Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class Science Book Solutions Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
PSEB 8th Class Science Guide Crop Production and Management Textbook Questions and Answers
Exercises
Question 1.
Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks:
float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation
(a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called ……………..
Answer:
crop
(b) The first step before growing crops is …………………. of the soil.
Answer:
preparation
(c) Damaged seeds would ………………… on top of water.
Answer:
float
(d) For growing of crop, sufficient sunlight, ……………… and ……………… from the soil are essential.
Answer:
water, nutrients
Question 2.
Match items in colun,.n ‘A’ with those in column ‘B’:
| (A) | (B) |
| (i) Kharif crops | (a) Food for cattle |
| (ii) Rabi crops | (b) Urea and super phosphate |
| (iii) Chemical fertilizers | (c) Animal excreta, cow dung, urine and plant waste |
| (iv) Organic manure | (d) Wheat, gram and pea |
| (e) Paddy and maize |
Answer:
| (A) | (B) |
| (i) Kharif crops | (e) Paddy and maize |
| (ii) Rabi crops | (d) Wheat, gram and pea |
| (iii) Chemical fertilizers | (b) Urea and super phosphate |
| (iv) Organic manure | (c) Animal excreta, cow dung, urine and plant waste |
![]()
Question 3.
Give two examples of each.
(a) Kharif Crop
(b) Rabi Crop
Answer:
(a) Kharif Crop – (i) Paddy (ii) Maize.
(6) Rabi Crop – (i) Wheat (ii) Gram.
Question 4.
Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following:
(a) Preparation of soil
(b) Sowing
(c) Weeding
(d) Threshing.
Answer:
(a) Preparation of Soil.
Soil is loosened and overturned to make it better ventilated and suitable for the growth of tiny organisms living in it. The entire process is called tillage and ploughing.
Soil if ploughed in dry season gets into big mud pieces or crumbs. These are broken down by plying a soil plank.
The ploughed soil is liable to be removed by wind and water. Wooden leveller is used to press the soil.
(b) Sowing.
The process of putting seeds in the soil is called sowing. It is the most important part of crop production. Before sowing, good quality of seeds are selected. The seeds are sown in the fields by hand (broadcasting) and by seed drill.
(c) Weeding.
It is a process of removal of unwanted plants i.e. weeds from the fields. It is necessary to remove the weeds since they compete with the main crop for water, nutrients, sunlight etc. The weeds may be removed manually by uprooting or cutting. The best time to remove them is before they produce flowers and seeds. It is done with a khurpi and a tractor driven harrow. Some chemicals called weedicides are used to control the weeds. They are sprayed in the fields for killing the weeds e.g. linazine, dalapon, etc.
(d) Threshing.
The separation of grains from the chaff in the harvested plants is called threshing. Animals are used on a large scale for threshing. In large farms, a machine called ‘thresher’ or a motorized machine called ‘combine’ are used for both harvesting and threshing.
Question 5.
Explain how fertilizers are different from manure.
Answer:
Differences between Manure and Fertilizers
| Fertilizers | Manure |
| 1. These are mixtures of chemical compounds rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and manufactured in factories. | 1. These are organic substances prepared from the decomposition of plant and animal wastes. |
| 2. Chemical fertilizers are nutrients specific i.e. nitrogenous, phosphatic, etc. | 2. They contain a mixture of various nutrients recycled from biomass wastes. |
| 3. They are in a concentrated form. | 3. They are not in a concentrated form. |
| 4. They are easy to store or transport. | 4. They are not easy to store or transport. |
| 5. They are harmful if used in excess. | 5. They are never harmful to the soil. |
Question 6.
What is irrigation ? Describe two methods of irrigation which conserve water.
Answer:
Irrigation. Giving water to the fields at different intervals is called irrigation. The time and frequency of irrigation varies from crop to crop, soil to soil and season to season.
