Punjab State Board PSEB 9th Class Science Book Solutions Chapter 6 Tissues Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues
PSEB 9th Class Science Guide Tissues Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Define the term ’tissue’.
Answer:
Tissue: A group of cells that are similar in structure and/or work together a particular function is called tissue.
![]()
Question 2.
How many types of elements together make xylem tissue? Name them.
Answer:
Four types of elements make xylem tissue. They are:
- Tracheids
- Vessels
- Xylem parenchyma
- Xylem fibres
Question 3.
How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
Answer:
Differences between simple tissue and complex tissue in plants:
| Simple tissue | Complex tissue |
| 1. Similar types of cells which have common origin and function. 2. All cells are similar in origin and structure. 3. Parenchyma, Collenchyma and Sclerenchyma are the three types. |
1. A group of more than one type of cells having common origin and working! together as a unit. 2. The cells have different origin and structure. 3. Xylem and phloem are the two main types.! |
Complex tissue
Question 4.
Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma on the basis of their cell walls.
Answer:
| Feature | Parenchyma | Collenchyma | Sclerenchyma |
| Cell wall | Thin walls | Thickened cell wall at comers | Thickened walls due to lignin. |
![]()
Question 5.
What are functions of stomata?
Answer:
Functions of stomata:
- They are necessary for exchanging gases with the atmosphere.
- Transpiration also takes place through stomata.
Question 6.
Diagrammatically show the differences between three types of muscle fibres.
Answer:
Three Types of Muscle Fibres:
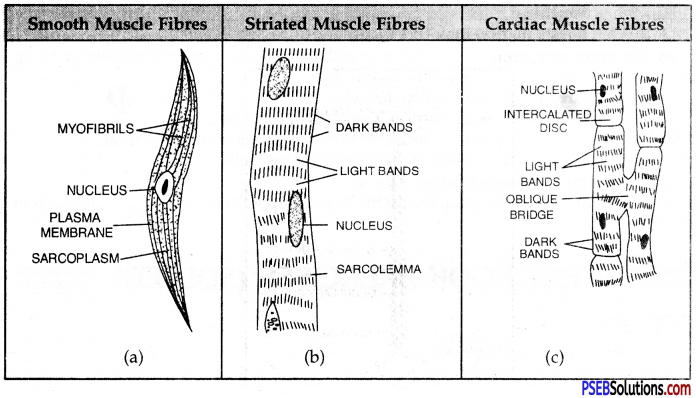
Question 7.
What is the specific function of cardiac muscles?
Answer:
Cardiac muscles undergo rhythmic contraction and relaxation. They are responsible for heart beat and thus plays a role in circulation (pumping) of blood in the body.
Question 8.
Differentiate between striated, unstriated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site/location in the body.
Answer:
Differences between Striated, Non-Striated and Cardiac Muscle Fibres:
| Striated Muscle Fibres | Non-striated Muscle Fibres | Cardiac Muscle Fibres |
| Structure: 1. The fibres or cells are long and cylindrical.2. The fibres are unbranched.3. Sarcolemma is present.4. The cells are multinucleate.5. They bear striations or alternate light and dark bands.6. The ends are blunt.7. They are capable of quick contraction. Location8. Occur in body wall, limbs, tongue, pharynx and beginning of oesophagus. |
1. The fibres or cells are narrow and spindleshaped. They are comparatively short.
2. The fibres are unbranched. 3. Sarcolemma is absent. 4. They are uninucleate. 5. Striations are absent. 6. The ends are tapering. 7. Contraction is slow. 8. Occur in walls of hollow visceral organs, iris of eye, and dermis of skin. |
1. The cells are short but cylindrical.
2. They develop lateral outgrowths at places to form cross-connections. 3. Sarcolemma is present. 4. The cells are uninucleate. 5. Striations are present but slightly fainter than found in striated fibres. 6. The ends are blunt. 7. The fibres show rhythmic contractions. 8. Occur in the wall of heart. |
![]()
Question 9.
Draw a labelled diagram of a neuron.
Answer:
Structure of neuron
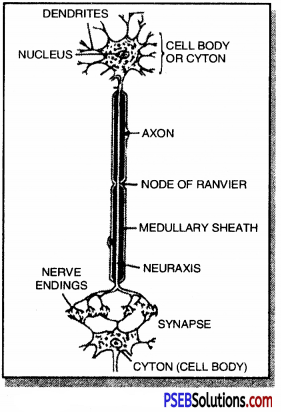
Question 10.
Name the following:
(a) Tissue that forms inner lining of our mouth.
(b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans.
(c) Tissue that transports food in plants.
(d) Tissue that stores fat in our body.
(e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix.
(f) Tissue present in the brain.
Answer:
(a) Squamous epithelium
(c) Phloem
(e) Blood (Vascular tissue)
Question 11.
Identify the type of tissue in the following: skin, bark of tree, bone, lining of kidney tubule, vascular bundle.
Answer:
- Skin
- Bark of tree
- Bone
- Lining of kidney tubule
- Vascular bundle
Question 12.
Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
Answer:
Pith and cortex of stem and root.
![]()
Question 13.
What is the role of epidermis in plants?
Answer:
Role of epidermis:
- Protection of all parts of plant.
- Secretion of waxy-water resistant layer on their outer surface.
- Epidermis aids in protection against loss of water, mechanical injury and invasion by parasitic fungi.
Question 14.
How does cork act as a protective tissue?
Answer:
Cell of cork are dead and compactly arranged without intercellular spaces. They have a chemical called suberin in their walls that makes them impervious to gases and water. Thus cork acts as a protective tissue.
Question 15.
Complete the table:
Answer:
- Parenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
- Phloem
Science Guide for Class 9 PSEB Tissues InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is a tissue?
Answer:
Tissue: A group of cells that are similar in structure and/or work together a particular function is called tissue.
![]()
Question 2.
What is utility of tissues in multicellular organisms?
Answer:
- They provide protection and mechanical strength.
- Tissues provide highest possible efficiency of function.
Question 3.
Name types of simple tissues.
Answer:
Types of simple tissues:
- Parenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma.
Question 4.
Where is apical meristem found?
Answer:
Apical meristem is present at the growing tips of stems and roots of plants.
Question 5.
Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?
Answer:
Sclerenchyma tissue.
Question 6.
What are constituents of phloem?
Answer:
Four types of elements constitute phloem:
- Sieve tubes
- Companion cells
- Phloem fibers
- Phloem parenchyma
Question 7.
Name the tissue responsible for the movement of our body.
Answer:
Muscular tissue.
Question 8.
What does a neuron look like?
Answer:
A neuron consists of cell body cyton with hair-like parts called dendrites and a long axon. Thus gives the appearance of a miniature tree.
![]()
Question 9.
Give three features of cardiac muscles.
Answer:
- Heart muscles are cylindrical, branched, and uninucleate.
- They are involuntary and undergo rhythmic contraction and relaxation.
- Intercalated discs are present at the junction of two cells.
Question 10.
What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Answer:
Areolar tissue fills space inside the organ, supports internal organs, and helps in repairing the tissues.