Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class English Book Solutions Chapter 5 The Punjab: A Glimpse Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Class 8th English Solutions Chapter 5 The Punjab: A Glimpse Question Answers
The Punjab: A Glimpse Class 8 Questions and Answers
Activity 1.
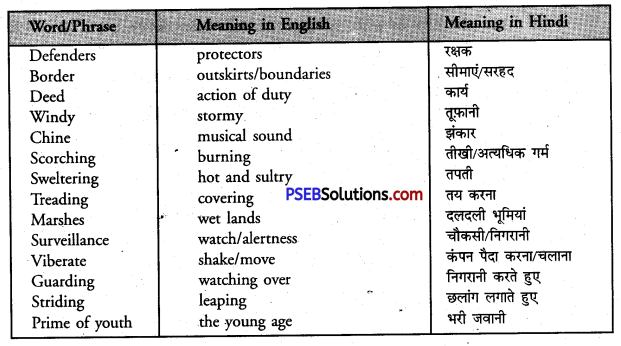
Look up the following words in a dictionary. You should seek the following information about the words and put them in your WORDS notebook.
1. Meaning of the words as used in the lesson (adjective/noun / verb, etc.)
2. Pronunciation (The teacher may refer to the dictionary or a mobile phone for correct pronunciation.)
3. Spellings
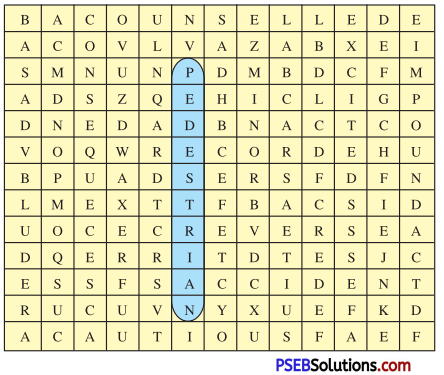
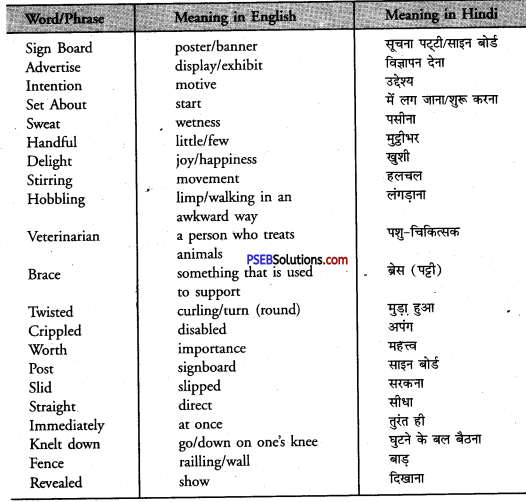
| recognize | pavilion | zest | invasion |
| brutal | procession | irrigate | melodious |
| shrine | pilgrimage | architect | manufacture |
![]()
Vocabulary Expansion
Activity 2
Match the words under column A with their antonyms (विपरीतार्थक) under column B.
| S. No. | A | B |
| 1 | exit | fail |
| 2 | lead | south |
| 3 | raise | lower |
| 4 | order | follow |
| 5 | broad | slavery |
| 6 | north | narrow |
| 7 | famous | request |
| 8 | succeed | disperse |
| 9 | freedom | entrance |
| 10 | assemble | notorious |
Answer:
1. exist – entrance
2. lend – follow
3. raise – lower
4. Order – request
5. broad – narrow
6. north-south
7. famous – notorious
8. succeed – fail
9. freedom – slavery
10. assemble – disperse.
Activity 3.
The sentences given below have two blanks each. Two words are given in the brackets after each sentence.
Fill in the blanks choosing the correct word from the brackets.
1. With a …………… face she said, “My purse is ………………. (empty, black)
2. ………….. children have …………… hands. (small, little)
3. That ……………. young man has a ……………. wife. (handsome, beautiful)
4. The …………….. old man spoke in a ……………..voice. (feeble, weak)
5. The of ………….. of our school is a man of …………….. (principal, principles)
6. You should live in ……………. because …………… is strength. (union, unity)
7. He is a …………….. man with a round face and a …………….. forehead. (tall, high)
Answer:
1. blank, empty
2. little, small
3. handsome, beautiful
4. weak, feeble
5. principal, principles
6. unity, union
7. tall, high.
Learning to Read and Comprehend
Activity 4.
Answer each question briefly.
a.. What is special about Bhangra ?
भांगड़ा नृत्य के बारे में विशेष क्या है ?
Answer:
The Bhangra dance is full of energy. It shows the great zest for life of the Punjabis.
b. Why do you think that the Punjabis are self-respecting people ?
आप ऐसे क्यों सोचते हैं कि पंजाबी लोग स्वाभिमानी लोग हैं ?
Answer:
We can say that because Punjabis would never beg or show their back in battle field.
![]()
c. What was Punjab’s role in the struggle for India’s Independence ?
भारत के स्वतन्त्रता संघर्ष में पंजाबियों का क्या योगदान था ?
Answer:
Lala Lajpat Rai, Bhagat Singh, Sukhdev, Udham Singh, Kartar Singh Sarabha and many other Punjabis sacrificed their lives for the sake of their motherland.
d. What did General O’Dwyer do at the Jallianwala Bagh in Amritsar ?
जनरल ओ’डायर ने अमृतसर के जलियांवाला बाग़ में क्या किया ?
Answer:
On April 13, 1919 about 20,000 people had gathered here for a public meeting.General Dyer ordered his riflemen to fire at the crowd.
e. Which states have benefitted from the Bhakra-Nangal Project ?
