PSEB 12th Class Physical Education Practical Swimming
Swimming Game History
Swimming was an ancient game and found on the rock painting at Egypt and Babylonion caves. In India, swimming pool was found in Mohenjodaro’s palace. Swimming became a competitive sport in the early 1800s. It came into prominence when Matthew Webb crossed English Channel. He became the first person to swim across the English Channel. Swimming was one of the events in First Modem Olympic Games held in Athens in 1896.
In the inaugural Modem Olympics men competed in four swimming events and women first participated in the year 1912 Summer Olympics at Stockholm. FINA (International Swimming Federation) was established on 19 July 1908. Swimming Federation of India was formed in 1948.

![]()
Swimming Game Important Points
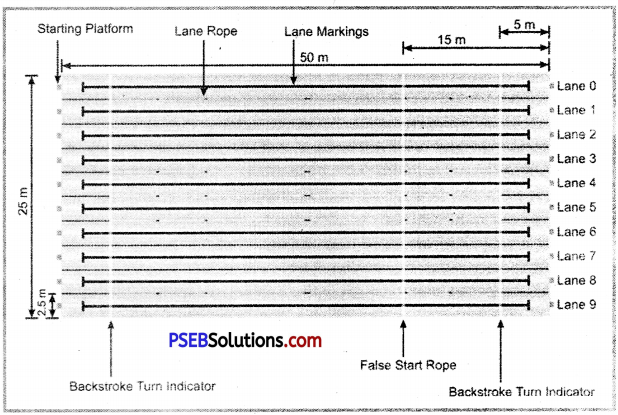
- Length of the Swimming Pool:50 m
- Width of the Swimming Pool:25 m
- Number of Lane:08
- Width of the Lane:2.5 m
- Depth of the Swimming Pool:1.80 m
- Height of the Platform from Water:0.5 to 0.75 m
- Temperature of Water:24° C
- Total Referees:06 to 07
![]()
Fundamental Skills:
1. Free Style:
Free style, often called the “crawl,” is the most flexible in its rules, and it is typically the fastest stroke. Freestyle is swum face-down with alternating arm strokes; side-breathing; and rapid, alternating up-and-down kicks.
2. Back Stroke:
Backstroke is often thought of as “upside-down freestyle.” As in freestyle, backstroke is swum with alternating arm strokes and rapid, alternating, up-and-down kicks. Unlike freestyle, the swimmer must be on his/her back, facing the sky.
3. Breast Stroke:
Breaststroke is often thought of as the “frog stroke,” as the kick is reminiscent of a frog’s kick. A breaststroke swimmer’s arms and legs must move simultaneously, on the same horizontal plane, and identically to each other. The arms and legs stay mostly underwater, but a swimmer’s head must break the surface every stroke. So-called scissor kicks are not allowed. The arm stroke begins and ends in streamline position. The hands scoop water out to the sides, before sweeping in toward the middle of the body and then shooting forward. Swimmers are not allowed to pull their hands down past their hips, and must keep their elbows in the water when their hands are shooting forward.
4. Butterfly Stroke:
Butterfly is swum with an undulating, dolphin-like movement at the surface of the water. The arms pull underwater simultaneously, and recover over the water, also simultaneously. Both hands must come out of the water at the same time on every stroke. During each arm pull, swimmers perform two dolphin kicks, one when the hands enter the water, and the other when the hands exit the water. A swimmer’s feet must kick up and down together, ideally with the feet kept close together.
![]()
Events in swimming:
The following events are conducted in swimming:
| Category | Events for Men | Events for Women |
| 1. Free Style | 50, 100, 200, 400, 800 and
1500 metres 1500 metres |
50, 100, 200, 400, 800 and |
| 2. Back Stroke | 100 and 200 metres | 50, 100 and 200 metres |
| 3. Breast Stroke | 50, 100 and 200 metres | 50, 100 and 200 metres |
| 4. Butterfly | 50, 100 and 200 metres | 50, 100 and 200 metres |
| 5. Individual Medley | 100, 200 and 400 metres | 100, 200 and 400 metres |
| 6. Freestyle Relays | 4 x 100 and 4 x 200 metres | 4 x 100 and 4 x 200 metres |
| 7. Medley Relay | 4 x 100 metres | 4 x 100 metres |
| 8. Mixed Relays | 4 x 100 metres free style and
4 x 100 metres medley |
4 x 100 metres free style and
4 x 100 metres medley |
Rules In Swimming:
There are few rules as follow:
The four competitive strokes are
1. Free Style
2. Back Stroke
3. Breast Stroke
4. Butterfly.
Events are held in all of the competitive strokes at varying distances depending on the age- group of the swimmer. In addition, there is a combination of the strokes swum by one swimmer called the individual medley (IM). Other swimming events include relays, which are a group of four swimmers who either all swim freestyle (freestyle relay) or each swim one of the competitive strokes in the order of backstroke, breaststroke, butterfly and freestyle (medley relay).
1. Free Style:
In freestyle events, the competitor may swim any stroke. The stroke most commonly used is sometimes called the crawl, which is characterized by the alternate stroking of the arms over the water surface and an alternating (up- and-down) flutter kick. On turns and finishes, some part of the swimmer must touch the wall. Most swimmers do a flip turn.

2. Back Stroke:
The backstroke consists of an alternating motion of the arms with a flutter kick while on the hack. On turns, swimmers may rotate to the stomach and perform a flip turn and some pari of the swimmer must touch the wall. The swimmer must finish on the back.

