Punjab State Board PSEB 9th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 4 Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 4.4 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 4 Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 4.4
Question 1.
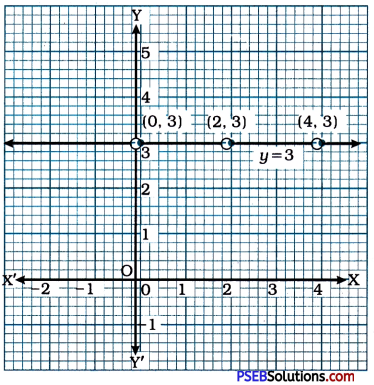
Give the geometric representation of y = 3 as an equation
(i) in one variable
Answer:
If the equation y = 3 is treated as an equation in one variable, its graphical representation is a point on the number line as shown below:

![]()
(ii) in two variables.
Answer:
If the equation y = 3 is treated as an equation in two variables, it can be written as 0x + y = 3. Here, for any value of x, the value of y remains 3. Hence, we can easily take (0, 3), (2, 3) and (4, 3) as three solutions of the equation 0x + y = 3. Then, we plot these points in the Cartesian plane and draw the line passing through them. This line is the graph of equation y = 3 as an equation in two variables. This graph is perpendicular to the y-axis and parallel to the x-axis.
Question 2.
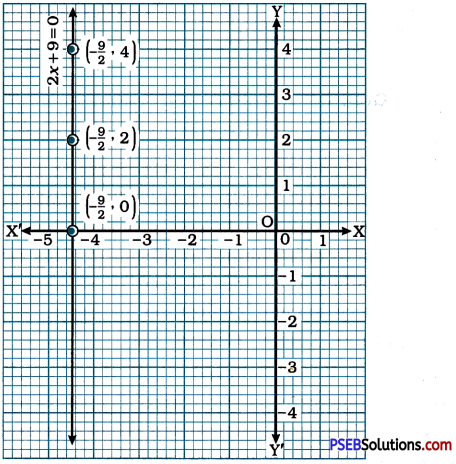
Give the geometric representations of 2x + 9 = 0 as an equation
(i) In one variable
Answer:
If the equation 2x + 9 = 0, i.e., x = – \(\frac{9}{2}\) is treated as an equation in one variable. its graphical representation is a point on the number line as shown below:

![]()
(ii) In two variables.
Answer:
If the equation 2x + 9 = 0 is treated as an equation in two variables, it can be written as 2x + 0y + 9 = 0. Here, for any value of y, the value of x remains – \(\frac{9}{2}\). Hence, we can easily take \(\left(-\frac{9}{2}, 0\right)\), \(\left(-\frac{9}{2}, 2\right)\), and \(\left(-\frac{9}{2}, 4\right)\) as three solutions of the equation 2x + 9 = 0. Then, we plot these points in the Cartesian plane and draw the line passing through them. This line is the graph of the equation 2x + 9 = 0 as an equation in two variables. This graph is perpendicular to the x-axis and parallel to the y-axis.