Punjab State Board PSEB 9th Class Social Science Book Solutions Geography Chapter 1a India: Size and Location Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Geography Chapter 1a India: Size and Location
SST Guide for Class 9 PSEB India: Size and Location Textbook Questions and Answers
Map Work:
Question 1.
Show in the ouline map of India :
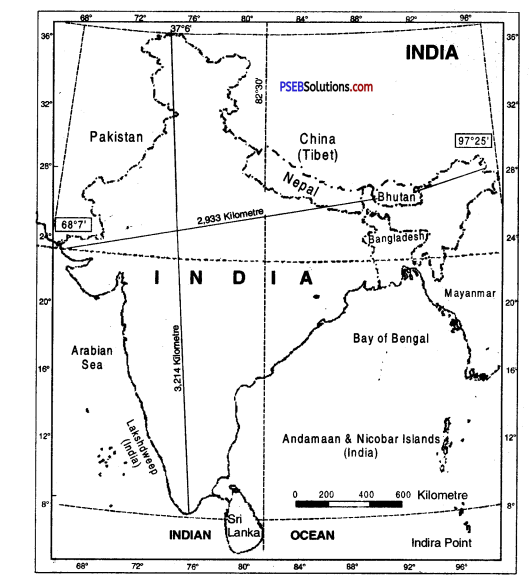
(i) Indian Standard Meridian (82/4°E)
(ii) Tropic of Cancer
Based upon Survey of India map with the permission of the Surveyor General of India. The responsibility for the correctness of internal details rests with the publisher. The territorial waters of india extend into the sea to a distance of twelve nautical miles measured from the appropriate base line. The external boundaries and coastlines of India agree with the Record Master Copy certified by Surveyor General of India.
(iii) States and Territories using Punjabi as their language.
(iv) Two neighbours of India the boundaries of which do not touch sea.
(v) India’s neighbouring island country.
Answer:
(iii) Punjab, Jammu & Kashmir, Delhi and Chandigarh
(iv) Nepal, Bhutan
(v) SriLanka
Do it yourself with the help of India Map.
Activity:
(i) Colour India’s neighbouring SAARC nations in a map and display map in classroom.
(ii) Show 29 states and 7 union territories with their capitals in two outline maps of India.
Answer:
Do it yourself.
Objective Type Questions:
Answer the following questions in a single word to one sentence length.
Question 1.
Which country stands third in the world on the basis of area?
Answer:
China.
Question 2.
Which country is fifth in the world on the basis of area and population?
Answer:
Brazil.
![]()
Question 3.
Saurashtra is region of which state among the following?
(i) Manipur
(ii) Gujarat
(iii) Maharashtra
(iv) Nagaland
Answer:
(ii) Gujarat.
Question 4.
Which city among the following is not a capital?
(i) Raipur
(ii) Ahmedabad
(iii) Ranchi
(iv) Panaji
Answer:
(ii) Ahmedabad.
Question 5.
Which latitudinal extent among following is right for India?
(i) 8°4′ N to 37°6′ N
(ii) 8°4′ S to 37°6′ S
(iii) 6°2′ N to 35°2′ N
(iv) 6°2′ S to 35°2′ S
Answer:
(i) 8°4’N to 37°6’N.
Question 6.
What is the constitutional name given to India?
Answer:
Indian Republic.
Short Answer Questions:
Give short answers for the following questions :
Question 1.
Name the northern, southern, eastern and western extents of India.
Answer:
- Northern comer – Daftar
- Southern comer – Kanya Kumari (Indira Point)
- Eastern comer – Kibithu
- Western comer – Guhar Moti (Kutch)
Question 2.
Write a note on Indian Standard Meridian.
Answer:
India is a vast country. In order to maintain a uniformity of time within the country, 82!40E longitude is taken as the standard meridian of India. The local time along this meridian, serves as the Indian Standard Time (I.S.T.). This central meridian passes through the towns of Allahabad and Mirzapur (U.P.) Indian standard Time is 514 hours ahead of Greenwich Mean Time (G.M.T.).
