Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class Chemistry Book Solutions Chapter 15 Polymers Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 15 Polymers
PSEB 12th Class Chemistry Guide Polymers InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain the terms polymer and monomer.
Answer:
- Polymer is a high molecular mass macromolecule consisting of repeating structural units derived from monomers.
- A monomer is a simple molecule capable of undergoing polymerisation and leading to the formation of the corresponding polymer.
Question 2.
What are natural and synthetic polymers? Give two examples of each type.
Answer:
- Natural polymers are high molecular mass macromolecules and are found in plants and animals. For example, proteins and nucleic acids,
- Synthetic polymers are man-made high molecular mass macromolecules. These include synthetic plastics, fibres and rubbers. For example, polythene and dacron.
Question 3.
Distinguish between the terms homopolymer and copolymer and give an example of each.
Answer:
Homopolymer: Polymers whose repeating structural units are derived from only one type of monomer units are called homopolymers. For example, polythene, PAN, Teflon, nylon-6, etc.
Copolymer: Polymers whose repeating structural units are derived from two or more types of monomer molecules are called copolymers. For example, Buna-S, Buna-N, nylon-6,6 polyester, bakelite, etc.
Question 4.
How do you explain the functionality of a monomer?
Answer:
The functionality of a monomer is the number of binding sites in a molecule. For example, the functionality of ethene, propene, styrene, acrylonitrile is one and that of 1, 3-butadiene, adipic acid, terephthalic acid, hexamethylenediamine is two.
Question 5.
Define the term polymerisation.
Answer:
The polymerisation is a process of formation of a high molecular mass polymer from one or more monomers by linking together a large number of repeating structural units through covalent bonds.
Question 6.
![]()
Answer:
![]() is a homopolymer because it is obtained from a single monomer unit, NH2-CHR-COOH.
is a homopolymer because it is obtained from a single monomer unit, NH2-CHR-COOH.
Question 7.
In which classes, the polymers are classified on the basis of molecular forces?
Answer:
On the basis of molecular forces of attraction polymers are classified into the following classes :
- Elastomers
- Fibres
- Thermoplastic polymers and
- Thermosetting polymers.
Question 8.
How can you differentiate between addition and condensation polymerisation?
Answer:
(i) Addition polymerisation: In this, polymers are formed by the repeated addition of monomers molecules possessing double or triple bonds.
For example :
![]()
(ii) Condensation polymerisation: It is a process in which two or more bi-functional molecules undergo a series of condensation reactions with the elimination of some simple molecules and leading to the formation of polymers.
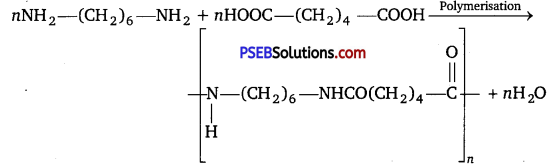
Question 9.
Explain the term copolymerisation and give two examples.
Answer:
When a mixture containing more than one monomeric species is allowed to polymerise, the product obtained is called a copolymer and the process is called copolymerisation. For example, Buna-S, a copolymer of 1,3-butadiene and styrene and Buna-N, a copolymer of 1,3-butadiene and acrylonitrile.
![]()
Question 10.
Write the free radical mechanism for the polymerisation of ethene.
Answer:
The mechanism of chain growth polymerisation of ethene of free radical mechanism is given below :
Step I. Chain initiation step :
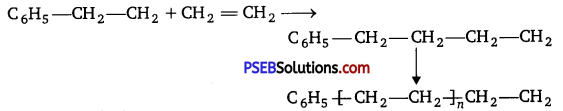
Step II. Chain propagation step :
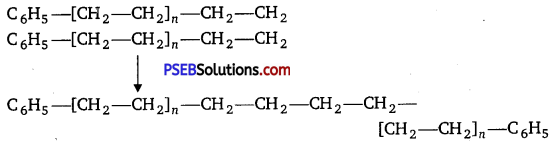
Step III. Chain terminating step :
Question 11.