भाखड़ा-नंगल परियोजना से किन राज्यों को लाभ पहुंचा है ?
Answer:
Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan and Gujarat have benefitted from this Project.
f. If. What is the religious importance of Anandpur Sahib ?
आनंदपुर साहिब का क्या धार्मिक महत्त्व है ?
Answer:
In Anandpur Sahib the Khalsa was founded by Guru Gobind Singh Ji. Lakhs of Sikhs gather here every year to celebrate the founding of the Khalsa.
g. Where is Chandigarh situated ? What is it known for ?
चंडीगढ़ कहां स्थित है ? यह किस लिए प्रसिद्ध है ?
Answer:
Chandigarh is situated at the foot of the Shivalik Hills. It is known for its “rose gardens.
h. What are Jalandhar and Ludhiana famous for ?
जालन्धर और लुधियाना किस बात के लिए प्रसिद्ध हैं ?
Answer:
Jalandhar is famous for its sports goods while Ludhiana is famous for its woollen hosiery industry.
![]()
i. Who compiled the holy Sri Guru Granth Sahib ?
पवित्र श्री गुरु ग्रंथ साहिब का संकलन किसने किया ?
Answer:
Sri Guru Arjun Dev Ji, the fifth Guru of the Sikhs, compiled Sri Guru Granth Sahib.
j. What do you know about the holiest shrine of the Sikhs ?
आप सिक्खों के सबसे पवित्र धार्मिक स्थल के विषय में क्या जानते हैं ?
Answer:
Golden Temple of Amritsar is the holiest shrine of Sikhs. It is built in the middle of a tank. It has a golden dome on the top.
Activity 5
Write ‘true’ or ‘false’ for the following statements in the given space.
a. General O’Dwyer lived in Jallianwala Bagh. — False
b. Le Corbusier was a great Indian architect. — False
c. Bhagat Singh was hanged on 13 April 1919. — False
d. The Golden Temple has a tank all around it. — True
e. India became an independent country in 1947. — True
f. The Punjabis have faced many foreign invasions. — True
g. Guru Gobind Singh founded the Khalsa in 1669.– False
h. Lala Lajpat Rai is known as Shaheed-e-Azam of India .– False
i. The Bhakra Dam is 518 feet high and 740 feet wide. — False
j. Fifty per cent of India’s hosiery industry is in Ludhiana. — False
k. Dr. Rajendra Prasad was the President of India in 1953. — True
I. Chandigarh is situated on the left bank of the Sutlej River.– False
Activity 6
Tick (√) the correct choice to complete each sentence.
Question 1.
The Jallianwala Bagh massacre took place in ……
(a) 1919
(6) 1928
(c) 1947
(d) 1926.
Answer:
(a) 1919. (√)
Question 2.
The reorganisation of Punjab took place in …….
(a) 1947
(b) 1950
(c) 1966
(d). 1953.
Answer:
(c) 1966. (√)
Question 3.
Kulu and Manali are parts of …
(a) Haryana
(b) Himachal Pradesh
(c) Jammu and Kashmir
(d) Punjab.
Answer:
(b) Himachal Pradesh. (√)
![]()
Question 4.
Sri Guru Arjun Dev was …………….. of the Sikhs.
(a) the fifth Guru
(b) the sixth Guru
(c) the fourth Guru
(d) the tenth Guru.
Hint :
(a) the fifth Guru. (√)
Learning Language
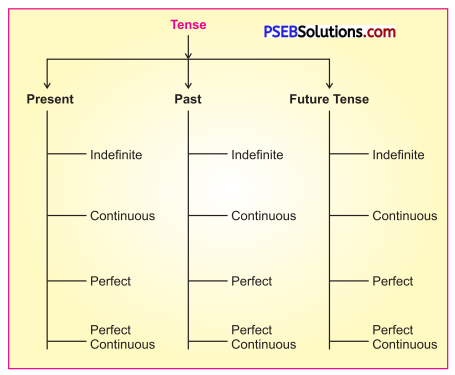
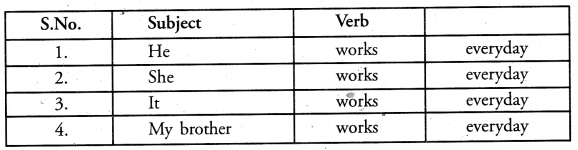
Subject-Verb Agreement
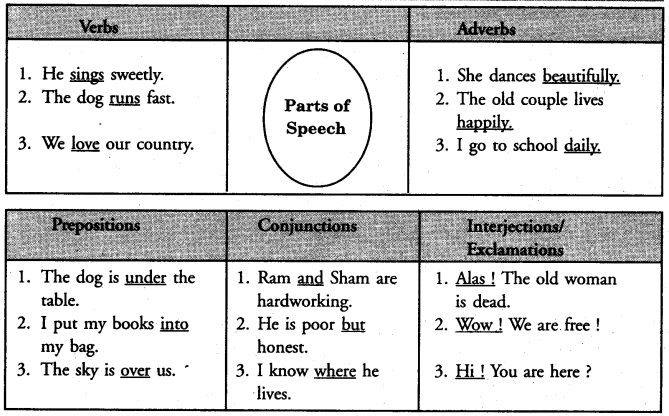
1. A verb must agree with its subject, number and person i.e. when the subject is singular, the verb must also be singular. When the subject is plural, the verb must be plural. For example :
1. He plays cricket.
2. They play cricket.
3. I am sad.
4. We are sad.
5. A girl is running.
6. Girls are running.
7. A list of boys was prepared.
8. One of my friends has gone to the USA.
Let us look at some more aspects of how the verb should agree with the subject in a sentence.