Question 3.
Explain the difference of two hours in time of Arunachal Pradesh and Gujarat.
Answer:
India has a longitudinal extent of 30°. Due to this there is a time lag of two hours between the sunrise on the easternmost and the westernmost horizons of India. Due to rotation, the earth takes 4 minutes to rotate through 1° of longitude. The difference in time is one hour for 15° of longitude. Therefore, for a longitudinal extent of 30° of India, there is a time lag of 2 hours. When it is 6 a.m. in Arunachal Pradesh, it is still 4 a.m. in Gujarat. But the watches in all parts of India run according to standard time measured from 82/4° E longitude. So the watches in Arunachal Pradesh and Gujarat show the same time despite the different sunrise.
Question 4.
Which languages are used in Jammu & Kashmir and Telangana?
Answer:
- Jammu & Kashmir – Urdu, Kashmiri, Ladakhi, Dogri, Gujri, Dadri and Punjabi.
- Telangana – Telugu and Urdu.
![]()
Question 5.
Write a short note on SAARC.
Answer:
SAARC is a union of South Asian Countries formed for the mutual co-operation. Its complete form is South Asian Association for Regional Co-operation. It has 8 members and, these are – India, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal and SriLanka. India keeps the most important place among the SAARC members.
Long Answer Questions :
Answer the following questions in detail :
Question 1.
Give details of India’s international trade.
Answer:
India’s position is quite conducive from the point of view of international trade.
Following facts will clarify the picture :
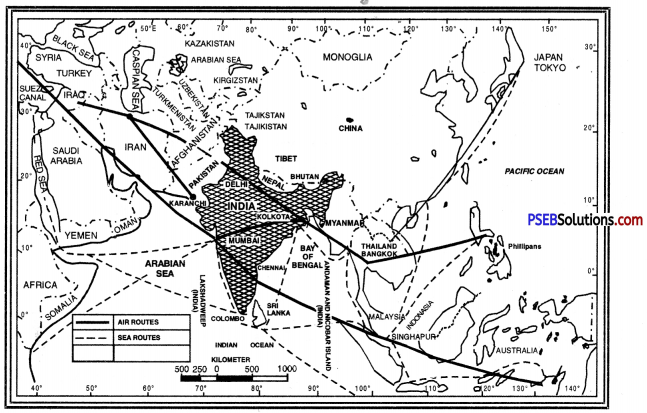
India on International Highway of Trade and Commerce
- Central Location. India is centrally located in the Eastern Hemisphere.
- Trade Routes. India is favourably located for international trade. Many trade routes pass through the Indian Ocean.
- Nearness to tropic of cancer. The tropic of cancer passes through the centre of India. So India is a tropical country. The long growing season makes India an agricultural country.
- Long Coastline. India has long coastline which provides many deep, protected and natural harbours.
- Defence. The natural boundaries are favourably located from defence point of view.
- Effect of Indian Ocean. The Indian Ocean leads to the origin of rain giving monsoons.
- Effect of Himalayas. The unbroken chain of Himalayas acts as a climatic barrier. It forces monsoons to give rainfall and protects northern India from cold polar winds.
Question 2.
Write names of any 10 states and 5 union territories of India with their capitals.
Answer:
The list of 10 Indian States and 5 Union Territories alongwith their capitals is given below :
States and Capitals
| 1. Arunachal Pradesh | Itanagar |
| 2. Assam | Dispur |
| 3. Bihar | Patna |
| 4. Gujarat | Gandhi Nagar |
| 5. Haryana | Chandigarh |
| 6. Himachal Pradesh | Shimla |
| 7. Tamil Nadu | Chennai |
| 8. Karnataka | Benguluru |
| 9. Punjab | Chandigarh |
| 10. Rajasthan | Jaipur |
Union Territories and Capitals
| 1. Andaman and Nicobar | Port Blair |
| 2. Chandigarh | Chandigarh |
| 3. Dadra and Nagar | Haveli and |
| Daman and Diu | Daman |
| 4. Delhi (N.C.R.) | Delhi |
| 5. Jammu and Kashmir | Srinagar |
Question 3.
