Punjab State Board PSEB 11th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 15 Plant Growth and Development Important Questions and Answers.
PSEB 11th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 15 Plant Growth and Development
Very short answer type questions
Question 1.
Identify the actively dividing cells in plants.
Answer:
Meristems are the actively dividing cells present in the plants.
Question 2.
What happens if the meristematic cells ever cease to divide?
Answer:
If meristematic cells cease to divide, the growth of the plant will be hindered and will undergo a period of dormancy depending upon the seasonal changes in the climate. „
Question 3.
Growth is one of the characteristics of all living organisms? Do unicellular organisms also grow? If so, what are the parameters?
Answer:
Yes, unicellular organisms also grow. Their cell size increases up to a certain fixed dimension only.
![]()
Question 4.
Mention the name of the internal factors that control development in plants.
Answer:
Internal factors that control development in plants are as follows:
- Genetic factors (intracellular)
- Plant growth regulators (intercellular).
Question 5.
Identify the plant hormone-related with intermodal elongation.
Answer:
Gibberellin is the plant hormone-related with internodal elongation.
Question 6.
Mention the name the growth regulator, which was first isolated from endosperm of maize. Give its main biological activity.
Answer:
Zeatin is the growth regulator isolated from endosperm of maize. It controls cell division (cytokinesis) even in non-meristematic tissues.
Question 7.
In most plants, the terminal bud suppresses the development of lateral buds into branches. What is this phenomenon called? Name one phytohormone that can promote this phenomenon.
Answer:
The phenomenon is called apical dominance. Auxin is the phytohormone involved in prompting this phenomenon.
Question 8.
Which air pollutant also acts as a plant hormone?
Answer:
Ethylene.
Question 9.
How do gibberellin help in promoting seed germination?
Answer:
The gibberellin mobilize storage reserves by amylases during germination of seeds.
Question 10.
What are the plant organs responsible for the perception of light variation? What is the pigment responsible for this perception?
Answer:
- Leaves are mainly responsible for perception of light intensity in plants.
- The pigment that performs this perception is called phytochrome.
Question 11.
Name the hormones involved in photoperiodism.
Answer:
Florigen is the hormone involved in photoperiodism.
![]()
Question 12.
Beetroot is often known as a long-day plant. Explain why?
Answer:
Beetroot is known as long-day plant because flowering takes place when the plants are exposed to day length longer than a critical period.
Short answer type questions
Question 1.
An owner of an apple orchard wants to get better yield and wants to wait for good market conditions to sell his apples. Which PGR should he use to achieve his goals?
Answer:
He should use Gibberellins. Gibberellins help increase the size of apples. Moreover, they also delay senescence so apples can be left on branches for a longer duration. This will give the orchard owner enough time to wait for good market conditions.
Question 2.
What are plasticity and heterophylly?
Answer:
In some plants, certain structures show different forms, in response to environment or to phases of life. This ability is known as plasticity.
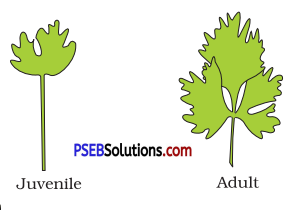
For example, in cotton, coriander, and larkspur, leaves of juvenile plants are different in shape compared to leaves in mature plants. This is called heterophylly. Juvenile In buttercup shape of leaves produced in air is different from that produced in water.
Question 3.
What are the favorable conditions for seed germination?
Answer:
Favorable conditions for seed germination are given below:
- Proper temperature
- Moisture
- Sunlight
- Oxygen.
Question 4.
What are the various man-made meant of overcoming seed dormancy?
Answer:
Man-made means of overcoming seed dormancy are given below :
The seed-coat barrier in some seeds can be broken by mechanical abrasions using knives, sandpaper, etc. or by vigorous shaking.
Effect of inhibitory substances can be removed by subjecting the seeds to chilling conditions or by application of certain chemicals like gibberellic acid and nitrates. Changing environment conditions: like light and temperature.
![]()
Question 5.
What do you understand by apical dominance?
Answer:
In most of the higher plants, growing apical bud inhibits the growth of lateral (axillary buds). This phenomenon is called apical dominance. Removal of short tips (decapitation) normally results in the growth of lateral buds. Decapitation is used in tea plantations to get more leaves from a plant.
Long answer type questions
Question 1.
Mention the phenomenon of growth in plants. Explain the phases of growth in detail.
Answer:
Growth is defined as a permanent or irreversible increase in dry weight, mass or volume of cell, organ or organism.
Plant growth takes place in three steps or phases cell, division (meristematic), cell elongation and cell maturation.
(i) Cell Division (Meristematic) Phase:
- It is also called formative phase.
- New cells are produced by mitotic divisions of the pre-existing cells. The meristematic cells have thin cellulose walls with abundant plasmodesma connections, dense protoplasm and conspicuous nuclei.
- In higher plants cell division occurs in meristems or growing points.
- As the formation of new cells requires intense biosynthetic activity, the rate of respiration in the cells of formation phase is very high.
(ii) Cell Elongation Phase:
- It is also called phase of cell enlargement.
- This phase lies just behind the growing points and is mainly responsible for growth of plant parts.
- The newly formed cells, produced informative phase undergo enlargement.
- The cell walls of the enlarging of cell show plastic extension through enzymatic loosening of microfibrils and deposition of new materials.
- The enlarging cell also develops a central vacuole, rate of respiration is high but less than that of the cells in the formative phase.
- Thus, this phase is characterized by cell enlargement, new cell wall deposition and increased vacuolation.
(iii) Cell Maturation Phase
- This phase occurs just behind the phase of elongation.
- The enlarged cells develop into particular type of cells by undergoing structural and physiological differentiation.
- Hence, at this phase, all the diverse tissue types observed in root or stem.