2. If the subject consists of two or more singular nouns or pronouns joined by ‘and, It take a plural verb.
For example :
(i) Jolly and John were two brothers.
(ii) The poet and the dramatist are being honoured. (Two separate persons).
(iii) Kolkata, Mumbai, Chennai and Delhi are the most important cities of India.
(iv) He and I were present.
Exceptions:
(a) If the nouns refer to the same person or thing or express one idea, the verb is singular.
For example :
(i) The poet and dramatist is being honoured. (same person – one only)
(ii) My friend, philosopher and guide was invited to preside over the function. (same person one only)
(iii) Rice and curry is his favourite dish.
(iv) Slow and steady wins the race.
(v) Bread and butter is wholesome food.
(b) If two singular subjects joined by ‘and are qualified by ‘each’ or ‘every they take a singular verb.
For example :
(i) Every man and every woman desires happiness.
(ii) Each hour and each minute is important.
![]()
3. Sigular subjects connected by ‘or’, ‘either – or’ and ‘neither – nor,’ are following by singular verb.
For example :
(a) No prize or trophy was given to him.
(b) Either Minesh or Parag has won the prize.
(c) Neither Sanjeev nor Amit has gone to school today.
4. When the subjects connected by ‘or’ or ‘nor are of different numbers, the plural subject should be written in the last and it is followed by a plural verb.
For example :
(a) Either Raghu or his parents are to blame.
(b) Neither Parul nor her friends have joined the college.
(c) Neither the headmaster nor the teachers were present there.
5. When the subjects connected by ‘nor’ or ‘or’ ate of different persons, the verb agrees in person with the subject nearest to it.
For example :
(a) Neither you nor Rosy is responsible for our defeat.
(b) Neither you not Rahul seems to be interested in this plan.
(c) Neither Neelu nor I have any money to buy a house.
6. When the subject consists of two nouns or pronouns joined by ‘with’ or ‘as well as’, the verb agrees with the first of them.
For examples :
(a) All the students with their teacher, were present at the show.
(b) He with all his friends, was ready to do or die.
(c) They as well as I are sick of his behaviour.
(d) Good leaders as well as a responsible public are essential for the success of democracy
7. When two subjects are connected by ‘not only … ‘but also’, the verb agrees with the second subject.
For example :
(a) Not only the master but his servants have also been badly wounded.
(b) Not only the soldiers but the captain has also been arrested.
8. When the subject is the formal ‘there’, the verb agrees with the real subject that follows it.
For example :
(a) There is no hope of his success.
(b) There were many difficulties to be removed.
![]()
9. ‘Either’, ‘neither’, ‘each, “.everyone’, ‘one of the take a singular verb.
For example :
(a) Neither of the two books was interesting.
(b) Everyone of these workers is an expert.
(c) One of the students is differently abled.
(d) Each of these two girls is intelligent.
(e) Either of these two boys is fit for this work.
10. Nouns which are plural. in form but singular in meaning should be followed by singular verbs.
For example :
(a) Mathematics is my favourite subject.
(b) Politics is a dirty game.
(c) The wages of sin is death.
(d) The news is too good to be true.
(e) Gulliver’s Travels’ is an interesting book.
11. Collective noun (crew, jury, committee) is followed by a singular verb when the group is thought of as a single unit. But when individual members of the group are referred to, the plural verb is used.
For example :
(a) A committee was appointed to suggest some reforms.
(b) The committee were divided on the issue.
(c) The jury was unanimous in its verdict.
(d) The jury were divided in their opinions.
12. When the subject of a verb is a relative pronoun, the verb agrees in number and person with the antecedent of the relative pronoun.
For example :
(a) The boy, who always stands first, is my son.
(b) The time, which is lost, is lost forever.
(c) I, who am your friend, will certainly help you.
(d) This is one of the most interesting books that have (not has) ever appeared.
![]()
13. When the subject is a sum of money considered as a whole, a singular verb is used. If the subject is a sum of money and it refers to the notes or coins considered separately, a plural verb is used.
For example :
(a) Hundred rupees is not a small amount.
(b) Hundred rupees were found in his purse.
(c) Five thousand rupees is a good price for this camera.
(d) There were fifty rupees in his pocket.
(e) There are ten silver rupees in my box.
Activity 7.
Select the correct verb from the brackets to fill in the blanks.
1. The tallest of these boys ………………. next door to me. (live, lives)
2. All the players in my team ……………… done well. (has, have)
3. The toys that were bought by Anil … ………….. really useful. (are, is)
4. He ……………… regularly. (walk, walks).
5. Slow and steady …… ………… the race. (win, wins)
6. Time and tide ……………… for none. (wait, waits)
7. Oil and water ……………. mix. (does not, do not).
8. Tobacco and alcohol ……………. injurious to health. (is, are)
9. Either Ashok or Rakesh ………………. done this mischief. (has, have)
10. Either you or he ……………… mistaken. (is, are)
11. Neither the judge nor the witnesses ……………… him. (believe, believes)
12. Neither the Captain nor the soldiers …………… been arrested. (has, have)
13. Either he or I …………….. wrong. (am, are)
14. He as well as you ………………. innocent. (is, are)
15. Each day and each hour …………….. its own importance. (has, have)
16. Either of these two proposals ………………. acceptable to me. (is, are)
17. The jury ………………. divided in their opinion. (was, were)
18. The assembly ………………. in session. (is, are).
19. I am the one who ……………. always stood for justice. (has, have)
20. This is one of the most difficult lessons that ……. …….. been taught. (has, have)
Answer:
1. lives
2. have
3. are
4. walks
5. wins
6. wait
7. do not
8. are
9. has
10. is
11. believe
12. been arrested
13. am
14. is
15. has
16. is
17. were
18. is
19. have
20. has.