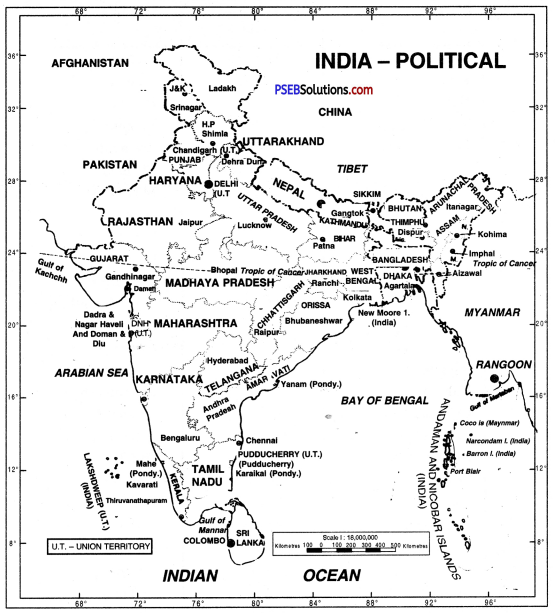
Distribute India politically and explain biggest and smallest state on the basis of area.
Answer:
India is a Union of states. Politically, it can be divided into two parts :
- States
- Union Territories
There are 28 States and 8 Union Territories. Their names along with their capitals and area are given ahead :
| S. No.States | Area(sq. kms.) | Capitals |
| 1. Uttar Pradesh | 2,38,566 | Lucknow |
| 2. Maharashtra | 3,07,713 | Mumbai |
| 3. Bihar | 94,163 | Patna |
| 4. West Bengal | 88,752 | Kolkata |
| 5. Andhra Pradesh | 1,60,205 | Amravati |
| 6. Tamil Nadu | 1,30,058 | Chennai |
| 7. Madhya Pradesh | 3,08,000 | Bhopal |
| 8. Rajasthan | 3,42,239 | Jaipur |
| 9. Karnataka | 1,91,791 | Bengaluru |
| 10. Gujarat | 1,96,024 | Ganc.ainagar |
| 11. Orissa | 1,55,707 | Bhubaneshwar |
| 12. Kerala | 38,863 | Thiruvananthapuram |
| 13. Jharkhand | 79,714 | Ranchi |
| 14. Assam | 78,438 | Dispur |
| 15. Punjab | 50,362 | Chandigarh |
| 16. Haryana | 44,212 | Chandigarh |
| 17. Chhattisgarh | 1,35,191 | Raipur |
| 18. Uttarakhand | 53,483 | Dehradun |
| 19. Himachal Pradesh | 55,673 | Shimla |
| 20. Tripura | 10,491 | Agartala |
| 21. Manipur | 22,327 | Imphal |
| 22. Meghalaya | 22,429 | Shillong |
| 23. Nagaland | 16,579 | Kohima |
| 24. Goa | 3,702 | Panaji |
| 25. Arunachal Pradesh | 83,743 | Itanagar |
| 26. Mizoram | 20,987 | Aizawal |
| 27. Sikkim | 7,096 | Gangtok |
| 28. Telangana | 1,14,840 | Hyderabad |
Based upon Survey of India map with the permission of the Surveyor General of India. The responsibility for the correctness of internal details rests with the publisher. The territorial waters of india extend into the sea to a distance of twelve nautical miles measured from the appropriate base line. The external boundaries and coastlines of India agree with the Record Master Copy certified by Surveyor General of India.