The latest irrigation methods help us to use water economically. The main methods used which conserve water are as follows:
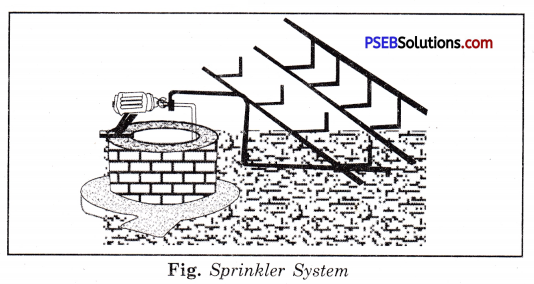
1. Sprinkler System.
This system is more useful on the uneven lands where water is available in smaller quantity. The perpendicular pipes, having rotating nozzles on the top, are joined to the main pipe line at regular intervals. The water is allowed to flow through it with the help of a pump. The water escapes from the rotating nozzles. It is sprinkled on the crop as if it is raining. Sprinkler method is very useful for the sandy soil.
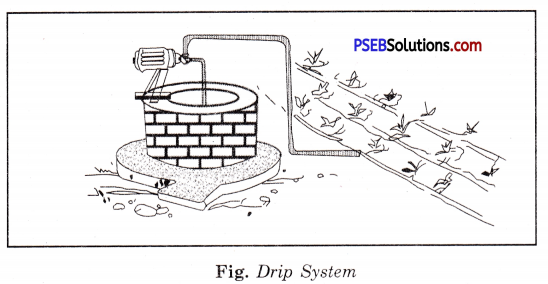
2. Drip System.
In this system, the water falls drop by drop just at the position of the roots. So it is called drip system.
Fig. Sprinkler System.
It is the best technique of watering fruit plants, gardens and trees. Drip system consists of a main pipe to which lateral pipes are joined. The specially prepared nozzles are attached to these lateral pipes. It provides water to plants drop by drop. In this way, water is not wasted. So, it is a boon in regions where availability of water is poor.
Question 7.
If wheat is sown in the Kharif season, what would happen ? Discuss.
Answer:
Wheat is a Rabi crop i.e. it is grown in winter season where there is low temperature and needs less water. So, if wheat is sown in Kharif season during rainy season, it gets more water which is harmful to the crop. The wheat crop droops down. It would not grow healthy.
![]()
Question 8.
Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Answer:
For the continuous plantation and better growth of crops, manure and fertilizers are added regularly in the field. Manure and fertilizers are the nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium etc. They can change the nature of the soil. The soil may become more alkaline or acidic with addition of the nutrients.
Question 9.
What are weeds ? How can we control them ?
Answer:
Weeds. Weeds are undesirable plants that may grow naturally along with the crop. The removal of weeds is called weeding.
Methods to Control Weeds. Following methods are used to control the weeds:
- Tilling. The process of loosening and turning of the soil is called tilling or ploughing. This is done by using plough. Tilling helps in uprooting and killing of weeds.
- Manual Removal. This method includes the physical removal of weeds by uprooting or cutting them close to the ground. This is done with the help of Khurpa or Harrow.
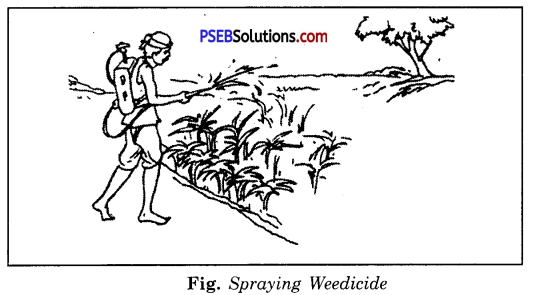
- Chemical Method. In this method weeds are controlled by using some chemicals, called weedicides like 2, 4-D. The weedicides are sprayed in the fields with a sprayer.
Question 10.
Arrange the following boxes in proper order to make a flow chart of sugarcane crop production.
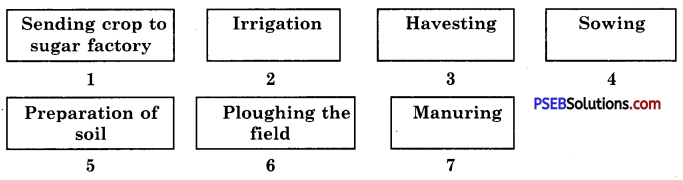
Answer:

Question 11.
Complete the following word puzzle with the help of clues given below.