![]()
Activity 8.
Listen to the words spoken by your teacher. Each word will be spoken twice. You will repeat after her/him. The teacher must check the pronunciation from the dictionary.
Answer:
1. February
2. Wednesday
3. Clothes
4. Desk
5. Library
6. Suite
7. April
8. Arithmetic
9. Bear
10. Plumber
11. Cleanliness
12. Creature
13. Debris
14. Depot
15. Develop
16. Hotel
17. Photography
18. Democracy
19. Police
20. Tortoise
Learning to Write
Paragraph Writing
A paragraph is a group of sentences that are written on a topic. It requires unity, order, coherence amnd completeness of an idea. When we write a paragraph, we should focus on one idea. Let us write a paragraph on a ‘A Picnic’ we went for.
A School Picnic
Picnic — Look forward to — all excited — woke up early – packed food — reached in time — teachers accompanied — bus started — enjoyed – reached the spot – took swings – high spirits —- took lunch — great fun — journey back — reached home – a day worth – remembering.
Picnic is one thing that we all always look forward to. This time, it was announced that we would go on a school picnic to the local city garden. We were all very excited.
On the day of the picnic, I woke up early. My mother packed a lot of food items for me and my friends. We reached school in time to board the bus. Our English teacher and sports teacher were accompanying us. The bus started at 8 a.m. We enjoyed the journey and had great fun singing songs.
![]()
Finally, we reached the garden. It was very peaceful there. The weather was also very pleasant. We got busy on swings and started running and playing. We were all in high spirits. In the afternoon, we had lunch. We shared our food with each other. After lunch, our teachers made us play many games. It was fun. We laughed and enjoyed ourselves. Soon it was evening and time to go back. We boarded the bus again and reached home by 7. It was a memorable day and I am going to cherish it forever.
Activity 9.
Write a paragraph on Our School Library using the hints given below :
Answer:
School a temple of learning–library the most useful place a big library in my school – more than 50,000 books – kept subjectwise – story books and comics-newspapers and magazines – librarian very helpful and kind – enjoy going to the library
Our School Library
A school is a temple of learning. A library is an altar in it. My school too has a big library. It is housed in a cornor. It has about 50,000 books in it. The books are kept subject-wise. They are kept in almirahs with glass-panes. The library has a number of newspapers and magazines too.
They are in Punjabi, Hindi and English. We can borrow books from the library. But no student can keep a book for more than fifteen days. The librarian is very helpful, kind and gentle. But he is very strict. He maintains perfect silence and discipline in the library. We go to the library thrice a week. We read newspapers and magazines. The library is really very useful to all of us.
Activity 10.
Write a paragraph on ‘An Indian Farmer’ looking at the hints given below :
Answer:
India land of villages–agriculture major profession-agriculture is lifeline of Indian economy-keeps the Indian economy prospering – the citizens with food-grows food grains, vegetables and fruits-grows cotton – works from morning to evening-provides employment – 40% of Indian farmers – requires a lot of labour – difficult task requires discipline and patience-grows crops for our country – crop is his wealth – important place in society – backbone of India – very useful member of the society
An Indian Farmer India is a land of villages. Most of the villagers are farmers. Therefore agriculture plays the most important role in the Indian economy. It is called the lifeline of Indian economy. It keeps the economy of the country prospering. Agriculture provides the citizens with food. About 40% of Indian farmers get their livehood. It provides employment directly through farming to many other people also. On the whole Indian farmer and farming together keep our economy alive. Farmers work hard (Hera) labour in their fields and grow various crops. Therefore, Indian farmer enjoys an important place in the society. He is the backbone of India.
Comprehension of Passage
Read the following passage and answer the questions given below each :
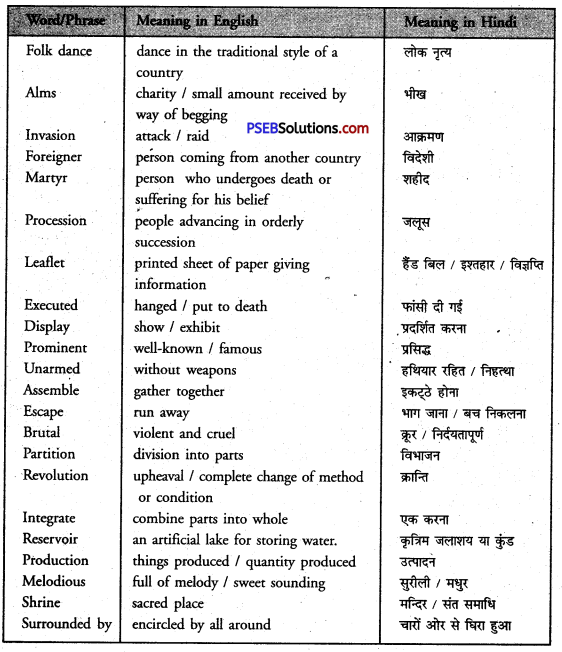
(1) According to the history of Punjab, the Punjabis have faced all the foreign invasions boldly. During the struggle for India’s freedom, Punjab gave the country great heroes. They included patriots such as Lala Lajpat Rai, Bhagat Singh, Sukhdev, Udham Singh, Kartar Singh Sarabha and many others. We call Lala Lajpat Rai Sher-e-Punjab and Bhagat Singh Shaheed-e-Azam. All these brave sons of Punjab sacrificed their lives for their country. Lala Lajpat Rai died as a result of the brutal lathi charge while he was leading a procession against the British in 1928. Bhagat Singh, Sukhdev and Rajguru were hanged for raising their voice against the British cruelties. Bhagat Singh was just 26 years old then.
