Punjab State Board PSEB 11th Class Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 10 The s-Block Elements Important Questions and Answers.
PSEB 11th Class Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 10 The s-Block Elements Important Questions
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Complete the following reactions,
(i) \(\mathbf{O}_{2}^{2-}\) +H2O →
(ii) O2 +H2O →
Answer:
(i) Peroxide ions react with water to form H202.
\(\mathbf{O}_{2}^{2-}\) + 2H2O→ 20H’ + H2O2
(ii) Superoxides react with water to form H202 and 02.
\(2 \mathrm{O}_{2}^{-}\) + 2H2O → 20H– + H2O2 + O2
Question 2.
(i) Predict giving reason, the outcome of the reaction
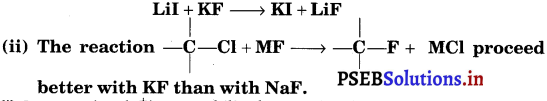
Answer:
(i) Large cation (K+) can stabilise large anion (I–).
(ii) This is because the larger cation (K+) can stabilise larger anion (Cl–).
![]()
Question 3.
Which colours are imparted to flame when the following elements are introduced in the flame one by one?
(i) Strontium (ii) Barium (iii) Calcium
Answer:
(i) Strontium — Brick red
(ii) Barium — Grassy green
(iii) Calcium — Crimson red
Question 4.
Sodium fire in the laboratory should not be extinguished by pouring water. Why?
Answer:
This is because sodium produces hydrogen gas with water which catches fire because of the exothermic nature of the reaction.
Question 5.
What is light soda ash? Wliy is it called so?
Answer:
Light soda ash is anhydrous Na2CO3. It is called so because it is fluffy solid with a low packing density of about 0.5 g cm-3.
Question 6.
What is baryta water? Give its one use.
Answer:
Baryta is an aqueous solution of barium hydroxide. It can also be used for detection of CO2.
Question 7.
Give the chemical formula of quick lime, slaked lime and lime water.
Answer:
Quick lime is CaO, slaked lime is Ca(OH)2 and lime water is an aqueous solution of Ca(OH)2.
Question 8.
Which magnesium compounds are the constituents of toothpaste?
Answer:
Mg(OH)2 and MgCO3 are the constituents of toothpaste.
Question 9.
What is the mixture of CaCN2 and carbon known as?
Answer:
A mixture of calcium cyanamide (CaCN2) and carbon is known as nitrolim. It is used as a fertiliser.
![]()
Question 10.
It is necessary to add gypsum in the final stages of preparation of cement. Explain why?
Answer:
Gypsum (CaSO4 . 2H2O) is added in the final stages of preparation of cement because it slows down the process of setting of cement so that it gets sufficiently hardened thereby imparting greater strength to it.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How would you distinguish between
(i) Be(OH)2 and Ba(OH)2
(ii) BeSO4 and BaSO4
Answer:
(i) Be(OH)2, beryllium hydroxide is soluble in aqueous sodium hydroxide solution whereas Ba(OH)2, (barium hydroxide) does not, because Be(OH)2 is amphoteric in nature and Ba(OH)2 is basic in nature. Be(OH)2 + 2NaOH → Na2[Be(OH)4] (Sodium beryllate)
(ii) BeSO4 is soluble in water whereas BaSO4 is insoluble in water.
Question 2.
Element A bums in nitrogen to give an ionic compound B. Compound B reacts with water to give C and D. A solution of C becomes milky on bubbling carbon dioxide. Identify A, B, C and D.
Answer:
Element A is calcium
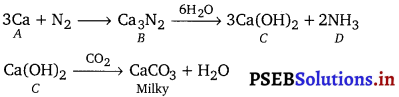
Compounds = Ca3N2 ; CompoundC = Ca(OH)2 and Compound D = NH3
Question 3.
What happens when
(i) chlorine gas is passed through a cold and dilute solution of NaOH?
(ii) yellow phosphorus is heated with NaOH solution?
(iii) carbon dioxide is passed through ammonical brine solution?
(iv) sodium hydrogen carbonate is heated?
Answer:
(i) Sodium hypochlorite and sodium chloride are obtained.