Down
1. Providing water to the crops.
2. Keeping crop grains for a long time under proper conditions.
5. Certain plants of the same kind grown on a large scale.
Across
3. A machine used for cutting the matured crop.
4. A rabi crop that is also one of the pulses.
6. A process of separating the grain from chaff.
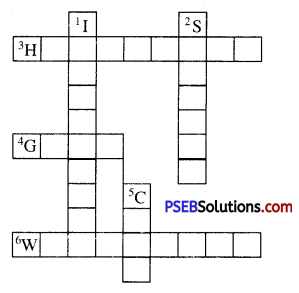
Answer:

PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Science Crop Production and Management Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The following implement is related to which agriculture practice.

(a) Irrigation
(b) Sowing
(c) Weeding
(d) Harvesting.
Answer:
(d) Harvesting.
Question 2.
The figure given below represents which conventional method of irrigation ?

(a) Pulley
(b) Chain Pump
(c) Dhekli
(d) Rahat.
Answer:
(c) Dhekli.
Question 3.
Mohan is sprinkling chemical solution to destroy weed plants growing along with main crops in his field. What is this chemical solution called ?
(a) Fertilizer
(b) Weedicides
(c) Yeast
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(b) Weedicides.
![]()
Question 4.
The mother of Naresh collects the waste material of living beings in an open space. According to her, after a few days, micro-organisms break the waste material of living beings and turn it into fertilizers. What is this fertilizer called ?
(a) Fertilizer
(b) Chemical fertilizer
(c) Manure
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(c) Manure.
Question 5.
Jasbeer saw some weeds (unwanted plants) growing in his field along with main crops. What is this process called in which these weeds are removed from the field ?
(a) Sowing
(b) Irrigating
(c) Weeding
(d) Cutting.
Answer:
(c) Weeding.
Question 6.
In which season Kharif crops are grown ?
(a) Rainy season
(b) Autumn season
(c) Winter season
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(a) Rainy season.
Question 7.
The process of loosening and overturning the soil is called:
(a) Ploughing
(b) Sowing
(c) Irrigation
(d) Weeding.
Answer:
(a) Ploughing.
Question 8.
The roots of bean plants have nodules and the microorganism which lives inside them is called:
(a) Virus
(b) fungi
(c) Rhizobium bacterium
(d) Algae
Answer:
(c) Rhizobium bacterium.
Question 9.
Which weedicides are used to remove weeds from the crops ?
(a) 2.4 D
(b) B.H.C.
(c) DDT
(d) All of the above.
Answer:
(a) 2.4 D.
Question 10.
What percentage of water is in plants ?
(a) 70%
(b) 80%
(c) 60%
(d) 90%
Answer:
(d) 90%.
Question 11.
Weeds are:
(a) Unwanted plants growing along with main crops
(b) Crop plants
(c) Bean plants
(d) Useful plants
Answer:
(a) Unwanted plants growing along with main plants.
![]()
Question 12.
Which of the following is not the source of irrigation ?
(a) Well
(b) Sea
(c) River
(d) All of the above.
Answer:
(b) Sea.
Question 13.
The modern method of irrigation is
(a) Dhekli
(b) Chain pump
(c) Rahat
(d) Sprinkle system.
Answer:
(d) Sprinkle system.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Define agriculture.
Answer:
Agriculture. The word agriculture consists of two Latin words – ager means field and culture means cultivate. So, agriculture is defined as to cultivate the fields.
Question 2.
What is staple Food ?
Answer:
Staple food. The food which forms the main part of our diet is called staple food e.g. rice and wheat. These are grown on a large scale in vast fields as they are consumed in large amounts.
Question 3.
What time does a crop take to mature ?
Answer:
It normally takes about 3-4 months for a good crop to mature.
Question 4.
What are weedicides ?
Answer:
Weedicides. Those chemicals which are sprayed over the field to check the growth of the weeds are known as weedicides.
Question 5.
What is animal husbandry ?
Answer:
Animal Husbandry. The study of all aspects such as food, shelter, health care of domesticated animals is called animal husbandry.
Question 6.
What is crop ?
Answer:
Crop. The plants of the same kind grown at a place is referred to as crop.
![]()
Question 7.
Name two main crops of our country.
Answer:
Main crops of country. Wheat and Paddy are two main crops of India.
Question 8.
Define Produce.