1. What led to Lala Lajpat Rai’s death?
लाला लाजपत राय की मृत्यु किस कारण हुई ?
2. Name three freedom fighters who were hanged.
तीन स्वतंत्रता सेनानियों के नाम बताओ जिन्हें फांसी दी गई।
3. Choose true and false statements and write them in your answer-book :
(a) Bhagat Singh was 16 years old when he was hanged.
जब भगत सिंह को फांसी दी गई उस समय उनकी आयु केवल 16 साल थी।
![]()
(b) Lala Lajpat Rai died in 1928.
तीन स्वतंत्रता सेनानियों के नाम बताओ जिन्हें फांसी दी गई
4. Complete the following sentences according to the meaning of the passage :
(a) Lala Lajpat Rai was leading a procession
(b) Bhagat Singh, Sukhdev and Rajguru were hanged for ……….
Or
Match the words with their meanings :
| (i) crueltics | photographs |
| (ii) portraits | patriots |
| atrocities |
Answer:
1. The British lathi-charge on Lalaji led to his death.
2. Bhagat Singh, Sukhdev and Rajguru.
3.
(a) False
(b) True.
4.
(a) Lala Lajpat Rai was lending a procession against the British in 1928.
(b) Bhagat Singh, Sukhdev and Rajguru were hanged for raising voice against the British cruelties.
Or
(i) cruelties – atrocities
(ii) portraits – photographs.
(2) Mr Mathew told Chinta. ‘This is the famous Jallanwala Bagh of Amritsar and these are Bullet marks. On 31 April 1919, a crowd of around 20,000 people had gathered for a public meeting here. They included men, women and children. The British General O’Dwyer came there with his armed soliders. He blocked all the exit point. Then he ordered his men to start firing without giving any warning to the people gathered there. About 1000 people were killed and more than 1500 were wounded.”
1. What happened in Jalliandwala Bagh on April 13, 1919 ?
13 अप्रैल 1919 को जलियांवाला बाग में क्या घटना घटी
2. For what purpose had the people gathered in Jallianwala Bagh ?
लोग जलियांवाला बाग में किस उद्देश्य से इकट्ठे हुए थे ?
3. Choose true and false statements and write them in your answer-book :
(a) The park had no exit.
पार्क से बाहर जाने का कोई रास्ता नहीं था।
(b) The British General O’Dwyer came there with his riflemen.
ब्रिटिश जनरल डायर अपने बंदूकधारियों के साथ वहां आया।
4. Complete the following sentence according to the meaning of the passage :
(a) Dyer blocked …………
(b) The crowd gathered at the Bagh included ………….
Or
Match the words with their meanings :
| (i) blocked | injured |
| (ii) wounded | closed |
| killed |
Answer:
1. On 13 April, 1919, the British General O’Dwyer ordered his riflemen to fire at the crowd. About 1000 people were killed and more than 1500 were wounded.
2. The people had gathered for a public meeting.
3.
(a) False
(b) True
4.
(a) Dyer blocked all the exist points.
(b) The crowd gathered at the Bagh included men, women and children.
Or
(i) blocked – closed
(ii) wounded – injured.
![]()
(3) “Sir, they say this temple is surrounded by water”, said Chintu. “Yes, it is built in the middle of a square tank. To reach the temple, there is a 60-metre long marble path. This path has marble railings on both sides. The temple is double-storeyed. It has a golden dome on the top. The marble slabs used in the construction of the temple have on them fine artistic engravings. The inner walls are decorated with precious stones. They have on them priceless paintings and other works of art. On the ground floor, under the dome-shaped roof lies Sri Guru Granth Sahib. It is the holy book of the Sikhs.” explained Mr. Mathew. “Do you know it was Sri Guru Arjun Dev, the fifth Guru of the Sikhs, who compiled this holy book ?” asked Mr. Mathew.
1. How can the temple be reached ?
मंदिर तक कैसे पहुँचा जा सकता है ?
2. What lies on the ground floor, under the dome-shaped roof?
गुम्बदाकार छत के नीचे भूतल पर क्या विराजमान है ?
3. Choose true and false statements and write them in your answer-book
(a) Marble slabs have been used for the decoration of the temple.
मंदर की सजावट के लिए संगमरमर की पट्टिकाएं प्रयोग में लाई गई हैं।
(b) The path has a marble railing on one side.
मार्ग के एक ओर संगमरमर का जंगला है।
4. Complete the following sentences according to the meaning of the passage :
(a) Sri Guru Granth Sahib was compiled by ……..
(b) The inner walls of the temple are decorated with …………
Or
Match the words with their meanings :
| (i) decorated | destroyed |
| (ii) precious | beautified |
| Costly |
Answer:
1. It can be reached by a 60-metre long marble path.
2. Sri Guru Granth Sahib, the holy book of the Sikhs, lies on the ground floor under the dome-shaped roof.
3.
(a) True
(b) False
4.
(a) Sri Guru Granth Sahib was compiled by Sri Guru Arjun Dev, the fifth Guru of the Sikhs.
(b) The inner walls of the temple are decorated with precious stones.
Or
(i) decorated – beautified
(ii) precious – costly.
(4) Mr Mathew replied, “Yes, this is Chandigarh. This beautiful city is situated at the foot of the Shivalik Hills. It was designed by a famous French architect, Le Corbusier. Being very close to the hills, Chandigarh has a calm and pleasant atmosphere. The Rose Garden of Chandigarh is world famous. The city was formally declared open in October 1953 by Dr Rajendra Prasad, the former President of India.“
![]()
1. Where is Chandigarh situated ?
चण्डीगढ़ कहां स्थित है ?
