Punjab State Board PSEB 9th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 4 Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 4.3 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 4 Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 4.3
Question 1.
Draw the graph of each of the following linear equations in two variables:
(i) x + y = 4
Answer:
To draw the graph of x + y = 4, we need at least two solutions of x + y = 4. And to be on the safer side, we get three solutions of x + y = 4.
For x = 0, we get 0 + y = 4, i.e., y = 4.
For x = 2, we get 2 + y = 4. i.e., y = 2.
For x = 4. we get 4 + y = 4, i.e., y = 0.
We can represent these solutions In the tabular form as below:
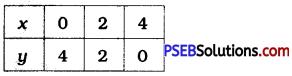
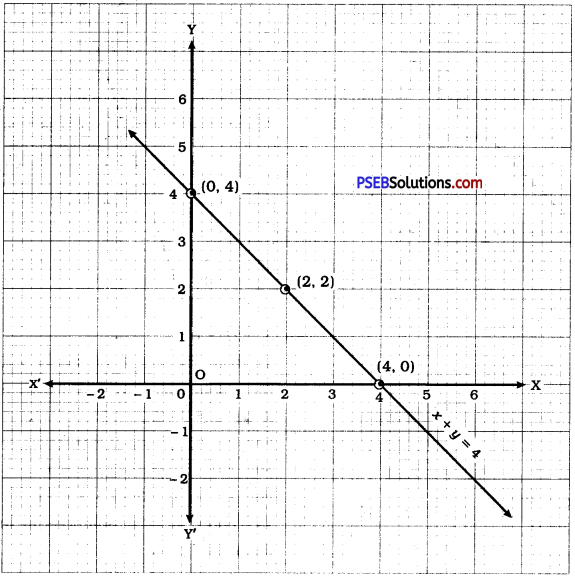
Then, we plot these points on the Cartesian plane and draw the line passing through them.
This line is the graph of x + y = 4.

(ii) x – y = 2
Answer:
x – y = 2
To draw the graph of x – y = 2, we
find three solutions of x – y = 2. For convenience, we express the equation in y-form as y = x – 2.
For x = 0, y = – 2.
For x = 2, y = 0.
For x = 4, y = 2.
We represent these solutions in the tabular form as below:
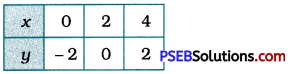
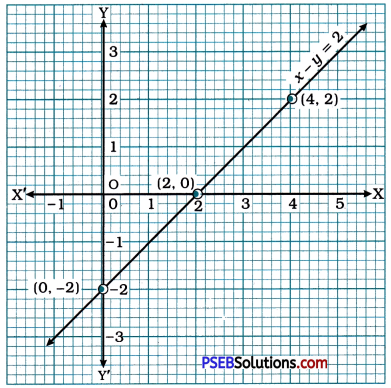
Then, we plot these points on the Cartesian plane and draw the line passing through them. This line is the graph of x – y = 2.

(iii) y = 3x
Answer:
y = 3x
To draw the graph of y = 3x, we find three solutions of y = 3x.
For x = 0, y = 3 × 0 = 0.
For x = 1, y = 3 × 1 = 3.
For x = 2, y = 3 × 2 = 6.
We represent these solutions in the tabular form as below:
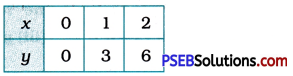
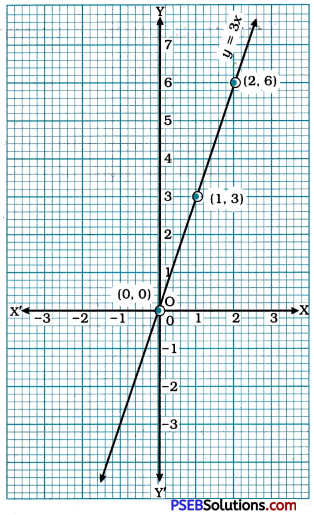
Then, we plot these points on the Cartesian plane and draw the line passing through them. This line is the graph of y = 3x.

