Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable Ex 2.5 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable Ex 2.5
Solve the following linear equations.
Question 1.
\(\frac{x}{2}-\frac{1}{5}=\frac{x}{3}+\frac{1}{4}\)
Solution:
\(\frac{x}{2}-\frac{1}{5}=\frac{x}{3}+\frac{1}{4}\)
∴ \(\frac {1}{2}\) [Transposing \(\frac{x}{3}\) to LHS and \(\frac {-1}{2}\) to RHS]
∴ \(\frac{3 x-2 x}{6}=\frac{1 \times 5+1 \times 4}{20}\) [LCM = 6, LCM = 20]
∴ \(\frac{x}{6}=\frac{5+4}{20}\)
∴ \(\frac{x}{6}=\frac{9}{20}\)
∴ \(\frac{x}{6} \times 6=\frac{9}{20} \times 6\) (Multiplying both the sides by 6)
∴ \(\frac {27}{10}\)
∴ x = 2.7
Question 2.
\(\frac{n}{2}-\frac{3 n}{4}+\frac{5 n}{6}\) = 21
Solution:
\(\frac{n}{2}-\frac{3 n}{4}+\frac{5 n}{6}\) = 21
∴ \(\frac{n \times 6}{2 \times 6}-\frac{3 n \times 3}{4 \times 3}+\frac{5 n \times 2}{6 \times 2}\) = 21
∴ \(\frac{6 n-9 n+10 n}{12}\) = 21
∴ \(\frac {7 n}{12}\) = 21
∴ 7n = 21 × 12 (Multiplying both the sides by 12)
∴ n = \(\frac{21 \times 12}{7}\) (Dividing both the sides by 7)
∴ n = 36
![]()
Question 3.
\(x+7-\frac{8 x}{3}=\frac{17}{6}-\frac{5 x}{2}\)
Solution:
\(x+7-\frac{8 x}{3}=\frac{17}{6}-\frac{5 x}{2}\)
(Multipljdng both the sides by 6, the LCM of 3, 6 and 2.)
(6 × x) + (6 × 7) – \(\left(\frac{6 \times 8 x}{3}\right)\) = \(\left(6 \times \frac{17}{6}\right)-\left(\frac{6 \times 5 x}{2}\right)\)
∴ 6x + 42 – 16x = 17- 15x
∴ – 10x + 42 = 17 – 15x
∴ – 10x + 15x = 17 – 42 [Transposing (-15x) to LHS and 42 to RHS]
∴ 5x = – 25
∴ x = – 5 (Dividing both the sides by 5)
Question 4.
\(\frac{x-5}{3}=\frac{x-3}{5}\)
Solution:
\(\frac{x-5}{3}=\frac{x-3}{5}\)
∴ 5(x – 5) = 3 (x – 3) (Cross multiplication)
∴ 5x – 25 = 3x – 9
∴ 5x – 3x = 25 – 9 [Transposing 3x to LHS and (-25) to RHS]
∴ 2x = 16
∴ \(\frac{2 x}{2}=\frac{16}{2}\) (Dividing both the sides by 2)
∴ x = 8
Question 5.
\(\frac{3 t-2}{4}-\frac{2 t+3}{3}=\frac{2}{3}-t\)
Solution:
\(\frac{3 t-2}{4}-\frac{2 t+3}{3}=\frac{2}{3}-t\)
(Multiplying both the sides by 12, the LCM of 4 and 3)
12\(\left(\frac{3 t-2}{4}\right)\) – 12\(\left(\frac{2 t+3}{3}\right)\) = 12 × \(\frac {1}{2}\) – 12t
∴ 3(3t – 2) -4 (2t + 3) = 8 – 12t
∴ 9t – 6 – 8t – 12 = 8 – 12t
∴ t – 18 = 8 – 12t
∴ t + 12t = 8 + 18 [Transposing (-12t) to LHS and (-18) to RHS]
∴ 13t = 26
∴ \(\frac{13 t}{13}=\frac{26}{13}\) (Dividing both the sides by 13)
∴ t = 2
![]()
Question 6.
\(m-\frac{m-1}{2}=1-\frac{m-2}{3}\)
Solution:
\(m-\frac{m-1}{2}=1-\frac{m-2}{3}\)
(Multiplying both the sides by 6, the LCM of 2 and 3)
6m – 6 \(\left(\frac{m-1}{2}\right)\) = 1 × 6 – 6\(\left(\frac{m-2}{3}\right)\)
∴ 6m – 3(m- 1) = 6 – 2(m-2)
∴ 6m – 3m + 3 = 6 – 2m + 4
∴ 3m + 3 = 10 – 2m
∴ 3m + 2m = 10 – 3 [Transposing (-2 m) to LHS and 3 to RHS]
∴ 5m = 7
∴ \(\frac{5 m}{5}=\frac{7}{5}\) (Dividing both the sides by 5)
∴ m = \(\frac {7}{5}\)
Simplify and solve the following linear equations.
Question 7.
3(t – 3) = 5(2t + 1)
Solution:
3(t – 3) = 5(2t + 1)
∴ 3t – 9 = 10t + 5
∴ 3t – 10t = 5 + 9 [Transposing 10t to LHS and (-9) to RHS]
∴ – 7t = 14
∴ 7t = – 14 [Multiplying both the sides by (-1)]
∴ \(\frac{7 t}{7}=\frac{-14}{7}\) (Dividing both the sides by 7)
∴ t = -2
Question 8.
15 (y – 4) – 2 (y – 9) + 5 (y + 6) = 0
Solution:
15 (y – 4) – 2 (y – 9) + 5 (y + 6) = 0
∴ 15y – 60 – 2y + 18 + 5y + 30 = 0
∴ 15y – 2y + 5y – 60 + 18 + 30 = 0
∴ 15y + 5y – 2y + 18 + 30 – 60 = 0 (Arranging the terms)
∴ 18y – 12 = 0
∴ 18y = 12 [Transposing (- 12) to RHS]
∴ \(\frac{18 y}{18}=\frac{12}{18}\) (Dividing both the sides by 18)
∴ y = \(\frac {2}{3}\)
![]()
Question 9.
3(5z – 7) -2 (9z – 11) = 4(8z – 13) – 17
Solution:
3(5z – 7) -2 (9z – 11) = 4(8z – 13) – 17
∴ 15z – 21 – 18z + 22 = 32z – 52 – 17
∴ 15z – 18z – 21 + 22 = 32z + (-52 – 17)
∴ – 3z + 1 = 32z – 69
∴ – 3z – 32z = – 69 – 1 (Transposing 1 to RHS and 32z to LHS)
∴ – 35z = – 70
∴ 35z = 70[Multiplying both the sides by (-1)]
∴ \(\frac{35 z}{35}=\frac{70}{35}\) (Dividing both the sides by 35)
∴ z = 2.
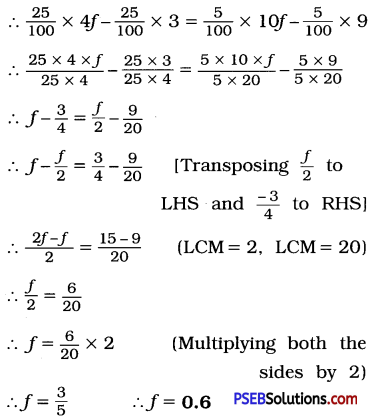
Question 10.
0.25 (4f – 3) = 0.05(10f – 9)
Solution:
0.25 (4f – 3) = 0.05(10f – 9)
0.25 × 4f – 0.25 × 3
= 0.05 × 10f – 0.05 × 9