2. When and by whom was it formally declared open ?
इसका औपचारिक रूप से शुभारम्भ कब और किसके द्वारा किया गया ?
3. Choose true and false statements and write them in your answer-book :
(a) Chandigarh has a calm and pleasant atmosphere.
चण्डीगढ़ का वातावाण शान्ति और सुटावाना है
(b) Stone gardens of Chandigarh are world famous. :
चण्डीगढ़ के पत्थर के बाग जगत् प्रसिद्ध हैं।
4. Complete the following sentences according to the meaning of the passage :
(a) Le Corbusier was
(b) Chandigarh is a ………….
Or
Match the words with their meanings :
| (i) pleasant | well-known |
| (ii) famous | fine |
| helpful |
Answer:
1. Chandigarh is situated at the foot of the Shivalik Hills.
2. It was formally declared open in October 1953 by the then President of India,Dr. Rajendra Prasad.
3.
(a) True
(b) False
4.
(a) Le Corbusier was a famous French architect.
(b) Chandigarh is a beautiful city.
Or
(i) pleasant-fine.
(ii) famous-well-known.
![]()
Use of Words and Phrases in Sentences
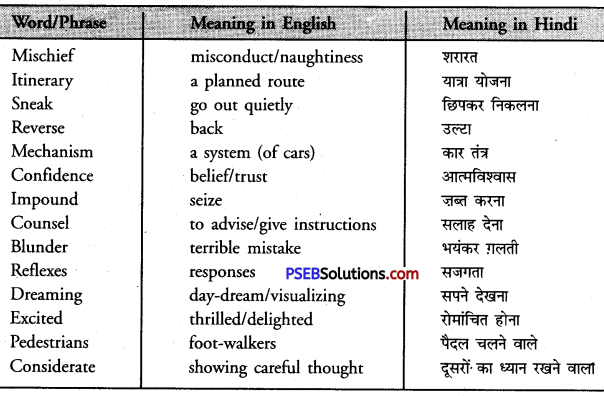
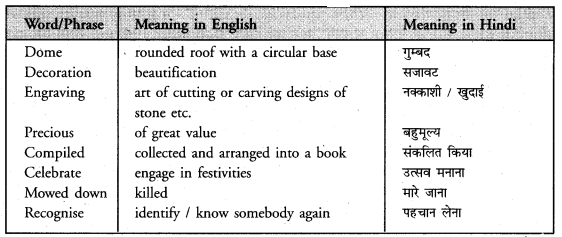
1. alms (charity, small, amounts received by way of begging) – The beggar stretched his hand out for alms.
2. celebrate – (engage in festivities) – I celebrated my birthday in a hotel.
3. compile – (to collect and arrange into a book) -Sri Guru Granth Sahib was compiled by Sri Guru Arjun Dev Ji.
4. curb (put control or check on, obstruct) – His arrest curbed his liberty in a big way.
5. distributary-(a narrow waterway to distribute canal or river water for irrigation, छोटी नदी/वितरिका A network of distributaries irrigates the fields in this state
6. executed – (done to death/hanged,) – The murderer was executed on Sunday.
7. exuberance (lively spirit, ) – The Bhangra shows the exuberance of the people of Punjab.
8. invasion – (attack) -India faced many invasions by the foreigners.
9. mowed down – (killed,) – Hundreds of freedom fighters were mowed down in the firing.
10. prominent – (well known) – My uncle is a prominent political figure.
11. precious – (of great value) – Gold is a precious metal.
12. recognize – (identify/know somebody again) – Do you recognize this picture ?
13. successive – (continuously/one after the other) – He had to keep awake for three successive nights.
14. vigorous – (fast and active/full of spirit and movement) – He made vigorous efforts to achieve his goal.
15. vitality – (liveliness) – The dance was full of life and vitality.
Word Meanings
The Punjab: A Glimpse Summary in Hindi
Balle, Balle ! …………… in the pavilion.
बल्ले, बल्ले ! ओह् बल्ले बल्ले ! मि० मैथ्यू अपने छात्रों को अमृतसर की यात्रा पर ले गए। मि० मैथ्यू ने पंजाब पैवेलियन (पंडाल) के सामने भांगड़ा नर्तकों की ओर इशारा करते हुए कहा, “बच्चो, तुम पंजाब के इस प्रसिद्ध लोकनृत्य को अवश्य पहचान गए होंगे।”
बच्चों ने उत्तर दिया, “हाँ, श्रीमान् जी, हम यह लोक नृत्य इस वर्ष के गणतंत्र दिवस के समारोह में देख चुके हैं।” मि० मैथ्यू ने कहा, “यह नृत्य जोश से भरा है। यह पंजाबियों के जीवन के प्रति अति उत्साह को दर्शाता है। पंजाबी स्वाभिमानी और बहुत ही परिश्रमी लोग होते हैं। तुम इन्हें गलियों में भीख माँगते नहीं देखोगे। वे बहुत बहादुर लड़ाई के मैदान में कभी भी अपनी पीठ नहीं दिखाते।
![]()
पंजाब के इतिहास के अनुसार पंजाब के लोगों ने सभी विदेशी आक्रमणकारियों का दृढ़ता से सामना किया । भारत के स्वतंत्रता संग्राम में पंजाब ने देश को महान नायक दिए। उनमें लाला लाजपत राय, भगत सिंह, सुखदेव, ऊधम सिंह, करतार सिंह सराभा जैसे तथा कई अन्य देशभक्त शामिल थे। हम लाला लाजपत राय को शेर-ए-पंजाब तथा भगत सिंह को शहीद-ए-आजम कहकर पुकारते हैं। पंजाब के इन सभी वीर पुत्रों ने अपनी मातृभूमि के लिए अपने प्राणों की आहुति दे दी। लाला लाजपत राय की मृत्यु 1928 में अंग्रेजों के विरुद्ध एक जलूस का नेतृत्व करते समय उन पर किए गए निर्दयतापूर्ण लाठीचार्ज के परिणामस्वरूप हुई। भगत सिंह, सुखदेव और राजगुरू को अंग्रेजों के अत्याचारों के विरुद्ध आवाज़ उठाने पर फांसी पर लटका दिया गया। भगत सिंह उस समय केवल 26 वर्ष के थे। बच्चो! तुम पंडाल में इन सभी स्वतंत्रता सेनानियों के चित्र देखोगे।”
“Sir, what is ….. work of the Punjabis.”