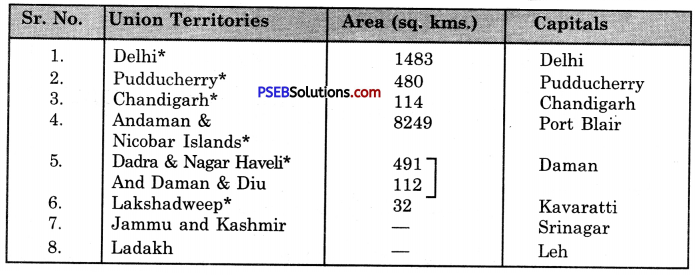
Note: Delhi is now known as the National Capital Region, Delhi, Its area is 1483 square kilometre.
PSEB 9th Class Social Science Guide India: Size and Location Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions :
Question 1.
India has a total geographical area of lakh km2.
(a) 32.80
(b) 22.80
(e) 42.08
(d) 30.80.
Answer:
(a) 32.80.
![]()
Question 2.
Which line of latitude bisects India into two halves?
(a) Equator
(b) Tropic of Cancer
(c) Tropic of Capricorn
(d) Arctic Circle.
Answer:
(b) Tropic of Cancer.
Question 3.
Which is the largest state of India? (as regards area)
(a) Maharashtra
(b) Uttar Pradesh
(c) Rajasthan
(d) Madhya Pradesh.
Answer:
(c) Rajasthan.
Question 4.
India has total number of states:
(a) 18
(b) 24
(c) 28
(d) 30.
Answer:
(c) 28.
Question 5.
Where does India rank in the world ? (as regards area)
(a) Fifth
(b) Sixth
(c) Seventh
(d) Eighth.
Answer:
(c) Seventh.
Question 6.
(a) Bay of Bengal
(b) Arabian Sea
(c) Indian Ocean
(d) Gulf of Cambay
Answer:
(b) Arabian Sea.
Question 7.
Which is the southernmost point of India?
(a) Kanyakumari
(b) Indira point
(c) Rameshwaram
(d) Barren island.
Answer:
(b) Indira point.
Question 8.
Where does standard meridian of India pass through
(a) Srinagar
(b) Delhi
(c) Mirzapur
(d) Kolkata.
Answer:
(c) Mirzapur.
![]()
Question 9.
India has a coastline of:
(a) 6500 kms
(b) 7500 kms
(c) 8500 kms
(d) 9500 kms.
Answer:
(b) 7500 kms.
Question 10
Suez canal was opened in year :
(a) 1849
(b) 1859
(c) 1869
(d) 1879.
Answer:
(c) 1869.
Question 11.
The capital of Sikkim is :
(a) Dispur
(b) Shillong
(c) Gangtok
(d) Kohima.
Answer:
(c) Gangtok.
Question 12.
What is total length of land frontier of India?
(a) 12200 km
(b) 13200 km
(c) 14200 km
(d) 15200 km.
Answer:
Fill in the blanks :
Question 1.
________ keeps the first place in the world from the point of view of population.
Answer:
China
Question 2.
________ divides India in two equal parts.
Answer:
Tropic of Cancer
Question 3.
Geographically is the largest country of the world.
Answer:
Russia
Question 4.
India is situated in continent.
Answer:
Asia
![]()
Question 5.
________ is the capital of Uttrakhand.
Answer:
Dehradun
Question 6.
The boundaries of Jammu & Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan and are alongwith Pakistan.
Answer:
Gujarat
Question 7.
__________ is the capital of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
Answer:
Hyderabad
Question 8.
__________ is the capital of Punjab and Haryana.
Answer:
Chandigarh.
True/False:
Question 1.
Goa is the smallest Indian State.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Suez canal was opened in 1869 A.D.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
Sri Lanka is situated in eastern side of India.
Answer:
False.
Question 4.
Shimla is the capital of two Indian states.
Answer:
False.
![]()
Question 5.
Northern plains have lots of minerals.
Answer:
False.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How much percentage of world’s population lived in India in 2011?
Answer:
17.5%.