Define thermoplastics and thermosetting polymers with two examples Of each.
Answer:
Thermoplastic polymers: These polymers are the linear or slightly. branched long-chain molecules capable of repeatedly softening on heating and hardening on cooling. These polymers possess intermolecular forces of attraction intermediate between elastomers and fibres. Some common examples are polythene, polystyrene, polyvinyl, etc.
Thermosetting polymers: These polymers are cross-linked or heavily branched molecules, which on heating undergo extensive cross-linking in moulds and again become infusible. These polymers cannot be reused. Some common examples are bakelite, urea-formaldehyde resins, etc.
Question 12.
Write the monomers used for getting the following polymers :
(i) Polyvinyl chloride
(ii) Teflon
(iii) Bakelite
Answer:
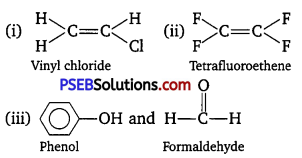
Question 13.
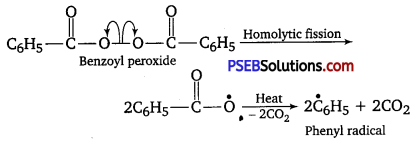
Write the name and structure of one of the common initiators used in free radical addition polymerisation.
Answer:
One common initiator used in free radical addition polymerisation is benzoyl peroxide. Its structure is given below:
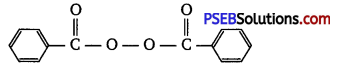
Question 14.
How does the presence of double bonds in rubber molecules influence their structure and reactivity?
Answer:
- In natural rubber (cis- 1,4-polyisoprene), double bonds are located between C2 and C3 of isoprene units.
- The double bonds are reactive sites and helps in vulcanisation of natural rubber forming S-S linkages between chains.
- The cis-configuration about double bonds do not allow the chains to come closer and so there are weak intermolecular attractions between the chains. This leads to coiled structure and elasticity for natural rubber.
Question 15.
Discuss the main purpose of vulcanisation of rubber.
Answer:
Natural rubber becomes soft at high temperatures (> 335K) and brittle at low temperatures (< 283 K) and shows high water absorption capacity. It is soluble in non-polar solvents and is non-resistant to attack by oxidising agents. To improve upon these physical properties, a process of vulcanisation is carried out. This process consists of heating a mixture of raw rubber with sulphur and an appropriate additive at a temperature range between 373 K and 415 K. On vulcanisation, sulphur forms cross-links at the reactive sites of double bonds and thus the rubber gets stiffened.
Question 16.
What are the monomeric repeating units of Nylon-6 and Nylon-6,6?
Answer:

(ii) Nylon-6,6: 1,6-Hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid.
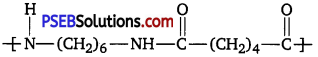
Question 17.
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers:
(i) Buna-S,
(ii) Buna-N,
(iii) Dacron,
(iv) Neoprene
Answer:
The names and structures of monomers are :
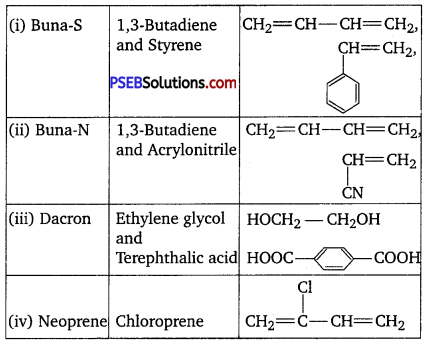
Question 18.
Identify the monomer in the following polymeric structures :
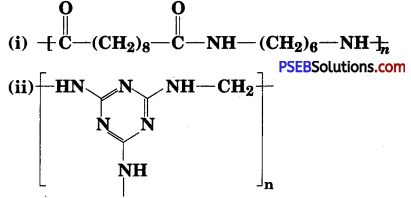
Answer:
The monomers forming the polymer are :
(i) Decanoic acid HOOC-(CH2)8-COOH and Hexamethylenediamine H2N-(CH2)6-NH2.