चिंटू ने पूछा, ” श्रीमान् जी, यह भवन, कौन सा है जिसकी दीवारें पूरी तरह निशानों से भरी पड़ी हैं ?” मि० मैथ्यू ने चिंटू को बताया, “यह अमृतसर का प्रसिद्ध जलियाँवाला बाग़ है और ये गोलियों के निशान हैं। यहाँ 13 अप्रैल, 1919 को लगभग 20,000 लोगों की एक भीड़ सार्वजनिक सभा के लिए यहां एकत्रित हुई थी। इसमें स्त्री, पुरुष तथा बच्चे शामिल थे। ब्रिटिश जनरल ओ’डायर अपने बन्दूकधारियों के साथ वहाँ पहुँचा। उसने बाहर निकलने के सभी रास्ते बंद कर दिए। बिना कोई चेतावनी दिए उसने अपने बंदूकधारियों को भीड़ पर गोली चलाने का आदेश दे दिया। लगभग एक हज़ार लोग मारे गए और पंद्रह सौ से अधिक लोग घायल हुए।”
मि० मैथ्यू ने अपने छात्रों को 1947 के बटवारे के बारे में बताया। उन्होंने बताया “पंजाब को 1947 में भारत की स्वतंत्रता की पूर्व संध्या के समय अनेक कष्ट उठाने पड़े। यहाँ भयंकर खून-खराबा हुआ। हज़ारों लोगों को अपने घरों को छोड़ना पड़ा और शरणार्थियों की तरह रहना पड़ा। फिर भी, वीर पंजाबियों ने कड़ा परिश्रम किया और जीवन की नये सिरे से शुरुआत की। उन्होंने राज्य के पुनर्निर्माण में एक महान् भूमिका निभाई। उन्होंने कड़ी मेहनत और कृषि कौशल से पंजाब को भारत का अन्न भण्डार बना दिया। वे देश में हरित क्रांति लाए। शीघ्र ही भारत एक विकासशील देश बन गया और इसका मुख्य कारण पंजाबियों का कड़ा परिश्रम है।
“Sir wasn’t Punjab. ………….. modern India.”
राजू ने पूछा, “श्रीमान् जी, क्या उस समय पंजाब का विभाजन फिर से नहीं किया गया था जब इसमें से हरियाणा राज्य का निर्माण किया गया था ?” मि० मैथ्यू ने बताया, “राजू, तुम ठीक कह रहे हो। 1966 में पंजाबी भाषा और हिन्दी भाषा के आधार पर पंजाब राज्य का पुनर्गठन किया गया। पंजाब के कुछ पहाड़ी क्षेत्र जैसे कि लाहौल-स्पीति, कुल्लू एवं मनाली की घाटियाँ, कांगड़ा, डल्हौज़ी और शिमला हिमाचल प्रदेश के साथ मिला दिए गए। चण्डीगढ़ को पंजाब एवं हरियाणा दोनों की सांझी राजधानी बना दिया गया। उसे केंद्र शासित प्रदेश घोषित कर दिया गया।”
“पुनर्गठित पंजाब नवंबर 1966 में अस्तित्व में आया। अब इसके पश्चिम में पाकिस्तान, उत्तर में जम्मू और कश्मीर, उत्तर-पूर्व में हिमाचल प्रदेश और दक्षिण में हरियाणा और राजस्थान हैं।”राजू ने कहा, “श्रीमान् जी, यहाँ एक बांध का मॉडल (नमूना) है। मेरे विचार से यह प्रसिद्ध भाखड़ा बांध है।”
मि० मैथ्यू ने कहा, “राजू, तुम ठीक कह रहे हो। यह बांध 740 फुट ऊँचा है। इसकी लम्बाई 518 मीटर है और यह 9 मीटर चौड़ा है। इसके जलाशय जिसे गोबिन्द सागर के नाम से जाना जाता है, इसमें 9 बिलियन क्यूषिक मीटर पानी इकट्ठा किया जा सकता है। इसका उपयोग हिमाचल प्रदेश, पंजाब तथा हरियाणा की 10 मिलियन एकड़ भूमि की सिंचाई के लिए किया जाता है। भाखड़ा और नंगल विद्युत केंद्रों में पैदा होने वाली बिजली को हिमाचल प्रदेश, पंजाब, हरियाणा, राजस्थान और गुजरात राज्यों को दिया जाता है। पंडित नेहरू ने भाखड़ा बांध को आधुनिक भारत का मंदिर कहा है।”
“Sir, I can ………………….. asked Mr. Mathew.?”