Answer:
Produce. The crops are grown on ground or in water and what we obtain from the crop is called produce.
Question 9.
What are Kharif crops ?
Answer:
Kharif Crops. The crops grown during June-October are called Kharif crops, for example, paddy, maize.
Question 10.
What are Rabi crops ?
Answer:
Rabi Crops. The crops grown during November-April are called Rabi crops. These are not based on monsoon.
Example. Wheat, legumes like clover.
Question 11.
Name three crops sown by sowing seeds.
Answer:
Wheat, maize and millet.
Question 12.
Define irrigation.
Answer:
Irrigation. The supply of water at different levels is called irrigation.
Question 13.
Name two legume crops.
Answer:
Clover (barseem) and Gram.
![]()
Question 14.
What is weeding ?
Answer:
Weeding. The removal of weeds is called weeding.
Question 15.
What is crop rotation ?
Answer:
Crop rotation. Sowing of different crops alternately in the field is called crop rotation.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why is soil turned and loosened before seeds are sown ?
Answer:
Soil is turned and loosened before seeds are sown because of following reasons:
- It allows the roots to penetrate freely and deeper.
- It allows the roots to breathe easily.
- The plant is secured more firmly.
- It aids the growth of worms and microbes present in the soil.
Question 2.
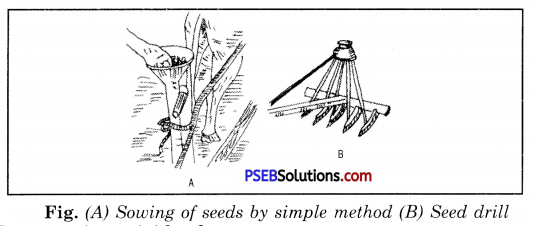
What are broadcasting and transplanting ?
Answer:
Broadcasting.
After the soil has been prepared, seeds of crop plants are sown in it. There are two methods of sowing them. Sowing by land or by using seed drill is called broadcasting.
Transplanting.
It is a process of taking out young plants or seedlings from nursery beds and transfer them to fields with required spacing, water and minerals for adequate growth.
Question 3.
What are insecticides ?
Answer:
Insecticides.
The special chemicals which selectively kill the pests or harmful insects as well as their eggs and larvae, but do not affect the plants are called insecticides or pesticides.
Question 4.
Why should the harvested grains be protected from moisture ?
Answer:
Moisture and humidity promotes the growth of fungi or moulds on grains. Some of these microorganisms are poisonous also. So, it is very important to store harvested grains dry.
Question 5.
How does a farmer rotate crops in the fields ?
Answer:
Crop rotation involves the change of crop every year as alternate sowing of crops so that pathogen is killed in absence of suitable host.
Repeated growing of the same plant however may deplete the soil severely of specific nutrients. To prevent this it is advisable to cultivate two different types of plants alternately. For example, maize and wheat are grown alternately with groundnut. The groundnut plant, with its nitrogen fixing, bacteria enriches the soil with some nutrients, which are beneficial for wheat. Rotating different crops in this manner thus replenishes the soil naturally.
![]()
Question 6.
How are pests controlled in a crop field ?
Answer:
Pests are living organisms which cause diseases or kill or destroy the crop plants. In order to control the pests, pesticides such as Malathion, Disyston, B.H.C. etc. are used. They are sprayed on the crops. They kill the microbes without causing harm to plants and human beings who consume them.

Question 7.
What are the harms of excess of water in the fields ?
Answer:
Harms of excess of water
- It can destroy crops.
- Continued water logging increases the amount of salt in the soil and can damage it permanently.
Excess water can be drained off by providing a suitable outlet.
Question 8.
Why is it important to wash off fruits, grains or vegetables before being consumed ?
Answer:
It is important to wash off fruits, grains or vegetables because these when brought from fields to the market often have a coating of pesticides. Otherwise they prove to be harmful.
Question 9.
What is field fallow ? Why is it important ?
Answer:
Field Fallow.
Some fields are allowed to rest and regenerate for at least a season to support a crop. This is called field fallow.
Importance.
The growth of humus picks up which in turn promotes the growth of soil micro-organisms during such undisturbed periods. It leads to a rich replenishment of nutrients.
Question 10.
How are the stored grains damaged ?
