Punjab State Board PSEB 10th Class Physical Education Book Solutions Chapter 2 ਸੰਤੁਲਿਤ ਭੋਜਨTextbook Exercise Questions, and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 10 Physical Education Chapter 2 ਸੰਤੁਲਿਤ ਭੋਜਨ
Physical Education Guide for Class 10 PSEB ਸੰਤੁਲਿਤ ਭੋਜਨ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵTextbook Questions and Answers
ਬਹੁਤ ਛੋਟੇ ਉੱਤਰਾਂ ਵਾਲੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ (Very Short Answer Type Questions)
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਪੋਟੀਨ ਕਿੰਨੇ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਦੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ, ਉਹਨਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਂ ਲਿਖੋ । (Name the types of Protein.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਦੋ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਦੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ-ਪਸ਼ੂ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਅਤੇ ਬਨਸਪਤੀ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ ਕੀ ਹਨ ? (What is Carbohydrates ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ ਕਾਰਬਨ, ਹਾਈਡਰੋਜਨ ਅਤੇ ਆਕਸੀਜਨ ਦਾ ਮਿਸ਼ਰਨ ਹਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਕਿੰਨੀ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਦੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ? (Mention the types of Vitamins ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਛੇ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਦੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ‘ਏ’, ‘ਬੀ’, ‘ਸੀ’, ‘ਡੀ’, ‘ਈ’ ਅਤੇ ‘ਕੇ’ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਕਿਹੜੇ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਪਾਣੀ ਵਿਚ ਘੁਲਣਸ਼ੀਲ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦੇ ? (Which Vitamins are not soluble in water ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਸੀ’, ‘ਡੀ’ ਅਤੇ ‘ਕੇ’|

ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 5.
ਛੋਟੇ ਬੱਚੇ ਲਈ ਕਿਹੜਾ ਦੁੱਧ ਚੰਗਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ? (Which milk is better for a child ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਮਾਂ ਦਾ ਦੁੱਧ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 6.
ਸਾਡੇ ਰੋਜ਼ਾਨਾ ਦੇ ਭੋਜਨ ਵਿਚ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਕਿੰਨੀ ਹੋਣੀ ਚਾਹੀਦੀ ਹੈ ? (How much proteins we should take in our daily meals ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
700 ਤੋਂ 100 ਗ੍ਰਾਮ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 7.
ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ ਕਿਹੜੇ ਦੋ ਰੂਪਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਮਿਲਦੇ ਹਨ ? (Name the Isomers of Carbohydrates ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਸਟਾਰਚ ਅਤੇ ਸ਼ੱਕਰ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 8.
ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਕਿਹੜੇ ਤੱਤਾਂ ਦਾ ਮਿਸ਼ਰਨ ਹਨ ? (Of what elements protein is a mixture ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਕਾਰਬਨ, ਨਾਈਟਰੋਜਨ, ਹਾਈਡਰੋਜਨ ਤੇ ਗੰਧਕ |
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 9.
ਜੀਵਨ ਤੱਤ ਕਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ? (Which thing is known as life saving ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨਾਂ ਨੂੰ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 10.
ਸਾਡੇ ਭੋਜਨ ਵਿਚ ਚਰਬੀ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਕਿੰਨੀ ਹੋਣੀ ਚਾਹੀਦੀ ਹੈ ? (How much Fat one should take daily ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
50 ਤੋਂ 70 ਗ੍ਰਾਮ ।
ਛੋਟੇ ਉੱਤਰਾਂ ਵਾਲੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ (Short Answer Type Questions)
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਭੋਜਨ ਦੇ ਕਿਹੜੇ-ਕਿਹੜੇ ਮੁੱਖ ਕੰਮ ਹਨ ? (What are the functions of food ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਅਸੀਂ ਜਿਹੜਾ ਭੋਜਨ ਖਾਂਦੇ ਹਾਂ ਉਹ ਪਚਣ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਕਈ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਉਹਨਾਂ ਕੰਮਾਂ ਦਾ ਵੇਰਵਾ ਹੇਠ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ
1. ਸਰੀਰਕ ਵਾਧੇ ਵਿਚ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ-ਭੋਜਨ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਵਾਧੇ ਵਿਚ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਵੱਖ-ਵੱਖ ਅੰਗਾਂ ਦਾ ਨਿਰਮਾਣ ਅਤੇ ਵਾਧਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
2. ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ-ਭੋਜਨ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਸਾਡਾ ਸਰੀਰ ਕਈ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਕਿਰਿਆਵਾਂ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਕਿਰਿਆਵਾਂ ਲਈ ਲੋੜੀਂਦੀ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਭੋਜਨ ਤੋਂ ਹੀ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
3. ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਗਰਮੀ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਨਾ-ਭੋਜਨ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਗਰਮੀ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਜਦੋਂ ਖਾਧਾ ਹੋਇਆ ਭੋਜਨ ਹਜ਼ਮ ਹੋ ਕੇ ਸਾਹ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਆਈ ਆਕਸੀਜਨ ਵਿਚ ਮਿਲ ਕੇ ਖੂਨ ਵਿਚ ਉਬਲਦਾ ਹੈ ਤਾਂ ਗਰਮੀ ਪੈਦਾ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਗਰਮੀ ਸਰੀਰ ਲਈ ਬਹੁਤ ਹੀ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਦੇ ਬਿਨਾਂ ਅਸੀਂ ਜਿਉਂਦੇ ਨਹੀਂ ਰਹਿ ਸਕਦੇ ।
4. ਨਵੇਂ ਸੈੱਲਾਂ ਦਾ ਬਣਾਉਣਾ ਅਤੇ ਟੁੱਟੇ-ਭੱਜੇ ਸੈੱਲਾਂ ਦੀ ਮੁਰੰਮਤ ਕਰਨਾ-ਭੋਜਨ ਟੁੱਟੇ-ਭੱਜੇ ਸੈੱਲਾਂ ਦੀ ਮੁਰੰਮਤ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ, ਭੋਜਨ ਨਾਲ ਨਵੇਂ ਸੈੱਲ ਵੀ ਬਣਦੇ ਹਨ । ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਚਲ ਰਹੀਆਂ ਕਿਰਿਆਵਾਂ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਕੁੱਝ ਕੀਟਾਣੂ ਨਸ਼ਟ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ਤੇ ਕੁੱਝ ਟੁੱਟ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ । ਭੋਜਨ ਦਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡਾ ਕੰਮ ਟੁੱਟੇ-ਫੁੱਟੇ ਸੈੱਲਾਂ ਦੀ ਮੁਰੰਮਤ ਕਰਨਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਨਸ਼ਟ ਹੋਏ ਸੈੱਲਾਂ ਦੀ ਥਾਂ ਨਵੇਂ ਸੈੱਲ ਵੀ ਭੋਜਨ ਹੀ ਤਿਆਰ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
5. ਬਿਮਾਰੀਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਰੱਖਿਆ-ਭੋਜਨ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਬਿਮਾਰੀਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਬਚਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਭੋਜਨ ਖਾਣ ਨਾਲ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਪੈਦਾ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਸਾਨੂੰ ਬਿਮਾਰੀਆਂ ਦਾ ਮੁਕਾਬਲਾ ਕਰਨ ਦੇ ਯੋਗ ਬਣਾ ਦਿੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਅਸੀਂ ਕਈ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਬਿਮਾਰੀਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਬਚ ਸਕਦੇ ਹਾਂ ! ਉੱਪਰ ਦੱਸੇ ਸਾਰੇ ਕੰਮ ਭੋਜਨ ਦੇ ਮੁੱਖ ਕੰਮ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।

ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਭੋਜਨ ਕੀ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ? ਅਸੀਂ ਭੋਜਨ ਕਿਉਂ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਾਂ ? (What is Food ? Why we take it ?).
