Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation Important Questions and Answers.
PSEB 12th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation
Very short answer type questions
Question 1.
Why is genetic variation important in the plant Rauwolfia vomitoria? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Genetic variation affects the variation in potency and concentration of me drug reserpine in the medicinal plant Rauwolfia vomitoria.
Question 2.
Name the type of biodiversity represented by the following:
(i) 50,000 different strains of rice in India
(ii) Estuaries and alpine meadows in India.
Answer:
(i) Genetic diversity
(ii) Ecological diversity
Question 3.
Identify ‘a’ and ‘b’ in the figure given below representing proportionate number of major vertebrate taxa.
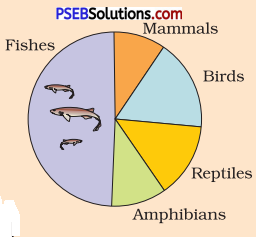
Answer:
(a) Mammals
(b) Amphibians
Question 4.
Suggest two practices giving one example by each, that help protect rare or threatened species.
Answer:
- By using cryopreservation (preservation at -196°C) technique, sperms, eggs, tissues, and embryos can be stored for long period in gene banks, seed banks etc.
- Plants are propagated in vitro using tissue culture methods.
Question 5.
According to David Tilman, greater the diversity greater is the primary productivity. Can you think of a very low diversity man-made ecosystem that has high productivity? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Agricultural fields like wheat field or paddy field which are also examples of monoculture practices.
![]()
Question 6.
What is Red Data Book? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
The Red Data Book is a compilation of data on species threatened with extinction and is maintained by IUCN. ‘
Question 7.
What is the expanded form of IUCN? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
International Union for Conservation of Nature.
Question 8.
Why Western Ghats in India have been declared as biological hotspots?
Answer:
Western Ghats are biological hotspots because they have species richness and species evenness.
Question 9.
What is a national park?
Answer:
It is a protected area reserved for wildlife where human activities are not permitted.
Question 10.
What is the difference between endemic and exotic species? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Endemic species are native species restricted to a particular geographical region. Exotic species are species which are introduced from other geographical regions into an area.
Question 11.
How is the presently occurring species extinction different from the earlier mass extinctions? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Species extinction occurring at present is due to anthropogenic or man-made causes whereas the earlier extinction was due to natural causes.
Question 12.
Differentiate between in situ and ex situ approaches of conservation of biodiversity.
Answer:
| In situ approach | Ex-situ approach |
| 1. It involves protection of endangered species of plants and animals. | It involves protection of endangered species by removing them from the natural habitat. |
| 2. This is done by protecting the natural habitat or ecosystem. | This is done by placing the species under special care. |
Short answer type questions
Question 1.
What is biodiversity? Why is it a matter of concern now?
Answer:
Biodiversity is the occurrence of different types of genes, gene pools, species, habitats and ecosystems at a particular place and various parts of earth. It is a matter of concern because species are continuously lost, limiting the diversity and this will affect our survival and well-being on earth due to the changes in environment.
![]()
Question 2.
Where would you expect more species biodiversity-in tropics or in polar regions? Give reasons in support of your answer.
Answer:
More biodiversity is found in the tropics. This is because tropical regions remain undisturbed from frequent glaciations as in polar regions. Also, the tropics are less seasonal/more constant.
Question 3.
Is it true that there is more solar energy available in the tropics? Explain briefly. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
As one moves from the equator to the polar regions, the length of the day decreases and the length of the night increases. The length of day and night are same at the equator. Therefore, it is true that there is more solar energy available in the tropics.
Question 4.
The given graph alongside shows species-area relationship. Write the equation of the curve ‘a’ and explain.
Answer:
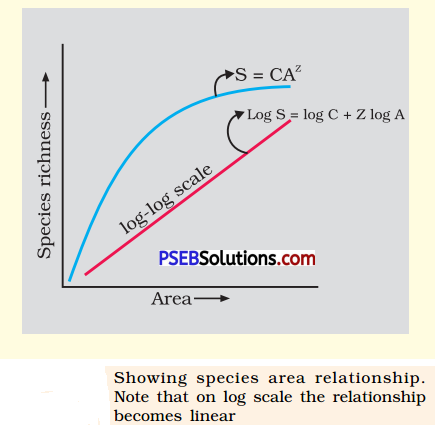
The equation of the curve ‘a’ is S = CAZ.
