Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 3 Human Reproduction Important Questions and Answers.
PSEB 12th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 3 Human Reproduction
Very short answer type questions
Question 1.
Why are the human testes located outside the abdominal cavity? Name the pouch in which they are present.
Answer:
The human testes need lower temperature, 2-2.5°C less than the body temperature, for the formation of sperms which is provided outside the body. Testes are present in scrotal sac or scrotum.
Question 2.
Write the location and function of the sertoli cells in humans.
Answer:
Sertoli cells are present in seminiferous tubules. They provide nutrition to the germ cells or sperms.
Question 3.
Mention the location and the function of leydig cells in humans.
Answer:
Leydig cells are present in seminiferous tubules. They synthesise and secrete androgens.
![]()
Question 4.
The path of sperm transport is given below. Provide the missing steps in blank boxes. [NCERT Exemplar]
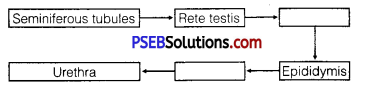
Answer:
Vasa efferentia, Vas deferens.
Question 5.
Female reproductive organs and associated functions are given below in column A and B. Fill in the blank boxes. [NCERT Exemplar]
| Column A | Column B |
| Ovaries | Ovulation |
| Oviduct | A |
| B | Pregnancy |
| Vagina | Birth |
Answer:
A – Fertilisation
B – Uterus
Question 6.
What is the role of cervix of the human female system in reproduction? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Cervix helps in regulating the passage of sperms into the uterus and forms the birth canal to facilitate parturition.
Question 7.
When do the oogenesis and the spermatogenesis initiate in human females and males respectively?
Answer:
In females; oogenesis initiates during foetal life. In males, spermatogenesis begins at the time of puberty.
![]()
Question 8.
Mention the importance of LH surge during menstrual cycle. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
LH surge is essential for the events leading to ovulation.
Question 9.
Menstrual cycles are absent during pregnancy. Why? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
The high levels of progesterone and estrogens during pregnancy suppress the release of gonadotropins required for the development of new follicles. Therefore, new cycle cannot be initiated.
Question 10.
How does the sperm penetrate through the zona pellucida in [ human ovum?
Answer:
The sperm penetrates through zona pellucida with the help of secretions from acrosome.
Question 11.
Mention the function of trophoblast in human embryo.
Answer:
Trophoblast is the outer layer of blastocyst which helps in the attachment of blastocyst to the endometrium of the uterus.
Question 12.
Explain the function of umbilical cord.
Answer:
It transports nutrients and respiratory gases and metabolic wastes to and from mother and foetus.
![]()
Question 13.
Given below are the stages in human reproduction. Write them ‘ in correct sequential order.
Insemination, Gametogenesis, Fertilisation, Parturition, Gestation, Implantation. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Gametogenesis, Insemination, Fertilisation, Implantation, Gestation, Parturition.
Question 14.
What stimulates pituitary to release the hormone responsible for parturition? Name the hormone.
Answer:
The signal from the fully developed foetus and placenta or the foetal , ejection reflex induces mild uterine contraction. The hormone released is oxytocin.
Question 15.
Name the important mammary gland secretions that help in resistance of the new bom baby. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Colostrum
Question 16.
Mention the function of mitochondria in sperm.
Answer:
It provide energy for the movement of sperm tail.
Short answer type questions
Question 1.
Write the function of each of the following:
(a) Middle piece in human sperm.
(b) Luteinising hormone in human males.
Answer:
(a) Provides energy for movement.
(b) Stimulates synthesis and secretion of androgens or male hormones for spermatogenesis.
![]()
Question 2.
Differentiate between mayor structural changes in the human ovary during the follicular and luteal phase of the menstrual cycle.
Answer:
| Follicular phase | Luteal phase |
| 1. During this, primary follicles grow to become fully mature Graafian follicle. | During this, remaining part of Graafian follicle transforms into corpus luteum. |
| 2. Endometrium regenerates through proliferation. | Endometrium further thickens secreting progesterone for implantation after fertilisation. If fertilisation does not occur, corpus luteum degenerates. |
Question 3.
Explain the events in a normal woman during her menstrual cycle on the following days :
(a) Pituitary hormone levels from 8 to 12 days.
(b) Uterine events from 13 to 15 days.
(c) Ovarian events from 16 to 23 days.
Answer:
(a) The level of LH and FSH secreted by anterior lobe of pituitary, stimulated by GnRH, increases.
(b) The endometrium of the uterus regenerates through proliferation. It grows and become thickened. There is repair of ruptured blood vessels and new blood capillaries develop. Uterine glands elongate.