Answer:
Rats and other rodents damage the stored grains. The amount of grain eaten by rats and rodents is estimated to be over 25% of the total produce.
Stored grains are also damaged by insects and worms. Such infested grains if consumed by people, cause many diseases.
Question 11.
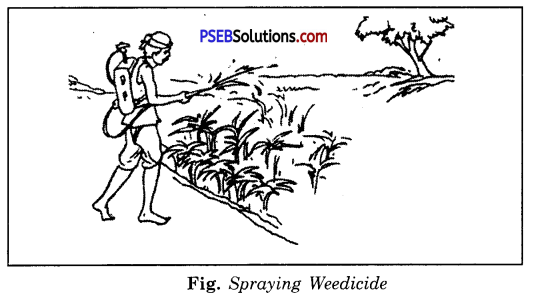
What are weeds ? How are they removed ?
Answer:
Weeds. Weeds are undesirable plants that may grow naturally along with the crop. The removal of weeds is called weeding.
Methods to Control Weeds. Following methods are used to control the weeds:
1. Tilling. The process of loosening and turning of the soil is called tilling or ploughing. This is done by using plough. Tilling helps in uprooting and killing of weeds.
2. Manual Removal. This method includes the physical removal of weeds by uprooting or cutting them close to the ground. This is done with the help of Khurpa or Harrow.
3. Chemical Method. In this method weeds are controlled by using some chemicals, called weedicides like 2, 4-D. The weedicides are sprayed in the fields with a sprayer.
Question 12.
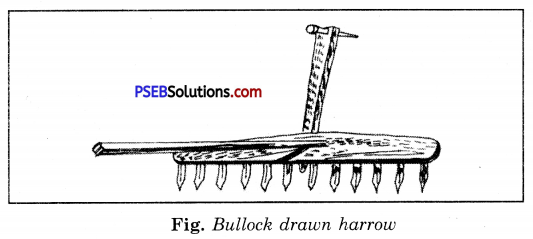
Give the structure of harrow. What is its main use ?
Answer:

Structure of Harrow. It has small pointed iron rods or wooden rods. A strong, broad plate of iron is fixed to one of its ends and works like a blade. It uproots the weeds when moved in a crop field just like a plough.
Uses. It is used to remove the weeds of the field.
![]()
Question 13.
Why is ploughing of soil necessary before sowing seeds or crop plants ?
Answer:
- Ploughing tills the soil deeply. It may involve partial or complete turning over of soil.
- Ploughing clears land of the preceding crop and leaves the soil loosened.
- Repeated ploughing eliminates all weeds.
- Harmful insects are destroyed by ploughing.
- Ploughing makes the soil porous.
- Ploughing makes the soil soft, clean and suitable for sowing.
Question 14.
Why are fields manured ?
Answer:
Manuring of Fields.
Plants get their nutrients from the soil. If crops are grown continuously, they use all the nutrients present in the soil. To make up this deficiency of soil, manures are added to the soil.
Question 15.
What do you mean by harvesting and threshing ?
Answer:
Harvesting.
The cutting of the crop when it matures is called harvesting. Most of the crops are harvested with help of a sickle or huge combines.
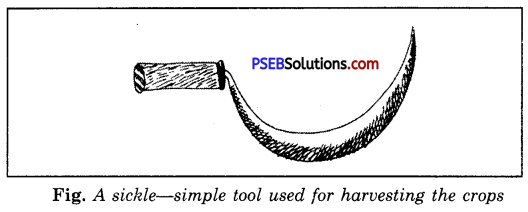
Threshing.
The separation of grains from the chaff is called threshing. Animals are used on a large scale for threshing.
Question 16.
What are the types of crops on the basis of seasons ? Give examples of each type.
Answer:
Crops are of two kinds on the basis of season:
- Kharif Crops. The crops which are grown during the monsoon season are called Kharif Crops.
Examples. Maize, Bajra and Cotton etc. - Rabi Crops. Those crops which are grown during the winter season are called Rabi Crops.
Examples. Wheat, Gram and Mustard etc. - Summer Crops. Those crops which are grown during summer seasons are called Summer Crops.
Examples. Moong, Water melon, Cucumber, gourd etc.
Question 17.