(iv) 3 = 2x + y
Answer:
To draw the graph of 3 = 2x + y. we find three solutions of 3 = 2x + y by expressing it as y = 3 – 2x.
For x = 0, y = 3 – 2 × 0 = 3.
For x = 1, y = 3 – 2 × 1 = 1.
For x = 2, y = 3 – 2 × 2 = – 1.
We represent these solutions in the tabular form as below:
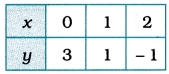
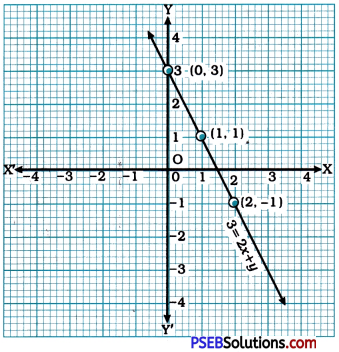
Then, we plot these points on the Cartesian plane and draw the line passing through them. This line is the graph of 3 = 2x + y.
Question 2.
Give the equations of two lines passing through (2, 14). How many more such lines are there, and why?
Answer:
Equations y = 7x and x + y = 16 are two equations of lines passing through point (2, 14) as the coordinates of the point satisfy both the equations.
There are infinitely many equations which are satisfied by the coordinates of the point. Few examples of such equations are y – x = 12, y = 6x + 2, x – y = – 12, etc. This happens so because infinitely many lines pass through a point given in a plane.

Question 3.
If the point (3, 4) lies on the graph of the equation 3y = ax + 7, find the value of a.
Answer:
As the point (3, 4) lies on the graph of the equation 3y = ax + 7, its coordinates, i.e., x = 3 and y = 4 must satisfy the equation.
Hence, we get
3(4) = a(3) + 7
∴ 12 = 3a + 7
∴ 12 – 7 = 3a
∴ 5 = 3a
∴ 3a = 5
∴ a = \(\frac{5}{3}\)
Question 4.
The taxi fare in a city is as follows: For the first kilometre, the fare is ₹ 8 and for the subsequent distance it is ₹ 5 per km. Taking the distance covered a x km and total fare as ₹ y, write a linear equation for this information, and draw its graph.
Answer:
Let the total distance covered be x km and the total fare be ₹ y. Now, the fare for the first km is ₹ 8 and for the remaining (x – 1) km, it is ₹ 5 per km. Hence, the total fare will turn out to be ₹ [(8 + 5 (x – 1)]. Hence, we get the equation as
8 + 5(x – 1) = y
∴ 8 + 5x – 5 = y
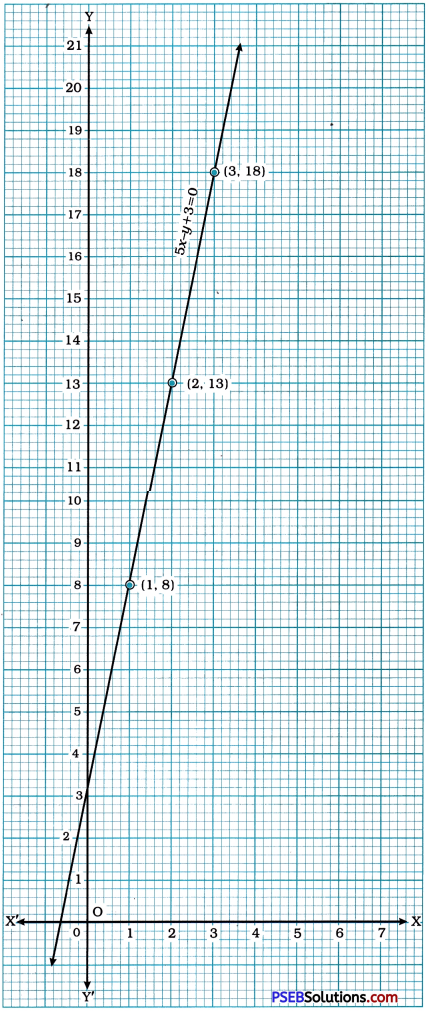
∴5x – y + 3 = 0
To draw the graph of this equation, we find three solutions of the equation by expressing the equation in the form y = 5x + 3.
Note: Distance travelled cannot be zero or negative. Hence, we choose only positive values of x.
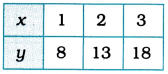
For x = 1, y = 5(1) + 3 = 8.
For x = 2, y = 5(2) + 3 = 13.
For x = 3, y = 5(3) + 3 = 18.
We represent these solutions in the tabular form as below:
 Then, we plot these points on the Cartesian plane and draw the line passing through them. This line is the graph of the equation 5x – y + 3 = o derived above.
Then, we plot these points on the Cartesian plane and draw the line passing through them. This line is the graph of the equation 5x – y + 3 = o derived above.