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਭੋਜਨ ਕੀ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ? (What is Food ?)-ਭੋਜਨ ਇਕ ਅਜਿਹੀ ਵਸਤੁ ਦਾ ਨਾਂ ਹੈ ਜੋ ਸਾਡੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਜਾ ਕੇ ਲਹੂ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ, ਨਵੇਂ ਸੈੱਲਾਂ ਦਾ ਨਿਰਮਾਣ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ, ਅੰਦਰਲੀ ਟੁੱਟ-ਭੱਜ ਦੀ ਮੁਰੰਮਤ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਗਰਮੀ ਅਤੇ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਇਸ ਦੇ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਕੰਮ ਹਨ –
1. ਹਾਨੀ ਪੂਰਤੀ ਜਾਂ ਨਵੇਂ ਸੈੱਲਾਂ ਦਾ ਬਣਾਉਣਾ (Formation of new cells) ਮਨੁੱਖੀ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਹਰ ਸਮੇਂ ਕਿਰਿਆਵਾਂ ਕਰਨ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਸੈੱਲ (Cells) ਟੁੱਟਦੇ-ਭੱਜਦੇ ਰਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਉੱਚਿਤ ਭੋਜਨ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਪੁਰਾਣੇ ਸੈੱਲਾਂ ਦੀ ਮੁਰੰਮਤ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਨਵੇਂ ਸੈੱਲਾਂ ਦਾ ਨਿਰਮਾਣ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
2. ਭੋਜਨ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ (Food supplies energy to body)-ਰੋਜ਼ਾਨਾ ਜੀਵਨ ਦੇ ਕੰਮਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਦੀ ਲੋੜ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਭੋਜਨ ਦੇ ਜਲਣ (Combustion) ਨਾਲ ਤਾਪ ਪੈਦਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਪੈਦਾ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
3. ਭੋਜਨ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਗਰਮੀ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ (Food supplies heat to body)-ਭੋਜਨ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਗਰਮੀ ਮਿਲਦੀ ਹੈ । ਜੇਕਰ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਗਰਮੀ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਘੱਟ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ਤਾਂ ਜੀਵਨ ਅਸੰਭਵ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
4. ਭੋਜਨ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਵਾਧੇ ਵਿਚ ਸਹਾਇਕ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ (Food helps growth of body)-ਭੋਜਨ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਅੰਗਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਜੇ ਕਿਸੇ ਬੱਚੇ ਨੂੰ ਭੋਜਨ ਨਾ ਮਿਲੇ ਜਾਂ ਉੱਚਿਤ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਵਿਚ ਨਾ ਮਿਲੇ ਤਾਂ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਅੰਗਾਂ ਦਾ ਉੱਚਿਤ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੋ ਸਕਦਾ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਕੀ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ? ਇਹ ਸਾਡੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਲਈ ਕਿਉਂ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ? (What are Vitamins ? Why these are needed for our body ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ (Vitamins)-ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਅਜਿਹੇ ਰਸਾਇਣਿਕ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਹਨ ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਸਾਡੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਲਈ ਲੋੜ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਹੁਣ ਤਕ ਕਈ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਖੋਜ ਕੀਤੀ ਜਾ ਚੁੱਕੀ ਹੈ ਪਰ ਮੁੱਖ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਛੇ ਹੀ ਮੰਨੇ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ਜੋ ਇਸ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਹਨ : ‘ਏ’, ‘ਬੀ’, ‘ਸੀ’, ‘ਡੀ’, ‘ਬੀ’ ਅਤੇ ‘ਕੇ’ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਬੀ’ ਤੇ ‘ਸੀ ਪਾਣੀ ਵਿਚ ਘੁਲਣਸ਼ੀਲ ਹਨ ਤੇ ਬਾਕੀ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਏ’ ‘ਡੀ’ ਤੇ ‘ਕੇ ਚਰਬੀ ਵਿਚ ਘੁਲਣਸ਼ੀਲ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਕਈ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਖ਼ੁਰਾਕ ਪਦਾਰਥਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਪਾਏ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ । ਭੋਜਨ ਵਿਚ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਉੱਚਿਤ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਦਾ ਹੋਣਾ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਹੈ । ਭੋਜਨ ਦੀ ਜੀਵਨ ਲਈ ਬਹੁਤ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾ ਮਹੱਤਤਾ ਨੂੰ ਅਨੁਭਵ ਕਰਦੇ ਹੋਏ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਜੀਵਨ-ਦਾਤਾ ਵੀ ਆਖਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਡੀ ਧੁੱਪ ਤੋਂ ਮਿਲਦਾ ਹੈ । ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਦੀ ਸਰੀਰ ਲਈ ਜ਼ਰੂਰਤ (Need of Vitamins) –
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਦੀ ਸਾਡੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਲਈ ਜ਼ਰੂਰਤ ਅੱਗੇ ਲਿਖੇ ਤੱਤਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਬਿਲਕੁਲ ਸਪੱਸ਼ਟ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ –
- ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਸਾਡੀ ਸਿਹਤ ਨੂੰ ਠੀਕ ਰੱਖਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹ ਸਾਡੇ ਸਰੀਰਕ ਵਾਧੇ ਵਿਚ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹ ਸਾਡੀ ਪਾਚਨ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਵਧਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹ ਸਾਡਾ ਖੂਨ ਸਾਫ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ਅਤੇ ਖੂਨ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਵਿਚ ਵਾਧਾ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਦੰਦਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਬਣਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹ ਸਾਨੂੰ ਬਿਮਾਰੀਆਂ ਦਾ ਮੁਕਾਬਲਾ ਕਰਨ ਦੇ ਯੋਗ ਬਣਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਚਮੜੀ ਦੇ ਰੋਗ ਦੂਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਵਿਚ ਵਾਧਾ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਮੁੱਖ ਭੋਜਨ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਅਤੇ ਉਹਨਾਂ ਦੇ ਗੁਣਾਂ ਦਾ ਵਰਣਨ ਕਰੋ | (Discuss the main constituents of food and give their advantages.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
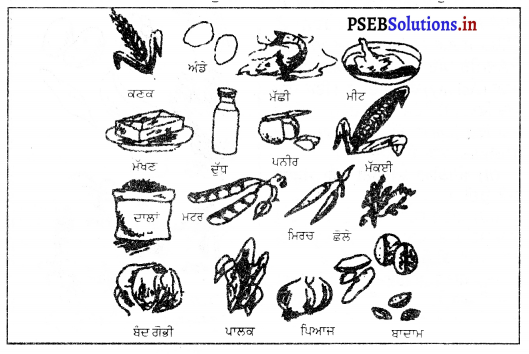
ਅਨਾਜ, ਦਾਲਾਂ, ਸਬਜ਼ੀਆਂ, ਫਲ, ਸੁੱਕੇ ਮੇਵੇ, ਦੁੱਧ, ਮੀਟ, ਮੱਛੀ ਆਦਿ ਮੁੱਖ ਭੋਜਨ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਹਨ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦੇ ਗੁਣ ਹੇਠਾਂ ਦਿੱਤੇ ਗਏ ਹਨ
1. ਅਨਾਜ (Cereals-ਕਣਕ, ਚੌਲ, ਛੋਲੇ, ਜੌ, ਮੱਕੀ ਤੇ ਬਾਜਰਾ ਆਦਿ ਅਨਾਜ ਆਮ ਖਾਧੇ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਗੁਣ (Advantages)-ਅਨਾਜ ਦੇ ਗੁਣ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਦਿੱਤੇ ਗਏ ਹਨ –
- ਇਹਨਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਸਾਡੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਦਾ ਨਿਰਮਾਣ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਵੀ ਪ੍ਰਦਾਨ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹਨਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ ਬਹੁਤ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦੇ ਬਾਹਰਲਿਆਂ ਛਿਲਕਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਲੋਹਾ, ਚੂਨਾ, ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਅਤੇ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
2. ਦਾਲਾਂ (Pulses) -ਸੋਇਆਬੀਨ, ਮਾਂਹ, ਮਸਰ, ਅਰਹਰ, ਸੁੱਕੇ ਮਟਰ, ਰਾਜਮਾਂਹ ਆਦਿ ਦੀ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਮੁੱਖ ਦਾਲਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਗੁਣ (Advantages)-ਦਾਲਾਂ ਦੇ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਗੁਣ ਹਨ –
- ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਕਰਨ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਮਿਲਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਭੁੱਖ ਵਧਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਪਾਚਨ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਤੇਜ਼ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਇਹਨਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਏ, ਬੀ ਤੇ ਸੀ ਬਹੁਤ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਸ ਤੋਂ ਬਿਨਾਂ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ, ਖਣਿਜ ਲੂਣ, ਲੋਹਾ ਤੇ ਫਾਸਫੋਰਸ ਵੀ ਮਿਲਦੇ ਹਨ !
3. ਸਬਜ਼ੀਆਂ (Vegitables)-ਬੰਦ ਗੋਭੀ, ਪਾਲਕ, ਸਰੋਂ ਦਾ ਸਾਗ, ਮੇਥੀ, ਗਾਜਰ, ਮੂਲੀ, ਸਲਾਦ, ਚੁਕੰਦਰ, ਟਮਾਟਰ, ਆਲੂ, ਮਟਰ, ਕਰੇਲਾ, ਬੈਂਗਣ, ਭਿੰਡੀ, ਫੁੱਲਗੋਭੀ ਅਤੇ ਸ਼ਲਗਮ ਆਦਿ ਮੁੱਖ ਸਬਜ਼ੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
ਗੁਣ (Advantages)-ਸਬਜ਼ੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਗੁਣ ਇਸ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਹਨ-
- ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੀ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਤੰਦਰੁਸਤ ਬਣਾਈ ਰੱਖਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹ ਲਹੂ ਸਾਫ਼ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਕਮਜ਼ੋਰ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੋਣ ਦਿੰਦੀਆਂ ।
4, ਫਲ (Fruit)-ਅੰਗੂਰ, ਅਮਰੂਦ, ਔਲਾ, ਨਾਰੰਗੀ, ਸੰਤਰਾ, ਮਾਲਟਾ, ਅਨਾਰ, ਮੁਸੰਮੀ, ਨਿੰਬੂ, ਅੰਬ, ਕੇਲਾ, ਸੇਬ, ਨਾਸ਼ਪਤੀ ਅਤੇ ਆਲੂ-ਬੁਖਾਰਾ ਆਦਿ ਫਲਾਂ ਦੀ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਕਰਨੀ ਚਾਹੀਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਗੁਣ (Advantages)-ਫਲਾਂ ਦੇ ਗੁਣ ਇਸ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਹਨ-
- ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੀ ਸਫ਼ਾਈ ਵਿਚ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹਨਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਲੋਹਾ, ਲੂਣ ਅਤੇ ਸਾਰੇ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਰੋਗਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਬਚਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
5. ਸੁੱਕੇ ਮੇਵੇ (Dry Fruits)-ਬਦਾਮ, ਅਖਰੋਟ, ਪਿਸਤਾ, ਕਾਜੂ, ਖਜੂਰ ਤੇ ਮੂੰਗਫਲੀ ਆਦਿ ਸੁੱਕੇ ਮੇਵੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ, ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਅਤੇ ਚਰਬੀ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਗੁਣ-
- ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰਕ ਵਾਧੇ ਵਿਚ ਸਹਾਇਕ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹ ਦਿਮਾਗੀ ਤਾਕਤ ਨੂੰ ਵਧਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
6. ਦੁੱਧ ਅਤੇ ਉਸ ਤੋਂ ਬਣਨ ਵਾਲੇ ਪਦਾਰਥ (Milk)-ਮੱਖਣ, ਘਿਓ, ਦਹੀਂ, ਪਨੀਰ ਤੇ ਲੱਸੀ ਆਦਿ ਦੁੱਧ ਤੋਂ ਤਿਆਰ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਭੋਜਨ ਦੇ ਸਾਰੇ ਤੱਤ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਗਰਮੀ ਤੇ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਦਾ ਵਾਧਾ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ਅਤੇ ਟੁੱਟੇ-ਭੱਜੇ ਤੰਤੂਆਂ ਦੀ ਮੁਰੰਮਤ ਵੀ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਸਾਫ਼ ਖ਼ੂਨ ਵੀ ਤਿਆਰ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
7. ਮੀਟ, ਮੱਛੀ ਤੇ ਆਂਡੇ ਆਦਿ (Meat, Fish and Eggs)-ਮੀਟ, ਮੱਛੀ ਤੇ ਆਂਡਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਵੀ ਆਮ ਕੀਤੀ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ, ਚਰਬੀ, ਕੈਲਸ਼ੀਅਮ, ਲੋਹਾ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਏ’ ‘ਬੀ’ ਤੇ ‘ਡੀ’ ਬਹੁਤ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਵਿਚ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਵਾਧੇ ਵਿਚ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ਅਤੇ ਇਸ ਨੂੰ ਕਈ ਰੋਗਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਬਚਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 5.
ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ ਅਤੇ ਚਰਬੀ ਸਾਡੇ ਲਈ ਕਿਉਂ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਹਨ ? (Why Carbohydrates and fats are necessary for us ?) .
