Punjab State Board PSEB 6th Class Science Book Solutions Chapter 9 The Living Organisms and Their Surroundings Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 9 The Living Organisms and Their Surroundings
PSEB 6th Class Science Guide The Living Organisms and Their Surroundings Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Fill in the Blanks :
(a) The respiratory organs of fish are ………………
Answer:
Gills
(b) Environment consist of ……………. and ……………… component.
Answer:
Biotic and Abiotic
(c) Sunlight is ………………. component of a habitat.
Answer:
Abiotic
![]()
(d) Animals that live on land are called …………………
Answer:
Terrestrial animals
(e) All ……………….. beings show growth and reproduction.
Answer:
Living
2. Write True or False:
(a) Cactus carry out photosynthesis using their stems.
Answer:
True
(b) A camel’s hump stores food and water.
Answer:
False
(c) All green plants are consumers.
Answer:
False
(d) Biotic components consist of water, air and soil.
Answer:
False
3. Match the Column A with Column B:
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Main source of energy on earth | (a) Plants or animals |
| 2. Arboreal | (b) Waxy coating on stem |
| 3. Cactus | (c) Monkey |
| 4. Biotic components | (d) The sun. |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Main source of energy on earth | (d) The sun |
| 2. Arboreal | (c) Monkey |
| 3. Cactus | (b) Waxy coating on stem |
| 4. Biotic components | (a) Plants or animals. |
4. Choose the Correct Answer:
Question (i)
Abiotic components include:
(a) Air, water, plants
(b) Air, water, soil
(c) Plants and animals
(d) Soil, plants, water.
Answer:
(c) Plants and animals
Question (ii)
Cactus is a ……………..
(a) Xerophyte
(b) Decomposer
(c) Hydrophyte
(d) Herb.
Answer:
(a) Xerophyte
![]()
Question (iii)
…………….. have a streamlined body.
(a) Earthworms
(b) Tigers
(c) Fishes
(d) Polar bears.
Answer:
(b) Tigers
Question (iv)
Organisms living in water are called ……………….. animals.
(a) Aquatic
(b) Terrestrial
(c) Xerophytes
(d) Aerial.
Answer:
(a) Aquatic
5. Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Question (i)
Define habitat.
Answer:
The place where living beings live is called Habitat.
Question (ii)
Define adaptation.
Answer:
The ability of living things to adjust themselves to their surroundings is called adaptation.
Question (iii)
Give two examples -each of terrestrial and aquatic animals.
Answer:
Terrestrial animals : Monkey, Human beings
Question (iv)
What are the producers ?
Answer:
Organisms that can manufacture their own food are called producers.
Question (v)
What are biotic components ?
Answer:
Living things like plants, animals, human beings and micro-organisms in a habitat are biotic components.
![]()
6. Short Answer Type Questions:
Question (i)
Define scavengers and decomposers.
Answer:
Scavengers. The animals that feed on dead animals and help us in keeping our environment clean, e.g. vultures, dogs etc.
Decomposers. Micoorganisms which feed on dead bodies of plants and animals and break them into simple substances are called Decomposers.
Question (ii)
What are two adaptations of fish ?
Answer:
Two adaptations of fish are :
- They have streamlined body to reduce resistance due to water.
- Fins in fish and flippers in whales help them in swimming.
Question (iii)
Which animal is called ‘ship of desert’ ? Write its two features.
Answer:
Camel is known as ‘ship of desert’.
Question (iv)
What is Hibernation ? Give one example.
Answer:
The long winter sleep of animals for survival is called Hibernation.
For example : Frogs, Lizards.
7. Long Answer Type Questions:
Question (i)
Write short notes on :
(1) Producers
(2) Consumers
(3) Decomposers.
Answer:
(1) Producers. Organisms that can manufacture their own food are called producers. For example, green plants make their own food by photosynthesis.
(2) Consumers. Organisms that cannot prepare their own food but consume food pepared by green plants are consumers. They also obtain their food by eating other living or dead animals.
Types of Consumers :
(a) Primary Consumers or Herbivores. Animals that get their food directly from plants are Herbivores, e.g. cow, dear, goat etc.
(b) Secondary Consumers or Carnivores. They eat primary consumers, e.g. snakes, frog, lizard.
(c) Tertiary Consumers. They eat secondary consumers, e.g. lion, tiger, leopards etc.
(3) Decomposers. The microorganisms which fed on the dead bodies of plants and animals and break them into simple substances are caled Decomposers, e.g. Bacteria and fungi.