3. Breast Stroke:
The breaststroke requires simultaneous movements of the arms on the same horizontal plane. The hands are pressed out from in front of the breast in a heart shaped pattern and recovered under or
on the surface of the water. The kick is a simultaneous somewhat circular motion similar to the action of a frog. On turns and at the finish, the swimmer must touch the wall with both hands simultaneously at, above or below the water surface.

4. Butterfly:
The butterfly features a simultaneous recovery of the arms over the water combined with an undulating dolphin kick. In the kick, the swimmer must keep both legs together and may not flutter, scissors or use the breaststroke kick. Both hands must touch the wall simultaneously on the turns and the finish,

5. Individual Medley:
Commonly referred to as the I.M., features all four strokes. In the EM. the swimmer begins with the butterfly, then changes after one-fourth of the race to backstroke, then breaststroke and finally freestyle.
6. Starts:
The swimmers are not allowed a false start. If they jump the start and the starter thinks they are trying to get an advantage, they will be taken out of the race. This is not like the Olympics where they are allowed two false starts.
![]()
Turns And Finishes:
Technical rule violations for each stroke may include:
1. Free Style:
Feet have to touch the wall.
- Walking on the bottom.
- Pulling on the lane rope.
- Not touching the wall on a turn.
- Not completing the distance.
2. Back Stroke:
Swimmers have to be on their back when they touch the wall. After he/she touches, he/she can then turn around, but he/she must push off on their back. At the finish a swimmer must finish on his/her back. A swimmer may not roll over and grab the wall until they have first touched it.
- Turning past the vertical onto the stomach and gliding or kicking into the wall on the turn.
- Pushing off the wall on the stomach after a turn.
- Not remaining on back while swimming.
- Turning onto stomach before the finish.
3. Breast Stroke and Butterfly:
- Swimmers have to touch with both hands at the same time.
- A swimmer may not freestyle kick off the wall in either breaststroke or butterfly.
- When swimming butterfly, both arms must move at the same time.
Breast Stroke:
- Using either a flutter, dolphin, or scissor kick instead of the breaststroke kick.
- Shoulders not at level.
- Alternating movements of the arms.
- Head not coming out of the water for each stroke including one pull and kick.
- Touching with one hand at the turns or at the finish.
Butterfly:
- Alternating movements of the arms or legs.
- Pushing the arms forward under instead of over the surface of the water.
- Using a breaststroke style kick.
- Touching with only one hand at the turns or at the finish.
![]()
Swimming Game Important Terminologies
1. Lane Line:
In swimming, a specific lane is assigned to swimmer. These lanes often are numbered. The assigned lane is your designated swimming area. The lanes are separated by lane lines, or floating markers attached to cables.
2. Flag:
Rags are triangular banners featuring two or more colors and hanging down over the lanes on lines. Backstroke flags are placed at the end of each lane to let the swimmers performing backstroke, who have limited visibility, know that they are approaching the wall.
3. Deck and Lap:
The pool is surrounded by a hard surface called a deck. When an athlete swim from one end of a pool to the other, the distance is commonly called a lap, although a lap also can be used to mean the down-and-back distance that is twice the length of the pool.
4. Back Stroke:
Breast Stroke and Freestyle. The backstroke, is performed lying on the back. The breaststroke, in which a swimmer keep his body on his breast. The freestyle, or crawl, is the most common stroke, which is performed on stomach while alternating your arms and using a flutter kick.
5. Diving and Relay: Other common terms include diving, a method of entering the water by jumping in head first.
![]()
Swimming Game Important Tournaments
International Level
- Olympics Games
- Common Wealth Games
- Asian Games
- World Cup
- World University
National Level:
- Senior National Championship
- All India Intervarsity Championship.
- Junior National Championship.
Arjuna Award Winners
- Banjari Bharagava, Khajan Singh, Shikha Tondon-2006
- J. Banjari Dass-1961
- Reema Dutta-1966
- Arun Shah-1967
- VaidNath-1969
- Bhanwar Singh-1971
- Dhanvir-1973
- Avinash Narang & Majari Bhargav-1974
- M.M. Sunita Desai, M.M. Rana & Persis Meidan-1975
- Anita Sood-1983
- Tara Nath-1985
- Wilson Chorian-1988
- NishaMilate-2000
- Sabischares & J. Abhijeet-2001
![]()
Swimming Game Important Questions
Question 1.
What is the length of the swimming pool?
Answer:
The length of the swimming pool is 50 m.
Question 2.
What is the breadth of the swimming pool?
Answer:
The breadth of the swimming pool is 25 m.
Question 3.
What will he the depth of the pool?
Answer:
The depth of the pool is 1.80 m
Question 4.
How many lanes are in the swimming pool?
Answer:
Total numbers of the lane are 08 in the pool.
![]()
Question 5.
What will be the width of each lane?
Answer:
The width of each lane is 2.5 m.
Question 6.
What is the height of the platform from water?
Answer:
The height of the platform from water is 0.5 to 0.75 m.
Question 7.
What will be the temperature of the water?
Answer:
The temperature of the water is 24°C.
Question 8.
How many officials perform duty in swimming competition?
Answer:
There are 6 to 7 officials performing duties during competition.
Question 9.
How many types of events are there in free style?
Answer:
There are 6 types of events played in freestyle. For example 50,100,200,400,800, and 1500 m.
![]()
Question 10.
What kind of strokes are used in swimming during competition?
Answer:
There are four main styles used in swimming competition i.e. free style, back stroke, breast stroke and butterfly stroke.
Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class Physical Education Book Solutions 12th Class Physical Education Practical Swimming Important Notes, Questions and Answers.