What is mixed cropping ? Give an example.
Answer:
Mixed Cropping.
The practice of cultivating two crops simultaneously is done to economise the time and energy. This is called mixed cropping.
Example. The crop of groundnut is grown in the fields along with cotton.
Question 18.
Why is it necessary to sow seeds at an appropriate depth ?
Answer:
It is necessary to sow seeds at an appropriate depth because if the seeds are sown too deep, they will not be able to germinate. On the other hand, if they are sown at a shallow depth, then they will be eaten away by birds or animals.
Question 19.
How is the crop produce stored ?
Answer:
The crop produce is stored in godowns by agencies like Food Corporation of India and State Warehousing Corporations. Grains are sun dried before storing to reduce moisture contents of grains. This prevents the attack of pests. Large scale storing of grains is done in granaries and silos to protect grains from pests like rats and insects.
![]()
Question 20.
Define Fertilizer.
Answer:
Fertilizers.
These are the chemical substances that are man-made and are rich in nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, i.e. they are rich in organic macronutrients which are needed by plants.
Question 21.
Why should we use organic manures ?
Answer:
We should use organic manure because it helps in replenishing the soil nutrients without causing any harm to the soil. This manure is considered much better than the fertilizers. Crops like vegetables and fruits grown by organic manure are considered safe as compared to the crops grown by using chemical fertilizers. Therefore, we should use organic manure in growing vegetables and fruits.
Question 22.
Some seeds are given to you to grow. What factors will you keep in mind ?
Answer:
We will keep the following factors in mind. These are:
- We would sow them at the correct depth.
- We would water them regularly and check the amount of water that we are putting.
- We would use manure at the proper time.
- We would ensure that no weeds grow with the plant.
- We would also spray pesticides.
- We would also ensure that the plant gets adequate sunlight.
Question 23.
Why should we discourage the use of chemical fertilizers ?
Answer:
Chemical fertilizers are harmful in the following ways thus the use of such fertilizers be discouraged:
- They damage the soil by reducing its natural recomposting ability.
- They change the chemical nature of soil.
- These chemicals are leached in the soil and are again absorbed by crop plants and enter food chain and damage the plants and animals.
Question 24.
How do we store grains ? What is cold storage ?
Answer:
Storage of Grains.
- Farmers make small boxes of metal or mud to store dried grains. These are called granaries.
- Dried grains are transferred to properly ventilated cemented halls. These cemented halls are called godowns.
- The storage of some fruits and vegetables at a low temperature is called cold storage.
Question 25.
What are the basic requirements for growing a crop in an area ?
Answer:
The basic requirements for growing a crop in an area are as follows:
- Proper type of soil
- Use of manures
- Irrigation
- Better varieties of seeds
- Agricultural tools
- Chemicals to prevent diseases of the plant crop.
Question 26.
Why all the crops do not grow in the same season ?
Answer:
All crops do not grow in the same season because every crop has its own specific requirements of soil and climatic conditions like light, temperature and air at the various stages of its growth and development.
Question 27.
Do all the crops have identical requirements of manures and fertilizers ?
Answer:
No, every crop has specific requirements of manures and fertilizers for growth and development of the plants. Farmyard manure is useful for paddy crops. The groundnut plants have nodulated roots. These nodulated roots contain nitrogen-fixing bacteria which convert the atmospheric nitrogen into the compounds of nitrites and nitrates. For the crop of wheat, farmyard manure and green manure of sunhemp plants are mixed in the soil.
![]()
Question 28.
Write any two points of difference between Insecticides and Weedicides.
Answer:
Differences between insecticides and weedicides
| Insecticides | Weedicides |
| 1. These are the chemicals used to kill the plant pests i.e. organisms attacking plants. | 1. These are the chemicals used to kill the weeds i.e. unwanted plants. |
| 2. These affect human life. | 2. These enter food chain. |
| 3. Examples : DDT, BHC etc. | 3. Examples : Bulachlor 2-4D. Linazine, Dalapon etc. |
Question 29.
What is transplanting ?
Answer:
Transplanting.
It is a process of taking out young plants or seedlings from nursery beds and transfer them to fields with required spacing, water and minerals for adequate growth.
Question 30.
Discuss the various tranditional ways of irrigation diagramatically.