Question (ii)
Briefly describe the various types of habitats.
Answer:
Types of Habitat. There are three main kinds of habitat :
(1) Terrestrial
(2) Aquatic and
(3) Aerial or Arboreal Habitat.
(1) Terrestrial habitat. The organisms that live on land are called Terrestrial organisms and their habitat is terrestrial habitat. Examples of terrestrial habitats are desert, grasslands, mountain.
(2) Aquatic (water) habitat. Organisms that live in lakes, ponds, rivers and oceans are aquatic organisms and their habitats are aquatic habitat. Examples of aquatic habitats are Oceans, seas, certain lakes etc.
(3) Aerial or Arboreal habitat. Organisms that live in air are called aerial or arboreal animals and their habitats are called aerial or arboreal habitats. Most birds and winged animals are arboreal in habit. Organisms are adapted for aerial existence as no organism is bom in air.
![]()
Question (iii)
Distinguish between living and non-living things.
Answer:
| Living things | Non-living things |
| (1) Living things grow. | (1) They do not grow. |
| (2) They show movement. | (2) They never move. |
| (3) They can reproduce. | (3) They cannot reproduce. |
| (4) Living things can respire. | (4) They do not respire. |
| (5) Living beings need food. | (5) They don’t feed. |
PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Science The Living Organisms and Their Surroundings Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
Pick out living among following :
(a) Plough
(b) Mushroom
(c) Water
(d) Wool.
Answer:
(b) Mushroom
Question 2.
The process by which waste materials of a body are thrown out, is:
(a) Digestion
(b) Excretion
(c) Reproduction
(d) None.
Answer:
(b) Excretion
Question 3.
Gills are breathing organs of :
(a) Fishes
(b) Frog
(c) Flies
(d) None.
Answer:
(a) Fishes
Question 4.
Pups of a dog grows into adult. This characteristic of living organisms is
(a) Reproduction
(b) Growth
(c) Respiration
(d) None
Answer:
(b) Growth
Question 5.
Basic unit of life is:
(a) Tissue
(b) Organ
(c) Cell
(d) None
Answer:
(c) Cell
Question 6.
Average life span of Bacteria is :
(a) Two days
(b) 20 minutes
(c) 10 seconds
(d) 20 seconds
Answer:
(b) 20 minutes
Question 7.
Which of the following is a Decomposer ?
(a) Lion
(b) Deer
(c) Monkey
(d) Bacterium.
Answer:
(d) Bacterium.
![]()
Question 8.
Plants live on desert area are:
(a) Hydrophytes
(b) Xerophytes
(c) Aquatic
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Xerophytes
Question 9.
Which of the following has webbed feet for swimming ?
(a) Fishes
(b) Whales
(c) Jelly fish
(d) Duck.
Answer:
(d) Duck.
Question 10.
Forelimbs are modified in :
(a) Animals
(b) Plants
(c) Birds
(d) None.
Answer:
(c) Birds
Fill in the Blanks :
(a) In every habitat, there are many ……………… of various kinds.
Answer:
organisms
(b) Bones are …………… in aerial organisms.
Answer:
hollow
(c) Winter sleep by animals are called ……………….
Answer:
Hibernation
(d) The plants live in water are ………………..
Answer:
Hydrophytes
(e) In cactus plants, leaves are reduced to ……………….
Answer:
spines
![]()
(f) Lion and …………… are animals of ………………..
Answer:
deer, grasslands
(g) Steamlined body is present in …………………
Answer:
fishes
(h) Frogs have ……………….. feet to swim in water.
Answer:
webbed
(i) The ability of animals to adapt themselves according to the environment is called ………………
Answer:
Adaptation
(j) …………….. feed on dead animals.
Answer:
Scavangers
True/False:
(a) There is lot of water available in deserts.
Answer:
False
(b) All animals cannot adapt themselves to their surroundings.
Answer:
False
![]()
(c) Sunlight and heat form biotic components of a habitat.
Answer:
False
(d) Desert plants have deep roots for absorbing water.
Answer:
True
(e) Snow leopard has no fur to cover its body.
Answer:
False
(f) All living organisms excrete.
Answer:
True
(g) Aquatic plants are found on the land.
Answer:
False
(h) Frogs have strong back legs for jumping.
Answer:
True
(i) Car, scooter, bus etc. are moving but are non-living.