(i) Within a region, species richness increases with increasing explored area but only up to a limit.
(ii) Relationship between species richness and area for a wide variety of taxa turns out to be a rectangular hyperbola.
Question 5.
Explain ‘rivet popper hypothesis. Name the ecologist who proposed it.
Answer:
Paul Ehrlich proposed the rivet popper hypothesis. This hypothesis states that in an airplane (ecosystem) all parts are joined together using thousands of rivets (species). If every passenger traveling in it starts popping a rivet to take home (causing a species to become extinct), it may not affect flight safety (proper functioning of the ecosystem) initially but as more and more rivets are removed, the plane becomes dangerously weak over a period of time. Also, which rivet is removed may also be critical like loss of rivets on the wings (key species) is more serious threat to flight safety than loss of few rivets on the seats or windows inside the plane.
Question 6.
How do human activities cause desertification?
Answer:
Human activities like over-cultivation, unrestricted grazing, deforestation, and poor irrigation practices result in arid patches of land. The fertile topsoil that may take centuries to develop is eroded due to these activities. When large barren patches extend and meet over time, a desert is created. Increased urbanization is also one of the causes of desertification.
Question 7.
Why are conventional methods not suitable for the assessment of biodiversity of bacteria? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Many bacteria are not culturable under normal conditions in the laboratory. This becomes a problem in studying their morphological, biochemical, and other characterizations which are useful for their assessment.
Question 8.
List any four techniques where the principle of ex-situ conservation of biodiversity has been employed.
Answer:
Ex-situ Conservation (off-site conservation)
- Zoological parks and botanical gardens.
- Wildlife safari parks, aquaria.
- Preservation of germplasm-seed gene banks, tissue culture, cryopreservation.
- Sacred plants grown in homes, villages, and religious places.
Long answer type questions
Question 1.
(a) Why should we conserve biodiversity? How can we do it?
(b) Explain the importance of biodiversity hotspots and sacred groves.
Or
Why should biodiversity be conserved? List any two ethical arguments in its support. ‘
Answer:
(a) Need for Conservation of Biodiversity: Reasons for conservation of biodiversity can be grouped into three categories :
- narrowly utilitarian
- broadly utilitarian and
- ethical.
(i) Narrowly Utilitarian: The reasons for conserving biodiversity are obvious because of their :
(a) direct economic benefits such as
- food (cereals, pulses, fruits)
- firewood
- fiber
- construction material
- products of medicinal importance
- industrial products (tannins, gums, lubricants, dyes, resins, perfumes).
(b) More than 25% of the drugs are derived from plants.
![]()
(c) 25,000 species of plants are used as traditional medicines by native people.
(ii) Broadly Utilitarian: Biodiversity plays a major role in providing ecosystem services that nature provides and which cannot be given a price tag are :
- Production of Oxygen
- Pollination of flowers by bees, bumblebees, birds, and bats, etc.
- Resulting in the formation of fruits and seeds.
- Aesthetic pleasures like bird watching, walking through the thick forests, waking up to bulbul’s song, etc.
(iii) Ethical :
(a) We share this planet with millions of plants, animals, and microbe species. Every species has an intrinsic value even if it is not of current or any economic value to us.
(b) We have an essential duty to care for their well-being and pass on the biological legacy in a proper form to our future generations. We can conserve biodiversity by two major approaches
- In situ conservation (on site/ conservation)
- Ex situ conservation (off-site conservation).
(c) Hotspots are the areas identified by conservationists for the very high level of species richness and high degree of endemism (species confined to a particular area and not found anywhere else). Hotspots help in protection of certain biodiversity-rich regions.
Sacred groves are the tracts of forest set aside where all the trees and wildlife within are given religious sanctity and total protection. Such sacred groves are found in Khasi and Jaintia hills in Meghalaya, Aravalli Hills of Rajasthan etc.