(ii)
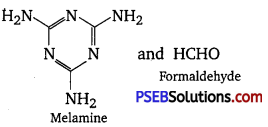
![]()
Question 19.
How is dacron obtained from ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid?
Answer:
Dacron is a synthetic condensation polymer which has ester group in the polymer chain. Terylene was also known by the name.
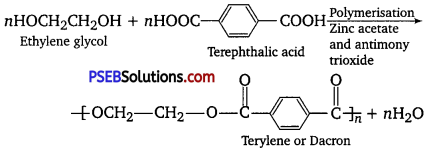
Question 20.
What is a biodegradable polymer? Give an example of a biodegradable aliphatic polyester.
Answer:
A polymer that can be decomposed by bacteria is called a biodegradable polymer.
Poly-β-hydroxybutyrate-CO-β-hydroxy valerate (PHBV) is a biodegradable aliphatic polyester.
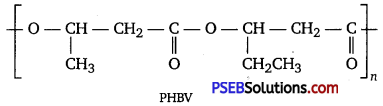
Chemistry Guide for Class 12 PSEB Polymers Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are polymers?
Answer:
Polymers are high molecular mass macromolecules, which consist of repeating structural units derived from monomers. Polymers have a high molecular mass (103 – 107 u). In a polymer, various monomer units are joined by strong covalent bonds. These polymers can be natural as well as synthetic. Polythene, rubber, and nylon 6, 6 are examples of polymers.
Question 2.
How are polymers classified on the basis of structure?
Answer:
Polymers are classified on the basis of structure as follows:
1. Linear polymers: These polymers are formed of long straight chains. They can be depicted as :
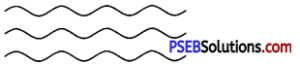
e.g., high-density polythene (HDP), polyvinyl chloride PVC, etc.
2. Branched-chain polymers: These polymers are basically linear chain polymers with some branches. These polymers are represented as:
![]()
e.g., low-density polythene (LDP), amylopectin, etc.
3. Cross-linked or Network polymers: These polymers have many cross-linking bonds that give rise to a network-like structure. These polymers contain bi-functional and tri-functional monomers and strong covalent bonds between various linear polymer chains. Examples of such polymers include bakelite and Melmac.
![]()
Question 3.
Write the names of monomers of the following polymers:
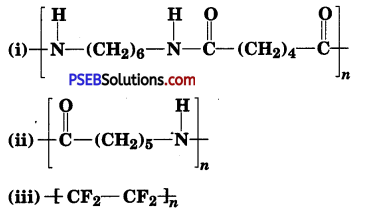
Answer:
(i) Hexamethylenediamine [H2N—(CH2)6—NH2] and adipic acid [HOOC—(CH2)4 —COOH].
(ii) Caprolactam
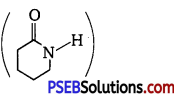
(iii) Tetrafluoroethene, (F2C – CF2).
Question 4.
Classify the following as addition and condensation polymers: Terylene, Bakelite, Polyvinyl chloride, Polythene.
Answer:
Addition polymers: Polyvinyl chloride, polythene.
Condensation polymers: Terylene, bakelite.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the difference between Buna-N and Buna-S.
Answer:
Both are copolymers. Buna-N is a copolymer of 1, 3-butadiene and acrylonitrile while Buna-S is a copolymer of 1,3-butadiene and styrene.
Question 6.
Arrange the following polymers in increasing order of their intermolecular forces:
(i) Nylon-6,6, Buna-S, Polythene
(ii) Nylon-6, Neoprene, Polyvinylchloride.
Answer:
(i) Buna-S < Polythene < Nylon-6,6
(ii) Neoprene < Polyvinyl chloride < Nylon-6