Answer:
True
(j) All living things have same characteristics.
Answer:
True
![]()
Match the following:
| Column A | Column B |
| (1) Hydrilla | Webbed feet |
| (2) Cactus | Streamlined body |
| (3) Ducks | Modified leaves into spines |
| (4) Whales | Hydrophytic plant |
Answer:
(1) Hydrilla – Hydrophytic plant
(2) Cactus – Modified leaves into spines
(3) Ducks – Webbed feet
(4) Whales – Streamlined body.
(b)
| Column A | Column B |
| (1) Camel | Cold habitat |
| (2) Lion | Aerial Habitat |
| (3) Bat | Desert animal |
| (4) Penguine | Aquatic animal |
| (5) Fish | Terrestrial animal |
Answer:
(1) Camel – Desert animal
(2) Lion – Terrestrial animal
(3) Bat – Aerial Habitat
(4) Penguine – Cold habitat
(5) Fish – Aquatic animal.
(c)
| Column A | Column B |
| (1) Vultures | Consumers/carnivores |
| (2) Fungi | Producers |
| (3) Green plants | Decomposers |
| (4) Lion | Scavengers |
Answer:
(1) Vultures – Scavengers
(2) Fungi – Decomposers
(3) Green plants – Producers
(4) Lion – Consumers/camivores.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name the trees found on mountains.
Answer:
Oaks, pines, deodars.
Question 2.
Give example of unicellular organisms.
Answer:
Amoeba.
Question 3.
Why do living beings need food ?
Answer:
They need food to cany out their daily activities.
Question 4.
Define stimuls.
Answer:
Living things respond to immediate and long term changes in their environment called stimulus.
Question 5.
What do you mean by life span ?
Answer:
The duration if life for which living organisms live.
![]()
Question 6.
What is life span of a housefly ?
Answer:
1 – 4 years.
Question 7.
Can plants reproduce ?
Answer:
Yes, they reproduce with the help of seeds.
Question 8.
Define respiration.
Answer:
Process of taking oxygen in, combining with food and throwing out carbon dioxide and water vapour.
Question 9.
How do plants take carbon dioxide ?
Answer:
Through stomata.
Question 10.
In what forms our body excrete ?
Answer:
Our body exretes in the form of urine, faeces, sweat and exhaled air.
Question 11.
Why do organisms move ?
Answer:
They move to protect themselves from their enemies and natural calamities.
Question 12.
Where cactus plants grow ?
Answer:
Cactus grows in hot and dry areas of deserts.
Question 13.
Name some tertiary consumers.
Answer:
Lion, tiger, leopards.
![]()
Question 14.
How sunlight is helpful ?
Answer:
Plants make their food with the help of sunlight.
Question 15.
How water is essential ?
Answer:
Water is essential for life as the bodies of plants and animals contain large amounts of water.
Question 16.
How cactus is adapted in xerophytic conditions ?
Answer:
Cactus have very long roots, small leaves or spines and wax coated stem to conserve water.
Question 17.
Who is “ship of desert” ?
Answer:
Camel.
Question 18.
What is the function of Humb in camels ?
Answer:
It stores fat as reserve food.
Question 19.
What is the role of air bladder in Ducks ?
Answer:
They help ducks to float on water.
Question 20.
Name the animals who Hibernate.
Answer:
Frogs, Lizards, Bears.
![]()
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is function of scales on the body of fish ?
Answer:
Functions of scales. The scales present on the body of fish are slippery in nature. They protect the fish and help for easy movement in water.
Question 2.
Why do camels have long legs ?
Answer:
Camels have long legs to keep its body away from the intense heat during hot days.
Question 3.
How are animals adapted to live in mountain regions ?
Answer:
Adaptations of animals for living in mountain regions.
- Thick skin or fur to protect from cold e.g. yak.
- Strong hooves (goat) for running up rocky slopes.
Question 4.
Name the sea animals which do not have gills. How do they respire ?
Answer:
Dolphins and Whales do not have gills. They respire through nostrils or blowholes, which are present on the upper parts of their heads. They swim near to the surface and breathe in fresh air. They can stay inside the water for a long time without breathing.
Question 5.
Define respiration, growth, and excretion.
Answer:
Respiration. The process of taking in oxygen and giving out carbondioxide is called respiration.
Growth. The process of changing from a child to a-grown up is called growth. A seed grows into a plant.
Excretion. The process of throwing out waste materials from the body is known as excretion.
Question 6.