Question 5.
From the choices given below, choose the equation whose graphs are given in figure (1) and figure (2):
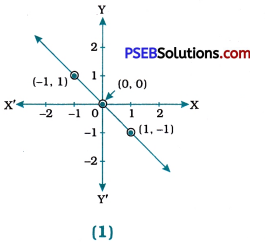
For figure (1)
(i) y = x
(ii) x + y = 0
(iii) y = 2x
(iv) 2 + 3y = 7x
Answer:
For figure (1): The graph of equation (ii) x + y = 0 is given in figure (1) as all the three points represented on the line, i.e., (- 1, 1), (0, 0) and (1, – 1) satisfy equation x + y = 0. For other equations, (1) y = x and (iii) y = 2x are satisfied by the point (0, 0), but not by the other two points. Equation (iv) 2 + 3y = 7x is not satisfied by any point.
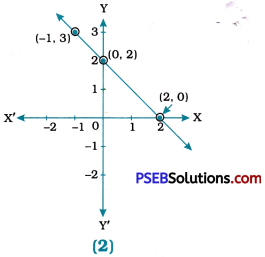
For figure (2)
(i) y = x + 2
(ii) y = x – 2
(iii) y = – x + 2
(iv) x + 2y = 6
Answer:
For figure (2): The graph of equation (iii) y = – x + 2 is given in figure (2) as all the three points represented on the line, i.e., (- 1, 3), (0, 2) and (2, 0) satisfy equation y = – x + 2. Equation (i) y = x + 2 is satisfied by only one point (0, 2). Equation (ii) y = x – 2 is satisfied by only one point (2, 0). Equation (iv) x + 2y = 6 is not satisfied by any point.

Question 6.
If the work done by a body on application of a constant force is directly proportional to the distance travelled by the body, express this in the form of an equation in two variables and draw the graph of the same by taking the constant force as 5 units. Also read from the graph the work done when the distance travelled by the body is (i) 2 units (ii) 0 unit.
Answer:
We know well that
Work done = Force × Distance travelled.
Let the work done be y, the distance travelled be x and here the constant force applied is 5 units.
Then, the relation reduces to y = 5x which is a linear equation in two variables.
To draw the graph of y = 5x. we find three solutions of the equation and represent them in the tabular form.
For x = 1, y = 5 × 1 = 5.
For x = 3, y = 5 × 3 = 15.
For x = 4, y = 5 × 4 = 20.
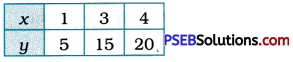
Then, we plot these points on the Cartesian plane and draw the line passing through them. This line is the graph of the equation derived above. The coordinates of any point on the line will satisfy the derived equation.
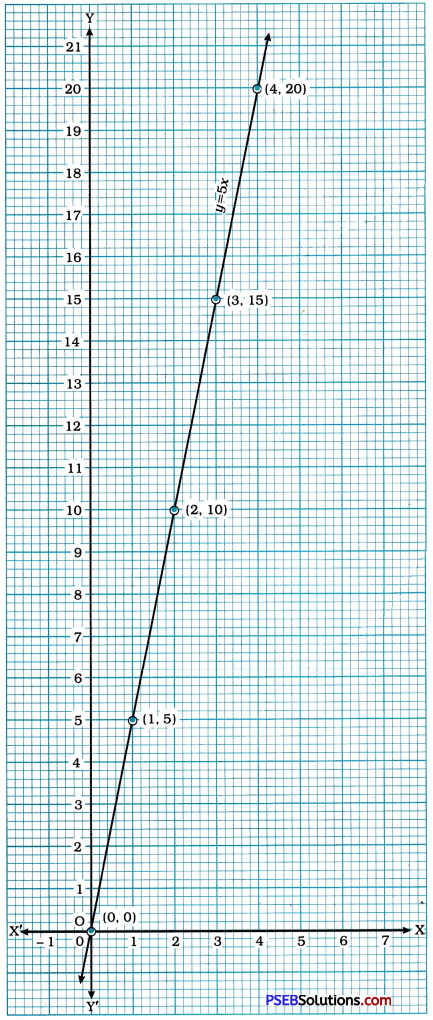
(i) From the graph, we observe that when the distance travelled (x) is 2 units, the work done (y) is 10 units.
(ii) From the graph, we observe that when the distance travelled (x) is 0 unit, the work done (y) is 0 unit.