Question 2.
Which fertile Indian plains provide food security to India?
Answer:
The Ganga-Brahmaputra Plains.
Question 3.
Geographically, name the largest country of the world.
Answer:
Russia.
Question 4.
What is the total geographical area of India?
Answer:
32.80 lakh square kilometre.
Question 5.
Which Indian region is rich in mineral resources?
Answer:
Peninsular Plateau.
![]()
Question 6.
Name the island groups situated in the Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal.
Answer:
- Arabian Sea: Lakshadweep Islands.
- Bay of Bengal: Andaman and Nicobar Islands
Question 7.
Name the countries which are larger than India, geographically.
Answer:
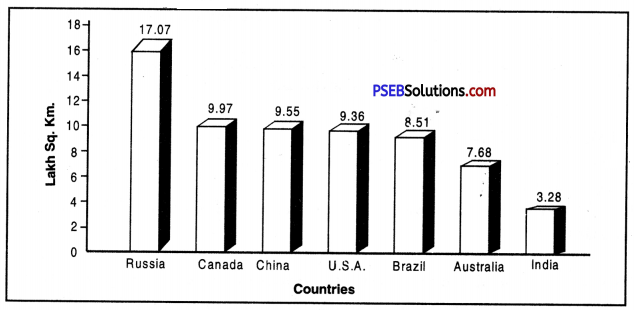
Australia, Brazil, China, U.S.A., Canada and Russia.
Question 8.
Name the seas situated on three sides of India.
Answer:
Arabian Sea on the western side, Bay of Bengal on the eastern side and Indian Ocean on the southern side.
Question 9.
In which hemisphere is India situated?
Answer:
India is situated in the northern hemisphere.
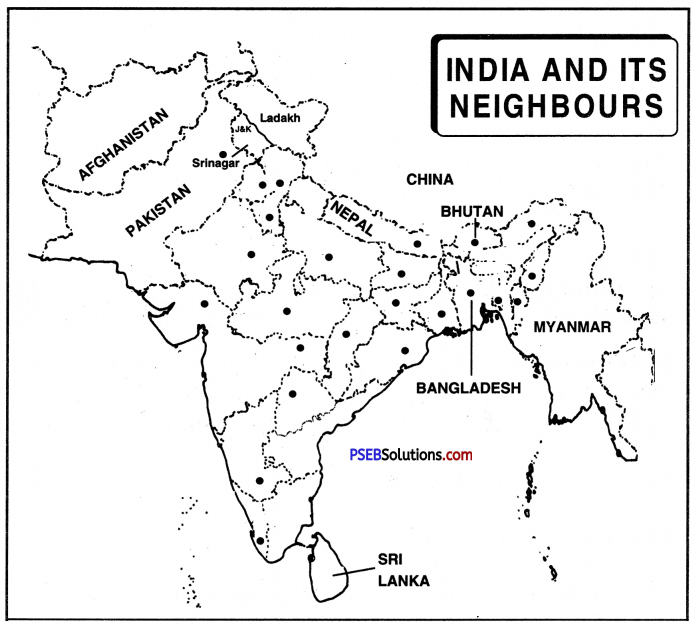
Question 10.
Which Latitudinal line divides India in two parts and what is its latitude?
Answer:
Tropic of Cancer divides India in two parts and its latitude is 23°30′ North.
Question 11.
Name the two neighbouring Island countries of India.
Answer:
SriLanka and Maldives.
Question 12.
Name the two neighbouring countries of India on the eastern side.
Answer:
Bangladesh and Myanmar.
![]()
Question 13.
The boundaries of which countries touch the Indian boundary on the northern side.
Answer:
China, Nepal and Bhutan.
Question 14.
What do you mean by the term sub-continent?
Answer:
A sub-continent is a vast independent geographical unit which is distinctly separated from the main continent.
Question 15.
In how many States and Union Territories, India is divided?
Answer:
There are 28 states and 8 union territories in India.