Cl2 + 2NaOH → NaCl + NaClO + H2O
(ii) Phosphine gas is obtained.
P4 + 3NaOH + 3H2O → 3NaH2PO2 + PH3
(iii) Sodium hydrogen carbonate is precipitated.
NH3 + H2O + CO2 + NaCl → NH4Cl + NaHCO3↓
(iv) Sodium ash is obtained.
![]()
![]()
Question 4.
Mention the various sources of sodium chloride and explain the preparation of sodium chloride from sea-water and salt mines.
Answer:
NaCl occurs abundantly in nature. Its major sources are (a) Sea water which contains 2.7 to 2.9 % NaCl.
(b) Water of inland lakes such as Sambhar Lake in Rajasthan.
(c) Salt-mines which contain rock salt are located in England, Australia, and Himachal Pradesh.
Preparation
(i) From sea water : Sea water is filled in big tanks where it slowly evaporates, leaving behind solid salt. In cold countries, where temperatures are very low, pure water get freeze. Ice formed is removed and concentration of NaCl in solution increases. The concentrated sodium can be separated and evaporated to get NaCl.
(ii) From salt-mines : Salt mines are located deep under the surface of the earth. Holes are made into these mines with the help of drillers and broken pieces of salt rocks are taken out by suitable means.
Question 5.
When water is added to compound (A) of calcium, solution of compound (B) is formed. When carhon dioxide is passed into the solution, it turns milky due to the formation of compound (C). If excess of carbon dioxide is passed into the solution, milkiness disappears due to the formation of compound (D). Identify the compound A, B, C and D. Explain why the milkiness disappears in the last step? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Appearance of milkiness on passing CO2 in the solution of compound B indicates that compound B is lime water and compound C is CaCO3. Since, compound B is obtained by adding H2O to compound A, therefore compound A is quicklime, CaO. The reactions are as follows :
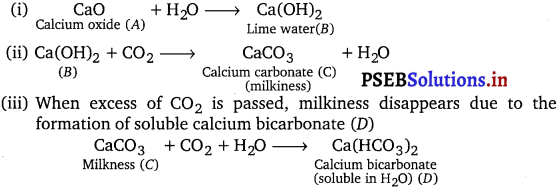
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Ions of an element of group 1 participate in the transmission of nerve signals and transport of sugars and amino acids into cells. This element imparts yellow colour to the flame in flame test and forms an oxide and a peroxide with oxygen. Identify the element and write chemical reaction to show the formation of
its peroxide. Why does the element impart colour to the flame?
Answer:
Yellow colour flame in flame test indicates that the alkali metal must be sodium. It reacts with O2 to form a mixture of sodium peroxide, Na2O2 and sodium oxide, Na2O.
![]()
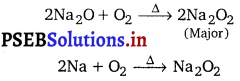
Ionization enthalpy of sodium is low. When sodium metal or its salt is heated in Bunsen flame, the flame energy causes an excitation of the outermost electron which on reverting back to its initial position gives out the absorbed energy as visible light. That’s why sodium imparts yellow colour to the flame.
Question 2.
The stability of peroxide and superoxide of alkali metals increase as we go down the group. Explain giving reason.
Answer:
The stabilit-y of peroxides or superoxides increases as the size of metal ion increases, i.e., KO2 < RbO2 < CsO2.
The reactivity of alkali metals towards oxygen to form different oxides is due to strong positive field around each alkali metal cation. Li+ is smallest, it does not allow 02- ion to react with O2 further. Na+ is larger than Li, its positive field is weaker than Li+. It cannot prevent the conversion of O2- into \(\mathrm{O}_{2}^{2-}\). The larger K+, Rb+ and Cs+ ions permit \(\mathrm{O}_{2}^{2-}\)ion to react with O2 further forming superoxide ion (\(\mathrm{O}_{2}^{-}\)).
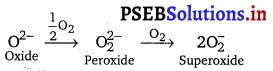
![]()
Further more, increased stability of the peroxide or superoxide with increase in the size of metal ion is due to the stabilisation of large anions by larger cations through lattice energy effect.