Question 7.
Yamini and Fatima, two students of class IX of a school, together contributed ₹ 100 towards the Prime Minister’s Relief Fund to help the earthquake victims. Write a linear equation which satisfies this data. (You may take their contributions as ₹ x and ₹ y). Draw the graph of the same.
Answer:
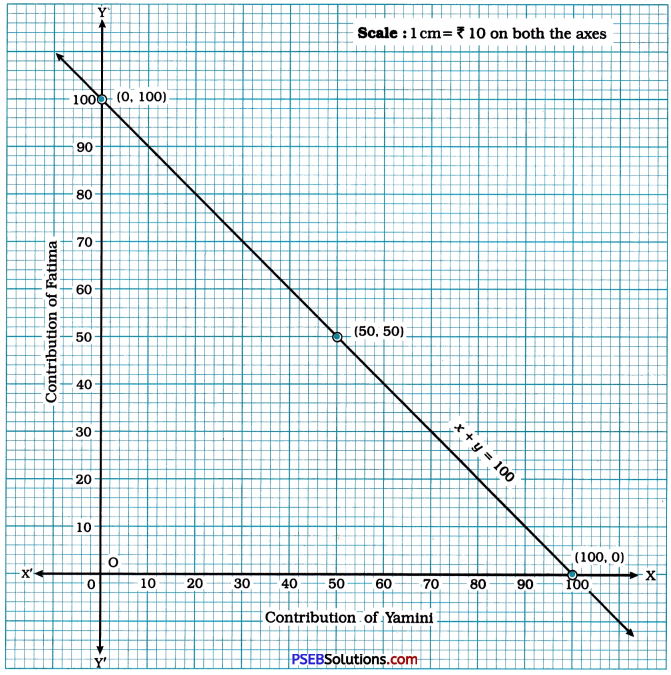
1et the contribution of Yamini be ₹ x and the contribution of Fatima be ₹ y. Then, their total contribution is ₹ (x + y). Their total contribution is given to be ₹ 100. Hence, we get the linear equation x + y = 100.
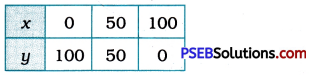
Now, to draw the graph, we find three solutions.
For x = 0, y = 100. For x = 50, y = 50, For x = 100, y = 0.
We represent these solution in the tabular form as below:
We plot these three point in the Cartesian plane and draw the line passing through them. This line is the graph of the mathematical representation of the information given in the data.