Question 16.
Name any four Indian states which border the other countries.
Answer:
Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, Gujarat, West Bengal.
Question 17.
Name four Indian states situated on the eastern coast.
Answer:
Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Odisha and West Bengal.
Question 18.
What is the total length of land border of India?
Answer:
India’s total land border is 15,200 km.
![]()
Question 19.
What is the total length of Indian coastline?
Answer:
7516 km.
Question 20.
Geographically, what is India’s position in the world? Name the countries larger than India.
Answer:
Geographically, India is seventh largest country of the world. Russia, China, Canada, U.S.A., Brazil and Australia are larger than India.
Question 21.
Name the seas situated on eastern and western side of India.
Answer:
Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea respectively.
Question 22.
Give similarity in the latitudinal and longitudinal extent of India.
Answer:
Their extension is almost 30°.
Question 23.
What is the difference between 1ST and GMT?
Answer:
Five and half hours.
Question 24.
Name four Indian states along with the Arabian Sea.
Answer:
Gujarat, Maharashtra, Karnataka and Kerala.
![]()
Question 25.
Name four Indian states whose border touches with the border of Bangladesh.
Answer:
West Bengal, Assam, Meghalaya and Mizoram.
Question 26.
Name the capitals of Uttrakhand, Chhattisgarh and Jharkhand.
Answer:
Uttarakhand-Dehradun, Chhattisgarh – Raipur, Jharkhand – Ranchi.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Reason out why the north-south extent of India is larger than its east-west extent even though the country’s latitudinal and longitudinal extent (in degrees) is of the same value.
Answer:
The East-West extent of India is 2933 kilometres, but the North-South extent is 3214 kilometres. Thus North-South extent is longer than the East-West extent by 281 kms. The fact is that latitudinal extent (31°02′) and the longitudinal extent (29°18′) of the country are almost of the same value. This is due to the spherical shape of the earth. The equator is the longest circle on the earth (one degree of longitude measures 111 km.). But the length of other parallels goes on decreasing from the equator towards the poles due t.o the curvature of the earth. At 25° latitude, the length of one degree of longitude is 100 kms. Therefore, the East-West extent is shorter than North-South extent in kilometres. The East-West extent for 30° will be reduced by 30 x 10 kms = 300 kms. approximately.
Question 2.
Why is India given the status of sub-continent? Which countries form the Indian sub-continent?
Answer:
The great mountain wall of Himalayas isolates these countries from the mainland of Asia. India forms the core of the sub-continent.
The following countries are included in the Indian sub-continent:
- Pakistan is in the North-West.
- Nepal is in the North,
- Bhutan is in the North-East.
- Bangladesh is in the East.
- Sri Lanka in the South.
- Myanmar in the external East.
Question 3.
What is the location of the Tropic of Cancer? What are its implications?
Or
‘Tropic of Cancer divides the country into almost two equal parts.’ Discuss.
Answer:
The Tropic of Cancer (23 1/2° N) runs almost through the centre of the country being 15° away from either end. It divides the country into almost two equal halves :
- Sub-tropical zone: Northern India.
- Tropical zone—Southern India.
Thus, India is considered a tropical country of the Northern Hemisphere. The climate of India is dominated by tropical monsoons. The sun’s rays never fall vertically in the areas north of the tropic, but the southern areas experience overhead sun twice a year.
![]()
Question 4.
State the reason for selecting a Standard Meridian of India with so odd value of 82°30′ E.
Or
Why do we need a Standard Meridian for India? Why 8214° E has been selected as the Standard Meridian of India?
Answer:
8254° East Meridian is taken as the Standard Meridian of India. It passes through the town of Allahabad. Local time of Mirzapur near Allahabad is taken as the standard time all over India. It is a central meridian for India as it divides the country into two equal halves. So it suits most parts of the country. Moreover, Nepal and Sri Lanka also adopt 82/4° E as the Standard Meridian to have a uniformity of time with India.