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ (Carbohydrates)-ਇਹ ਸਾਨੂੰ ਸ਼ੱਕਰ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿਚ ਮਿਲਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਅਤੇ ਸਟਾਰਚ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿਚ ਮਿਲਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਤੱਤਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ, ਜਿਵੇਂਅੰਬ, ਗੰਨੇ ਦਾ ਰਸ, ਗੁੜ, ਸ਼ੱਕਰ, ਅੰਗੂਰ, ਖਜੂਰ, ਗਾਜਰ, ਸੁੱਕੇ ਮੇਵੇ ਅਤੇ ਕਣਕ, ਮੱਕੀ, ਜੋਂ, ਜੁਆਰ, ਸ਼ਕਰਕੰਦੀ, ਅਖਰੋਟ ਤੇ ਕੇਲੇ ਆਦਿ ਤੋਂ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਜ਼ਰੂਰਤ (Need)-
- ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ ਸਾਡੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਗਰਮੀ ਤੇ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਦਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਚਰਬੀ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹ ਚਰਬੀ ਨਾਲੋਂ ਸਸਤੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਗ਼ਰੀਬ ਤੇ ਘੱਟ ਆਮਦਨੀ ਵਾਲੇ ਲੋਕ ਵੀ ਇਸ ਦੀ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਕਰ ਸਕਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਚਿਕਨਾਈ (Fat) -ਇਹ ਸਾਨੂੰ ਬਨਸਪਤੀ ਅਤੇ ਪਸ਼ੂਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਹੋਣ ਵਾਲੀ ਚਰਬੀ ਤੋਂ ਮਿਲਦੀ ਹੈ । ਸਬਜ਼ੀਆਂ, ਸੁੱਕੇ ਮੇਵਿਆਂ, ਫਲਾਂ, ਅਖਰੋਟ, ਬਦਾਮ, ਮੂੰਗਫਲੀ, ਬੀਜਾਂ ਦੇ ਤੇਲ ਅਤੇ ਘਿਉ, ਦੁੱਧ, ਮੱਖਣ, ਮੱਛੀ ਦਾ ਤੇਲ, ਆਂਡੇ ਆਦਿ ਤੋਂ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਜ਼ਰੂਰਤ (Need)-
- ਚਰਬੀ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਸ ਦੇ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਗਰਮੀ ਪੈਦਾ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਬਾਲਣ ਦਾ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਚਰਬੀ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਸਰੀਰ ਮੋਟਾ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 6.
ਵੱਖ-ਵੱਖ ਖਣਿਜ ਲੂਣ ਸਾਡੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਲਈ ਕਿਉਂ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਹਨ ? (Why the different Mineral Salts are useful for our body ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਸਾਡੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਕੈਲਸ਼ੀਅਮ, ਫਾਸਫੋਰਸ, ਸੋਡੀਅਮ, ਲੋਹਾ, ਮੈਗਨੀਸ਼ੀਅਮ, ਪੋਟਾਸ਼ੀਅਮ, ਆਇਉਡੀਨ, ਕਲੋਰੀਨ ਅਤੇ ਗੰਧਕ ਜਿਹੇ ਤੱਤਾਂ ਦੀ ਬਹੁਤ ਜ਼ਰੂਰਤ ਹੈ । ਸਾਡੇ ਭੋਜਨ ਵਿਚ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਖਣਿਜ ਲੂਣਾਂ ਦਾ ਹੋਣਾ ਬਹੁਤ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਖਣਿਜ ਲੂਣ ਸਾਡੀ ਤੰਦਰੁਸਤੀ ਲਈ ਬਹੁਤ ਹੀ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਹੈ ।
ਇਹਨਾਂ ਖਣਿਜ ਲੂਣਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਸਾਡੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਲਈ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਉਪਯੋਗਿਤਾ ਦਾ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਵਰਣਨ ਹੇਠਾਂ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ –
1. ਕੈਲਸ਼ੀਅਮ ਅਤੇ ਫ਼ਾਸਫ਼ੋਰਸ (Calcium and Phosphorus)-ਇਹ ਖਣਿਜ ਲੂਣ, ਦੁੱਧ, ਦਹੀਂ, ਪਨੀਰ, ਆਂਡੇ, ਮੱਛੀ, ਮੀਟ, ਹਰੀਆਂ ਸਬਜ਼ੀਆਂ, ਤਾਜ਼ੇ ਫਲ, ਦਲੀਏ, ਦਾਲਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਬਦਾਮਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਬਹੁਤ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਦਾ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ, ਦੰਦ ਅਤੇ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਦਾ ਨਿਰਮਾਣ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਦਿਲ ਤੇ ਦਿਮਾਗ਼ ਲਈ ਲਾਭਦਾਇਕ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
2. ਲੋਹਾ (Iron)-ਲੋਹਾ ਹਰੀਆਂ ਸਬਜ਼ੀਆਂ, ਫਲਾਂ, ਅਨਾਜਾਂ, ਆਂਡਿਆਂ ਤੇ ਮੀਟ ਵਿਚ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਨਵਾਂ ਖ਼ੂਨ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ਤੇ ਭੁੱਖ ਵਧਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਖੂਨ ਸਾਫ਼ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
3. ਸੋਡੀਅਮ (Sodium-ਇਹ ਆਮ ਤੌਰ’ ਤੇ ਭਿੰਡੀ, ਅੰਜੀਰ, ਨਾਰੀਅਲ, ਆਲੂ-ਬੁਖਾਰਾ, ਲਸਣ, ਮੂਲੀ, ਗਾਜਰ ਅਤੇ ਸ਼ਲਗਮ ਆਦਿ ਵਿਚ ਮਿਲਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਮਿਹਦੇ ਤੇ ਗੁਰਦੇ ਦੇ ਕਈ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਰੋਗਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਰੋਕਦਾ ਹੈ ।
4. ਪੋਟਾਸ਼ੀਅਮ (Potasium-ਇਹ ਨਾਸ਼ਪਾਤੀ, ਆਲੂ-ਬੁਖਾਰਾ, ਨਾਰੀਅਲ, ਨਿੰਬੂ, ਅੰਜੀਰ, ਬੰਦ ਗੋਭੀ, ਕਰੇਲੇ, ਮੂਲੀ, ਸ਼ਲਗਮ ਆਦਿ ਵਿਚ ਮਿਲਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਜਿਗਰ ਤੇ ਦਿਲ ਨੂੰ ਤਾਕਤ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਤੇ ਕਬਜ਼ ਦੂਰ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
5. ਆਇਓਡੀਨ (Iodean)-ਇਹ ਸਮੁੰਦਰੀ ਮੱਛੀ, ਸਮੁੰਦਰੀ ਲੂਣ, ਪਿਆਜ਼, ਲਸਣ, ਟਮਾਟਰ, ਸੇਬ, ਪਾਲਕ, ਗਾਜਰ ਅਤੇ ਦੁੱਧ ਆਦਿ ਤੋਂ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਇਸ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਦਾ ਭਾਰ ਤੇ ਤਾਕਤ ਵਧਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਦੀ ਕਮੀ ਨਾਲ ਗਿਲੜ ਦਾ ਰੋਗ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
6. ਮੈਗਨੀਸ਼ੀਅਮ (Magnesium)-ਇਹ ਨਾਰੰਗੀ, ਸੰਤਰਾ, ਅੰਜੀਰ, ਆਲੂ-ਬੁਖਾਰਾ, ਕਣਕ, ਟਮਾਟਰ ਅਤੇ ਪਾਲਕ ਆਦਿ ਵਿਚ ਬਹੁਤ ਮਿਲਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਚਮੜੀ ਦੇ ਰੋਗ ਰੋਕਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਪੱਠਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਬਣਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
7. ਗੰਧਕ (Sulphur)-ਇਹ ਪਿਆਜ਼, ਮੂਲੀ, ਬੰਦ-ਗੋਭੀ ਆਦਿ ਵਿਚ ਬਹੁਤ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਨਹੁੰਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਵਾਲਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਵਧਾਉਂਦੀ ਹੈ । ਚਮੜੀ ਨੂੰ ਸਾਫ਼ ਰੱਖਦੀ ਹੈ।
8. ਕਲੋਰੀਨ (Chlorine-ਇਹ ਪਿਆਜ਼, ਪਾਲਕ, ਮੂਲੀ, ਗਾਜਰ, ਬੰਦ ਗੋਭੀ ਅਤੇ ਟਮਾਟਰ ਵਿਚ ਬਹੁਤ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਗੰਦੇ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਬਾਹਰ ਕੱਢਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੀ ਸਫ਼ਾਈ ਕਰਦੀ ਹੈ ।

ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 7.
ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖਿਆਂ ‘ਤੇ ਨੋਟ ਲਿਖੋ
(ੳ) ਸੰਤੁਲਿਤ ਭੋਜਨ ਅਤੇ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ
(ੲ) ਕੈਲਸ਼ੀਅਮ
(ਸ) ਫ਼ਾਸਫੋਰਸ
(ਹ) ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਕਮੀ ।
(ਅਭਿਆਸ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ-4) (Write down a brief note on the following
(a) Balance diet
(b) Proteins
(c) Calcium
(d) Phosphorus
(e) Lack of Vitamins.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
(ੳ) ਸੰਤੁਲਿਤ ਭੋਜਨ (Balance diet) -ਜਿਸ ਭੋਜਨ ਵਿਚ ਬਹੁਤ ਸਾਰੇ ਤੱਤ ਉੱਚਿਤ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਵਿਚ ਹੋਣ ਅਤੇ ਜਿਹੜਾ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੀਆਂ ਸਾਰੀਆਂ ਲੋੜਾਂ ਦੀ ਪੂਰਤੀ ਕਰਨ ਦੇ ਯੋਗ ਹੋਵੇ, ਉਸ ਨੂੰ ਸੰਤੁਲਿਤ ਭੋਜਨ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਸੰਤੁਲਿਤ ਭੋਜਨ ਵਿਚ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ, ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ, ਚਰਬੀ, ਖਣਿਜ ਲੂਣ, ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਤੇ ਪਾਣੀ ਉੱਚਿਤ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਵਿਚ ਹੋਣੇ ਚਾਹੀਦੇ ਹਨ । ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਪੂਰੇ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਲਈ, ਉਸ ਨੂੰ ਰੋਗਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਬਚਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਅਤੇ ਚੰਗੀ ਸਿਹਤ ਵਾਸਤੇ ਸਾਨੂੰ ਸੰਤੁਲਿਤ ਭੋਜਨ ਦੀ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਕਰਨੀ ਚਾਹੀਦੀ ਹੈ । ਕੋਈ ਵੀ ਇਕੱਲਾ ਭੋਜਨ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਸੰਤੁਲਿਤ ਭੋਜਨ ਨਹੀਂ । ਸਿਰਫ਼ ਦੁੱਧ ਹੀ ਇਕ ਅਜਿਹਾ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਵਿਚ ਸਾਰੇ ਪੌਸ਼ਟਿਕ ਤੱਤ ਮਿਲਦੇ ਹਨ ।
(ਅ) ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ (Protein) -ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ, ਕਾਰਬਨ, ਹਾਈਡਰੋਜਨ, ਆਕਸੀਜਨ ਅਤੇ ਗੰਧਕ ਤੇ ਰਸਾਇਣਿਕ ਮਿਸ਼ਰਨ ਤੋਂ ਬਣਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਦੋ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਤੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ-ਪਸ਼ੂ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਅਤੇ ਬਨਸਪਤੀ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ | ਪਸ਼ੂ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਮੀਟ, ਮੱਛੀ, ਆਂਡੇ, ਦੁੱਧ ਅਤੇ ਪਨੀਰ ਆਦਿ ਤੋਂ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ | ਬਨਸਪਤੀ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਦਾਲਾਂ, ਮਟਰ, ਫੁੱਲ ਗੋਭੀ, ਸੋਇਆਬੀਨ, ਛੋਲੇ, ਪਾਲਕ, ਹਰੀ ਮਿਰਚ, ਪਿਆਜ਼ ਅਤੇ ਸੁੱਕੇ ਮੇਵਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਮਿਲਦੇ ਹਨ । ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਨਿਰਮਾਣ ਤੇ ਭੋਜਨ ਪਚਾਉਣ ਵਿਚ ਮਦਦ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਘੱਟ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਕਮਜ਼ੋਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
(ੲ) ਕੈਲਸ਼ੀਅਮ (Calcium)-ਕੈਲਸ਼ੀਅਮ ਦੁੱਧ, ਦਹੀਂ, ਪਨੀਰ, ਆਂਡੇ, ਮੱਛੀ, ਮੀਟ, ਹਰੀਆਂ ਸਬਜ਼ੀਆਂ, ਤਾਜ਼ੇ ਫਲਾਂ, ਲੂਣ, ਦਲੀਏ, ਦਾਲਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਬਦਾਮਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਬਹੁਤ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਦਾ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਦੰਦਾਂ ਤੇ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਲਈ ਇਹ ਬਹੁਤ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਦਿਲ ਤੇ ਦਿਮਾਗ਼ ਲਈ ਬਹੁਤ ਲਾਭਦਾਇਕ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਵਿੰਗੀਆਂ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ਅਤੇ ਦੰਦ ਵੀ ਡਿੱਗ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
(ਸ) ਫ਼ਾਸਫੋਰਸ (Phosphorus)-ਫ਼ਾਸਫੋਰਸ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾਤਰ ਦੁੱਧ, ਦਹੀਂ, ਪਨੀਰ, ਆਂਡੇ, ਮੱਛੀ, ਮੀਟ, ਹਰੀਆਂ ਸਬਜ਼ੀਆਂ ਤੇ ਤਾਜ਼ੇ ਫਲਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਨਾਲ ਵੀ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਤੇ ਦੰਦ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਸ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਵਿੰਗੀਆਂ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
(ਹ) ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਕਮੀ (Lack of Vitamins)-ਮੁੱਖ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਛੇ ਹਨ-ਏ, ਬੀ, ਸੀ, ਡੀ, ਈ ਅਤੇ ਕੇ ! ਇਹਨਾਂ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਕਮੀ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਕਈ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਦੀਆਂ ਬਿਮਾਰੀਆਂ ਉਤਪੰਨ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਇਸ ਦਾ ਵੇਰਵਾ ਹੇਠਾਂ ਕੂਮ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ –
1. ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਏ (Vitamin A)
- ਇਸਦੀ ਕਮੀ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਅੰਧਰਾਤਾ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਗਲੇ ਅਤੇ ਨੱਕ ਦੇ ਰੋਗ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਫੇਫੜੇ ਕਮਜ਼ੋਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਚਮੜੀ ਦੇ ਰੋਗ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਛੂਤ ਦੇ ਰੋਗ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
2. ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਬੀ (Vitamin B)
- ਭੁੱਖ ਦਾ ਨਾ ਲੱਗਣਾ |
- ਚਮੜੀ ਦੇ ਰੋਗਾਂ ਦਾ ਪੈਦਾ ਹੋਣਾ ।
- ਵਾਲਾਂ ਦਾ ਝੜਨਾ ।
- ਜੀਭ ਦੇ ਛਾਲਿਆਂ ਦਾ ਪੈ ਜਾਣਾ ।
- ਖੂਨ ਦਾ ਘੱਟ ਹੋਣਾ ।
3. ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਸੀ (Vitamin C)
- ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਕਮਜ਼ੋਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਜ਼ਖ਼ਮਾਂ ਦਾ ਛੇਤੀ ਨਾ ਭਰਨਾ ।
- ਅੱਖਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਮੋਤੀਆ ਉਤਰ ਆਉਣਾ ।
- ਹੱਥ-ਪੈਰ ਸੁੱਜਣ ਲੱਗ ਪੈਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਸ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਸਕਰਵੀ ਦਾ ਰੋਗ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
4. ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਡੀ (Vitamin D)
- ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਕਮਜ਼ੋਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਮਿਰਗੀ ਤੇ ਸੋਕੜੇ ਦਾ ਰੋਗ ਵੱਧ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਟੇਢੀਆਂ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਕਮਜ਼ੋਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
5. ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਈ (vitamin E)
- ਇਸ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਕਾਰਨ ਨਾਮਰਦੀ ਅਤੇ ਬਾਂਝਪਨ ਦੇ ਰੋਗ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਫੋੜੇ ਫਿਨਸੀਆਂ ਨਿਕਲ ਆਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਸਰੀਰ ਕਮਜ਼ੋਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
6. ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਕੇ (Vitamin K)
- ਚਮੜੀ ਦੇ ਰੋਗ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਜ਼ਖ਼ਮਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਵਗਦਾ ਖੂਨ ਛੇਤੀ ਬੰਦ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 8.
ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ, ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ ਅਤੇ ਚਿਕਨਾਈ ਦੀ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤੀ ਦੇ ਕੀ ਸਾਧਨ ਹਨ ਅਤੇ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਉੱਚਿਤ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਕਿੰਨੀ ਲੈਣੀ ਚਾਹੀਦੀ ਹੈ ?[ ਅਭਿਆਸ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ-2] (What are the main sources of Proteins, Carbohydrates and Fats. How much quantities we should take of these ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
(ਉ) ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ (Proteins)- ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ, ਕਾਰਬਨ, ਹਾਈਡਰੋਜਨ, ਆਕਸੀਜਨ, ਨਾਈਟਰੋਜਨ, ਗੰਧਕ ਅਤੇ ਫਾਸਫੋਰਸ ਦੇ ਰਸਾਇਣਿਕ ਮੇਲ ਨਾਲ ਬਣਿਆ ਮਿਸ਼ਰਿਤ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਹੈ । ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਦੋ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਦੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ-ਬਨਸਪਤੀ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਅਤੇ ਪਸ਼ੂ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਬਨਸਪਤੀ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਸੋਇਆਬੀਨ, ਮੂੰਗਫਲੀ, ਬਾਦਾਮ, ਅਖਰੋਟ, ਕਣਕ, ਬਾਜਰਾ, ਮੱਕੀ ਆਦਿ ਵਿਚ ਪਾਈ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ । ਪਸ਼ੂ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਮਾਸ, ਮੱਛੀ, ਆਂਡਾ, ਦੁੱਧ, ਪਨੀਰ ਆਦਿ ਵਿਚ ਪਾਈ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ। ਇਕ ਸਾਧਾਰਨ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਨੂੰ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ-ਦਿਨ 70 ਤੋਂ 100 ਗਰਾਮ ਤਕ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਲੈਣੀ ਚਾਹੀਦੀ ਹੈ ।
(ਅ) ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ (Carbohydrates) ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਗਰਮੀ ਅਤੇ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਪ੍ਰਦਾਨ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ | ਭਾਰਤੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਭੋਜਨ ਵਿਚ 70-80% ਤਕ ਇਹੀ ਤੱਤ ਪਾਇਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਕ ਸਾਧਾਰਨ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦੇ ਰੋਜ਼ਾਨਾ ਭੋਜਨ ਵਿਚ 400 ਤੋਂ 700 ਗਰਾਮ ਤਕ ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਹੋਣੀ ਚਾਹੀਦੀ ਹੈ ।
(ਈ) ਚਰਬੀ ਜਾਂ ਚਿਕਨਾਈ (Fat) -ਚਰਬੀ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਦਿੰਦੀ ਹੈ। ਚਰਬੀ ਦੋ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ-ਬਨਸਪਤੀ ਚਰਬੀ ਤੇ ਪਸ਼ੂ ਚਰਬੀ | ਬਨਸਪਤੀ ਚਰਬੀ ਸਰੋਂ, ਮੁੰਗਫਲੀ, ਅਖਰੋਟ ਆਦਿ ਵਿਚ ਪਾਈ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ । ਓ, ਮੱਖਣ, ਦੁੱਧ, ਮੱਛੀ, ਮਾਸ, ਆਂਡੇ ਆਦਿ ਪਸ਼ੂ ਬਨਸਪਤੀ ਦੇ ਮੁੱਖ ਸੋਮੇ ਹਨ । ਇਕ ਸਾਧਾਰਨ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦੇ ਭੋਜਨ ਵਿਚ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਦਿਨ ਲਗਭਗ 50 ਤੋਂ 75 ਗਰਾਮ ਤਕ ਚਰਬੀ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਹੋਣੀ ਚਾਹੀਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 9.
ਫੋਕਟ ਸਾਡੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਲਈ ਬੜੇ ਹੀ ਲਾਭਦਾਇਕ ਹਨ, ਕਿਵੇਂ ? (Waste Product are useful for us. How ?) ਅਭਿਆਸ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ-
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਫੋਕਟ- ਸਰੀਰਕ ਵਾਧੇ ਤੇ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਲਈ ਅਸੀਂ ਸੰਤੁਲਿਤ ਭੋਜਨ ਖਾਂਦੇ ਹਾਂ ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਭੋਜਨ ਦੇ ਸਾਰੇ ਤੱਤ ਠੀਕ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਵਿਚ ਹੋਣ ਜਿਵੇਂ ਕਿ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ, ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ, ਥੰਧਿਆਈ, ਖਣਿਜ ਲੂਣ, ਪਾਣੀ ਤੇ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨਜ਼ | ਪਰ ਜੇ ਇਹ ਸਾਰੇ ਤੱਤ ਨਿਰੋਲ ਹੀ ਲਏ ਜਾਣ ਤਾਂ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦਾ ਫਾਇਦਾ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੋ ਸਕਦਾ | ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਜਿਸ ਗੰਦਗੀ ਨੇ ਬਾਹਰ ਨਿਕਲਣਾ ਹੈ, ਉਹ ਵੀ ਨਹੀਂ ਨਿਕਲ ਸਕੇਗੀ, ਮਿਹਦੇ ਤੇ ਅੰਤੜੀਆਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਅੰਦਰਲੀਆਂ ਝੱਲੀਆਂ ਨਾਲ ਜੰਮ ਜਾਵੇਗੀ ।
ਇਸ ਲਈ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਸਾਰੇ ਤੱਤਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਜਾਂ ਇਕੱਲੇ ਨੂੰ ਨਿਰੋਲ ਕਿਸਮ ਨਹੀਂ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾ ਸਕਦਾ ਅਤੇ ਕੱਚੀਆਂ ਸਬਜ਼ੀਆਂ ਜਿਵੇਂ ਕਿ ਮੂਲੀ, ਸ਼ਲਗਮ, ਗਾਜਰ, ਟਮਾਟਰ, ਖੀਰਾ, ਸਲਾਦ, ਛਿਲਕੇ ਵਾਲੇ ਅਨਾਜ ਜਿਵੇਂ ਕਣਕ, ਛੋਲਿਆਂ ਦਾ ਆਟਾ, ਖਾਣ ਵੇਲੇ ਆਟਾ ਛਾਣ ਕੇ ਛਿਲਕੇ ਸੁੱਟਣੇ ਨਹੀਂ ਚਾਹੀਦੇ । ਮਿਹਦੇ ਤੇ ਅੰਤੜੀਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਜਾ ਕੇ ਇਹ ਛਿੱਲੜ ਸਫ਼ਾਈ ਵਾਲੇ ਬੁਰਸ਼ ਦੀ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਕੰਮ ਦਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਸਰੀਰ ਤਾਜ਼ਾ ਦਮ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਲਈ ਖਾਣ ਵਾਲੀਆਂ ਚੀਜ਼ਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਰੇਸ਼ੇ ਹੋਣੇ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਹਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 10.
