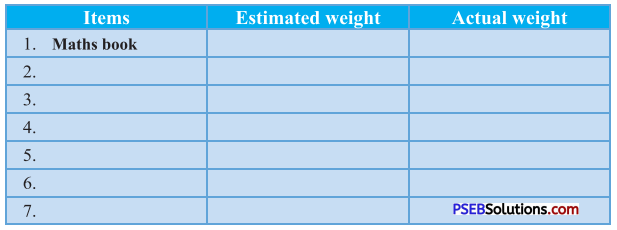
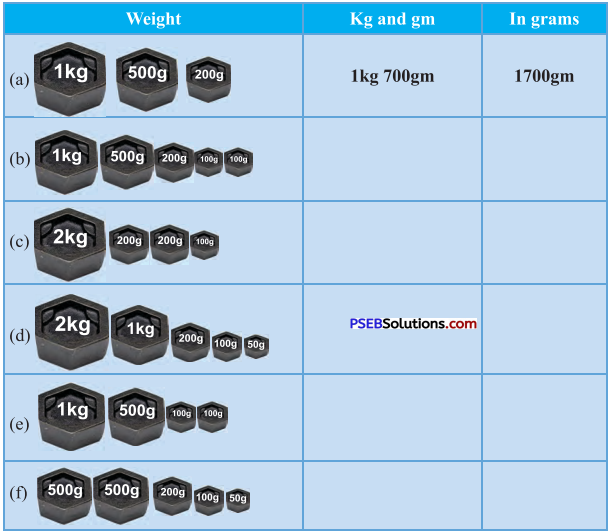
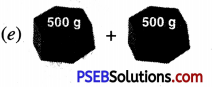
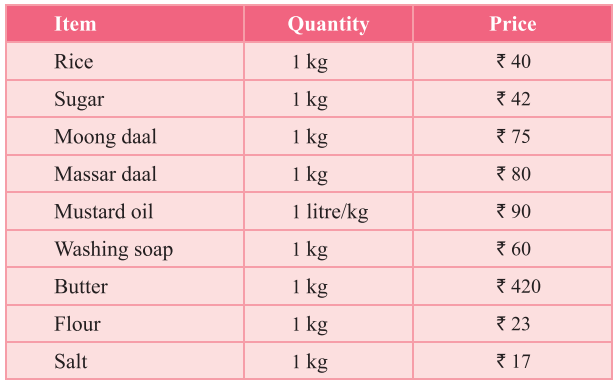
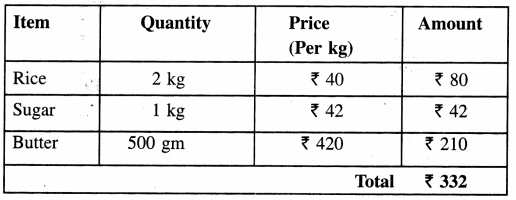
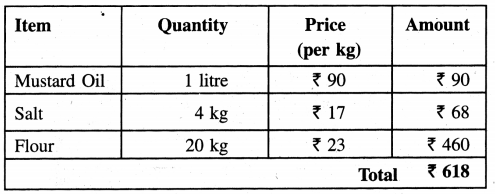
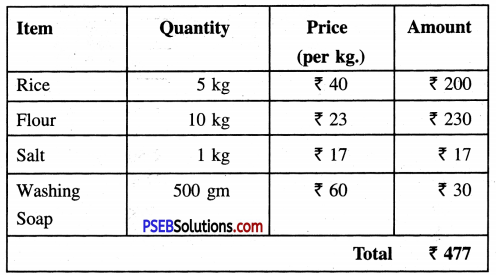
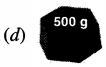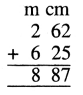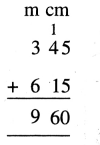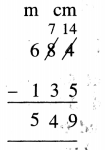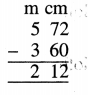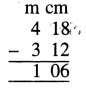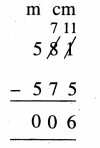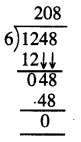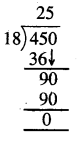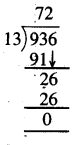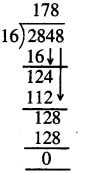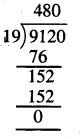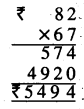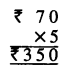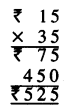Punjab State Board PSEB 4th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 5 Measurement Ex 5.9 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 4 Maths Chapter 5 Measurement Ex 5.9
1. Add the following :
Question 1.
8 litre 675 ml + 1 litre 210 ml
Solution:

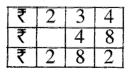
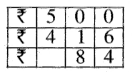
Question 2.
3 litre 225 ml + 2 litre 205 ml
Solution:
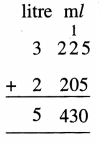
![]()
Question 3.
2 litre 605 ml + 7 litre 327 ml
Solution:
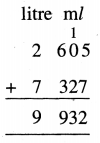
Question 4.
4 litre 175 ml + 2 litre 290 ml
Solution:
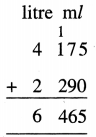
Question 5.
9 litre 220 ml + 2 litre 735 ml
Solution:

Question 6.
5 litre 125 ml + 8 litre 425 ml
Solution:
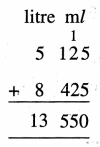
2. Subtract :
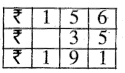
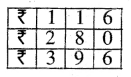
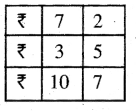
Question 1.
5 litre 470 ml – 3 litre 315 ml
Solution:
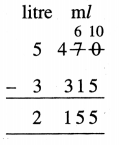
![]()
Question 2.
6 litre 705 ml – 5 litre 550 ml
Solution:
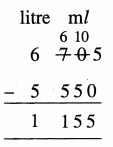
Question 3.
4 litre 970 ml – 1 litre 237 ml
Solution:

Question 4.
6 litre 500 ml – 2 litre 370 ml
Solution:
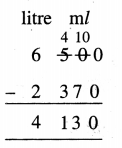
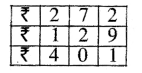
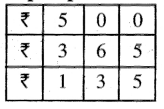
Question 5.
7 litre 075 ml – 2 litre 025 ml
Solution:
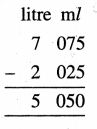
![]()
Question 6.
9 litre 700 ml – 7 litre 425 ml
Solution:
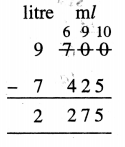
Question 3.
A confectioner required 75 litre of milk for making condensed milk (khoya), 40 litre of milk for cheese and 8 litre of milk for tea. How many litres of milk does he require ?
Solution:
Milk required by the confectioner for making condensed milk = 75 litre
Milk required by the confectioner for making cheese = 40 litre
Milk required by the confectioner for making tea = 8 litre
Total quantity of milk required by him = 123 litre

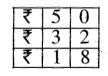
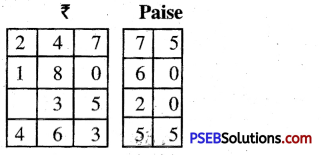
Question 4.
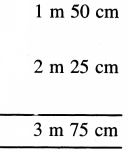
Sunita’s mom bought 5 litre 500 ml milk. She used 2 litre milk for Rice pudding (kheer). How much milk was left ?
Solution:
Quantity of milk bought by Sunita’s mom = 5 l 500 ml
Quantity of milk used for rice pudding (Kheer) = 2 l 1000 ml
Quantity of milk left = 3 l 500 ml

![]()
Question 5.
The capacity of a water tank is 750 litre. There is 475 litre water in it. How much more water is required to fill the tank?
Solution:
The capacity of water tank = 750 litre
Quantity of water already in it = 475 litre
Quantity of more water required = 275 litre