to dear mother
Your loving son
Arun Kumar
Word-Meanings- Taking = दे रहा हृं, Over = समाप्त, Tough = कठिन, Do well = अच्छ करना
23. To Father for Change of School
Write a letter to your father asking him to allow you to change school.
512 Naya Nagar
…….. City
March 10, 20……..
My dear Father
I feel sad to tell you about my school. Once it was a great school. It was considered one of the best schools in the town. Now it is not. We have no Principal these days. We have no English teacher even. So I do not feel good at studies. I want to change my school. Jain High School is a good school. Kindly allow me to join it.
Your loving son
Raj Kumar
Address:
Mr. Mohan Lal Sharma
1 New Road
Patiala
Word Meanings-Considered = समझा जाता था, Feel good = मन लगना, Allow = अनुमति देना।
![]()
![]()