(c) The remnant of Graafian follicle forms corpus luteum which secretes large amount of progesterone essential for maintenance of endometrium for implantation and for pregnancy.
Question 4.
What happens to corpus luteum in human female if the ovum is (a) fertilised, (b) not fertilised?
Answer:
(a) In case the ovum is fertilised, the corpus luteum persists and secretes a large amount of progesterone. The progesterone is essential for maintenance of endometrium, a necessity for implantation and for pregnancy.
(b) In the absence of fertilisation, corpus luteum degenerates. The level of LH and progesterone decreases very low. The absence of hormonal support, leads to the disintegration of endometrium and results in menstrual flow.
![]()
Question 5.
A large number of married couples the world over are childless. It is shocking to know that in India the female partner is often blamed for the couple being childless.
(a) Why in your opinion the female partner is often blamed for such situations in India? Mention any two values that you as a biology student can promote to check this Social evil.
(b) State any two reasons responsible for the cause of infertility.
(c) Suggest a technique that can help the couple to have a child where the problem is with the male partner.
Answer:
(a) The female partner is wrongly blamed for not bearing the child. It is due to the lack of proper information and knowledge about the reproduction and reproductive organs. Being a biology student I will advise and explain the couple as well as their other family members. Both male and female are equally responsible for bearing child. The two value, promoted are (i) concern for others (ii) scientific
temperament.
(b) Infertility is the inability to produce children inspite of unprotected sex and sexual co-habitation. It may be due to (i) physical/congenital disease (ii) immuno- logical or even physiological reason.
(c) In case, the problem is with male partner, artificial insemination (AI) is adopted. Semen collected either from the husband or a healthy donor is artificially introduced in the vagina or into the uterus of the female.
Question 6.
Name and explain the role of inner and middle walls of the human uterus.
Answer:
The inner wall of the uterus is called endometrium. It supports foetal growth and helps in placenta formation after implantation.
The middle wall of the uterus is called myometrium, exhibits strong contraction during delivery of baby.
Question 7.
Write a brief account of the structure and functions of placenta. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Placenta connects the foetus to the uterus through an umbilical chord. Both the foetal and the maternal tissues contribute to its formation. The foetal part is the chorionic villi and the maternal part is the uterine mucosa.
![]()
Long answer type questions
Question 1.
(a) Briefly explain the events of fertilisation and implantation in an adult human female.
(b) Comment on the role of placenta as an endocrine gland.
Or
Name the stage of human embryo of which it gets implanted.
Explain the process of implantation.
Or Draw a labelled diagram of a human blastocyst. How does it get implanted in the uterus?
Answer:
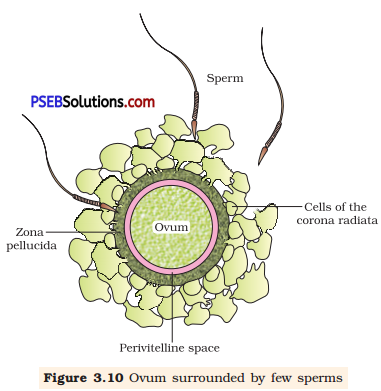
(a) (i) Fertilisation : Fertilisation occurs, if the ovum and sperms are transported simultaneously to the ampullary-isthmic junction and involve fusion of sperm with an ovum.
Secretions of acrosome of sperm help it to enter into the cytoplasm of ovum through zona pellucida and the plasma membrane. It induces meiotic division-II to form haploid ovum (ootid) and secondary polar body. The fusion of sperm with ovum to form diploid zygote is called fertilisation.
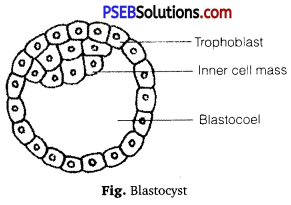
(ii) Implantation: Zygote undergoes cleavage to form a solid mass of 16 cells-morula, with daughter cells called blastomeres. Morula develops into a embryo with about 64 cells and with a cavity called blastocoel and the embryo is termed as blastocyst. It consists of outer layer of cells-trophoblast and inner cell mass.
The trophoblast gets attached to the endometrium- uterine wall of mother, after 7 days of fertilisation by a process called implantation leading to pregnancy. The uterine cells divide rapidly and cover blastocyst. The blastocyst gets embedded in the endometrium. Inner cell mass forms embryo.
(b) Placenta beside providing nutrients to the foetus also act as an endocrine gland. Placenta secretes human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG), human placental lactogen (hPL), estrogen, progesterone etc., and later relaxin is secreted by ovary which facilitates parturition. Increased level of hormones like cortisol, prolactin and thyroxine etc., help in foetal growth, metabolic changes in the mother and maintenance of pregnancy.