Answer:
The various traditional ways are :
(a) Moat (Pulley system) (b) Chain pump (c) “Dhekli” (Lever system) (d) “Rahat” [Fig. (a) to (d)]. ‘
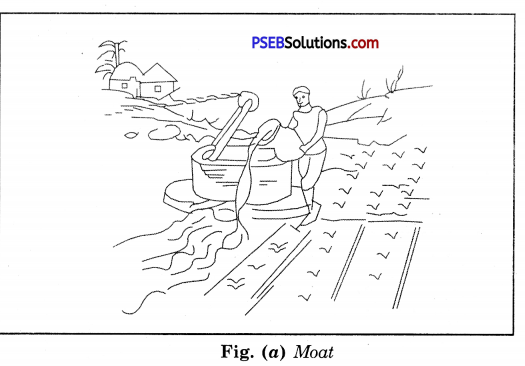
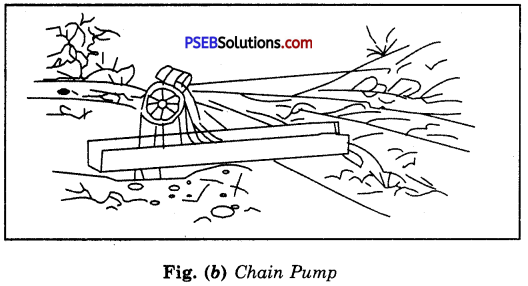
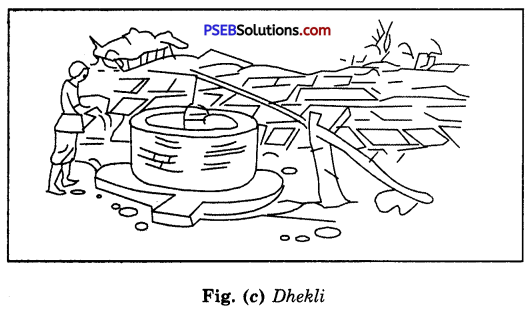
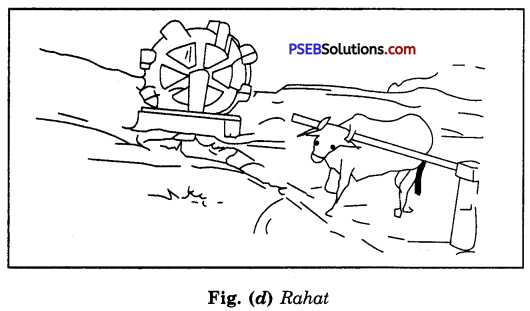
For lifting water, pumps are commonly used. Diesel, biogas, electricity and solar energy are used to run the pumps. The pumps of various power are available. They are selected according to the requirement of the particular field.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the main agricultural practices.
Answer:
Main agricultural practices. The main agricultural practices are as follows:
1. Ploughing.
The process of loosening and turning the soil is called ploughing. This is done by using a plough. Ploughs are made of wood or iron. The ploughed land is then levelled so that the soil is not blown off by wind or drained off by water.
2. Sowing.
After the preparation of the soil, the seeds are sown in the fields by hand (broadcasting) or by seeds drill.
3. Irrigation.
Crop plants absorb water from the soil by roots. Water is essential for the growth of plants. Irrigation is done by various ways like lift irrigation, water wheel, swinging baskets, sprinklers and tubewells.
4. Manuring.
Every crop uses substantial amount of nutrients present in the soil. Soil is replenished with nutrients by adding manures to it.
5. Weeding.
Many unwanted plants also germinate and grow in the field. These plants compete with the crop for water, sunlight and nutrients. Therefore, it is necessary to remove these plants to get better crops. This is called weeding.
6. Protection of Crops.
Crops are spoiled by insects, fungi, bacteria and rodents etc. Chemicals like insecticides and weedicides are used to kill them.
7. Harvesting and Storage.
When the crop is ready, it is harvested at proper time. Crops are harvested by hand, using a sickle or by a harvester. The grains are separated from the chaff in the harvested plant. Then the grains are stored in big store houses. The amount of moisture in the grains should not be more than 14%.
Question 2.
What are the practices adopted to improve crop production ?