Question 5.
Reason out why Ahmedabad in the west and Kolkata in the east are able to see the noon sun exactly overhead twice a year, but not Delhi.
Answer:
The latitude of a place affects the altitude of the overhead sun at different places. On 21st June, the sun is overhead at tropic of cancer. The latitude of Ahmedabad is 23° N and that of Kolkata is also 23°N. These two places experience overhead sun twice a year. But Delhi (29°N) is situated beyond the tropic of cancer (23/4° N). Therefore, Delhi does not have overhead sun at any time of the year, because the sun is never overhead beyond the tropics.
Question 6.
Reason out why the difference between the duration of day and night is hardly felt at Kanyakumari, but it is not so in Kashmir.
Or
“The latitudinal extent influences the duration of day and night.” Explain.
Answer:
The North-South extent affects the length of day and night in different parts of India. Kanyakumari (8°N) is close to the equator. Here the sun is almost overhead all the year-round. With a result, the days and nights are equal. The maximum difference between the length of day and night is hardly 45 minutes. But in Kashmir (37°N), the rays of the sun are always oblique. The difference between the length of day and night is as large as five hours. Days are longer than nights, due to the inclination of this part towards the sun.
Question 7.
What is the longitudinal extent of India? What are its implications?
Answer:
India extends between 68°7’E to 97°25′ E longitudes. The East-West extent is 2933 kms. which is roughly 1/12th of the circumference of the earth. Thus, India has a longitudinal extent of about 30° longitudes. There is a time lag of 2 hours between the sunrise in the easternmost and the westernmost horizons of India. It means that the sun takes two hours to rise in Saurashtra after it has risen in Arunachal Pradesh.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Give major features of the size and extent of India.
Answer:
India is a vast country. Geographically, India is seventh largest country of the world. The major features of the size and extent of India are given below:
- India’s mainland is extended between 8°4′ N to 37°6′ N latitude. Its longitudinal extent is 68°7′ E to 97°25′ E. In this way, the latitudinal and longitudinal extent of India (30°) is same. Even then its North-South extent in kilometres is more than East-West extent.
- In the context of Equator, India is situated in the northern hemisphere and in the context of Prime Meridian, India is in the eastern hemisphere.
- Tropic of cancer (23°3’N) divides India in almost two equal parts. India’s northern part is mountainous and plain and the southern part is a plateau.
- India’s geographical area is around 32.8 lakh square kilometre. It is around 2.4% of world’s geographical area.
- Due to its central position in the Indian ocean, India’s location is quite favourable for international trade. That’s why India has trading contacts with almost all the countries.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain that the exchange of ideas and goods from India dates back to ancient times.
Or
‘India had strong geographical and historical links with her neighbours.’ Explain giving examples.
Or
India’s strategic location on the head of the Indian Ocean has helped her in establishing land and maritime contacts with the outside world in the ancient and medieval times. Explain.
Answer:
India has been linked with S.E. Asia, West Asia, Africa, Central Asia. Indian culture spread to many distant countries such as Indonesia, Bali island, Combodia and Egypt. These cultures also had an impact on Indian culture.
- The Indian culture spread to distant lands through ocean routes of the Indian Ocean. The muslin, spices, were sent to other countries.
- The mountain passes in the north provided many openings and transport facilities for the outsiders.
(а) The pastoral nomads entered India through the mountain passes of Khyber and Bolan.
(b) The Buddhist Bhikshus crossed into Tibet, China and Japan to carry their message of peace.
(c) Alexander invaded India through these mountain passes and brought Greek sculptures, domes, minarets to India.
(d) Indian merchants had trade links with Central Asia, Afghanistan and Iran through these routes.
(e) The Mongols, Turks, Arabs and Iranians came as conquerors and settled down in India. They took back the Indian numerals, the decimal system and the ideas of the Upanishads to their countries.
This gives and takes, this exchange of ideas, goods, and art have enriched the Indian culture.