Show with an example that living things respond to stimuli.
Answer:
Living things respond to stimuli. When we move from a dark room into bright sunlight, our eyes shut themselves automatically for a moment to adjust themselves to the changed conditions. Similarly, when light is switched on in a dark room, cockroaches run to move in dark comers. Some plants also respond to light and touch (e.g. Touch-me not).
Question 7.
What are adaptations of camel ?
Answer:
- Camel has no sweat glands in order to reduce water loss.
- Hump is present to reserve food in the form of fat.
- They have thick skin to bear heat of desert.
- Their toes are bread and pedded that are suitable for walking on hot and loose sand.
![]()
Question 8.
Write the adaptations of hydrophyts.
Answer:
- They have poorly developed roots.
- Their stems are flexible
- Leaves are wax coated.
Question 9.
What do you mean by terrestrial and aquatic habitat ?
Answer:
Terrestrial habitat. This includes habitat of all the organisms which live and propagate on land. Example; Cow, camel, horse, dog are terrestrial organisms and forest is their terrestrial habitat.
Aquatic habitat. The habitats of plants and animals that live in water are called aquatic habitat. Examples : fishes, crocodile, snake etc. are aquatic organisms and water is their aquatic habitat.
Question 10.
What are biotic and abiotic components ?
Answer:
All living organisms like plants, animals and human beings include biotic components. All non-living parts such as light, water, soil and air are abiotic components.
Question 11.
What are the characteristics of xerophytes ?
Answer:
Characteristics of Xerophytes.
- These plants have extensive long root system.
- The stem of plants become thick and store water. Example, Opuntia.
- Leaves are modified into spines as in cactus.
- Leaves are coated with cuticle to check the loss of water.
Question 12.
Write physical conditions of Terrestrial habitat.
Answer:
Physical conditions of terrestrial habitat,
- Oxygen supply is uniform, sufficient and easily available.
- Temperature varies from place to place and season to season.
- Light is available in sufficient quantity and for sufficient duration.
- In certain region organisms have to adapt to avoid dehydration.
Question 13.
Write physical conditions of aquatic habitat.
Answer:
Physical conditions of aquatic habitat,
- Except in deep ocean, uniform supply of light, temperature, oxygen is available.
- Light and temperature vary in deep oceans at different depths.
- Pressure also varies in deep oceans at different depths.
Question 14.
Write the main characteristics of living and nor living things.
Answer:
We have many things around us which are two types i.e. living and non-living.
Living things. In living things life processes take place, so they need food. They grow upto a certain age. They respire and respond to external stimuli. They have ability to produce their young ones. They die after a certain age.
Non-living things. In non-living things, no life processes take place, so they do not need food. They do not grow and do not respond to external stimuli. They do not excrete. There is no death in the case of non-living things.
![]()
Question 15.
What are hydrophytes ?
Answer:
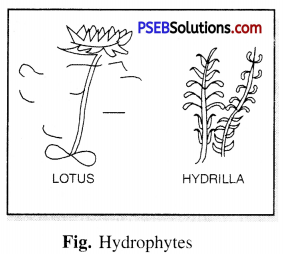
Hydrophytes. These are the plants which grow in watery places or the places which remain wet throughout the year. Examples : Hydrilla, Pista,
Lotus, Vallsneria.
Question 16.
What are the differences between Aquatic and Terrestrial habitat ?
Answer:
Difference between Aquatic and Terrestrial habitat:
| Aquatic habitat | Terrestrial habitat |
| (1) These include habitat of organisms that live and propagate in water. | (1) These include habitat of organisms that live and propagate on land. |
| (2) Water absorbs and loses heat gradually therefore, sudden fluctuation in temperature is not found in aquatic habitat. | (2) The terrestrial habitat have rapid fluctuation in the climate, temperature, moisture, i.e. it is not uniform everywhere. |
Question 17.
What are unicellular of multicellular organisms ?
Answer:
Organisms made up of only one cell are Unicellular organisms, e.g. : Amoeba, Paramoecium. Organisms made up of large number of cells are called multicellular organisms, e.g. Humans, cat, dog etc.
Question 18.
What do you mean by excretion ? Write different modes of excretion in animals.
Answer:
Excretion.
The process of getting rid of waste or removal of waste materials from body is called excretion.
Mode of Excretion.
Larger animals even the human beings remove these wastes in the form of fluids like urine and faecal matter. The removal of waste is necessary since these may be poisonous and harmful to the organism.