Question 8.
In countries like USA and Canada, temperature is measured In Fahrenheit, whereas in countries like India, it is measured in Celsius. Here is a linear equation that converts Fahrenheit to Celsius:
F = \(\left(\frac{9}{5}\right)\)C + 32
(i) Draw the graph of the linear equation above using Celsius for x-axis and Fahrenheit for y-axis.
Answer:
F = \(\left(\frac{9}{5}\right)\)C + 32
For C = – 15,
F = \(\frac{9}{5}\)(- 15) + 32 = – 27 + 32 = 5
For C = 10,
F = \(\frac{9}{5}\)(10) + 32 = 18 + 32 = 50
For C = 60,
F = \(\frac{9}{5}\)(60) + 32 = 108 + 32 = 140
Hence, three solutions of F = \(\left(\frac{9}{5}\right)\)c + 32 can be given in the tabular form as below:
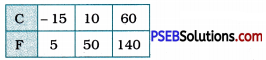
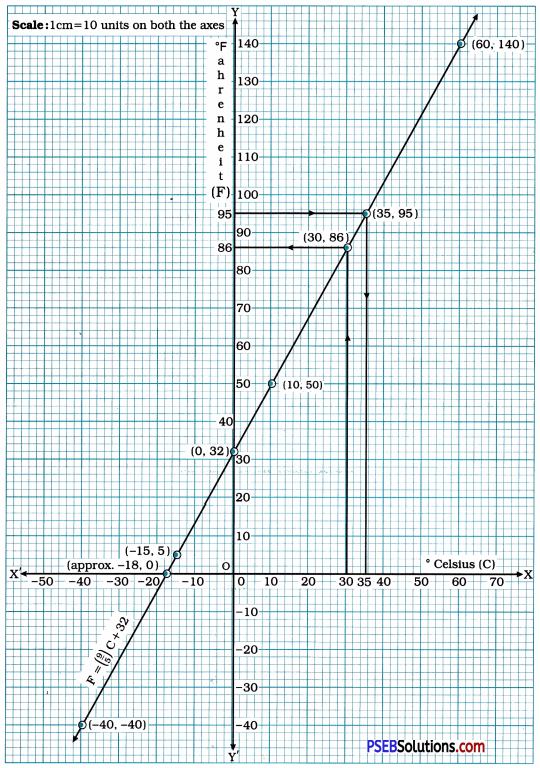
To draw the graph of F = \(\left(\frac{9}{5}\right)\)c + 32.
we take Celsius (°C) on the x-axis and Fahrenheit (°F) on the y-axis with scale 1 cm = 10 units on both the axes.
Then, we plot the points (- 15, 5), (10, 50) and (60, 140) and draw the line passing through them which is the graph of the equation F = \(\left(\frac{9}{5}\right)\)C + 32.
(ii) If the temperature is 30°C, what is the temperature in Fahrenheit?
Answer:
If the temperature is 30 °c means the x-coordinate of the point is 30. Now, the point on the graph of F = \(\left(\frac{9}{5}\right)\)C + 32 having x-coordinate 30 has y-coordinate 86.
From the equation for C = 30, we get
F = \(\left(\frac{9}{5}\right)\)3o + 32 = 54 + 32 = 86.
Hence, if the temperature is 30°C, in the Fahrenheit scale it is 86°F.
(iii) If the temperature is 95 °E what is the temperature in Celsius?
Answer:
If the temperature is 95°F means the y-coordinate of the point is 95. Now, the point on the graph of F = \(\left(\frac{9}{5}\right)\)C + 32 having y-coordinate 95 has x-coordinate 35.
From the equation for F = 95, we get
95 = \(\left(\frac{9}{5}\right)\)C + 32
∴ 63 = \(\left(\frac{9}{5}\right)\)C
∴ C = 63 × \(\frac{5}{9}\)
∴ C = 35

(iv) If the temperature is 0°C, what is the temperature in Fahrenheit and if the temperature is 0 °F, what is the temperature in Celsius?
Answer:
As explained in (ii) and (iii) above, if the temperature is 0 °C, in the Fahrenheit scale it is 32°F. And if the temperature is 0 °F, in the Celsius scale it is – 18 °C approximately as observed from the graph. From the equation, for C = 0, we get
F = \(\left(\frac{9}{5}\right)\)0 + 32 = 0 + 32 = 32, and for
F = 0, we get
0 = \(\left(\frac{9}{5}\right)\)C + 32
∴ – 32 = \(\left(\frac{9}{5}\right)\)C
∴ C = – 32 × \(\frac{5}{9}\)
∴ C = – \(\frac{160}{9}\)
∴ C = – 17 \(\frac{7}{9}\)
(v) Is there a temperature which is numerically the same in both Fahrenheit and Celsius? If yes, find it.
Answer:
Yes, there is a temperature which is numerically the same in both Fahrenheit and Celsius.
As we see, the graph of F = \(\left(\frac{9}{5}\right)\)C + 32 passes through the point (- 40, – 40), i.e., – 40°C = – 40°F.
From the equation for F = C, we get
C = \(\left(\frac{9}{5}\right)\)C + 32
∴ – 32 = \(\frac{9}{5}\)C – C
∴ – 32 = \(\frac{4}{5}\)C
∴ C = – 32 × \(\frac{5}{4}\)
∴ C = – 40
Hence, – 40 is the temperature which is numerically the same in both Fahrenheit and Celsius.

![]()

![]()








 Then, we plot these points on the Cartesian plane and draw the line passing through them. This line is the graph of the equation 5x – y + 3 = o derived above.
Then, we plot these points on the Cartesian plane and draw the line passing through them. This line is the graph of the equation 5x – y + 3 = o derived above.