Answer:
The practices adopted to improve crop production are as follows:
1. Addition of fertilizers to the soil.
2. Selective breeding.
3. Weed control.
4. Control of plant diseases.
1. Fertilizers.
These are the chemical compounds which are added to the soil to increase the fertility. They make up for the deficiency of the required nutrients and help in increasing the crop production.
2. Selective Breeding.
Disease resistant seeds are produced by selective breeding. Regular use of high yield variety results in better crop production.
3. Weed Control.
The unwanted plants or weeds are controlled by using certain chemicals called weedicides.
4. Control of Plant Diseases.
Crops should be protected from insects, fungi, animals and other diseases. It is very useful practice for increasing crop production. Insects are very harmful to crops. So insecticides should be used to kill insects.
Question 3.
What are fertilizers ? What are mixed fertilizers ? Why do farmers add fertilizer to the soil ? How should we store fertilizers ?
Answer:
Fertilizers. Fertilizers are the chemical substances which maintain the fertility of soil.
Mixed Fertilizers. The fertilizers which supply many elements are known as mixed fertilizers.
Example.
1. NPK has nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.
2. CAN is a mixed fertilizer of calcium, ammonium, nitrate.
Importance of Fertilizers.
The fertilizers and mixed fertilizers are added to the soil to make up for the deficiency for mineral elements like nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. This deficiency is produced in the soil by growing the crops in succession. That is why farmers add fertilizers to the soil to improve crop-production.
Storing of Fertilizers.
Some fertilizers are moisture lover i.e. they are hygroscopic. If the fertilizers are stored in moist places, it is difficult to apply them in the fields. Some fertilizers spoil the bags in which they are stored. They should be stored in dry places.
Question 4.
Explain the various tools used for ploughing.
Answer:
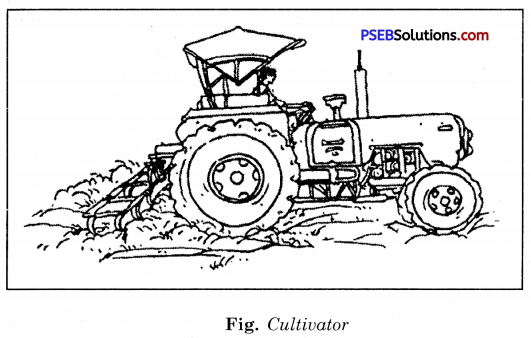
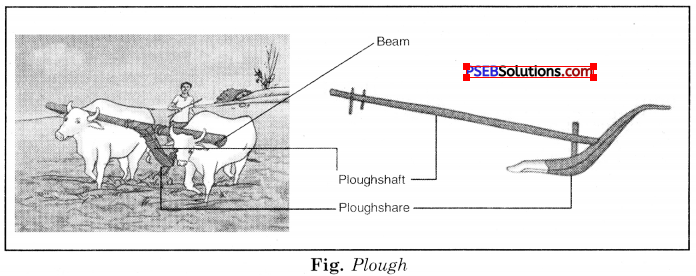
Main tools used for ploughing. The tools used for ploughing are plough, hoe and cultivator.
1. Plough.
This is being used for tilling of soil, adding fertilizers to the crop, removing the weeds, scrapping of soil, etc. It is made of wood and drawn by a pair of bulls. It contains a strong triangular iron strip called ploughshare. The main part of the plough is a long log of wood which is called a plough shaft. There is a handle on one end. The other end is attached to a beam which is hung on the neck of bulls. One pair of bulls and a man can easily operate the plough.
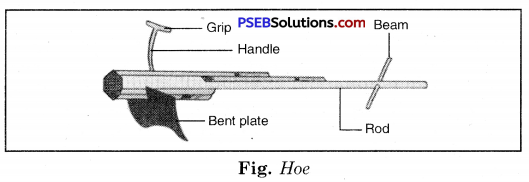
2. Hoe.
Hoe is a simple tool which is used for removing weeds and for loosening the soil. It has a long rod of wood or iron. A strong, broad and bent plate of iron is fixed to one of its ends and works like a blade. The other end of plough shaft is pulled by a pair of bulls.
3. Cultivator.
Nowadays ploughing is done by tractor driven cultivator. Cultivator saves labour and time.