Smaller organisms like bacteria, amoeba (one celled animals) remove their waste through body surfaces.
Question 19.
Differentiate living and non-livings on the basis of Growth and Respiration.
Answer:
Living organisms can grow as well as respire but non-living cannot.
Question 20.
What are the saline water habitats and fresh water habitats include ?
Answer:
Fresh water habitat. Rivers, ponds, lakes.
Saline water habitat. Oceans, seas, certain lakes.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by the term ‘Adaptation’ ?
Answer:
Adaptation.
The development of characteristics which help an organism to sun’ive in a particular environment is known as adaptation.
Adaptation commonly involves a combination of characteristics, shape, size, structure, colour and mode of life. For example, a fish shows many adaptations for aquatic life. It has a streamlined body provided with fins which enables it to swim in water, presence of gills for breathing.
![]()
Question 2.
How biotic and abiotic components of a habitat are interacted ? Draw its chart also.
Answer:
Interaction of biotic and abiotic environment.
All biotic components such as plants, animals and micro-organisms are influenced by abiotic components such as water, light, air, oxygen and temperature in different ways. Green plants prepare their own food and all the animals depend upon plants for the food. Some animals feed on other animals. Plants also provide shelter to the animals thus all the organisms are related through food chain.
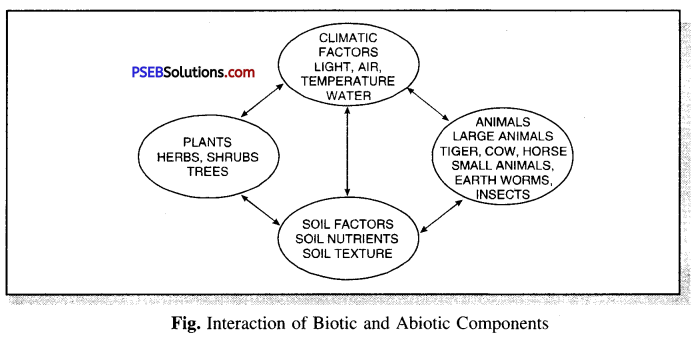
After death and decay of the plants and animals, they are decomposed into simple minerals into soil. These minerals are again used by plants through the roots. Thus they are interrelated and share common surroundings.
Thus we see that all the plants and animals and the abiotic components involving air. light, water are related and interdependent on each other in the habitat.
Question 3.
In what ways living things differ from non-living things ?
Answer:
Differences between living and non-living things :
| Living things | Non-living things |
| (1) Food is necessary for the life processes in living things. | (1) In non-living things, no life processes take place, so they do not need food. |
| (2) Respiration is necessary for living things. | (2) There is no respiration in non-living things. |
| (3) Living things grow upto a certain age. | (3) These do not grow on their own. |
| (4) Living things respond to external stimuli. | (4) Non-living things do not respond to external stimuli. |
| (5) Living things excrete waste product from their body. | (5) Non-living things do not excrete. |
| (6) Living things produce their young ones. | (6) There is no procreation in non-living things. |
| (7) The body structure of living things is cellular. | (7) Non-living things do not have cellular body. |
Question 4.
How is camel adapted for xeric adaptation / deserts ?
Answer:

The camel is superbly adapted for xeric conditions that is why it is rightly called the ‘ship of the desert’. The following adaptations are found in camel :
- It uses its entire foot while walking and its hooves are covered by a large sole which helps it to move on hot, slippery sand.
- It has a hump on the back which is filled with fat. This stores food that is utilized during the time when the camel does not get anything to eat.
- It can drink as much as 50 litres of water in one gulp when water is available to it.
- It excretes very little water from its body.
- It passes nearly dry dung.
- It does not perspire.
Question 5.
What are the abiotic components? Explain.
Answer:
The non-living components like rocks, roil, air, water, sunlight, temperature are abiotic components
- Air. Both plants and animals require air to live. Animals take oxygen and give out carbon dioxide while plants give out oxygen and take carbon dioxide. Photosynthesis also takes place in the air.
- Soil. It contains water, air, and living organisms. It provides nutrients to plants.
- Sunlight. Plants perform photosynthesis in the presence of sunlight. Humans require sunlight for vitamin D. So, All organisms depend on sunlight directly and indirectly.
- Water. Water is essential for life as it is present in large amounts in plants and animals.
- Temperature. All living organisms can receive only within a specific range of temperature