ਕੈਲੋਰੀ ਕੀ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਭੋਜਨ ਦਾ ਤੱਤ ਨਾਪਣ ਦੀ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਛੋਟੀ ਇਕਾਈ ਨੂੰ ਕੈਲੋਰੀ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ।

ਵੱਡੇ ਉੱਤਰਾਂ ਵਾਲੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ (Long Answer Type Questions)
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਕਿੰਨੀ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ? ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦੇ ਮੁੱਖ ਕੰਮ ਦੱਸੋ । ਇਹ ਕਿਹੜੇ-ਕਿਹੜੇ ਭੋਜਨ ਪਦਾਰਥਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਮਿਲਦੇ ਹਨ ? (Give the types of Vitamins ? Describe their main functions and sources.)
ਜਾ
ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤੀ ਦੇ ਸੋਮੇ ਅਤੇ ਲਾਭ ਦੱਸੋ । ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਏ, ਬੀ, ਸੀ, ਡੀ ਅਤੇ ਕੇ । (ਅਭਿਆਸ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ-6) (Write down the sources of the following Vitamins and their uses. Vitamins A, B, C, D and K.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ (Vitamins)-ਹੁਣ ਤਕ ਬਹੁਤ ਸਾਰੇ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਖੋਜ ਹੋ ਚੁੱਕੀ ਹੈ, ਪਰ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਏ, ਬੀ, ਸੀ, ਡੀ, ਈ ਅਤੇ ਕੇ ਹੀ ਮੰਨੇ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ।
ਇਹਨਾਂ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਹਰ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਦਾ ਮੁੱਖ ਕੰਮ ਅਤੇ ਇਹ ਕਿਹੜੇ ਭੌਜਨ ਪਦਾਰਥਾਂ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਮਿਲਦਾ ਹੈ, ਵਰਣਨ ਹੇਠਾਂ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ
1. ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਏ (Vitamin A)ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਏ’ ਦੇ ਕੰਮ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਹਨ-
- ਇਸ ਨਾਲ ਅੱਖਾਂ ਦੀ ਰੌਸ਼ਨੀ ਵਧਦੀ ਹੈ |
- ਭੁੱਖ ਵਧਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਪਾਚਨ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਠੀਕ ਰਹਿੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਹ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਵਧਾਉਣ ਤੇ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਕਰਨ ਵਿਚ ਮੱਦਦੇ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।

ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਹਾਨੀਆਂ (Abuses)-
- ਇਸ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਅੰਧਰਾਤਾ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਚਮੜੀ ਖੁਸ਼ਕ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਗਲਾ, ਨੱਕ ਤੇ ਅੱਖਾਂ ਤੇ ਚਮੜੀ ਨੂੰ ਹਰ ਛੂਤ ਦੀ ਬਿਮਾਰੀ ਛੇਤੀ ਲੱਗਦੀ ਹੈ |
- ਸਰੀਰ ਕਮਜ਼ੋਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਤੇ ਵਾਧਾ ਰੁਕ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਫੇਫੜੇ ਕਮਜ਼ੋਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤੀ ਸੋਮਾ (Sources) -ਇਹ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾ ਦੁੱਧ, ਦਹੀਂ, ਮੱਖਣ, ਪਨੀਰ, ਆਂਡੇ, ਮੱਛੀ, ਤਾਜ਼ੀਆਂ ਸਬਜ਼ੀਆਂ ਤੇ ਪੱਤਿਆਂ ਜਿਵੇਂ-ਪਾਲਕ, ਗਾਜਰ, ਬੰਦ-ਗੋਭੀ, ਟਮਾਟਰ, ਕੇਲਾ, ਸੰਤਰਾ, ਅੰਬ, ਪਪੀਤਾ, ਅਨਾਨਾਸ ਆਦਿ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਮਿਲਦਾ ਹੈ ।
2. ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਬੀ (Vitamin B) ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਬੀ’ ਦੇ ਕੰਮ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਹਨ
- ਇਸ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਨਾਲ ਨਾੜੀ ਸਿਸਟਮ (Nervous System) ਠੀਕ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਹ ਨਾੜੀਆਂ, ਪੱਠਿਆਂ, ਦਿਲ ਤੇ ਦਿਮਾਗ਼ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਭੁੱਖ ਤੇਜ਼ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਚਮੜੀ ਦੇ ਰੋਗਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ।

ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਹਾਨੀਆਂ (Abuses)-
- ਭੁੱਖ ਘੱਟ ਲੱਗਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਦਾ ਵਾਧਾ ਰੁਕ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਬੇਰੀ-ਬੇਰੀ ਰੋਗ ਤੇ ਚਮੜੀ ਦੇ ਕਈ ਰੋਗ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਜੀਭ ‘ਤੇ ਛਾਲੇ ਪੈ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਵਾਲ ਡਿੱਗਣ ਲੱਗ ਪੈਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤੀ ਸੋਮਾ (Sources) – ਇਹ ਦੁੱਧ, ਦਹੀਂ, ਮੱਖਣ, ਪਨੀਰ, ਸਾਬਤ ਦਾਲਾਂ, ਅਨਾਜ, ਸੋਇਆਬੀਨ, ਮਟਰ, ਆਂਡੇ, ਹਰੀਆਂ ਸਬਜ਼ੀਆਂ ਤੇ ਪੱਤਿਆਂ ਜਿਵੇਂ ਬੰਦੇ-ਗੋਭੀ, ਪਿਆਜ, ਪਾਲਕ, ਟਮਾਟਰ, ਸ਼ਲਗਮ ਤੇ ਸਲਾਦ ਆਦਿ ਵਿਚ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
3. ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਸੀ’ (Vitamin C) ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਸੀ’ ਦੇ ਕੰਮ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਹਨ
- ਇਹ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਲਹੂ ਨੂੰ ਸਾਫ਼ ਰੱਖਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਦੰਦਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਰੱਖਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਜ਼ਖ਼ਮਾਂ ਤੇ ਟੁੱਟੀਆਂ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਵੀ ਜਲਦੀ ਠੀਕ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਛੂਤ ਦੀਆਂ ਬਿਮਾਰੀਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਬਚਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਗਲੇ ਨੂੰ ਠੀਕ ਰੱਖਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਜ਼ੁਕਾਮ ਤੋਂ ਬਚਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਹਾਨੀਆਂ (Abuses)
- ਦੰਦਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪਾਇਓਰੀਆ ਰੋਗ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਕਮਜ਼ੋਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਜ਼ਖ਼ਮ ਜਲਦੀ ਠੀਕ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੋ ਸਕਦੇ ।
- ਅਨੀਮੀਆ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਲਹੂ ਵਹਿਣਾ ਜਲਦੀ ਬੰਦ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦਾ ।

ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤੀ ਸੋਮਾ (Sources) ਇਹ ਆਮ ਤੌਰ ‘ਤੇ ਰਸਦਾਰ ਖੱਟੇ ਫਲਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ, ਜਿਵੇਂ- ਸੰਤਰਾ, ਮਾਲਟਾ, ਮੁਸੰਮੀ, ਅੰਗੂਰ, ਅਨਾਰ, ਨਿੰਬੂ, ਅਮਰੂਦ ਅਤੇ ਔਲਾ ਆਦਿ । ਇਸ ਤੋਂ ਬਿਨਾਂ ਹਰੀਆਂ ਸਬਜ਼ੀਆਂ, ਟਮਾਟਰ, ਬੰਦਗੋਭੀ, ਗਾਜਰ, ਪਾਲਕ, ਸ਼ਲਗਮ ਆਦਿ ਵਿਚ ਵੀ ਮਿਲਦਾ ਹੈ ।
4. ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਡੀ’ (Vitamin D) –
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਡੀ ਦੇ ਕੰਮ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਹਨ –
- ਇਹ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਤੇ ਦੰਦ ਬਣਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਉਹਨਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਵੀ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਸਰੀਰਕ ਵਾਧੇ ਲਈ ਇਸ ਦੀ ਬਹੁਤ ਜ਼ਰੂਰਤ ਹੈ ।

ਧਰਪਤੀ ਸੋਸਾ (Sources) – ਇਹ ਦੁੱਧ, ਆਂਡੇ ਦੀ ਜ਼ਰਦੀ, ਮੱਖਣ, ਘਿਓ, ਮੱਛੀ ਦੇ ਤੇਲ ਆਦਿ ਵਿਚ ਬਹੁਤ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਸੂਰਜ ਦੀਆਂ ਕਿਰਨਾਂ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ ਨਾਲ ਆਪਣੇ ਆਪ ਹੀ ਬਣਦਾ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਹਾਨੀਆਂ (Abuses)
- ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਕਮਜ਼ੋਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਦੰਦ ਠੀਕ ਸਮੇਂ ਤੇ ਨਹੀਂ ਨਿਕਲਦੇ ।
- ਮਿਰਗੀ, ਹਿਸਟੀਰੀਆ ਤੇ ਸੋਕਾ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਕਮਜ਼ੋਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
5. ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਈ (Vitamin E) – ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਈ’ ਦੇ ਕੰਮ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਹਨ
- ਇਹ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਔਰਤਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਮਰਦਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਸੰਤਾਨ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਨ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਨੂੰ ਵਧਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਹ ਨਾਮਰਦੀ ਤੇ ਬਾਂਝਪਣ ਨੂੰ ਰੋਕਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਹਾਨੀਆਂ (Abuses)
- ਫਿਨਸੀਆਂ ਨਿਕਲਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਬਾਂਝਪਣ ਰੋਗ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ |
ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤੀ ਸੋਮਾ (Sources)-ਇਹ ਬੰਦਗੋਭੀ, ਗਾਜਰ, ਸਲਾਦ, ਮਟਰ, ਪਿਆਜ਼, ਟਮਾਟਰ, ਫੁੱਲ ਗੋਭੀ ਵਿਚ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਤੋਂ ਬਿਨਾਂ ਸ਼ਹਿਦ, ਕਣਕ, ਚੌਲ, ਬੀਜਾਂ ਦੇ ਤੇਲ, ਆਂਡੇ ਦੀ ਜ਼ਰਦੀ, ਬਾਦਾਮ, ਪਿਸਤੇ, ਛੋਲਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਦਾਲ ਤੇ ਦਲੀਏ ਵਿਚ ਬਹੁਤ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
6. ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਕੇ (Vitamin K)-
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਕੇ’ ਦੇ ਕੰਮ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਹਨ –
- ਇਹ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਜ਼ਖ਼ਮਾਂ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਰਿਸਦੇ ਖੂਨ ਨੂੰ ਰੋਕਦਾ ਹੈ :
- ਉਸ ਦੇ ਜਮਾਓ ਵਿਚ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਹ ਚਮੜੀ ਤੇ ਰੋਗਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਹਾਨੀਆਂ (Abuses)-
- ਲਹੁ ਜੰਮਣ ਦੀ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਵਿਚ ਰੋਕ ਪੈਂਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਚਮੜੀ ਦੇ ਰੋਗ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਪਤੀ ਸੋਮਾ (Sources)-ਇਹ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾਤਰ ਬੰਦਗੋਭੀ, ਪਾਲਕ, ਮੱਛੀ, ਸੋਇਆਬੀਨ, ਟਮਾਟਰ ਤੇ ਆਂਡੇ ਦੀ ਜ਼ਰਦੀ ਆਦਿ ਵਿਚ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।

ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਸੰਤੁਲਿਤ ਭੋਜਨ ਦੇ ਵੱਖ-ਵੱਖ ਤੱਤ ਕਿਹੜੇ ਹਨ ? (ਅਭਿਆਸ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ-1) (What are the various constituents of Balanced Diet ?)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਸੰਤੁਲਿਤ ਭੋਜਨ (Balanced Diet)-ਸੰਤੁਲਿਤ ਭੋਜਨ ਉਹ ਭੋਜਨ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਵਿਚ ਸਰੀਰ ਲਈ ਸਭ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਤੱਤ ਉੱਚਿਤ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਵਿਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਹਨ, ਜਿਵੇਂ-ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ, ਚਰਬੀ, ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ, ਖਣਿਜ ਲੂਣ, ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ, ਪਾਣੀ ਆਦਿ । ਇਹਨਾਂ ਤੱਤਾਂ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦੀ ਉਮਰ, ਸਿਹਤ ਅਤੇ ਕਾਰਜ ‘ਤੇ ਨਿਰਭਰ ਕਰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਸੰਤੁਲਿਤ ਭੋਜਨ ਦੇ ਤੱਤ (Constituents of Balanced Diet)-ਸੰਤੁਲਿਤ ਭੋਜਨ ਦੇ ਭਿੰਨ-ਭਿੰਨ ਤੱਤਾਂ ਦਾ ਸੰਖੇਪ ਵਰਣਨ ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਹੈ
1. ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ (Proteins) -ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਕਾਰਬਨ, ਹਾਈਡਰੋਜਨ, ਆਕਸੀਜਨ, ਨਾਈਟਰੋਜਨ, ਗੰਧਕ ਅਤੇ ਫਾਸਫੋਰਸ ਦੇ ਰਸਾਇਣਿਕ ਮੇਲ ਨਾਲ ਬਣਿਆ ਇਕ ਮਿਸ਼ਚਿਤ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਹੈ। ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਦੋ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ-ਬਨਸਪਤੀ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਅਤੇ ਪਸੂ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ |
ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤੀ ਦੇ ਸੋਮੇ (Sources)-
- ਬਨਸਪਤੀ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ–ਇਹ ਸੋਇਆਬੀਨ, ਮੂੰਗਫਲੀ, ਕਾਜੂ, ਪਿਸਤਾ, ਅਖਰੋਟ, ਕਣਕ, ਬਾਜਰਾ, ਮੱਛੀ ਆਦਿ ਵਿਚ ਪਾਇਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਪਸ਼ੂ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ -ਇਹ ਮਾਸ, ਮੱਛੀ, ਕਲੇਜੀ, ਆਂਡਾ, ਪਨੀਰ ਆਦਿ ਵਿਚ ਪਾਇਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਦੇ ਲਾਭ (Advantages)-
- ਇਸ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰਕ ਵਾਧਾ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਟੁੱਟੇ-ਫੁੱਟੇ ਸੈੱਲਾਂ ਦੀ ਮੁਰੰਮਤ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ |
- ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਦਾ ਤਾਪਮਾਨ ਠੀਕ ਰੱਖਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਜਦੋਂ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ ਜਾਂ ਚਰਬੀ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਘੱਟ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ਤਾਂ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਨ ਦਾ ਕੰਮ ਵੀ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਹੀ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਹਾਨੀਆਂ (Abuses) –
ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਰੋਗ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ
- ਕਵਾਸ਼ੀਓਰਕਰ (Kwashiorkar)-ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਇਕ ਸਾਲ ਤੋਂ ਲੈ ਕੇ ਤਿੰਨ ਸਾਲ ਤਕ ਦੀ ਉਮਰ ਦੇ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਇਹ ਰੋਗ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਬੱਚੇ ਦੀਆਂ ਲੱਤਾਂ ਸੁੱਕ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ਅਤੇ ਫੇਰ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਮੂੰਹ ਅਤੇ ਸਾਰੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਸੋਜ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ । ਚਮੜੀ ਖੁਰਦਰੀ ਅਤੇ ਲਾਲ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ । ਬੱਚਾ ਚਿੜਚਿੜਾ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ |
- ਸੋਕਾ-ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਸੋਕਾ ਨਾਮੀ ਰੋਗ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਬੱਚਾ ਪਤਲਾ ਅਤੇ ਕਮਜ਼ੋਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ। ਉਸਦੇ ਮਾਸ ਦੇ ਹੇਠਾਂ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਨਜ਼ਰ ਆਉਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
3. ਭੁੱਖ ਨਾਲ ਸੋਜਾ (litige oedenaa)-ਭੁੱਖੇ ਰਹਿਣ ਨਾਲ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਦੀ ਕਮੀ ਕਾਰਨ ਮਨੁੱਖ ਦੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਘੱਟ ਖ਼ੁਰਾਕ ਪਹੁੰਚਦੀ ਹੈ, ਸੈੱਲਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਪਾਣੀ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਇਕੱਠਾ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਸੁੱਜਿਆ ਹੋਇਆ ਨਜ਼ਰ ਆਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
4. ਪਲੈਗਰਾ (Pellagra) – ਇਸ ਰੋਗ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਚਮੜੀ ਖੁਰਦਰੀ ਅਤੇ ਖੁਸ਼ਕ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ।
5. ਜਿਗਰ ਦੀ ਖ਼ਰਾਬੀ-ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਜਿਗਰ ਖ਼ਰਾਬ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਦੀ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਤੀ ਨਾਲ ਹਾਨੀਆਂ (Abuses)-ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਦੀ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਲੈਣ ਨਾਲ ਗੁਰਦਿਆਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਕਈ ਬਿਮਾਰੀਆਂ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
ਖੂਨ ਦੀਆਂ ਨਾੜੀਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਵੀ ਫ਼ਰਕ ਆਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਜੋੜਾਂ ਦੇ ਦਰਦ ਵੀ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਦੀ ਉੱਚਿਤ ਮਾਤਰਾ (Proper Quantity)-ਇਕ ਸਾਲ ਤੋਂ ਲੈ ਕੇ ਛੇ ਸਾਲ ਤਕ ਦੀ ਉਮਰ ਦੇ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਦੀ ਬਹੁਤ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾ ਜ਼ਰੂਰਤ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਕ ਸਾਧਾਰਨ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਨੂੰ ਪ੍ਰਤੀਦਿਨ 10 ਤੋਂ 100 ਗ੍ਰਾਮ ਤਕ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਲੈਣੀ ਚਾਹੀਦੀ ਹੈ ।
2. ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ (Carbohydrates)-ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਅਤੇ ਗਰਮੀ ਪ੍ਰਦਾਨ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ | ਭਾਰਤੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਭੋਜਨ ਦਾ 70-80% ਭਾਗ ਇਸ ਤੱਤ ਨਾਲ ਪੂਰਾ ਕੀਤਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤੀ ਦੇ ਸੋਮੇ (Sources)-ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ ਕਣਕ, ਚਾਵਲ, ਜਵਾਰ (ਜੋਂ, ਮੱਕੀ, ਬਾਜਰਾ, ਗੁੜ, ਖੰਡ, ਸ਼ਕਰਕੰਦੀ, ਆਲੂ ਆਦਿ ਵਸਤੂਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਪਾਏ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ ਦੇ ਲਾਭ (Advantages)-
- ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਅਤੇ ਗਰਮੀ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਉਹ ਚਰਬੀ ਪਚਾਉਣ ਵਿਚ ਮਦਦ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਸ ਨਾਲ ਜਿਗਰ ਅਤੇ ਅੰਤੜੀਆਂ ਦੀ ਸਫ਼ਾਈ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਘਾਟ ਅਤੇ ਹਾਨੀਆਂ (Abuses)-
- ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ ਦੀ ਉੱਚਿਤ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਨਾ ਮਿਲਣ ਨਾਲ ਖੂਨ ਵਿਚ ਐਲਕਲੀਨ ਘੱਟ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਤੇਜ਼ਾਬੀ ਮਾਦਾ (Acidity) ਵੱਧ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।ਇਸ ਦਸ਼ਾ ਵਿਚ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਬੇਹੋਸ਼ ਹੋ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ | ਅਜਿਹੀ ਦਸ਼ਾ ਵਿਚ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾ ਭੁੱਖੇ ਰਹਿਣ ਨਾਲ ਸ਼ੱਕਰ (Diabetes) ਰੋਗ ਹੋ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਅੰਤੜੀਆਂ ਦੀ ਪੂਰੀ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਸਫ਼ਾਈ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦੀ ।
- ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ ਤੇ ਘੱਟ ਖਾਣ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੀ ਚਰਬੀ ਵੀ ਠੀਕ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਹਜ਼ਮ ਨਹੀਂ ਕੀਤੀ ਜਾ ਸਕਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ ਦੇ ਘੱਟ ਖਾਣ ਨਾਲ ਜਿਗਰ ਵਿਚ ਤੇਜ਼ਾਬੀ ਤੱਤਾਂ ਦਾ ਵਾਧਾ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਹਾਨੀ ਪੁੱਜਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਸ ਦੀ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਬਹੁਤ ਕਮਜ਼ੋਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦੀ ਮੌਤ ਹੋ ਸਕਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਜ਼ਿਆਦਤੀ ਨਾਲ ਹਾਨੀਆਂ (Abuses)-
- ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ ਦੀ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਤੀ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਮੋਟਾਪਾ ਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ :
- ਉੱਚਾ ਰਕਤਚਾਪ |
- ਸ਼ੱਕਰ ਅਤੇ ਜੋੜਾਂ ਦੇ ਦਰਦ ਆਦਿ ਰੋਗ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ ਦੀ ਉੱਚਿਤ ਮਾਤਰਾ (Proper Qualtity) – ਸਾਡੇ ਭੋਜਨ ਵਿਚ 50-80% ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ ਤੱਤ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਸੰਤੁਲਿਤ ਭੋਜਨ ਦਾ 50-6% ਭਾਰ ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ ਦਾ ਹੀ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ | ਇਹ ਸਾਧਾਰਨ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦੇ ਭੋਜਨ ਵਿਚ ਪ੍ਰਤੀਦਿਨ 400 ਤੋਂ 70 ਗਰਾਮ ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਹੋਣੀ ਚਾਹੀਦੀ ਹੈ ।

3. ਚਰਬੀ ਜਾਂ ਚਿਕਨਾਈ (Fats) – ਚਰਬੀ ਜਾਂ ਚਿਕਨਾਈ ਦੋ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਬਨਸਪਤੀ ਚਰਬੀ ਤੇ ਪਸ਼ੂ ਚਰਬੀ ।
ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤੀ ਦੇ ਸੋਮੇ (Sources)-
- ਬਨਸਪਤੀ ਚਰਬੀ-ਸਰੋਂ, ਮੁੰਗਫਲੀ ਅਤੇ ਨਾਰੀਅਲ ਦਾ ਤੇਲ, ਅਖ਼ਰੋਟ, ਬਾਦਾਮ, ਮੂੰਗਫਲੀ, ਸੋਇਆਬੀਨ ਆਦਿ ਵਿਚ ਪਾਈ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਪਸ਼ੂ ਚਰਬੀ–ਇਹ ਘਿਓ, ਮੱਖਣ, ਦੁੱਧ, ਮਾਸ, ਮੱਛੀ, ਆਂਡਿਆਂ ਆਦਿ ਵਿਚ ਪਾਈ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ !
ਚਰਬੀ ਦੇ ਲਾਭ (Advantages)-
- ਇਸ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਪੈਦਾ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਤਾਪਮਾਨ ਨੂੰ ਸਥਿਰ ਰੱਖਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਸਭ ਅੰਗਾਂ ਦੀ ਬਾਹਰੀ ਚੋਟ ਤੋਂ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਕਰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਹ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਏ, ਡੀ ਅਤੇ ਕੇ ਨੂੰ ਸਰੀਰਕ ਜ਼ਰੂਰਤ ਦੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਸੰਭਾਲ ਕੇ ਰੱਖ ਸਕਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਹਾਨੀਆਂ (Disadvantages)-ਚਰਬੀ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਕਈ ਹਾਨੀਆਂ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ
- ਚਮੜੀ (Skin) ਖ਼ੁਸ਼ਕ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਏ, ਡੀ, ਈ ਅਤੇ ਕੇ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ |
- ਚਰਬੀ ਤੇਜ਼ਾਬਾਂ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਚਮੜੀ ਖੁਸ਼ਕ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਜ਼ਿਆਦਤੀ ਨਾਲ ਹਾਨੀਆਂ (Abuses)-ਭੋਜਨ ਵਿਚ ਚਰਬੀ ਦੀ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਵੀ ਹਾਨੀਕਾਰਕ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ
- ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਮੋਟਾਪਾ ਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਦਿਲ ਦਾ ਰੋਗ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਹਾਜ਼ਮਾ ਖ਼ਰਾਬ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਸ਼ੱਕਰ (Diabetes) ਰੋਗ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਪੇਟ ਵਿਚ ਪੱਥਰੀ (Stone) ਬਣ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਚਰਬੀ ਦੀ ਉੱਚਿਤ ਮਾਤਰਾ (Proper Quantity)-ਇਕ ਸਾਧਾਰਨ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦੇ ਝੋਜਨ ਵਿਚ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ-ਦਿਨ ਲਗਪਗ 50 ਗਰਾਮ ਤੋਂ 75 ਗਰਾਮ ਚਰਬੀ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਹੋਣੀ ਚਾਹੀਦੀ ਹੈ ।
4. ਖਣਿਜ ਲੂਣ (Mineral Salts)-ਸਾਡੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਖਣਿਜ ਲੂਣ 4% ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਫਾਸਫੋਰਸ, ਕੈਲਸ਼ੀਅਮ, ਸੋਡੀਅਮ, ਕਲੋਰੀਨ, ਪੋਟਾਸ਼ੀਅਮ, ਮੈਗਨੀਸ਼ੀਅਮ, ਮੈਂਗਨੀਜ਼, ਆਇਓਡੀਨ ਅਤੇ ਕੈਲਸ਼ੀਅਮ ਜ਼ਿੰਕ ਆਦਿ ਮੁੱਖ ਖਣਿਜ ਲੂਣ ਹਨ ।

ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤੀ ਦੇ ਸੋਮੇ (Sources)-ਇਹ ਖਣਿਜ ਹਰੇ ਪੱਤਿਆਂ ਵਾਲੇ ਸਾਗ ਅਤੇ ਹਰੇ ਫਲਾਂ, ਮਾਸ, ਮੱਛੀ, ਦੁੱਧ ਆਦਿ ਵਿਚ ਕਾਫ਼ੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਵਿਚ ਪਾਏ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ । ਦੁੱਧ ਵਿਚ ਲੋਹੇ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਘੱਟ ਹੈ, ਪਰ ਹੋਰ ਸਭ ਖਣਿਜ ਲੂਣ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਲਾਭ (Advantages)
- ਇਹ ਦੰਦਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਬਣਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਤੰਤੂਆਂ (Muscular Tissues) ਦਾ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹ ਖੂਨ ਦੇ ਰੰਗ ਨੂੰ ਲਾਲ ਬਣਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਕੈਲਸ਼ੀਅਮ ਖ਼ੂਨ ਦੇ ਜਮਾ ਵਿਚ ਯੋਗਦਾਨ ਦਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਖਣਿਜ ਲੂਣ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਸਭ ਕੰਮਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਠੀਕ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਚਲਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਪਾਣੀ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਹਾਨੀਆਂ (Disadvantages) –
- ਕੈਲਸ਼ੀਅਮ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਦੰਦ ਕਮਜ਼ੋਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਸਰੀਰ ਹਰੇਕ ਰੋਗ ਦਾ ਜਲਦੀ ਸ਼ਿਕਾਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਆਇਓਡੀਨ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਗਿੱਲ੍ਹੜ ਨਾਮੀ ਰੋਗ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
5. ਪਾਣੀ (Water) -ਸਾਡੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਦਾ ਪੁਤ ਭਾਗ ਪਾਣੀ ਦਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਆਕਸੀਜਨ ਅਤੇ ਹਾਈਡਰੋਜਨ ਦੇ ਮੇਲ ਨਾਲ ਬਣਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਇਸ ਦਾ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਲਈ ਉੱਨਾ ਹੀ ਮਹੱਤਵ ਹੈ ਜਿੰਨਾ ਕਿ ਹਵਾ ਦਾ ।
ਸੋਮੇ (Sources)-ਪਾਣੀ ਸਾਨੂੰ ਕਈ ਕਿਸਮ ਦੇ ਭੋਜਨ ਦੇ ਤੱਤਾਂ ਦੁੱਧ, ਫਲ ਅਤੇ ਸਬਜ਼ੀਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਸ਼ੁੱਧ ਰੂਪ ਵਿਚ ਮਿਲਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪਾਣੀ ਦੇ ਲਾਭ (Advantages) –
- ਪਾਣੀ ਸੈੱਲਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਿਰਮਾਣ ਵਿਚ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਹ ਸੈਂਲਾਂ ਤਕ ਖ਼ੁਰਾਕ ਪਹੁੰਚਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਗੰਦੇ ਪਦਾਰਥਾਂ ਦਾ ਨਿਕਾਸ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਹ ਭੋਜਨ ਨੂੰ ਪਚਾਉਣ ਵਿਚ ਮਦਦ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਹ ਸਾਡੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੀ ਗਰਮੀ ਨੂੰ ਨਿਯਮਬੱਧ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਪਾਣੀ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਭੋਜਨ ਦੇ ਤੱਤ ਖੂਨ ਵਿਚ ਮਿਲਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਜੋੜਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਅੰਗਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਨਰਮ ਰੱਖਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਪਾਣੀ ਦੇ ਸਹਾਰੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਖੂਨ ਦਾ ਚੱਕਰ ਚਲਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪਾਣੀ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਹਾਨੀਆਂ (Disadvantages) ਪਾਣੀ ਘੱਟ ਪੀਣ ਨਾਲ ਬਹੁਤ ਸਾਰੀਆਂ ਹਾਨੀਆਂ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਪਾਣੀ ਘੱਟ ਪੀਣ ਨਾਲ ਖਾਧਾ ਹੋਇਆ ਭੋਜਨ ਚੰਗੀ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਨਹੀਂ ਪਚਦਾ ।
- ਜਿਗਰ ਭਾਰਾ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਕਬਜ਼ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਸਿਰ ਹਮੇਸ਼ਾਂ ਥੱਕਿਆ ਜਿਹਾ ਮਹਿਸੂਸ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਸਰੀਰ ਕਮਜ਼ੋਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਚਿਹਰਾ ਪੀਲਾ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਗੰਦੇ ਪਦਾਰਥਾਂ ਦਾ ਘੱਟ ਨਿਕਾਸ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਜੋੜਾਂ ਦਾ ਦਰਦ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਗੁਰਦਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਪੱਥਰੀ ਬਣ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਪਾਣੀ ਦੀ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਤੀ ਨਾਲ ਹਾਨੀਆਂ (Abuses) -ਪਾਣੀ ਹਮੇਸ਼ਾ ਉੱਚਿਤ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਵਿਚ ਹੀ ਪੀਣਾ ਚਾਹੀਦਾ ਹੈ। ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾ ਪਾਣੀ ਪੀਣ ਨਾਲ ਜਿਗਰ ਭਰਿਆ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਭੁੱਖ ਘੱਟ ਲੱਗਦੀ ਹੈ । ਭੋਜਨ ਕਰਦੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਨਾਲ-ਨਾਲ ਪਾਣੀ ਪੀਣ ਨਾਲ ਭੋਜਨ ਜਲਦੀ ਹਜ਼ਮ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦਾ |
ਪਾਣੀ ਦੀ ਉੱਚਿਤ ਮਾਤਰਾ (Proper Quantity) -ਪਾਣੀ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਵਿਚ ਰੁੱਤ, ਕਸਰਤ ਜਾਂ ਖ਼ੁਰਾਕ ਦੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਪਰਿਵਰਤਨ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਸਾਧਾਰਨ ਤੌਰ ‘ਤੇ ਦਿਨ ਵਿਚ 5-6 ਗਲਾਸ ਪਾਣੀ ਪੀਣਾ ਚਾਹੀਦਾ ਹੈ ।

6. ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ (Vitamin) -ਭੋਜਨ ਵਿਚ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਉੱਚਿਤ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਹੋਣੀ ਚਾਹੀਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦਾ ਮਨੁੱਖੀ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਲਈ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ ਮਹੱਤਵ ਹੈ । ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਬਿਨਾਂ ਸਰੀਰ ਦਾ ਕੋਈ ਕੰਮ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੋ ਸਕਦਾ । ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਰਹਿਤ ਭੋਜਨ ਸੰਤੁਲਿਤ ਭੋਜਨ ਨਹੀਂ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾ ਸਕਦਾ । ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਆਮ ਤੌਰ ‘ਤੇ ਤਾਜ਼ੇ ਫਲ, ਹਰੀਆਂ ਸਬਜ਼ੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਆਂਡਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਮਿਲਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ 6 ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ-ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਏ, ਬੀ, ਸੀ, ਡੀ, ਈ ਅਤੇ ਕੇ ।
ਲਾਭ (Advantages)-
- ਇਹ ਪਾਚਨ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਨੂੰ ਵਧਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਭਿੰਨ-ਭਿੰਨ ਰੋਗਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਰੋਕਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਸਾਡੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੀ ਚਮੜੀ ਦੇ ਰੋਗਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਸਾਡੀਆਂ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਬਣਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਖਣਿਜ ਲੂਣ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨਾਂ ਦੇ ਲਾਭ ਦੱਸੋ । [ਅਭਿਆਸ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ-4] (Describe the advantages of Mineral Salt and Vitamins.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਖਣਿਜ ਲੂਣਾਂ ਦੇ ਲਾਭ (Advantages of Mineral Salts)- ਮਨੁੱਖੀ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ, ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡਰੇਟਸ, ਚਰਬੀ ਅਤੇ ਪਾਣੀ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ 96% ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਬਾਕੀ 4% ਖਣਿਜ ਲੂਣ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਕੈਲਸ਼ੀਅਮ, ਫਾਸਫੋਰਸ, ਸੋਡੀਅਮ, ਕਲੋਰੀਨ, ਸਲਫਰ, ਆਇਰਨ, ਆਇਓਡੀਨ ਆਦਿ ਪ੍ਰਮੁੱਖ ਲੂਣ ਹਨ |
ਖਣਿਜ ਲੂਣਾਂ ਦੇ ਅੱਗੇ ਲਿਖੇ ਲਾਭ ਹਨ –
- ਇਹ ਦੰਦਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਦਾ ਵਾਧਾ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ਅਤੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਬਣਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹ ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਟਿਸ਼ੂਆਂ (Muscular Tissues) ਦਾ ਵਾਧਾ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ |
- ਇਹ ਖੂਨ ਦਾ ਰੰਗ ਲਾਲ ਬਣਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਕੈਲਸ਼ੀਅਮ ਖ਼ੂਨ ਦੇ ਜਮਾਅ ਵਿਚ ਯੋਗਦਾਨ ਦਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਦਾ ਸਾਰਾ ਕੰਮ ਠੀਕ ਢੰਗ ਨਾਲ ਚਲਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਹਨ ।
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨਾਂ ਦੇ ਲਾਭ (Advantages of vitamins)-ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਭੋਜਨ ਦੇ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਨ ਤੱਤ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਸੰਖਿਆ ਵਿਚ ਛੇ ਹਨ-ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਏ, ਬੀ, ਸੀ, ਡੀ, ਈ ਅਤੇ ਕੇ । ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਮਵਾਰ ਲਾਭ ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਹਨ –
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਏ’ ਦੇ ਲਾਭ (Advantages of Vitamin A) –
- ਇਹ ਅੱਖਾਂ ਦੀ ਰੋਸ਼ਨੀ ਤੇਜ਼ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਹ ਅੱਖਾਂ, ਜਿਗਰ ਅਤੇ ਅੰਤੜੀਆਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਝਿੱਲੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਬਣਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਛੂਤ ਦੇ ਰੋਗ ਤੋਂ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਵਧਾਉਣ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਕਰਨ ਵਿਚ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਪ੍ਰਦਾਨ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਹ ਭੁੱਖ ਵਧਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਪਾਚਨ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਨੂੰ ਠੀਕ ਰੱਖਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘‘ਬੀ’ ਦੇ ਲਾਭ (Advantages of Vitamin B)-
- ਇਹ ਦਿਮਾਗ਼ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਪ੍ਰਦਾਨ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਹ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਬਣਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਸ ਨਾਲ ਪਾਚਨ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਠੀਕ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਭੁੱਖ ਲੱਗਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਹ ਚਮੜੀ ਨੂੰ ਠੀਕ ਰੱਖਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਸੀ’ ਦੇ ਲਾਭ (Advantages of Vitamin C)-
- ਸਰੀਰ ਦੀ ਛੂਤ ਦੇ ਰੋਗ ਤੋਂ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਦੰਦਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਮਸੂੜਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਬਣਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਜ਼ੁਕਾਮ ਨੂੰ ਰੋਕਦਾ ਹੈ |
- ਜ਼ਖ਼ਮਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਭਰਨ ਅਤੇ ਟੁੱਟੀਆਂ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਠੀਕ ਕਰਨ ਵਿਚ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਡੀ’ ਦੇ ਲਾਭ (Advantages of Vitamin D)-ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਈਂ’ ਦੇ ਲਾਭ (Advantages of Vitamin E)-ਇਹ ਜਨਣ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਨੂੰ ਵਧਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ ਕੇ` ` ਦੇ ਲਾਭ (Advantages of Vitamin K)-ਇਹ ਖੂਨ ਨੂੰ ਜੰਮਣ ਦੀ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਵਿਚ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਪਹੁੰਚਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
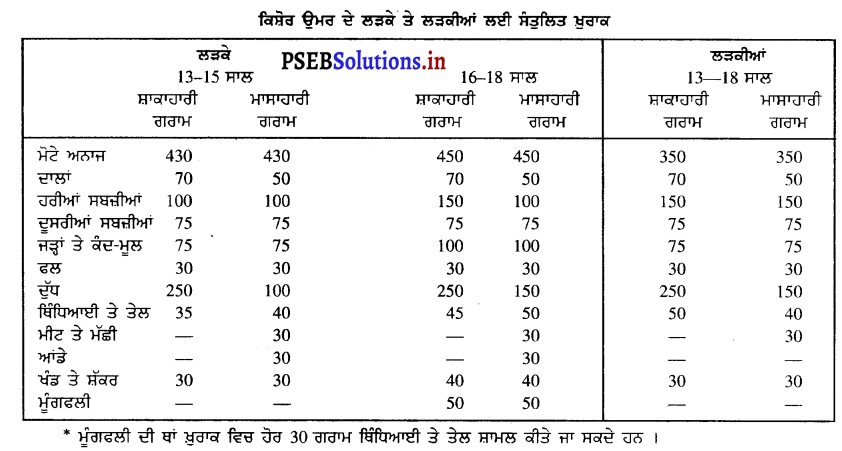
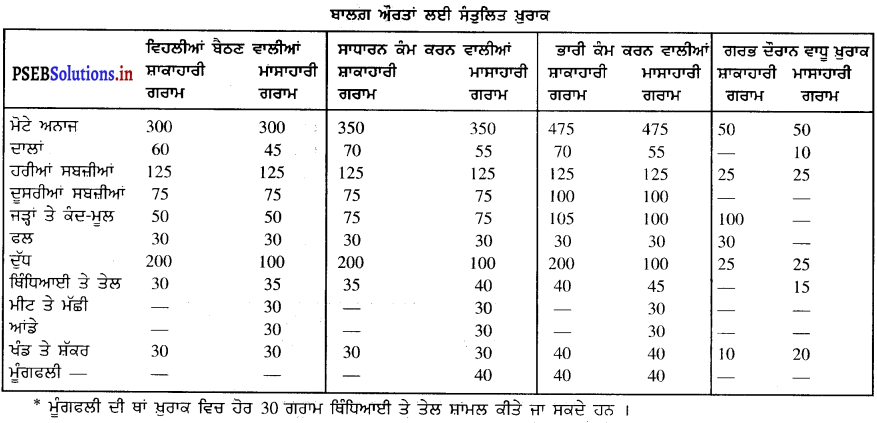
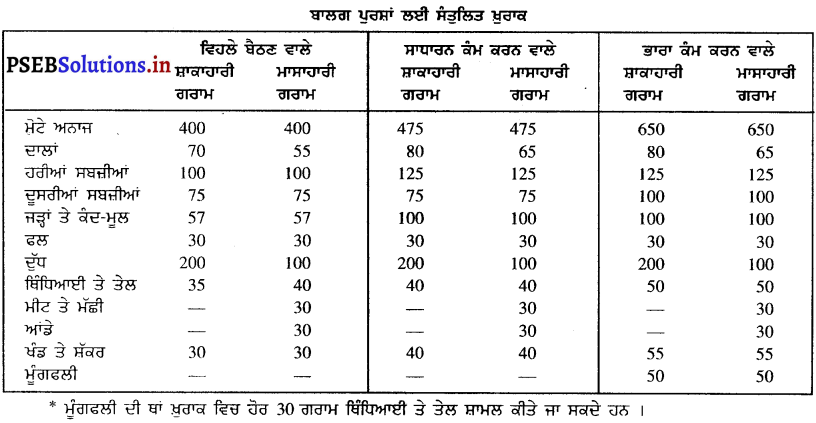
ਇਕ ਆਮ ਖਿਡਾਰੀ ਲਈ ਉੱਚਿਤ ਖ਼ੁਰਾਕ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਦੱਸੋ । [ਅਭਿਆਸ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ-5]. (Describe the balance diet of an ordinary sports person.)
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਇਕ ਆਮ ਸਾਧਾਰਨ ਖਿਡਾਰੀ ਲਈ ਉੱਚਿਤ ਖ਼ੁਰਾਕ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਹੇਠਾਂ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ –


![]()
![]()