विक्की ने कहा, “श्रीमान् जी, मुझे गुरूवाणी के मधुर स्वर सुनाई दे रहे हैं। पास में अवश्य ही कोई गुरुद्वारा होगा।”मि० मैथ्यू ने कहा, “ठीक है, हम अमृतसर के श्री दरबार साहिब के निकट हैं। यह सिखों का सबसे पवित्र धार्मिक स्थल है।”
चिंटू ने कहा, “कहते हैं कि यह मंदर जल से घिरा हुआ है।” मि० मैथ्यू ने बताया, “हां, यह एक वर्गाकार सरोवर के बीच में बना है। मंदर में पहुँचने के लिए 60 मी० लम्बा संगमरमर का मार्ग बना हुआ है। इस मार्ग के दोनों ओर संगमरमर की रेलिंग (जंगला) है। मंदर दो मंजिला है। इसके शीर्ष पर एक सुनहरी गुंबद है। मंदर के निर्माण में लगाई गईं संगमरमर की पट्टिकाओं पर कलात्मक नक्काशी की गई है। अंदर की दीवारें कीमती पत्थरों से सुसज्जित हैं। उन पर अनमोल चित्रकारी और अन्य कलाकारियां की गई हैं। भूतल पर गुंबदाकार छत के नीचे ‘श्री गुरु ग्रंथ साहिब’ विराजमान हैं। यह सिक्खों का पवित्र ग्रंथ है। मि० मैथ्यू ने कहा, “क्या आप जानते हैं कि इस पवित्र पुस्तक का संकलन सिखों के पाँचवें गुरु अर्जुन देव जी ने किया था ?”
![]()
“Anandpur Sahib ……… President of India.”
“आनंदपुर साहिब सिखों का एक अन्य तीर्थ-स्थल है। इसकी स्थापना श्री गुरु तेग बहादुर जी ने की थी। यह सतलुज नदी के बायें किनारे पर स्थित एक छोटा सा शहर है। यहां हर साल लाखों सिख ‘खालसा’ जिसकी स्थापना 1699 में गुरु गोबिन्द सिंह जी ने की थी, का स्थापना दिवस मनाने के लिए इकट्ठे होते हैं।” राजू ने पूछा, “श्रीमान् जी, इधर देखो। यह सुन्दर ढंग से नियोजित एक शहर का नमूना है। इसमें बहुत से बाग़ हैं। क्या यह चण्डीगढ़ नहीं है ?”
मि० मैथ्यू ने उत्तर दिया, “हाँ, यह चण्डीगढ़ ही है। यह सुंदर शहर शिवालिक पहाड़ियों की तलहटी में स्थित है। इसका नमूना प्रसिद्ध फ्रांसीसी वास्तुकार ली कॉरबुज़िअर ने तैयार किया था। पहाड़ियों के बहुत अधिक निकट होने के कारण चण्डीगढ़ का वातावरण शांत और सुहावना है। चण्डीगढ़ के रोज़ गार्डन्ञ् संसार भर में प्रसिद्ध हैं। इस नगर का औपचारिक रूप से शुभारंभ भारत के तत्कालीन राष्ट्रपति डा. राजेन्द्र प्रसाद ने अक्तूबर 1953 में किया था।”
“Sir, there are …………………….. on their faces.
” विक्की ने कहा, “श्रीमान जी, यहाँ खेलों का सामान बेचने वाली कुछ दुकानें हैं। मैं क्रिकेट का बल्ला और गेंद खरीदना चाहता हूँ।” मि० मैथ्यू ने कहा, “परन्तु खरीदने से पहले, क्या तुम मुझे बता सकते हो कि पंजाब के किस शहर में यह सामान बनाया जाता है ?” विक्की ने उत्तर दिया, “नहीं, श्रीमान् जी।” मि० मैथ्यू ने कहा, “अच्छा, तो सुनो, यह जालंधर है। यह देश में खेलों का सामान बनाने वाले प्रमुख केंद्रों में से एक है। वहां, दूसरी दुकान में ऊनी हौजरी का सामान है। वह लुधियाना से है। हमारे हौजरी उद्योग का 95 प्रतिशत भाग लुधियाना में है। क्या तुम हौजरी का कुछ सामान भी खरीदना पसंद करोगे ?” चिंटू ने कहा, “नहीं, श्रीमान् जी, क्या खरीदा जाये, मैं उसका निर्णय नहीं ले सकता। ऐसी खरीददारी मेरे मातापिता करते हैं।” मि० मैथ्यू ने मिठाई की दुकान की ओर बढ़ते हुए कहा, “अच्छा, बच्चो, शायद तुम अमृतसर की यह जलेबियाँ चखना पसंद करोगे।” सभी बच्चे अपने चेहरों पर मुस्कान बिखेरे उनके पीछे-पीछे चलने लगे।
![]()
Retranslation From English to Hindi
1. This dance is full of energy. — यह नृत्य जोश से भरा हुआ है।
2. The country was partitioned. — देश का बंटवारा कर दिया गया।
3. About 1000 people were killed. — लगभग 1000 लोग मारे गए।
4. Punjab suffered a lot. — पंजाब को बहुत अधिक हानि उठानी पड़ी।
5. You are right. — आपकी बात ठीक है।
6. It is the holiest shrine of the Sikhs. — यह सिखों का सबसे पवित्र धार्मिक स्थल है।
7. This temple is surrounded by water. — यह मंदर जल से घिरा है।
8. It has a number of gardens. — इसमें कई बाग हैं।
9. The temple is double storeyed. — मंदर दो-मंजिला है।
10. They are from Ludhiana. — वे लुधियाना के रहने वाले हैं।
11. It is a small town. — यह एक छोटा सा शहर है।
12. I can hear the melodious strains of Gurbani.– मुझे गुरूवाणी के मधुर स्वर सुनाई दे रहे हैं।
English Guide for Class 8 PSEB Prose